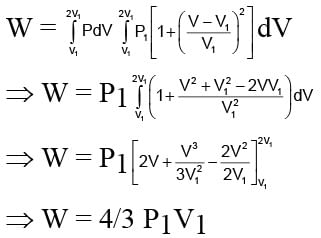All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of December Week 1 for NEET Exam
What is not true for a cyclic process?a) System returns to its initial state
b) ΔU = 0
c) ΔW= 0
d) ΔQ = -ΔW
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
b) ΔU = 0
c) ΔW= 0
d) ΔQ = -ΔW
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
As work is a path function rather than a state function, we can easily say that work can often be graphically represented as the area under the PV graph. And as cyclic processes are represented as closed shapes on PV graph it is obvious that they have non zero area and thus work done is non zero.
If TLC is 5500ml, IRV is 2950ml, ERV is 900ml and TV is 500ml then what will be value of RV ?- a)2550ml
- b)1100ml
- c)1200ml
- d)1150ml
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If TLC is 5500ml, IRV is 2950ml, ERV is 900ml and TV is 500ml then what will be value of RV ?
a)
2550ml
b)
1100ml
c)
1200ml
d)
1150ml
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
RV = TLC - IRV – ERV– TV. On substituting the values, we get 1150ml.
Habit of Cigarette smoking can lead to :- a)loss of cilia lining the respiratory tract
- b)all of the following
- c)coughing
- d)emphysema
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Habit of Cigarette smoking can lead to :
a)
loss of cilia lining the respiratory tract
b)
all of the following
c)
coughing
d)
emphysema
|
|
Syed Aakif answered |
Because which contains Nictogen and other harmful compounts which can affect our whole body it supress our body function
Which of the following are the extensive variables?- a)Internal energy, pressure and volume
- b)Pressure, temperature and density
- c)Internal energy, volume, total mass
- d)Pressure, temperature and volume
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are the extensive variables?
a)
Internal energy, pressure and volume
b)
Pressure, temperature and density
c)
Internal energy, volume, total mass
d)
Pressure, temperature and volume
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
An extensive variable is one which depends on system size (like mass or volume). ... An intensive variable is one which does not depend on system size (like temperature, pressure, or density).
Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)- a)Naphthalene
- b)Aniline
- c)Pyridine
- d)Tropolone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)
a)
Naphthalene
b)
Aniline
c)
Pyridine
d)
Tropolone

|
Sai Mishra answered |
Pyridine is heterocyclic aromatic compound. Whereas naphthalene and aniline are benzenoid aromatic compounds and tropolone is a non-benzenoid aromatic compound.
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
- a)alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
- b)Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
- c)Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
- d)Open chain compounds and closed compounds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
a)
alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
b)
Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
c)
Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
d)
Open chain compounds and closed compounds

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
The correct answer is option D
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Find the final temperature of one mole of an ideal gas at an initial temperature to t K.The gas does 9 R joules of work adiabatically. The ratio of specific heats of this gas at constant pressure and at constant volume is 4/3.- a)(t-9)K
- b)(t - 4/3)K
- c)t + 3K
- d)(t - 3)K
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the final temperature of one mole of an ideal gas at an initial temperature to t K.The gas does 9 R joules of work adiabatically. The ratio of specific heats of this gas at constant pressure and at constant volume is 4/3.
a)
(t-9)K
b)
(t - 4/3)K
c)
t + 3K
d)
(t - 3)K
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
TInitial = t K
Work, W = 9R
Ratio of specific heats, γ = Cp / Cv = 4/3
In an adiabatic process, we have
W = R(TFinal – Tinitial) / (1-γ)
9R = R (TFinal – t) / (1 – 4/3)
TFinal – t = 9 (-1/3) = -3
TFinal = (t-3) K
Work, W = 9R
Ratio of specific heats, γ = Cp / Cv = 4/3
In an adiabatic process, we have
W = R(TFinal – Tinitial) / (1-γ)
9R = R (TFinal – t) / (1 – 4/3)
TFinal – t = 9 (-1/3) = -3
TFinal = (t-3) K
Aliphatic compound is the other name for- a)Acyclic compounds
- b)Alicyclic compounds
- c)Ring compounds
- d)Closed chain compounds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Aliphatic compound is the other name for
a)
Acyclic compounds
b)
Alicyclic compounds
c)
Ring compounds
d)
Closed chain compounds

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Respiration in insects is direct due to exchange of gases- a)Directly with the air outside through body surface
- b)By tracheal tubes directly with haemocoel which then exchange with tissues.
- c)Directly with coelomic fluid
- d)Directly with the air in tubes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Respiration in insects is direct due to exchange of gases
a)
Directly with the air outside through body surface
b)
By tracheal tubes directly with haemocoel which then exchange with tissues.
c)
Directly with coelomic fluid
d)
Directly with the air in tubes
|
|
Raza Great answered |
Direct respiration means exchange of gases without using any special respiratory organ and blood. In case of insects, the tracheal tubes exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with the haemocoel which then exchange then with tissues
In humans, what is true about RBCs?
- a)They transport about 80% of oxygen, and the remaining 20% is dissolved in blood plasma.
- b)About 20-25% of CO2 is carried by them
- c)They transport 99.5% of oxygen
- d)CO2 is not held by them
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In humans, what is true about RBCs?
a)
They transport about 80% of oxygen, and the remaining 20% is dissolved in blood plasma.
b)
About 20-25% of CO2 is carried by them
c)
They transport 99.5% of oxygen
d)
CO2 is not held by them

|
Bs Academy answered |
Red blood cells (RBCs) transport 99.5% of Oxygen and carry about 20-25% of Carbon Dioxide (CO2). The remaining 0.5% of oxygen is transported in the dissolved state in blood plasma, while the rest of the CO2 is exhaled during respiration.
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group- a)Isocyanide
- b)Isocyano
- c)Carboxyl
- d)Carbonyl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group
a)
Isocyanide
b)
Isocyano
c)
Carboxyl
d)
Carbonyl

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Isocyanide is a compound and it is not a functional group.
Isothermal process can be represented by which law?- a)Charle’s law
- b)Boyle’s law
- c)Gay-Lussac’s law
- d)2nd law of thermodynamics
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Isothermal process can be represented by which law?
a)
Charle’s law
b)
Boyle’s law
c)
Gay-Lussac’s law
d)
2nd law of thermodynamics
|
|
Janhavi Choudhury answered |
's law
b)Boyle's law
c)Gay-Lussac's law
d)Joule's law
d) Joule's law.
b)Boyle's law
c)Gay-Lussac's law
d)Joule's law
d) Joule's law.
Identify the odd one among the following- a)Indene
- b)Anthracene
- c)o,m,p-xylene
- d)Azulene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the odd one among the following
a)
Indene
b)
Anthracene
c)
o,m,p-xylene
d)
Azulene

|
Saumya Ahuja answered |
Azulene is a non- benzenoid compound. Whereas, Indene, anthracene, and o,m,p-Xylene are examples of benzenoid aromatic compounds.
The principle of exchange of gases at the lungs is :- a)Filtration
- b)Conditioning and facilitated transport
- c)both diffusion and filtration
- d)Diffusion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The principle of exchange of gases at the lungs is :
a)
Filtration
b)
Conditioning and facilitated transport
c)
both diffusion and filtration
d)
Diffusion
|
|
Jananignanamurugan Janan answered |
Gas exchange during respiration occurs primarily through diffusion. Diffusion is a process in which transport is driven by a concentration gradient. ... The air in thelungs has a higher concentration of oxygen than that of oxygen-depleted blood and a lower concentration of carbon dioxide.
A body of mass 2kg is dragged on a horizontal surface with a constant speed of 2 m/s. If the coefficient of friction between the body and the surface is 0.2, then find the heat generated in 5 sec.- a)18.66 cal
- b)10 cal
- c)8.71 cal
- d)9.33 cal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A body of mass 2kg is dragged on a horizontal surface with a constant speed of 2 m/s. If the coefficient of friction between the body and the surface is 0.2, then find the heat generated in 5 sec.
a)
18.66 cal
b)
10 cal
c)
8.71 cal
d)
9.33 cal
|
|
Pallavi Pillai answered |
Understanding the Problem
A body with a mass of 2 kg is being dragged on a horizontal surface at a constant speed of 2 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the body and the surface is 0.2. We need to find the heat generated due to friction over a period of 5 seconds.
Calculating the Force of Friction
- The formula for the force of friction (F_friction) is given by:
- F_friction = coefficient of friction * normal force
- For a horizontal surface, the normal force (N) equals the weight of the body:
- N = mass * g (where g is approximately 9.81 m/s²)
- Therefore:
- N = 2 kg * 9.81 m/s² = 19.62 N
- F_friction = 0.2 * 19.62 N = 3.924 N
Calculating Work Done Against Friction
- Work done (W) against friction is given by:
- W = F_friction * distance
- The distance traveled in 5 seconds at 2 m/s:
- Distance = speed * time = 2 m/s * 5 s = 10 m
- Thus, the work done:
- W = 3.924 N * 10 m = 39.24 J
Converting Work to Heat
- The heat generated (Q) is equal to the work done against friction.
- To convert joules to calories, use the conversion factor:
- 1 cal = 4.184 J
- Converting the work done to calories:
- Q = 39.24 J / 4.184 J/cal ≈ 9.38 cal
Final Answer
- Rounding off gives approximately 9.33 cal, which corresponds to option D.
In conclusion, the heat generated due to friction in this scenario is approximately 9.33 calories.
A body with a mass of 2 kg is being dragged on a horizontal surface at a constant speed of 2 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the body and the surface is 0.2. We need to find the heat generated due to friction over a period of 5 seconds.
Calculating the Force of Friction
- The formula for the force of friction (F_friction) is given by:
- F_friction = coefficient of friction * normal force
- For a horizontal surface, the normal force (N) equals the weight of the body:
- N = mass * g (where g is approximately 9.81 m/s²)
- Therefore:
- N = 2 kg * 9.81 m/s² = 19.62 N
- F_friction = 0.2 * 19.62 N = 3.924 N
Calculating Work Done Against Friction
- Work done (W) against friction is given by:
- W = F_friction * distance
- The distance traveled in 5 seconds at 2 m/s:
- Distance = speed * time = 2 m/s * 5 s = 10 m
- Thus, the work done:
- W = 3.924 N * 10 m = 39.24 J
Converting Work to Heat
- The heat generated (Q) is equal to the work done against friction.
- To convert joules to calories, use the conversion factor:
- 1 cal = 4.184 J
- Converting the work done to calories:
- Q = 39.24 J / 4.184 J/cal ≈ 9.38 cal
Final Answer
- Rounding off gives approximately 9.33 cal, which corresponds to option D.
In conclusion, the heat generated due to friction in this scenario is approximately 9.33 calories.
Find the odd one among the following:- a)Alicyclic compounds
- b)Heterogeneous compounds
- c)Branched chain compounds
- d)Aromatic compounds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the odd one among the following:
a)
Alicyclic compounds
b)
Heterogeneous compounds
c)
Branched chain compounds
d)
Aromatic compounds

|
Shruti Ahuja answered |
Branched chain compound is a classification of open-chain compounds. Whereas, alicyclic, aromatic and heterogeneous compounds are sub-classifications of cyclic compounds.
The correct sequence of respiration is
i) Breathing in oxygen
ii) Transportation of gases by the blood
iii) Diffusion of gases between blood and tissues
iv) Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane
v) Using of oxygen and releasing of carbondioxide- a)i), ii), iii), iv), v)
- b)i), iv), ii), iii), v)
- c)i), ii), iv), iii)
- d)i), iii), iv), ii), v)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence of respiration is
i) Breathing in oxygen
ii) Transportation of gases by the blood
iii) Diffusion of gases between blood and tissues
iv) Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane
v) Using of oxygen and releasing of carbondioxide
i) Breathing in oxygen
ii) Transportation of gases by the blood
iii) Diffusion of gases between blood and tissues
iv) Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane
v) Using of oxygen and releasing of carbondioxide
a)
i), ii), iii), iv), v)
b)
i), iv), ii), iii), v)
c)
i), ii), iv), iii)
d)
i), iii), iv), ii), v)
|
|
Mahi Desai answered |
Respiration is the process by which living organisms exchange gases with the environment. The correct sequence of respiration is as follows:
i) Breathing in oxygen
ii) Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane
iii) Transportation of gases by the blood
iv) Diffusion of gases between blood and tissues
v) Using of oxygen and releasing of carbon dioxide
Explanation:
i) Breathing in oxygen: The process of respiration begins with the inhalation of air which contains oxygen. The air enters the body through the nostrils and mouth and travels down the trachea to reach the lungs.
ii) Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane: In the lungs, oxygen diffuses across the alveolar membrane and enters the bloodstream. At the same time, carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses across the alveolar membrane and enters the lungs to be exhaled.
iii) Transportation of gases by the blood: The oxygen-rich blood is transported by the circulatory system to all parts of the body where it is needed for cellular respiration. The carbon dioxide produced by cellular respiration is transported back to the lungs by the blood to be exhaled.
iv) Diffusion of gases between blood and tissues: In the tissues, oxygen diffuses from the blood into the cells, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the blood.
v) Using of oxygen and releasing of carbon dioxide: Inside the cells, oxygen is used in cellular respiration to produce energy, while carbon dioxide is produced as a waste product. This carbon dioxide is transported back to the lungs to be exhaled, and the process of respiration starts again.
Therefore, the correct sequence of respiration is i) Breathing in oxygen, ii) Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane, iii) Transportation of gases by the blood, iv) Diffusion of gases between blood and tissues, and v) Using of oxygen and releasing of carbon dioxide.
i) Breathing in oxygen
ii) Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane
iii) Transportation of gases by the blood
iv) Diffusion of gases between blood and tissues
v) Using of oxygen and releasing of carbon dioxide
Explanation:
i) Breathing in oxygen: The process of respiration begins with the inhalation of air which contains oxygen. The air enters the body through the nostrils and mouth and travels down the trachea to reach the lungs.
ii) Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane: In the lungs, oxygen diffuses across the alveolar membrane and enters the bloodstream. At the same time, carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses across the alveolar membrane and enters the lungs to be exhaled.
iii) Transportation of gases by the blood: The oxygen-rich blood is transported by the circulatory system to all parts of the body where it is needed for cellular respiration. The carbon dioxide produced by cellular respiration is transported back to the lungs by the blood to be exhaled.
iv) Diffusion of gases between blood and tissues: In the tissues, oxygen diffuses from the blood into the cells, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the blood.
v) Using of oxygen and releasing of carbon dioxide: Inside the cells, oxygen is used in cellular respiration to produce energy, while carbon dioxide is produced as a waste product. This carbon dioxide is transported back to the lungs to be exhaled, and the process of respiration starts again.
Therefore, the correct sequence of respiration is i) Breathing in oxygen, ii) Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane, iii) Transportation of gases by the blood, iv) Diffusion of gases between blood and tissues, and v) Using of oxygen and releasing of carbon dioxide.
An increase in lung ventilation rate is caused by which of the following conditions?- a)Increase of CO2 content in inhaled air
- b)Addition of CO2 content in exhaled air
- c)Decrease of O2 content in exhaled air
- d)Reduction of O2 content in inhaled air
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An increase in lung ventilation rate is caused by which of the following conditions?
a)
Increase of CO2 content in inhaled air
b)
Addition of CO2 content in exhaled air
c)
Decrease of O2 content in exhaled air
d)
Reduction of O2 content in inhaled air

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) levels triggers an increase in the lung ventilation rate as it signals a need for more oxygen to be obtained. This leads to an increased demand for oxygen, which increases respiratory rate and depth.
The exchange of gases in :
i. the alveoli that lowers the pO2 of blood and raises its pCO2 is external respiration
ii. the tissues that lowers the pCO2 of blood and raises its pO2 is internal respiration- a)statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
- b)both statements are correct.
- c)statementi) is wrong and ii) is correct.
- d)both statements are wrong.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The exchange of gases in :
i. the alveoli that lowers the pO2 of blood and raises its pCO2 is external respiration
ii. the tissues that lowers the pCO2 of blood and raises its pO2 is internal respiration
i. the alveoli that lowers the pO2 of blood and raises its pCO2 is external respiration
ii. the tissues that lowers the pCO2 of blood and raises its pO2 is internal respiration
a)
statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
b)
both statements are correct.
c)
statementi) is wrong and ii) is correct.
d)
both statements are wrong.
|
|
Ipsita Menon answered |
In the alveoli, there is high pO2 , low pCO2 , lesser H+ concentration and lower temperature,
Which among these is not associated with aliphatic compounds- a)They contain (4n+2)pi electrons
- b)Contain straight chain compounds
- c)Contain branched chain compounds
- d)Has appropriate number of H-atoms and functional groups
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among these is not associated with aliphatic compounds
a)
They contain (4n+2)pi electrons
b)
Contain straight chain compounds
c)
Contain branched chain compounds
d)
Has appropriate number of H-atoms and functional groups

|
Ruchi Basak answered |
The aromatic compounds (4n+2)pi electrons, which comes under the classification of cyclic compounds and hence they are not associated with aliphatic compounds.
Which among the following is not an example of Acyclic compound- a)Acetaldehyde
- b)Ethane
- c)Cyclopropane
- d)Isobutane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an example of Acyclic compound
a)
Acetaldehyde
b)
Ethane
c)
Cyclopropane
d)
Isobutane

|
Rithika Mukherjee answered |
Cyclopropane is a ring (cyclic) compound and hence it does not come with the examples of open chain compounds.
The work done per mole in an isothermal process is- a)RT log10 (V2/V1)
- b)RT log10 (V1/V2)
- c)RT loge (V2/V1)
- d)RT loge(V1/V2)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The work done per mole in an isothermal process is
a)
RT log10 (V2/V1)
b)
RT log10 (V1/V2)
c)
RT loge (V2/V1)
d)
RT loge(V1/V2)
|
|
Pragati Nambiar answered |
Understanding Isothermal Processes
In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant while a gas expands or contracts. The work done during this process can be derived from the first law of thermodynamics and the ideal gas law.
Work Done in Isothermal Process
- The formula for work done (W) when a gas expands or compresses is given by:
W = ∫ P dV
- For an ideal gas, pressure (P) can be expressed using the ideal gas equation:
P = nRT/V
- Substituting this into the work integral, we have:
W = ∫ (nRT/V) dV
- This integration occurs from the initial volume (V1) to the final volume (V2).
Integrating the Expression
- The work done then simplifies to:
W = nRT ∫ (1/V) dV from V1 to V2
- Performing this integral yields:
W = nRT [log(V2) - log(V1)]
- This can be further simplified using logarithmic properties:
W = nRT log(V2/V1)
Per Mole of Gas
- Since the question asks for the work done per mole, we set n = 1 (per mole):
W = RT log(V2/V1)
- To express this in terms of natural logarithms, we recognize that:
log(a/b) = log(a) - log(b)
Final Answer
- Thus, the correct expression for work done per mole during an isothermal process is:
W = RT loge(V2/V1)
This corresponds to option 'C', confirming that the work done is related to the natural logarithm of the volume ratio during an isothermal expansion or compression.
In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant while a gas expands or contracts. The work done during this process can be derived from the first law of thermodynamics and the ideal gas law.
Work Done in Isothermal Process
- The formula for work done (W) when a gas expands or compresses is given by:
W = ∫ P dV
- For an ideal gas, pressure (P) can be expressed using the ideal gas equation:
P = nRT/V
- Substituting this into the work integral, we have:
W = ∫ (nRT/V) dV
- This integration occurs from the initial volume (V1) to the final volume (V2).
Integrating the Expression
- The work done then simplifies to:
W = nRT ∫ (1/V) dV from V1 to V2
- Performing this integral yields:
W = nRT [log(V2) - log(V1)]
- This can be further simplified using logarithmic properties:
W = nRT log(V2/V1)
Per Mole of Gas
- Since the question asks for the work done per mole, we set n = 1 (per mole):
W = RT log(V2/V1)
- To express this in terms of natural logarithms, we recognize that:
log(a/b) = log(a) - log(b)
Final Answer
- Thus, the correct expression for work done per mole during an isothermal process is:
W = RT loge(V2/V1)
This corresponds to option 'C', confirming that the work done is related to the natural logarithm of the volume ratio during an isothermal expansion or compression.
Which among the following is not a class of organic compound- a)Carbonyl compound
- b)Nitro compound
- c)Amides
- d)Electro compounds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not a class of organic compound
a)
Carbonyl compound
b)
Nitro compound
c)
Amides
d)
Electro compounds

|
Ishani Mehta answered |
Classes of organic compounds are those which involves organic compounds such as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Hence, electro compounds is not a class of organic compounds.
Calculate the work done by the gas in an isothermal process from A to B. PA = 1Pa, VA = 3m3, PB = 3Pa.- a)3.3 J
- b)3 J
- c)- 3.3 J
- d)- 4.58 J
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the work done by the gas in an isothermal process from A to B. PA = 1Pa, VA = 3m3, PB = 3Pa.
a)
3.3 J
b)
3 J
c)
- 3.3 J
d)
- 4.58 J

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Since the process is isothermal, the product PV will be constant.
PAVA = PBVB.
Therefore, VB = 1 × 3/3 = 1m3.
Work done in an isothermal process is given by:
W = nRT × ln(VB/VA) = PAVAln(VB/VA)
= 3 × ln(1/3)
To elaborate: ln(1/3) is the natural logarithm of 1/3, which is approximately -1.0986. Therefore, 3 × -1.0986 = -3.3 J.
PAVA = PBVB.
Therefore, VB = 1 × 3/3 = 1m3.
Work done in an isothermal process is given by:
W = nRT × ln(VB/VA) = PAVAln(VB/VA)
= 3 × ln(1/3)
To elaborate: ln(1/3) is the natural logarithm of 1/3, which is approximately -1.0986. Therefore, 3 × -1.0986 = -3.3 J.
Which among the following is not an example of alicyclic compound- a)Cyclohexane
- b)Cyclohexene
- c)Tetrahydrofuran
- d)Acetic acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an example of alicyclic compound
a)
Cyclohexane
b)
Cyclohexene
c)
Tetrahydrofuran
d)
Acetic acid

|
Shruti Ahuja answered |
Acetic acid is a linear chain compound (acyclic) and hence it is not an example of ring compound (alicyclic).
The regulatory centres for respiration are located in :- a)Diencephalon and pons
- b)medulla oblongata & pons
- c)pons & cerebellum
- d)cerebellum and medulla oblongata
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The regulatory centres for respiration are located in :
a)
Diencephalon and pons
b)
medulla oblongata & pons
c)
pons & cerebellum
d)
cerebellum and medulla oblongata
|
|
Rahul Kumar answered |
The main regulation center responsible for respiration is medulla oblongata and pons virolli which lie in brain.
The given graph corresponds to which equation?

- a)V = 0
- b)PV = constant
- c)V/T = constant
- d)PT = constant
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The given graph corresponds to which equation?


a)
V = 0
b)
PV = constant
c)
V/T = constant
d)
PT = constant
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
In the given graph temperature remains constant with variation in volume. So the process is isothermal and PV = constant.
The figure shows the change in a thermodynamic system is going from an initial state A to the state B and C and returning to the state A. if UA = 0, UB = 30J an the heat given to the system in the process B → C, 50J, then determine:
(i) internal energy in the state C
(ii) heat given to the system in the process A B
- a)80J, 90J
- b)120J, 60J
- c)90J, 80J
- d)50J, 60J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure shows the change in a thermodynamic system is going from an initial state A to the state B and C and returning to the state A. if UA = 0, UB = 30J an the heat given to the system in the process B → C, 50J, then determine:
(i) internal energy in the state C
(ii) heat given to the system in the process A B

(i) internal energy in the state C
(ii) heat given to the system in the process A B

a)
80J, 90J
b)
120J, 60J
c)
90J, 80J
d)
50J, 60J

|
Bs Academy answered |
Work done in the process B → C, W = 0
Volume is constant and heat given to the system
Q = 50J (given)
Hence, by the first law of thermodynamics, the change in the internal energy is
ΔU = (UC - UB) = Q - W = 50J
UC = UB + ΔU = 30 + 50 = 80J
(ii) For the process A → B, ΔU = UB - UA
= 30Joule and W = area ABCD = DE × DA
= 2 × 30 = 60J
∴ Q = ΔU + W = 30 + 60 = 90J
Volume is constant and heat given to the system
Q = 50J (given)
Hence, by the first law of thermodynamics, the change in the internal energy is
ΔU = (UC - UB) = Q - W = 50J
UC = UB + ΔU = 30 + 50 = 80J
(ii) For the process A → B, ΔU = UB - UA
= 30Joule and W = area ABCD = DE × DA
= 2 × 30 = 60J
∴ Q = ΔU + W = 30 + 60 = 90J
Two gases X and Y kept in separate cylinders with same initial temperature and pressure are compressed to one third of their volume through isothermal and adiabatic process respectively. Which gas would have more pressure?- a)Gas X has higher temperature
- b)Gas Y has higher pressure
- c)Gas Y has lower pressure
- d)Gas X and Y are at 0 atm pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two gases X and Y kept in separate cylinders with same initial temperature and pressure are compressed to one third of their volume through isothermal and adiabatic process respectively. Which gas would have more pressure?
a)
Gas X has higher temperature
b)
Gas Y has higher pressure
c)
Gas Y has lower pressure
d)
Gas X and Y are at 0 atm pressure

|
Ambition Institute answered |
To determine which gas has more pressure after compression, consider the processes:
- Gas X undergoes an isothermal process, where the temperature remains constant. According to Boyle's Law, if volume decreases, pressure increases.
- Gas Y undergoes an adiabatic process, where no heat enters or leaves the system. The pressure increase is more significant than in an isothermal process, as both temperature and pressure increase due to compression.
Therefore, Gas Y will have a higher pressure than Gas X after compression.
Isothermal curves are obtained by drawing –- a)P against V
- b)P against T
- c)PV against R
- d)PV against V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Isothermal curves are obtained by drawing –
a)
P against V
b)
P against T
c)
PV against R
d)
PV against V

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
In an isothermal process, temperature remains constant and process equation is, PV = constant
So a graph is drawn between P and V.
So a graph is drawn between P and V.
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is caused to go through the cycle shown in fig. then the change in the internal energy in expanding the gas from a to c along path abc is 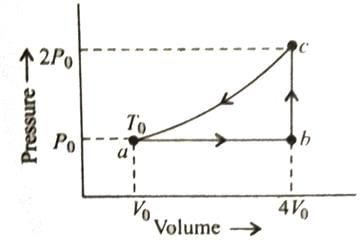
- a)3P0V0
- b)6RT0
- c)4.5 RT0
- d)10.5 RT0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is caused to go through the cycle shown in fig. then the change in the internal energy in expanding the gas from a to c along path abc is

a)
3P0V0
b)
6RT0
c)
4.5 RT0
d)
10.5 RT0

|
Stepway Academy answered |
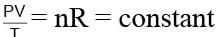
For any state of an ideal gas. Therefore
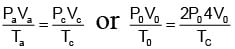
Tc = 8T0
Thus change in internal energy
ΔU = nCvΔT
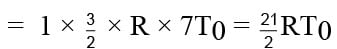
= 10.5 RT0
Which statement is incorrect about the transport of gases in the blood?- a)About 97% of oxygen is transported by the RBCs, with the remainder in a dissolved state in plasma.
- b)Nearly 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate in the blood.
- c)The enzyme carbonic anhydrase is absent in RBCs, which hinders CO2 transport.
- d)Oxyhemoglobin forms in the lung surface where conditions favor its formation, and dissociates at the tissues where conditions favor oxygen release.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is incorrect about the transport of gases in the blood?
a)
About 97% of oxygen is transported by the RBCs, with the remainder in a dissolved state in plasma.
b)
Nearly 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate in the blood.
c)
The enzyme carbonic anhydrase is absent in RBCs, which hinders CO2 transport.
d)
Oxyhemoglobin forms in the lung surface where conditions favor its formation, and dissociates at the tissues where conditions favor oxygen release.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The incorrect statement regarding the transport of gases in the blood is Option c. The enzyme carbonic anhydrase is not absent in RBCs; rather, it is highly abundant and plays a critical role in facilitating the rapid conversion of carbon dioxide and water into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. This reaction is vital for the efficient transport of carbon dioxide from tissues back to the lungs. The presence of carbonic anhydrase in RBCs greatly enhances the blood’s capacity to carry carbon dioxide, which is primarily transported as bicarbonate.
Topic in NCERT: Transport of gases
Line in NCERT: "rbcs contain a very high concentration of the enzyme, carbonic anhydrase and minute quantities of the same is present in the plasma too."
Chapter doubts & questions for December Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of December Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup

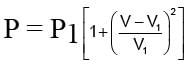 work done is
work done is