All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of May Week 4 for NEET Exam
Chemical used in salt bridge isa. KOHb. KCIc. KNO2d. KBrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anand Saha answered |
KCl is used as salt bridge because it provides positive K+ ions and negative Cl- ions as the salt bridge needs to maintain the neutrality in the system by providing enough negative ions equal to the positive ions during oxidation.
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V.What can be concluded from this?- a)A will be a good oxidising agent
- b)A will accept electrons easily
- c)A will undergo reduction easily
- d)A will undergo oxidation easily
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V.What can be concluded from this?
a)
A will be a good oxidising agent
b)
A will accept electrons easily
c)
A will undergo reduction easily
d)
A will undergo oxidation easily
|
|
Avantika Dasgupta answered |
Reduction Potential of Element A
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V. This means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. The more negative the reduction potential value, the easier it is for the element to undergo oxidation and lose electrons.
Explanation of Options
a) A will be a good oxidising agent - This statement is incorrect. A good oxidizing agent is one that accepts electrons from other species and undergoes reduction. But, since the reduction potential of element A is negative, it indicates that the element A is likely to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, so it is not a good oxidizing agent.
b) A will accept electrons easily - This statement is incorrect. The reduction potential value is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to lose electrons and undergo oxidation, rather than accepting electrons and undergoing reduction.
c) A will undergo reduction easily - This statement is incorrect. The reduction potential value is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, rather than undergoing reduction and gaining electrons.
d) A will undergo oxidation easily - This statement is correct. The reduction potential value of element A is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. The more negative the reduction potential value, the easier it is for the element to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. Therefore, element A will undergo oxidation easily.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D'. The reduction potential value of an element indicates its tendency to undergo oxidation or reduction. A negative reduction potential value indicates a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, while a positive reduction potential value indicates a strong tendency to undergo reduction and gain electrons.
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V. This means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. The more negative the reduction potential value, the easier it is for the element to undergo oxidation and lose electrons.
Explanation of Options
a) A will be a good oxidising agent - This statement is incorrect. A good oxidizing agent is one that accepts electrons from other species and undergoes reduction. But, since the reduction potential of element A is negative, it indicates that the element A is likely to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, so it is not a good oxidizing agent.
b) A will accept electrons easily - This statement is incorrect. The reduction potential value is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to lose electrons and undergo oxidation, rather than accepting electrons and undergoing reduction.
c) A will undergo reduction easily - This statement is incorrect. The reduction potential value is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, rather than undergoing reduction and gaining electrons.
d) A will undergo oxidation easily - This statement is correct. The reduction potential value of element A is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. The more negative the reduction potential value, the easier it is for the element to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. Therefore, element A will undergo oxidation easily.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D'. The reduction potential value of an element indicates its tendency to undergo oxidation or reduction. A negative reduction potential value indicates a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, while a positive reduction potential value indicates a strong tendency to undergo reduction and gain electrons.
A half cell reaction A- → A + e- has a large negative reduction potential. It follows that :- a)A is easily reduced
- b)A – is easily reduced
- c)A – is easily oxidised
- d)A is easily oxidised
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A half cell reaction A- → A + e- has a large negative reduction potential. It follows that :
a)
A is easily reduced
b)
A – is easily reduced
c)
A – is easily oxidised
d)
A is easily oxidised
|
|
Kalyan Chavan answered |
Can you please provide more details or context about the half-cell reaction you are referring to?
Hydrogen gas is not liberated when the following metal is added to dil. HCl.- a)Mg
- b)Sn
- c)Ag
- d)Zn
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen gas is not liberated when the following metal is added to dil. HCl.
a)
Mg
b)
Sn
c)
Ag
d)
Zn
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The metals, present below hydrogen in the electrochemical series, cannot liberate hydrogen from the dilute acids.
Among the given metals only Ag is present below hydrogen in electrochemical series, so it does not evolve hydrogen with dil HCl.
Ag−I−dilHCl ⟶ No reaction
Among the given metals only Ag is present below hydrogen in electrochemical series, so it does not evolve hydrogen with dil HCl.
Ag−I−dilHCl ⟶ No reaction
Temperature for the measurement of standard electrode potential is- a)298K
- b)300K
- c)30?C
- d)310K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Temperature for the measurement of standard electrode potential is
a)
298K
b)
300K
c)
30?C
d)
310K
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The standard electrode potentials are customarily determined at solute concentrations of 1 Molar, gas pressures of 1 atmosphere, and a standard temperature which is usually 25°C i.e, 298 K.
Consider the following reaction which of the following statement is true for this cell reaction.
(Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu)- a)Zn2+ ions are oxidized to Zn
- b)Zn is oxidized to Zn2+ ions
- c)Zn is reduced to Zn2+ ions
- d)Cu2+ ions are oxidized to Cu
-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction which of the following statement is true for this cell reaction.
(Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu)
(Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu)
a)
Zn2+ ions are oxidized to Zn
b)
Zn is oxidized to Zn2+ ions
c)
Zn is reduced to Zn2+ ions
d)
Cu2+ ions are oxidized to Cu
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- For the reaction Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu, Zn is oxidized to Zn2+ while Cu2+ is reduced to Cu
- In a redox reaction, the reactant that loses electrons (is oxidized) causes a reduction and is called a reducing agent. In the example above, zinc metal is the reducing agent; it loses two electrons (is oxidized) and becomes Zn2+ ion.
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V.What can be concluded from this?- a)A will be a good oxidising agent
- b)A will accept electrons easily
- c)A will undergo reduction easily
- d)A will undergo oxidation easily
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V.What can be concluded from this?
a)
A will be a good oxidising agent
b)
A will accept electrons easily
c)
A will undergo reduction easily
d)
A will undergo oxidation easily

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
Reduction potential means to accept electrons to reduce oneself.
A + e- → A- ∆Ereduction = +ve value
Since, the reduction potential is negative, it means that the reaction will reverse to make ∆E value +ve. So the reaction becomes,
A → A+ + e-
This becomes oxidation of A. So oxidation of A will be easy.
A + e- → A- ∆Ereduction = +ve value
Since, the reduction potential is negative, it means that the reaction will reverse to make ∆E value +ve. So the reaction becomes,
A → A+ + e-
This becomes oxidation of A. So oxidation of A will be easy.
The reduction potential of an element A is 1.71 V. What can be concluded from this?- a)A will lose electrons easily
- b)A will undergo reduction easily
- c)A will undergo oxidation easily
- d)A will be a good reducing agent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reduction potential of an element A is 1.71 V. What can be concluded from this?
a)
A will lose electrons easily
b)
A will undergo reduction easily
c)
A will undergo oxidation easily
d)
A will be a good reducing agent
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The standard reduction potential is the tendency for a chemical species to be reduced, and is measured in volts at standard conditions. The more positive the potential is the more likely it will be reduced. Hence, A will undergo reduction easily.
Stronger the oxidizing agent, greater is the:- a)Reactivity
- b)Ionic behaviour
- c)Oxidation potential
- d)Reduction potential
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Stronger the oxidizing agent, greater is the:
a)
Reactivity
b)
Ionic behaviour
c)
Oxidation potential
d)
Reduction potential
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Lithium is strongest Reducing agent because of lowest standard reduction potential. When something is oxidized, it reduces another substance, becoming a reducing agent. Hence lithium is the strongest reducing agent. remember, Li is the strongest reducing agent and F is the strongest oxidizing agent!
Enzyme for fertilization present in -- a)Acrosome of Sperm
- b)Nucleus of Sperm
- c)Tail of Sperm
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzyme for fertilization present in -
a)
Acrosome of Sperm
b)
Nucleus of Sperm
c)
Tail of Sperm
d)
None
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
In Eutherian mammals the acrosome contains degradative enzymes (including hyaluronidase and acrosin). These enzymes break down the outer membrane of the ovum, called the zona pellucida, allowing the haploid nucleus in the sperm cell to join with the haploid nucleus in the ovum.
So, correct answer is "Acrosome of sperm".
The electrode potential measures the :- a)tendency of a cell reaction to occur
- b)current carried by an elelctrode
- c)tendency of the electrode to gain or lose electrons
- d)difference in the ionisation of electrode and metal ion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The electrode potential measures the :
a)
tendency of a cell reaction to occur
b)
current carried by an elelctrode
c)
tendency of the electrode to gain or lose electrons
d)
difference in the ionisation of electrode and metal ion
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The tendency of an electrode to lose or gain electrons when it is in contact with its own ions in solution is called electrode potential.
Since the tendency to lose electrons means also the tendency to get oxidised, this tendency is called oxidation potential. Similarly, the tendency to gain electrons means the tendency to get reduced. Hence this tendency is called reduction potential.
Which of the following is the correct number of chromosomes based on the cell type?- a)Sperm: 23; Egg: 23; Zygote: 23
- b)Sperm: 46; Egg: 46; Zygote: 46
- c)Sperm: 23; Egg: 23; Zygote: 46
- d)Sperm: 46; Egg: 46; Zygote: 23
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct number of chromosomes based on the cell type?
a)
Sperm: 23; Egg: 23; Zygote: 23
b)
Sperm: 46; Egg: 46; Zygote: 46
c)
Sperm: 23; Egg: 23; Zygote: 46
d)
Sperm: 46; Egg: 46; Zygote: 23

|
Bs Academy answered |
- Sperm and egg are haploid cells hence have only one set of chromosomes.
- Zygote on the other hand is diploid thus has 46 chromosomes.
What layer of egg cell prevents entry of other sperms?- a)Corpus luteum
- b)Zona pellucida
- c)Endometrium
- d)Corona radiata
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What layer of egg cell prevents entry of other sperms?
a)
Corpus luteum
b)
Zona pellucida
c)
Endometrium
d)
Corona radiata
|
|
Baishali Joshi answered |
Explanation:
The process of fertilization involves the fusion of a sperm cell with an egg cell. However, only one sperm can fertilize an egg cell. If more than one sperm fertilizes an egg cell, it can result in a genetic abnormality which is non-viable for development. Therefore, the entry of other sperms needs to be prevented. This is achieved by the presence of the zona pellucida layer in the egg cell.
Zona Pellucida:
The zona pellucida is a thick glycoprotein layer that surrounds the plasma membrane of the mammalian oocyte. It is formed after the egg is released from the ovary and helps maintain the shape of the egg cell. It also plays a vital role in fertilization by preventing the entry of other sperm cells.
Prevents Entry of Other Sperms:
When a sperm cell approaches an egg cell, it releases enzymes that break down the outer layer of the zona pellucida. This allows the sperm to bind to the egg cell and fuse with it, resulting in fertilization. However, once a sperm has penetrated the zona pellucida and fused with the egg cell, the zona pellucida becomes impenetrable to other sperm cells. This is because the zona pellucida undergoes a biochemical change that makes it resistant to the penetration of other sperm cells.
Therefore, the zona pellucida layer of the egg cell prevents the entry of other sperm cells. This ensures that only one sperm fertilizes the egg cell, and the genetic material from both parents is mixed in the correct amount to produce a viable offspring.
The process of fertilization involves the fusion of a sperm cell with an egg cell. However, only one sperm can fertilize an egg cell. If more than one sperm fertilizes an egg cell, it can result in a genetic abnormality which is non-viable for development. Therefore, the entry of other sperms needs to be prevented. This is achieved by the presence of the zona pellucida layer in the egg cell.
Zona Pellucida:
The zona pellucida is a thick glycoprotein layer that surrounds the plasma membrane of the mammalian oocyte. It is formed after the egg is released from the ovary and helps maintain the shape of the egg cell. It also plays a vital role in fertilization by preventing the entry of other sperm cells.
Prevents Entry of Other Sperms:
When a sperm cell approaches an egg cell, it releases enzymes that break down the outer layer of the zona pellucida. This allows the sperm to bind to the egg cell and fuse with it, resulting in fertilization. However, once a sperm has penetrated the zona pellucida and fused with the egg cell, the zona pellucida becomes impenetrable to other sperm cells. This is because the zona pellucida undergoes a biochemical change that makes it resistant to the penetration of other sperm cells.
Therefore, the zona pellucida layer of the egg cell prevents the entry of other sperm cells. This ensures that only one sperm fertilizes the egg cell, and the genetic material from both parents is mixed in the correct amount to produce a viable offspring.
In a parallel plate capacitor, the capacity increases if- a)area of the plate is decreased
- b)distance between the plates increases
- c)area of the plate is increased
- d)dielectric constant decreases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a parallel plate capacitor, the capacity increases if
a)
area of the plate is decreased
b)
distance between the plates increases
c)
area of the plate is increased
d)
dielectric constant decreases
|
|
Muraad answered |
Since C = AEô/d
therefore, capacitance is proportional to area
as, the area increases capacitance also increases.
therefore, capacitance is proportional to area
as, the area increases capacitance also increases.
What is the correct order of travel of sperm through the female reproductive tract before it reaches the egg?- a)Vagina → Fallopian tube → Uterus → Cervix
- b)Vagina → Cervix → Uterus → Oviduct
- c)Vagina → Uterus → Cervix → Oviduct
- d)Vagina → Fallopian tube → Cervix → Uterus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct order of travel of sperm through the female reproductive tract before it reaches the egg?
a)
Vagina → Fallopian tube → Uterus → Cervix
b)
Vagina → Cervix → Uterus → Oviduct
c)
Vagina → Uterus → Cervix → Oviduct
d)
Vagina → Fallopian tube → Cervix → Uterus
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Sperms are released into the vagina. From here, they travel through the cervix and uterus before reaching oviduct or fallopian tube, where they can encounter an egg.
Two elements A and B have reduction potential’s 0.23V and 0.46V which statement is true regarding these two elements.- a)A will have Ionization energy two times than B
- b)A will have Ionization energy half than B
- c)B will lose electrons easily than A
- d)A will lose electrons easily than B
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two elements A and B have reduction potential’s 0.23V and 0.46V which statement is true regarding these two elements.
a)
A will have Ionization energy two times than B
b)
A will have Ionization energy half than B
c)
B will lose electrons easily than A
d)
A will lose electrons easily than B
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The more positive the reduction potential value, more is the tendency of the element to reduce itself and hence more will be the tendency to accept electrons. Hence the other element will have more tendency to lose electrons.
Consider the following two statements:
I. Not all copulations lead to fertilization and pregnancy
II. Fertilization can occur if the ovum and the sperms are simultaneously transported to the ampullary - isthmic junction.
- a)Both I and II are correct but II does not explain I
- b)Both I and II are correct and II correctly explains I
- c)I is correct but II is incorrect
- d)I is incorrect but II is correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following two statements:
I. Not all copulations lead to fertilization and pregnancy
II. Fertilization can occur if the ovum and the sperms are simultaneously transported to the ampullary - isthmic junction.
I. Not all copulations lead to fertilization and pregnancy
II. Fertilization can occur if the ovum and the sperms are simultaneously transported to the ampullary - isthmic junction.
a)
Both I and II are correct but II does not explain I
b)
Both I and II are correct and II correctly explains I
c)
I is correct but II is incorrect
d)
I is incorrect but II is correct

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Statement I is correct: Not all instances of copulation result in fertilization and pregnancy due to various factors such as timing, fertility issues, and other conditions.
Statement II is correct: Fertilization can indeed occur if both the ovum and sperm are present in the fallopian tubes simultaneously. However, this alone does not guarantee fertilization or pregnancy, as other conditions also play a role.
Therefore, both statements are correct, but Statement II does not fully explain Statement I.
Statement II is correct: Fertilization can indeed occur if both the ovum and sperm are present in the fallopian tubes simultaneously. However, this alone does not guarantee fertilization or pregnancy, as other conditions also play a role.
Therefore, both statements are correct, but Statement II does not fully explain Statement I.
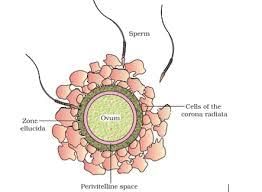
What is the order of layers or spaces from outside to inside of ovum? - a)Perivitelline space - Plasma membrane - Zona pellucida
- b)Plasma membrane - Perivitelline space - Zona pellucida
- c)Perivitelline space - Zona pellucida - Ovum cytoplasm
- d)Zona pellucida - Perivitelline space - Plasma membrane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the order of layers or spaces from outside to inside of ovum?
a)
Perivitelline space - Plasma membrane - Zona pellucida
b)
Plasma membrane - Perivitelline space - Zona pellucida
c)
Perivitelline space - Zona pellucida - Ovum cytoplasm
d)
Zona pellucida - Perivitelline space - Plasma membrane

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The correct order of layers or spaces from outside to inside is:
- Zona pellucida: The glycoprotein layer surrounding the oocyte.
- Perivitelline space: The space between the zona pellucida and the plasma membrane of the oocyte.
- Plasma membrane: The membrane that encloses the oocyte cytoplasm.
Thus, the order is Zona pellucida → Perivitelline space → Plasma membrane.
A parallel plate capacitor has two square plates with equal and opposite charges. The surface charge densities on the plate are +σ and −σ respectively. In the region between the plates the magnitude of electric field is:- a)σ/2ε0
- b)σ/ε0
- c)0
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate capacitor has two square plates with equal and opposite charges. The surface charge densities on the plate are +σ and −σ respectively. In the region between the plates the magnitude of electric field is:
a)
σ/2ε0
b)
σ/ε0
c)
0
d)
none of these
|
|
Aditi Mukherjee answered |
Denoted by σ and -σ, where σ is the surface charge density. The electric field between the plates is given by the equation:
E = σ / (2ε₀),
where ε₀ is the permittivity of free space.
The potential difference (V) between the plates is related to the electric field by the equation:
V = Ed,
where d is the distance between the plates.
The capacitance (C) of the parallel plate capacitor is given by the equation:
C = ε₀A / d,
where A is the area of each plate.
The capacitance can also be written as:
C = Q / V,
where Q is the charge on each plate.
So, the surface charge densities on the plates are directly related to the electric field, potential difference, and capacitance of the parallel plate capacitor.
E = σ / (2ε₀),
where ε₀ is the permittivity of free space.
The potential difference (V) between the plates is related to the electric field by the equation:
V = Ed,
where d is the distance between the plates.
The capacitance (C) of the parallel plate capacitor is given by the equation:
C = ε₀A / d,
where A is the area of each plate.
The capacitance can also be written as:
C = Q / V,
where Q is the charge on each plate.
So, the surface charge densities on the plates are directly related to the electric field, potential difference, and capacitance of the parallel plate capacitor.
A parallel plate air capacitor is charged to a potential difference of V volts. After disconnecting the charging battery the distance between the plates of the capacitor is increased using an insulating handle. As a result the potential difference between the plates
- a)increases
- b)decreases
- c)does not change
- d)becomes zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate air capacitor is charged to a potential difference of V volts. After disconnecting the charging battery the distance between the plates of the capacitor is increased using an insulating handle. As a result the potential difference between the plates
a)
increases
b)
decreases
c)
does not change
d)
becomes zero
|
|
Nandini Sharma answered |
Explanation:
When a capacitor is charged, it stores electrical energy in the form of electric field between its plates. The potential difference between the plates is directly proportional to the amount of charge stored in the capacitor, and inversely proportional to the distance between the plates.
When the distance between the plates is increased, the capacitance of the capacitor decreases. This means that the same amount of charge stored in the capacitor is now distributed over a larger area, resulting in a decrease in the potential difference between the plates.
However, since the capacitor is initially charged to a potential difference of V volts, it still contains that amount of charge even after the distance between the plates is increased. This means that the same amount of charge is now distributed over a larger area, resulting in a lower electric field strength between the plates.
Since the electric field strength is directly proportional to the potential difference between the plates, and the distance between the plates has increased, the potential difference between the plates increases to maintain the same electric field strength.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': the potential difference between the plates increases.
When a capacitor is charged, it stores electrical energy in the form of electric field between its plates. The potential difference between the plates is directly proportional to the amount of charge stored in the capacitor, and inversely proportional to the distance between the plates.
When the distance between the plates is increased, the capacitance of the capacitor decreases. This means that the same amount of charge stored in the capacitor is now distributed over a larger area, resulting in a decrease in the potential difference between the plates.
However, since the capacitor is initially charged to a potential difference of V volts, it still contains that amount of charge even after the distance between the plates is increased. This means that the same amount of charge is now distributed over a larger area, resulting in a lower electric field strength between the plates.
Since the electric field strength is directly proportional to the potential difference between the plates, and the distance between the plates has increased, the potential difference between the plates increases to maintain the same electric field strength.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': the potential difference between the plates increases.
The haploid ovum is also called as _____________.- a)oogonium
- b)oocyte
- c)ootid
- d)osteoid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The haploid ovum is also called as _____________.
a)
oogonium
b)
oocyte
c)
ootid
d)
osteoid
|
|
Shalini Ahuja answered |
Haploid Ovum: Also known as Ootid
The haploid ovum is the female reproductive cell produced by the ovary. It is also known as the egg cell or the female gamete. The ovum is a highly specialized cell that is essential for sexual reproduction in humans and many other animals. The term "haploid" means that the ovum contains only one set of chromosomes, which is half the number found in other cells of the body. Therefore, the ovum has 23 chromosomes in humans, while other body cells have 46 chromosomes.
The process of producing the haploid ovum is called oogenesis. It begins before birth and continues until menopause. During oogenesis, the ovary produces immature ova called oocytes. These oocytes undergo meiosis, a process of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes by half, to form haploid ovum. The ovum is then released from the ovary into the fallopian tube, where it may be fertilized by a sperm to form a zygote.
The term "ootid" is another name for the haploid ovum. It is used to describe the ovum immediately after completion of meiosis II. At this point, the ovum has completed its maturation process and is ready for fertilization.
In conclusion, the haploid ovum is also known as the ootid, which is a highly specialized female reproductive cell produced by the ovary through oogenesis. It contains only one set of chromosomes and is essential for sexual reproduction in humans and many other animals.
The haploid ovum is the female reproductive cell produced by the ovary. It is also known as the egg cell or the female gamete. The ovum is a highly specialized cell that is essential for sexual reproduction in humans and many other animals. The term "haploid" means that the ovum contains only one set of chromosomes, which is half the number found in other cells of the body. Therefore, the ovum has 23 chromosomes in humans, while other body cells have 46 chromosomes.
The process of producing the haploid ovum is called oogenesis. It begins before birth and continues until menopause. During oogenesis, the ovary produces immature ova called oocytes. These oocytes undergo meiosis, a process of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes by half, to form haploid ovum. The ovum is then released from the ovary into the fallopian tube, where it may be fertilized by a sperm to form a zygote.
The term "ootid" is another name for the haploid ovum. It is used to describe the ovum immediately after completion of meiosis II. At this point, the ovum has completed its maturation process and is ready for fertilization.
In conclusion, the haploid ovum is also known as the ootid, which is a highly specialized female reproductive cell produced by the ovary through oogenesis. It contains only one set of chromosomes and is essential for sexual reproduction in humans and many other animals.
What part of the oviduct does the sperm encounter the egg?- a)Infundibulum
- b)Isthmus
- c)Ampulla
- d)Fundus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What part of the oviduct does the sperm encounter the egg?
a)
Infundibulum
b)
Isthmus
c)
Ampulla
d)
Fundus

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- The egg is released and awaits in ampulla for the sperm.
- The sperms cross the reproductive tract barriers before reaching the ampulla to fertilize the egg.
The fusion of haploid sperm and egg nuclei during fertilization leads to formation of a __________- a)Haploid zygote
- b)Haploid embryo
- c)Diploid zygote
- d)Diploid embryo
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The fusion of haploid sperm and egg nuclei during fertilization leads to formation of a __________
a)
Haploid zygote
b)
Haploid embryo
c)
Diploid zygote
d)
Diploid embryo

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The fusion of sperm and egg restores the chromosome number.
The new cell is called zygote having the potential to develop into a new organism.
A parallel plate capacitor is charged and then isolated. What is the effect of increasing the plate separation on charge, potential, capacitance, respectively?- a)constant, decreases, decreases
- b)increases, decreases, decreases
- c)constant, decreases, increases
- d)constant, increases, decreases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate capacitor is charged and then isolated. What is the effect of increasing the plate separation on charge, potential, capacitance, respectively?
a)
constant, decreases, decreases
b)
increases, decreases, decreases
c)
constant, decreases, increases
d)
constant, increases, decreases
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
As the capacitor is isolated after charging, charge on it remains constant. Plate separation increases d, decreases C = ϵ0A/d and hence increases potential V = q/C.
What triggers the completion of meiosis of secondary oocyte?- a)Entry of sperm into the egg cell
- b)Maturation of Graafian follicle
- c)Release of estrogen
- d)Coitus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What triggers the completion of meiosis of secondary oocyte?
a)
Entry of sperm into the egg cell
b)
Maturation of Graafian follicle
c)
Release of estrogen
d)
Coitus

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- The secondary oocyte released from the ovary has finished first round of meiosis.
- The second round of meiosis occurs in ampulla after the egg encounters the sperm.
- This leads to formation of large ovum and a tiny second polar body.
Meiosis II completed in female when-- a)It is in infundibulum
- b)It is in Ampulla region before fertilization
- c)In ampulla region after fertilization
- d)At morula stage
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis II completed in female when-
a)
It is in infundibulum
b)
It is in Ampulla region before fertilization
c)
In ampulla region after fertilization
d)
At morula stage
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Fertilization of ovum induce meiosis II in Secondary oocyte to form ootid
Anaphase promoting complex get active in Ovum or Secondary oocyte when-- a)Entry of sperm occur
- b)During Meiosis I
- c)After fusion of male and female nuclei
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Anaphase promoting complex get active in Ovum or Secondary oocyte when-
a)
Entry of sperm occur
b)
During Meiosis I
c)
After fusion of male and female nuclei
d)
None
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Sperm entry activate APC which promote ovum nuclei from metaphase II to Anaphase II so that meiosis II get completed.
A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a battery as shown in figure. Consider two situations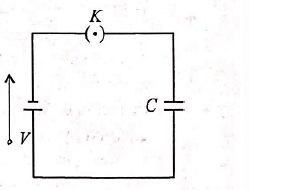
(i) key KK is kept closed and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle
(ii) key KK is opened and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle
Which of the following statements is correct?- a)In (i), Q remains same but C changes
- b)In (ii) V remains same but C changes
- c)In (i) V remains same and hence Q changes
- d)In (ii) both Q and V changes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a battery as shown in figure. Consider two situations

(i) key KK is kept closed and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle
(ii) key KK is opened and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle
Which of the following statements is correct?
a)
In (i), Q remains same but C changes
b)
In (ii) V remains same but C changes
c)
In (i) V remains same and hence Q changes
d)
In (ii) both Q and V changes
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
When key K is kept closed, condenser C is charged to potential V. When plates of capacitors are moved apart, its capacitance, C = ϵoA/d decreases.
As potential of condenser remains same, charge Q = CV decreases. So option is correct. Once key K is closed, condenser gets charged, Q = CV.
Now, if key K is opened, battery is disconnected, no more charging can occur i.e. Q remains same.
As plates or capacitor are moved apart, its capacity C = ϵoA/d decreases.
Therefore, its potential, V = q/C increases
As potential of condenser remains same, charge Q = CV decreases. So option is correct. Once key K is closed, condenser gets charged, Q = CV.
Now, if key K is opened, battery is disconnected, no more charging can occur i.e. Q remains same.
As plates or capacitor are moved apart, its capacity C = ϵoA/d decreases.
Therefore, its potential, V = q/C increases
Chapter doubts & questions for May Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of May Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









