All Exams >
Class 10 >
Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of July Week 4 for Class 10 Exam
Which pair of the given quadrilaterals is similar?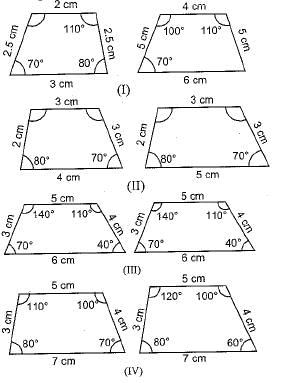
a)I only
b)III onlyc)I and IIId)IVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Quadrilaterals are similar if their angles are equal and corresponding sides are proportional.
If ΔABC ~ ΔEDF then which of the following is not true?
- a)BC . EF = AC . FD
- b)AB . EF = AC . DE
- c)BC . DE = AB . EF
- d)BC . DE = AB . FD
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If ΔABC ~ ΔEDF then which of the following is not true?
a)
BC . EF = AC . FD
b)
AB . EF = AC . DE
c)
BC . DE = AB . EF
d)
BC . DE = AB . FD
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Since △ABC~△EDF
Then, AB/ED = BC/DF = AC/EF
A) BC/DF = AC/EF
⇒BC.EF=AC.FD
So, A) is true
B) AB/ED = AC/EF
⇒AB.EF=AC.DE
So,B) is true
D) AB/ED = BC/DF
BC.DE=AB.EF
So, D) is not true
Therefore, Option C is not true
In triangles ABC and DEF, ∠B = ∠E, ∠F = ∠C and AB = 3DE. Then, the two triangles are- a)congruent but not similar
- b)similar but not congruent
- c)neither congruent nor similar
- d)congruent as well as similar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In triangles ABC and DEF, ∠B = ∠E, ∠F = ∠C and AB = 3DE. Then, the two triangles are
a)
congruent but not similar
b)
similar but not congruent
c)
neither congruent nor similar
d)
congruent as well as similar
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
to be congruent, the conditions are
S S S - three sides
S A S - two sides and the included angle
A S A - two angles and one side
R H S - R H S - Right angle, Hypotenuse and one side
But to be similar,
A A A means 3 angles
A A means only two angles ....
in both triangles should be equal.
In the problem, equality of two angles is given, but equality of sides is not given.
So, given triangles are not congruent.
But they are similar.
S S S - three sides
S A S - two sides and the included angle
A S A - two angles and one side
R H S - R H S - Right angle, Hypotenuse and one side
But to be similar,
A A A means 3 angles
A A means only two angles ....
in both triangles should be equal.
In the problem, equality of two angles is given, but equality of sides is not given.
So, given triangles are not congruent.
But they are similar.
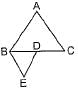
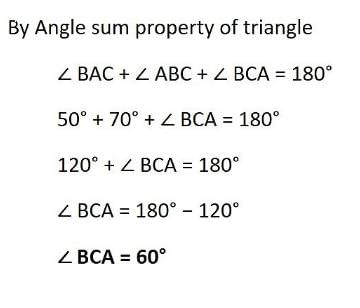
In the given figure, AD/BD = AE/EC and ∠ADE = 70°, ∠BAC = 50°, then angle ∠BCA =
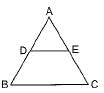
- a)70°
- b)50°
- c)80°
- d)60°
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given figure, AD/BD = AE/EC and ∠ADE = 70°, ∠BAC = 50°, then angle ∠BCA =


a)
70°
b)
50°
c)
80°
d)
60°
|
|
Trisha sharma answered |
Explanation: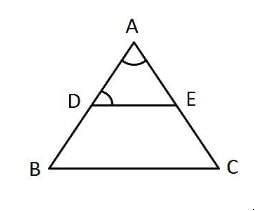

By converse of Thale’s theorem DE II BC
∠ADE = ∠ABC = 70 degree
Given ∠BAC = 50 degree

You can read Important Definitions & Formulas related to Triangles through the document:
D and E are respectively the points on the sides AB and AC of a triangle ABC such that AD = 3 cm, BD = 5 cm, BC = 12.8 cm and DE || BC. Then length of DE (in cm) is- a)4.8 cm
- b)7.6 cm
- c)19.2 cm
- d)2.5 cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
D and E are respectively the points on the sides AB and AC of a triangle ABC such that AD = 3 cm, BD = 5 cm, BC = 12.8 cm and DE || BC. Then length of DE (in cm) is
a)
4.8 cm
b)
7.6 cm
c)
19.2 cm
d)
2.5 cm
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
GIVEN: In Δ ABC, D and E are points on AB and AC , DE || BC and AD = 2.4 cm, AE = 3.2 cm, DE = 2 cm and BE = 5 cm.
In Δ ADE and Δ ABC,
∠ADE =∠ABC (corresponding angles)
[DE || BC, AB is transversal]
∠AED =∠ACB (corresponding angles)
[DE || BC, AC is transversal]
So, Δ ADE ~ Δ ABC (AA similarity)
Therefore, AD/AB = AE/AC = DE/BC
[In similar triangles corresponding sides are proportional]
AD/AB = DE/BC
2.4/(2.4+DB) = 2/5
2.4 × 5 = 2(2.4+ DB)
12 = 4.8 + 2DB
12 - 4.8 = 2DB
7.2 = 2DB
DB = 7.2/2
DB = 3.6 cm
Similarly, AE/AC = DE/BC
3.2/(3.2+EC) = 2/5
3.2 × 5 = 2(3.2+EC)
16 = 6.4 + 2EC
16 - 6.4 = 2EC
9.6 = 2EC
EC = 9.6/2
EC = 4.8 cm
Hence,BD = 3.6 cm and CE = 4.8 cm.
In Δ ADE and Δ ABC,
∠ADE =∠ABC (corresponding angles)
[DE || BC, AB is transversal]
∠AED =∠ACB (corresponding angles)
[DE || BC, AC is transversal]
So, Δ ADE ~ Δ ABC (AA similarity)
Therefore, AD/AB = AE/AC = DE/BC
[In similar triangles corresponding sides are proportional]
AD/AB = DE/BC
2.4/(2.4+DB) = 2/5
2.4 × 5 = 2(2.4+ DB)
12 = 4.8 + 2DB
12 - 4.8 = 2DB
7.2 = 2DB
DB = 7.2/2
DB = 3.6 cm
Similarly, AE/AC = DE/BC
3.2/(3.2+EC) = 2/5
3.2 × 5 = 2(3.2+EC)
16 = 6.4 + 2EC
16 - 6.4 = 2EC
9.6 = 2EC
EC = 9.6/2
EC = 4.8 cm
Hence,BD = 3.6 cm and CE = 4.8 cm.
If ΔPRQ ~ ΔXYZ, then- a)
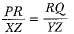
- b)
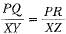
- c)
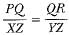
- d)
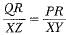
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If ΔPRQ ~ ΔXYZ, then
a)
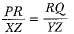
b)
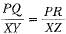
c)
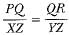
d)
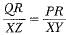
|
|
Kuldeep Kuldeep answered |
Since the two triangles are similar, therefore, they will have their corresponding angles congruent and the corresponding sides in proportion.
What is the basic filtration unit in the kidneys called?- a)Alveoli
- b)Glomerulus
- c)Nephron
- d)Bowman's capsule
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the basic filtration unit in the kidneys called?
a)
Alveoli
b)
Glomerulus
c)
Nephron
d)
Bowman's capsule
|
|
Saptarshi Yadav answered |
Basic Filtration Unit in the Kidneys
The correct answer is option 'C' - Nephron. The nephron is the fundamental structural and functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and forming urine.
Structure of Nephron
- Each kidney contains approximately one million nephrons.
- A nephron consists of two main parts:
- Renal Corpuscle: This includes the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule.
- Renal Tubule: This is divided into several segments - proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct.
Function of Nephron
- Filtration: Blood enters through the glomerulus, where water, ions, and small molecules are filtered into Bowman's capsule.
- Reabsorption: Essential nutrients and water are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream from the renal tubule.
- Secretion: Waste products and excess substances are secreted into the tubule from the blood.
Importance of Nephrons
- Nephrons regulate the body's fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and waste removal.
- They play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, ensuring that the body functions optimally.
Conclusion
In summary, the nephron is the basic filtration unit of the kidneys, essential for the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion, which together ensure proper kidney function and overall health.
The correct answer is option 'C' - Nephron. The nephron is the fundamental structural and functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and forming urine.
Structure of Nephron
- Each kidney contains approximately one million nephrons.
- A nephron consists of two main parts:
- Renal Corpuscle: This includes the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule.
- Renal Tubule: This is divided into several segments - proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct.
Function of Nephron
- Filtration: Blood enters through the glomerulus, where water, ions, and small molecules are filtered into Bowman's capsule.
- Reabsorption: Essential nutrients and water are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream from the renal tubule.
- Secretion: Waste products and excess substances are secreted into the tubule from the blood.
Importance of Nephrons
- Nephrons regulate the body's fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and waste removal.
- They play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, ensuring that the body functions optimally.
Conclusion
In summary, the nephron is the basic filtration unit of the kidneys, essential for the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion, which together ensure proper kidney function and overall health.
Which of the following is NOT a method used by plants for excretion?- a)Transpiration
- b)Storage in vacuoles
- c)Shedding of leaves
- d)Active transport into the atmosphere
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a method used by plants for excretion?
a)
Transpiration
b)
Storage in vacuoles
c)
Shedding of leaves
d)
Active transport into the atmosphere
|
|
Shambavi dubey answered |
Explanation:
Active transport into the atmosphere is NOT a method used by plants for excretion
Plants have several mechanisms for excretion, which help them to get rid of waste products and maintain their internal environment. However, active transport into the atmosphere is not one of these methods.
Transpiration:
- Transpiration is a process where plants release water vapor through small openings on their leaves called stomata. This helps in the regulation of water and mineral balance in the plant.
Storage in vacuoles:
- Plants can store waste products in vacuoles, which are membrane-bound organelles inside plant cells. These vacuoles can store various substances, including waste products, until they can be safely disposed of.
Shedding of leaves:
- Plants can also excrete waste products by shedding leaves. As leaves age and become damaged, plants will shed them to get rid of waste products and make way for new growth.
Active transport into the atmosphere:
- Unlike the other methods mentioned above, active transport into the atmosphere is not a common method used by plants for excretion. Plants primarily use transpiration, storage in vacuoles, and shedding of leaves to excrete waste products and maintain their internal environment.
Active transport into the atmosphere is NOT a method used by plants for excretion
Plants have several mechanisms for excretion, which help them to get rid of waste products and maintain their internal environment. However, active transport into the atmosphere is not one of these methods.
Transpiration:
- Transpiration is a process where plants release water vapor through small openings on their leaves called stomata. This helps in the regulation of water and mineral balance in the plant.
Storage in vacuoles:
- Plants can store waste products in vacuoles, which are membrane-bound organelles inside plant cells. These vacuoles can store various substances, including waste products, until they can be safely disposed of.
Shedding of leaves:
- Plants can also excrete waste products by shedding leaves. As leaves age and become damaged, plants will shed them to get rid of waste products and make way for new growth.
Active transport into the atmosphere:
- Unlike the other methods mentioned above, active transport into the atmosphere is not a common method used by plants for excretion. Plants primarily use transpiration, storage in vacuoles, and shedding of leaves to excrete waste products and maintain their internal environment.
Why is it significant that the kidney’s filtration units, nephrons, are packed close together?- a)It aids in storing more urine
- b)It increases the efficiency of filtration
- c)It helps in producing more urea
- d)It allows for more glucose reabsorption
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is it significant that the kidney’s filtration units, nephrons, are packed close together?
a)
It aids in storing more urine
b)
It increases the efficiency of filtration
c)
It helps in producing more urea
d)
It allows for more glucose reabsorption
|
|
Rohit Patel answered |
Significance of Nephrons Packed Close Together
The close packing of nephrons in the kidneys plays a crucial role in enhancing the organ's ability to filter blood efficiently. Here are the key points explaining why this arrangement is significant:
1. Enhanced Filtration Efficiency
- The proximity of nephrons allows for a greater surface area for filtration.
- With more nephrons working simultaneously, the kidneys can process larger volumes of blood, effectively removing waste products and excess substances.
2. Concentrated Functionality
- Nephrons consist of glomeruli and tubules that work together to filter blood and reabsorb necessary substances.
- Close arrangement enables quick communication and cooperation between these components, leading to optimal performance.
3. Maximized Resource Utilization
- By packing nephrons together, the kidneys minimize the distance over which filtrate must travel, thus reducing the energy required for filtration and reabsorption processes.
- This efficiency is vital for maintaining homeostasis in the body, ensuring that crucial nutrients and electrolytes are preserved while waste is excreted.
4. Effective Waste Removal
- The design facilitates rapid filtration and concentration of urine by allowing multiple nephrons to contribute to the overall filtering process.
- This means toxins and waste products can be efficiently cleared from the bloodstream, maintaining the body's internal environment.
In summary, the close packing of nephrons significantly increases the efficiency of filtration in the kidneys, allowing for effective blood purification and waste removal, which is essential for overall health.
The close packing of nephrons in the kidneys plays a crucial role in enhancing the organ's ability to filter blood efficiently. Here are the key points explaining why this arrangement is significant:
1. Enhanced Filtration Efficiency
- The proximity of nephrons allows for a greater surface area for filtration.
- With more nephrons working simultaneously, the kidneys can process larger volumes of blood, effectively removing waste products and excess substances.
2. Concentrated Functionality
- Nephrons consist of glomeruli and tubules that work together to filter blood and reabsorb necessary substances.
- Close arrangement enables quick communication and cooperation between these components, leading to optimal performance.
3. Maximized Resource Utilization
- By packing nephrons together, the kidneys minimize the distance over which filtrate must travel, thus reducing the energy required for filtration and reabsorption processes.
- This efficiency is vital for maintaining homeostasis in the body, ensuring that crucial nutrients and electrolytes are preserved while waste is excreted.
4. Effective Waste Removal
- The design facilitates rapid filtration and concentration of urine by allowing multiple nephrons to contribute to the overall filtering process.
- This means toxins and waste products can be efficiently cleared from the bloodstream, maintaining the body's internal environment.
In summary, the close packing of nephrons significantly increases the efficiency of filtration in the kidneys, allowing for effective blood purification and waste removal, which is essential for overall health.
Which of the following structures in the kidney is responsible for the initial filtration of blood?- a)Ureter
- b)Urinary bladder
- c)Urethra
- d)Bowman's capsule
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following structures in the kidney is responsible for the initial filtration of blood?
a)
Ureter
b)
Urinary bladder
c)
Urethra
d)
Bowman's capsule
|
|
Urvashi dasgupta answered |
Introduction
The kidney is a vital organ in the human body responsible for filtering blood, eliminating waste, and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance. Among its various structures, the Bowman's capsule plays a crucial role in the filtration process.
Bowman's Capsule: The Filtration Unit
- The Bowman's capsule is a cup-shaped structure that encases the glomerulus, a network of tiny blood vessels (capillaries).
- It is located in the nephron, the functional unit of the kidney, where blood filtration begins.
Filtration Process
- Blood Flow: Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery and reaches the glomerulus, where high pressure forces fluid and small solutes out of the blood.
- Filtration Barrier: The walls of the glomerulus and the Bowman's capsule form a selective barrier. This barrier allows water, ions, glucose, and small waste molecules to pass while retaining larger molecules like proteins and blood cells.
- Formation of Filtrate: The fluid that collects in the Bowman's capsule is called glomerular filtrate. This filtrate then moves into the renal tubules for further processing and reabsorption.
Other Structures Explained
- Ureter: A tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary Bladder: A storage organ for urine before it is expelled from the body.
- Urethra: The duct through which urine is discharged from the bladder.
Conclusion
In summary, the Bowman's capsule is the key structure in the kidney responsible for the initial filtration of blood. It initiates the process of waste removal, setting the stage for the kidneys' essential role in maintaining homeostasis.
The kidney is a vital organ in the human body responsible for filtering blood, eliminating waste, and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance. Among its various structures, the Bowman's capsule plays a crucial role in the filtration process.
Bowman's Capsule: The Filtration Unit
- The Bowman's capsule is a cup-shaped structure that encases the glomerulus, a network of tiny blood vessels (capillaries).
- It is located in the nephron, the functional unit of the kidney, where blood filtration begins.
Filtration Process
- Blood Flow: Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery and reaches the glomerulus, where high pressure forces fluid and small solutes out of the blood.
- Filtration Barrier: The walls of the glomerulus and the Bowman's capsule form a selective barrier. This barrier allows water, ions, glucose, and small waste molecules to pass while retaining larger molecules like proteins and blood cells.
- Formation of Filtrate: The fluid that collects in the Bowman's capsule is called glomerular filtrate. This filtrate then moves into the renal tubules for further processing and reabsorption.
Other Structures Explained
- Ureter: A tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary Bladder: A storage organ for urine before it is expelled from the body.
- Urethra: The duct through which urine is discharged from the bladder.
Conclusion
In summary, the Bowman's capsule is the key structure in the kidney responsible for the initial filtration of blood. It initiates the process of waste removal, setting the stage for the kidneys' essential role in maintaining homeostasis.
Which waste product mentioned is directly associated with photosynthesis in plants?- a)Urea
- b)Uric acid
- c)Oxygen
- d)Carbon dioxide
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which waste product mentioned is directly associated with photosynthesis in plants?
a)
Urea
b)
Uric acid
c)
Oxygen
d)
Carbon dioxide

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
- During photosynthesis in plants, carbon dioxide (CO2) is taken in from the atmosphere, and water (H2O) is absorbed from the soil.
- In the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll, these raw materials are converted into glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
- Oxygen is a waste product of photosynthesis and is released into the atmosphere through stomata in plant leaves.
Which structure collects the filtrate in the kidneys?- a)Glomerulus
- b)Urethra
- c)Bowman's capsule
- d)Ureter
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structure collects the filtrate in the kidneys?
a)
Glomerulus
b)
Urethra
c)
Bowman's capsule
d)
Ureter

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
Bowman's capsule collects the filtrate from the glomerulus in the kidneys.
Assertion (A): Water scarcity in many regions is primarily due to over-exploitation and unequal access rather than its natural availability.Reason (R): The hydrological cycle ensures a consistent supply of fresh water through precipitation and surface runoff, making water scarcity a non-issue.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Water scarcity in many regions is primarily due to over-exploitation and unequal access rather than its natural availability.
Reason (R): The hydrological cycle ensures a consistent supply of fresh water through precipitation and surface runoff, making water scarcity a non-issue.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false
|
|
Renuka malhotra answered |
Understanding the Assertion and Reason
The assertion and reason provided relate to the critical issue of water scarcity. Let's break down their meanings and implications.
Assertion (A)
- Water scarcity in many regions is primarily attributed to:
- Over-exploitation of water resources.
- Unequal access to available water.
- This implies that the management and distribution of water are significant factors contributing to scarcity, rather than the sheer availability of water.
Reason (R)
- The hydrological cycle is responsible for:
- A consistent supply of fresh water via precipitation and surface runoff.
- This suggests that, theoretically, water scarcity should not be a major concern because nature continuously replenishes water sources.
Analysis of the Truthfulness
- Both assertion and reason are indeed true:
- Water scarcity does stem from human actions (over-exploitation) and social issues (unequal access).
- The hydrological cycle does provide a constant supply of freshwater.
Why Option B is Correct
- While both statements are true, the reason does not adequately explain the assertion:
- Water scarcity exists not because of a lack of water supply but due to how water is utilized and distributed.
- The assertion focuses on human-induced factors, while the reason addresses a natural process.
In summary, while both the assertion and reason are true, the reason does not correctly elucidate why water scarcity is a pressing issue, leading us to select option 'B'.
The assertion and reason provided relate to the critical issue of water scarcity. Let's break down their meanings and implications.
Assertion (A)
- Water scarcity in many regions is primarily attributed to:
- Over-exploitation of water resources.
- Unequal access to available water.
- This implies that the management and distribution of water are significant factors contributing to scarcity, rather than the sheer availability of water.
Reason (R)
- The hydrological cycle is responsible for:
- A consistent supply of fresh water via precipitation and surface runoff.
- This suggests that, theoretically, water scarcity should not be a major concern because nature continuously replenishes water sources.
Analysis of the Truthfulness
- Both assertion and reason are indeed true:
- Water scarcity does stem from human actions (over-exploitation) and social issues (unequal access).
- The hydrological cycle does provide a constant supply of freshwater.
Why Option B is Correct
- While both statements are true, the reason does not adequately explain the assertion:
- Water scarcity exists not because of a lack of water supply but due to how water is utilized and distributed.
- The assertion focuses on human-induced factors, while the reason addresses a natural process.
In summary, while both the assertion and reason are true, the reason does not correctly elucidate why water scarcity is a pressing issue, leading us to select option 'B'.
A dam is primarily used for ____ water flow, often creating a reservoir or lake.- a)controlling
- b)ignoring
- c)enhancing
- d)reducing
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A dam is primarily used for ____ water flow, often creating a reservoir or lake.
a)
controlling
b)
ignoring
c)
enhancing
d)
reducing
|
|
Ramya chauhan answered |
Understanding the Purpose of Dams
Dams serve a critical function in water management and environmental control. Their primary purpose is to manage water flow effectively.
Key Functions of Dams:
- Controlling Water Flow:
Dams regulate the flow of rivers and streams. By holding back water, they can prevent flooding during heavy rains and manage the distribution of water during dry periods. This control is essential for both human settlements and ecosystems.
- Creating Reservoirs:
When a dam is constructed, it often leads to the formation of a reservoir or lake. These bodies of water serve multiple purposes, including water storage for irrigation, drinking water supply, and recreational activities.
- Hydropower Generation:
Many dams are equipped with turbines that harness the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. This renewable energy source is vital for powering homes and industries.
- Irrigation Support:
Dams provide a reliable water source for agricultural activities, ensuring that crops receive adequate water even during drought conditions. This is crucial for food security in many regions.
- Recreational Opportunities:
Reservoirs created by dams offer recreational activities like fishing, boating, and swimming, which can boost local economies through tourism.
Conclusion:
In summary, the primary function of a dam is to control water flow, which is essential for managing resources, preventing disasters, generating energy, and supporting agriculture and recreation. This multifaceted utility underscores the importance of dams in modern society.
Dams serve a critical function in water management and environmental control. Their primary purpose is to manage water flow effectively.
Key Functions of Dams:
- Controlling Water Flow:
Dams regulate the flow of rivers and streams. By holding back water, they can prevent flooding during heavy rains and manage the distribution of water during dry periods. This control is essential for both human settlements and ecosystems.
- Creating Reservoirs:
When a dam is constructed, it often leads to the formation of a reservoir or lake. These bodies of water serve multiple purposes, including water storage for irrigation, drinking water supply, and recreational activities.
- Hydropower Generation:
Many dams are equipped with turbines that harness the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. This renewable energy source is vital for powering homes and industries.
- Irrigation Support:
Dams provide a reliable water source for agricultural activities, ensuring that crops receive adequate water even during drought conditions. This is crucial for food security in many regions.
- Recreational Opportunities:
Reservoirs created by dams offer recreational activities like fishing, boating, and swimming, which can boost local economies through tourism.
Conclusion:
In summary, the primary function of a dam is to control water flow, which is essential for managing resources, preventing disasters, generating energy, and supporting agriculture and recreation. This multifaceted utility underscores the importance of dams in modern society.
Which of the following statements about plant excretion is FALSE?- a)Plants excrete waste products into the soil
- b)Plants store waste products in cellular vacuoles
- c)Plants excrete urea and uric acid
- d)Plants can lose waste products through falling leaves
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about plant excretion is FALSE?
a)
Plants excrete waste products into the soil
b)
Plants store waste products in cellular vacuoles
c)
Plants excrete urea and uric acid
d)
Plants can lose waste products through falling leaves

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
Plants do not excrete urea and uric acid. These are nitrogenous wastes primarily excreted by animals. Plants handle waste products through vacuoles, fallen leaves, and excretion into the soil.
Which structure in the human excretory system is responsible for storing urine until it is expelled from the body?- a)Kidney
- b)Ureter
- c)Urinary bladder
- d)Urethra
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structure in the human excretory system is responsible for storing urine until it is expelled from the body?
a)
Kidney
b)
Ureter
c)
Urinary bladder
d)
Urethra
|
|
Rohit Patel answered |
Understanding the Human Excretory System
The human excretory system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's internal balance by removing waste products and excess substances. Among its components, the urinary bladder is specifically responsible for storing urine until it is expelled from the body.
Key Structures of the Excretory System
- Kidney:
- The kidneys are vital organs that filter blood to produce urine. They remove waste and excess substances from the bloodstream.
- Ureter:
- The ureters are tubes that transport urine from each kidney to the urinary bladder. They do not store urine but are essential for its movement.
- Urinary Bladder:
- The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that temporarily holds urine. It can expand and contract, allowing it to accommodate varying volumes of urine. When the bladder is full, nerve signals prompt the urge to urinate, leading to the expulsion of urine.
- Urethra:
- The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. It plays a role in the final step of excretion but does not store urine.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'C', the urinary bladder, as it is specifically designed for storing urine until the body is ready to expel it. This organ's ability to stretch and hold urine is essential for the controlled release of waste, ensuring that excretion is managed effectively.
The human excretory system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's internal balance by removing waste products and excess substances. Among its components, the urinary bladder is specifically responsible for storing urine until it is expelled from the body.
Key Structures of the Excretory System
- Kidney:
- The kidneys are vital organs that filter blood to produce urine. They remove waste and excess substances from the bloodstream.
- Ureter:
- The ureters are tubes that transport urine from each kidney to the urinary bladder. They do not store urine but are essential for its movement.
- Urinary Bladder:
- The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that temporarily holds urine. It can expand and contract, allowing it to accommodate varying volumes of urine. When the bladder is full, nerve signals prompt the urge to urinate, leading to the expulsion of urine.
- Urethra:
- The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. It plays a role in the final step of excretion but does not store urine.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'C', the urinary bladder, as it is specifically designed for storing urine until the body is ready to expel it. This organ's ability to stretch and hold urine is essential for the controlled release of waste, ensuring that excretion is managed effectively.
Where organ helps in expelling urine out from the body?- a)Kidneys
- b)Ureters
- c)Urethra
- d)Urinary Bladder
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Where organ helps in expelling urine out from the body?
a)
Kidneys
b)
Ureters
c)
Urethra
d)
Urinary Bladder

|
Get Idea answered |
Urine is expelled from the body through the urethra.
What is the role of the muscular urinary bladder in the excretory system?- a)To filter blood
- b)To reabsorb water
- c)To store urine until it can be excreted
- d)To produce urea
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the role of the muscular urinary bladder in the excretory system?
a)
To filter blood
b)
To reabsorb water
c)
To store urine until it can be excreted
d)
To produce urea

|
Nk Classes answered |
- The muscular urinary bladder plays a crucial role in the excretory system by storing urine temporarily until it can be excreted from the body through the urethra.
- The bladder expands as it fills with urine, and its muscular walls contract to expel urine during urination (micturition).
Chapter doubts & questions for July Week 4 - Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of July Week 4 - Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup