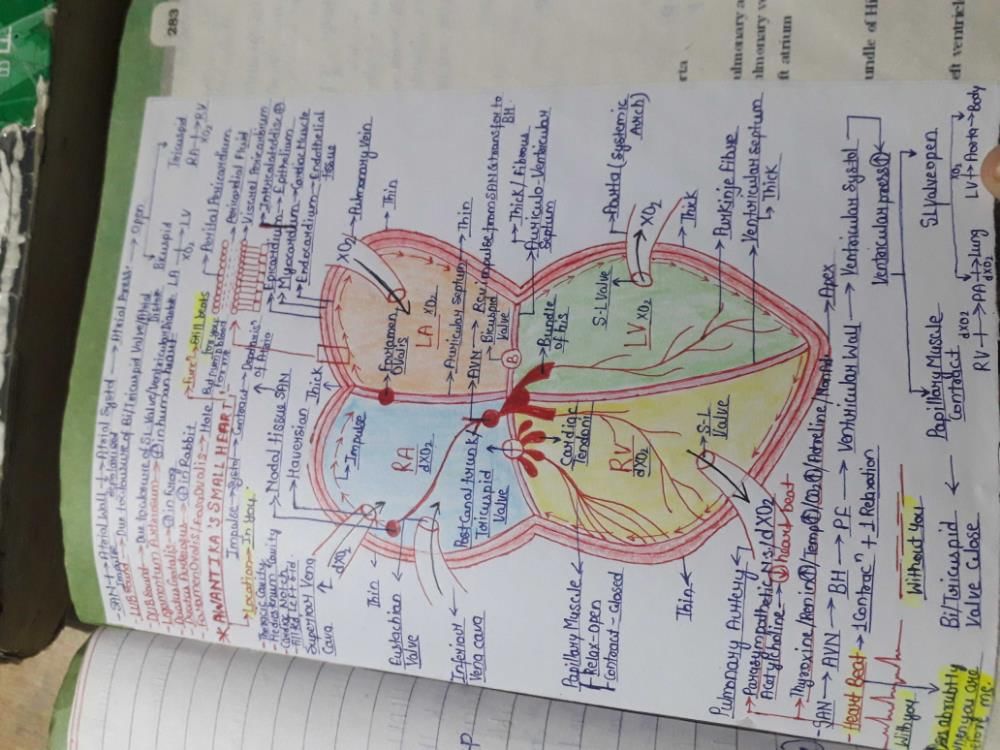
All questions of Circulatory System for Grade 9 Exam
How many contraction nodes are found in heart of Human :-- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Many
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many contraction nodes are found in heart of Human :-
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Many
d)
None
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Two contraction nodes...SAN and AVN..option B
Which of these has a closed type of circulatory system :-- a)Cockroach
- b)Fish
- c)Mollusca
- d)Scorpion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these has a closed type of circulatory system :-
a)
Cockroach
b)
Fish
c)
Mollusca
d)
Scorpion
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Phylum Arthropoda and Mollusca include open circulatory system . Fish is member of phylum Chordata which contain close circulatory system.
Cockroach and scorpion are members of class inscecta phylum Arthropoda.
Cockroach and scorpion are members of class inscecta phylum Arthropoda.
Blood circulation take following course in heart of man :-- a)Left auricle - left ventricle - body - right auricle -right ventricle
- b)Right auricle - left ventricle
- c)Left auricle - left ventricle - lungs-right auricle -right ventricle
- d)None of them
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood circulation take following course in heart of man :-
a)
Left auricle - left ventricle - body - right auricle -right ventricle
b)
Right auricle - left ventricle
c)
Left auricle - left ventricle - lungs-right auricle -right ventricle
d)
None of them
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The blood pumped by the right ventricle enters the pulmonary artery, whereas the left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta. The deoxygenated blood pumped into the pulmonary artery is passed onto the lungs from where the oxygenated blood is carried by the pulmonary veins into the left atrium. This pathway constitutes the pulmonary circulation. The oxygenated blood entering the aorta is carried by a network of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries to the tissues from where the deoxygenated blood is collected by a system of venules, veins and vena cava and emptied into the right atrium. This is the systemic circulation. The systemic circulation provides nutrients, O2 and other essential substances to the tissues and takes CO2 and other harmful substances away for elimination.
So, the correct answer is option A.
So, the correct answer is option A.
The blood during diastole :-- a)Leaves the heart
- b)Enters the heart
- c)Enters lungs
- d)Leaves the ventricles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The blood during diastole :-
a)
Leaves the heart
b)
Enters the heart
c)
Enters lungs
d)
Leaves the ventricles
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Diastole This should really be called “ventricular diastole”, but don't worry about this for GCSE. During diastole the thick muscular walls of the ventricles relax. Again, this happens to both sides of the heart. The pressure of the blood in the ventricles falls low enough for the bicuspid valve to open.
Cardiac cycle in man takes about :-- a)0.5 seconds
- b)1.0 seconds
- c)1.2 seconds
- d)0.8 seconds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cardiac cycle in man takes about :-
a)
0.5 seconds
b)
1.0 seconds
c)
1.2 seconds
d)
0.8 seconds
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The average adult person at rest has 65 to 75 heartbeats per minute. One complete cardiac cycle takes about 0.8 seconds.
The heart pumps only deoxygenated blood :-- a)shark
- b)frog
- c)whale
- d)crocodile
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The heart pumps only deoxygenated blood :-
a)
shark
b)
frog
c)
whale
d)
crocodile
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
In the shark, the heart is only 2 chambered so a single circulation takes place through the heart. The heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the gills for oxygenation and from their oxygenated blood is distributed to the body directly.
Q. Heart with single circulation is found in :-A:Mammals and birdsB:ReptilesC:Fishes and amphibiansD:Fishes onlyThe answer is D.
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Fish have a single systemic circuit for blood, where the heart pumps the blood to the gills to be re-oxygenated (gill circulation), after which the blood flows to the rest of the body and back to the heart.
Other animals, such as amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, have a pulmonary circuit, where blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs and back, and a second, systemic circuit where blood is pumped to the body and back.
In the diagram of the vertical section of human heart given below certain parts have been indicated by alphabets.Choose the answer in which these alphabets have been correctly matched with the parts they indicate :- 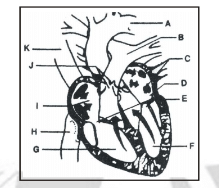
- a)A = Aorta, B = Pulmonary vein, C = Pulmonary arteries, D = Left ventricle, E = Semilunar valves,F = Left auricle, G = Right auricle, H = Superior vena cava, I = Right ventricle, J = Tricuspid valves,K = Inferior vena cava
- b)A = Aorta, B = Pulmonary artery, C = Pulmonary veins, D = Left auricle, E = Tricuspid and Mitral valves,F = Left ventricle, G = Right ventricle, H = Inferior vena cava, I = Right auricle, J = Semilunar valves,K = Superior vena cava
- c)A = Aorta, B = Superior vena cava, C = Inferior vena cava, D = Right ventricle, E = Tricuspid and Mitralvalves, F = Right auricle, G = Left auricle, H = Pulmonary vein, I = Left ventricle, J = Semilunar valves,K = Pulmonary artery
- d)A = Aorta, B = Superior vena cava, C = Inferior vena cava, D = Left ventricle, E = Semilunar valves,F = Left auricle, G = Right auricle, H = Pulmonary artery, I = Right ventricle, J = Tricuspid valves,K = Pulmonary vein
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the diagram of the vertical section of human heart given below certain parts have been indicated by alphabets.
Choose the answer in which these alphabets have been correctly matched with the parts they indicate :-
a)
A = Aorta, B = Pulmonary vein, C = Pulmonary arteries, D = Left ventricle, E = Semilunar valves,
F = Left auricle, G = Right auricle, H = Superior vena cava, I = Right ventricle, J = Tricuspid valves,
K = Inferior vena cava
b)
A = Aorta, B = Pulmonary artery, C = Pulmonary veins, D = Left auricle, E = Tricuspid and Mitral valves,
F = Left ventricle, G = Right ventricle, H = Inferior vena cava, I = Right auricle, J = Semilunar valves,
K = Superior vena cava
c)
A = Aorta, B = Superior vena cava, C = Inferior vena cava, D = Right ventricle, E = Tricuspid and Mitral
valves, F = Right auricle, G = Left auricle, H = Pulmonary vein, I = Left ventricle, J = Semilunar valves,
K = Pulmonary artery
d)
A = Aorta, B = Superior vena cava, C = Inferior vena cava, D = Left ventricle, E = Semilunar valves,
F = Left auricle, G = Right auricle, H = Pulmonary artery, I = Right ventricle, J = Tricuspid valves,
K = Pulmonary vein
|
|
Madhu answered |
Option b
Where are red blood cells formed ?- a)Spleen
- b)Liver
- c)Red bone marrow of short bones
- d)Thyroid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Where are red blood cells formed ?
a)
Spleen
b)
Liver
c)
Red bone marrow of short bones
d)
Thyroid
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Red blood cells are formed in the red bone marrow of bones. Stem cells in the red bone marrow called hemocytoblasts give rise to all of the formed elements in blood. If a hemocytoblast commits to becoming a cell called a proerythroblast, it will develop into a new red blood.
Erythrocytes of adult rabbit and other mammals are formed in :-- a)Kidney
- b)Liver
- c)Spleen
- d)Bone marrow
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Erythrocytes of adult rabbit and other mammals are formed in :-
a)
Kidney
b)
Liver
c)
Spleen
d)
Bone marrow

|
Mehak Jaju answered |
Blood formation area is bone marrow only
Clotting of blood is achieved with the help of the following :-- a)vitamin K, fibrinogen and calcium ions
- b)prothrombin, fibrinogen and thromboplastin
- c)vitamin B, fibrinogen, thrombin and potassium ions
- d) vitamin K, fibrinogen, prothrombin and calcium ions
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Clotting of blood is achieved with the help of the following :-
a)
vitamin K, fibrinogen and calcium ions
b)
prothrombin, fibrinogen and thromboplastin
c)
vitamin B, fibrinogen, thrombin and potassium ions
d)
vitamin K, fibrinogen, prothrombin and calcium ions
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Platelet aggregation and fibrin formation both require the Proteolytic enzyme thrombin. Clotting also requires :- Calcium ions about a dozen other protein clotting factors. Vitamin K refers to a group of fact soluble vitamins that play a role in blood clotting, bone metabolism and regulating blood calcium levels.
The pH value of blood varies between :-- a)6.00–7.00
- b)7.00–8.00
- c)7.30–7.45
- d)7.50–8.00
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The pH value of blood varies between :-
a)
6.00–7.00
b)
7.00–8.00
c)
7.30–7.45
d)
7.50–8.00
|
|
Anjana Khatri answered |
A pH of 7.0, in the middle of this scale, is neutral. Blood is normally slightly basic, alkaline, with a pH range of 7.35 to 7.45. To function properly, the body maintains the pH of blood close to 7.40. An important property of blood is its degree of acidity and alkalinity, and this is referred to as acid-base balance.
Heart beat originates from :-- a)Left atrium
- b)Right ventricle
- c)Pacemaker
- d)Cadiac muscles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Heart beat originates from :-
a)
Left atrium
b)
Right ventricle
c)
Pacemaker
d)
Cadiac muscles
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Your heartbeat is triggered by electrical impulses that travel down a special pathway through your heart: SA node (sinoatrial node) – known as the heart's natural pacemaker. The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells located in the right atrium, called the SA node.
Heart of Man is :-- a)Myogenic
- b)Neurogenic
- c)Cardiogenic
- d)Digenic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Heart of Man is :-
a)
Myogenic
b)
Neurogenic
c)
Cardiogenic
d)
Digenic
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |
The muscles of the human heart are stimulated to contract by nerve impulses generated by the Sino Atrial(SA) node. It is a cluster of cells which are part of the heart muscle.
•Hence the human heart is myogenic.
•Hence the human heart is myogenic.
Rate of heart beat is under the control of :-- a)Autonomic nervous system
- b)Vagus nerve
- c)Glossopharyngeal nerve
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of heart beat is under the control of :-
a)
Autonomic nervous system
b)
Vagus nerve
c)
Glossopharyngeal nerve
d)
None

|
M. Vishnu answered |
Heart rate is controlled by the two branches of the autonomic(involuntary) nervous system. Thesympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) releases the hormones (catecholamines - epinephrine and norepinephrine) to accelerate the heart rate.
What divides the left side of the heart from the left side?- a)Atrium
- b)Ventricles
- c)Wall
- d)Septum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What divides the left side of the heart from the left side?
a)
Atrium
b)
Ventricles
c)
Wall
d)
Septum
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
The left and right sides of the heart are divided by walls called septums. There is an atrial septum that separates the right and left atriums, and a ventricular septum that separates the right and left ventricles.
The circulation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to the lungs is classified as- a)pulmonary circulation
- b)systematic circulation
- c)digestive system
- d)lymphatic circulation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The circulation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to the lungs is classified as
a)
pulmonary circulation
b)
systematic circulation
c)
digestive system
d)
lymphatic circulation
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Pulmonary circulation moves blood between the heart and the lungs. It transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood then flows back to the heart. Systemic circulation moves blood between the heart and the rest of the body. It sends oxygenated blood out to cells and returns deoxygenated blood to the heart.
In a normal man blood pressure is :-- a)120/80mm of Hg
- b)80/100 mm of Hg
- c)80/120 mm of Hg
- d)100/80 mm of Hg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a normal man blood pressure is :-
a)
120/80mm of Hg
b)
80/100 mm of Hg
c)
80/120 mm of Hg
d)
100/80 mm of Hg
|
|
Harshitha Reddy answered |
Normal Blood Pressure
The normal blood pressure in a man is 120/80 mm of Hg.
Explanation
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of arteries. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). The two numbers in blood pressure readings represent systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
The normal blood pressure reading for an adult is 120/80 mm of Hg. The systolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart beats and pumps blood into the arteries. The diastolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats.
If the blood pressure reading is consistently higher than normal, it may indicate hypertension or high blood pressure. Hypertension can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
On the other hand, if the blood pressure reading is consistently lower than normal, it may indicate hypotension or low blood pressure. Hypotension can cause dizziness, fainting, and other health problems.
It's important to monitor blood pressure regularly and take necessary steps to maintain normal blood pressure. A healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help maintain normal blood pressure levels.
The normal blood pressure in a man is 120/80 mm of Hg.
Explanation
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of arteries. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). The two numbers in blood pressure readings represent systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
The normal blood pressure reading for an adult is 120/80 mm of Hg. The systolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart beats and pumps blood into the arteries. The diastolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats.
If the blood pressure reading is consistently higher than normal, it may indicate hypertension or high blood pressure. Hypertension can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
On the other hand, if the blood pressure reading is consistently lower than normal, it may indicate hypotension or low blood pressure. Hypotension can cause dizziness, fainting, and other health problems.
It's important to monitor blood pressure regularly and take necessary steps to maintain normal blood pressure. A healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help maintain normal blood pressure levels.
A sudden increase in the number of white blood cells in the blood is a sign of :-- a)deficiency disease
- b)better health
- c)bacterial disease, infection
- d)mental tension
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A sudden increase in the number of white blood cells in the blood is a sign of :-
a)
deficiency disease
b)
better health
c)
bacterial disease, infection
d)
mental tension
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
WBCs or white blood cells are nothing but the cells present in our blood which help in the defense mechanism. In case any disease causing pathogens enter in our body the WBCs help to kill it. Effectively, the sudden increase in number of WBCs in our blood stream is a sign of bacterial disease / infection.
Match the different leucocytes given under Column I with their functions given under Column II. Choose theanswer that gives the correct combination of alphabets of two columns :- 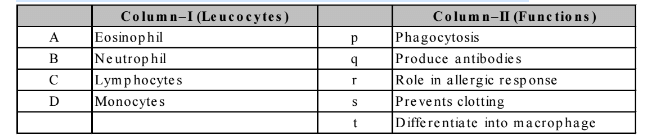
- a)A = t, B = p, C = q, D = f
- b)A = r, B = p, C = q, D = t
- c)A = q, B = r, C = s, D = t
- d)A = p, B = q, C = r, D = s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the different leucocytes given under Column I with their functions given under Column II. Choose the
answer that gives the correct combination of alphabets of two columns :-
a)
A = t, B = p, C = q, D = f
b)
A = r, B = p, C = q, D = t
c)
A = q, B = r, C = s, D = t
d)
A = p, B = q, C = r, D = s
|
|
Samridhi answered |

By counting the number of which of the following waves, the heartbeat of a person can be determined?- a)QRS complex
- b)P-wave
- c)ST-segment
- d)PQ interval
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
By counting the number of which of the following waves, the heartbeat of a person can be determined?
a)
QRS complex
b)
P-wave
c)
ST-segment
d)
PQ interval
|
|
Adebisi Ekpe answered |
Understanding Heartbeat Measurement
The heartbeat of a person can be determined by analyzing specific components of an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). Among these components, the QRS complex plays a crucial role.
What is the QRS Complex?
- The QRS complex represents the electrical activity associated with the contraction of the ventricles, which are the heart's main pumping chambers.
- It is a critical part of the cardiac cycle, as it indicates that the heart is actively pumping blood.
Counting the QRS Complexes
- By counting the number of QRS complexes in a given time frame, healthcare professionals can calculate the heart rate.
- Each QRS complex corresponds to one heartbeat. Therefore, counting these complexes over a specific period allows for an accurate measurement of heart rate.
Other Components Explained
- P-Wave: Represents atrial depolarization. Its primary role is to indicate the contraction of the atria but does not directly reflect the heart rate.
- ST-Segment: Indicates the period between ventricular depolarization and repolarization. It is important for diagnosing certain heart conditions but is not used for heart rate determination.
- PQ Interval: Represents the time between atrial and ventricular depolarization. While it provides insight into the conduction system, it does not serve as a direct measure of heart rate.
Conclusion
The QRS complex is essential for determining the heartbeat because it directly correlates to ventricular contractions. Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer for measuring heart rate effectively.
The heartbeat of a person can be determined by analyzing specific components of an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). Among these components, the QRS complex plays a crucial role.
What is the QRS Complex?
- The QRS complex represents the electrical activity associated with the contraction of the ventricles, which are the heart's main pumping chambers.
- It is a critical part of the cardiac cycle, as it indicates that the heart is actively pumping blood.
Counting the QRS Complexes
- By counting the number of QRS complexes in a given time frame, healthcare professionals can calculate the heart rate.
- Each QRS complex corresponds to one heartbeat. Therefore, counting these complexes over a specific period allows for an accurate measurement of heart rate.
Other Components Explained
- P-Wave: Represents atrial depolarization. Its primary role is to indicate the contraction of the atria but does not directly reflect the heart rate.
- ST-Segment: Indicates the period between ventricular depolarization and repolarization. It is important for diagnosing certain heart conditions but is not used for heart rate determination.
- PQ Interval: Represents the time between atrial and ventricular depolarization. While it provides insight into the conduction system, it does not serve as a direct measure of heart rate.
Conclusion
The QRS complex is essential for determining the heartbeat because it directly correlates to ventricular contractions. Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer for measuring heart rate effectively.
The heart sound "DUP" is Produced when :-- a)Mitral valve opens
- b)Mitral valve closes
- c)Semilunar valve at the base of aorta closes
- d)Tricuspid valve opens
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The heart sound "DUP" is Produced when :-
a)
Mitral valve opens
b)
Mitral valve closes
c)
Semilunar valve at the base of aorta closes
d)
Tricuspid valve opens
|
|
Pankaj Singh answered |
The heart sound ‘’DUP’’ is produced when a semilunar valve at the base of aorta classes.
Two distinct sounds can be heard during a heart beat with the help of a stethoscope. These are 'lubb' and 'dup'.Lubb is the first sound which has a low pitch and produced by the closure of tricuspid and bicuspid valves (collectively called atrioventricular valves) at the beginning of ventricular systole.
Dup is the second sound which is sharp and has a high pitch. It is produced by closure of semilunar valves by the end of ventricular systole.
Two distinct sounds can be heard during a heart beat with the help of a stethoscope. These are 'lubb' and 'dup'.Lubb is the first sound which has a low pitch and produced by the closure of tricuspid and bicuspid valves (collectively called atrioventricular valves) at the beginning of ventricular systole.
Dup is the second sound which is sharp and has a high pitch. It is produced by closure of semilunar valves by the end of ventricular systole.
Which of these occurs during the atrial systole?- a)Action potential is generated by the AVN initially
- b)Both atria contract simultaneously
- c)Tricuspid valve closes
- d)The semilunar valves remain open
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these occurs during the atrial systole?
a)
Action potential is generated by the AVN initially
b)
Both atria contract simultaneously
c)
Tricuspid valve closes
d)
The semilunar valves remain open
|
|
Chirag Unni answered |
Atrial Systole Overview
Atrial systole is a crucial phase in the cardiac cycle where the atria contract, pushing blood into the ventricles. During this phase, several important physiological events occur.
Key Events During Atrial Systole
- Both Atria Contract Simultaneously: This is the defining characteristic of atrial systole. The sinoatrial (SA) node generates an action potential that spreads through the atria, causing them to contract together. This synchronous contraction efficiently fills the ventricles with blood.
- Action Potential Generation by AV Node: While the atrial contraction is initiated by the SA node, the atrioventricular node (AVN) plays a role in conducting the electrical impulse to the ventricles. However, the AVN does not generate the initial action potential during atrial systole.
- Tricuspid Valve Status: The tricuspid valve remains open during atrial systole, allowing blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. It closes after atrial contraction as the ventricles begin to contract.
- Semilunar Valves Status: The semilunar valves (pulmonary and aortic valves) remain closed during this phase. They only open when the ventricles contract, allowing blood to exit the heart.
Conclusion
In summary, option 'B' is correct because during atrial systole, both atria contract simultaneously, facilitating efficient blood flow into the ventricles. Understanding these dynamics is essential for grasping cardiac physiology, particularly for NEET aspirants.
Atrial systole is a crucial phase in the cardiac cycle where the atria contract, pushing blood into the ventricles. During this phase, several important physiological events occur.
Key Events During Atrial Systole
- Both Atria Contract Simultaneously: This is the defining characteristic of atrial systole. The sinoatrial (SA) node generates an action potential that spreads through the atria, causing them to contract together. This synchronous contraction efficiently fills the ventricles with blood.
- Action Potential Generation by AV Node: While the atrial contraction is initiated by the SA node, the atrioventricular node (AVN) plays a role in conducting the electrical impulse to the ventricles. However, the AVN does not generate the initial action potential during atrial systole.
- Tricuspid Valve Status: The tricuspid valve remains open during atrial systole, allowing blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. It closes after atrial contraction as the ventricles begin to contract.
- Semilunar Valves Status: The semilunar valves (pulmonary and aortic valves) remain closed during this phase. They only open when the ventricles contract, allowing blood to exit the heart.
Conclusion
In summary, option 'B' is correct because during atrial systole, both atria contract simultaneously, facilitating efficient blood flow into the ventricles. Understanding these dynamics is essential for grasping cardiac physiology, particularly for NEET aspirants.
In the joint diastole state, which of these events do not occur?- a)All four chambers are relaxed
- b)Blood from pulmonary vein flows into the right atrium
- c)Both tricuspid and bicuspid valves are open
- d)Both semilunar valves are closed
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the joint diastole state, which of these events do not occur?
a)
All four chambers are relaxed
b)
Blood from pulmonary vein flows into the right atrium
c)
Both tricuspid and bicuspid valves are open
d)
Both semilunar valves are closed

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
- In the joint diastole state, all four chambers of the heart are relaxed.
- The tricuspid and bicuspid valves are open while the semilunar valves are closed.
- Blood from pulmonary vein flows into the left ventricle.
Which of the following represents the depolarisation of the ventricles?- a)P-wave
- b)T-wave
- c) PQ interval
- d)QRS complex
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents the depolarisation of the ventricles?
a)
P-wave
b)
T-wave
c)
PQ interval
d)
QRS complex

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
- The QRS complex represents the depolarisation of the ventricles, which initiate the ventricular contraction.
- The contraction starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
What happens when the ventricular pressure decreases?- a)Blood from pulmonary artery flows into ventricle
- b)The semilunar valves remain open
- c)Atrial pressure decreases
- d)The tricuspid and bicuspid valves open
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens when the ventricular pressure decreases?
a)
Blood from pulmonary artery flows into ventricle
b)
The semilunar valves remain open
c)
Atrial pressure decreases
d)
The tricuspid and bicuspid valves open
|
|
Adenike Adebayo answered |
Understanding Ventricular Pressure Changes
When ventricular pressure decreases during the cardiac cycle, several important physiological events occur. This decrease typically happens at the end of ventricular contraction (systole) and leads to the subsequent filling of the heart chambers.
Key Effects of Decreasing Ventricular Pressure:
- Blood from the Pulmonary Artery:
When ventricular pressure decreases, blood does not flow back from the pulmonary artery into the ventricle. Instead, it remains in the pulmonary artery unless the pressure in the ventricles becomes lower than in the pulmonary artery.
- Semilunar Valves:
The semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonary) close when the ventricular pressure falls below the arterial pressure. Therefore, these valves do not remain open when the pressure decreases.
- Atrial Pressure:
Atrial pressure typically increases as the atria fill with blood during diastole. It does not decrease when the ventricular pressure drops.
- Tricuspid and Bicuspid Valves Open:
As the ventricular pressure decreases, it becomes lower than the pressure in the atria. This pressure difference causes the tricuspid (right side) and bicuspid (left side) valves to open, allowing blood to flow from the atria into the ventricles. This is a crucial step in the cardiac cycle known as ventricular filling.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'. The opening of the tricuspid and bicuspid valves facilitates the filling of the ventricles with blood, preparing them for the next contraction. Understanding this mechanism is vital in comprehending how the heart functions effectively.
When ventricular pressure decreases during the cardiac cycle, several important physiological events occur. This decrease typically happens at the end of ventricular contraction (systole) and leads to the subsequent filling of the heart chambers.
Key Effects of Decreasing Ventricular Pressure:
- Blood from the Pulmonary Artery:
When ventricular pressure decreases, blood does not flow back from the pulmonary artery into the ventricle. Instead, it remains in the pulmonary artery unless the pressure in the ventricles becomes lower than in the pulmonary artery.
- Semilunar Valves:
The semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonary) close when the ventricular pressure falls below the arterial pressure. Therefore, these valves do not remain open when the pressure decreases.
- Atrial Pressure:
Atrial pressure typically increases as the atria fill with blood during diastole. It does not decrease when the ventricular pressure drops.
- Tricuspid and Bicuspid Valves Open:
As the ventricular pressure decreases, it becomes lower than the pressure in the atria. This pressure difference causes the tricuspid (right side) and bicuspid (left side) valves to open, allowing blood to flow from the atria into the ventricles. This is a crucial step in the cardiac cycle known as ventricular filling.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'. The opening of the tricuspid and bicuspid valves facilitates the filling of the ventricles with blood, preparing them for the next contraction. Understanding this mechanism is vital in comprehending how the heart functions effectively.
What is the approximate stroke volume?- a)250 ml
- b)5000 ml
- c)70 ml
- d)500 ml
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the approximate stroke volume?
a)
250 ml
b)
5000 ml
c)
70 ml
d)
500 ml

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
- 72 cardiac cycles take place in one minute.
- The duration of one cardiac cycle is 0.8 seconds.
- During each cardiac cycle, each of the two ventricles pump 70 ml of blood, which is known as the stroke volume.
The blood leaving the lungs is richer than the blood entering the lung in :-- a)Oxygen
- b)CO2
- c)Hydrogen
- d)Moisture
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The blood leaving the lungs is richer than the blood entering the lung in :-
a)
Oxygen
b)
CO2
c)
Hydrogen
d)
Moisture

|
Isha Akhtar answered |
Lungs purify the CO2 and convert it into O2 The blood coming to the lungs contain deoxygenated blood because it is collected from the body tissues and is rich in CO2. After leaving the lungs..the blood is oxygenated.
To reach the left side of heart the blood must pass through :-- a)Sinus venosus
- b)Kidneys
- c)Liver
- d)Lungs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To reach the left side of heart the blood must pass through :-
a)
Sinus venosus
b)
Kidneys
c)
Liver
d)
Lungs
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium of the heart. ... As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs where it is oxygenated.
Oxygenated blood is carried by :-- a)Pulmonary artery
- b)Pulmonary vein
- c)Renal vein
- d)Hepatic portal vein
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygenated blood is carried by :-
a)
Pulmonary artery
b)
Pulmonary vein
c)
Renal vein
d)
Hepatic portal vein
|
|
Sadiya Siddique answered |
Pulmonary artery carries blood from right ventricle to lungs for oxygenation, Hepatic Portal vein carries blood from liver and renal vein from kidneys to inferior vena cava of heart . All of them carry deoxygenated blood . Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lungs back to left auricle of heart. so op B
First heart sound is :-- a)Lubb sound at the end of systole
- b)Lubb sound at the begining of ventricular systole
- c)'Dup' sound at the end of systole
- d)Dup sound at the begining of ventricular systole
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
First heart sound is :-
a)
Lubb sound at the end of systole
b)
Lubb sound at the begining of ventricular systole
c)
'Dup' sound at the end of systole
d)
Dup sound at the begining of ventricular systole

|
Shruti Ahuja answered |
Ans.
The first heart sound, or S1, forms the "lub" of "lub-dub" and is composed of components M1 (mitral valve closure) and T1 (tricuspid valve closure). ... It is caused by the closure of the atrioventricular valves, i.e. tricuspid and mitral (bicuspid), at the beginning of ventricular contraction, or systole.
Chapter doubts & questions for Circulatory System - Biology 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Circulatory System - Biology in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology
153 videos|283 docs|127 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily