All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of September Week 1 for NEET Exam
Which combination of magnetic field lines and poles shows two magnets repelling each other?- a)
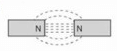
- b)
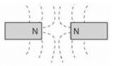
- c)
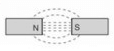
- d)
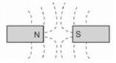
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which combination of magnetic field lines and poles shows two magnets repelling each other?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
- The discovery that one particular pole of a magnet orients northward, whereas the other pole orients southward allowed people to identify the north and south poles of any magnet.
- It was then noticed that the north poles of two different magnets repel each other, and likewise for the south poles. Conversely, the north pole of one magnet attracts the south pole of other magnets.
- This situation is analogous to that of electric charge, where like charges repel and unlike charges attract. In magnets, we simply replace the charge with a pole: Like poles repel and unlike poles attract.
When the switch is closed a magnetic field is produced by the coil. Which answer shows the shape of the field?- a)
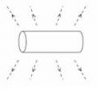
- b)
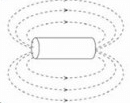
- c)
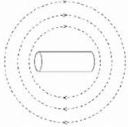
- d)
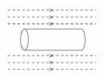
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the switch is closed a magnetic field is produced by the coil. Which answer shows the shape of the field?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Anand Kumar answered |
Ya it's B ....
Emerges from one side and enter from another side...
Emerges from one side and enter from another side...
In which of the following oxidation states La achieve the noble gas configuration?- a)+7
- b)+3
- c)+5
- d)+2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following oxidation states La achieve the noble gas configuration?
a)
+7
b)
+3
c)
+5
d)
+2
|
|
Shail Chawla answered |
La stands for Lanthanum, which is a member of the lanthanide series of elements in the periodic table. It has an atomic number of 57 and an electronic configuration of [Xe]5d1 6s2.
Achieving Noble Gas Configuration
To achieve a noble gas configuration, an element must have its outermost shell filled with electrons. The noble gases are stable because they have a filled outermost shell. Lanthanum can achieve this configuration by losing three electrons from its outermost shell.
Oxidation States
The oxidation state of an element is the charge that it carries when it forms a compound or ion. Lanthanum can form compounds in various oxidation states, including +2, +3, and +4.
In order to determine in which oxidation state La achieves noble gas configuration, we need to look at its electron configuration and determine how many electrons it needs to lose to achieve a filled outermost shell.
La3+ (Oxidation State of +3)
When Lanthanum loses three electrons, it forms a +3 ion (La3+). In this oxidation state, La has a noble gas configuration of [Xe]. Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Other Oxidation States
Lanthanum can also form compounds in other oxidation states, but they do not achieve a noble gas configuration. For example, in the +2 oxidation state, La has an electron configuration of [Xe]5d1, which is not a filled outermost shell.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lanthanum achieves noble gas configuration in the +3 oxidation state by losing three electrons and forming a La3+ ion.
Achieving Noble Gas Configuration
To achieve a noble gas configuration, an element must have its outermost shell filled with electrons. The noble gases are stable because they have a filled outermost shell. Lanthanum can achieve this configuration by losing three electrons from its outermost shell.
Oxidation States
The oxidation state of an element is the charge that it carries when it forms a compound or ion. Lanthanum can form compounds in various oxidation states, including +2, +3, and +4.
In order to determine in which oxidation state La achieves noble gas configuration, we need to look at its electron configuration and determine how many electrons it needs to lose to achieve a filled outermost shell.
La3+ (Oxidation State of +3)
When Lanthanum loses three electrons, it forms a +3 ion (La3+). In this oxidation state, La has a noble gas configuration of [Xe]. Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Other Oxidation States
Lanthanum can also form compounds in other oxidation states, but they do not achieve a noble gas configuration. For example, in the +2 oxidation state, La has an electron configuration of [Xe]5d1, which is not a filled outermost shell.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lanthanum achieves noble gas configuration in the +3 oxidation state by losing three electrons and forming a La3+ ion.
The electronic configuration of Eu 3+ ion is:- a)[Xe] 4f4
- b)[Xe] 4f7
- c)[Xe] 4f2
- d)[Xe] 4f6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The electronic configuration of Eu 3+ ion is:
a)
[Xe] 4f4
b)
[Xe] 4f7
c)
[Xe] 4f2
d)
[Xe] 4f6

|
Aditi Azade answered |
Atomic number of Eu is 63...so electronic configuration of Eu is, Eu=[xe] 4f^9 Hence,Eu^+3=[xe]4f^6
What is the most common oxidation state for actinoids?- a)+3
- b)+7
- c)+2
- d)+5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the most common oxidation state for actinoids?
a)
+3
b)
+7
c)
+2
d)
+5

|
Mamali . answered |
Unlike lanthanides which show the +3, oxidation States,actinides show a variety of Oxidation State from +3to+6.However+3&+4 are the principal Oxidation State.The+3 Oxidation state is the most stable in AC and all the other elements of the series.Thats it.
PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism are methods for- a)Genetic fingerprinting
- b)Genetic transformation
- c)DNA sequencing
- d)Study of enzymes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism are methods for
a)
Genetic fingerprinting
b)
Genetic transformation
c)
DNA sequencing
d)
Study of enzymes
|
|
Janhavi Menon answered |
Genetic Fingerprinting
Genetic fingerprinting or DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profiles. PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) are two commonly used methods for genetic fingerprinting.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR is a powerful technique used to amplify a specific DNA sequence. It involves a series of repeated cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension, resulting in the exponential amplification of a specific DNA fragment. PCR is used in genetic fingerprinting to amplify DNA from a sample, such as blood or tissue, and create multiple copies of a specific DNA fragment for analysis.
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
RFLP is a technique used to identify variations in DNA sequences between individuals. It involves the use of restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sites, resulting in fragments of different sizes. The resulting fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis and visualized using a staining agent. The pattern of fragment sizes is unique to each individual and can be used to identify them.
Applications of Genetic Fingerprinting
Genetic fingerprinting has a wide range of applications, including:
- Forensic investigations: DNA evidence can be used to identify suspects or victims in criminal investigations.
- Paternity testing: DNA analysis can be used to determine biological relationships, such as paternity or maternity.
- Medical diagnosis: Genetic fingerprinting can be used to diagnose genetic diseases and identify carriers of genetic mutations.
- Evolutionary studies: Genetic fingerprinting can be used to study the evolutionary relationships between different species.
Conclusion
PCR and RFLP are two powerful techniques used in genetic fingerprinting. These techniques have revolutionized the field of forensic science and have a wide range of applications in medicine, biology, and genetics.
Genetic fingerprinting or DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profiles. PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) are two commonly used methods for genetic fingerprinting.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR is a powerful technique used to amplify a specific DNA sequence. It involves a series of repeated cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension, resulting in the exponential amplification of a specific DNA fragment. PCR is used in genetic fingerprinting to amplify DNA from a sample, such as blood or tissue, and create multiple copies of a specific DNA fragment for analysis.
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
RFLP is a technique used to identify variations in DNA sequences between individuals. It involves the use of restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sites, resulting in fragments of different sizes. The resulting fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis and visualized using a staining agent. The pattern of fragment sizes is unique to each individual and can be used to identify them.
Applications of Genetic Fingerprinting
Genetic fingerprinting has a wide range of applications, including:
- Forensic investigations: DNA evidence can be used to identify suspects or victims in criminal investigations.
- Paternity testing: DNA analysis can be used to determine biological relationships, such as paternity or maternity.
- Medical diagnosis: Genetic fingerprinting can be used to diagnose genetic diseases and identify carriers of genetic mutations.
- Evolutionary studies: Genetic fingerprinting can be used to study the evolutionary relationships between different species.
Conclusion
PCR and RFLP are two powerful techniques used in genetic fingerprinting. These techniques have revolutionized the field of forensic science and have a wide range of applications in medicine, biology, and genetics.
Which of the following group contain mostly radioactive elements ?- a)Lanthanoids
- b)3 d transition series
- c)4 d transition series
- d)Actinoids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following group contain mostly radioactive elements ?
a)
Lanthanoids
b)
3 d transition series
c)
4 d transition series
d)
Actinoids

|
Parth Sharma answered |
The actinoids are said to be most radioactive metals because in this group all the metals have very oxidation number and are very rare metals found on earth and it has all the elements radioactive in its group and it has most radioactive metal uranium in it's group.
Mischmetal is an alloy of:
- a)Lanthanoid metal and Iron
- b)Actinoid metal and Iron
- c)Manganese, nickel and iron
- d)Zinc ,cobalt and iron
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mischmetal is an alloy of:
a)
Lanthanoid metal and Iron
b)
Actinoid metal and Iron
c)
Manganese, nickel and iron
d)
Zinc ,cobalt and iron
|
|
Snehal Iyer answered |
Explanation:
Mischmetal is an alloy of Lanthanoid Metal and Iron. It is a rare earth alloy, which is primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys.
Composition:
Mischmetal typically contains 50-55% cerium, 20-25% lanthanum, and small amounts of other rare earth metals such as neodymium, praseodymium, and gadolinium. The remaining portion of the alloy is typically iron.
Properties:
Mischmetal has a number of unique properties that make it an attractive alloy for use in a variety of applications. These properties include:
- High heat resistance
- High strength and durability
- Corrosion resistance
- Good machinability
Applications:
Mischmetal is primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys. It is also used in the production of magnesium alloys, which are used in a variety of applications, including aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods.
Some other applications of Mischmetal are:
- In the production of lighter flints
- As a pyrophoric material for the ignition of torches and lighters
- In the production of certain types of electrodes for welding and cutting
- In the production of certain types of batteries
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Mischmetal is an alloy of lanthanoid metal and iron, primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys. It has a number of unique properties that make it an attractive alloy for use in a variety of applications.
Mischmetal is an alloy of Lanthanoid Metal and Iron. It is a rare earth alloy, which is primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys.
Composition:
Mischmetal typically contains 50-55% cerium, 20-25% lanthanum, and small amounts of other rare earth metals such as neodymium, praseodymium, and gadolinium. The remaining portion of the alloy is typically iron.
Properties:
Mischmetal has a number of unique properties that make it an attractive alloy for use in a variety of applications. These properties include:
- High heat resistance
- High strength and durability
- Corrosion resistance
- Good machinability
Applications:
Mischmetal is primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys. It is also used in the production of magnesium alloys, which are used in a variety of applications, including aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods.
Some other applications of Mischmetal are:
- In the production of lighter flints
- As a pyrophoric material for the ignition of torches and lighters
- In the production of certain types of electrodes for welding and cutting
- In the production of certain types of batteries
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Mischmetal is an alloy of lanthanoid metal and iron, primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys. It has a number of unique properties that make it an attractive alloy for use in a variety of applications.
Each species has a characteristic set of chromosome number called- a)Aneuploid
- b)Monoploid
- c)Euploid
- d)Polyploid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Each species has a characteristic set of chromosome number called
a)
Aneuploid
b)
Monoploid
c)
Euploid
d)
Polyploid
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Most human cells have 2 of each of the 23 homologous monoploid chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A human cell with an extra set out of the 23 normal ones would be considered euploid. Euploid karyotypes would consequentially be a multiple of the haploid number, which in humans is 23.
Which was the last human chromosome to be completely sequenced?- a)Chromosome 21
- b)Chromosome X
- c)Chromosome 1
- d)Chromosome 11
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which was the last human chromosome to be completely sequenced?
a)
Chromosome 21
b)
Chromosome X
c)
Chromosome 1
d)
Chromosome 11

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
Chromosome 1 was the last completed chromosome, sequenced two decades after the beginning of the human Genome Project(hGP). It is the designation for the largest human chromosome.
In genetic fingerprinting, the ‘probe’ refers to- a)A radioactively labelled double-stranded DNA molecule
- b)A radioactively labelled single-stranded DNA molecule
- c)stranded RNA molecule
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In genetic fingerprinting, the ‘probe’ refers to
a)
A radioactively labelled double-stranded DNA molecule
b)
A radioactively labelled single-stranded DNA molecule
c)
stranded RNA molecule
d)
none
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
For DNA fingerprinting special single stranded DNA-probes are made in the laboratory. DNA-probes contain repeated sequences of bases complementary to those on VNTRs. These probes are made radioactive by labeling with radioactive isotopes. This step helps in detecting DNA fingerprints or variable number of tandem repeats (VNTRs).
Which one of the Maxwell’s laws leads to the conclusion that there are no magnetic field loops that are not closed?- a)Faraday’s law
- b)Gauss’ law for magnetism
- c)Gauss’ law for electricity
- d)Ampere-Maxwell law
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the Maxwell’s laws leads to the conclusion that there are no magnetic field loops that are not closed?
a)
Faraday’s law
b)
Gauss’ law for magnetism
c)
Gauss’ law for electricity
d)
Ampere-Maxwell law
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
In physics, Gauss's law for magnetism is one of the four Maxwell's equations that underlie classical electrodynamics. It states that the magnetic field B has divergence equal to zero,in other words, that it is a solenoidal vector field. It is equivalent to the statement that magnetic monopoles do not exist.Rather than "magnetic charges", the basic entity for magnetism is the magnetic dipole. (If monopoles were ever found, the law would have to be modified, as elaborated below.)
Gauss's law for magnetism can be written in two forms, a differential form and an integral form. These forms are equivalent due to the divergence theorem.
The name "Gauss's law for magnetism"is not universally used. The law is also called "Absence of free magnetic poles";one reference even explicitly says the law has "no name".It is also referred to as the "transversality requirement"because for plane waves it requires that the polarization be transverse to the direction of propagation.
In which of the following oxidation state Cerium achieves the noble gas configuration?- a)+5
- b)+2
- c)+7
- d)+4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following oxidation state Cerium achieves the noble gas configuration?
a)
+5
b)
+2
c)
+7
d)
+4

|
Mamali . answered |
The reason for this behaviour is a result of the stability of half filled, empty or fulfilled F orbitals that these elements achieve in these Oxidation State.Thats it.
How can a magnetic field be produced?- a)Using a permanent magnet
- b)Electric current
- c)Using a temporary magnet
- d)Using a permanent magnet or electric current
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How can a magnetic field be produced?
a)
Using a permanent magnet
b)
Electric current
c)
Using a temporary magnet
d)
Using a permanent magnet or electric current
|
|
Sanaya Kumar answered |
Production of Magnetic Field
Magnetic field can be produced in various ways. The correct answer is option 'D', which states that a magnetic field can be produced using a permanent magnet or electric current. Let's discuss both of these methods in detail.
Using a Permanent Magnet
A permanent magnet is a magnet that retains its magnetic properties even in the absence of an external magnetic field. The magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is due to the alignment of its atomic dipoles. The magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is static and does not change in strength or direction over time.
Using an Electric Current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge through a conductor. When an electric current flows through a conductor, it produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The strength and direction of the magnetic field depend on the strength and direction of the current flowing through the conductor. The magnetic field produced by an electric current is dynamic and can change in strength and direction over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a magnetic field can be produced using a permanent magnet or electric current. While the magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is static, the magnetic field produced by an electric current is dynamic and can change in strength and direction over time.
Magnetic field can be produced in various ways. The correct answer is option 'D', which states that a magnetic field can be produced using a permanent magnet or electric current. Let's discuss both of these methods in detail.
Using a Permanent Magnet
A permanent magnet is a magnet that retains its magnetic properties even in the absence of an external magnetic field. The magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is due to the alignment of its atomic dipoles. The magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is static and does not change in strength or direction over time.
Using an Electric Current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge through a conductor. When an electric current flows through a conductor, it produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The strength and direction of the magnetic field depend on the strength and direction of the current flowing through the conductor. The magnetic field produced by an electric current is dynamic and can change in strength and direction over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a magnetic field can be produced using a permanent magnet or electric current. While the magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is static, the magnetic field produced by an electric current is dynamic and can change in strength and direction over time.
Which of the following statement is true?- a)Actinoid contraction is smaller than lanthanoid contraction.
- b)There is no actinoid contraction observed.
- c)Actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoid contraction.
- d)Actinoid contraction is equally same as lanthanoid contraction.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is true?
a)
Actinoid contraction is smaller than lanthanoid contraction.
b)
There is no actinoid contraction observed.
c)
Actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoid contraction.
d)
Actinoid contraction is equally same as lanthanoid contraction.
|
|
Anshika Menon answered |
Actinoid Contraction and Lanthanoid Contraction
Actinoid contraction and lanthanoid contraction are terms used to describe the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the actinide and lanthanide series, respectively.
Actinoid Contraction
- Actinoid contraction refers to the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the actinide series.
- It is caused by the imperfect shielding of the 5f electrons by the 6s and 6p electrons.
- The 5f electrons are located closer to the nucleus and experience a greater effective nuclear charge, which leads to a smaller atomic and ionic radius.
- Actinoid contraction is observed in the actinide series from thorium (Z=90) to lawrencium (Z=103).
Lanthanoid Contraction
- Lanthanoid contraction refers to the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series.
- It is caused by the imperfect shielding of the 4f electrons by the 5s, 5p, and 6s electrons.
- The 4f electrons are located closer to the nucleus and experience a greater effective nuclear charge, which leads to a smaller atomic and ionic radius.
- Lanthanoid contraction is observed in the lanthanide series from cerium (Z=58) to lutetium (Z=71).
Comparison of Actinoid Contraction and Lanthanoid Contraction
- Actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoid contraction.
- The 5f electrons in the actinide series experience a greater effective nuclear charge than the 4f electrons in the lanthanide series, which leads to a greater decrease in atomic and ionic radii.
- Actinoid contraction is also observed over a smaller range of elements than lanthanoid contraction.
Actinoid contraction and lanthanoid contraction are terms used to describe the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the actinide and lanthanide series, respectively.
Actinoid Contraction
- Actinoid contraction refers to the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the actinide series.
- It is caused by the imperfect shielding of the 5f electrons by the 6s and 6p electrons.
- The 5f electrons are located closer to the nucleus and experience a greater effective nuclear charge, which leads to a smaller atomic and ionic radius.
- Actinoid contraction is observed in the actinide series from thorium (Z=90) to lawrencium (Z=103).
Lanthanoid Contraction
- Lanthanoid contraction refers to the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series.
- It is caused by the imperfect shielding of the 4f electrons by the 5s, 5p, and 6s electrons.
- The 4f electrons are located closer to the nucleus and experience a greater effective nuclear charge, which leads to a smaller atomic and ionic radius.
- Lanthanoid contraction is observed in the lanthanide series from cerium (Z=58) to lutetium (Z=71).
Comparison of Actinoid Contraction and Lanthanoid Contraction
- Actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoid contraction.
- The 5f electrons in the actinide series experience a greater effective nuclear charge than the 4f electrons in the lanthanide series, which leads to a greater decrease in atomic and ionic radii.
- Actinoid contraction is also observed over a smaller range of elements than lanthanoid contraction.
Magnetic field strength due to a short bar magnet on its axial line at a distance x is B. What is its value at the same distance on the equatorial line?- a)B/2
- b)B
- c)2B
- d)4B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Magnetic field strength due to a short bar magnet on its axial line at a distance x is B. What is its value at the same distance on the equatorial line?
a)
B/2
b)
B
c)
2B
d)
4B
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The magnetic field at any axial point is given by, B = 2μo/ 4πx3
Similarly, the field at any equatorial point is given by, B = μo/ 4πx3
Thus, the field at any equatorial point is half of what it is at an axial point.
Similarly, the field at any equatorial point is given by, B = μo/ 4πx3
Thus, the field at any equatorial point is half of what it is at an axial point.
The common oxidation state of the elements of lanthanoids series is:- a)+3
- b)+1
- c)+4
- d)+2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The common oxidation state of the elements of lanthanoids series is:
a)
+3
b)
+1
c)
+4
d)
+2
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
All the elements in the lanthanide series show an oxidation state of +3. Earlier it was believed that some of the metals (samarium, europium, and ytterbium) also show +2 oxidation states.
How many elements belong to lanthanide series?- a)13
- b)14
- c)28
- d)12
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many elements belong to lanthanide series?
a)
13
b)
14
c)
28
d)
12
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
The lanthanides and actinides form a group that appears almost disconnected from the rest of the periodic table. This is the f block of elements, known as the inner transition series. This is due to the proper numerical position between Groups 2 and 3 of the transition metals.
What is it that forms the basis of DNA fingerprinting?- a)The relative amount of DNA in the ridges and grooves of the fingerprints.
- b)The relative proportions of purines and pyrimidines in DNA.
- c)The relative difference in the DNA occurrence in blood, skin and saliva.
- d)Satellite DNA occurring as highly repeated short DNA segments.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is it that forms the basis of DNA fingerprinting?
a)
The relative amount of DNA in the ridges and grooves of the fingerprints.
b)
The relative proportions of purines and pyrimidines in DNA.
c)
The relative difference in the DNA occurrence in blood, skin and saliva.
d)
Satellite DNA occurring as highly repeated short DNA segments.

|
Mahi Shah answered |
The basis of identification by DNA Profiling is the polymorphism. ... These highly variable sequences of DNA are known as VNTRs (Variable Number of Tandem Repeats) and STRs (Short Tandem Repeats) often referred to as Minisatellites and Microsatellites. These are noncoding regions and are repeated within genes.
Chapter doubts & questions for September Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of September Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









