All Exams >
NEET >
1 Year Dropper Course for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Plant - Growth & Development for NEET Exam
The natural plant hormones were first isolated from- a)Cotton fruits, spinach leaves and rice plant
- b)Avena coleoptiles, spinach leaves and fungus Gibberella
- c)Human urine and corn germ oil
- d)Human urine and rice plant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The natural plant hormones were first isolated from
a)
Cotton fruits, spinach leaves and rice plant
b)
Avena coleoptiles, spinach leaves and fungus Gibberella
c)
Human urine and corn germ oil
d)
Human urine and rice plant
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Auxins were first isolated from human urine. The term auxin is applied to the indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), and to other natural and synthetic compounds having certain growth-regulating properties.
Cytokinins have specific effects on cytokinesis and were discovered as kinetin from the autoclaved herring sperm DNA.
Kinetin does not occur naturally in plants. Search for natural substances with cytokinin-like activities led to the isolation of zeatin from corn kernels (corn germ oil) and coconut milk.
Kinetin does not occur naturally in plants. Search for natural substances with cytokinin-like activities led to the isolation of zeatin from corn kernels (corn germ oil) and coconut milk.
Hence option C is correct.
Seedless fruits can be obtained by treating the unpollinated ovaries with :-- a)Colchicine
- b)Sucrose solution
- c)Hormones
- d)Pure lanolin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Seedless fruits can be obtained by treating the unpollinated ovaries with :-
a)
Colchicine
b)
Sucrose solution
c)
Hormones
d)
Pure lanolin

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Seedless fruits like grapes and papaya are called Parthenocarpic fruits. These fruits are developed from unfertilized ovaries.
Plant hormones like auxins induce parthenocarpy.
Example: Tomatoes.
Plant hormones like auxins induce parthenocarpy.
Example: Tomatoes.
How many cells per hour does a single maize root apical meristem can give?- a)1,75,000
- b)17,500
- c)175
- d)1,750
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many cells per hour does a single maize root apical meristem can give?
a)
1,75,000
b)
17,500
c)
175
d)
1,750
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
One single maize root apical meristem can give rise to more than 17,500 new cells per hour.
What is the last stage of a plant called?- a)Senescence
- b)Scarification
- c)Dormancy
- d)Vernalisation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the last stage of a plant called?
a)
Senescence
b)
Scarification
c)
Dormancy
d)
Vernalisation
|
|
Gulzar Ahmad answered |
Of course it is senescence (ageing)....
Leaf fall occurs when the content of :-- a)Auxin increases
- b)Auxin decreases
- c)Abscisic acid decreases
- d)Gibberellic acid decreases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Leaf fall occurs when the content of :-
a)
Auxin increases
b)
Auxin decreases
c)
Abscisic acid decreases
d)
Gibberellic acid decreases
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Due to a reduction in photosynthesis, this may trigger the abscission of leaves (separation of leaves) and this abscission layer is produced when auxin content falls below a minimum causing leaf or other plant part to fall off.CORRECT OPTION IS B.
Apical dominance means :-- a)Suppression of growth of apical bud by axillary buds
- b)Suppression of growth of axillary buds by the presence of apical bud.
- c)Stimulation of growth of axillary buds by removal of apical bud
- d)Inhibition of growth of axillary buds by removal of apical bud.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Apical dominance means :-
a)
Suppression of growth of apical bud by axillary buds
b)
Suppression of growth of axillary buds by the presence of apical bud.
c)
Stimulation of growth of axillary buds by removal of apical bud
d)
Inhibition of growth of axillary buds by removal of apical bud.
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
Auxins are generally produced by the growing apices of the stems and roots, from where they migrate to the regions of their action. In most higher plants, the growing apical bud inhibits the growth of the lateral (axillary) buds, a phenomenon called apical dominance.
Stem elongation is affected by :-- a)Gibberellin and florigen
- b)Auxin and gibberellin
- c)Florigen and kinin
- d)Kinin and auxin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Stem elongation is affected by :-
a)
Gibberellin and florigen
b)
Auxin and gibberellin
c)
Florigen and kinin
d)
Kinin and auxin
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Auxins promote stem elongation, inhibit growth of lateral buds (maintains apical dominance). They are produced in the stem, buds, and root tips. Example: Indole Acetic Acid (IA). Auxin is a plant hormone produced in the stem tip that promotes cell elongation.
Gibberellic acid is a simple gibberellin, a pentacyclic diterpene acid promoting growth and elongation of cells. .Gibberellins have a number of effects on plant development. They can stimulate rapid stem and root growth, induce mitotic division in the leaves of some plants, and increase seed germination rate.
Auxanometer is meant for measuring -- a)Respiratory activity
- b)Photosynthetic activity
- c)Growth activity
- d)Osmotic pressure
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Auxanometer is meant for measuring -
a)
Respiratory activity
b)
Photosynthetic activity
c)
Growth activity
d)
Osmotic pressure
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Auxanometer is a simple instrument to measure growth of a plant. Most common type of auxanometer is arc auxanometer, which measures growth as the increase in length of axis. This increase can be caused due to increase in mass of protoplasm (cell division) or simply by absorption of water (increase in length or surface of existing cells).
Auxin inhibits the growth of -- a)Apical bud
- b)Lateral axillary buds
- c)Roots on stem cutting
- d)Parthenocarpic development of fruits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Auxin inhibits the growth of -
a)
Apical bud
b)
Lateral axillary buds
c)
Roots on stem cutting
d)
Parthenocarpic development of fruits
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The apical bud produces an auxin hormone that inhibits the growth of the lateral buds further down on the stem towards the axillary bud.
Hormone responsible for senescence [2001]- a)ABA
- b)auxin
- c)GA
- d)cytokinin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormone responsible for senescence [2001]
a)
ABA
b)
auxin
c)
GA
d)
cytokinin

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
ABA or Abscisic acid is responsible for leaf fall or senescence.
In a growing plant, the first phase during the process of growth is -- a)Cell division
- b)Cell enlargement
- c)Cell differentiation
- d)Cell maturation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a growing plant, the first phase during the process of growth is -
a)
Cell division
b)
Cell enlargement
c)
Cell differentiation
d)
Cell maturation
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Phases Of Plant Growth
Meristematic Phase
The cells in the root and shoot apex of a plant are constantly dividing. They represent the meristematic phase of growth. The cells in these regions have large nuclei and are rich in protoplasm and their cell walls are thin and contain cellulose.
Elongation Phase
The cells in the zone just after the meristematic region represent the phase of elongation. The characteristics of cells in this zone are cell enlargement, increased vacuole formation and new cell wall deposition.
Maturation Phase
Just close to the phase of elongation, but away from the apex lies the phase of maturation. The cells in this region reach their maximum size with respect to their protoplasm and cell wall thickening.
Apical dominance in higher plants is due to -- a)Phyto hormones
- b)Enzymes
- c)Carbohydrates
- d)Photoperiodism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Apical dominance in higher plants is due to -
a)
Phyto hormones
b)
Enzymes
c)
Carbohydrates
d)
Photoperiodism
|
|
Anshul Nair answered |
Apical Dominance in higher plants is due to Phytohormones. Phytohormones are naturally occurring organic substances that regulate plant growth and development. They are also known as plant hormones or growth regulators. Phytohormones are synthesized in one part of the plant and transported to other parts where they exert their effects.
Explanation:
1. Definition of Apical Dominance:
Apical dominance is the phenomenon in which the apical bud of a plant inhibits the growth of lateral buds below it. This ensures that the plant grows in a single, upward direction, with a dominant main stem.
2. Role of Phytohormones:
Phytohormones play a crucial role in apical dominance. The apical bud releases a hormone called auxin, which inhibits the growth of lateral buds. Auxin is produced in the apical meristem (the growing tip of the plant) and is transported downwards towards the base of the plant.
3. Mechanism of Phytohormones:
Auxin acts by inhibiting the growth of lateral buds by inducing the production of cytokinins in the roots. Cytokinins are another type of phytohormone that promote cell division and growth. When auxin is transported downwards towards the roots, it induces the production of cytokinins in the roots. These cytokinins are then transported upwards towards the lateral buds, where they promote cell division and growth. However, the concentration of cytokinins is not enough to overcome the inhibitory effect of auxin, so the lateral buds remain dormant.
4. Importance of Apical Dominance:
Apical dominance is an important mechanism for plants because it ensures that the plant grows in a single, upward direction, with a dominant main stem. This is important for plants that need to compete for light and space. By growing upwards, the plant can maximize its exposure to sunlight and outcompete other plants for resources.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Apical Dominance in higher plants is due to Phytohormones. Auxin is the hormone responsible for inhibiting the growth of lateral buds, while cytokinins promote cell division and growth. The balance between these two hormones ensures that the plant grows in a single, upward direction, with a dominant main stem.
Explanation:
1. Definition of Apical Dominance:
Apical dominance is the phenomenon in which the apical bud of a plant inhibits the growth of lateral buds below it. This ensures that the plant grows in a single, upward direction, with a dominant main stem.
2. Role of Phytohormones:
Phytohormones play a crucial role in apical dominance. The apical bud releases a hormone called auxin, which inhibits the growth of lateral buds. Auxin is produced in the apical meristem (the growing tip of the plant) and is transported downwards towards the base of the plant.
3. Mechanism of Phytohormones:
Auxin acts by inhibiting the growth of lateral buds by inducing the production of cytokinins in the roots. Cytokinins are another type of phytohormone that promote cell division and growth. When auxin is transported downwards towards the roots, it induces the production of cytokinins in the roots. These cytokinins are then transported upwards towards the lateral buds, where they promote cell division and growth. However, the concentration of cytokinins is not enough to overcome the inhibitory effect of auxin, so the lateral buds remain dormant.
4. Importance of Apical Dominance:
Apical dominance is an important mechanism for plants because it ensures that the plant grows in a single, upward direction, with a dominant main stem. This is important for plants that need to compete for light and space. By growing upwards, the plant can maximize its exposure to sunlight and outcompete other plants for resources.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Apical Dominance in higher plants is due to Phytohormones. Auxin is the hormone responsible for inhibiting the growth of lateral buds, while cytokinins promote cell division and growth. The balance between these two hormones ensures that the plant grows in a single, upward direction, with a dominant main stem.
All are extrinsic factors responsible for the development of an organism except- a)Light
- b)Amount of oxygen
- c)Temperature
- d)Hormones
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
All are extrinsic factors responsible for the development of an organism except
a)
Light
b)
Amount of oxygen
c)
Temperature
d)
Hormones
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Light, amount of oxygen and temperature are extrinsic factors responsible for the development of an organism but hormones are intrinsic factors.
So the correct option is 'Hormones.'
So the correct option is 'Hormones.'
Growth is primarily affected by two climatic factors which are ?- a)Light and temperature
- b)Temperature and relative humidity
- c)Light and wind
- d)Rainfall and temperature
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Growth is primarily affected by two climatic factors which are ?
a)
Light and temperature
b)
Temperature and relative humidity
c)
Light and wind
d)
Rainfall and temperature
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
The climatic factors include rainfall and water, light, temperature, relative humidity, air, and wind. They are abiotic components, including topography and soil, of the environmental factors that influence plant growth and development.
Coconut milk contains a cytokinin called ____ which promotes plant growth.- a)Naphthalene acetic acid
- b)Indole-3-acetic acid
- c)Gelatin
- d)Zeatin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Coconut milk contains a cytokinin called ____ which promotes plant growth.
a)
Naphthalene acetic acid
b)
Indole-3-acetic acid
c)
Gelatin
d)
Zeatin
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
trans-zeatin riboside is the most abundant type of cytokinin found in coconut water (Table 2). trans-zeatin is normally used to induce plantlet regeneration from callus in plant tissue culture. Based on experimental data, trans-zeatin plays a key role in the G2-M transition of tobacco cells.
In plants growth is -- a)Restricted to certain regions or structure
- b)Irreversible
- c)Change in size
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In plants growth is -
a)
Restricted to certain regions or structure
b)
Irreversible
c)
Change in size
d)
All the above
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The key to plant growth is meristem, a type of plant tissue consisting of undifferentiated cells that can continue to divide and differentiate. Meristem allows plant stems and roots to grow longer (primary growth) and wider (secondary growth).
During seed germination its stored food is mobilized [NEET 2013]- a)Cytokinin
- b)ABA
- c)Gibberellin
- d)Ethylene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During seed germination its stored food is mobilized [NEET 2013]
a)
Cytokinin
b)
ABA
c)
Gibberellin
d)
Ethylene

|
Naveen Menon answered |
Gibberellins stimulate the synthesis of α-amylase and proteases enzyme in germinating grains of cereals. They are involved in the conversion of starch into sugar. The proteases convert an inactive β-amylase to the active form. The active β-amylase and α-amylase together digest starch to glucose which is mobilized to meet the metabolic demands of embryo.
Removal of apical bud results in [1993, 2000]- a)formation of new apical bud
- b)elongation of main stem
- c)death of plant
- d)formation of lateral branching
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Removal of apical bud results in [1993, 2000]
a)
formation of new apical bud
b)
elongation of main stem
c)
death of plant
d)
formation of lateral branching

|
Gowri Nair answered |
Apical buds inhibit lateral branching due to apical dominance. Removal of apical bud promotes lateral branching.
What breaks bud dormancy of potato tuber?- a)Gibberellin
- b)IAA [2001]
- c)ABA
- d)Zeatin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What breaks bud dormancy of potato tuber?
a)
Gibberellin
b)
IAA [2001]
c)
ABA
d)
Zeatin

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
IAA promotes apical dominance. ABA induces dormancy in buds.
Which plant hormone is named anti-ageing hormone?- a)Cytokinin
- b)Gibberellins
- c)Abscisic acid
- d)Ethylene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which plant hormone is named anti-ageing hormone?
a)
Cytokinin
b)
Gibberellins
c)
Abscisic acid
d)
Ethylene

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
Cytokinin is named as anti-ageing hormone.
Auxin was isolated from tips of coloeptile of oat seedlings by- a)Miller
- b)F.W.Went
- c)E.Kurosawa
- d)Skoog
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Auxin was isolated from tips of coloeptile of oat seedlings by
a)
Miller
b)
F.W.Went
c)
E.Kurosawa
d)
Skoog
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
F. W Went first isolated the Auxins in 1928 from the tips of the coleooptiles of oat seedlings. F.W Went was secondly able to isolate a chemical from coleoptile juice.
Which of the following prevents fall of fruits?[2001]- a)GA3
- b)NAA
- c)Ethylene
- d)Zeatin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following prevents fall of fruits?[2001]
a)
GA3
b)
NAA
c)
Ethylene
d)
Zeatin

|
Devansh Mehra answered |
NAA or Naphthalene Acetic Acid is synthetic auxin. It is used to check fruit fall specially in tomato.
Type of cambium located between phloem and xylem is classified as- a)shoot cambium
- b)root cambium
- c)vascular cambium
- d)cork cambium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Type of cambium located between phloem and xylem is classified as
a)
shoot cambium
b)
root cambium
c)
vascular cambium
d)
cork cambium
|
|
Ankit Patel answered |
The vascular cambium is a type of cambium located between the phloem and xylem in plants. It is responsible for secondary growth in plants, which results in an increase in girth of the stem or root.
Structure of vascular cambium:
The vascular cambium consists of a single layer of meristematic cells that divide to form secondary xylem cells towards the inside and secondary phloem cells towards the outside.
Function of vascular cambium:
The vascular cambium is responsible for the production of new xylem and phloem cells, which allows for the growth of the plant. It also helps in the transportation of water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant.
Importance of vascular cambium:
The vascular cambium plays a crucial role in the life of a plant as it is responsible for the growth and development of the stem and root. Without the vascular cambium, plants would not be able to grow taller or wider, and they would eventually die.
Conclusion:
The vascular cambium is a vital part of the plant's anatomy as it is responsible for the growth and development of the stem and root. Its role in the production of new xylem and phloem cells is essential for the transportation of water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Structure of vascular cambium:
The vascular cambium consists of a single layer of meristematic cells that divide to form secondary xylem cells towards the inside and secondary phloem cells towards the outside.
Function of vascular cambium:
The vascular cambium is responsible for the production of new xylem and phloem cells, which allows for the growth of the plant. It also helps in the transportation of water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant.
Importance of vascular cambium:
The vascular cambium plays a crucial role in the life of a plant as it is responsible for the growth and development of the stem and root. Without the vascular cambium, plants would not be able to grow taller or wider, and they would eventually die.
Conclusion:
The vascular cambium is a vital part of the plant's anatomy as it is responsible for the growth and development of the stem and root. Its role in the production of new xylem and phloem cells is essential for the transportation of water and nutrients throughout the plant.
A farmer grows cucumber plants in his field. He wants to increase the number of female flowers in them. Which plant hormones can be applied to achieve this?- a)Abscisic acid
- b)Gibberellins
- c)Ethylene
- d)Auxins
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A farmer grows cucumber plants in his field. He wants to increase the number of female flowers in them. Which plant hormones can be applied to achieve this?
a)
Abscisic acid
b)
Gibberellins
c)
Ethylene
d)
Auxins

|
Bhavya Yadav answered |
Ethylene promotes female flowers in cucumbers thereby increasing the yield.
The regulator which retards ageing/ senescence of plant parts is : [1993]- a)cytokinin
- b)auxin
- c)gibberellin
- d)abscisic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The regulator which retards ageing/ senescence of plant parts is : [1993]
a)
cytokinin
b)
auxin
c)
gibberellin
d)
abscisic acid

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
Cytokinin help in retaining chlorophyll, hence delay senescense.
The xylem which differentiates has a thick secondary wall made of- a)Suberin
- b)Cellulose
- c)Pectin
- d)Lignin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The xylem which differentiates has a thick secondary wall made of
a)
Suberin
b)
Cellulose
c)
Pectin
d)
Lignin
|
|
Kritishna Samal answered |
Well the correct answer is 'D'. because as you kno... morew xylem is the principle water conducting complex tissue in higher plants . so the water present in the xylem cells will be surely under negative pressure and to just avoid collapsing of walls of xylem cells , lignin is present. liginin is also less hydrophillic then other polysacchrides like cellulose and hemicellulose hence prevents absorption of water by them and allow an efficient pathway for transport of water in xylem.
The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]- a)2, 4-D
- b)IBA
- c)IAA
- d)NAA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]
a)
2, 4-D
b)
IBA
c)
IAA
d)
NAA
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
2, 4-D, widely used to kill dicotyledonous weeds, does not affect mature monocotyledonous plants.
They help to initiate rooting in stem cuttings, an application widely used for plant propagation. Auxins promote flowering e.g. in pineapples. They help to prevent fruit and leaf drop at early stages but promote the abscission of older mature leaves and fruits.
In most higher plants, the growing apical bud inhibits the growth of the lateral (axillary) buds, a phenomenon called apical dominance. Removal of shoot tips (decapitation) usually results in the growth of lateral buds (Figure 15.11). It is widely applied in tea plantations, hedge-making. Can you explain why?
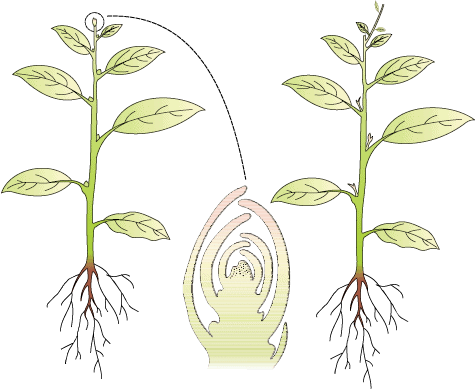
In most higher plants, the growing apical bud inhibits the growth of the lateral (axillary) buds, a phenomenon called apical dominance. Removal of shoot tips (decapitation) usually results in the growth of lateral buds (Figure 15.11). It is widely applied in tea plantations, hedge-making. Can you explain why?

Auxins are generally produced in- a)Phloem
- b)root and shoot tips
- c)xylem
- d)leaves
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Auxins are generally produced in
a)
Phloem
b)
root and shoot tips
c)
xylem
d)
leaves
|
|
Pallavi Choudhary answered |
Explanation:
Auxins are a group of plant hormones that play a crucial role in various plant growth and developmental processes. They are primarily produced in the shoot and root tips of plants.
- Shoot tips: In the shoot tips, auxins are mainly produced in the apical meristem region, which is responsible for the growth and development of the stem and leaves. The apical meristem contains undifferentiated cells that can give rise to different types of tissues. Auxins produced in this region help in the elongation of the stem and the formation of new leaves.
- Root tips: In the root tips, auxins are mainly produced in the root apical meristem, which is responsible for the growth and development of the root system. The root apical meristem contains undifferentiated cells that can give rise to different types of root tissues. Auxins produced in this region help in the elongation of the root and the formation of lateral roots.
Other sources of auxins:
- Leaves: Although auxins are primarily produced in the shoot and root tips, leaves also contain a small amount of auxins. These auxins play a role in leaf abscission, which is the shedding of leaves from the plant.
- Phloem: The phloem is a vascular tissue that transports nutrients and other molecules from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Auxins are also transported through the phloem to other parts of the plant.
- Xylem: The xylem is a vascular tissue that transports water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant. Although auxins are primarily produced in the shoot and root tips, they can also be transported through the xylem to other parts of the plant.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, auxins are primarily produced in the shoot and root tips of plants, where they play a crucial role in various growth and developmental processes. Although auxins can also be found in other parts of the plant, their main source is the shoot and root tips.
Auxins are a group of plant hormones that play a crucial role in various plant growth and developmental processes. They are primarily produced in the shoot and root tips of plants.
- Shoot tips: In the shoot tips, auxins are mainly produced in the apical meristem region, which is responsible for the growth and development of the stem and leaves. The apical meristem contains undifferentiated cells that can give rise to different types of tissues. Auxins produced in this region help in the elongation of the stem and the formation of new leaves.
- Root tips: In the root tips, auxins are mainly produced in the root apical meristem, which is responsible for the growth and development of the root system. The root apical meristem contains undifferentiated cells that can give rise to different types of root tissues. Auxins produced in this region help in the elongation of the root and the formation of lateral roots.
Other sources of auxins:
- Leaves: Although auxins are primarily produced in the shoot and root tips, leaves also contain a small amount of auxins. These auxins play a role in leaf abscission, which is the shedding of leaves from the plant.
- Phloem: The phloem is a vascular tissue that transports nutrients and other molecules from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Auxins are also transported through the phloem to other parts of the plant.
- Xylem: The xylem is a vascular tissue that transports water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant. Although auxins are primarily produced in the shoot and root tips, they can also be transported through the xylem to other parts of the plant.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, auxins are primarily produced in the shoot and root tips of plants, where they play a crucial role in various growth and developmental processes. Although auxins can also be found in other parts of the plant, their main source is the shoot and root tips.
Which of the following instrument can be used to record plant growth by seconds ?- a)Arc auxanometer
- b)Arc indicator
- c)Space marker disc
- d)Crescograph
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following instrument can be used to record plant growth by seconds ?
a)
Arc auxanometer
b)
Arc indicator
c)
Space marker disc
d)
Crescograph
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Crescograph is a sensitive devise, devised by J.C. Bose. It records primary growth very accurately. It magnifies growth upto 10,000 times giving information of growth per second.
Which pair of enzyme promotes femaleness in flowers?- a)Ethylene and cytokinins
- b)Auxin and abscisic acid
- c)Auxin and ethylene
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which pair of enzyme promotes femaleness in flowers?
a)
Ethylene and cytokinins
b)
Auxin and abscisic acid
c)
Auxin and ethylene
d)
None of these

|
Rohan Unni answered |
Auxin and ethylene are the plant hormone that promotes femaleness in flower.
If GA3 is applied to the rice seedlings, the plant will show- a)Delayed ripening
- b)Early flowering
- c)Dwarfing
- d)Extra elongation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If GA3 is applied to the rice seedlings, the plant will show
a)
Delayed ripening
b)
Early flowering
c)
Dwarfing
d)
Extra elongation

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
GA3 is a gibberellins that help in elongation of stem of the plant. If GA3 plant hormone is applied to the rice seedling the plant will show extra elongation of plant body.
It is the testing of a biological activity like growth response of a substance by employing a living material like plant or plant part.- a)Separation
- b)Fractionalisation
- c)Bioassay
- d)Autopsy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
It is the testing of a biological activity like growth response of a substance by employing a living material like plant or plant part.
a)
Separation
b)
Fractionalisation
c)
Bioassay
d)
Autopsy

|
Swara Desai answered |
Testing of biological activity like growth response of a substance by employing a living material like plant or plant part is called bioassay. It is used to know the effect of substance on plant growth.
Mathematically arithmetic growth is expressed as- a)Lt = L0.rt
- b)Lt = L0/rt
- c)Lt = L0 + rt
- d)Lt = L0 - rt
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mathematically arithmetic growth is expressed as
a)
Lt = L0.rt
b)
Lt = L0/rt
c)
Lt = L0 + rt
d)
Lt = L0 - rt
|
|
Anshika Shah answered |
Arithmetic growth is a type of growth where a quantity increases or decreases by a fixed amount over a fixed interval of time. It can be represented mathematically using the formula Lt = L0 + rt, where Lt is the value of the quantity at time t, L0 is the initial value of the quantity, r is the rate of change, and t is the time interval.
Explanation of the formula:
- Lt represents the value of the quantity at time t. This is the value that we want to find.
- L0 represents the initial value of the quantity. This is the starting point of the growth.
- r represents the rate of change. It determines how much the quantity changes over the time interval.
- t represents the time interval. It is the amount of time that has passed since the initial value.
In arithmetic growth, the rate of change is constant. This means that the quantity increases or decreases by the same amount for each unit of time. The formula Lt = L0 + rt captures this concept by adding the rate of change multiplied by the time interval to the initial value.
For example, let's say we have an initial quantity of 100 and a rate of change of 5. If we want to find the value of the quantity after 3 time intervals, we can use the formula Lt = 100 + 5 * 3 = 115. This means that the quantity has increased to 115 after 3 time intervals.
In option C, Lt = L0 + rt, the formula correctly represents arithmetic growth. The other options do not accurately capture the concept of arithmetic growth or contain incorrect mathematical operations.
Explanation of the formula:
- Lt represents the value of the quantity at time t. This is the value that we want to find.
- L0 represents the initial value of the quantity. This is the starting point of the growth.
- r represents the rate of change. It determines how much the quantity changes over the time interval.
- t represents the time interval. It is the amount of time that has passed since the initial value.
In arithmetic growth, the rate of change is constant. This means that the quantity increases or decreases by the same amount for each unit of time. The formula Lt = L0 + rt captures this concept by adding the rate of change multiplied by the time interval to the initial value.
For example, let's say we have an initial quantity of 100 and a rate of change of 5. If we want to find the value of the quantity after 3 time intervals, we can use the formula Lt = 100 + 5 * 3 = 115. This means that the quantity has increased to 115 after 3 time intervals.
In option C, Lt = L0 + rt, the formula correctly represents arithmetic growth. The other options do not accurately capture the concept of arithmetic growth or contain incorrect mathematical operations.
Production of Cucumber has increased manifold in recent years. Application of which of the following phytohormones has resulted in this increased yield as the hormone is known to produce female flowers in the plants: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)- a)ABA
- b)Gibberellin
- c)Ethylene
- d)Cytokinin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Production of Cucumber has increased manifold in recent years. Application of which of the following phytohormones has resulted in this increased yield as the hormone is known to produce female flowers in the plants: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
a)
ABA
b)
Gibberellin
c)
Ethylene
d)
Cytokinin
|
|
Sanaya Banerjee answered |
Introduction to Phytohormones and Cucumber Production
The increased production of cucumbers is significantly influenced by the application of phytohormones. Among these hormones, ethylene plays a crucial role in promoting female flower formation, which is essential for enhancing cucumber yields.
Role of Ethylene in Flower Development
- Promotion of Female Flowers: Ethylene is known to stimulate the production of female flowers in cucumber plants. This is critical since female flowers develop into the fruits that we harvest.
- Balance of Flower Types: In cucumber cultivation, a higher ratio of female to male flowers is desirable for maximizing fruit yield. Ethylene shifts this balance, favoring the formation of female flowers.
Application of Ethylene
- Timing: Ethylene can be applied at specific growth stages to ensure the optimal flowering pattern. This can be done through various methods, including the use of ethylene-releasing compounds or controlled environmental conditions.
- Impact on Yield: By increasing the number of female flowers, ethylene directly contributes to higher fruit set and overall yield, making it a valuable tool in cucumber cultivation.
Conclusion
In summary, the application of ethylene is a key factor in the significant increase in cucumber production in recent years. Its ability to induce female flower formation is essential for improving yields, making it an invaluable phytohormone in agricultural practices for cucumbers.
The increased production of cucumbers is significantly influenced by the application of phytohormones. Among these hormones, ethylene plays a crucial role in promoting female flower formation, which is essential for enhancing cucumber yields.
Role of Ethylene in Flower Development
- Promotion of Female Flowers: Ethylene is known to stimulate the production of female flowers in cucumber plants. This is critical since female flowers develop into the fruits that we harvest.
- Balance of Flower Types: In cucumber cultivation, a higher ratio of female to male flowers is desirable for maximizing fruit yield. Ethylene shifts this balance, favoring the formation of female flowers.
Application of Ethylene
- Timing: Ethylene can be applied at specific growth stages to ensure the optimal flowering pattern. This can be done through various methods, including the use of ethylene-releasing compounds or controlled environmental conditions.
- Impact on Yield: By increasing the number of female flowers, ethylene directly contributes to higher fruit set and overall yield, making it a valuable tool in cucumber cultivation.
Conclusion
In summary, the application of ethylene is a key factor in the significant increase in cucumber production in recent years. Its ability to induce female flower formation is essential for improving yields, making it an invaluable phytohormone in agricultural practices for cucumbers.
Which one of the following generally acts as an antagonist to gibberellins? [2012M]- a)Zeatin
- b)Ethylene
- c)ABA
- d)IAA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following generally acts as an antagonist to gibberellins? [2012M]
a)
Zeatin
b)
Ethylene
c)
ABA
d)
IAA

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
Gibberellins & ABA are antagonistic with each other. ABA counteracts many effects of gibberellins like induction of hydrolases and alpha- amylases in barley seedlings.
What reason will you assign for coconut milk used in tissue culture? [2000, 03]- a)Gibberellins
- b)Cytokinins
- c)Auxins
- d)Ethylene
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What reason will you assign for coconut milk used in tissue culture? [2000, 03]
a)
Gibberellins
b)
Cytokinins
c)
Auxins
d)
Ethylene

|
Shivani Rane answered |
The medium in tissue culture provides all the essential nutrients required for growth and division of callus. Coconut milk contains cytokinins which is useful in tissue culture.
Gibberellic acid is a/an:- a)lndole compound
- b)Terpene
- c)Adenine derivative
- d)Carotenoid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Gibberellic acid is a/an:
a)
lndole compound
b)
Terpene
c)
Adenine derivative
d)
Carotenoid
|
|
Ashutosh Rane answered |
Terpene
Gibberellic acid is a type of plant hormone known as a terpene. Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers and flowering plants. They are often responsible for the characteristic scents of plants and have a wide range of biological functions.
Role of Gibberellic Acid
Gibberellic acid plays a crucial role in plant growth and development. It is involved in various processes such as seed germination, stem elongation, leaf expansion, and flowering. This hormone promotes cell division and cell elongation, leading to overall plant growth and development.
Chemical Structure
Gibberellic acid is a diterpenoid compound with a complex structure. It is derived from the terpene precursor geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. The unique structure of gibberellic acid allows it to interact with specific receptors in plant cells, triggering various physiological responses.
Applications
Due to its role in promoting plant growth, gibberellic acid is widely used in agriculture. It is used to increase crop yields, improve fruit quality, and promote flowering in ornamental plants. Additionally, gibberellic acid can be applied to induce seed germination and break seed dormancy in certain plant species.
In conclusion, gibberellic acid is a terpene compound that plays a crucial role in regulating plant growth and development. Its unique chemical structure and biological functions make it an important plant hormone with various applications in agriculture and horticulture.
Gibberellic acid is a type of plant hormone known as a terpene. Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers and flowering plants. They are often responsible for the characteristic scents of plants and have a wide range of biological functions.
Role of Gibberellic Acid
Gibberellic acid plays a crucial role in plant growth and development. It is involved in various processes such as seed germination, stem elongation, leaf expansion, and flowering. This hormone promotes cell division and cell elongation, leading to overall plant growth and development.
Chemical Structure
Gibberellic acid is a diterpenoid compound with a complex structure. It is derived from the terpene precursor geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. The unique structure of gibberellic acid allows it to interact with specific receptors in plant cells, triggering various physiological responses.
Applications
Due to its role in promoting plant growth, gibberellic acid is widely used in agriculture. It is used to increase crop yields, improve fruit quality, and promote flowering in ornamental plants. Additionally, gibberellic acid can be applied to induce seed germination and break seed dormancy in certain plant species.
In conclusion, gibberellic acid is a terpene compound that plays a crucial role in regulating plant growth and development. Its unique chemical structure and biological functions make it an important plant hormone with various applications in agriculture and horticulture.
Which of the following meristem is not responsible for the secondary growth of plants?- a)Apical meristem
- b)Vascular cambium
- c)Lateral meristem
- d)Cork cambium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following meristem is not responsible for the secondary growth of plants?
a)
Apical meristem
b)
Vascular cambium
c)
Lateral meristem
d)
Cork cambium

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- In dicotyledonous plants and gymnosperms, the lateral meristems, vascular cambium and cork cambium appear later in life.
- These are the meristems that cause an increase in the girth of the organs in which they are active.
- This is known as secondary growth of the plant.
Which hormone is responsible for dormancy?- a)Gibberellin
- b)Auxin
- c)Cytokinin
- d)ABA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which hormone is responsible for dormancy?
a)
Gibberellin
b)
Auxin
c)
Cytokinin
d)
ABA

|
Bhavya Yadav answered |
Abscisic acid (ABA)was discovered for its role in regulating abscission and dormancy.
What would be expected to happen if a rotten fruit gets mixed with unripe fruits- a)Slow down the ripening of unripe fruits
- b)Rot the unripe fruits
- c)Unripe fruits have no effect
- d)Hastening ripening of unripe fruits
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What would be expected to happen if a rotten fruit gets mixed with unripe fruits
a)
Slow down the ripening of unripe fruits
b)
Rot the unripe fruits
c)
Unripe fruits have no effect
d)
Hastening ripening of unripe fruits

|
Maitri Mukherjee answered |
Rotten fruit produce ethylene gas that hasten the ripening of unripe fruits. So, if a rotten fruit get mixed with unripe fruits the remaining unripe get ripen faster.
All the cells of the plant are descendants of which of the following?- a)Apical tissue
- b)Intercalary tissue
- c)Meristem
- d)Zygote
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
All the cells of the plant are descendants of which of the following?
a)
Apical tissue
b)
Intercalary tissue
c)
Meristem
d)
Zygote
|
|
Arpita Saha answered |
Understanding Plant Cell Origins
The correct answer to the question regarding the descendants of all plant cells is the zygote. Here’s a detailed explanation:
What is a Zygote?
- A zygote is the initial cell formed when two gametes (sperm and egg) fuse during fertilization.
- This single-celled entity contains genetic material from both parents, representing the beginning of a new organism.
Development from Zygote to Plant Cells
- The zygote undergoes a series of mitotic divisions, leading to the formation of an embryo.
- As the embryo develops, it differentiates into various types of tissues and cells, eventually forming all the organs of the plant.
Comparison with Other Options
- Apical Tissue: This refers to the regions of active growth at the tips of roots and shoots but arises from the meristematic cells developed from the zygote.
- Intercalary Tissue: These tissues are found between mature tissues in plants, especially in monocots, and are also derived from the meristem.
- Meristem: Meristematic tissues are regions of undifferentiated cells and are responsible for growth; however, they originate from the zygote as well.
Conclusion
- All plant cells trace their lineage back to the zygote, making it the foundational cell from which every plant cell type ultimately derives.
- This highlights the importance of the zygote in the plant life cycle and cellular development.
The correct answer to the question regarding the descendants of all plant cells is the zygote. Here’s a detailed explanation:
What is a Zygote?
- A zygote is the initial cell formed when two gametes (sperm and egg) fuse during fertilization.
- This single-celled entity contains genetic material from both parents, representing the beginning of a new organism.
Development from Zygote to Plant Cells
- The zygote undergoes a series of mitotic divisions, leading to the formation of an embryo.
- As the embryo develops, it differentiates into various types of tissues and cells, eventually forming all the organs of the plant.
Comparison with Other Options
- Apical Tissue: This refers to the regions of active growth at the tips of roots and shoots but arises from the meristematic cells developed from the zygote.
- Intercalary Tissue: These tissues are found between mature tissues in plants, especially in monocots, and are also derived from the meristem.
- Meristem: Meristematic tissues are regions of undifferentiated cells and are responsible for growth; however, they originate from the zygote as well.
Conclusion
- All plant cells trace their lineage back to the zygote, making it the foundational cell from which every plant cell type ultimately derives.
- This highlights the importance of the zygote in the plant life cycle and cellular development.
In dicotyledonous plants, girth of stem and root increase due to- a)Development
- b)Primary growth
- c)Secondary growth
- d)Differentiation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In dicotyledonous plants, girth of stem and root increase due to
a)
Development
b)
Primary growth
c)
Secondary growth
d)
Differentiation

|
Maitri Mukherjee answered |
In dicotyledonous plants, girth of stem and root increase due to secondary growth. Secondary growth occurs due to cambium formation in stem and root.
Differentiation of shoot is controlled by [2003]- a)high gibberellin : cytokinin ratio
- b)high auxin : cytokinin ratio
- c)high cytokinin : auxin ratio
- d)high gibberellin : auxin ratio
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Differentiation of shoot is controlled by [2003]
a)
high gibberellin : cytokinin ratio
b)
high auxin : cytokinin ratio
c)
high cytokinin : auxin ratio
d)
high gibberellin : auxin ratio

|
Naveen Menon answered |
Ratio of cytokinins to auxins controls differentiation. If both of these are present in equal quantities, the cells divide but fail to differentiate. If there is more cytokinin than auxin, shoot buds develop. If there is more auxin than cytokinin, roots develop.
One of the synthetic auxin is: [2009]- a)IAA
- b)GA
- c)IBA
- d)NAA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the synthetic auxin is: [2009]
a)
IAA
b)
GA
c)
IBA
d)
NAA

|
Naveen Menon answered |
NAA is a synthetic auxins. Some of the most widely used weed killers are synthetic auxins. Synthetic auxin analogs include 1–naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA), 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid (2,4-D) and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy acetic acid (2,4,5- T).
Phototropic curvature is the result of uneven distribution of: [2010]- a)gibberellin
- b)phytochrome
- c)cytokinins
- d)auxin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Phototropic curvature is the result of uneven distribution of: [2010]
a)
gibberellin
b)
phytochrome
c)
cytokinins
d)
auxin

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
Phototrophic curvature is the result of uneven distribution of auxin. The experiments conducted by Charles Darwin concluded that the tip of coleoptile of canary grass contain auxin that causes the bending of the entire coleoptile towards the light source.
What is a stress hormone? or The hormone produced during adverse environmental conditions is [1993]- a)benzyl aminopurine
- b)dichlorophenoxy acetic acid
- c)ethylene
- d)abscisic acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a stress hormone? or The hormone produced during adverse environmental conditions is [1993]
a)
benzyl aminopurine
b)
dichlorophenoxy acetic acid
c)
ethylene
d)
abscisic acid

|
Devansh Mehra answered |
Abscisic Acid (ABA) is called stress hormone which works in adverse environmental condition when there is low water content in atmosphere or in drought conditions. ABA causes the stomatal closure of leaves due to which the water loss by the plant is minimized.
Which of the following is not the characteristics of the cells of the phase of elongation?- a)Increased vacuolation
- b)Plasmodesmatal connections
- c)Cell enlargement
- d)Cell wall deposition
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not the characteristics of the cells of the phase of elongation?
a)
Increased vacuolation
b)
Plasmodesmatal connections
c)
Cell enlargement
d)
Cell wall deposition

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- Plasmodesmatal connections are not the characteristic cells of the phase of elongation, rather they represent the cells of the meristematic phase of growth.
- Some characteristics of the cells of the phase of elongation include increased vacuolation, cell enlargement and new cell wall deposition which gives strength to the existing cell wall.
Chapter doubts & questions for Plant - Growth & Development - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Plant - Growth & Development - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily











