All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of August Week 4 for NEET Exam
In E. coli, the lac operon gets switched on when- a)Lactose is present and it binds to the repressor
- b)RNA polymerase binds to the operator
- c)Lactose is present and it binds to RNA polymerase
- d)Repressor binds to operator
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In E. coli, the lac operon gets switched on when
a)
Lactose is present and it binds to the repressor
b)
RNA polymerase binds to the operator
c)
Lactose is present and it binds to RNA polymerase
d)
Repressor binds to operator
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
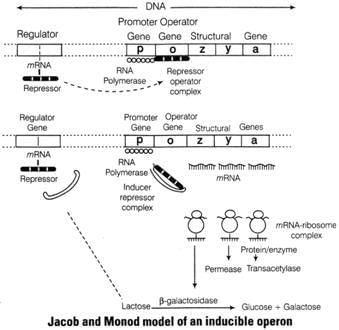
In case of lactose presence
(i) Lactose acts as an inducer which binds to the repressor and forms an inactive repressor.
(ii) The repressor fails to bind to the operator region.
(iii) The RNA polymerase binds to the operator and transcript lac mRNA.
(iv) lac mRNA is polycistronic, i.e., produces all three enzymes, β -galactosidase, permeaseand transacetylase.
(v) The lac operon is switched on.
In case of lactose absence
(i) When lactose is absent, i gene regulates and produces repressor mRNA which translate repression.
(ii) The repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon and as a resultprevents RNA polymerase to bind to the operon.
(iii) The operon is switched off.
A conductor of length l, carrying current I and placed in a magnetic field B experiences a force F given by- a)
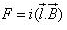
- b)
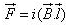
- c)
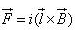
- d)
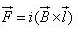
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A conductor of length l, carrying current I and placed in a magnetic field B experiences a force F given by
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Deepali Tripathi answered |
F=q(v x B)
=q(dl/dt x B)
=q/dt(l x B)
=i(l x B)
=q(dl/dt x B)
=q/dt(l x B)
=i(l x B)
A wire of length l, carrying current is bent into a loop and placed with its plane perpendicular to a magnetic field. In which of the following shapes, is the torque acting on the loop maximum?- a)Rectangle
- b)Circle
- c)Square
- d)Equilateral triangle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A wire of length l, carrying current is bent into a loop and placed with its plane perpendicular to a magnetic field. In which of the following shapes, is the torque acting on the loop maximum?
a)
Rectangle
b)
Circle
c)
Square
d)
Equilateral triangle
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The torque on a current loop depends upon the area of the current loop, when the magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the loops the torque has its maximum value,
Τ=I A B
We know I and B for all these cases but A depends upon the geometry. The circle has the greatest area so it should provide the greatest torque.
Τ=I A B
We know I and B for all these cases but A depends upon the geometry. The circle has the greatest area so it should provide the greatest torque.
During splicing, the exons are joined and the enzyme which catalyses this reaction is- a)RNA ligase
- b)RNA polymerase
- c)RNA catalase
- d)RNA permease
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During splicing, the exons are joined and the enzyme which catalyses this reaction is
a)
RNA ligase
b)
RNA polymerase
c)
RNA catalase
d)
RNA permease

|
Ved Patidar answered |
Joint joining of nucleotide in RNA and DNA is done by DNA/RNA ligase.
Transition metals with highest melting point is- a)Cr
- b)W
- c)Hg
- d)Sc
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Transition metals with highest melting point is
a)
Cr
b)
W
c)
Hg
d)
Sc

|
Pragati Choudhury answered |
W belongs to 5d series and also it have lot of unpaired electrons thus it forms strong metallic bonding.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Repressor protein is produced by
- A:
Operator gene
- B:
Promotor gene
- C:
Structural gene
- D:
Regulator gene
The answer is d.
Repressor protein is produced by
Operator gene
Promotor gene
Structural gene
Regulator gene
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
In prokaryotes, regulator genes often code for repressor proteins. Repressor proteins bind to operators or promoters, preventing RNA polymerase from transcribing RNA. They are usually constantly expressed so the cell always has a supply of repressor molecules on hand.
Ag+ ion is isoelectronic with- a)Zn2+
- b)Cd2+
- c)Pd2+
- d)Cu2+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ag+ ion is isoelectronic with
a)
Zn2+
b)
Cd2+
c)
Pd2+
d)
Cu2+

|
Malavika Shah answered |
Ag+ is isoelectronic with Cd2+
Repressor protein is produced by- a)Operator gene
- b)Promotor gene
- c)Structural gene
- d)Regulator gene
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Repressor protein is produced by
a)
Operator gene
b)
Promotor gene
c)
Structural gene
d)
Regulator gene

|
Nidhi Nambiar answered |
Regulator gene controls the expression of operon and produces a small protein molecule known as repressor. It is a DNA or RNA binding protein that inhibits the expression of one or more genes by binding to the operator or associated silencers. It blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter.hence, it prevents translation of mRNA into protein and this entire process is known as repression.
In the Lac operon system, β-galactosidase is coded by- a)y-gene
- b)I-gene
- c)z-gene
- d)a-gene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the Lac operon system, β-galactosidase is coded by
a)
y-gene
b)
I-gene
c)
z-gene
d)
a-gene

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
The gene product of lacZ is beta-galactosidase which cleaves lactose, a disaccharide, into glucose and galactose. LacY encodes Beta-galactoside permease, a membrane protein that becomes embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane to enable the cellular transport of lactose into the cell.
Mohr’s salt is a- a)Acidic salt
- b)Double salt
- c)Basic Acidic salt
- d)Normal salt
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohr’s salt is a
a)
Acidic salt
b)
Double salt
c)
Basic Acidic salt
d)
Normal salt

|
Amar Pillai answered |
Mohr salt is an example of double salt. Mohr Salt is
FeSO4 . (NH4)2 SO4.6H2O
The lac operon consists of- a)One regulatory gene and three structural genes
- b)Two regulatory genes and two structural genes
- c)Three regulatory genes and three structural genes
- d)Four regulatory genes only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The lac operon consists of
a)
One regulatory gene and three structural genes
b)
Two regulatory genes and two structural genes
c)
Three regulatory genes and three structural genes
d)
Four regulatory genes only

|
Syed Hussain answered |
It consists of three adjacent structural genes, a promoter, a terminator, and anoperator. The lac operon is regulated by several factors including the availability of glucose and lactose. It can be activated by allolactose. Lactose binds to the repressor protein and prevents it from repressinggene transcription.
Which is called chromic acid?- a)Cr2O3
- b)Cr3O4
- c)CrO
- d)H2CrO4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is called chromic acid?
a)
Cr2O3
b)
Cr3O4
c)
CrO
d)
H2CrO4
|
|
Shraddha Dey answered |
Chromic Acid is a naturally occurring oxide with a formula H2CrO4.
Ferrous sulphate on heating gives- a)SO2 and SO3
- b)SO2 and O2
- c)SO2
- d)SO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ferrous sulphate on heating gives
a)
SO2 and SO3
b)
SO2 and O2
c)
SO2
d)
SO3

|
M. Vishnu answered |
On heating, ferrous sulphate crystals lose water and anhydrous ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) is formed. So their colour changes from light green to white. On furtherheating, anhydrous ferrous sulphate decomposes to form ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2) and sulphur trioxide (SO3).
Lucas reagent is
- a)ZnCl2 + HCl
- b)MnO2 + H2O
- c)H2SO4 + HCl
- d)NO + H2O
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lucas reagent is
a)
ZnCl2 + HCl
b)
MnO2 + H2O
c)
H2SO4 + HCl
d)
NO + H2O

|
Arshiya Choudhury answered |
Lucas Test is done to distinguish primary secondary and tertiary alcohols. Lucas reagent is ZnCl2 + HCl
Maximum magnetic moment is shown by- a)d6
- b)d8
- c)d5
- d)d7
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum magnetic moment is shown by
a)
d6
b)
d8
c)
d5
d)
d7
|
|
Shraddha Chavan answered |
Magnetic Moment and d-orbitals
To understand why the maximum magnetic moment is shown by d5, we need to understand the concept of magnetic moment and the behavior of d-orbitals in transition metals.
Magnetic Moment
Magnetic moment is a measure of the strength and orientation of a magnet in a magnetic field. In the context of transition metals, it refers to the magnetic properties of unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals. The magnetic moment can be calculated using the formula:
Magnetic moment (μ) = √[n(n+2)] BM
Where n is the number of unpaired electrons and BM is the Bohr magneton, a unit of magnetic moment.
d-orbitals
d-orbitals are the five orbitals (dxy, dxz, dyz, dx²-y², dz²) available for electrons to occupy in the d-subshell. These orbitals have different shapes and orientations, and they can accommodate a maximum of 10 electrons.
Explanation
In the given options, the maximum magnetic moment is shown by d5. Let's analyze each option to understand why d5 has the highest magnetic moment.
- d6: In d6 configuration, there are 4 unpaired electrons. Applying the magnetic moment formula, we get μ = √[4(4+2)] BM = √24 BM.
- d8: In d8 configuration, there are 2 unpaired electrons. Applying the magnetic moment formula, we get μ = √[2(2+2)] BM = √8 BM.
- d5: In d5 configuration, there are 5 unpaired electrons. Applying the magnetic moment formula, we get μ = √[5(5+2)] BM = √35 BM.
- d7: In d7 configuration, there are 3 unpaired electrons. Applying the magnetic moment formula, we get μ = √[3(3+2)] BM = √15 BM.
Comparing the magnetic moments calculated for each option, we can see that d5 has the highest magnetic moment of √35 BM. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
It is important to note that the magnetic moment depends on the number of unpaired electrons. The more unpaired electrons present in the d-orbitals, the higher the magnetic moment. This is because unpaired electrons have individual magnetic moments that align with an external magnetic field, resulting in a stronger overall magnetic moment.
Which of the following pairs of ions have same paramagnetic moment?- a)Cu2+, Ti3+
- b)Ti3+, Ni2+
- c)Ti4+, Cu2+
- d)Mn2+, Cu2+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs of ions have same paramagnetic moment?
a)
Cu2+, Ti3+
b)
Ti3+, Ni2+
c)
Ti4+, Cu2+
d)
Mn2+, Cu2+
|
|
Ameya Pillai answered |
Explanation:
Paramagnetic Moment:
Paramagnetic substances are those substances that are weakly attracted by an external magnetic field. The paramagnetic moment is a measure of the strength of this attraction. It is given by the formula:
Paramagnetic Moment (μ) = √(n(n+2)) BM
Where:
- n is the number of unpaired electrons in the atom or ion
- BM stands for Bohr Magneton, a unit of magnetic moment.
Identifying the Number of Unpaired Electrons:
To determine which pairs of ions have the same paramagnetic moment, we need to first identify the number of unpaired electrons in each ion. Unpaired electrons are those that do not have a partner or are not paired with another electron in the same orbital.
Calculating the Number of Unpaired Electrons:
To calculate the number of unpaired electrons, we need to know the electron configuration of each ion. Let's calculate the number of unpaired electrons for each pair of ions:
a) Cu2+ (Copper ion with +2 charge)
- The electron configuration of Cu2+ is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9
- In Cu2+, there are 9 electrons in the 3d orbital, which means there is 1 unpaired electron.
b) Ti3+ (Titanium ion with +3 charge)
- The electron configuration of Ti3+ is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d1
- In Ti3+, there is 1 electron in the 3d orbital, which means there is 1 unpaired electron.
c) Ti4+ (Titanium ion with +4 charge)
- The electron configuration of Ti4+ is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
- In Ti4+, all the electrons are paired, which means there are no unpaired electrons.
d) Mn2+ (Manganese ion with +2 charge)
- The electron configuration of Mn2+ is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5
- In Mn2+, there are 5 electrons in the 3d orbital, which means there are 5 unpaired electrons.
Comparing the Number of Unpaired Electrons:
From the calculations above, we can see that:
- Cu2+ and Ti3+ both have 1 unpaired electron.
- Ti4+ and Mn2+ have 0 unpaired electrons.
Conclusion:
Based on the number of unpaired electrons, we can conclude that the pair of ions with the same paramagnetic moment is:
a) Cu2+ (1 unpaired electron)
b) Ti3+ (1 unpaired electron)
Paramagnetic Moment:
Paramagnetic substances are those substances that are weakly attracted by an external magnetic field. The paramagnetic moment is a measure of the strength of this attraction. It is given by the formula:
Paramagnetic Moment (μ) = √(n(n+2)) BM
Where:
- n is the number of unpaired electrons in the atom or ion
- BM stands for Bohr Magneton, a unit of magnetic moment.
Identifying the Number of Unpaired Electrons:
To determine which pairs of ions have the same paramagnetic moment, we need to first identify the number of unpaired electrons in each ion. Unpaired electrons are those that do not have a partner or are not paired with another electron in the same orbital.
Calculating the Number of Unpaired Electrons:
To calculate the number of unpaired electrons, we need to know the electron configuration of each ion. Let's calculate the number of unpaired electrons for each pair of ions:
a) Cu2+ (Copper ion with +2 charge)
- The electron configuration of Cu2+ is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9
- In Cu2+, there are 9 electrons in the 3d orbital, which means there is 1 unpaired electron.
b) Ti3+ (Titanium ion with +3 charge)
- The electron configuration of Ti3+ is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d1
- In Ti3+, there is 1 electron in the 3d orbital, which means there is 1 unpaired electron.
c) Ti4+ (Titanium ion with +4 charge)
- The electron configuration of Ti4+ is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
- In Ti4+, all the electrons are paired, which means there are no unpaired electrons.
d) Mn2+ (Manganese ion with +2 charge)
- The electron configuration of Mn2+ is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5
- In Mn2+, there are 5 electrons in the 3d orbital, which means there are 5 unpaired electrons.
Comparing the Number of Unpaired Electrons:
From the calculations above, we can see that:
- Cu2+ and Ti3+ both have 1 unpaired electron.
- Ti4+ and Mn2+ have 0 unpaired electrons.
Conclusion:
Based on the number of unpaired electrons, we can conclude that the pair of ions with the same paramagnetic moment is:
a) Cu2+ (1 unpaired electron)
b) Ti3+ (1 unpaired electron)
Which one of the following combines with Fe2+ ion to form a brown complex?- a)N2O
- b)N2O3
- c)N2O5
- d)NO
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following combines with Fe2+ ion to form a brown complex?
a)
N2O
b)
N2O3
c)
N2O5
d)
NO
|
|
Keerthana Chakraborty answered |
Introduction
The question pertains to the interaction between Fe2+ ions and various nitrogen oxides to form complexes. The correct option is NO (Nitric Oxide), which forms a characteristic brown complex with Fe2+ ions.
Fe2+ Ion Characteristics
- Fe2+ (ferrous ion) is a transition metal ion known for its ability to form complexes.
- It has an incomplete d-orbital, allowing it to bind with various ligands.
Role of Nitric Oxide (NO)
- NO is a signaling molecule and can act as a ligand in coordination chemistry.
- It has a unique ability to coordinate with metal ions, particularly transition metals like iron.
Complex Formation
- When NO combines with Fe2+, it forms a complex known as the nitrosyl complex.
- This complex exhibits a distinct brown color, which is a significant characteristic of NO-Fe2+ interactions.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- N2O: Does not effectively coordinate with Fe2+ and lacks sufficient donor atoms for complex formation.
- N2O3: Primarily an oxidizing agent and does not form stable complexes with Fe2+.
- N2O5: A stronger oxidizer and also does not interact with Fe2+ to form a colored complex.
Conclusion
The formation of a brown complex with Fe2+ ions is unique to nitric oxide (NO), making it the correct answer to the question. Other nitrogen oxides do not exhibit this behavior due to their chemical properties and coordination abilities.
The question pertains to the interaction between Fe2+ ions and various nitrogen oxides to form complexes. The correct option is NO (Nitric Oxide), which forms a characteristic brown complex with Fe2+ ions.
Fe2+ Ion Characteristics
- Fe2+ (ferrous ion) is a transition metal ion known for its ability to form complexes.
- It has an incomplete d-orbital, allowing it to bind with various ligands.
Role of Nitric Oxide (NO)
- NO is a signaling molecule and can act as a ligand in coordination chemistry.
- It has a unique ability to coordinate with metal ions, particularly transition metals like iron.
Complex Formation
- When NO combines with Fe2+, it forms a complex known as the nitrosyl complex.
- This complex exhibits a distinct brown color, which is a significant characteristic of NO-Fe2+ interactions.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- N2O: Does not effectively coordinate with Fe2+ and lacks sufficient donor atoms for complex formation.
- N2O3: Primarily an oxidizing agent and does not form stable complexes with Fe2+.
- N2O5: A stronger oxidizer and also does not interact with Fe2+ to form a colored complex.
Conclusion
The formation of a brown complex with Fe2+ ions is unique to nitric oxide (NO), making it the correct answer to the question. Other nitrogen oxides do not exhibit this behavior due to their chemical properties and coordination abilities.
Which of the following ion has smallest radii?- a)V2+
- b)Ni2+
- c)Mn2+
- d)Ti2+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following ion has smallest radii?
a)
V2+
b)
Ni2+
c)
Mn2+
d)
Ti2+

|
Preethi Bose answered |
In period when we move from left to right in a period atomic radii 1st decreases till nickel then starts increasing so Ni2+ has smallest radii.
A plane square loop PQRS of side ‘a’ made of thin copper wire has ‘n’ turns and it carries a direct current ‘I’ ampere in the direction shown in the adjoining figure. This wire loop is placed in a magnetic field of flux density ‘B’ tesla, which is directed perpendicularly in to the plane of the loop. What is the torque acting on the loop?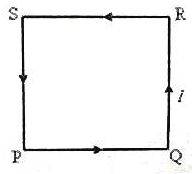
- a)nIaB
- b)Zero
- c)IaB
- d)nIa2B
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A plane square loop PQRS of side ‘a’ made of thin copper wire has ‘n’ turns and it carries a direct current ‘I’ ampere in the direction shown in the adjoining figure. This wire loop is placed in a magnetic field of flux density ‘B’ tesla, which is directed perpendicularly in to the plane of the loop. What is the torque acting on the loop?
a)
nIaB
b)
Zero
c)
IaB
d)
nIa2B
|
|
Ram Mohith answered |
The magnetic moment of this loop is in direction perpendicular to the plane of loop and coming out of the plane. The magnetic field is also directed perpendicularly into the loop. So, magnetic moment magnetic field are antiparallel. The torque acting on the loop, which is given by the cross product of moment and field, is zero since sin 180 = 0
Which of the following methods is based on distribution law?- a)Parke’s process
- b)Poling process
- c)Mond’s process
- d)Cupellation process
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following methods is based on distribution law?
a)
Parke’s process
b)
Poling process
c)
Mond’s process
d)
Cupellation process

|
Saptarshi Ghoshal answered |
Parkes process is a process for removing silver from Pb. It is an example of Liquid liquid extractions
Red hot steel rods on suddenly immersing in water become- a)Fibrous
- b)Hard and brittle
- c)Soft and malleable
- d)Tough and ductile
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Red hot steel rods on suddenly immersing in water become
a)
Fibrous
b)
Hard and brittle
c)
Soft and malleable
d)
Tough and ductile

|
Sinjini Tiwari answered |
Explanation:
Introduction:
When red hot steel rods are suddenly immersed in water, they undergo a process known as quenching. Quenching is a rapid cooling process that is used to harden steel. During quenching, the steel undergoes a structural transformation which results in changes in its properties.
Explanation:
When red hot steel rods are immersed in water, the following changes occur:
1. Rapid cooling: The red hot steel rods are at a high temperature, and when they come into contact with water, the heat is rapidly transferred from the steel to the water. This rapid cooling causes the steel to undergo a phase transformation.
2. Phase transformation: The rapid cooling causes the steel to undergo a phase transformation from austenite to martensite. Austenite is a high-temperature phase of steel that has a face-centered cubic crystal structure. Martensite, on the other hand, is a low-temperature phase of steel that has a body-centered tetragonal crystal structure.
3. Change in microstructure: The phase transformation from austenite to martensite results in a change in the microstructure of the steel. Martensite is a hard and brittle phase of steel, which is why the steel rods become hard and brittle after quenching.
4. Hardness: Martensite is known for its high hardness. The rapid cooling during quenching traps carbon atoms in the crystal lattice of the steel, forming a supersaturated solid solution. This solid solution increases the hardness of the steel, making it hard and brittle.
5. Brittleness: The formation of martensite also leads to an increase in the internal stresses within the steel. These internal stresses can cause the steel to become brittle and prone to cracking or fracturing under applied loads.
Therefore, when red hot steel rods are suddenly immersed in water, they become hard and brittle due to the phase transformation from austenite to martensite.
Introduction:
When red hot steel rods are suddenly immersed in water, they undergo a process known as quenching. Quenching is a rapid cooling process that is used to harden steel. During quenching, the steel undergoes a structural transformation which results in changes in its properties.
Explanation:
When red hot steel rods are immersed in water, the following changes occur:
1. Rapid cooling: The red hot steel rods are at a high temperature, and when they come into contact with water, the heat is rapidly transferred from the steel to the water. This rapid cooling causes the steel to undergo a phase transformation.
2. Phase transformation: The rapid cooling causes the steel to undergo a phase transformation from austenite to martensite. Austenite is a high-temperature phase of steel that has a face-centered cubic crystal structure. Martensite, on the other hand, is a low-temperature phase of steel that has a body-centered tetragonal crystal structure.
3. Change in microstructure: The phase transformation from austenite to martensite results in a change in the microstructure of the steel. Martensite is a hard and brittle phase of steel, which is why the steel rods become hard and brittle after quenching.
4. Hardness: Martensite is known for its high hardness. The rapid cooling during quenching traps carbon atoms in the crystal lattice of the steel, forming a supersaturated solid solution. This solid solution increases the hardness of the steel, making it hard and brittle.
5. Brittleness: The formation of martensite also leads to an increase in the internal stresses within the steel. These internal stresses can cause the steel to become brittle and prone to cracking or fracturing under applied loads.
Therefore, when red hot steel rods are suddenly immersed in water, they become hard and brittle due to the phase transformation from austenite to martensite.
The diagram shows an important concept in the genetic implication of DNA. Fill in the blanks A to C.
- a)A – transcription B – translation C – Francis Crick
- b)A – translation B – extension C – Rosalind Franklin
- c)A – transcription B – replication C – James Watson
- d)A – translation B – transcription C – Erwin Chargaff
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The diagram shows an important concept in the genetic implication of DNA. Fill in the blanks A to C.
a)
A – transcription B – translation C – Francis Crick
b)
A – translation B – extension C – Rosalind Franklin
c)
A – transcription B – replication C – James Watson
d)
A – translation B – transcription C – Erwin Chargaff

|
Maitri Mukherjee answered |
The process by which RNA is synthesised from DNA is transcription. Hence, A is transcription.
The process by which proteins are made from mRNA is translation. Hence, B is translation.
This scheme represents Central dogma of molecular biology which was proposed by Francis Crick.
So, the correct answer is 'A-transcription, B-translation, C-Francis Crick'
Transition metals with lowest melting point is- a)Zn
- b)Cr
- c)Cd
- d)Hg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Transition metals with lowest melting point is
a)
Zn
b)
Cr
c)
Cd
d)
Hg
|
|
Abhijeet Sharma answered |
Zinc (Zn) has the lowest melting point in 3d series because of the absence of d-electrons.
Maximum oxidation state is shown by- a)Os
- b)Co
- c)Cr
- d)Mn
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum oxidation state is shown by
a)
Os
b)
Co
c)
Cr
d)
Mn

|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Os shows maximum oxidation state of +8.
Which is least soluble in water?- a)Ag2S
- b)AgBr
- c)AgCl
- d)AgI
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is least soluble in water?
a)
Ag2S
b)
AgBr
c)
AgCl
d)
AgI
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Water is polar. Using the axiom, “like dissolves like”, hexane would water- insoluble. CH3OH, CH3CO2H and CH3NH2 are polar and can participate in hydrogen- bonding interactions with water, which would make these compounds quite water- soluble.Silver sulfide (Ag 2S) is the sulfide of silver. It is useful as a photosensitizer in photography. .... The crystallography of silver sulfide, Ag2S. Zeitschrift fur ... Ag2S. least soluble in water
Which one of the following enzyme brings about hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose?- a)Transacetylase
- b)Amylase
- c)β-galactosidase
- d)Permease
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following enzyme brings about hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose?
a)
Transacetylase
b)
Amylase
c)
β-galactosidase
d)
Permease

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The lac operon consists of the following parts:
- Structural Gene - It consists of 3 genes:
- z - codes for β-galactosidase
- y - codes for permease
- a - codes for transacetylase
- Operator -
- It is present adjacent to the structural gene.
- It is the site for the binding of repressor protein.
- Regulator -
- It comprises of the i-gene, which codes for the repressor protein.
- The repressor protein is synthesized all the time constitutively.
- Promoter -
- It is the transcription initiation site where RNA polymerase binds.
- Inducer -
- It is the molecule that determines whether the repressor will bind to the operator or not.
- Hence, it regulates the operon.
- Example - Lactose in lac operon.
Which of the following metals have only one oxidation state?- a)Co
- b)Sc
- c)Fe
- d)Al
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following metals have only one oxidation state?
a)
Co
b)
Sc
c)
Fe
d)
Al
|
|
Avantika Dasgupta answered |
Sc,Al has only one oxidation state i.e. +3.
Co,Fe has various oxidation states; most common are +2 and +3.
A reduction in the atomic size with increase in atomic number is characteristic of the elements of- a)high atomic masses
- b)d – block
- c)f – block
- d)radioactive series
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A reduction in the atomic size with increase in atomic number is characteristic of the elements of
a)
high atomic masses
b)
d – block
c)
f – block
d)
radioactive series

|
Nidhi Nambiar answered |
In f block elements with increase in atomic number atomic radii decreases smoothly.
Which is the most stable oxidation state of iron?- a)+2
- b)+3
- c)0
- d)+1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the most stable oxidation state of iron?
a)
+2
b)
+3
c)
0
d)
+1

|
Charvi Ahuja answered |
Fe has d5 configuration in +3 oxidation state.
Which among the following transition metal has lowest melting point?- a)Titanium
- b)Cobalt
- c)Mercury
- d)Scandium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following transition metal has lowest melting point?
a)
Titanium
b)
Cobalt
c)
Mercury
d)
Scandium

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Mercury is a transition metal that exhibits an unusually low melting point compared to other transition metals. This is due to its unique electron configuration and the relativistic effects that weaken its metallic bonding, resulting in a melting point of -38.83°C.
Vitamin B12 contains?- a)Zn2+
- b)Co3+
- c)Fe2+
- d)Ca2+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Vitamin B12 contains?
a)
Zn2+
b)
Co3+
c)
Fe2+
d)
Ca2+

|
Keerthana Mehta answered |
Vitamin B12 contains Co3+.
In the reaction, SnCl2 + HgCl2 → A + SnCl4- a)HgCl
- b)HgCl3
- c)HgCl2
- d)Hg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the reaction, SnCl2 + HgCl2 → A + SnCl4
a)
HgCl
b)
HgCl3
c)
HgCl2
d)
Hg

|
Asha Nair answered |
SnCl2 + HgCl2 → Hg + SnCl4
Select the correct match- a)Alec Jeffreys - Streptococcus pneumoniae
- b)Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod - Lac operon
- c)Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase - TMV
- d)Matthew Meselson and F. Stahl - Pisum sativum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct match
a)
Alec Jeffreys - Streptococcus pneumoniae
b)
Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod - Lac operon
c)
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase - TMV
d)
Matthew Meselson and F. Stahl - Pisum sativum

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Option 1:
- Alec Jeffreys discovered a technique known as DNA fingerprinting. It is used for the identification of organisms based on their DNA profiles.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae is a gram-positive anaerobic bacterium that causes pneumonia. It also causes middle ear infections in children.
Option 2:
- Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod discovered the lac operon.
- Lac operon or lactose operon is found in E. coli for the metabolism of lactose and its utilization and uptake.
- Genes in lac operon code for a protein that allow them to use lactose as a source of energy.
Option 3:
- Hershey and Chase experimented to prove that DNA is the genetic material. They used bacteriophages to perform this experiment. Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria.
- TMV stands for tobacco mosaic virus. It contains a single-stranded RNA virus that causes mosaic disease in tobacco. This virus affects tomatoes also.
Option 4:
- Mathew Meselson and F. Stahl discovered the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication. It means that during DNA replication, one new strand and one old strand are synthesized.
- Pisum sativum, a pea plant was used by Mendel to carry out his genetic experiments. He took seven contrasting characters of Pisum sativum and carried out crossing experiments for several generations to understand the inheritance pattern of genes.
So, the correct answer is option 2.
Chapter doubts & questions for August Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of August Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup














