All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of August Week 2 for NEET Exam
If we double the radius of a current carrying coil keeping the current unchanged. what happens to the magnetic field at its Centre?- a)halved
- b)doubled
- c)remains unchanged
- d)becomes four times
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If we double the radius of a current carrying coil keeping the current unchanged. what happens to the magnetic field at its Centre?
a)
halved
b)
doubled
c)
remains unchanged
d)
becomes four times

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
As,
B=μonI/2a
a ->radius
B ∝1/a
B1/B2=a2/a1
B1=2B2
B2=(1/2) x B1,
Magnetic field is halved.
B=μonI/2a
a ->radius
B ∝1/a
B1/B2=a2/a1
B1=2B2
B2=(1/2) x B1,
Magnetic field is halved.
Two concentric coils carry the same current in opposite directions. The diameter of the inner coil is half that of the outer coil. If the magnetic field produced by the outer coil at the common centre are 1 T, the net field at the centre is
- a)4T
- b)2T
- c)1T
- d)3T
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two concentric coils carry the same current in opposite directions. The diameter of the inner coil is half that of the outer coil. If the magnetic field produced by the outer coil at the common centre are 1 T, the net field at the centre is
a)
4T
b)
2T
c)
1T
d)
3T
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
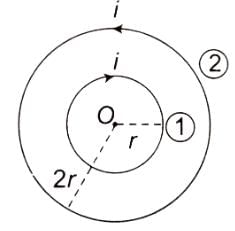
The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying coil at its center is given by the formula,
B = μ0 * (N*I/R),
where,
B is the magnetic field,
μ0 is the permeability of free space,
N is the number of turns in the coil,
I is the current through the coil, and
R is the radius of the coil.
In this case, both the coils carry the same current but in opposite directions. So, the fields produced by them will be in opposite directions. Also, the diameter of the inner coil is half that of the outer coil. Thus, the radius of the inner coil will be half that of the outer coil.
Therefore, the field at the center due to the inner coil will be double that due to the outer coil (because the magnetic field is inversely proportional to the radius).
Since the fields are in opposite directions, the net field at the center will be the difference between the two fields. That is, 2B (due to the inner coil) - B (due to the outer coil) = B.
So, if the field due to the outer coil is 1 T (Tesla), the net field at the center will also be 1 T.
Hence, the correct answer is 3. 1T.
The magnetic field due to circular coil of 200 turns of diameter 0.1m carrying a current of 5A at a point on the axis of the coil at a distance 0.15m from the center of the coil will be- a)
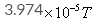
- b)
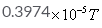
- c)
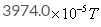
- d)
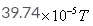
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic field due to circular coil of 200 turns of diameter 0.1m carrying a current of 5A at a point on the axis of the coil at a distance 0.15m from the center of the coil will be
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
B=μ02πnIa2/4π (a2+x2)3/2
=10−7×2×(22/7)×200×5×(0⋅1/2)2/ [(0⋅1/2)2+(0⋅15)2]3/2
=39.74x10-5
=10−7×2×(22/7)×200×5×(0⋅1/2)2/ [(0⋅1/2)2+(0⋅15)2]3/2
=39.74x10-5
Wire of length l, carries a steady current I. It is bent first to form a circular coil of one turn. The same wire of same length is now bent more sharply to give two loops of smaller radius the magnetic field at the centre caused by the same current is- a)one third of its initial value
- b)nine times of its initial value
- c)four times of its initial value
- d)unaltered
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Wire of length l, carries a steady current I. It is bent first to form a circular coil of one turn. The same wire of same length is now bent more sharply to give two loops of smaller radius the magnetic field at the centre caused by the same current is
a)
one third of its initial value
b)
nine times of its initial value
c)
four times of its initial value
d)
unaltered
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Let the radii be r1 and r2 respectively.
Since there are two turns of radius r2, r1=2r2
Magnetic field B at the centre of the coil of radius r1 B1=μoi/2r1=μoi/4r2
Magnetic field B at the center of the coil of radius r2 B2=2×μoi/2r2
∴ B2/B1 =(2× μoi/2r2)/(μoi /4r2) =4
Hence the answer is option C, four times its initial value.
Since there are two turns of radius r2, r1=2r2
Magnetic field B at the centre of the coil of radius r1 B1=μoi/2r1=μoi/4r2
Magnetic field B at the center of the coil of radius r2 B2=2×μoi/2r2
∴ B2/B1 =(2× μoi/2r2)/(μoi /4r2) =4
Hence the answer is option C, four times its initial value.
A circular coil of radius r carries current I. The magnetic field at its center is B. at what distance from the center on the axis of the coil magnetic field will be B/8- a)√3R
- b)√2R
- c)2R
- d)3R
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A circular coil of radius r carries current I. The magnetic field at its center is B. at what distance from the center on the axis of the coil magnetic field will be B/8
a)
√3R
b)
√2R
c)
2R
d)
3R

|
Shilpa Saha answered |
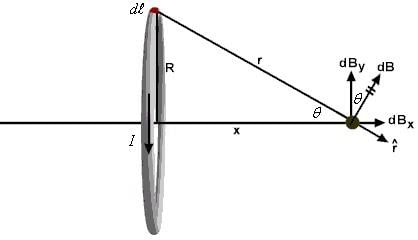
As you know that magnetic field at point on the axis of current carrying ring is
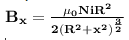
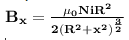
where x is the point on the axis of ring, R is the radius of ring , i is the current carrying on ring and N is the number of turns .
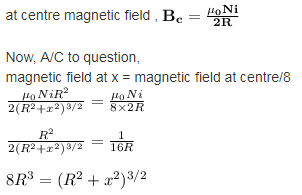
This is possible only when x = +-√3R
Hence, √3R distance from the centre magnetic field is equal to magnetic field at centre .

A straight conductor carrying current I is split into circular loop as shown in figure a , the magnetic induction at the center of the circular loop is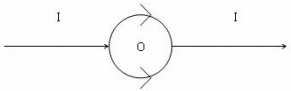
- a)Zero
- b)
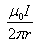
- c)
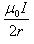
- d)Infinite
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A straight conductor carrying current I is split into circular loop as shown in figure a , the magnetic induction at the center of the circular loop is
a)
Zero
b)
c)
d)
Infinite
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The magnetic field at the center O due to the upper side of the semicircular current loop is equal and opposite to that due to the lower side of the loop.
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
|
|
Nandita Ahuja answered |
Fluorine atom have 2+7 electrons so an F2 molecule contain 18 electrons.
Hence, 8 electrons occupy the antibonding orbitals.
Hence, 8 electrons occupy the antibonding orbitals.
A circular loop of radius 0.0157 m carries a current of 2 A. The magnetic field at the centre of the loop is- a)3.14 x 10-5 weber /m2
- b)1.57 x 10-5 weber /m2
- c)1.57 x 10-5 weber /m2
- d)8.0 x 10-5 weber /m2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A circular loop of radius 0.0157 m carries a current of 2 A. The magnetic field at the centre of the loop is
a)
3.14 x 10-5 weber /m2
b)
1.57 x 10-5 weber /m2
c)
1.57 x 10-5 weber /m2
d)
8.0 x 10-5 weber /m2
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The magnetic field due to a circular loop is given by:
B= μ02πi/4πr
=10−7×2π×2/0.0157
=8×10−5 Wb/m2
B= μ02πi/4πr
=10−7×2π×2/0.0157
=8×10−5 Wb/m2
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?- a)SRP values of halogens F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
- b)Bond dissociation enthalpy of Br2 > F2 > Cl2 > I2
- c)Boiling points of I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
- d)Reducing power of I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
a)
SRP values of halogens F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
b)
Bond dissociation enthalpy of Br2 > F2 > Cl2 > I2
c)
Boiling points of I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
d)
Reducing power of I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
The correct order of bond dissociation enthalpy is
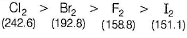
When chlorine reacts with hot, cone. NaOH, the products formed are- a)NaCI
- b)NaOCI
- c)NaCIO3
- d)HCI
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
When chlorine reacts with hot, cone. NaOH, the products formed are
a)
NaCI
b)
NaOCI
c)
NaCIO3
d)
HCI

|
Anupama Nair answered |
When Cl2 reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH, then....6NaOH+3Cl2→5NaCl +NaClO3+3H2O...When Cl2 reacts with cold and dilute NaOH then ...2NaOH+Cl2→NaCl+NaOCl+H2O
The magnetic field due to current element depends upon which of the following factors:- a)Current flowing through it.
- b)Distance from it.
- c)Its length.
- d)All of above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic field due to current element depends upon which of the following factors:
a)
Current flowing through it.
b)
Distance from it.
c)
Its length.
d)
All of above.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
From Biot-Savart law, magnetic field at a point p, B= (μ0/4π)∫ [(Idl×r)/ r3]
where r is the distance of point p from conductor and I is the current in the conductor.
Thus magnetic field due to current carrying conductor depends on the current flowing through conductor and distance from the conductor and length of the conductor.
where r is the distance of point p from conductor and I is the current in the conductor.
Thus magnetic field due to current carrying conductor depends on the current flowing through conductor and distance from the conductor and length of the conductor.
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given:
What would be the base sequence of RNA transcript obtained from the given DNA segment?
5-G C A T T C G G C T A G T A A C-3 Coding strand of DNA
3-C G T A A G C C G A T C A T T G-5 Non-coding strand of DNA- a)5′−GCAUUCGGCUAGUAAC−3′
- b)5′−CGUAAGCCGAUCAUUG−3′
- c)5′−GCATTCGGCTAGTAAC−3′
- d)3′−CGTAAGCCGATCATTG−5′
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given:
What would be the base sequence of RNA transcript obtained from the given DNA segment?
5-G C A T T C G G C T A G T A A C-3 Coding strand of DNA
3-C G T A A G C C G A T C A T T G-5 Non-coding strand of DNA
What would be the base sequence of RNA transcript obtained from the given DNA segment?
5-G C A T T C G G C T A G T A A C-3 Coding strand of DNA
3-C G T A A G C C G A T C A T T G-5 Non-coding strand of DNA
a)
5′−GCAUUCGGCUAGUAAC−3′
b)
5′−CGUAAGCCGAUCAUUG−3′
c)
5′−GCATTCGGCTAGTAAC−3′
d)
3′−CGTAAGCCGATCATTG−5′
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Since the two strands have opposite polarity and the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase also catalyse the polymerisation in only one direction, that is, 5'→3' the strand that has the sequence same as RNA (except thymine at the place of uracil ) is displaced during transcription. This strand (which does not code for anything ) is referred to as coding strand.
The total number of positive oxidation states shown by fluorine is
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
The total number of positive oxidation states shown by fluorine is
|
|
Puja Gupta answered |
Fluorine is an element that belongs to the halogen group in the periodic table. It has an atomic number of 9, and its electron configuration is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^5. Fluorine is highly electronegative, meaning it has a strong tendency to attract electrons towards itself when it forms chemical bonds. This property is due to its relatively small atomic size and high effective nuclear charge.
Fluorine has a total of 7 valence electrons, which are electrons in its outermost energy level (2s^2 2p^5). In order to achieve a stable electron configuration, fluorine tends to gain one electron to complete its octet. By gaining one electron, fluorine achieves a stable electron configuration similar to the nearest noble gas, neon (1s^2 2s^2 2p^6).
Fluorine's strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain electrons result in it having only one common oxidation state, which is -1. In this oxidation state, fluorine gains one electron to achieve a stable configuration of 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6. This oxidation state is commonly observed in compounds where fluorine acts as an anion, such as in the compound sodium fluoride (NaF). In NaF, fluorine gains an electron from sodium to form the F- ion.
It is important to note that although fluorine is highly electronegative and tends to gain electrons, it does not have the capability to lose electrons easily and form positive oxidation states. This is because fluorine's valence shell is almost full, and losing electrons would require a significant amount of energy.
In conclusion, fluorine has only one common oxidation state, which is -1. This is due to its strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Fluorine has a total of 7 valence electrons, which are electrons in its outermost energy level (2s^2 2p^5). In order to achieve a stable electron configuration, fluorine tends to gain one electron to complete its octet. By gaining one electron, fluorine achieves a stable electron configuration similar to the nearest noble gas, neon (1s^2 2s^2 2p^6).
Fluorine's strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain electrons result in it having only one common oxidation state, which is -1. In this oxidation state, fluorine gains one electron to achieve a stable configuration of 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6. This oxidation state is commonly observed in compounds where fluorine acts as an anion, such as in the compound sodium fluoride (NaF). In NaF, fluorine gains an electron from sodium to form the F- ion.
It is important to note that although fluorine is highly electronegative and tends to gain electrons, it does not have the capability to lose electrons easily and form positive oxidation states. This is because fluorine's valence shell is almost full, and losing electrons would require a significant amount of energy.
In conclusion, fluorine has only one common oxidation state, which is -1. This is due to its strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration.
The process of copying genetic information from one strand of DNA to RNA is termed as __________- a)replication
- b)transcription
- c)translation
- d)reverse transcription
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of copying genetic information from one strand of DNA to RNA is termed as __________
a)
replication
b)
transcription
c)
translation
d)
reverse transcription
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The process of copying genetic information from one strand of the DNA into RNA is termed as transcription. Unlike the process of replication, which once sets in, the total DNA of an organism gets duplicated, in transcription only a segment of DNA and only one of the strands is copied into RNA.
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. The fluoride ores are- a)carnalite
- b)cryolite
- c)fluorspar
- d)chile saltpetre
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
The fluoride ores are
a)
carnalite
b)
cryolite
c)
fluorspar
d)
chile saltpetre

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
The cryolite (Na3AIF6) and fluorspar (CaF2) are two ores of fluoride.
Solid iodine is an example of- a)covalent solid
- b)ionic solid
- c)molecular solid
- d)metallic solid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Solid iodine is an example of
a)
covalent solid
b)
ionic solid
c)
molecular solid
d)
metallic solid

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
Solid iodine is a molecular solid.
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from- a)zero to +1 and zero to -5
- b)zero to -1 and zero to +5
- c)zero to -1 and zero to +5
- d)zero to +1 and zero to -3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from
a)
zero to +1 and zero to -5
b)
zero to -1 and zero to +5
c)
zero to -1 and zero to +5
d)
zero to +1 and zero to -3

|
Shail Chakraborty answered |
When chlorine gas reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH solution, it disproportionates into Chloride (Cl-) and Chlorate (ClO3-) ions.
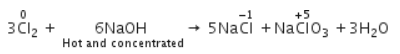
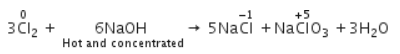
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.Q. Statement I : All halogens are coloured.Statement II : Halogens absorbs part of the light in the visible region.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : All halogens are coloured.
Statement II : Halogens absorbs part of the light in the visible region.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
Halogen molecule absorbs light in the visible region as a result of which their electrons are excited to higher energy level while the remaining light is transmitted.
The colour of halogens is actually the colour of this transmitted light, i.e. halogens have complementary colours.
The colour of halogens is actually the colour of this transmitted light, i.e. halogens have complementary colours.
In transcription in eukaryotes, heterogenous nuclear RNA (hn RNA) is transcribed by- a)RNA polymerase I
- b)RNA polymerase II
- c)RNA polymerase III
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In transcription in eukaryotes, heterogenous nuclear RNA (hn RNA) is transcribed by
a)
RNA polymerase I
b)
RNA polymerase II
c)
RNA polymerase III
d)
All of these
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases. RNA polymerase I is located in the nucleolus and transcribes for RNAs (28S, 18S and 5.8S) whereas RNA polymerase II is localised in the nucleoplasm and used for hnRNA, mRNA and RNA polymerase Ill is localised in the nucleus, possibly the nucleolar-nucleoplasm interface and transcribes for tRNA, 5S, RNA and nRNAs.
The fully processed hnRNA is called (i) and is transported out of the (ii) into (iii) for translation.- a)(i) mRNA, (ii) Nucleus, (iii) Cytoplasm
- b)(i) mRNA, (ii) Cytoplasm, (iii) Nucleus
- c)(i) tRNA, (ii) Cytoplasm, (iii) Nucleus
- d)(i) tRNA, (ii) Nucleus, (iii) Cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The fully processed hnRNA is called (i) and is transported out of the (ii) into (iii) for translation.
a)
(i) mRNA, (ii) Nucleus, (iii) Cytoplasm
b)
(i) mRNA, (ii) Cytoplasm, (iii) Nucleus
c)
(i) tRNA, (ii) Cytoplasm, (iii) Nucleus
d)
(i) tRNA, (ii) Nucleus, (iii) Cytoplasm
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Heterogeneous nuclear RNA or hnRNA is a term that encompasses various types and sizes of RNAs found in the eukaryotic cell nucleus. When this undergoes modifications and processing it will give rise to the mature mRNA that has the inherent code for the protein synthesis (amino acid code). The mRNA in eukaryotes is synthesized in the nucleus and hence should be transported to the cytoplasm and into the ribosome for protein synthesis by the process of translation.
The structural genes, in eukaryotes possess coding and non-coding sequences called as (i) and (ii) respectively.- a)(i) promoter, (ii) operator
- b)(i) introns, (ii) exons
- c)(i) exons, (ii) introns
- d)(i) enhancer, (ii) silencer
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The structural genes, in eukaryotes possess coding and non-coding sequences called as (i) and (ii) respectively.
a)
(i) promoter, (ii) operator
b)
(i) introns, (ii) exons
c)
(i) exons, (ii) introns
d)
(i) enhancer, (ii) silencer
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
In eukaryotes, the coding sequences or expressed sequences are defined as exons. Exons appear in mature or processed RNA. The exons are interrupted by introns, they do not appear in mature or processed RNA.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Which of the following property decreases down the group in the halogens?- a)Electropositive nature
- b)Density
- c)Boiling point
- d)Ionisation enthalp
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the following property decreases down the group in the halogens?
a)
Electropositive nature
b)
Density
c)
Boiling point
d)
Ionisation enthalp

|
Amar Jain answered |
Due to increase in atomic size, ionisation enthalpy decreases down the group.
One gas bleaches the colour of flowers by reduction and another gas by oxidation. The gases respectively are- a)SO2 and CI2
- b)CO2 and CI2
- c)NO and CI2
- d)H2S and Br2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One gas bleaches the colour of flowers by reduction and another gas by oxidation. The gases respectively are
a)
SO2 and CI2
b)
CO2 and CI2
c)
NO and CI2
d)
H2S and Br2
|
|
Maya Reddy answered |
Gas Bleaching of Flowers by Reduction and Oxidation
Reduction and oxidation reactions play a crucial role in various chemical processes. In the context of bleaching the color of flowers, two gases are involved, one causing bleaching by reduction and the other by oxidation. Let us examine the given options to identify the correct gases.
Option A: SO2 and Cl2
Option B: CO2 and Cl2
Option C: NO and Cl2
Option D: H2S and Br2
Based on the given options, the correct gases are SO2 and Cl2.
Explanation:
1. Reduction and Oxidation Reactions:
Reduction is a process that involves the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state, while oxidation is a process that involves the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state. In the context of bleaching, reduction and oxidation reactions are responsible for altering the color of flowers.
2. SO2 and Cl2:
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is an example of a reducing agent. It can bleach the color of flowers by undergoing reduction reactions. SO2 is capable of reacting with pigments responsible for the color of flowers and reducing them, resulting in a loss of color.
Chlorine gas (Cl2), on the other hand, is an example of an oxidizing agent. It can bleach the color of flowers by undergoing oxidation reactions. Cl2 can react with pigments responsible for the color of flowers and oxidize them, leading to a loss of color.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A: SO2 and Cl2. SO2 acts as a reducing agent, while Cl2 acts as an oxidizing agent to bleach the color of flowers.
In summary, reduction and oxidation reactions are involved in bleaching the color of flowers. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) acts as a reducing agent, while chlorine gas (Cl2) acts as an oxidizing agent to bleach the color of flowers.
Reduction and oxidation reactions play a crucial role in various chemical processes. In the context of bleaching the color of flowers, two gases are involved, one causing bleaching by reduction and the other by oxidation. Let us examine the given options to identify the correct gases.
Option A: SO2 and Cl2
Option B: CO2 and Cl2
Option C: NO and Cl2
Option D: H2S and Br2
Based on the given options, the correct gases are SO2 and Cl2.
Explanation:
1. Reduction and Oxidation Reactions:
Reduction is a process that involves the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state, while oxidation is a process that involves the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state. In the context of bleaching, reduction and oxidation reactions are responsible for altering the color of flowers.
2. SO2 and Cl2:
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is an example of a reducing agent. It can bleach the color of flowers by undergoing reduction reactions. SO2 is capable of reacting with pigments responsible for the color of flowers and reducing them, resulting in a loss of color.
Chlorine gas (Cl2), on the other hand, is an example of an oxidizing agent. It can bleach the color of flowers by undergoing oxidation reactions. Cl2 can react with pigments responsible for the color of flowers and oxidize them, leading to a loss of color.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A: SO2 and Cl2. SO2 acts as a reducing agent, while Cl2 acts as an oxidizing agent to bleach the color of flowers.
In summary, reduction and oxidation reactions are involved in bleaching the color of flowers. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) acts as a reducing agent, while chlorine gas (Cl2) acts as an oxidizing agent to bleach the color of flowers.
When carnallite is dissolved in water the number of ions formed are
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
When carnallite is dissolved in water the number of ions formed are

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
Carnallite is a double salt. It will dissociate into simple substances or ions completely when dissolved in water.
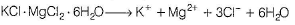
Hence, 5 ions are produced.
Hence, 5 ions are produced.
If the sequence of bases in DNA is GCTTAGGCAA then the sequence of bases in its transcript will be- a)GCTTAGGCAA
- b)CGAATCCGTT
- c)CGAAUCCGUU
- d)AACGGAUUCG
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the sequence of bases in DNA is GCTTAGGCAA then the sequence of bases in its transcript will be
a)
GCTTAGGCAA
b)
CGAATCCGTT
c)
CGAAUCCGUU
d)
AACGGAUUCG
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
mRNA strand is complementary to one of the DNA strands i.e., template strand. In RNA, uracil is present instead of thymine which is complementary to adenine. Cytosine and guanine are also complementary to each other. Hence, the sequence of bases in transcript would be CGAAUCCGUU.
Menthyl guanosine triphosphate is added to the 5' end of hnRNA in a process of- a)splicing
- b)capping
- c)tailing
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Menthyl guanosine triphosphate is added to the 5' end of hnRNA in a process of
a)
splicing
b)
capping
c)
tailing
d)
none of these
|
|
Diya Khanna answered |
Explanation:
Capping of hnRNA:
- The process of adding a modified nucleotide (menthyl guanosine triphosphate) to the 5' end of hnRNA is known as capping.
- This modification protects the mRNA from degradation and helps in the recognition of the mRNA by ribosomes during translation.
Function of capping:
- The capping of hnRNA is essential for the proper processing and translation of mRNA.
- It also plays a role in regulating gene expression and facilitating the export of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Importance of capping:
- Capping helps in the stability of mRNA by protecting it from exonuclease degradation.
- It also assists in the initiation of translation by providing a recognition signal for ribosomes.
Therefore, in the given question, the addition of menthyl guanosine triphosphate to the 5' end of hnRNA is a part of the capping process, which is crucial for the proper functioning of mRNA in gene expression.
Capping of hnRNA:
- The process of adding a modified nucleotide (menthyl guanosine triphosphate) to the 5' end of hnRNA is known as capping.
- This modification protects the mRNA from degradation and helps in the recognition of the mRNA by ribosomes during translation.
Function of capping:
- The capping of hnRNA is essential for the proper processing and translation of mRNA.
- It also plays a role in regulating gene expression and facilitating the export of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Importance of capping:
- Capping helps in the stability of mRNA by protecting it from exonuclease degradation.
- It also assists in the initiation of translation by providing a recognition signal for ribosomes.
Therefore, in the given question, the addition of menthyl guanosine triphosphate to the 5' end of hnRNA is a part of the capping process, which is crucial for the proper functioning of mRNA in gene expression.
Which of the following represents the decreasing order of van der Waals’ forces in halogens ?- a)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
- b)I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
- c)Br2 > Cl2 > F2 > I2
- d)Cl2 > F2 > I2 > Br2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents the decreasing order of van der Waals’ forces in halogens ?
a)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
b)
I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
c)
Br2 > Cl2 > F2 > I2
d)
Cl2 > F2 > I2 > Br2
|
|
Nishtha Dasgupta answered |
The question is incomplete as it does not provide the options for the van der Waals forces. Please provide the options so I can assist you further.
The source of iodine is- a)in free state
- b)in seaweeds
- c)as caliche
- d)As Agl
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The source of iodine is
a)
in free state
b)
in seaweeds
c)
as caliche
d)
As Agl

|
Ishita Deshpande answered |
Certain deep seaweeds contain 0.5% of iodine in their ashes. Caliche or crude chile saltpetre contain about 0.2% of NaIO3.
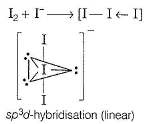
Direction (Q, Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. The num ber of lone pair of electrons present on the central iodine in I-3 ion is
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q, Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
The num ber of lone pair of electrons present on the central iodine in I-3 ion is

|
Baishali Chakraborty answered |
Three lone pairs are present on the central iodine in triiodide ion.
In an animal cell, the processes of transcription and translation occur in- a)nucleus only
- b)cytoplasm only
- c)nucleus and cytoplasm respectively
- d)endoplasmic reticulum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an animal cell, the processes of transcription and translation occur in
a)
nucleus only
b)
cytoplasm only
c)
nucleus and cytoplasm respectively
d)
endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
As eukaryotes possess compartmentalization of cell organelles, therefore, transcription occurs in nucleus and translation occurs in the cytoplasm in eukaryotes.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).Passage
Group 17 elements are known as halogens ( sea salt forming). Their general configuration is ns2np5 where, n = 2 to 7. Fluorine is the first member of the group differs in several ways from the rest of the group. Halogens are highly reactive elements having strong affinity for hydrogen. All the halogens form both ionic and covalent compounds .Fluorine is always monovalent and shows -1 oxidation state in its compounds .The other halogens exhibit 1, 3, 5, 7 valencies in their compounds and show - 1 to + 7 oxidation states.
Q. Valence shell configuration that belongs to most reactive non-metal is
a) (n-1)s2p6ns1
b) ns2np5
c) ns2np6
d) (n-1)s2p6ns2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a) (n-1)s2p6ns1
b) ns2np5
c) ns2np6
d) (n-1)s2p6ns2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
All the halogens are highly reactive. They react with metals and non-metals to form halides due to readily acceptance of an electron
The number of water insoluble salts amongAgF, AgCI, AgBr, Agl BeF2, CaF2,KF, PbCI2, HgCI2- a)

- b)

- c)
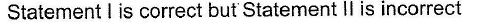
- d)
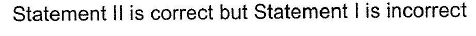
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of water insoluble salts among
AgF, AgCI, AgBr, Agl BeF2, CaF2,KF, PbCI2, HgCI2
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Pritam Malik answered |
AgCI, AgBr, Agl CaF2, PbCI2, HgCI2, are water insoluble.
Which option is incorrect among the following for the given property?- a)Dipole moment (HF > HCI > HBr > HI)
- b)Bond length (HI > HBr > HCI > HF)
- c)Acidic strength (HI > HBr > HCI > HF)
- d)Thermal stability (HF < HCI < HBr < HI)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which option is incorrect among the following for the given property?
a)
Dipole moment (HF > HCI > HBr > HI)
b)
Bond length (HI > HBr > HCI > HF)
c)
Acidic strength (HI > HBr > HCI > HF)
d)
Thermal stability (HF < HCI < HBr < HI)

|
Preethi Kaur answered |
D. Thermal stability (HF HCI HBr HI)
Explanation:
Thermal stability refers to the ability of a compound to withstand high temperatures without undergoing decomposition. In general, thermal stability decreases down a group and increases across a period.
HF (Hydrogen fluoride)
- HF is thermally stable and does not decompose easily at high temperatures.
- This is due to the strong hydrogen bonding present in HF, which results in a high boiling point and thermal stability.
HCI (Hydrogen chloride)
- HCI is also thermally stable and does not decompose easily at high temperatures.
- Similar to HF, HCI exhibits strong hydrogen bonding, resulting in a high boiling point and thermal stability.
HBr (Hydrogen bromide)
- HBr is less thermally stable compared to HF and HCI.
- It can decompose at high temperatures to form hydrogen and bromine gases.
- This is because the strength of hydrogen bonding in HBr is weaker than that in HF and HCI, resulting in a lower boiling point and lower thermal stability.
HI (Hydrogen iodide)
- HI is the least thermally stable among the given options.
- It decomposes readily at high temperatures to form hydrogen and iodine gases.
- The strength of hydrogen bonding in HI is the weakest among the options, leading to a lower boiling point and lower thermal stability.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanations, the incorrect option among the given properties is option D, which states that HI is thermally stable. In reality, HI is the least thermally stable compound among HF, HCI, HBr, and HI.
Explanation:
Thermal stability refers to the ability of a compound to withstand high temperatures without undergoing decomposition. In general, thermal stability decreases down a group and increases across a period.
HF (Hydrogen fluoride)
- HF is thermally stable and does not decompose easily at high temperatures.
- This is due to the strong hydrogen bonding present in HF, which results in a high boiling point and thermal stability.
HCI (Hydrogen chloride)
- HCI is also thermally stable and does not decompose easily at high temperatures.
- Similar to HF, HCI exhibits strong hydrogen bonding, resulting in a high boiling point and thermal stability.
HBr (Hydrogen bromide)
- HBr is less thermally stable compared to HF and HCI.
- It can decompose at high temperatures to form hydrogen and bromine gases.
- This is because the strength of hydrogen bonding in HBr is weaker than that in HF and HCI, resulting in a lower boiling point and lower thermal stability.
HI (Hydrogen iodide)
- HI is the least thermally stable among the given options.
- It decomposes readily at high temperatures to form hydrogen and iodine gases.
- The strength of hydrogen bonding in HI is the weakest among the options, leading to a lower boiling point and lower thermal stability.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanations, the incorrect option among the given properties is option D, which states that HI is thermally stable. In reality, HI is the least thermally stable compound among HF, HCI, HBr, and HI.
Polycistronic mesenger RNA (mRNA) usually occurs in- a)bacteria
- b)prokaryotes
- c)eukaryotes
- d)both a and b
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Polycistronic mesenger RNA (mRNA) usually occurs in
a)
bacteria
b)
prokaryotes
c)
eukaryotes
d)
both a and b
|
|
Niti Kumar answered |
Polycistronic mRNA in Bacteria and Prokaryotes
Polycistronic mRNA refers to a type of messenger RNA that carries the information for multiple genes in a single transcript. This phenomenon is commonly observed in bacteria and prokaryotes.
Bacteria
- In bacteria, the genetic material is organized in a single circular chromosome, and the transcription and translation processes are coupled.
- Bacterial mRNA is often polycistronic, meaning that a single mRNA molecule can encode multiple proteins that are part of the same functional pathway or protein complex.
- This arrangement allows for the coordinated expression of multiple genes that are involved in related cellular functions.
Prokaryotes
- Prokaryotes, including bacteria, lack a true nucleus and have a simpler organization of genetic material compared to eukaryotic cells.
- In prokaryotes, such as archaea, polycistronic mRNA is also common, serving as an efficient way to regulate gene expression and coordinate the synthesis of multiple proteins.
- The presence of polycistronic mRNA in prokaryotes allows for the rapid adaptation to changing environmental conditions and the simultaneous expression of genes that are functionally related.
Conclusion
Polycistronic mRNA is a characteristic feature of bacteria and prokaryotes, where it plays a crucial role in the regulation of gene expression and coordination of protein synthesis. This unique feature highlights the differences in gene expression mechanisms between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Polycistronic mRNA refers to a type of messenger RNA that carries the information for multiple genes in a single transcript. This phenomenon is commonly observed in bacteria and prokaryotes.
Bacteria
- In bacteria, the genetic material is organized in a single circular chromosome, and the transcription and translation processes are coupled.
- Bacterial mRNA is often polycistronic, meaning that a single mRNA molecule can encode multiple proteins that are part of the same functional pathway or protein complex.
- This arrangement allows for the coordinated expression of multiple genes that are involved in related cellular functions.
Prokaryotes
- Prokaryotes, including bacteria, lack a true nucleus and have a simpler organization of genetic material compared to eukaryotic cells.
- In prokaryotes, such as archaea, polycistronic mRNA is also common, serving as an efficient way to regulate gene expression and coordinate the synthesis of multiple proteins.
- The presence of polycistronic mRNA in prokaryotes allows for the rapid adaptation to changing environmental conditions and the simultaneous expression of genes that are functionally related.
Conclusion
Polycistronic mRNA is a characteristic feature of bacteria and prokaryotes, where it plays a crucial role in the regulation of gene expression and coordination of protein synthesis. This unique feature highlights the differences in gene expression mechanisms between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
During transcription, the site of DNA molecule at which RNA polymerase binds is called- a)promoter
- b)regulator
- c)receptor
- d)enhancer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During transcription, the site of DNA molecule at which RNA polymerase binds is called
a)
promoter
b)
regulator
c)
receptor
d)
enhancer
|
|
Ankit Iyer answered |
Answer:
Promoter:
The site on a DNA molecule where RNA polymerase binds during transcription is called a promoter. Promoters are specific sequences of DNA that are located near the beginning of a gene.
Function of Promoter:
- Promoters play a crucial role in initiating the process of transcription by providing a binding site for RNA polymerase.
- They help in determining the starting point for transcription and also regulate the expression of genes by controlling the rate of transcription.
Types of Promoters:
- There are different types of promoters such as constitutive promoters, which are always active, and inducible promoters, which are activated in response to specific signals or environmental conditions.
Structure of Promoter:
- Promoters consist of several components, including the TATA box, which is a short sequence of DNA that helps in positioning RNA polymerase at the correct site to start transcription.
- Other elements like enhancers and silencers may also be present in the promoter region, which can influence transcriptional activity.
Importance of Promoter:
- Promoters are essential for the proper regulation of gene expression in cells. They ensure that genes are transcribed at the right time and in the right amount, which is crucial for the normal functioning of living organisms.
In conclusion, the promoter is a critical component of the transcription process as it serves as the binding site for RNA polymerase and helps in initiating the synthesis of RNA from DNA.
Promoter:
The site on a DNA molecule where RNA polymerase binds during transcription is called a promoter. Promoters are specific sequences of DNA that are located near the beginning of a gene.
Function of Promoter:
- Promoters play a crucial role in initiating the process of transcription by providing a binding site for RNA polymerase.
- They help in determining the starting point for transcription and also regulate the expression of genes by controlling the rate of transcription.
Types of Promoters:
- There are different types of promoters such as constitutive promoters, which are always active, and inducible promoters, which are activated in response to specific signals or environmental conditions.
Structure of Promoter:
- Promoters consist of several components, including the TATA box, which is a short sequence of DNA that helps in positioning RNA polymerase at the correct site to start transcription.
- Other elements like enhancers and silencers may also be present in the promoter region, which can influence transcriptional activity.
Importance of Promoter:
- Promoters are essential for the proper regulation of gene expression in cells. They ensure that genes are transcribed at the right time and in the right amount, which is crucial for the normal functioning of living organisms.
In conclusion, the promoter is a critical component of the transcription process as it serves as the binding site for RNA polymerase and helps in initiating the synthesis of RNA from DNA.
In eukaryotes, the process of processing of primary transcript involves- a)removal of introns
- b)capping at 5' end
- c)tailing (polyadenylation) at 3' end
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In eukaryotes, the process of processing of primary transcript involves
a)
removal of introns
b)
capping at 5' end
c)
tailing (polyadenylation) at 3' end
d)
all of these
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The primary mRNA transcript is longer and localised into the nucleus, where it is also called heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) or pre-mRNA. At the 5' end of hnRNA, a cap (consisting of 7-emthyl guanosine triphosphate or 7 mG) and a tail of poly A (Adenylate residues) at the 3' end are added. These processes are respectively called as capping and tailing. The cap is a chemically modified molecule of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). The primary mRNA are made up of two types of segments, non-coding introns and the coding exons. The introns are removed by a process called RNA splicing and the exons are joined in a defined order.
Transcription unit- a)starts with TATA box
- b)starts-with pallendrous regions and ends with rho factor
- c)starts with promoter region and ends in terminator region
- d)starts with CAAT region
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Transcription unit
a)
starts with TATA box
b)
starts-with pallendrous regions and ends with rho factor
c)
starts with promoter region and ends in terminator region
d)
starts with CAAT region
|
|
Arya Nambiar answered |
The correct answer is option 'C': Transcription starts with the promoter region and ends in the terminator region. Let's break down the process of transcription and explain why this is the correct answer.
Transcription is the first step in gene expression, where the information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. This process involves several key regions and factors that play important roles. Let's discuss each option and why they are correct or incorrect.
a) Starts with TATA box:
- The TATA box is a DNA sequence found upstream of the transcription start site in many eukaryotic genes. It serves as a binding site for transcription factors and helps in the initiation of transcription.
- While the TATA box is an important element in the promoter region, it is not the starting point of transcription. Therefore, option 'a' is incorrect.
b) Starts with palindromic regions and ends with rho factor:
- Palindromic regions are DNA sequences that read the same on both strands when oriented in the same direction. They can be involved in various regulatory processes, but they are not the starting points of transcription.
- The rho factor is a protein involved in the termination of transcription in prokaryotes. It binds to the RNA molecule and causes the release of the RNA from the DNA template.
- While these regions and factors are involved in transcription, they do not mark the starting point. Therefore, option 'b' is incorrect.
c) Starts with promoter region and ends in terminator region:
- The promoter region is the DNA sequence where RNA polymerase binds and initiates transcription. It contains specific sequences and elements, such as the TATA box, that help in the recognition and binding of transcription factors.
- The terminator region is a DNA sequence that signals the end of transcription. It contains signals for the termination of RNA synthesis and the release of the RNA molecule.
- Therefore, option 'c' is correct as transcription starts with the promoter region and ends in the terminator region.
d) Starts with CAAT region:
- The CAAT box is another DNA sequence found in the promoter region of many eukaryotic genes. It is involved in the binding of transcription factors and the regulation of gene expression.
- While the CAAT region is important in the promoter, it is not the starting point of transcription. Therefore, option 'd' is incorrect.
In summary, transcription starts with the promoter region and ends in the terminator region. These regions contain specific sequences and elements that play crucial roles in the initiation and termination of transcription.
Transcription is the first step in gene expression, where the information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. This process involves several key regions and factors that play important roles. Let's discuss each option and why they are correct or incorrect.
a) Starts with TATA box:
- The TATA box is a DNA sequence found upstream of the transcription start site in many eukaryotic genes. It serves as a binding site for transcription factors and helps in the initiation of transcription.
- While the TATA box is an important element in the promoter region, it is not the starting point of transcription. Therefore, option 'a' is incorrect.
b) Starts with palindromic regions and ends with rho factor:
- Palindromic regions are DNA sequences that read the same on both strands when oriented in the same direction. They can be involved in various regulatory processes, but they are not the starting points of transcription.
- The rho factor is a protein involved in the termination of transcription in prokaryotes. It binds to the RNA molecule and causes the release of the RNA from the DNA template.
- While these regions and factors are involved in transcription, they do not mark the starting point. Therefore, option 'b' is incorrect.
c) Starts with promoter region and ends in terminator region:
- The promoter region is the DNA sequence where RNA polymerase binds and initiates transcription. It contains specific sequences and elements, such as the TATA box, that help in the recognition and binding of transcription factors.
- The terminator region is a DNA sequence that signals the end of transcription. It contains signals for the termination of RNA synthesis and the release of the RNA molecule.
- Therefore, option 'c' is correct as transcription starts with the promoter region and ends in the terminator region.
d) Starts with CAAT region:
- The CAAT box is another DNA sequence found in the promoter region of many eukaryotic genes. It is involved in the binding of transcription factors and the regulation of gene expression.
- While the CAAT region is important in the promoter, it is not the starting point of transcription. Therefore, option 'd' is incorrect.
In summary, transcription starts with the promoter region and ends in the terminator region. These regions contain specific sequences and elements that play crucial roles in the initiation and termination of transcription.
The magnetic field B on the axis of a circular coil at distance x far away from its centre are related as:- a)Bαx-1
- b)Bαx-4
- c)Bαx-3
- d)Bαx-2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic field B on the axis of a circular coil at distance x far away from its centre are related as:
a)
Bαx-1
b)
Bαx-4
c)
Bαx-3
d)
Bαx-2
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
The formula for the magnetic field B (flux density) at P at a distance d from the center of O the coil on the axis of the coil of radius r :
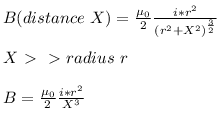
Put appropriate punctuation marks in the following sentences.Sorry to disturb you could I speak to you for a moment Correct answer is 'Sorry to disturb you – could I speak to you for a moment?'. Can you explain this answer?
Put appropriate punctuation marks in the following sentences.
Sorry to disturb you could I speak to you for a moment

|
Gowri Chakraborty answered |
In the sentence "Sorry to disturb you – could I speak to you for a moment?", the appropriate punctuation marks are a hyphen (-) after "disturb you" and a question mark (?) after "moment".
The hyphen is used to join two words together, in this case "disturb" and "you", to form a compound adjective. A compound adjective is an adjective made up of two or more words that describes a noun. In this sentence, the compound adjective "sorry to disturb you" describes the speaker and indicates that they feel apologetic about interrupting the person they are speaking to.
The question mark is used to indicate that the sentence is a question. In this case, the speaker is asking if they can speak to the person for a moment.
Overall, the punctuation in the sentence helps to clarify the meaning and structure of the sentence, making it easier for the reader to understand.
The correct order of in creasing order of radiiions 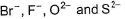 is as follow
is as follow- a)
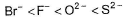
- b)
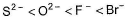
- c)
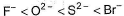
- d)
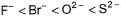
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of in creasing order of radiiions  is as follow
is as follow
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Atomic and ionic radii increase down the group due to increasing number of quantum shells.
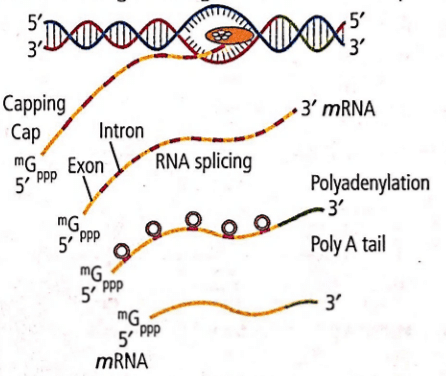
Refer to the given diagram. What does it represent?
- a)Transcription in prokaryotes
- b)Transcription in eukaryotes
- c)Translation in prokaryotes
- d)Translation in eukaryotes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer to the given diagram. What does it represent?


a)
Transcription in prokaryotes
b)
Transcription in eukaryotes
c)
Translation in prokaryotes
d)
Translation in eukaryotes
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The given diagram represents post-transcriptional processing resulting in the formation of mRNA. Since, introns and exons are present, it is transcription in eukaryotes.
PassageGroup 17 elements are known as halogens ( sea salt forming). Their general configuration is ns2np5 where, n = 2 to 7. Fluorine is the first member of the group differs in several ways from the rest of the group. Halogens are highly reactive elements having strong affinity for hydrogen. All the halogens form both ionic and covalent compounds .Fluorine is always monovalent and shows -1 oxidation state in its compounds .The other halogens exhibit 1, 3, 5, 7 valencies in their compounds and show - 1 to + 7 oxidation states.Q. In which of the following chlorine has different oxidation states?- a) CrO2CI2
- b)CaOCI2
- c)Cl2O7
- d)Ca(OCI)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage
Group 17 elements are known as halogens ( sea salt forming). Their general configuration is ns2np5 where, n = 2 to 7. Fluorine is the first member of the group differs in several ways from the rest of the group. Halogens are highly reactive elements having strong affinity for hydrogen. All the halogens form both ionic and covalent compounds .Fluorine is always monovalent and shows -1 oxidation state in its compounds .The other halogens exhibit 1, 3, 5, 7 valencies in their compounds and show - 1 to + 7 oxidation states.
Q.
In which of the following chlorine has different oxidation states?
a)
CrO2CI2
b)
CaOCI2
c)
Cl2O7
d)
Ca(OCI)2

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
In calcium oxychloride (CaOCI)CI) has different oxidation states, Hence, chlorine has +1 and -1 oxidation states.
Direction (Q. No. 18 and 19) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.Q. Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.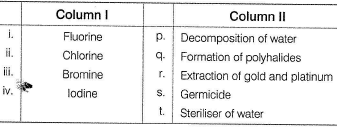
- a)
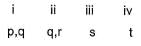
- b)
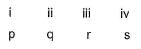
- c)
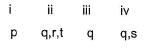
- d)
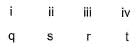
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. No. 18 and 19) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
a)
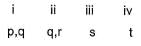
b)
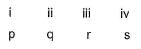
c)
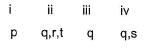
d)
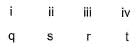

|
Nisha Banerjee answered |
Which of the following does not exist?- a)
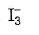
- b)
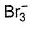
- c)
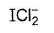
- d)
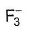
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not exist?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Nisha Banerjee answered |
Fluorine has no d-orbitals in the valence shell. Hence, it always show - 1 oxidation state and monovalency in its compounds.
Which one of the following arrangements do not give the correct picture of the trends indicated against it?- a)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Oxidising power
- b)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Electron gain enthalpy
- c)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Bond dissociation energy
- d)F >CI >Br >1 : Electronegativity
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following arrangements do not give the correct picture of the trends indicated against it?
a)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Oxidising power
b)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2: Electron gain enthalpy
c)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Bond dissociation energy
d)
F >CI >Br >1 : Electronegativity

|
Nisha Banerjee answered |
The negative electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less than that of chlorine. It is due to small size of fluorine atom.
Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram of mRNA.
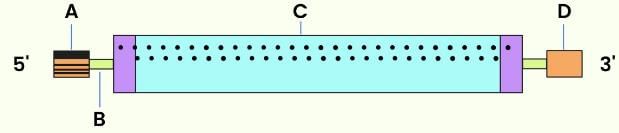
- a)Methylated cap, Initiation codon, Termination codon, Poly A tail
- b)Poly A tail, Termination codon, Initiation codon, Methylated cap
- c)Methylated cap, Non-coding region, coding region, Poly A tail
- d)Methylated cap, Coding region, Non-coding region, Poly A tail
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram of mRNA.


a)
Methylated cap, Initiation codon, Termination codon, Poly A tail
b)
Poly A tail, Termination codon, Initiation codon, Methylated cap
c)
Methylated cap, Non-coding region, coding region, Poly A tail
d)
Methylated cap, Coding region, Non-coding region, Poly A tail
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
mRNA has methylated region at the 5' terminus. It functions as a cap for attachment with ribosome. Cap is followed by an initiation codon (AUG) either immediately or after a small non-coding leader region. Then there is coding region followed by termination codons (UAA, UAG OF UGA). After termination codon there is a small non-coding trailer region and poly A area at the 3' terminus. These leader and trailer regions are called UTRs (Untranslated regions). Cap at 5' end and poly-A tail at 3' end also serves to protect mRNA from enzymatic decay.
The given figure represents the process of transcription in bacteria.
Select the option which correctly labels A, B and C.
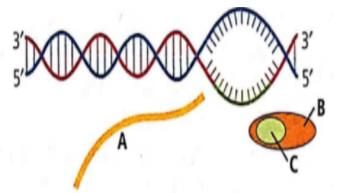
- a)A - DNA, B - RNA, C - Rho factor
- b)A - RNA, B - RNA polymerase, C - Rho factor
- c)A - RNA, B - RNA polymerase, C - Sigma factor
- d)A - DNA, B - DNA polymerase, C - Sigma factor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure represents the process of transcription in bacteria.
Select the option which correctly labels A, B and C.

Select the option which correctly labels A, B and C.

a)
A - DNA, B - RNA, C - Rho factor
b)
A - RNA, B - RNA polymerase, C - Rho factor
c)
A - RNA, B - RNA polymerase, C - Sigma factor
d)
A - DNA, B - DNA polymerase, C - Sigma factor
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
As transcription proceeds the initiation and elongation steps are mediated by the RNA Polymerase enzyme (DNA dependent RNA polymerase). As a result, the RNA transcript is synthesized as a single-stranded structure and is released when the Rho factor binds to the enzyme RNA polymerase to terminate the transcription.
Chapter doubts & questions for August Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of August Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup