All questions of Water and Its Solutions for Grade 9 Exam
The five kingdom classification was proposed by
a)Hutchinson
b)Bentham and Hooker
c)Engler and Prantl
d)WhittakerCorrect answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)Hutchinson
b)Bentham and Hooker
c)Engler and Prantl
d)Whittaker
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
The first major break from the Linnean model came from Thomas Whittaker. In 1969 Whittaker proposed a "five kingdom" system in which three kingdoms were added to the animals and plants: Monera (bacteria), Protista, and Fungi.
Classification given by Bentham and Hooker is- a)artificial
- b)natural
- c)phylogenetic
- d)numerical.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Classification given by Bentham and Hooker is
a)
artificial
b)
natural
c)
phylogenetic
d)
numerical.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Classification given by Bentham and Hooker is Natural System. Monocots were placed after dicots, closely related families were seperated, gymnosperms were placed between dicots and monocots.
Identify the virus in figure given below
- a)HIV
- b)Retrovirus
- c)Bacteriophage
- d)TMV
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the virus in figure given below
a)
HIV
b)
Retrovirus
c)
Bacteriophage
d)
TMV

|
Sarthak Verma answered |
A bacteriophage is a type of virus that infects bacteria. In fact, the word "bacteriophage" literally means "bacteria eater," because bacteriophages destroy their host cells. All bacteriophages are composed of a nucleic acid molecule that is surrounded by a protein structure.
Identify from the following, the only taxonomic category that has a real existence.- a)Phylum
- b)Species
- c)Genus
- d)Kingdom
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify from the following, the only taxonomic category that has a real existence.
a)
Phylum
b)
Species
c)
Genus
d)
Kingdom
|
|
Mrinalini Basak answered |
Explanation:
Archaebacteria are microorganisms that belong to the domain Archaea. They are prokaryotic organisms, meaning they lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles that are common in eukaryotic cells. Archaebacteria are known to survive in extreme environmental conditions that would be lethal for most other organisms. This is due to several factors, but the most important one is their rigid cell wall.
Rigid Cell Wall:
Archaebacteria have a unique cell wall composition that is different from that found in other bacteria. Their cell walls are made up of a complex polysaccharide called pseudomurein, which is more resistant to heat, acids, and other harsh environmental conditions than the peptidoglycan found in other bacterial cell walls. This rigid cell wall provides the archaebacteria with a protective barrier that helps them to withstand extreme temperatures, pH levels, and pressures.
Other Factors:
Apart from the rigid cell wall, there are several other factors that contribute to the ability of archaebacteria to survive in extreme environments. These include:
1. Unique metabolic pathways: Archaebacteria have evolved unique metabolic pathways that allow them to extract energy and nutrients from the environment in which they live. These pathways allow them to survive in environments that would be toxic to other organisms.
2. Resistance to radiation: Some archaebacteria are known to be resistant to high levels of radiation, which allows them to survive in environments such as hot springs and deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
3. Adaptability: Archaebacteria are highly adaptable and can adjust their metabolism and other cellular processes in response to changes in their environment. This allows them to survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, archaebacteria can survive in extreme conditions because of their unique cell wall composition, as well as other factors such as their metabolic pathways, radiation resistance, and adaptability. Their ability to survive in extreme environments makes them important models for studying the origin and evolution of life on Earth.
Archaebacteria are microorganisms that belong to the domain Archaea. They are prokaryotic organisms, meaning they lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles that are common in eukaryotic cells. Archaebacteria are known to survive in extreme environmental conditions that would be lethal for most other organisms. This is due to several factors, but the most important one is their rigid cell wall.
Rigid Cell Wall:
Archaebacteria have a unique cell wall composition that is different from that found in other bacteria. Their cell walls are made up of a complex polysaccharide called pseudomurein, which is more resistant to heat, acids, and other harsh environmental conditions than the peptidoglycan found in other bacterial cell walls. This rigid cell wall provides the archaebacteria with a protective barrier that helps them to withstand extreme temperatures, pH levels, and pressures.
Other Factors:
Apart from the rigid cell wall, there are several other factors that contribute to the ability of archaebacteria to survive in extreme environments. These include:
1. Unique metabolic pathways: Archaebacteria have evolved unique metabolic pathways that allow them to extract energy and nutrients from the environment in which they live. These pathways allow them to survive in environments that would be toxic to other organisms.
2. Resistance to radiation: Some archaebacteria are known to be resistant to high levels of radiation, which allows them to survive in environments such as hot springs and deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
3. Adaptability: Archaebacteria are highly adaptable and can adjust their metabolism and other cellular processes in response to changes in their environment. This allows them to survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, archaebacteria can survive in extreme conditions because of their unique cell wall composition, as well as other factors such as their metabolic pathways, radiation resistance, and adaptability. Their ability to survive in extreme environments makes them important models for studying the origin and evolution of life on Earth.
Which is the possible region of respiration in bacteria- a)Mitochondria
- b)Cell wall
- c)Nucleoid
- d)Mesosome
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the possible region of respiration in bacteria
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Cell wall
c)
Nucleoid
d)
Mesosome
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Mesosomes or chondrioids are folded invaginations in the plasma membrane of bacteria that are produced by the chemical fixation techniques used to prepare samples for electron microscopy.
Bacteria have a cell wall, a simple nuclear body without a nuclear membrane, ribosomes and mesosomes in the cytoplasm, and sometimes granules of reserve material, but no endoplasmic reticulum or organelles such as mitochondria or chloroplasts.
In five kingdom of classification, Whittaker assigned eukaryotes to- a)Only two of five kingdoms
- b)All five kingdoms
- c)Only three of five kingdoms
- d)Only four of five kingdoms
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In five kingdom of classification, Whittaker assigned eukaryotes to
a)
Only two of five kingdoms
b)
All five kingdoms
c)
Only three of five kingdoms
d)
Only four of five kingdoms
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
- In Whittaker’s five kingdom of classification, kingdom protista, kingdom fungi, kingdom plantae and kingdom animalia are eukaryotic organisms.
- The kingdom monera includes prokaryotic organisms.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:All prokaryotic, unicellular organisms are included under kingdomA:FungiB:MoneraC:ProtistaD:AnimaliaThe answer is b.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
- Monera is a kingdom that contains unicellular organisms with a prokaryotic (is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane- bound nucleus, mitocondria, or any other membrane- bound organelle.) cell organization, like bacteria.
- They are single- celled organisms with no true nuclear membrane. The taxon Monera was first proposed as a phylum by Ernst Haeckel in 1866.
Which one is important in nutrient recycle and act as decomposer and mineralisers of the biosphere?
- a)Bacteria:- Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- ascomycetes, Phycomycetes
- b)Bacteria:- Photosynthetic autotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- Basidiomycetes, deuteromycetes
- c)Bacteria:- Heterotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- Phycomycetes, Basidiomycetes
- d)Bacteria:- Heterotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- ascomycetes, deuteromycetes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is important in nutrient recycle and act as decomposer and mineralisers of the biosphere?
a)
Bacteria:- Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- ascomycetes, Phycomycetes
b)
Bacteria:- Photosynthetic autotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- Basidiomycetes, deuteromycetes
c)
Bacteria:- Heterotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- Phycomycetes, Basidiomycetes
d)
Bacteria:- Heterotrophic bacteria
Fungi:- ascomycetes, deuteromycetes
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Heterotrophic bacteria are most abundant in nature. The majority are important decomposers.
Commonly known as sac-fungi, the ascomycetes are mostly multicellular, e.g., Penicillium, or rarelyunicellular, e.g., yeast (Saccharomyces). They are saprophytic, decomposers, parasitic or coprophilous (growing on dung).
Some members of deuteromycetes are saprophytes or parasites while a large number of them are decomposers of litter and help in mineral cycling. Some examples are Alternaria, Colletotrichum and Trichoderma.
In which class of fungi the mushroom belongs to?
- a)Ascomycetes
- b)Basidiomycetes
- c)Deuteromycetes
- d)Phycomycetes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which class of fungi the mushroom belongs to?
a)
Ascomycetes
b)
Basidiomycetes
c)
Deuteromycetes
d)
Phycomycetes
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
- Mushrooms are the commonly known form of Basidiomycetes, called bracket fungi or puffballs.
- They grow in soil, on logs and tree stumps and in living plant bodies as parasites, e.g., rusts and smuts.

Hence, the correct option is B
NCERT Reference: Topic Basidiomycetes” of chapter "Biological Classification" of NCERT.
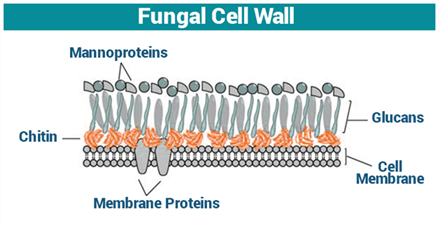
The cell wall of fungi consist of- a)Cellulose
- b)Chitin
- c)Glycopeptides
- d)Starch
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell wall of fungi consist of
a)
Cellulose
b)
Chitin
c)
Glycopeptides
d)
Starch
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- Chitin is a long-chain N-acetylglucosamine polymer and is a glucose derivative.
- This polysaccharide is a primary component of cell walls in the fungi, arthropod exoskeletons such as crustaceans and insects, mollusc's radula, cephalopod beaks, and fish.
- The cell wall of plants are made up of cellulose.
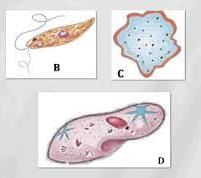
The asexual reproduction in fungi takes place by- a)endospore
- b)gametangia
- c)exospores
- d)conidiospore
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The asexual reproduction in fungi takes place by
a)
endospore
b)
gametangia
c)
exospores
d)
conidiospore
|
|
Prisha Bajaj answered |
Asexual Reproduction in Fungi by Conidiophores:
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which offspring arise from a single organism, and inherit the genes of that parent only. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction in fungi takes place through conidiophores.
Conidiophores:
Conidiophores are specialized structures that produce conidia or conidiospores. These are asexually produced spores that develop on the surface of the conidiophore. Conidiophores are produced by many different types of fungi, including both molds and yeasts.
How Conidiophores work:
Conidiophores are produced by the mycelium of the fungus. They are typically found in clusters, and can grow to be several millimeters in length. The conidiophore is composed of several cells, including a basal cell, a stalk cell, and a terminal cell. The terminal cell is where the conidia are produced.
The conidia are formed by a process called conidiation. This process involves the development of a small bud on the surface of the terminal cell. As the bud grows, it becomes surrounded by a protective layer of cells, which eventually break apart to release the conidiospore.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction:
Asexual reproduction has several advantages for fungi. First, it allows for rapid reproduction, since no mating is required. This is particularly important in environments where conditions are favorable for growth, but may not be stable over a long period of time.
Second, asexual reproduction allows for the production of large numbers of offspring that are genetically identical to the parent. This can be advantageous in environments where the parent organism is well adapted to the local conditions, since the offspring will also be well adapted.
Third, asexual reproduction allows for the spread of fungi over long distances, since the conidia can be carried by wind or other means.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the asexual reproduction in fungi takes place by conidiophores. These specialized structures produce conidia or conidiospores, which are asexually produced spores that develop on the surface of the conidiophore. This type of reproduction has several advantages for fungi, including rapid reproduction, large numbers of offspring, and the ability to spread over long distances.
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which offspring arise from a single organism, and inherit the genes of that parent only. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction in fungi takes place through conidiophores.
Conidiophores:
Conidiophores are specialized structures that produce conidia or conidiospores. These are asexually produced spores that develop on the surface of the conidiophore. Conidiophores are produced by many different types of fungi, including both molds and yeasts.
How Conidiophores work:
Conidiophores are produced by the mycelium of the fungus. They are typically found in clusters, and can grow to be several millimeters in length. The conidiophore is composed of several cells, including a basal cell, a stalk cell, and a terminal cell. The terminal cell is where the conidia are produced.
The conidia are formed by a process called conidiation. This process involves the development of a small bud on the surface of the terminal cell. As the bud grows, it becomes surrounded by a protective layer of cells, which eventually break apart to release the conidiospore.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction:
Asexual reproduction has several advantages for fungi. First, it allows for rapid reproduction, since no mating is required. This is particularly important in environments where conditions are favorable for growth, but may not be stable over a long period of time.
Second, asexual reproduction allows for the production of large numbers of offspring that are genetically identical to the parent. This can be advantageous in environments where the parent organism is well adapted to the local conditions, since the offspring will also be well adapted.
Third, asexual reproduction allows for the spread of fungi over long distances, since the conidia can be carried by wind or other means.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the asexual reproduction in fungi takes place by conidiophores. These specialized structures produce conidia or conidiospores, which are asexually produced spores that develop on the surface of the conidiophore. This type of reproduction has several advantages for fungi, including rapid reproduction, large numbers of offspring, and the ability to spread over long distances.
Classification based on comparative cytological studies, number of chromosome and behaviour of chromosome is called- a)Numerical taxonomy
- b)Cytotaxonomy
- c)Chemotaxonomy
- d)Artificial taxonomy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Classification based on comparative cytological studies, number of chromosome and behaviour of chromosome is called
a)
Numerical taxonomy
b)
Cytotaxonomy
c)
Chemotaxonomy
d)
Artificial taxonomy
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Cytotaxonomy is the classification on the basis of comparative cytological studies, number of chromosomes and behavior of chromosomes.
Which system of classification was developed during Linnaeus time?- a)Five kingdom of classification
- b)Three kingdom of classification
- c)Four kingdom of classificaition
- d)Two kingdom of classification
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which system of classification was developed during Linnaeus time?
a)
Five kingdom of classification
b)
Three kingdom of classification
c)
Four kingdom of classificaition
d)
Two kingdom of classification

|
Dipika Das answered |
In Linnaeus' time a TwoKingdomsystem of classification with Plantaeand Animaliakingdoms was developed that included all plants and animals respectively. This system was used till very recently.
The primitive prokaryotes responsible for the production of biogas from the dung of ruminant animals, include the - a)thermoacidophiles
- b)methanogens
- c)eubacteria
- d)halophiles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The primitive prokaryotes responsible for the production of biogas from the dung of ruminant animals, include the
a)
thermoacidophiles
b)
methanogens
c)
eubacteria
d)
halophiles
|
|
Mulinti Omkr answered |
Thermoacidophiles are the bacteria that survives in hot springs because of branched chain lipids in the cell membranes
the primitive prokaryotes responsible for the production of biogas from the dung of ruminant animals include the methanogens
halophiles are the bacteria that can live in the saline habitats
the primitive prokaryotes responsible for the production of biogas from the dung of ruminant animals include the methanogens
halophiles are the bacteria that can live in the saline habitats
Arranging organism on the basis of their shared similar or derived characters that differ from ancestral character is calleda)Homogramb)Monogramc)Histogramd)CladogramCorrect answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Arranging organisms on the basis of their shared similar or derived characters that differ from ancestral characters, will produce a phylogenetic tree called cladogram. Depending upon the type of system of classification, organisms are classified into two kingdoms or three kingdoms, four kingdoms, five kingdoms and now into six kingdoms.
A distinction between unicellular and multicellular is not possible in case of- a)Algae
- b)Plantae
- c)Protozoa
- d)Animalia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A distinction between unicellular and multicellular is not possible in case of
a)
Algae
b)
Plantae
c)
Protozoa
d)
Animalia
|
|
Roshni Basak answered |
Unicellular vs Multicellular
Unicellular organisms are those that are composed of a single cell, while multicellular organisms are those that are made up of multiple cells.
Algae
Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms that can be found in a variety of environments, from freshwater to saltwater. They can be either unicellular or multicellular, depending on the species.
Plantae
Plants, which belong to the kingdom Plantae, are multicellular organisms that are capable of photosynthesis. They are made up of a variety of specialized cells that work together to carry out the functions necessary for growth and survival.
Protozoa
Protozoa are a group of unicellular eukaryotic organisms that are found in a variety of environments, including water, soil, and the digestive tracts of animals. They are capable of a wide range of metabolic activities, including photosynthesis, and are an important part of many ecosystems.
Animalia
Animals, which belong to the kingdom Animalia, are multicellular organisms that are capable of movement and are characterized by a wide range of specialized tissues and organs. They are found in a variety of environments, from the depths of the ocean to the highest mountains.
Why is the answer A?
The answer to this question is A because algae can be either unicellular or multicellular. Some species of algae, such as Chlamydomonas, are unicellular, while others, such as kelp, are multicellular. Therefore, it is not possible to make a clear distinction between unicellular and multicellular when it comes to algae.
Unicellular organisms are those that are composed of a single cell, while multicellular organisms are those that are made up of multiple cells.
Algae
Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms that can be found in a variety of environments, from freshwater to saltwater. They can be either unicellular or multicellular, depending on the species.
Plantae
Plants, which belong to the kingdom Plantae, are multicellular organisms that are capable of photosynthesis. They are made up of a variety of specialized cells that work together to carry out the functions necessary for growth and survival.
Protozoa
Protozoa are a group of unicellular eukaryotic organisms that are found in a variety of environments, including water, soil, and the digestive tracts of animals. They are capable of a wide range of metabolic activities, including photosynthesis, and are an important part of many ecosystems.
Animalia
Animals, which belong to the kingdom Animalia, are multicellular organisms that are capable of movement and are characterized by a wide range of specialized tissues and organs. They are found in a variety of environments, from the depths of the ocean to the highest mountains.
Why is the answer A?
The answer to this question is A because algae can be either unicellular or multicellular. Some species of algae, such as Chlamydomonas, are unicellular, while others, such as kelp, are multicellular. Therefore, it is not possible to make a clear distinction between unicellular and multicellular when it comes to algae.
The organism that completely lack a cell wall and are smallest living cell known that can survive without oxygen is- a)Virus
- b)Bacteriophages
- c)Yeast
- d)Mycoplasma
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The organism that completely lack a cell wall and are smallest living cell known that can survive without oxygen is
a)
Virus
b)
Bacteriophages
c)
Yeast
d)
Mycoplasma

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Mycoplasma are the smallest living cells known and can survive without oxygen.
Which of the following is incorrect about Cyanobacteria?
- a)They are photoautotrophs
- b)They lack heterocysts
- c)They often form blooms in polluted water bodies
- d)They have chlorophyll similar to green plants
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is incorrect about Cyanobacteria?
a)
They are photoautotrophs
b)
They lack heterocysts
c)
They often form blooms in polluted water bodies
d)
They have chlorophyll similar to green plants

|
Lead Academy answered |
Cyanobacteria are indeed photoautotrophs, meaning they can perform photosynthesis to produce their own food using light energy.
While some Cyanobacteria lack heterocysts, others have specialized cells called heterocysts that are involved in nitrogen fixation.
Cyanobacteria often form blooms in polluted water bodies. These blooms can occur when excess nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen are present, leading to rapid Cyanobacteria growth.
Cyanobacteria have chlorophyll, like green plants, but it is not precisely the same as the chlorophyll found in green plants. They have chlorophyll a, which is similar to the chlorophyll found in higher plants, but they also have other pigments, such as phycocyanin and phycoerythrin, which can give them a bluish-green or red color.
So, the statement that Cyanobacteria have chlorophyll similar to green plants is incorrect because their chlorophyll is similar but not identical.
Which of the following pairs include photosynthetic and saprophytic organisms respectively?- a)Monocot and dicot
- b)Algae and fungi
- c)Mosses and ferns
- d)Ferns and gymnosperms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs include photosynthetic and saprophytic organisms respectively?
a)
Monocot and dicot
b)
Algae and fungi
c)
Mosses and ferns
d)
Ferns and gymnosperms

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Correct option is B.
- Photosynthetic organisms, also known as photoautotrophs, are organisms that are capable of photosynthesis. Some of these organisms include higher plants, some protists (algae and euglena), and cyanobacteria.
- A saprophytic organism is also referred to as a saprotroph, is any organism that feeds and grows on dead organisms. Such as fungi.
What is mycorrhiza?- a)A type of bacteria
- b)A fungal infection in plants
- c)A symbiotic association between fungi and plant roots
- d)A method of asexual reproduction in fungi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is mycorrhiza?
a)
A type of bacteria
b)
A fungal infection in plants
c)
A symbiotic association between fungi and plant roots
d)
A method of asexual reproduction in fungi

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Answer: C
Solution: Mycorrhiza refers to a symbiotic association between fungi and the roots of a plant. In this relationship, the fungus enhances the plant's nutrient and water absorption capabilities, while the plant provides the fungus with carbohydrates produced through photosynthesis. This mutually beneficial relationship is crucial for the health of many ecosystems, making Option C the correct answer.
Solution: Mycorrhiza refers to a symbiotic association between fungi and the roots of a plant. In this relationship, the fungus enhances the plant's nutrient and water absorption capabilities, while the plant provides the fungus with carbohydrates produced through photosynthesis. This mutually beneficial relationship is crucial for the health of many ecosystems, making Option C the correct answer.
Which one is not a member of kingdom Protista?- a)Slime molds
- b)Euglenoids
- c)Phycomycetes
- d)Protozoa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not a member of kingdom Protista?
a)
Slime molds
b)
Euglenoids
c)
Phycomycetes
d)
Protozoa

|
Rajat Roy answered |
Kingdom Protista includes unicellular, eukaryotic organisms only. Phycomycetes is a subdivision of fungus which are multicellular. Protozoa, slime molds and euglenoids are part of kingdom Protista.
Which of the following is incorrect about Cyanobacteria?- a)They are photoautotrophs.
- b)They lack heterocysts.
- c)They often form blooms in polluted water bodies.
- d)They have chlorophyll A similar to green plants.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is incorrect about Cyanobacteria?
a)
They are photoautotrophs.
b)
They lack heterocysts.
c)
They often form blooms in polluted water bodies.
d)
They have chlorophyll A similar to green plants.
|
|
Jaideep Choudhury answered |
Cyanobacteria and Heterocysts
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are a group of prokaryotic organisms that are found in various aquatic and terrestrial environments. They are photosynthetic and use sunlight to produce energy and organic compounds.
Heterocysts are specialized cells that some cyanobacteria have. They are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by the cell. Heterocysts are important for cyanobacteria because, unlike other organisms, they cannot take up nitrogen from the soil. Therefore, they need to be able to produce their own nitrogen.
The incorrect statement about cyanobacteria is option B, which states that they lack heterocysts. In fact, some cyanobacteria do have heterocysts, which are specialized cells that are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen. However, not all cyanobacteria have heterocysts.
Therefore, the correct statement about cyanobacteria is:
- They are photoautotrophs, meaning they use sunlight to produce energy and organic compounds.
- They often form blooms in polluted water bodies, which can be harmful to other organisms in the ecosystem.
- They have chlorophyll A similar to green plants, which allows them to capture sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Some cyanobacteria have heterocysts, specialized cells that are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are a group of prokaryotic organisms that are found in various aquatic and terrestrial environments. They are photosynthetic and use sunlight to produce energy and organic compounds.
Heterocysts are specialized cells that some cyanobacteria have. They are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by the cell. Heterocysts are important for cyanobacteria because, unlike other organisms, they cannot take up nitrogen from the soil. Therefore, they need to be able to produce their own nitrogen.
The incorrect statement about cyanobacteria is option B, which states that they lack heterocysts. In fact, some cyanobacteria do have heterocysts, which are specialized cells that are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen. However, not all cyanobacteria have heterocysts.
Therefore, the correct statement about cyanobacteria is:
- They are photoautotrophs, meaning they use sunlight to produce energy and organic compounds.
- They often form blooms in polluted water bodies, which can be harmful to other organisms in the ecosystem.
- They have chlorophyll A similar to green plants, which allows them to capture sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Some cyanobacteria have heterocysts, specialized cells that are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Which of the following organisms can be found in extreme saline conditions?- a)Eubacteria
- b)Archaebacteria
- c)Cyanobacteria
- d)Mycobacteria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organisms can be found in extreme saline conditions?
a)
Eubacteria
b)
Archaebacteria
c)
Cyanobacteria
d)
Mycobacteria
|
|
Megha Kulkarni answered |
Extreme Saline Conditions and Organisms
Extreme saline conditions refer to environments that have high levels of salt concentration, such as salt pans, salt lakes, and salt marshes. These environments pose significant challenges for most organisms due to the osmotic stress caused by the high salt concentration. However, some organisms have adapted to these extreme conditions and can thrive in saline habitats. One group of organisms that is well-suited to extreme saline conditions is the Archaebacteria.
Archaebacteria and Extreme Saline Conditions
Archaebacteria, also known as Archaea, are a group of single-celled microorganisms that are distinct from both eubacteria and eukaryotes. They are known for their ability to inhabit extreme environments, including high-temperature areas, acidic environments, and saline habitats. Archaebacteria that can be found in extreme saline conditions belong to the halophile category.
Adaptations of Halophilic Archaebacteria
Halophilic Archaebacteria have several adaptations that allow them to survive in extreme saline conditions:
1. Compatible Solutes: Halophiles produce or accumulate compatible solutes, such as potassium ions, amino acids, and polyols, to balance the osmotic pressure and prevent water loss. These compatible solutes help maintain the cell's internal water content and protect essential cellular structures.
2. Pigments: Some halophiles produce pigments, such as bacteriorhodopsin, which are involved in energy generation through photosynthesis or light-driven ion pumps. These pigments enable halophiles to utilize light as an additional energy source in saline environments.
3. Cell Membrane Adaptations: The cell membranes of halophiles have unique lipid compositions that help maintain membrane integrity and function in high salt concentrations. These adaptations include increased levels of branched-chain fatty acids and ether-linked lipids.
4. Enzyme Adaptations: Halophilic enzymes have adapted to function in high salt concentrations by having a higher number of acidic amino acids on their surfaces. This allows the enzymes to maintain their structural stability and activity in saline environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, among the organisms listed, only the Archaebacteria (option B) can be found in extreme saline conditions. Archaebacteria, specifically the halophilic group, have evolved various adaptations to survive in high salt environments, including the production of compatible solutes, unique cell membrane compositions, and specialized enzymes. These adaptations allow halophiles to maintain cellular homeostasis, protect essential cellular structures, and utilize light as an additional energy source.
Extreme saline conditions refer to environments that have high levels of salt concentration, such as salt pans, salt lakes, and salt marshes. These environments pose significant challenges for most organisms due to the osmotic stress caused by the high salt concentration. However, some organisms have adapted to these extreme conditions and can thrive in saline habitats. One group of organisms that is well-suited to extreme saline conditions is the Archaebacteria.
Archaebacteria and Extreme Saline Conditions
Archaebacteria, also known as Archaea, are a group of single-celled microorganisms that are distinct from both eubacteria and eukaryotes. They are known for their ability to inhabit extreme environments, including high-temperature areas, acidic environments, and saline habitats. Archaebacteria that can be found in extreme saline conditions belong to the halophile category.
Adaptations of Halophilic Archaebacteria
Halophilic Archaebacteria have several adaptations that allow them to survive in extreme saline conditions:
1. Compatible Solutes: Halophiles produce or accumulate compatible solutes, such as potassium ions, amino acids, and polyols, to balance the osmotic pressure and prevent water loss. These compatible solutes help maintain the cell's internal water content and protect essential cellular structures.
2. Pigments: Some halophiles produce pigments, such as bacteriorhodopsin, which are involved in energy generation through photosynthesis or light-driven ion pumps. These pigments enable halophiles to utilize light as an additional energy source in saline environments.
3. Cell Membrane Adaptations: The cell membranes of halophiles have unique lipid compositions that help maintain membrane integrity and function in high salt concentrations. These adaptations include increased levels of branched-chain fatty acids and ether-linked lipids.
4. Enzyme Adaptations: Halophilic enzymes have adapted to function in high salt concentrations by having a higher number of acidic amino acids on their surfaces. This allows the enzymes to maintain their structural stability and activity in saline environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, among the organisms listed, only the Archaebacteria (option B) can be found in extreme saline conditions. Archaebacteria, specifically the halophilic group, have evolved various adaptations to survive in high salt environments, including the production of compatible solutes, unique cell membrane compositions, and specialized enzymes. These adaptations allow halophiles to maintain cellular homeostasis, protect essential cellular structures, and utilize light as an additional energy source.
Who divided animals into two group based on the presence and absence of red blood cells?- a)Aristotle
- b)Whittaker
- c)Linnaeus
- d)Pasteur
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who divided animals into two group based on the presence and absence of red blood cells?
a)
Aristotle
b)
Whittaker
c)
Linnaeus
d)
Pasteur

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
Aristotle used simple morphological characters to classify plants into trees, shrubs and herbs. He also divided animals into two groups, those which had red blood and those that did not.
What is formed by slime molds under suitable conditions?- a)Mycelium
- b)Plasmodium
- c)Fruiting bodies
- d)Spores
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is formed by slime molds under suitable conditions?
a)
Mycelium
b)
Plasmodium
c)
Fruiting bodies
d)
Spores

|
Bs Academy answered |
. Under suitable conditions, they form an aggregation called plasmodium which may grow and spread over several feet. During unfavourable conditions, the plasmodium differentiates and forms fruiting bodies bearing spores at their tips. The spores possess true walls. They are extremely resistant and survive for many years, even under adverse conditions. The spores are dispersed by air currents.
A peculiar group of dual organism which are formed by an association between an alga and a fungus.- a)Mushroom
- b)Mucor
- c)Yeast
- d)Lichens
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A peculiar group of dual organism which are formed by an association between an alga and a fungus.
a)
Mushroom
b)
Mucor
c)
Yeast
d)
Lichens

|
Anand Jain answered |
Symbiotic association between an alga and a fungus is called Lichens. Algae prepare food due to presence of chlorophyll and fungus absorbs nutrients and provide protection to algae.
______of dinoflagellates have _______ flagella; one lies _________ and the other ________ in a furrow between the wall plates.- a)(1) All, 2, perpendicularly, longitudinal flagella
- b)(2) Many, 3, longitudinally, transverse flagella
- c)(3) Most, 2, londitudinally, transverse falgella
- d)4) All, 3, Transversally, longitudinal flagella
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
______of dinoflagellates have _______ flagella; one lies _________ and the other ________ in a furrow between the wall plates.
a)
(1) All, 2, perpendicularly, longitudinal flagella
b)
(2) Many, 3, longitudinally, transverse flagella
c)
(3) Most, 2, londitudinally, transverse falgella
d)
4) All, 3, Transversally, longitudinal flagella

|
Bs Academy answered |
Most of dinoflagellates have two flagella; one lies longitudinally and the other transversely in a furrow between the wall plates.
In the five-kingdom classification, _______ Kingdom has brought together Chlamydomonas, Chlorella (earlier placed in _____within Plants and both having cell walls) with Paramoecium and Amoeba (which were earlier placed in the _____kingdom which lack cell wall)
- a)Algae, Protista, monera
- b)Protista, thallophyta,animal
- c)Monera, fungi, protista
- d)Protista, thallophyta, fungi
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the five-kingdom classification, _______ Kingdom has brought together Chlamydomonas, Chlorella (earlier placed in _____within Plants and both having cell walls) with Paramoecium and Amoeba (which were earlier placed in the _____kingdom which lack cell wall)
a)
Algae, Protista, monera
b)
Protista, thallophyta,animal
c)
Monera, fungi, protista
d)
Protista, thallophyta, fungi
|
|
Naina Yadav answered |
**Explanation:**
In the five-kingdom classification system, organisms are classified into five main kingdoms based on their cellular structure, mode of nutrition, and complexity of their body organization. The five kingdoms are:
1. **Monera:** This kingdom includes prokaryotic organisms, which are single-celled and lack a true nucleus. They are further divided into bacteria and blue-green algae (cyanobacteria).
2. **Protista:** This kingdom consists of eukaryotic organisms that are mostly unicellular. They have a true nucleus and are more complex than organisms in the Monera kingdom. Protists are a diverse group that includes various types of microorganisms, such as algae, protozoa, and slime molds.
3. **Fungi:** This kingdom includes eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic and have a cell wall made of chitin. Fungi obtain nutrients by absorbing them from their surroundings. They include mushrooms, yeasts, molds, and mildews.
4. **Plantae:** This kingdom consists of multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are photosynthetic. They possess chloroplasts and cell walls made of cellulose. Plants are autotrophic and provide oxygen, food, and shelter to other organisms. They include trees, shrubs, herbs, and mosses.
5. **Animalia:** This kingdom includes multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic and lack cell walls. They have specialized tissues and organs, and most animals can move from place to place. Animals obtain their food by ingestion.
**Chlamydomonas** and **Chlorella** are both unicellular green algae. They are photosynthetic organisms that possess chloroplasts and cell walls made of cellulose. These characteristics are similar to organisms in the Plantae kingdom. However, unlike plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Therefore, they do not fit into the Plantae kingdom.
Instead, Chlamydomonas and Chlorella are classified under the Protista kingdom. Protists are a diverse group that includes various types of microorganisms, including algae. Chlamydomonas and Chlorella are examples of unicellular algae that are classified as protists. They are not considered plants because they lack the complex body organization and tissue differentiation found in true plants.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Protista.
In the five-kingdom classification system, organisms are classified into five main kingdoms based on their cellular structure, mode of nutrition, and complexity of their body organization. The five kingdoms are:
1. **Monera:** This kingdom includes prokaryotic organisms, which are single-celled and lack a true nucleus. They are further divided into bacteria and blue-green algae (cyanobacteria).
2. **Protista:** This kingdom consists of eukaryotic organisms that are mostly unicellular. They have a true nucleus and are more complex than organisms in the Monera kingdom. Protists are a diverse group that includes various types of microorganisms, such as algae, protozoa, and slime molds.
3. **Fungi:** This kingdom includes eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic and have a cell wall made of chitin. Fungi obtain nutrients by absorbing them from their surroundings. They include mushrooms, yeasts, molds, and mildews.
4. **Plantae:** This kingdom consists of multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are photosynthetic. They possess chloroplasts and cell walls made of cellulose. Plants are autotrophic and provide oxygen, food, and shelter to other organisms. They include trees, shrubs, herbs, and mosses.
5. **Animalia:** This kingdom includes multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic and lack cell walls. They have specialized tissues and organs, and most animals can move from place to place. Animals obtain their food by ingestion.
**Chlamydomonas** and **Chlorella** are both unicellular green algae. They are photosynthetic organisms that possess chloroplasts and cell walls made of cellulose. These characteristics are similar to organisms in the Plantae kingdom. However, unlike plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Therefore, they do not fit into the Plantae kingdom.
Instead, Chlamydomonas and Chlorella are classified under the Protista kingdom. Protists are a diverse group that includes various types of microorganisms, including algae. Chlamydomonas and Chlorella are examples of unicellular algae that are classified as protists. They are not considered plants because they lack the complex body organization and tissue differentiation found in true plants.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Protista.
How do two haploid hyphae of compatible mating types reproduce in some fungi?- a)They undergo direct fusion into diploid cells
- b)They form a dikaryotic stage
- c)They remain haploid indefinitely
- d)They form haploid spores immediately
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How do two haploid hyphae of compatible mating types reproduce in some fungi?
a)
They undergo direct fusion into diploid cells
b)
They form a dikaryotic stage
c)
They remain haploid indefinitely
d)
They form haploid spores immediately

|
Lead Academy answered |
When a fungus reproduces sexually, two haploid hyphae of compatible mating types come together and fuse. In some fungi the fusion of two haploid cells immediately results in diploid cells (2n). However, in other fungi (ascomycetes and basidiomycetes), an intervening dikaryotic stage (n + n, i.e., two nuclei per cell) occurs; such a condition is called a dikaryon and the phase is called dikaryophase of fungus
What are the two distinct phases in the life cycle of plants?- a)Sporophytic and Haploid
- b)Diploid and Gametophytic
- c)Haploid Sporophytic and Diploid Gametophytic
- d)Diploid Sporophytic and Haploid Gametophytic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the two distinct phases in the life cycle of plants?
a)
Sporophytic and Haploid
b)
Diploid and Gametophytic
c)
Haploid Sporophytic and Diploid Gametophytic
d)
Diploid Sporophytic and Haploid Gametophytic

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Life cycle of plants has two distinct phases – the diploid sporophytic and the haploid gametophytic – that alternate with each other. The lengths of the haploid and diploid phases, and whether these phases are free– living or dependent on others, vary among different groups in plants. This phenomenon is called alternation of generation.
Which of the following is a correct statement?- a)Mycoplasma have DNA, Ribosome and cell wall.
- b)Bacteria are exclusively heterotrophic organisms.
- c)Cyanobacteria are a group of autotrophic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera.
- d)Slime moulds are saprophytic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a correct statement?
a)
Mycoplasma have DNA, Ribosome and cell wall.
b)
Bacteria are exclusively heterotrophic organisms.
c)
Cyanobacteria are a group of autotrophic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera.
d)
Slime moulds are saprophytic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera.
|
|
Vandana Sharma answered |
Explanation:
Cyanobacteria are a group of autotrophic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are a group of photosynthetic bacteria that can produce their own food through photosynthesis. They are classified under the Kingdom Monera, which consists of prokaryotic organisms that lack a true nucleus.
Characteristics of Cyanobacteria:
- Cyanobacteria have chlorophyll and other pigments that allow them to carry out photosynthesis.
- They can be found in a wide range of environments, from freshwater to marine habitats.
- Some cyanobacteria are capable of nitrogen fixation, converting atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use.
- Cyanobacteria can form colonies or filaments, and some species can even produce toxins under certain conditions.
Importance of Cyanobacteria:
- Cyanobacteria play a crucial role in the environment as primary producers, providing food and oxygen for other organisms.
- Some cyanobacteria are used in biotechnology and research due to their ability to fix nitrogen and produce bioactive compounds.
- However, some cyanobacteria can also cause harmful algal blooms in bodies of water, posing risks to aquatic life and human health.
In conclusion, cyanobacteria are autotrophic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera, and they play important roles in various ecosystems.
Cyanobacteria are a group of autotrophic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are a group of photosynthetic bacteria that can produce their own food through photosynthesis. They are classified under the Kingdom Monera, which consists of prokaryotic organisms that lack a true nucleus.
Characteristics of Cyanobacteria:
- Cyanobacteria have chlorophyll and other pigments that allow them to carry out photosynthesis.
- They can be found in a wide range of environments, from freshwater to marine habitats.
- Some cyanobacteria are capable of nitrogen fixation, converting atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use.
- Cyanobacteria can form colonies or filaments, and some species can even produce toxins under certain conditions.
Importance of Cyanobacteria:
- Cyanobacteria play a crucial role in the environment as primary producers, providing food and oxygen for other organisms.
- Some cyanobacteria are used in biotechnology and research due to their ability to fix nitrogen and produce bioactive compounds.
- However, some cyanobacteria can also cause harmful algal blooms in bodies of water, posing risks to aquatic life and human health.
In conclusion, cyanobacteria are autotrophic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera, and they play important roles in various ecosystems.
The sex organs are______, but ___________is brought about by fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells of _________strains or genotypes. The resultant structure is dikaryotic which ultimately gives rise to________.
- a)Present, gametic contact, different, ascus.
- b)Absent, plasmogamy, different, basidium.
- c)Present, gametic copulation, different, basidium.
- d)Present, plasmogamy, different, ascus.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The sex organs are______, but ___________is brought about by fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells of _________strains or genotypes. The resultant structure is dikaryotic which ultimately gives rise to________.
a)
Present, gametic contact, different, ascus.
b)
Absent, plasmogamy, different, basidium.
c)
Present, gametic copulation, different, basidium.
d)
Present, plasmogamy, different, ascus.
|
|
Meera Dey answered |
Understanding the Concept
The question relates to the reproductive mechanisms in fungi, particularly focusing on how sexual reproduction occurs in certain fungal species.
Key Points of the Answer
- Sex Organs:
In many fungi, sex organs are absent, which sets them apart from higher organisms that have distinct male and female reproductive structures.
- Plasmogamy:
This term refers to the fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells, which is a critical step in the sexual reproduction of fungi. During this process, the cytoplasm of two parent cells merges, but their nuclei remain distinct initially.
- Different Strains or Genotypes:
The fusion occurs between cells from different strains or genotypes, which is essential for increasing genetic diversity in the resulting offspring.
- Dikaryotic Structure:
After plasmogamy, the resulting cell possesses two nuclei (one from each parent) and is termed dikaryotic. This stage is a unique characteristic of fungal sexual reproduction.
- Formation of Basidium:
Eventually, the dikaryotic structure gives rise to a basidium, which is a specialized reproductive structure found in certain fungi, notably in the class Basidiomycetes. The basidium is where karyogamy (the fusion of nuclei) occurs, leading to the production of spores.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'B': "Absent, plasmogamy, different, basidium." This highlights the unique reproductive strategies that fungi employ, distinguishing them from more familiar reproductive processes seen in higher organisms.
The question relates to the reproductive mechanisms in fungi, particularly focusing on how sexual reproduction occurs in certain fungal species.
Key Points of the Answer
- Sex Organs:
In many fungi, sex organs are absent, which sets them apart from higher organisms that have distinct male and female reproductive structures.
- Plasmogamy:
This term refers to the fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells, which is a critical step in the sexual reproduction of fungi. During this process, the cytoplasm of two parent cells merges, but their nuclei remain distinct initially.
- Different Strains or Genotypes:
The fusion occurs between cells from different strains or genotypes, which is essential for increasing genetic diversity in the resulting offspring.
- Dikaryotic Structure:
After plasmogamy, the resulting cell possesses two nuclei (one from each parent) and is termed dikaryotic. This stage is a unique characteristic of fungal sexual reproduction.
- Formation of Basidium:
Eventually, the dikaryotic structure gives rise to a basidium, which is a specialized reproductive structure found in certain fungi, notably in the class Basidiomycetes. The basidium is where karyogamy (the fusion of nuclei) occurs, leading to the production of spores.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'B': "Absent, plasmogamy, different, basidium." This highlights the unique reproductive strategies that fungi employ, distinguishing them from more familiar reproductive processes seen in higher organisms.
All prokaryotic, unicellular organisms are included under kingdom- a)Fungi
- b)Monera
- c)Protista
- d)Animalia
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
All prokaryotic, unicellular organisms are included under kingdom
a)
Fungi
b)
Monera
c)
Protista
d)
Animalia

|
Maheshwar Chawla answered |
Monera is a kingdom that contains unicellular organisms with a prokaryotic (is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle.) cell organization, like bacteria. They are single-celled organisms with no true nuclear membrane. The taxon Monera was first proposed as a phylum by Ernst Haeckel in 1866.
Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?- a)Rhizobium - Parasite in the roots of leguminous plants
- b)Mycorrhiza - Mineral uptake from soil
- c)Yeast- Production of biogas
- d)Myxomycetes - The disease ring worm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?
a)
Rhizobium - Parasite in the roots of leguminous plants
b)
Mycorrhiza - Mineral uptake from soil
c)
Yeast- Production of biogas
d)
Myxomycetes - The disease ring worm

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The correct match is:
- B: Mycorrhiza - Mineral uptake from soil
Explanation:
- Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between fungi and plant roots.
- Fungi help plants absorb essential nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen from the soil.
- In return, the fungi receive sugars and other organic compounds from the plant.
- This relationship enhances the plant's ability to uptake minerals, aiding in its growth and overall health.
- B: Mycorrhiza - Mineral uptake from soil
Explanation:
- Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between fungi and plant roots.
- Fungi help plants absorb essential nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen from the soil.
- In return, the fungi receive sugars and other organic compounds from the plant.
- This relationship enhances the plant's ability to uptake minerals, aiding in its growth and overall health.
Coenocytic hyphae are-- a) Continuous tubes filled with uninucleated cytoplasm
- b)Continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm
- c)Branched tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm
- d)Branched tubes filled with uninucleated cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Coenocytic hyphae are-
a)
Continuous tubes filled with uninucleated cytoplasm
b)
Continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm
c)
Branched tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm
d)
Branched tubes filled with uninucleated cytoplasm

|
Bs Academy answered |
Coenocytic hyphae are:
- Continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm
- Continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm
The organism that completely lack a cell wall and are smallest living cell know, can survive without oxygen is- a)Bacteriophages
- b)Yeast
- c)Mycoplasmas
- d)Virus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The organism that completely lack a cell wall and are smallest living cell know, can survive without oxygen is
a)
Bacteriophages
b)
Yeast
c)
Mycoplasmas
d)
Virus

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
Mycoplasmas are group of organism that lack cell wall and are smallest living organisms. They can survive without oxygen. Mycoplasmas are also called as PPLO (pleuro pneumonia like organism).
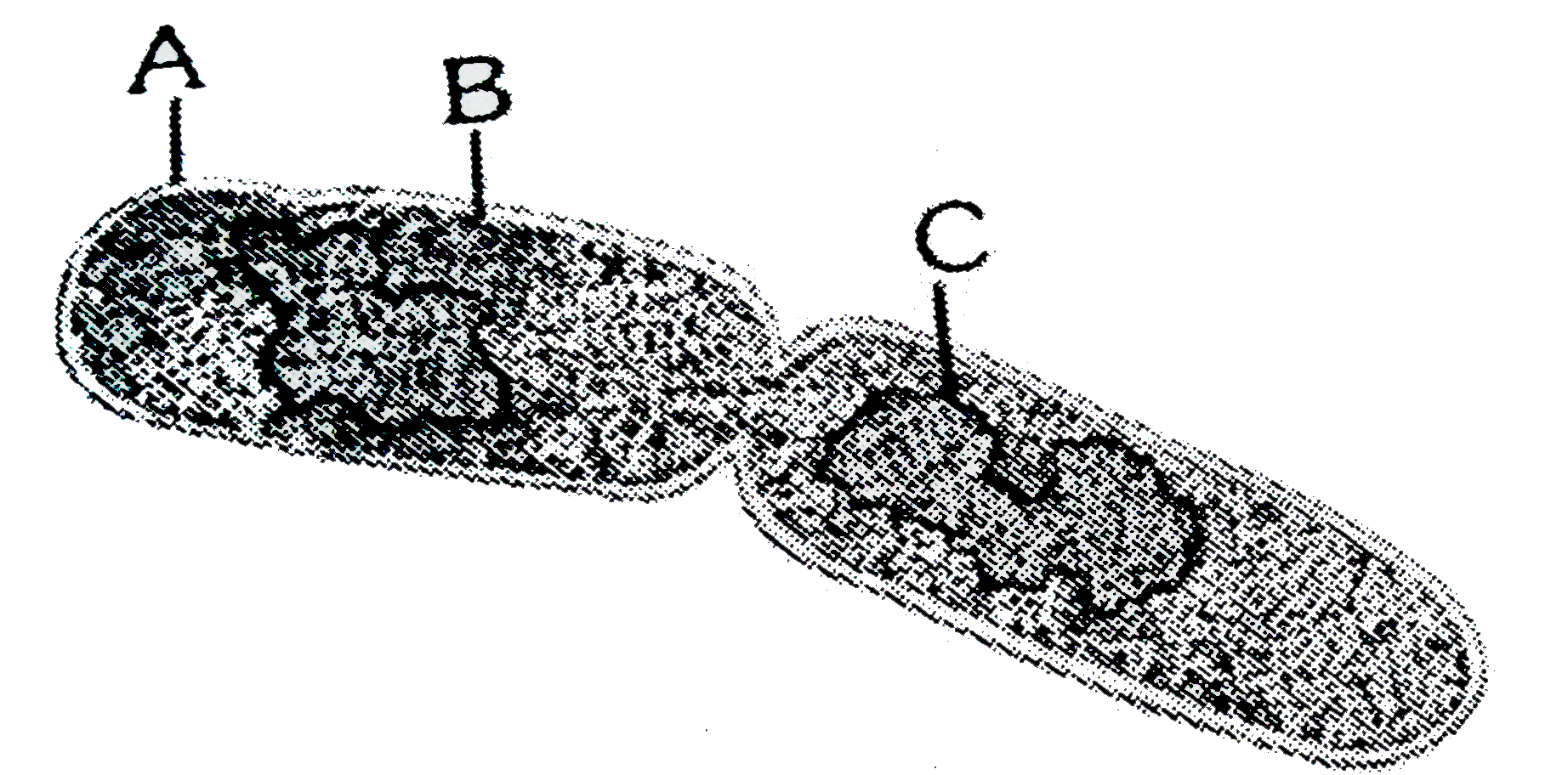
Identify the above process in bacteria and identify part A,B &C:- a)Process:- BuddingA- Cell membrane, B- cell wall, C- RNA
- b)Process:-Binary fissionA- Cell wall, Cell membrane, C- RNA
- c)Process:- FragmentationA-Plasma membrane, B- Cell wall, C- DNA
- d)Process:-Binary FissionA- Cell wall, B- Cell membrane, C- DNA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

Identify the above process in bacteria and identify part A,B &C:
a)
Process:- Budding
A- Cell membrane, B- cell wall, C- RNA
b)
Process:-Binary fission
A- Cell wall, Cell membrane, C- RNA
c)
Process:- Fragmentation
A-Plasma membrane, B- Cell wall, C- DNA
d)
Process:-Binary Fission
A- Cell wall, B- Cell membrane, C- DNA

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
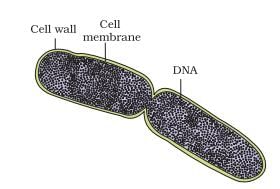
This process is binary fission.
Identify the group that is not matched correctly to all the characters shown: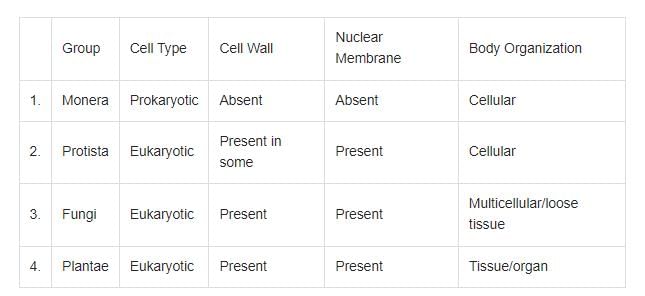
- a)1
- b)3
- c)2
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the group that is not matched correctly to all the characters shown:

a)
1
b)
3
c)
2
d)
4

|
Ambition Institute answered |
o identify the group that is not matched correctly with all the characters shown, let's analyze each group based on the provided characteristics:
- Monera
- Cell Type: Prokaryotic
- Cell Wall: Absent (This is incorrect; Monera, which includes bacteria, typically have a cell wall.)
- Nuclear Membrane: Absent (Correct; prokaryotic cells do not have a nuclear membrane.)
- Body Organization: Cellular (Correct; Monera are unicellular.)
- Protista
- Cell Type: Eukaryotic (Correct)
- Cell Wall: Present in some (Correct; some protists have a cell wall, but not all.)
- Nuclear Membrane: Present (Correct; eukaryotic cells have a nuclear membrane.)
- Body Organization: Cellular (Correct; many protists are unicellular.)
- Fungi
- Cell Type: Eukaryotic (Correct)
- Cell Wall: Present (Correct)
- Nuclear Membrane: Present (Correct)
- Body Organization: Multicellular/loose tissue (This is generally correct, but fungi are often classified as having a multicellular structure with a mycelial network or loose tissue.)
- Plantae
- Cell Type: Eukaryotic (Correct)
- Cell Wall: Present (Correct)
- Nuclear Membrane: Present (Correct)
- Body Organization: Tissue/organ (Correct; plants have a complex organization with tissues and organs.)
Conclusion: The group with a mismatch is Group 1 (Monera) because the cell wall is listed as "Absent," which is incorrect. Monera typically have a cell wall (e.g., bacteria have a peptidoglycan cell wall).
So, the answer is Group 1.
What is true for both (a) and (b)? 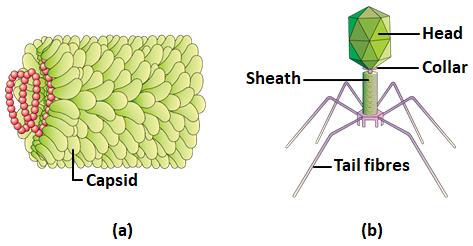
- a)RNA is the genetic material
- b)Capability to infect bacteria
- c) Being obligate endoparasites
- d)Can be killed by antibiotics
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true for both (a) and (b)?
a)
RNA is the genetic material
b)
Capability to infect bacteria
c)
Being obligate endoparasites
d)
Can be killed by antibiotics

|
Lead Academy answered |
A is TMV virus
B is Bacertiophage
Based on the provided statements, here is the correct assessment for both bacteriophages and Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV):
- RNA is the genetic material: This is true only for TMV. Bacteriophages can have either DNA as their genetic material.
- Capability to infect bacteria: This is true only for bacteriophages. TMV infects plants.
- Being obligate endoparasites: This is true for both bacteriophages and TMV. Both require a host cell to replicate.
- Can be killed by antibiotics: This is not true for either. Antibiotics target bacterial processes and do not affect viruses.
The correct statement that is true for both bacteriophages and TMV is:
- Being obligate endoparasites
Chapter doubts & questions for Water and Its Solutions - Biology 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Water and Its Solutions - Biology in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology
153 videos|283 docs|127 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup