All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg >
All Questions
All questions of Beams for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
Members used in bridges parallel to traffic are called- a)spandrel
- b)stringers
- c)purlin
- d)joist
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Members used in bridges parallel to traffic are called
a)
spandrel
b)
stringers
c)
purlin
d)
joist
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Stringers are members used in bridges parallel to traffic to carry the deck slab. They will be connected by transverse floor beams.
What is girt?- a)vertical beam spanning between wall column of industrial buildings
- b)horizontal beam spanning between wall column of industrial buildings
- c)vertical beam spanning between wall column of residential buildings
- d)horizontal beam spanning between wall column of residential buildings
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is girt?
a)
vertical beam spanning between wall column of industrial buildings
b)
horizontal beam spanning between wall column of industrial buildings
c)
vertical beam spanning between wall column of residential buildings
d)
horizontal beam spanning between wall column of residential buildings

|
Sahil Mehra answered |
What is girt?
Girt is a structural element used in the construction of industrial and residential buildings. It is a horizontal beam that spans between wall columns, providing support and stability to the structure. In the context of this question, the correct answer is option 'B', which refers to the horizontal beam spanning between wall columns of industrial buildings.
Explanation
1. Girt in Industrial Buildings:
- In industrial buildings, girts are typically used to support the exterior wall cladding and provide structural stability.
- These horizontal beams are installed parallel to the ground and are attached to the columns or vertical structural members of the building.
- Girts are commonly made of steel or wood, depending on the design requirements and building codes.
- They are placed at regular intervals along the height of the wall, providing a framework to attach the exterior cladding material such as metal sheets or panels.
2. Function of Girts:
- Girts play a crucial role in transferring the loads from the exterior cladding to the columns and other structural components of the building.
- They help distribute the wind loads, snow loads, and other lateral forces acting on the building, ensuring stability and preventing damage.
- Girts also provide additional support to the wall panels, preventing them from buckling or deforming under load.
- Moreover, they serve as a nailing surface for attaching the cladding material, allowing for a secure and aesthetically pleasing finish.
3. Girt in Residential Buildings:
- While girts are more commonly associated with industrial buildings, they can also be used in residential construction.
- In the context of residential buildings, girts are typically used as part of the structural system for timber-framed houses.
- These horizontal beams are installed between the vertical wall studs, providing additional strength and stability to the structure.
- Girts in residential buildings are often made of wood and are used in conjunction with other elements such as sheathing and insulation.
Conclusion
In summary, girts are horizontal beams that span between wall columns in both industrial and residential buildings. They provide structural support, distribute loads, and serve as a framework for attaching exterior cladding material. In the context of the given question, the correct answer is option 'B', which refers to the horizontal beam spanning between wall columns of industrial buildings.
Girt is a structural element used in the construction of industrial and residential buildings. It is a horizontal beam that spans between wall columns, providing support and stability to the structure. In the context of this question, the correct answer is option 'B', which refers to the horizontal beam spanning between wall columns of industrial buildings.
Explanation
1. Girt in Industrial Buildings:
- In industrial buildings, girts are typically used to support the exterior wall cladding and provide structural stability.
- These horizontal beams are installed parallel to the ground and are attached to the columns or vertical structural members of the building.
- Girts are commonly made of steel or wood, depending on the design requirements and building codes.
- They are placed at regular intervals along the height of the wall, providing a framework to attach the exterior cladding material such as metal sheets or panels.
2. Function of Girts:
- Girts play a crucial role in transferring the loads from the exterior cladding to the columns and other structural components of the building.
- They help distribute the wind loads, snow loads, and other lateral forces acting on the building, ensuring stability and preventing damage.
- Girts also provide additional support to the wall panels, preventing them from buckling or deforming under load.
- Moreover, they serve as a nailing surface for attaching the cladding material, allowing for a secure and aesthetically pleasing finish.
3. Girt in Residential Buildings:
- While girts are more commonly associated with industrial buildings, they can also be used in residential construction.
- In the context of residential buildings, girts are typically used as part of the structural system for timber-framed houses.
- These horizontal beams are installed between the vertical wall studs, providing additional strength and stability to the structure.
- Girts in residential buildings are often made of wood and are used in conjunction with other elements such as sheathing and insulation.
Conclusion
In summary, girts are horizontal beams that span between wall columns in both industrial and residential buildings. They provide structural support, distribute loads, and serve as a framework for attaching exterior cladding material. In the context of the given question, the correct answer is option 'B', which refers to the horizontal beam spanning between wall columns of industrial buildings.
Which of the following statement is correct?- a)beams are termed as fixed beams when end condition do not carry end moments
- b)beams are termed as simply supported beams when ends are rigidly connected to other members
- c)beams are termed as fixed beams when ends are rigidly connected to other members
- d)beams are termed as continuous beams when they do not extend across more than two support
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is correct?
a)
beams are termed as fixed beams when end condition do not carry end moments
b)
beams are termed as simply supported beams when ends are rigidly connected to other members
c)
beams are termed as fixed beams when ends are rigidly connected to other members
d)
beams are termed as continuous beams when they do not extend across more than two support
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Beams may be termed as simply supported beams when end condition do not carry any end moments from any continuity developed by connection. A beam is called continuous beam when it extends continuously across more than two supports. A fixed beam has its ends rigidly connected to other members, so that moments can be carried across the connection.
Design of lintel is carried out for- a)weight of slab
- b)no load is considered from masonry load above the opening
- c)small portion of masonry load above the opening
- d)large portion of masonry load above the opening
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Design of lintel is carried out for
a)
weight of slab
b)
no load is considered from masonry load above the opening
c)
small portion of masonry load above the opening
d)
large portion of masonry load above the opening

|
Shraddha Datta answered |
Understanding Lintel Design
When designing a lintel, it is essential to consider the loads it must support. Lintels are structural elements that span openings such as doors and windows, transferring loads from the structure above down to the supports (walls, columns).
Key Load Considerations
- Weight of Slab: While the weight of the slab is important, it is not the only load to be considered in lintel design. The slab's weight contributes to the overall vertical load, but it doesn't encompass the entire scenario.
- Masonry Load Above the Opening: The loads from the masonry walls above the opening are crucial. They can vary based on the height and material of the wall.
- Small Portion of Masonry Load: Ignoring masonry loads or considering only a small portion can lead to underestimating the lintel's required strength. This option is incorrect as proper design must account for a significant portion of the load.
- Large Portion of Masonry Load: This is where option 'C' becomes relevant. A lintel must be designed to carry a substantial portion of the masonry load above the opening. This ensures it can safely distribute the weight and prevent failure.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct approach to lintel design acknowledges that a lintel must carry a large portion of the masonry load above the opening to ensure structural integrity. Proper calculations and considerations of the loads involved will lead to a safe and effective design.
When designing a lintel, it is essential to consider the loads it must support. Lintels are structural elements that span openings such as doors and windows, transferring loads from the structure above down to the supports (walls, columns).
Key Load Considerations
- Weight of Slab: While the weight of the slab is important, it is not the only load to be considered in lintel design. The slab's weight contributes to the overall vertical load, but it doesn't encompass the entire scenario.
- Masonry Load Above the Opening: The loads from the masonry walls above the opening are crucial. They can vary based on the height and material of the wall.
- Small Portion of Masonry Load: Ignoring masonry loads or considering only a small portion can lead to underestimating the lintel's required strength. This option is incorrect as proper design must account for a significant portion of the load.
- Large Portion of Masonry Load: This is where option 'C' becomes relevant. A lintel must be designed to carry a substantial portion of the masonry load above the opening. This ensures it can safely distribute the weight and prevent failure.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct approach to lintel design acknowledges that a lintel must carry a large portion of the masonry load above the opening to ensure structural integrity. Proper calculations and considerations of the loads involved will lead to a safe and effective design.
Complex stresses may occur when- a)loads are inclined to principal axes
- b)loads are along principal axes
- c)symmetrical section are used
- d)small values of shear and bending moment occur at section
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Complex stresses may occur when
a)
loads are inclined to principal axes
b)
loads are along principal axes
c)
symmetrical section are used
d)
small values of shear and bending moment occur at section
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Complex stresses may arise when loads are inclined to principal axes, when unsymmetrical sections are used or when large values of shear and bending moment occur at section.
Which of the following aspects need not be considered for beam design?- a)deflection
- b)material of beam
- c)buckling
- d)lateral supports
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following aspects need not be considered for beam design?
a)
deflection
b)
material of beam
c)
buckling
d)
lateral supports
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The important aspects which need to be considered for beam design are moments, shears, deflection, crippling, buckling, and lateral support.
What are lintels?- a)beams provided in foundation
- b)beams on roof of building
- c)columns above openings in wall
- d)beams above openings in wall
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are lintels?
a)
beams provided in foundation
b)
beams on roof of building
c)
columns above openings in wall
d)
beams above openings in wall

|
Garima Kulkarni answered |
Lintels:
A lintel is a structural element that is used to support the load above an opening in a wall, such as a door or window. It is typically a horizontal beam that spans the opening and transfers the load from above down to the walls on either side. Lintels are an essential component in ensuring the stability and structural integrity of a building.
Importance of lintels:
- Lintels help distribute the weight of the structure above the opening evenly to prevent any sagging or collapsing.
- They provide support for the masonry or other materials above the opening, allowing for larger and more complex architectural designs.
- Lintels help to maintain the overall structural integrity of the building and prevent any potential damage or failure.
Types of lintels:
- Wooden lintels: Traditionally used in older buildings, wooden lintels are still used today in certain construction projects.
- Steel lintels: Commonly used in modern construction due to their strength and durability, steel lintels are often the preferred choice for larger openings.
- Concrete lintels: Made from precast concrete, these lintels are cost-effective and offer good load-bearing capacity.
Installation of lintels:
- Lintels are typically placed above doors, windows, and other openings in walls during the construction process.
- Proper installation is crucial to ensure that the lintel can support the load above and distribute it safely to the surrounding structure.
- The size and material of the lintel should be carefully chosen based on the design requirements and load calculations.
In conclusion, lintels play a critical role in the construction of buildings by providing support above openings in walls. Proper selection and installation of lintels are essential to ensure the structural integrity and stability of the overall building.
A lintel is a structural element that is used to support the load above an opening in a wall, such as a door or window. It is typically a horizontal beam that spans the opening and transfers the load from above down to the walls on either side. Lintels are an essential component in ensuring the stability and structural integrity of a building.
Importance of lintels:
- Lintels help distribute the weight of the structure above the opening evenly to prevent any sagging or collapsing.
- They provide support for the masonry or other materials above the opening, allowing for larger and more complex architectural designs.
- Lintels help to maintain the overall structural integrity of the building and prevent any potential damage or failure.
Types of lintels:
- Wooden lintels: Traditionally used in older buildings, wooden lintels are still used today in certain construction projects.
- Steel lintels: Commonly used in modern construction due to their strength and durability, steel lintels are often the preferred choice for larger openings.
- Concrete lintels: Made from precast concrete, these lintels are cost-effective and offer good load-bearing capacity.
Installation of lintels:
- Lintels are typically placed above doors, windows, and other openings in walls during the construction process.
- Proper installation is crucial to ensure that the lintel can support the load above and distribute it safely to the surrounding structure.
- The size and material of the lintel should be carefully chosen based on the design requirements and load calculations.
In conclusion, lintels play a critical role in the construction of buildings by providing support above openings in walls. Proper selection and installation of lintels are essential to ensure the structural integrity and stability of the overall building.
Castellated beams have ______ shear capacity than original beams- a)shear capacity does not change
- b)twice
- c)increased
- d)reduced
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Castellated beams have ______ shear capacity than original beams
a)
shear capacity does not change
b)
twice
c)
increased
d)
reduced

|
Pallabi Bajaj answered |
Introduction:
Castellated beams are structural members that have been modified by cutting a series of slots or openings along the web of the beam. These slots create a series of individual cells or castellations that reduce the weight of the beam without sacrificing its strength. The modification in the form of castellations affects various properties of the beam, including its shear capacity.
Explanation:
The shear capacity of a beam refers to its ability to resist shear forces. Shear forces are forces that act parallel to the cross-section of the beam and can cause the beam to slide or deform sideways. The shear capacity of a beam is directly related to its cross-sectional area and the material properties.
Comparison:
When comparing castellated beams to original beams, it is important to note that the modification in the form of castellations reduces the cross-sectional area of the beam. The slots or openings in the web of the beam result in a decrease in the effective area of the cross-section, thereby reducing its shear capacity.
Reason for reduced shear capacity:
The reduction in the cross-sectional area of the beam due to castellations leads to a decrease in the amount of material available to resist shear forces. As a result, the shear capacity of castellated beams is reduced compared to the shear capacity of original beams.
Effect on structural design:
The reduced shear capacity of castellated beams must be taken into account during structural design. Engineers need to consider the lower shear capacity when determining the load-bearing capacity of the beam and ensuring that it can safely support the applied loads.
Conclusion:
In summary, castellated beams have a reduced shear capacity compared to original beams. This reduction is due to the decrease in the cross-sectional area of the beam caused by the slots or openings in the web. Engineers must consider this reduced shear capacity during the design process to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the overall system.
Castellated beams are structural members that have been modified by cutting a series of slots or openings along the web of the beam. These slots create a series of individual cells or castellations that reduce the weight of the beam without sacrificing its strength. The modification in the form of castellations affects various properties of the beam, including its shear capacity.
Explanation:
The shear capacity of a beam refers to its ability to resist shear forces. Shear forces are forces that act parallel to the cross-section of the beam and can cause the beam to slide or deform sideways. The shear capacity of a beam is directly related to its cross-sectional area and the material properties.
Comparison:
When comparing castellated beams to original beams, it is important to note that the modification in the form of castellations reduces the cross-sectional area of the beam. The slots or openings in the web of the beam result in a decrease in the effective area of the cross-section, thereby reducing its shear capacity.
Reason for reduced shear capacity:
The reduction in the cross-sectional area of the beam due to castellations leads to a decrease in the amount of material available to resist shear forces. As a result, the shear capacity of castellated beams is reduced compared to the shear capacity of original beams.
Effect on structural design:
The reduced shear capacity of castellated beams must be taken into account during structural design. Engineers need to consider the lower shear capacity when determining the load-bearing capacity of the beam and ensuring that it can safely support the applied loads.
Conclusion:
In summary, castellated beams have a reduced shear capacity compared to original beams. This reduction is due to the decrease in the cross-sectional area of the beam caused by the slots or openings in the web. Engineers must consider this reduced shear capacity during the design process to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the overall system.
The new rolled section of castellated beam will have depth- a)50% more than original section
- b)50% less than original section
- c)25% less than original section
- d)depth does not change
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The new rolled section of castellated beam will have depth
a)
50% more than original section
b)
50% less than original section
c)
25% less than original section
d)
depth does not change

|
Rajat Sen answered |
Understanding Castellated Beams
Castellated beams are structural elements formed by cutting a standard beam and then reassembling it to create a section with openings. This design enhances the beam's strength-to-weight ratio and allows for the passage of services.
Depth Modification
When creating a castellated beam, the depth of the beam is influenced by the process of cutting and reconfiguring.
Why 50% More Depth?
- Increased Structural Capacity: The new design with castellations allows for a greater depth, improving the beam’s moment of inertia, which is crucial for resisting bending.
- Enhanced Load Distribution: A deeper section allows the beam to distribute loads more efficiently across its span, making it suitable for larger load applications.
- Design Flexibility: The increased depth provides more space for services such as HVAC, plumbing, and electrical systems, making it a versatile option in construction.
Applications
- Commercial Buildings: Used in offices and warehouses where large open spaces are required without columns.
- Bridges: Offers reduced self-weight with high load-carrying capacity, ideal for long spans.
Conclusion
The decision to make the new castellated beam 50% deeper than the original section is rooted in engineering principles aimed at enhancing structural performance. This modification results in a beam that is not only stronger but also more functional in modern construction applications.
Castellated beams are structural elements formed by cutting a standard beam and then reassembling it to create a section with openings. This design enhances the beam's strength-to-weight ratio and allows for the passage of services.
Depth Modification
When creating a castellated beam, the depth of the beam is influenced by the process of cutting and reconfiguring.
Why 50% More Depth?
- Increased Structural Capacity: The new design with castellations allows for a greater depth, improving the beam’s moment of inertia, which is crucial for resisting bending.
- Enhanced Load Distribution: A deeper section allows the beam to distribute loads more efficiently across its span, making it suitable for larger load applications.
- Design Flexibility: The increased depth provides more space for services such as HVAC, plumbing, and electrical systems, making it a versatile option in construction.
Applications
- Commercial Buildings: Used in offices and warehouses where large open spaces are required without columns.
- Bridges: Offers reduced self-weight with high load-carrying capacity, ideal for long spans.
Conclusion
The decision to make the new castellated beam 50% deeper than the original section is rooted in engineering principles aimed at enhancing structural performance. This modification results in a beam that is not only stronger but also more functional in modern construction applications.
_____ section is suitable for small openings and _____ section is suitable for large openings- a)flat, I-section
- b)I-section, flat
- c)angles, flat
- d)angles, angles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
_____ section is suitable for small openings and _____ section is suitable for large openings
a)
flat, I-section
b)
I-section, flat
c)
angles, flat
d)
angles, angles

|
Sanaya Sengupta answered |
Understanding Structural Sections
In civil engineering, the choice of structural sections is critical for ensuring that constructions are both efficient and safe. Different sections serve different purposes based on the size and load requirements of the application.
Flat Sections
- Flat sections, also known as plate sections, are ideal for small openings.
- They provide sufficient strength for minor load-bearing applications.
- Their simplicity allows for easy installation and cost-effectiveness in smaller structures.
I-Sections
- I-sections, or I-beams, are suitable for large openings.
- They offer greater load-bearing capacity due to their shape, which maximizes resistance to bending and shear.
- The design allows for efficient use of material, making them favorable for larger spans in beams and girders.
Comparison
- Flat sections are less complex and suitable for smaller loads, making them easier to work with in confined spaces.
- I-sections are robust and designed to handle significant structural loads, making them essential in larger constructions like bridges and high-rise buildings.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate section is vital for achieving structural integrity. Flat sections are best for small openings, while I-sections are designed to support larger openings and heavier loads. Understanding the application of each section is fundamental for any civil engineer involved in design and construction.
In civil engineering, the choice of structural sections is critical for ensuring that constructions are both efficient and safe. Different sections serve different purposes based on the size and load requirements of the application.
Flat Sections
- Flat sections, also known as plate sections, are ideal for small openings.
- They provide sufficient strength for minor load-bearing applications.
- Their simplicity allows for easy installation and cost-effectiveness in smaller structures.
I-Sections
- I-sections, or I-beams, are suitable for large openings.
- They offer greater load-bearing capacity due to their shape, which maximizes resistance to bending and shear.
- The design allows for efficient use of material, making them favorable for larger spans in beams and girders.
Comparison
- Flat sections are less complex and suitable for smaller loads, making them easier to work with in confined spaces.
- I-sections are robust and designed to handle significant structural loads, making them essential in larger constructions like bridges and high-rise buildings.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate section is vital for achieving structural integrity. Flat sections are best for small openings, while I-sections are designed to support larger openings and heavier loads. Understanding the application of each section is fundamental for any civil engineer involved in design and construction.
In which of the following cases are castellated beam desirable?- a)when more span to be covered than rolled section
- b)when beam subjected to substantial concentrated loads
- c)when beam to be used as continuous beam
- d)when higher fire resistance than rolled section required
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following cases are castellated beam desirable?
a)
when more span to be covered than rolled section
b)
when beam subjected to substantial concentrated loads
c)
when beam to be used as continuous beam
d)
when higher fire resistance than rolled section required
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The section of castellated beam will have more depth and section modulus than original rolled section. This allows the beam to span further than parent rolled section. Castellated beams may not be desirable when beam is subjected to substantial concentrated loads, or when castellated beam is used as a continuous beam across several supports. Castellated beams are less attractive when very high requirements for fire resistance are required because the fire resistant coating has to be around 20% thicker than for rolled sections in order to obtain the same fire resistance as rolled section.
When the slab over lintel is below apex of equilateral triangle formed on lintel, load of masonry is considered as- a)rectangular load
- b)triangular load
- c)trapezoidal load
- d)no load is considered
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the slab over lintel is below apex of equilateral triangle formed on lintel, load of masonry is considered as
a)
rectangular load
b)
triangular load
c)
trapezoidal load
d)
no load is considered
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
When the slab over lintel is below apex of equilateral triangle formed on lintel, the load of masonry in the rectangle is considered. The load of masonry in the rectangle is assumed to act over by taking length equal to span of lintel and height equal to clear height of slab above the lintel.
Which of the following buckling does not occur in beam?- a)lateral buckling of whole beam
- b)local buckling of web
- c)local buckling of flanges
- d)longitudinal buckling of web
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following buckling does not occur in beam?
a)
lateral buckling of whole beam
b)
local buckling of web
c)
local buckling of flanges
d)
longitudinal buckling of web
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Buckling may take place in many ways : (i) lateral buckling of whole beam between supports, (ii) local buckling of flanges, (iii) longitudinal buckling of web and buckling in depth direction under concentrated loads.
When the slab over lintel is above apex of equilateral triangle formed on lintel, load of masonry is considered as- a)rectangular load
- b)triangular load
- c)trapezoidal load
- d)no load is considered
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the slab over lintel is above apex of equilateral triangle formed on lintel, load of masonry is considered as
a)
rectangular load
b)
triangular load
c)
trapezoidal load
d)
no load is considered

|
Anuj Verma answered |
Explanation:
Equilateral Triangle:
- An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are equal in length and all three angles are equal to 60 degrees.
Slab over Lintel:
- When the slab is constructed over a lintel, the load of the masonry above the lintel needs to be considered for structural analysis.
Position of Slab:
- If the slab over the lintel is above the apex of the equilateral triangle formed on the lintel, the load of the masonry is considered as a triangular load.
Load Consideration:
- In this case, the load distribution on the lintel will be triangular in shape, with the maximum load at the apex of the equilateral triangle and decreasing towards the base.
Effect on Structural Analysis:
- Considering the load as a triangular load is important for accurate structural analysis and design, as it reflects the actual distribution of forces on the lintel.
Therefore, when the slab over the lintel is above the apex of the equilateral triangle formed on the lintel, the load of masonry is considered as a triangular load.
Equilateral Triangle:
- An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are equal in length and all three angles are equal to 60 degrees.
Slab over Lintel:
- When the slab is constructed over a lintel, the load of the masonry above the lintel needs to be considered for structural analysis.
Position of Slab:
- If the slab over the lintel is above the apex of the equilateral triangle formed on the lintel, the load of the masonry is considered as a triangular load.
Load Consideration:
- In this case, the load distribution on the lintel will be triangular in shape, with the maximum load at the apex of the equilateral triangle and decreasing towards the base.
Effect on Structural Analysis:
- Considering the load as a triangular load is important for accurate structural analysis and design, as it reflects the actual distribution of forces on the lintel.
Therefore, when the slab over the lintel is above the apex of the equilateral triangle formed on the lintel, the load of masonry is considered as a triangular load.
Which of the following measures can be taken to improve shear capacity of castellated beams?- a)openings can be made away from neutral axis
- b)openings can be made close to neutral axis
- c)making cuts in straight manner
- d)by not using stiffenings
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following measures can be taken to improve shear capacity of castellated beams?
a)
openings can be made away from neutral axis
b)
openings can be made close to neutral axis
c)
making cuts in straight manner
d)
by not using stiffenings
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Shear capacity of castellated beams can be improved by making openings close to neutral axis and making cuts in a wavy manner. Stiffening can be provided at load concentrations and reaction points to improve its shear carrying capacity.
What is beam?- a)structural member subjected to transverse loads
- b)structural member subjected to axial loads only
- c)structural member subjected to seismic loads only
- d)structural member subjected to transverse loads only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is beam?
a)
structural member subjected to transverse loads
b)
structural member subjected to axial loads only
c)
structural member subjected to seismic loads only
d)
structural member subjected to transverse loads only
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Beam is a structural member subjected to transverse loads that is loads perpendicular to its longitudinal axis. The mode of deflection of beam is primarily by bending.
Structural members subjected to bending and large axial compressive loads are known as- a)strut
- b)purlin
- c)beam-column
- d)lintel
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Structural members subjected to bending and large axial compressive loads are known as
a)
strut
b)
purlin
c)
beam-column
d)
lintel
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Structural members subjected to bending accompanied by large axial compressive loads at the same time are known as beam-column. A beam-column differs from column only by presence of eccentricity of load application, end moment, transverse load.
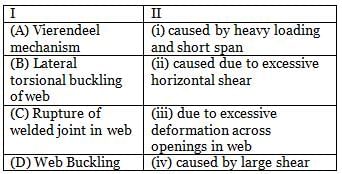
Match the Pairs
- a)A-i, B-ii, C-iii, D-iv
- b)A-iv, B-iii, C-ii, D-i
- c)A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
- d)A-i, B-iv, C-iii, D-ii
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the Pairs


a)
A-i, B-ii, C-iii, D-iv
b)
A-iv, B-iii, C-ii, D-i
c)
A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
d)
A-i, B-iv, C-iii, D-ii
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
There are number of possible modes of failure for castellated beams. Some of them are as follows:
(i) Vierendeel mechanism – occurs due to excessive deformation across one of the openings in web and formation of hinges in corners of castellation,
(ii) Lateral torsional buckling of web – caused by large shear at welded joint,
(iii) Rupture of welded joint in web – caused due to excessive horizontal shear at welded joint in the web,
(iv) Web Buckling – caused by heavy loading and short span of beam, this may be avoided at support by filling firt castellation by welding plate in the hole.
(i) Vierendeel mechanism – occurs due to excessive deformation across one of the openings in web and formation of hinges in corners of castellation,
(ii) Lateral torsional buckling of web – caused by large shear at welded joint,
(iii) Rupture of welded joint in web – caused due to excessive horizontal shear at welded joint in the web,
(iv) Web Buckling – caused by heavy loading and short span of beam, this may be avoided at support by filling firt castellation by welding plate in the hole.
Which of the following is not an advantage of castellated beam?- a)light in weight
- b)can be assembled fast
- c)cheaper
- d)high fire resistance than original rolled section
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an advantage of castellated beam?
a)
light in weight
b)
can be assembled fast
c)
cheaper
d)
high fire resistance than original rolled section
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Castellated beams are light in weight, cheaper, they have relatively high resistance and can be assembled fast at the construction site. They are less fire resistant than normal rolled sections. Castellated beams can very easily be cambered and cranked.
Load transfer by a beam is primarily by- a)bending only
- b)shear only
- c)bending and shear
- d)neither bending nor shear
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Load transfer by a beam is primarily by
a)
bending only
b)
shear only
c)
bending and shear
d)
neither bending nor shear

|
Navya Saha answered |
Load Transfer by a Beam
The transfer of loads in a beam primarily occurs through a combination of bending and shear. Both bending and shear forces play a significant role in determining the load-carrying capacity and behavior of a beam. Let's discuss each of these load transfer mechanisms in detail.
Bending
Bending is the most important load transfer mechanism in a beam. When a load is applied to a beam, it causes the beam to bend or deform. This bending occurs due to the moments induced by the applied load. The load causes one part of the beam to be in compression, while the other part experiences tension. This results in the formation of internal bending moments within the beam.
The bending moment varies along the length of the beam and is maximum at the points where the load is applied or supported. The magnitude of the bending moment depends on the load intensity, the distance of the load from the support, and the beam's cross-sectional properties. The bending moment induces stresses in the beam, and the beam's ability to resist these stresses determines its load-carrying capacity.
Shear
Shear is another important load transfer mechanism in a beam. When a load is applied to a beam, it also induces shear forces. These shear forces act parallel to the cross-section of the beam and cause the beam to deform in a shearing manner. The shear force varies along the length of the beam and is maximum at the points where the load is applied or supported.
The magnitude of the shear force depends on the load intensity and the beam's cross-sectional properties. The shear force induces shear stresses in the beam, and the beam's ability to resist these stresses determines its load-carrying capacity.
Combined Effect
In most cases, the load transfer in a beam is a combination of bending and shear. The applied load causes both bending moments and shear forces to develop in the beam. The beam's resistance to bending and shear stresses determines its overall load-carrying capacity.
It is important to consider both bending and shear in the design of beams to ensure their structural integrity and safety. Engineers analyze the forces and moments acting on a beam to determine its maximum bending and shear capacities. By designing beams that can efficiently resist both bending and shear, the load transfer can be effectively managed, ensuring the stability and strength of the structure.
In conclusion, the load transfer by a beam is primarily through a combination of bending and shear. Both bending moments and shear forces play a crucial role in determining the load-carrying capacity and behavior of a beam.
The transfer of loads in a beam primarily occurs through a combination of bending and shear. Both bending and shear forces play a significant role in determining the load-carrying capacity and behavior of a beam. Let's discuss each of these load transfer mechanisms in detail.
Bending
Bending is the most important load transfer mechanism in a beam. When a load is applied to a beam, it causes the beam to bend or deform. This bending occurs due to the moments induced by the applied load. The load causes one part of the beam to be in compression, while the other part experiences tension. This results in the formation of internal bending moments within the beam.
The bending moment varies along the length of the beam and is maximum at the points where the load is applied or supported. The magnitude of the bending moment depends on the load intensity, the distance of the load from the support, and the beam's cross-sectional properties. The bending moment induces stresses in the beam, and the beam's ability to resist these stresses determines its load-carrying capacity.
Shear
Shear is another important load transfer mechanism in a beam. When a load is applied to a beam, it also induces shear forces. These shear forces act parallel to the cross-section of the beam and cause the beam to deform in a shearing manner. The shear force varies along the length of the beam and is maximum at the points where the load is applied or supported.
The magnitude of the shear force depends on the load intensity and the beam's cross-sectional properties. The shear force induces shear stresses in the beam, and the beam's ability to resist these stresses determines its load-carrying capacity.
Combined Effect
In most cases, the load transfer in a beam is a combination of bending and shear. The applied load causes both bending moments and shear forces to develop in the beam. The beam's resistance to bending and shear stresses determines its overall load-carrying capacity.
It is important to consider both bending and shear in the design of beams to ensure their structural integrity and safety. Engineers analyze the forces and moments acting on a beam to determine its maximum bending and shear capacities. By designing beams that can efficiently resist both bending and shear, the load transfer can be effectively managed, ensuring the stability and strength of the structure.
In conclusion, the load transfer by a beam is primarily through a combination of bending and shear. Both bending moments and shear forces play a crucial role in determining the load-carrying capacity and behavior of a beam.
Simple bending takes place if- a)loading passes above shear centre for single symmetric open section
- b)loading passes below shear centre for single symmetric open section
- c)loading plane coincides with one of the principal planes of doubly symmetric section
- d)loading plane do not coincide with one of the principal planes of doubly symmetric section
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Simple bending takes place if
a)
loading passes above shear centre for single symmetric open section
b)
loading passes below shear centre for single symmetric open section
c)
loading plane coincides with one of the principal planes of doubly symmetric section
d)
loading plane do not coincide with one of the principal planes of doubly symmetric section
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Simple bending takes place if loading plane coincides with one of the principal planes of doubly symmetric section such as I-section or in case of singly symmetric open section such as channel section, the loading passes through shear centre and is parallel to the principal plane. Unsymmetrical bending occurs if loading does not pass through shear centre.
Match the Pair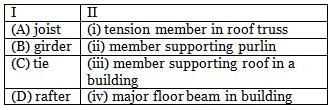
- a)A-i, B-ii, C-iii, D-iv
- b)A-iv, B-iii, C-ii, D-i
- c)A-ii, B-iv, C-iii, D-i
- d)A-iii, B-iv, C-i, D-ii
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the Pair

a)
A-i, B-ii, C-iii, D-iv
b)
A-iv, B-iii, C-ii, D-i
c)
A-ii, B-iv, C-iii, D-i
d)
A-iii, B-iv, C-i, D-ii
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Joist is a member supporting roof in a building. Girder is a major floor beam in building. Tie is tension member in roof truss and rafter is a member supporting purlin.
Members used to carry wall loads over wall openings are called- a)purlin
- b)rafter
- c)girder
- d)lintels
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Members used to carry wall loads over wall openings are called
a)
purlin
b)
rafter
c)
girder
d)
lintels
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Lintels are beam members used to carry wall loads over wall openings for doors, windows, etc.
What are spandrels?- a)exterior beams at floor level of buildings
- b)interior beams at floor level of buildings
- c)exterior columns
- d)interior columns
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What are spandrels?
a)
exterior beams at floor level of buildings
b)
interior beams at floor level of buildings
c)
exterior columns
d)
interior columns
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Spandrels are exterior beams at floor level of buildings, which carry part of floor load and exterior wall.
What is castellated beam?- a)beam with no openings in web
- b)beam with number of regular openings in web and flange
- c)beam with number of regular openings in web
- d)beam with number of regular openings in flange
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is castellated beam?
a)
beam with no openings in web
b)
beam with number of regular openings in web and flange
c)
beam with number of regular openings in web
d)
beam with number of regular openings in flange
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
A beam with number of regular openings in its web is called castellated beam. A castellated beam is formed by flame cutting a single rolled wide flange beam in a definite predetermined pattern and then rejoining the segments by welding to form a regular pattern of holes in the web.
Chapter doubts & questions for Beams - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Beams - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg
488 videos|1261 docs|878 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









