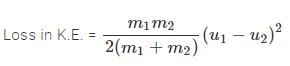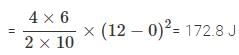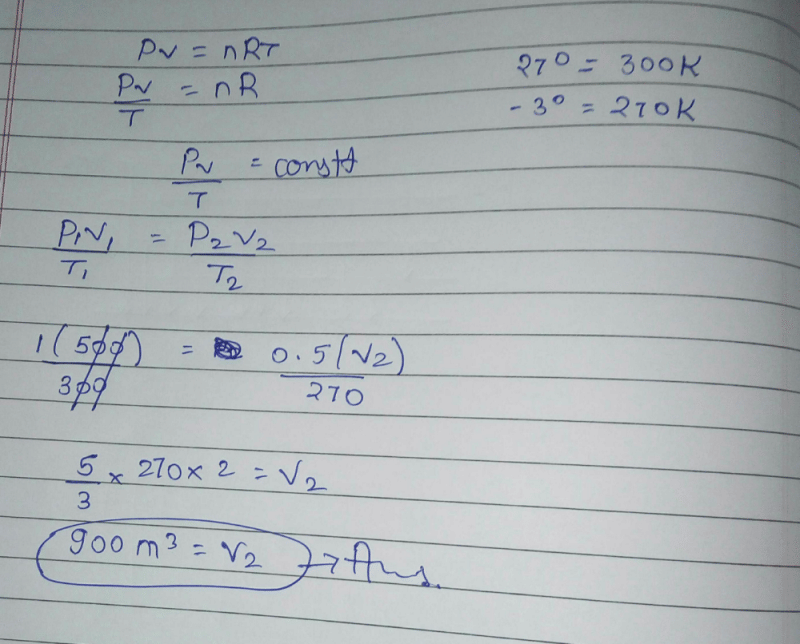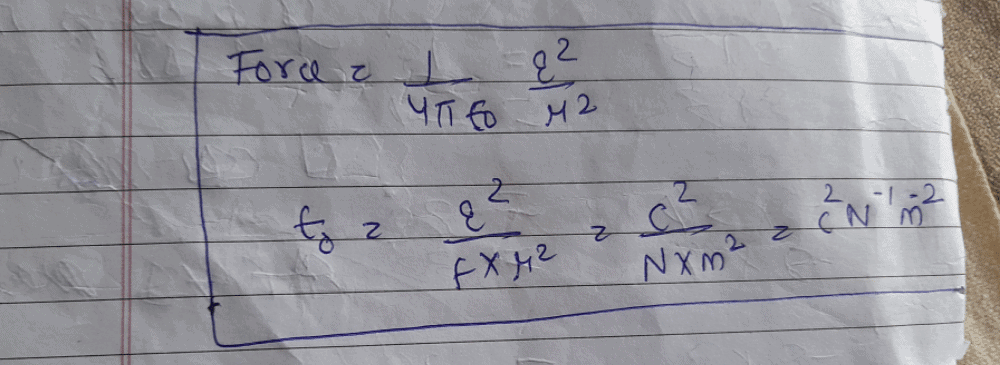All questions of 2012 for NEET Exam
Which of the following organisms completely lack cell wall, they are the smallest living cells known and can survive without oxygen?- a)Mycoplasma
- b)Euglenoids
- c)Slime moulds
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Anshika Sharmaa answered |
In a flowering plant, the pollen tube first arrives in- a)egg
- b)an antipodal cell
- c)a synergid
- d)central cell
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Which one of the following compounds is most acidic?
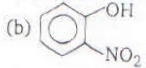
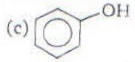
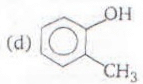
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Rekha Yadav answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A rod AB is l m long. The temperature of its one end A is maintained at 100’C and other end Bat 10°C, the temperature at a distance of 60 cm from point B is
- A:
64°C
- B:
36°C
- C:
46°C
- D:
72°C
The answer is a.
A rod AB is l m long. The temperature of its one end A is maintained at 100’C and other end Bat 10°C, the temperature at a distance of 60 cm from point B is
64°C
36°C
46°C
72°C
|
|
Aniket Das answered |
What is the correct order of the stages of cellular respiration?- a)Krebs’ cycle electron- transport- chain rilycolysis
- b)Election transport chain – Krebs’ cycle – glycolysis
- c)Glycolysis – Krebs’ cycle – electron transport chain
- d)Glycolysis – electron transport chain – Krebs’ cycle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Anshika Sharmaa answered |
A marble block of mass 2 kg lying on ice when given a velocity of 6 m/s is stopped by friction in 10 s. Then the coefficient offriction is- a)0.01
- b)0.02
- c)0.03
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?- a)Vitamin-B12 — Pernicious anaemia
- b)Vitamin-B6 — Loss of appetite
- c)Vitamin-B1 — Beri-beri
- d)Vitamin-B2 — Pellagra
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Anshika Sharmaa answered |
Who has been designated as the ‘Man of the Decade’ by Time Magazine?- a)Nelson Mandela
- b)Ronold Reagan
- c)Dalai Lama
- d)None of these
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Anshika Sharmaa answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A pea plant parent having violet-coloured flowers with unknown genotype was crossed with a plant having white-coloured flowers. In the progeny, 5O% of the flowers were violet and 50% were white. The genotypic constitution of the parent having violet-coloured flowers was
- A:
homozygous
- B:
merozygous
- C:
heterozygous
- D:
hemizygous
The answer is c.
A pea plant parent having violet-coloured flowers with unknown genotype was crossed with a plant having white-coloured flowers. In the progeny, 5O% of the flowers were violet and 50% were white. The genotypic constitution of the parent having violet-coloured flowers was
homozygous
merozygous
heterozygous
hemizygous

|
Muskan answered |
The ratio of radius of two bubbles is 2: 1. What is the ratio excess pressure inside them?- a)1 : 2
- b)1 : 4
- c)2 : 1
- d)4 : 1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
If the earth stops moving around its polar axis then what will be effect on body placed at south axis?- a)Remain same
- b)increase
- c)Decrease but not zero
- d)Decrease zero
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Monali Kumari answered |
Clamp connection is found In- a)Basidiomycetes
- b)Ascomycetes
- c)Saccharomycetes
- d)Haplomycetes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Jeeshan Ahmed answered |
1 mole of gas occupies a volume of 200 mL at 100 mm pressure. What is the volume occupied by two moles of gas at 400 mm pressure and at same temperature?- a)50 ml.
- b)100 mL
- c)200 mL
- d)400 mL
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Kirti Kulkarni answered |
PV= n RT
value of RT = PV/n
RT= 100×200/1 = 20000 .........(1)
equation 2:
PV = nRT
value of RT= PV/n
RT = 400×V/2 = 200V .........(2)
as both R And T are constant
we can equate both the equations
we get,
200V=20000
V= 100 ml
What is the correct relationship between the pHs of isoinolar solutions of sodium oxide (PH1), sodium sulphide (pH2), sodium selenide (pH3) and sodium telluride (pH4)?- a)pH1 > pH2 = pH3 > PH4
- b)pH1 < pH2 < pH3 < PH4
- c)pH1 < pH2 < pH3 ≈ PH4
- d)pH1 > pH2 > pH3 > PH4
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Nookilla Supriya answered |
The reduction potential at pH = 14 for the Cue2+/Cu couples is [Given, E°Cu2+/Cu = 0.34V; Ksp Cu(OH)2 = 1 x 10-19- a)0.34 V
- b)– 0.34 V
- c)0.22 V
- d)– 0.22 V
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anjali Chauhan answered |
The reduction potential of Cue2/Cu at pH = 14 can be calculated using the Nernst equation:
E = E° - (0.0592/n) x log([Cu]/[Cue2])
Since the reduction potential of Cu2+/Cu is given, we can assume that Cue2/Cu2+ is in equilibrium with Cu/Cue2-. Therefore, we can use the following equations:
[Cue2-]/[Cu2+] = exp[(E° - E)/ (0.0592/n)]
[Cu]/[Cue2-] = [Cu2+]/[Cue2-] x [Cue2-]/[Cu] = [Cu2+]/[Cu] x [Cue2-]/[Cue2+]
At pH = 14, the concentration of Cu2+ and Cue2- can be assumed to be equal to 10^-14 M, since the dissociation constant of water (Kw) is 10^-14 M^2.
Substituting the given values into the equations, we get:
[Cue2-]/[Cu2+] = exp[(0.34 - E)/ (0.0592/2)] = exp[(0.34 - E)/ 0.0296]
[Cu]/[Cue2-] = [Cu2+]/[Cu] x [Cue2-]/[Cue2+] = 1 x [Cue2-]/[Cu2+] = [Cue2-]^2/[Cu2+] = 10^-28/[Cu2+]
Substituting the values into the Nernst equation, we get:
E = 0.34 - (0.0592/2) x log(exp[(0.34 - E)/ 0.0296]/10^-14)
Simplifying the equation, we get:
E = 0.34 - (0.0296/2) x log(exp[(0.34 - E)/ 0.0296])
E = 0.34 - 0.0148 x log(exp[(0.34 - E)/ 0.0296])
E = 0.34 - 0.0148 x [(0.34 - E)/ 0.0296]
E = 0.34 - 0.503 x (0.34 - E)
E = 0.34 - 0.17 + 0.503E
0.497E = 0.17
E = 0.34 - 0.34
E = 0 V
Therefore, the reduction potential of Cue2/Cu at pH = 14 is 0 V. This indicates that the Cue2/Cu couple is not stable at pH = 14 and Cu2+/Cu couple is more stable.
Excess carbohydrates and proteins are stored in the body as- a)amino acids
- b)fats
- c)starch
- d)monosaccharides
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Jaga Priyan answered |
First National park developed in India is- a)Gir
- b)Kaziranga
- c)Jim Corbett
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Hitakshi 💞💞 answered |
If the total amount of adenine and thymine in a double•stranded DNA is 60%, the amount of guanine in this DNA will be- a)15%
- b)20%
- c)30%
- d)40%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Vedprakash Patidar answered |
The number of linkage group(s) present in Escherichia Coli is- a)one
- b)two
- c)four
- d)seven
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
If the total amount of adenine and thyrnine in a double-stranded DNA is 45%, the amount of guznine in this DNA will be- a)22.5%
- b)27 5%
- c)45%
- d)55%
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Keerthana Saha answered |
The four nitrogenous bases found in DNA are Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), and Cytosine (C).
In a double-stranded DNA, the amount of A always equals the amount of T and the amount of G always equals the amount of C.
If the total amount of A and T is 45%, then the total amount of G and C must also be 45% since they are always equal.
Therefore, the amount of G in this DNA would be 45% - 22.5% (since G and C are equal) = 22.5%
Hence, the correct answer is option B, 27.5%.
Equal volumes of three acid solutions of pH 3, 4 and 5 are mixed in a vessel. What will be the H+ ion concentration in the mixture?- a)1.11 x 10-4 M
- b)3.7 x 10-4 M
- c)1.11 x 10-3 M
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Hridoy Mehta answered |
∴ [H^+] after mixing
= 10^−3 x V/3V + 10^−4 x V/3V + 10^−5 x V/3V = 1.11 x 10^−3/3
= 3.7 x10^−4
The half-life of radioactive element is 600 yr. The fraction of sample that would remain after 3000 yr is- a)1/2
- b)1/16
- c)1/8
- d)1/32
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Devika Singh answered |
To find: Fraction of sample that would remain after 3000 yr
Solution:
We know that the half-life of a radioactive substance is the time taken for the substance to decay to half of its initial value.
Let the initial amount of the substance be 1 unit.
After 1 half-life, the amount of substance remaining = 1/2 unit
After 2 half-lives, the amount of substance remaining = (1/2) * (1/2) = 1/4 unit
After 3 half-lives, the amount of substance remaining = (1/2) * (1/2) * (1/2) = 1/8 unit
After 4 half-lives, the amount of substance remaining = (1/2) * (1/2) * (1/2) * (1/2) = 1/16 unit
Therefore, after 5 half-lives (i.e. 3000 years in this case), the amount of substance remaining = (1/2)^5 = 1/32 unit.
Hence, the correct answer is option D, i.e. 1/32.
HIV is a member of a group of viruses called- a)bacteriophages
- b)geminiviruses
- c)lysogenic viruses
- d)retroviruses
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Anshika Sharmaa answered |
The headquarters of UNESCO is at- a)Rome
- b)Geneva
- c)Paris
- d)New York
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Tides are comhlied and they vary from place to place because of- a)the movemeni of moon in relation to earth
- b)unevem distribution of water over the globe
- c)irregularities in the configuration of oceans
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Raza Great answered |
A solid sphere rolls without slipping on the roof. The ratio of its rotational kinetic energy and its total kinetic energy is- a)2/S
- b)4/5
- c)2/7
- d)3/7
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Gopal Mehra answered |
When a solid sphere rolls without slipping on a surface, its total kinetic energy is given by the sum of its translational kinetic energy and rotational kinetic energy.
Let the mass of the sphere be m, radius be R and velocity be v.
Translational kinetic energy = (1/2)mv^2
Rotational kinetic energy = (1/2)Iω^2, where I is the moment of inertia of the sphere and ω is the angular velocity of the sphere.
For a solid sphere, moment of inertia I = (2/5)mr^2, where r is the radius of the sphere.
Since the sphere is rolling without slipping, its translational velocity v is related to its angular velocity ω as v = ωR.
Therefore, the total kinetic energy of the rolling sphere is given by:
K = (1/2)mv^2 + (1/2)Iω^2
= (1/2)mv^2 + (1/2)(2/5)mr^2(ω/R)^2
= (1/2)mv^2 + (1/5)mv^2
= (7/10)mv^2
The ratio of rotational kinetic energy to total kinetic energy is given by:
(rotational kinetic energy) / (total kinetic energy)
= [(1/2)Iω^2] / [(1/2)mv^2 + (1/2)Iω^2]
= [(1/2)(2/5)mr^2(ω/R)^2] / [(1/2)mv^2 + (1/2)(2/5)mr^2(ω/R)^2]
= (2/5)(ω/R)^2 / [v^2 + (2/5)(ω/R)^2]
= (2/5)(ω/Rv)^2 / [1 + (2/5)(ω/Rv)^2]
Substituting ω = v/R, we get:
(rotational kinetic energy) / (total kinetic energy)
= (2/5)(v/Rv)^2 / [1 + (2/5)(v/Rv)^2]
= (2/5)(1/1)^2 / [1 + (2/5)(1/1)^2]
= 2/7
Therefore, the correct option is (C) 2/7.
The principle that distinguishes Jainism from Buddhism is the- a)practice of the eight-fold path
- b)rejection of the infallibility of the Vedas
- c)attribution of a i.oul to all beings and things
- d)belief in rebirth
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Kirti Khanna answered |
Jainism and Buddhism are two ancient religions that originated in India around the 6th century BCE. While they share some similarities, such as their emphasis on non-violence and the rejection of the caste system, there is a key principle that sets Jainism apart from Buddhism. This principle is the attribution of a soul, known as a jiva, to all beings and things.
Jainism and the Concept of Jiva
In Jainism, the concept of jiva is central to understanding the nature of existence. According to Jain philosophy, all living beings possess a soul or jiva, which is eternal and unchanging. This soul is believed to be distinct from the body and mind and is responsible for the individual's consciousness and experiences.
Belief in the Eternal Nature of the Soul
Jainism teaches that the soul is eternal and goes through a cycle of birth and death known as samsara. This belief in the transmigration of the soul is similar to the concept of rebirth in Buddhism. However, what sets Jainism apart is its assertion that not only humans and animals but also plants, rocks, and even inanimate objects possess a soul.
The Doctrine of Ahimsa
The concept of jiva is closely tied to the Jain principle of ahimsa, which means non-violence or non-harming. Jains believe that every living being, regardless of its form, possesses a soul and therefore deserves respect and compassion. This belief in the sanctity of all life forms has led Jains to adopt strict dietary and lifestyle practices, such as vegetarianism and avoiding harm to even the smallest organisms.
Buddhism and the Absence of a Permanent Soul
In contrast, Buddhism does not subscribe to the belief in a permanent, unchanging soul. According to Buddhist teachings, the self is an illusion or a construct of the mind, and there is no enduring entity that can be identified as a soul. Buddhism emphasizes the impermanence and interdependence of all phenomena, including sentient beings.
The Eightfold Path and the Rejection of the Vedas
Options a) and b) mentioned in the question, the practice of the eightfold path and the rejection of the infallibility of the Vedas, are not distinguishing principles of Jainism from Buddhism. The eightfold path is a fundamental practice in Buddhism that leads to the cessation of suffering, while the Vedas are ancient Hindu scriptures that both Jainism and Buddhism reject as authoritative texts.
In Conclusion
The key principle that distinguishes Jainism from Buddhism is the attribution of a soul to all beings and things. Jainism asserts that every living being, as well as non-living entities, possess an eternal and unchanging soul, known as jiva. This belief in the existence of a soul is central to Jain philosophy and shapes their understanding of the nature of existence and the practice of non-violence towards all forms of life. In contrast, Buddhism does not posit the existence of a permanent soul and instead focuses on the impermanence and interdependence of all phenomena.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Photon and electron are given same energy (10-20 J) Wavelength associated with photon statement will he and electron are λp and λe the correct
- A:
λp > λe
- B:
λp < λe
- C:
λp = λe
- D:
λe / λp = c
The answer is a.
Photon and electron are given same energy (10-20 J) Wavelength associated with photon statement will he and electron are λp and λe the correct
λp > λe
λp < λe
λp = λe
λe / λp = c

|
Supriya Senapati answered |
A charged particle travels along a straight line with a speed v in a region where both electric field E and magnetic field B are present. it follows that- a)|E| = v |B| and the two fields are parallel
- b)|E| = v |B| and the two fields are perpendicular
- c)|B| = v |E| and the two fields are parallel
- d)|B| = v |E| and the two fields are perpendicular
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
A. R. answered |
A non-conducting body floats in a liquid at 20°C with 2/3 of its volume immersed in the liquid. When liquid temperature is increased
to 100°C, 3 of body’s volume is immersed in the liquid. Then the coefficient of real expansion of the liquid is (neglecting the expansion of container of the liquid)- a)15.6 x 10-4°C-1
- b)156 x 10-4°C-1
- c) 1.56 x 10-4°C-1
- d)0.156 x 10-4°C-1
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
to 100°C, 3 of body’s volume is immersed in the liquid. Then the coefficient of real expansion of the liquid is (neglecting the expansion of container of the liquid)

|
Shalini Saha answered |
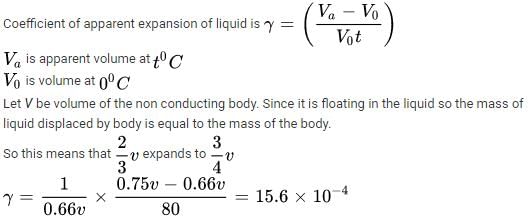
A solution of urea (mol. mass 56 g mol-l) boils at 100.18°C at the atmospheric pressureIf Kf and Kb for water are 1.86 and 0.52 K kg mol-1 respectively, the above solution will freeze at- a)-6.54°C
- b)654°C
- c)0.654°C
- d)-0.654T
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Yash Bhardwaj answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A mixture containing DNA fragments, a, b, c and d, with molecular weights of a b c. a > b and d > c, was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis. The positions of these fragments from cathode to anode sides of the gel would be
- A:
b, a, c, d
- B:
a, b, c, d
- C:
c, b, a, d
- D:
b, a. d, c
The answer is a.
A mixture containing DNA fragments, a, b, c and d, with molecular weights of a b c. a > b and d > c, was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis. The positions of these fragments from cathode to anode sides of the gel would be
b, a, c, d
a, b, c, d
c, b, a, d
b, a. d, c

|
Aastha Agarwal answered |
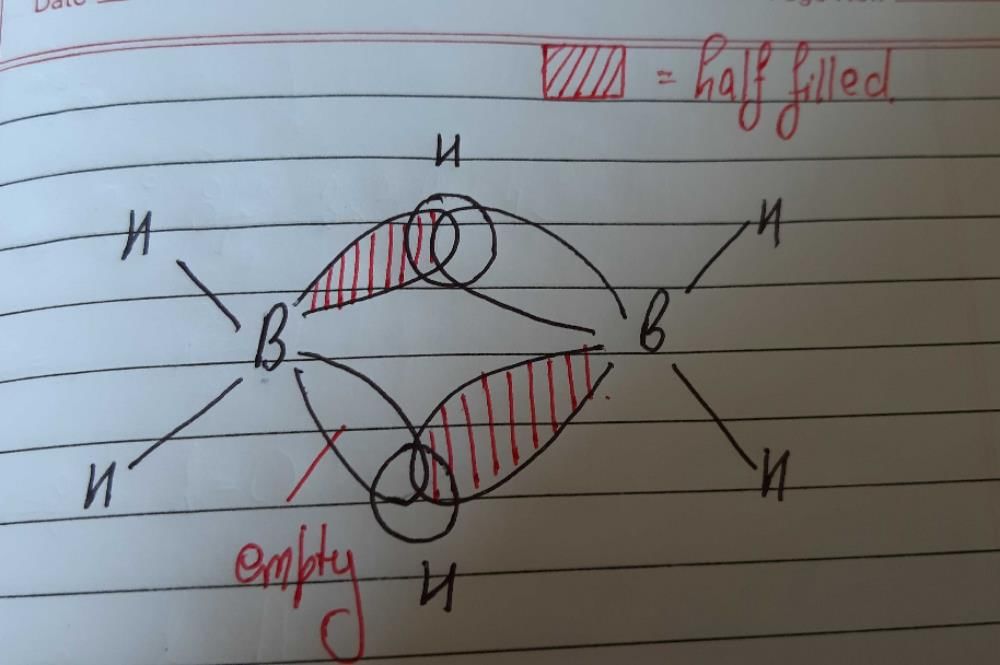
In the equation.

Identify the metal M.- a)Copper
- b)Iron
- c)Gold
- d)Zinc
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the metal M.

|
Aiims New Delhi answered |
A simple harmonic oscillator consists of a panicle of mass in and an ideal spring with spring constant k. The particle oscillates with a time period T. The spring is cut into two equal parts. If one part oscillates with the same particle, the time period will be- a)2T
- b)√2T
- c)T / √2
- d)T/2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poulomi Choudhury answered |
Concept:
- The time period of a simple harmonic oscillator is given by T = 2π√(m/k), where m is the mass of the particle and k is the spring constant.
When the spring is cut into two equal parts:
- When the spring is cut into two equal parts, the spring constant of each part becomes k/2.
- Due to conservation of energy, the time period of oscillation remains the same.
Calculation:
- For the original system with the full spring, T = 2π√(m/k).
- For each part of the spring after cutting, T' = 2π√(m/(k/2)) = 2π√(2m/k).
- Therefore, the new time period T' = T/√2.
Conclusion:
- When one part of the spring oscillates with the same particle, the time period of oscillation becomes T/√2.
- Hence, the correct answer is option 'C' - T/√2.
The coefficient of viscosity for hot air is- a)greater than the coefficient of viscosity for cold air
- b)smaller than the coefficient of viscosity for cold air
- c)same as the coefficient of viscosity for cold air
- d)increase ur decrease depending on the external pressure
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vanya Singh answered |
A transformer of 100% efficiency has 200 turns in the primary coil and 40000 rums in secondary coil. It is connected to a 220 V main supply and secondary feeds to a 100 kfl resistance. The potential difference per turn is- a)1.1 V
- b)25 V
- c)18 V
- d)11 V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anshika Shah answered |
Vp = Vs/Ns
Where:
Vp = potential difference per turn in the primary coil
Vs = potential difference across the secondary coil
Ns = number of turns in the secondary coil
Given data:
Number of turns in the primary coil (Np) = 200
Number of turns in the secondary coil (Ns) = 40000
Potential difference across the secondary coil (Vs) = 220 V
Resistance in the secondary coil (Rs) = 100 kΩ = 100000 Ω
Let's calculate the potential difference per turn:
Step 1: Calculate the current flowing through the secondary coil using Ohm's law.
Is = Vs / Rs
= 220 V / 100000 Ω
= 0.0022 A
Step 2: Calculate the current flowing through the primary coil using the transformer equation.
Is / Ip = Ns / Np
Ip = (Ns / Np) * Is
= (40000 / 200) * 0.0022 A
= 0.44 A
Step 3: Calculate the potential difference per turn in the primary coil.
Vp = Ip * Rp
= 0.44 A * 220 V
= 96.8 V
Since we have 200 turns in the primary coil, the potential difference per turn is:
Vp / Np = 96.8 V / 200
= 0.484 V
Therefore, the potential difference per turn in the primary coil is approximately 0.484 V. None of the given options match this value, so the correct answer is not provided in the options given.
Note: The given answer in option 'A' is incorrect.
A thin convex lens of refractive index 1.5 has 20 cm focal length in air. If the lens is completely immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.6, us focal length will be- a)– 160 cm,
- b)– 100 cm
- c)+ 10 cm
- d)+ 100 cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Harshitha Basak answered |
In air:
$n_1=1$ (air)
$n_2=1.5$ (lens)
$f=20\text{ cm}$
$\frac{1}{20}=(1.5-1)\left(\frac{1}{R_1}-\frac{1}{R_2}\right)$
Simplifying:
$R_1=R_2=10\text{ cm}$ (since it's a thin lens, the radii of curvature are the same and equal to half the focal length)
When the lens is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.6, we have:
$n_1=1.6$ (liquid)
$n_2=1.5$ (lens)
$f'=?$
$\frac{1}{f'}=(1.5-1.6)\left(\frac{1}{10}-\frac{1}{10}\right)$
Simplifying:
$\frac{1}{f'}=0.1\times0$
Since the term on the right-hand side is zero, we can't solve for $f'$ using this formula. However, we know that when a lens is immersed in a medium of higher refractive index, its focal length decreases. Therefore, we can conclude that the focal length of the lens will be less than 20 cm when it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.6.
Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?- a)Baz Bahadur ↔ Malwa
- b)Sultan Muzaffar Shah↔Gujarat
- c)Yusuf Adil Shah↔Ahmednagar
- d)Qutub Shah ↔Golkunda
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
These questions consist of two statements each printed as assertion and reason. Whole answering these questions you are required to choose any one of of following responses.
Assertion : If the bob of a simple pendulum is kept in a horizontal electric field, its period of oscillation will remain same.
Reason : If bob is charged and kept in horizontal electric field, then the time period will be decreased.- a)if both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If the Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not correct explanation of Assert ion
- c)If Assertion is true but, Reason is false
- d)If Assertion is false but, Reason Is true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : If the bob of a simple pendulum is kept in a horizontal electric field, its period of oscillation will remain same.
Reason : If bob is charged and kept in horizontal electric field, then the time period will be decreased.

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
These questions consist of two statements each printed as assertion and reason. Whole answering these questions you are required to choose any one of of following responses.
Assertion : Waxy and earth coating on plant parts reduce the transpiration.
Reason : These adaptation are found in xerophytes.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and reason is correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion : Waxy and earth coating on plant parts reduce the transpiration.
Reason : These adaptation are found in xerophytes.
|
|
Harini Subi answered |
So in order to avoid high rates of transpiration through which most of the water is lost, they possess waxy coating on their leaves.
Therefore both the assertion and reason is correct and the reason provides the right explaination.
An artificial satellite moving in a circular orbit around the earth has a total (kinetic + potential) energy E0. Its potential energy is- a)-E0
- b)1.5 E0
- c)2E0
- d)E0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Preethi Saha answered |
When an artificial satellite moves in a circular orbit around the earth, it experiences a gravitational force towards the center of the earth, which provides the necessary centripetal force to keep the satellite in the circular orbit.
The total energy of the satellite is the sum of its kinetic energy and potential energy.
1. Kinetic Energy of the Satellite:
The kinetic energy of the satellite is given by the formula:
KE = (1/2)mv^2
where m is the mass of the satellite and v is its velocity.
In a circular orbit, the velocity of the satellite is given by:
v = √(GM/r)
where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the earth, and r is the radius of the orbit.
Substituting the value of v in the formula for KE, we get:
KE = (1/2)m(GM/r)
KE = (1/2)(GMm/r)
2. Potential Energy of the Satellite:
The potential energy of the satellite is given by the formula:
PE = -GMm/r
where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the earth, m is the mass of the satellite, and r is the radius of the orbit.
3. Total Energy of the Satellite:
The total energy of the satellite is the sum of its kinetic energy and potential energy:
E0 = KE + PE
E0 = (1/2)(GMm/r) - (GMm/r)
E0 = -(1/2)(GMm/r)
Therefore, the potential energy of the satellite is given by:
PE = -E0/2
PE = -1/2(KE)
PE = -1/2(E0 - PE)
PE = -1/2E0 + 1/2PE
2PE = -E0
PE = -E0/2
Hence, option C is the correct answer: 2E0.
What kV potential is to be applied on X-ray tube so that minimum wavelength of emitted X-rays may be 1 A (h = 6.6 x 10-34J-5)- a)12.42 kV
- b)12.84 kV
- c)11.98 kV
- d)10.78 kV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
वर्तिका answered |
V= 12375/1=12375V
12.375 kV is nearly equals to 12.42 kV
The moment of inertia of a circular loop of radius R. at a distance of R / 2 around a rotating axis parallel to horizontal diameter of loop is- a)MR2
- b)1/2 MR2
- c)2MR2
- d)3/4 MR2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Shalini Saha answered |
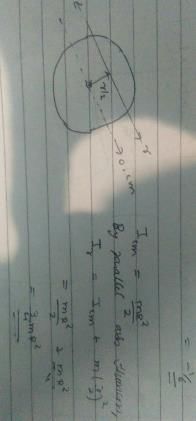
Chapter doubts & questions for 2012 - AIIMS Mock Tests & Previous Year Question Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.

Contact Support
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
Forgot Password
within 7 days!