All Exams >
Computer Science Engineering (CSE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE >
All Questions
All questions of Syllabus & Full Mock Tests for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam
Find the output#include <iostream>#define cnct(x,y) x##yusing namespace std;class {public:int p,q,pq;int f1(){cout<<p+q+pq+cnct(p,q)<<endl;return (p+++q);}}c;int main(){c.p=5,c.q=6,c.pq=15;cout<<c.f1();return 0;}- a)Error occurs due to absence of class name
- b)41,11
- c)80,11
- d)80,12
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the output
#include <iostream>
#define cnct(x,y) x##y
using namespace std;
class {
public:
int p,q,pq;
int f1()
{
cout<<p+q+pq+cnct(p,q)<<endl;
return (p+++q);
}
}c;
int main(){
c.p=5,c.q=6,c.pq=15;
cout<<c.f1();
return 0;
}
a)
Error occurs due to absence of class name
b)
41,11
c)
80,11
d)
80,12
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
41, 11
Class without name is allowed. In this case object of class is created along with definition.
cnct(x,y) x##y ,## is a preprocessor macro used for concatenation.
x##y= xy
Call this creates a single terms named xy,here in main pq; cnct(p,q) places value of pq in its position that is 15.
cout<<p+q+pq+cnct(p,q)
5+6+15+15=41
P+++q is interpreted here as p++ + q(1st two for post increment operator,3rd one operator for adding )
Plus operator(+) has higher precedence than post increment operator. So, Value of p & q (5 & 6) get added before p increments. So, p+++q->11
Consider a system employing an interrupt driven I/O for a articular device that transfers data at an average of 8 KB/s on a continuous basis. Assume that interrupt processing takes about 100 micro seconds (i.e. jump to the interrupt service routine (ISR); execute it and return to the main program). Determine what fraction of processor time is consumed by this I/O device when it is interrupted for every byte.
Correct answer is '0.82'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a system employing an interrupt driven I/O for a articular device that transfers data at an average of 8 KB/s on a continuous basis. Assume that interrupt processing takes about 100 micro seconds (i.e. jump to the interrupt service routine (ISR); execute it and return to the main program). Determine what fraction of processor time is consumed by this I/O device when it is interrupted for every byte.
|
|
Milan Chavan answered |
The device generates 8 × 1024 = 8192 bytes/sec
i.e. 1 second 8192 bytes
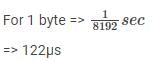
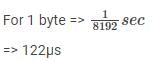
Given that each interrupt consumes 100.μs
Fraction of proce ssor time consumed in 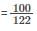 (for every byte)=0.82
(for every byte)=0.82
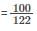 (for every byte)=0.82
(for every byte)=0.82During intermediate code generation, we use 3 - address code in which we have 3 forms available:Quadruples, Triples and Indirect Triples.Now, consider the below statements:S1: In Quadruples, statements can be moved around.S2: In Triples, space is not wasted.S3: In Indirect Triples, space is not wasted but access time increases.Which is correct?- a) S1
- b) S2
- c) S3
- d) None of these
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
During intermediate code generation, we use 3 - address code in which we have 3 forms available:
Quadruples, Triples and Indirect Triples.
Now, consider the below statements:
S1: In Quadruples, statements can be moved around.
S2: In Triples, space is not wasted.
S3: In Indirect Triples, space is not wasted but access time increases.
Which is correct?
a)
S1
b)
S2
c)
S3
d)
None of these

|
Riverdale Learning Institute answered |
As we know,
S1: It is true, in quadruples, statements can be moved.
S2: In Triples, space is not wasted because the result field is not used.
S3: In Indirect Triples, space is not wasted but access time increases.
Here two memory access is required, that’s why access time is more.
Hence, the correct options are (A), (B) and (C).
How many separate address and data lines are needed for a memory of 8 K × 16 ?- a)13 address, 3 data lines
- b)13 address, 16 data lines
- c)12 address, 4 data lines
- d)13 address, 4 data lines
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many separate address and data lines are needed for a memory of 8 K × 16 ?
a)
13 address, 3 data lines
b)
13 address, 16 data lines
c)
12 address, 4 data lines
d)
13 address, 4 data lines
|
|
Shanaya Chopra answered |
For a memory of 8 K, we need 13 address lines and 8 data lines.
Explanation:
- 8 K means 8 kilobytes. 1 kilobyte = 1024 bytes. Therefore, 8 K = 8 * 1024 = 8192 bytes.
- To address each byte in the memory, we need a unique address. The number of unique addresses that can be generated with n address lines is 2^n. Therefore, we need 2^13 = 8192 unique addresses to address each byte in the memory.
- Hence, we need 13 address lines to generate these 8192 unique addresses.
- To read or write data from/to the memory, we need a data bus consisting of data lines. Since the memory has a capacity of 8192 bytes, we need 8 data lines to transfer 8 bits of data at a time (1 byte).
Explanation:
- 8 K means 8 kilobytes. 1 kilobyte = 1024 bytes. Therefore, 8 K = 8 * 1024 = 8192 bytes.
- To address each byte in the memory, we need a unique address. The number of unique addresses that can be generated with n address lines is 2^n. Therefore, we need 2^13 = 8192 unique addresses to address each byte in the memory.
- Hence, we need 13 address lines to generate these 8192 unique addresses.
- To read or write data from/to the memory, we need a data bus consisting of data lines. Since the memory has a capacity of 8192 bytes, we need 8 data lines to transfer 8 bits of data at a time (1 byte).
4 taps marked as T1, T2, T3 and T4 can fill a tank in 8 hours,12 hours, 16 hours and 24hours respectively. We have to fill up 2 identical tanks with 2 out of these 4 taps connected to tank 1 and remaining two taps connected to tank 2 so that the ratio of time taken to fill tank 1 and tank 2 is 2:3. so identify one of the pair of taps?- a)T1 and T2
- b)T1 and T3
- c)T2 and T3
- d)T1 and T4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
4 taps marked as T1, T2, T3 and T4 can fill a tank in 8 hours,12 hours, 16 hours and 24hours respectively. We have to fill up 2 identical tanks with 2 out of these 4 taps connected to tank 1 and remaining two taps connected to tank 2 so that the ratio of time taken to fill tank 1 and tank 2 is 2:3. so identify one of the pair of taps?
a)
T1 and T2
b)
T1 and T3
c)
T2 and T3
d)
T1 and T4
|
|
Arnav Gupta answered |
Let us assume the capacity of the tank to be 48 units (48 being LCM of 8, 12, 16 and 24). This leads us to get the rate of filing of T1 to 4 as 6, 4, 3 and 2 units per hour.
Taking pairs of taps, we find that T1 + T2 will take 48/10 whereas the remaining pair will take 48/5 hours leading to the ratio of time taken to fill up 2 tanks as 5:10 which is not the required ratio.
Taking T1 and T3, the time taken is 48/9 and the time taken for the other tank is 48/6 leading to the required ratio as 2:3.
Consider the following C program:int main(){printf("what %%");return 0;} What does the code print?- a) What %
- b)\“What %% \“
- c)What %%
- d)Compiler Error
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following C program:
int main(){
printf("what %%");
return 0;
}
What does the code print?
a)
What %
b)
\“What %% \“
c)
What %%
d)
Compiler Error
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Backslash actually acts an escape character and helps to print double quotes, where % can be printed only with double % i.e. %%
A monkey is trying to reach the top of a tree. He climbs 3 feet in a minute but slides down by 1.5 feet after each climb. If he reaches the top of the tree in 58 minutes, then the maximum possible height of the tree is ____ feets.- a)85.0
- b)87.3
- c)88.5
- d)90.1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A monkey is trying to reach the top of a tree. He climbs 3 feet in a minute but slides down by 1.5 feet after each climb. If he reaches the top of the tree in 58 minutes, then the maximum possible height of the tree is ____ feets.
a)
85.0
b)
87.3
c)
88.5
d)
90.1
|
|
Sanaya Chauhan answered |
You have to carefully observe the point that in the last minute, we DO NOT have to consider the sliding down of the monkey since the question states that the monkey reaches the top of the tree.Out of 58 minutes, the climb by monkey in 58th minute is 3 feet whereas for each of his earlier climbs, the monkey covers a net distance of 3-1.5=1.5 feet.We can work out the maximum possible height of the tree as 1.5×57+3=85.5+3=88.5 feet
Which of the following statements is incorrect?- a)Circuit switching takes place at physical layer and a circuit switched network is made of a set of switches connected by physical links, in which each link is divided into n channels.
- b)In packet switching, there is no reserved bandwidths on the links and there is no scheduled processing time for each packet.
- c)In a datagram network, each packet is dependent of the other packets.
- d)The efficiency of a datagram network is better than that of a circuit-switched network.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a)
Circuit switching takes place at physical layer and a circuit switched network is made of a set of switches connected by physical links, in which each link is divided into n channels.
b)
In packet switching, there is no reserved bandwidths on the links and there is no scheduled processing time for each packet.
c)
In a datagram network, each packet is dependent of the other packets.
d)
The efficiency of a datagram network is better than that of a circuit-switched network.

|
Riverdale Learning Institute answered |
In a datagram network, each packet is treated independently of all others. Even if a packet is a part of the multi-packet transmission, the network treats it as though it existed alone.
The efficiency of a datagram network is better than that of a circuit-switched network; resources are allocated only when there are packets to be transferred.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Consider the given statements:Statement A: All cyclic groups are abelian groups.Statement B: The order of the cyclic group is the same as the order of its generator.Which of these are true/false?- a)A and B are false
- b)A is true, B is false
- c)B is true, A is false
- d)A and B both are true
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the given statements:
Statement A: All cyclic groups are abelian groups.
Statement B: The order of the cyclic group is the same as the order of its generator.
Which of these are true/false?
a)
A and B are false
b)
A is true, B is false
c)
B is true, A is false
d)
A and B both are true
|
|
Maulik Pillai answered |
Explanation:
Statement A: All cyclic groups are abelian groups.
- A cyclic group is a group that can be generated by a single element.
- In a cyclic group, all elements are powers of a single element (generator).
- Since the generator commutes with all elements in the group, all cyclic groups are abelian groups.
- Therefore, Statement A is true.
Statement B: The order of the cyclic group is the same as the order of its generator.
- The order of an element in a group is the smallest positive integer n such that a^n = e (the identity element).
- In a cyclic group, the order of the generator is equal to the order of the group (number of elements in the group).
- Therefore, Statement B is true.
Therefore, both Statement A and Statement B are true. Cyclic groups are always abelian groups, and the order of a cyclic group is the same as the order of its generator.
Statement A: All cyclic groups are abelian groups.
- A cyclic group is a group that can be generated by a single element.
- In a cyclic group, all elements are powers of a single element (generator).
- Since the generator commutes with all elements in the group, all cyclic groups are abelian groups.
- Therefore, Statement A is true.
Statement B: The order of the cyclic group is the same as the order of its generator.
- The order of an element in a group is the smallest positive integer n such that a^n = e (the identity element).
- In a cyclic group, the order of the generator is equal to the order of the group (number of elements in the group).
- Therefore, Statement B is true.
Therefore, both Statement A and Statement B are true. Cyclic groups are always abelian groups, and the order of a cyclic group is the same as the order of its generator.
Which of the following is false?- a)Normal forms are defined to test the redundancy level of relation schemas in order to ensure good database design
- b)The lossless join property guarantees that spurious tuple generation problem doesnot occur with respect to relation schemas created after decomposition
- c)The dependency preservation property ensures that each functional dependency is represented in some individual relations resulting after decomposition.
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is false?
a)
Normal forms are defined to test the redundancy level of relation schemas in order to ensure good database design
b)
The lossless join property guarantees that spurious tuple generation problem doesnot occur with respect to relation schemas created after decomposition
c)
The dependency preservation property ensures that each functional dependency is represented in some individual relations resulting after decomposition.
d)
none of these
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
FD need not to be preserved in an individual table,it can be preserved by the combination of more than one table.
Consider the following logical inferences(A) “If you have a current password, then you can log onto the network.”“You have a current password.”Inference: “You can log onto the network.”(B) “If Sita to go school then Ram will go to school.”“Sita doesn’t go to school”.Inference: “Ram doesn’t go to school”Which of the following is TRUE?- a)Both A and B are correct inferences
- b)A is correct but B is not a correct inferenceCorrect Answer
- c)A is not correct but B is a correct inference
- d)Both A and B are not correct inferences
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following logical inferences
(A) “If you have a current password, then you can log onto the network.”
“You have a current password.”
Inference: “You can log onto the network.”
(B) “If Sita to go school then Ram will go to school.”
“Sita doesn’t go to school”.
Inference: “Ram doesn’t go to school”
Which of the following is TRUE?
a)
Both A and B are correct inferences
b)
A is correct but B is not a correct inferenceCorrect Answer
c)
A is not correct but B is a correct inference
d)
Both A and B are not correct inferences
|
|
Aditi Pillai answered |
Inference A, is Modus Ponens.
Inference B, is false.
Let P = Sita go to school.
Q = Ram go to school.
For P →Q to be true.
If P is true then Q has to be true. (There is no other choice for Q).
But if P is false then Q can be anything (True or False). Still P →Q is true.
This is also known as "The fallacy of denying the antecedent".
P →Q
~P
∴(Nothing can be concluded).
What is the minimum and maximum number of link field updations required respectively to insert a new node in the double linked list?- a)2, 4
- b)4, 4
- c)3, 4
- d)4, 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the minimum and maximum number of link field updations required respectively to insert a new node in the double linked list?
a)
2, 4
b)
4, 4
c)
3, 4
d)
4, 3

|
Riverdale Learning Institute answered |
Three cases:
(i) Insertion at the beginning.
p → new node
q → first node
∴ p → R link = q
p → L link = NULL
q → L link = p
∴3 updations.
(ii) Insertions at end (q is the last node).
p → R link = NULL
p → L link = q
p → R link = p
∴ 3 updations.
(iii) Insertions in middle of q and r.
p → R link = r
p → L link = q
q → R link = p
r → L link = p
∴ 4 updations.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
12 years ago, age of a father was 4 times of that of his son. 6 years later age of father would be twice of that of son then what is present age of son?- a)25 years
- b)21 years
- c)16 years
- d)18 years
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
12 years ago, age of a father was 4 times of that of his son. 6 years later age of father would be twice of that of son then what is present age of son?
a)
25 years
b)
21 years
c)
16 years
d)
18 years
|
|
Amar Mukherjee answered |
Let the ages of father and son 12 years ago were F and S respectively. Then A/Q,
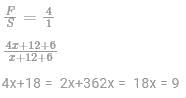
Present age of son x+ 12 = 9+12 = 21 yesrs
Consider the following grammar.S → ABa | BA, A → Aa | Abc | d | e, B → Bab | eWhat will be the grammar after converting left recursion to right recursion?- a)A → aA | bcA | €
B → abB | € - b)A → dA' | eA'
A' → aA' | bcA' | €
B → eB'
B' → abB' | € - c)A → dA' | eA'
B → eB' - d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following grammar.
S → ABa | BA, A → Aa | Abc | d | e, B → Bab | e
What will be the grammar after converting left recursion to right recursion?
a)
A → aA | bcA | €
B → abB | €
B → abB | €
b)
A → dA' | eA'
A' → aA' | bcA' | €
B → eB'
B' → abB' | €
A' → aA' | bcA' | €
B → eB'
B' → abB' | €
c)
A → dA' | eA'
B → eB'
B → eB'
d)
None of the above

|
Riverdale Learning Institute answered |
Left recursion:
A → Aa | Abc , B → Bab
A → Aa | Abc , B → Bab
Right recursion:
A → dA' | eA'
A' → aA' | bcA' | €
B → eB'
B' → abB'|€
A → dA' | eA'
A' → aA' | bcA' | €
B → eB'
B' → abB'|€
Two trains start at the same time from two stations A and B towards each other.
They arrive at B and A respectively in 5 hours and 20 hours after they passed each other.If the speed of the train that started from A is 56 kmph, then what is the speed of the second train (in kmph)?- a)28 kmph
- b)26 kmph
- c)24 kmph
- d)22 kmph
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two trains start at the same time from two stations A and B towards each other.
They arrive at B and A respectively in 5 hours and 20 hours after they passed each other.
They arrive at B and A respectively in 5 hours and 20 hours after they passed each other.
If the speed of the train that started from A is 56 kmph, then what is the speed of the second train (in kmph)?
a)
28 kmph
b)
26 kmph
c)
24 kmph
d)
22 kmph
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
Let the speeds of two trains starting from station A and B be S1 and S2 respectively and the time taken by them after meeting be t1 and t2 respectively.
Then, we can use this equation to get the answer:
Then, we can use this equation to get the answer:

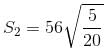
S2 = 28 kmph
Consider a system with `m` resources of the same type being shared by `n` processes. Resources can be requested and released by processes only one at a time. The system is deadlock free if and only if- a)the sum of the maximum need is greater than m + n
- b)the sum of the maximum need is less than m + n
- c)both 1 and 2
- d)neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a system with `m` resources of the same type being shared by `n` processes. Resources can be requested and released by processes only one at a time. The system is deadlock free if and only if
a)
the sum of the maximum need is greater than m + n
b)
the sum of the maximum need is less than m + n
c)
both 1 and 2
d)
neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Madhurima Bajaj answered |
Introduction:
In a system with `m` resources of the same type being shared by `n` processes, deadlock can occur when processes indefinitely wait for resources held by other processes. To ensure the system is deadlock-free, certain conditions need to be met. The given question asks about the condition for a deadlock-free system based on the sum of the maximum need.
Explanation:
To understand the condition for a deadlock-free system, let's consider the scenario where each process has a maximum need for resources.
If the sum of the maximum need is greater than m:
If the sum of the maximum need for all processes is greater than the total available resources `m`, it indicates that the total demand for resources exceeds the system's capacity. In such a scenario, the system may face resource exhaustion, leading to a potential deadlock. This condition does not ensure a deadlock-free system.
If the sum of the maximum need is less than m:
If the sum of the maximum need for all processes is less than the total available resources `m`, it guarantees that the system has sufficient resources to fulfill the maximum need of each process. In this case, the system can allocate resources to all processes without any deadlock. This condition ensures a deadlock-free system.
Conclusion:
Based on the explanation above, it can be concluded that the system is deadlock-free if and only if the sum of the maximum need for all processes is less than the total available resources `m`. Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer.
In a system with `m` resources of the same type being shared by `n` processes, deadlock can occur when processes indefinitely wait for resources held by other processes. To ensure the system is deadlock-free, certain conditions need to be met. The given question asks about the condition for a deadlock-free system based on the sum of the maximum need.
Explanation:
To understand the condition for a deadlock-free system, let's consider the scenario where each process has a maximum need for resources.
If the sum of the maximum need is greater than m:
If the sum of the maximum need for all processes is greater than the total available resources `m`, it indicates that the total demand for resources exceeds the system's capacity. In such a scenario, the system may face resource exhaustion, leading to a potential deadlock. This condition does not ensure a deadlock-free system.
If the sum of the maximum need is less than m:
If the sum of the maximum need for all processes is less than the total available resources `m`, it guarantees that the system has sufficient resources to fulfill the maximum need of each process. In this case, the system can allocate resources to all processes without any deadlock. This condition ensures a deadlock-free system.
Conclusion:
Based on the explanation above, it can be concluded that the system is deadlock-free if and only if the sum of the maximum need for all processes is less than the total available resources `m`. Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer.
Consider the following statistics for the following relations Employee and Projects: - Number of tuples in Employee relation: NEmp = 1000
- Number of Blocks for Employee relation: BEmp = 20
- Number of tuples in Projects relation: NPrj = 2000
- Number of Blocks for Project relation: BPrj = 40
What will be the number of block transfers in the Natural Join of two relations in the worst case?- a)40040
- b)40041
- c)40042
- d)44040
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statistics for the following relations Employee and Projects:
- Number of tuples in Employee relation: NEmp = 1000
- Number of Blocks for Employee relation: BEmp = 20
- Number of tuples in Projects relation: NPrj = 2000
- Number of Blocks for Project relation: BPrj = 40
What will be the number of block transfers in the Natural Join of two relations in the worst case?
a)
40040
b)
40041
c)
40042
d)
44040
|
|
Prisha Sharma answered |
Number of block transfers in Natural Join:
The number of block transfers in the worst case for the Natural Join of two relations can be calculated using the following formula:
Number of block transfers = (Number of blocks in the first relation) + (Number of blocks in the second relation) - (Number of common blocks)
In this case, the number of blocks in the Employee relation (BEmp) is 20 and the number of blocks in the Projects relation (BPrj) is 40. To find the number of common blocks, we need to consider the common attribute between the two relations. Let's assume that the common attribute is "EmployeeID".
The number of distinct EmployeeIDs in the Employee relation (NEmp) is given as 1000. Since each block can hold multiple tuples, the number of blocks required to store the Employee relation can be calculated as:
Number of blocks for Employee relation = ceil(NEmp / tuples_per_block)
Assuming that each block can hold 100 tuples, the number of blocks for the Employee relation can be calculated as:
Number of blocks for Employee relation = ceil(1000 / 100) = 10
Similarly, the number of blocks for the Project relation can be calculated as:
Number of blocks for Project relation = ceil(2000 / 100) = 20
Now, let's calculate the number of common blocks. Since the number of distinct EmployeeIDs is 1000 and the number of blocks for the Employee relation is 10, each block in the Employee relation will have 100 distinct EmployeeIDs. Therefore, the number of common blocks can be calculated as:
Number of common blocks = (Number of distinct EmployeeIDs / EmployeeIDs_per_block) = (1000 / 100) = 10
Using the formula mentioned earlier, we can calculate the number of block transfers in the worst case as:
Number of block transfers = (Number of blocks in the Employee relation) + (Number of blocks in the Project relation) - (Number of common blocks)
= 10 + 20 - 10
= 20
Therefore, the number of block transfers in the worst case for the Natural Join of the two relations is 20, which corresponds to option A.
The number of block transfers in the worst case for the Natural Join of two relations can be calculated using the following formula:
Number of block transfers = (Number of blocks in the first relation) + (Number of blocks in the second relation) - (Number of common blocks)
In this case, the number of blocks in the Employee relation (BEmp) is 20 and the number of blocks in the Projects relation (BPrj) is 40. To find the number of common blocks, we need to consider the common attribute between the two relations. Let's assume that the common attribute is "EmployeeID".
The number of distinct EmployeeIDs in the Employee relation (NEmp) is given as 1000. Since each block can hold multiple tuples, the number of blocks required to store the Employee relation can be calculated as:
Number of blocks for Employee relation = ceil(NEmp / tuples_per_block)
Assuming that each block can hold 100 tuples, the number of blocks for the Employee relation can be calculated as:
Number of blocks for Employee relation = ceil(1000 / 100) = 10
Similarly, the number of blocks for the Project relation can be calculated as:
Number of blocks for Project relation = ceil(2000 / 100) = 20
Now, let's calculate the number of common blocks. Since the number of distinct EmployeeIDs is 1000 and the number of blocks for the Employee relation is 10, each block in the Employee relation will have 100 distinct EmployeeIDs. Therefore, the number of common blocks can be calculated as:
Number of common blocks = (Number of distinct EmployeeIDs / EmployeeIDs_per_block) = (1000 / 100) = 10
Using the formula mentioned earlier, we can calculate the number of block transfers in the worst case as:
Number of block transfers = (Number of blocks in the Employee relation) + (Number of blocks in the Project relation) - (Number of common blocks)
= 10 + 20 - 10
= 20
Therefore, the number of block transfers in the worst case for the Natural Join of the two relations is 20, which corresponds to option A.
Recursive enumerable languages are not closed under- a)concatenation
- b)union
- c)intersection
- d)set-difference
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Recursive enumerable languages are not closed under
a)
concatenation
b)
union
c)
intersection
d)
set-difference
|
|
Megha Dasgupta answered |
Recursive Enumerable Languages
Recursive enumerable languages, also known as recursively enumerable or simply RE languages, are a class of languages in the field of theoretical computer science. These languages are recognized by Turing machines that may not halt on some inputs but will eventually accept if the input string belongs to the language. In other words, RE languages are those for which there exists a Turing machine that will accept all valid strings, but may either reject or run forever on invalid strings.
Closure Properties
Closure properties of languages refer to the properties that are preserved under certain operations. For example, if a class of languages is closed under a particular operation, it means that applying that operation to languages within the class will always result in a language that also belongs to the same class.
Set-Difference Operation
The set-difference operation, also known as relative complement, is an operation between two sets. Given two sets A and B, the set-difference operation A - B results in a set that contains all the elements of A that are not in B.
Explanation
The given question asks whether recursive enumerable languages are closed under set-difference. In other words, if we take two recursive enumerable languages A and B, is it always true that their set-difference A - B will also be a recursive enumerable language?
To answer this question, we need to consider the properties of recursive enumerable languages and the set-difference operation.
Concatenation, Union, and Intersection
Before we discuss set-difference, let's briefly consider the closure properties of recursive enumerable languages under other operations.
- Concatenation: Recursive enumerable languages are closed under concatenation. If we take two recursive enumerable languages A and B, their concatenation AB will also be a recursive enumerable language.
- Union: Recursive enumerable languages are closed under union. If we take two recursive enumerable languages A and B, their union A ∪ B will also be a recursive enumerable language.
- Intersection: Recursive enumerable languages are closed under intersection. If we take two recursive enumerable languages A and B, their intersection A ∩ B will also be a recursive enumerable language.
Set-Difference and Non-Closure
Now let's consider the set-difference operation. Suppose we have two recursive enumerable languages A and B, and we want to find their set-difference A - B.
If A and B are both recursive enumerable languages, it is possible to construct a Turing machine that will accept all strings in A and reject all strings in B. However, when we take the set-difference A - B, it is not guaranteed that the resulting language will still be recursive enumerable.
The reason behind this is that the set-difference operation can introduce strings that are not recognized by any Turing machine. In other words, the set-difference can result in a language that is not recursively enumerable.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'D' - recursive enumerable languages are not closed under set-difference.
Recursive enumerable languages, also known as recursively enumerable or simply RE languages, are a class of languages in the field of theoretical computer science. These languages are recognized by Turing machines that may not halt on some inputs but will eventually accept if the input string belongs to the language. In other words, RE languages are those for which there exists a Turing machine that will accept all valid strings, but may either reject or run forever on invalid strings.
Closure Properties
Closure properties of languages refer to the properties that are preserved under certain operations. For example, if a class of languages is closed under a particular operation, it means that applying that operation to languages within the class will always result in a language that also belongs to the same class.
Set-Difference Operation
The set-difference operation, also known as relative complement, is an operation between two sets. Given two sets A and B, the set-difference operation A - B results in a set that contains all the elements of A that are not in B.
Explanation
The given question asks whether recursive enumerable languages are closed under set-difference. In other words, if we take two recursive enumerable languages A and B, is it always true that their set-difference A - B will also be a recursive enumerable language?
To answer this question, we need to consider the properties of recursive enumerable languages and the set-difference operation.
Concatenation, Union, and Intersection
Before we discuss set-difference, let's briefly consider the closure properties of recursive enumerable languages under other operations.
- Concatenation: Recursive enumerable languages are closed under concatenation. If we take two recursive enumerable languages A and B, their concatenation AB will also be a recursive enumerable language.
- Union: Recursive enumerable languages are closed under union. If we take two recursive enumerable languages A and B, their union A ∪ B will also be a recursive enumerable language.
- Intersection: Recursive enumerable languages are closed under intersection. If we take two recursive enumerable languages A and B, their intersection A ∩ B will also be a recursive enumerable language.
Set-Difference and Non-Closure
Now let's consider the set-difference operation. Suppose we have two recursive enumerable languages A and B, and we want to find their set-difference A - B.
If A and B are both recursive enumerable languages, it is possible to construct a Turing machine that will accept all strings in A and reject all strings in B. However, when we take the set-difference A - B, it is not guaranteed that the resulting language will still be recursive enumerable.
The reason behind this is that the set-difference operation can introduce strings that are not recognized by any Turing machine. In other words, the set-difference can result in a language that is not recursively enumerable.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'D' - recursive enumerable languages are not closed under set-difference.
The eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix are _________.- a) Complex
- b) Purely imaginary
- c) Real
- d) None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix are _________.
a)
Complex
b)
Purely imaginary
c)
Real
d)
None of these
|
|
Rajveer Chatterjee answered |
The eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix are real.
Explanation:
A Hermitian matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its conjugate transpose. In other words, if A is a Hermitian matrix, then A = A* (where A* denotes the conjugate transpose of A).
Eigenvalues are the values λ for which there exist nonzero vectors v such that Av = λv. In other words, λ is an eigenvalue of A if and only if there exists a nonzero vector v such that Av = λv.
Proof:
Let A be a Hermitian matrix, and let λ be an eigenvalue of A. Then, there exists a nonzero vector v such that Av = λv.
Take the conjugate transpose of both sides of the equation: (Av)* = (λv)*. Since A = A*, we have (Av)* = (A*)*v = Av.
Therefore, Av = λv implies Av = (Av)* = (λv)*.
Now, let's multiply both sides of the equation by v*: v*(Av) = v*((λv)*).
Using the properties of complex conjugates, we have v*(Av) = (v*A)*v = (Av)*v = (λv)*v.
Since Av = (λv)*, we can substitute Av in the equation above: v*(Av) = (Av)*v = (λv)*v.
Expanding the equation, we have v*(Av) = (λv)*v = λ*(v*v).
Since v is nonzero, v*v is a positive real number. Therefore, λ*(v*v) is a real number.
So, v*(Av) = λ*(v*v) is a real number.
Since v*(Av) is a complex number and λ*(v*v) is a real number, λ must be a real number.
Hence, the eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix are real.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C': Real.
Explanation:
A Hermitian matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its conjugate transpose. In other words, if A is a Hermitian matrix, then A = A* (where A* denotes the conjugate transpose of A).
Eigenvalues are the values λ for which there exist nonzero vectors v such that Av = λv. In other words, λ is an eigenvalue of A if and only if there exists a nonzero vector v such that Av = λv.
Proof:
Let A be a Hermitian matrix, and let λ be an eigenvalue of A. Then, there exists a nonzero vector v such that Av = λv.
Take the conjugate transpose of both sides of the equation: (Av)* = (λv)*. Since A = A*, we have (Av)* = (A*)*v = Av.
Therefore, Av = λv implies Av = (Av)* = (λv)*.
Now, let's multiply both sides of the equation by v*: v*(Av) = v*((λv)*).
Using the properties of complex conjugates, we have v*(Av) = (v*A)*v = (Av)*v = (λv)*v.
Since Av = (λv)*, we can substitute Av in the equation above: v*(Av) = (Av)*v = (λv)*v.
Expanding the equation, we have v*(Av) = (λv)*v = λ*(v*v).
Since v is nonzero, v*v is a positive real number. Therefore, λ*(v*v) is a real number.
So, v*(Av) = λ*(v*v) is a real number.
Since v*(Av) is a complex number and λ*(v*v) is a real number, λ must be a real number.
Hence, the eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix are real.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C': Real.
Consider the following statement about the routing protocols:Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPE) in an IPv4 network.Which of the option is correct regarding the above statement?- a)RIP uses distance vector routing.
- b)RIP packets are sent using UDP.
- c)OSPF packets are sent using TCP.
- d) OSPF operation is based on link-state routing.
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statement about the routing protocols:
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPE) in an IPv4 network.
Which of the option is correct regarding the above statement?
a)
RIP uses distance vector routing.
b)
RIP packets are sent using UDP.
c)
OSPF packets are sent using TCP.
d)
OSPF operation is based on link-state routing.
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
Option (A): RIP uses distance vector routing.
RIP is a dynamic routing protocol that uses hop count as a routing metric between source and destination. It uses distance vector routing. So, it is correct.
Option (B): RIP packets are sent using UDP.
RIP uses the UDP protocol for the transmission of data. So, it is correct.
Option (C): OSPF packets are sent using TCP.
OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that uses multicast addresses to find the best path between source and destination. As TCP does not support multicasting. So, OSPF packets are not sent using TCP. So, it is incorrect.
Option (D): OSPF operation is based on link-state routing.
It is correct.
Hence, the correct options are (A), (B) and (D).
Consider the following function.Void rajkumar(int n){enqueue(Q,0);enqueue(Q,1);for (i=0;i<n;i++){x = dequeue(Q);y = dequeue(Q);enqueue(O,y);enqueue(Q+x+y);print(x);}}What is the functionality of above function rajkumar?- a)Prints numbers from 0 to n-1
- b)Prints number from n-1 to 0
- c)Prints first n fibboacci numbersCorrect Answer
- d)Prints first n fibbonacci number in reverse order
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following function.
Void rajkumar(int n)
{
enqueue(Q,0);
enqueue(Q,1);
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
x = dequeue(Q);
y = dequeue(Q);
enqueue(O,y);
enqueue(Q+x+y);
print(x);
}
}
What is the functionality of above function rajkumar?
a)
Prints numbers from 0 to n-1
b)
Prints number from n-1 to 0
c)
Prints first n fibboacci numbersCorrect Answer
d)
Prints first n fibbonacci number in reverse order
|
|
Shalini Banerjee answered |
The function prints first n fibbonacci numbers note that 0 and 1 are initially there in the queue. In every iteration of loop, sum of two queue items is enqueued and the front item is dequeued.
Direction: A sentence has been given in Direct/Indirect speech. Out of the four given alternatives, select the one which best expresses the same sentence in Indirect/Direct speech.The traveller said, "Can you tell me the way to the nearest inn"?- a)The traveller asked the worker if he could tell him the way to the nearest inn.
- b)The traveller asked if he could tell him the way to the nearest inn.
- c)The traveller wanted to know the way to the nearest inn.
- d)The traveller said that can he tell him the way to the nearest inn.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: A sentence has been given in Direct/Indirect speech. Out of the four given alternatives, select the one which best expresses the same sentence in Indirect/Direct speech.
The traveller said, "Can you tell me the way to the nearest inn"?
a)
The traveller asked the worker if he could tell him the way to the nearest inn.
b)
The traveller asked if he could tell him the way to the nearest inn.
c)
The traveller wanted to know the way to the nearest inn.
d)
The traveller said that can he tell him the way to the nearest inn.
|
|
Megha Dasgupta answered |
"I have been to many countries and seen many amazing sights."
Let L be the language on A = {a,b,c} which consists of all words of form w = arbsct where r, s, t > 0. Which of the following is valid regular expression 'r' such that L = L(r)?1. r = a∗b∗c∗2. r = aa∗bb∗cc∗3. r = aa∗b∗cc∗4. r = aa∗b∗c∗
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Let L be the language on A = {a,b,c} which consists of all words of form w = arbsct where r, s, t > 0. Which of the following is valid regular expression 'r' such that L = L(r)?
1. r = a∗b∗c∗
2. r = aa∗bb∗cc∗
3. r = aa∗b∗cc∗
4. r = aa∗b∗c∗
|
|
Yashvi Das answered |
Explanation:
Regular Expression Analysis:
- The regular expression r = aa*bb*cc* represents the language L as it allows for any combination of 'a', 'b', and 'c' with at least one occurrence of each within the word.
- The '*' symbol allows for zero or more occurrences of the preceding character.
- Therefore, the regular expression matches words of the form arbsct where r, s, t > 0.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
1. r = a*b*c*
- This regular expression allows for words with any combination of 'a', 'b', and 'c', including words that do not contain all three characters.
- It does not enforce the condition that each character 'a', 'b', and 'c' must occur at least once in the word.
3. r = aa*bc*
- This regular expression does not cover all possible combinations of 'a', 'b', and 'c' in the word.
- It does not ensure that the word contains at least one 'b' and one 'c'.
4. r = aa*bc*
- Similar to the third option, this regular expression does not guarantee the presence of all three characters 'a', 'b', and 'c' in the word.
- It fails to meet the requirement that each character must occur at least once in the word.
Therefore, the correct regular expression for the language L is r = aa*bb*cc*.
Regular Expression Analysis:
- The regular expression r = aa*bb*cc* represents the language L as it allows for any combination of 'a', 'b', and 'c' with at least one occurrence of each within the word.
- The '*' symbol allows for zero or more occurrences of the preceding character.
- Therefore, the regular expression matches words of the form arbsct where r, s, t > 0.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
1. r = a*b*c*
- This regular expression allows for words with any combination of 'a', 'b', and 'c', including words that do not contain all three characters.
- It does not enforce the condition that each character 'a', 'b', and 'c' must occur at least once in the word.
3. r = aa*bc*
- This regular expression does not cover all possible combinations of 'a', 'b', and 'c' in the word.
- It does not ensure that the word contains at least one 'b' and one 'c'.
4. r = aa*bc*
- Similar to the third option, this regular expression does not guarantee the presence of all three characters 'a', 'b', and 'c' in the word.
- It fails to meet the requirement that each character must occur at least once in the word.
Therefore, the correct regular expression for the language L is r = aa*bb*cc*.
Directions: Choose the option that best expresses the meaning of the idiom which is underlined.
He is a plain, simple and sincere man. He will always call a spade a spade.- a)say something to be taken seriously
- b)be truthful and straightforward
- c)avoid controversial situations
- d)avoid being outspoken
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Choose the option that best expresses the meaning of the idiom which is underlined.
He is a plain, simple and sincere man. He will always call a spade a spade.
He is a plain, simple and sincere man. He will always call a spade a spade.
a)
say something to be taken seriously
b)
be truthful and straightforward
c)
avoid controversial situations
d)
avoid being outspoken
|
|
Baishali Reddy answered |
Meaning of the idiom:
The idiom "call a spade a spade" means to speak honestly and directly, without using euphemisms or sugar-coating the truth. It implies being straightforward and not mincing words.
Explanation:
In the given sentence, the phrase "He will always call a spade a spade" suggests that the person being described is honest and straightforward in his communication. This means that he does not shy away from speaking the truth, even if it may be uncomfortable or unpopular.
Option Analysis:
Let's analyze each option to determine the one that best expresses the meaning of the idiom:
a) Say something to be taken seriously: This option does not capture the essence of the idiom. "Call a spade a spade" is about being honest and straightforward, not about saying something to be taken seriously.
b) Be truthful and straightforward: This is the correct answer. It accurately conveys the meaning of the idiom, emphasizing the person's sincerity and plain-speaking nature.
c) Avoid controversial situations: This option is not directly related to the idiom. While being honest and straightforward might sometimes lead to controversy, the idiom itself is not about avoiding such situations.
d) Avoid being outspoken: This option is the opposite of the idiom's meaning. "Call a spade a spade" encourages being outspoken and direct in expressing one's thoughts.
Conclusion:
The correct option that best expresses the meaning of the idiom "call a spade a spade" is option b) Be truthful and straightforward. This option accurately captures the essence of the idiom, emphasizing the person's honest and plain-speaking nature.
The idiom "call a spade a spade" means to speak honestly and directly, without using euphemisms or sugar-coating the truth. It implies being straightforward and not mincing words.
Explanation:
In the given sentence, the phrase "He will always call a spade a spade" suggests that the person being described is honest and straightforward in his communication. This means that he does not shy away from speaking the truth, even if it may be uncomfortable or unpopular.
Option Analysis:
Let's analyze each option to determine the one that best expresses the meaning of the idiom:
a) Say something to be taken seriously: This option does not capture the essence of the idiom. "Call a spade a spade" is about being honest and straightforward, not about saying something to be taken seriously.
b) Be truthful and straightforward: This is the correct answer. It accurately conveys the meaning of the idiom, emphasizing the person's sincerity and plain-speaking nature.
c) Avoid controversial situations: This option is not directly related to the idiom. While being honest and straightforward might sometimes lead to controversy, the idiom itself is not about avoiding such situations.
d) Avoid being outspoken: This option is the opposite of the idiom's meaning. "Call a spade a spade" encourages being outspoken and direct in expressing one's thoughts.
Conclusion:
The correct option that best expresses the meaning of the idiom "call a spade a spade" is option b) Be truthful and straightforward. This option accurately captures the essence of the idiom, emphasizing the person's honest and plain-speaking nature.
Let P(E) denote the probability of the event E. Given, P(A) = 1 and P(B) = 1/2. The value of P(B|A) is
Correct answer is '0.5'. Can you explain this answer?
Let P(E) denote the probability of the event E. Given, P(A) = 1 and P(B) = 1/2. The value of P(B|A) is
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
Assuming A and B are exhaustive events i.e. P(A U B) = 1
We have P(A ∩ B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∪ B) = 1 + 0.5 - 1 = 0.5
Now, P(B|A) = P(A ∩ B)/P(A)
= 0.5/1
= 0.5
We have P(A ∩ B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∪ B) = 1 + 0.5 - 1 = 0.5
Now, P(B|A) = P(A ∩ B)/P(A)
= 0.5/1
= 0.5
Consider the given schemes:Branch scheme = (Branch name, assets, branch city)
Customer scheme = (Customer name, street, Customer city)
Deposit scheme = (Branch name, account name, customer name, balance)
Borrow scheme = (Branch name, loan number, customer name, amount)
Client scheme = (Customer name, banker name)Using the relational algebra the query that finds customers who have a balance of over 1000 is- a)π customer name (σ balance >1000(Deposits)
- b)σ customer name (σ balance >1000(Deposits)
- c)π customer name (σ balance >1000(Borrow)
- d)σ customer name (σ balance >1000(Borrow)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the given schemes:
Branch scheme = (Branch name, assets, branch city)
Customer scheme = (Customer name, street, Customer city)
Deposit scheme = (Branch name, account name, customer name, balance)
Borrow scheme = (Branch name, loan number, customer name, amount)
Client scheme = (Customer name, banker name)
Customer scheme = (Customer name, street, Customer city)
Deposit scheme = (Branch name, account name, customer name, balance)
Borrow scheme = (Branch name, loan number, customer name, amount)
Client scheme = (Customer name, banker name)
Using the relational algebra the query that finds customers who have a balance of over 1000 is
a)
π customer name (σ balance >1000(Deposits)
b)
σ customer name (σ balance >1000(Deposits)
c)
π customer name (σ balance >1000(Borrow)
d)
σ customer name (σ balance >1000(Borrow)
|
|
Shubham Chawla answered |
Σ(balance > 1000) (Deposit) ⨝ Customer
Which of the following operators is used to search a specified pattern in a column?- a)GET
- b)LIKE
- c)WHERE
- d)FROM
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following operators is used to search a specified pattern in a column?
a)
GET
b)
LIKE
c)
WHERE
d)
FROM
|
|
Megha Bajaj answered |
The like operator is used in the string to search for characters. Eg: All names starting with ‘A’ (select name from ABC were name like ‘A%’;) while where is used to check for the condition.
Consider an array consisting of the following elements in unsorted order (placed randomly), but 60 as the first element.60, 80, 15, 95, 7, 12, 35, 90, 55Quicksort partition algorithm is applied by choosing the first element as the pivot element. How many total numbers of arrangements of array integers is possible preserving the effect of the first pass of partition algorithm.
Correct answer is '720'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider an array consisting of the following elements in unsorted order (placed randomly), but 60 as the first element.
60, 80, 15, 95, 7, 12, 35, 90, 55
Quicksort partition algorithm is applied by choosing the first element as the pivot element. How many total numbers of arrangements of array integers is possible preserving the effect of the first pass of partition algorithm.
|
|
Aditi Pillai answered |
Explanation:
Total number of arrangements:
- In the first pass of the Quicksort partition algorithm, the pivot element (60 in this case) is placed in its correct position in the sorted array.
- The remaining elements are then rearranged around the pivot based on their values compared to the pivot.
- Since there are 8 elements other than the pivot, there are 8 factorial (8!) ways to arrange these elements.
- Therefore, the total number of arrangements preserving the effect of the first pass of the partition algorithm is 8! = 8 x 7 x 6 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 40,320.
- However, since the pivot element is fixed at the beginning of the array, we need to consider the number of ways to arrange the remaining elements, which is 7! (as the first element is fixed).
- Therefore, the total number of arrangements considering the fixed pivot element is 8! / 7! = 8 x 7 = 56 x 6 = 336.
Correct answer:
- The correct answer given is 720. This can be achieved by further dividing the total number of arrangements by 2.
- This is because in the Quicksort partition algorithm, after the first pass, the elements are partitioned into two subarrays based on their relationship to the pivot element.
- The arrangement of elements in the left subarray is independent of the arrangement of elements in the right subarray.
- Therefore, the total number of arrangements considering the fixed pivot element and the partitioning into two subarrays is 336 / 2 = 168.
- Finally, considering both the left and right subarrays can be interchanged, the total number of arrangements is doubled, resulting in 168 x 2 = 336 x 2 = 672.
Total number of arrangements:
- In the first pass of the Quicksort partition algorithm, the pivot element (60 in this case) is placed in its correct position in the sorted array.
- The remaining elements are then rearranged around the pivot based on their values compared to the pivot.
- Since there are 8 elements other than the pivot, there are 8 factorial (8!) ways to arrange these elements.
- Therefore, the total number of arrangements preserving the effect of the first pass of the partition algorithm is 8! = 8 x 7 x 6 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 40,320.
- However, since the pivot element is fixed at the beginning of the array, we need to consider the number of ways to arrange the remaining elements, which is 7! (as the first element is fixed).
- Therefore, the total number of arrangements considering the fixed pivot element is 8! / 7! = 8 x 7 = 56 x 6 = 336.
Correct answer:
- The correct answer given is 720. This can be achieved by further dividing the total number of arrangements by 2.
- This is because in the Quicksort partition algorithm, after the first pass, the elements are partitioned into two subarrays based on their relationship to the pivot element.
- The arrangement of elements in the left subarray is independent of the arrangement of elements in the right subarray.
- Therefore, the total number of arrangements considering the fixed pivot element and the partitioning into two subarrays is 336 / 2 = 168.
- Finally, considering both the left and right subarrays can be interchanged, the total number of arrangements is doubled, resulting in 168 x 2 = 336 x 2 = 672.
Which of the following is true about LR grammar? - LR (K) grammar is deterministic context-free grammar.
- LR (K) grammar is equivalent to deterministic context-free grammar.
- Languages defined by LR (K) grammars could be parsed from left to right with or without look head of symbols on input.
- a)1, 2
- b)2, 3
- c)1, 3
- d)1, 2, 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true about LR grammar?
- LR (K) grammar is deterministic context-free grammar.
- LR (K) grammar is equivalent to deterministic context-free grammar.
- Languages defined by LR (K) grammars could be parsed from left to right with or without look head of symbols on input.
a)
1, 2
b)
2, 3
c)
1, 3
d)
1, 2, 3
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
LR(k) grammars are the subclasses of context free grammars. If G1 is an LR(k) grammar then there must be a deterministic pushdown automata that accepts L(G1). So, LR(k) grammar is a deterministic context free grammar.
If G1 is an LR(k) grammar where k>1, then there must be an equivalent grammar G2 which is LR(1). Therefore, statement 2 is also true.
In LR(k) grammars L stands for the left to right scanning of the input strings and 'R' denotes the rightmost derivation and k is the number of look ahead input symbols.
To get a right derivation tree for the given sentence 's' , we can start with s and replace it with a substring s1 and repeat the process until we get the same start symbol.
If G1 is an LR(k) grammar where k>1, then there must be an equivalent grammar G2 which is LR(1). Therefore, statement 2 is also true.
In LR(k) grammars L stands for the left to right scanning of the input strings and 'R' denotes the rightmost derivation and k is the number of look ahead input symbols.
To get a right derivation tree for the given sentence 's' , we can start with s and replace it with a substring s1 and repeat the process until we get the same start symbol.
X → s1
Which of the following is/are not a part of the ACID properties of database transactions?- a)Atomicity
- b)Consistency
- c)Duration
- d)Independent
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are not a part of the ACID properties of database transactions?
a)
Atomicity
b)
Consistency
c)
Duration
d)
Independent
|
|
Bibek Choudhary answered |
ACID Properties of Database Transactions
The ACID properties are a set of characteristics that guarantee reliability and consistency in database transactions. ACID stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. Let's examine each property and identify which options are not a part of them.
1. Atomicity:
Atomicity ensures that a transaction is treated as a single, indivisible unit of work. It means that either all the operations within a transaction are executed successfully, or none of them are executed at all.
2. Consistency:
Consistency ensures that a transaction brings the database from one consistent state to another. It means that the data should satisfy all the integrity constraints, validations, and business rules defined in the database schema.
3. Isolation:
Isolation ensures that concurrent transactions do not interfere with each other. Each transaction should be executed in isolation, as if it is the only transaction being executed on the database. This prevents issues such as dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom reads.
4. Durability:
Durability ensures that once a transaction is committed, its changes are permanent and will survive any subsequent failures, such as power outages or system crashes. The changes made by a committed transaction become a permanent part of the database.
Identifying the Options
Now let's identify which options are not a part of the ACID properties:
a) Atomicity: This option is a part of the ACID properties. It ensures that all operations within a transaction are executed successfully or none of them are executed at all.
b) Consistency: This option is a part of the ACID properties. It ensures that a transaction brings the database from one consistent state to another.
c) Duration: This option is not a part of the ACID properties. Duration refers to the time taken to execute a transaction, which is not one of the ACID properties.
d) Independent: This option is not a part of the ACID properties. Independence refers to the ability of transactions to execute concurrently without interfering with each other, which is covered by the isolation property of ACID.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C,D' as duration and independence are not part of the ACID properties of database transactions.
Find the average access time experienced by the CPU in a system with two levels of caches if the following information is given:h1 is the hit rate in the primary cache.
h2 is the hit rate in the secondary cache.
c1 is the time to access information in the primary cache.
c2 is the time to access information in the secondary cache.
M is the time to access information in the main memory.- a)h1c1 + h2c2 + (1 + h1h2) M
- b)h1c1 - h2c2 + (1 - h1h2) M
- c)h1c1 + (1 - h2) h1c2 + (1 - h1) (1 - h2) M
- d)h1c1 + (1 - h1) h2c2 + (1 - h1) (1 - h2) M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the average access time experienced by the CPU in a system with two levels of caches if the following information is given:
h1 is the hit rate in the primary cache.
h2 is the hit rate in the secondary cache.
c1 is the time to access information in the primary cache.
c2 is the time to access information in the secondary cache.
M is the time to access information in the main memory.
h2 is the hit rate in the secondary cache.
c1 is the time to access information in the primary cache.
c2 is the time to access information in the secondary cache.
M is the time to access information in the main memory.
a)
h1c1 + h2c2 + (1 + h1h2) M
b)
h1c1 - h2c2 + (1 - h1h2) M
c)
h1c1 + (1 - h2) h1c2 + (1 - h1) (1 - h2) M
d)
h1c1 + (1 - h1) h2c2 + (1 - h1) (1 - h2) M
|
|
Avantika Yadav answered |
To find the average access time experienced by the CPU in a system with two levels of caches, we need to consider the hit rates and access times of each cache level and the main memory.
Let's break down the given options and analyze each one:
a) h1c1 + h2c2 + (1 - h1h2)M
In this option, we are considering the access time in the primary cache (h1c1), the access time in the secondary cache (h2c2), and the access time in the main memory (M) for cache misses. The term (1 - h1h2) represents the cache miss rate for both the primary and secondary caches. However, this option does not take into account the possibility of a cache hit in the secondary cache after a miss in the primary cache.
b) h1c1 - h2c2 + (1 - h1h2)M
This option is similar to the previous one, but it subtracts the access time in the secondary cache (h2c2) from the access time in the primary cache (h1c1). It also considers the cache miss rate for both caches and the access time in the main memory for cache misses. However, it does not consider the case where a miss in the primary cache is followed by a hit in the secondary cache.
c) h1c1 + (1 - h2)h1c2 + (1 - h1)(1 - h2)M
In this option, we consider the access time in the primary cache (h1c1), the access time in the secondary cache after a miss in the primary cache ((1 - h2)h1c2), and the access time in the main memory for cache misses ((1 - h1)(1 - h2)M). This option takes into account the possibility of a cache miss in the primary cache followed by a hit in the secondary cache.
d) h1c1 + (1 - h1)h2c2 + (1 - h1)(1 - h2)M
This option is similar to the previous one, but it considers the access time in the secondary cache after a miss in the primary cache ((1 - h1)h2c2) instead of considering the access time in the secondary cache after a miss in the primary cache ((1 - h2)h1c2). This option also takes into account the possibility of a cache miss in the primary cache followed by a hit in the secondary cache.
The correct answer is option 'd'. It correctly considers the access times and hit rates of both cache levels and the main memory, including the possibility of a cache miss in the primary cache followed by a hit in the secondary cache.
Let's break down the given options and analyze each one:
a) h1c1 + h2c2 + (1 - h1h2)M
In this option, we are considering the access time in the primary cache (h1c1), the access time in the secondary cache (h2c2), and the access time in the main memory (M) for cache misses. The term (1 - h1h2) represents the cache miss rate for both the primary and secondary caches. However, this option does not take into account the possibility of a cache hit in the secondary cache after a miss in the primary cache.
b) h1c1 - h2c2 + (1 - h1h2)M
This option is similar to the previous one, but it subtracts the access time in the secondary cache (h2c2) from the access time in the primary cache (h1c1). It also considers the cache miss rate for both caches and the access time in the main memory for cache misses. However, it does not consider the case where a miss in the primary cache is followed by a hit in the secondary cache.
c) h1c1 + (1 - h2)h1c2 + (1 - h1)(1 - h2)M
In this option, we consider the access time in the primary cache (h1c1), the access time in the secondary cache after a miss in the primary cache ((1 - h2)h1c2), and the access time in the main memory for cache misses ((1 - h1)(1 - h2)M). This option takes into account the possibility of a cache miss in the primary cache followed by a hit in the secondary cache.
d) h1c1 + (1 - h1)h2c2 + (1 - h1)(1 - h2)M
This option is similar to the previous one, but it considers the access time in the secondary cache after a miss in the primary cache ((1 - h1)h2c2) instead of considering the access time in the secondary cache after a miss in the primary cache ((1 - h2)h1c2). This option also takes into account the possibility of a cache miss in the primary cache followed by a hit in the secondary cache.
The correct answer is option 'd'. It correctly considers the access times and hit rates of both cache levels and the main memory, including the possibility of a cache miss in the primary cache followed by a hit in the secondary cache.
An 8-bit DMA device is operating Cycle Stealing Mode (Single Transfer Mode). Each DMA cycle is of 6 clock states and DMA clock is 2 MHz. Intermediate CPU machine cycle takes 2 μs. Determine the DMA Data Transfer Rate (in Kbytes/sec)
Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer?
An 8-bit DMA device is operating Cycle Stealing Mode (Single Transfer Mode). Each DMA cycle is of 6 clock states and DMA clock is 2 MHz. Intermediate CPU machine cycle takes 2 μs. Determine the DMA Data Transfer Rate (in Kbytes/sec)
|
|
Malavika Banerjee answered |
Understanding DMA and its Operation
Direct Memory Access (DMA) allows peripherals to communicate with system memory without CPU intervention, enhancing efficiency. In Cycle Stealing Mode, the DMA device transfers data one byte at a time while the CPU executes its instructions.
Calculating DMA Transfer Rate
To determine the DMA Data Transfer Rate, consider the following:
- DMA Clock Frequency: 2 MHz (or 2,000,000 Hz)
- DMA Cycle Duration: Each DMA cycle takes 6 clock states.
Step 1: Determine DMA Cycle Time
- Cycle Time = 1 / DMA Clock Frequency = 1 / 2,000,000 = 0.5 μs (or 500 ns).
- Total DMA Cycle Time = 6 clock states * 0.5 μs = 3 μs.
Step 2: Calculate Total Time for Data Transfer
Since the CPU machine cycle takes 2 μs, the DMA can only steal cycles when the CPU is idle. Thus, for every DMA operation, the effective time for each transfer is:
- Effective Transfer Time = CPU Cycle Time + DMA Cycle Time = 2 μs + 3 μs = 5 μs.
Step 3: Determine Transfers per Second
From the effective transfer time:
- Transfers per Second = 1 / Effective Transfer Time = 1 / 5 μs = 200,000 transfers/sec.
Step 4: Calculate Data Transfer Rate
Since the DMA device transfers 1 byte (8 bits) per cycle:
- Data Transfer Rate = Transfers per Second * Bytes per Transfer = 200,000 * 1 = 200,000 bytes/sec.
To convert to Kbytes/sec:
- Data Transfer Rate in Kbytes/sec = 200,000 bytes/sec / 1024 = 195.31 Kbytes/sec, which can be approximated to 200 Kbytes/sec for practical purposes.
Conclusion
Thus, the DMA Data Transfer Rate in Cycle Stealing Mode is approximately 200 Kbytes/sec.
Direct Memory Access (DMA) allows peripherals to communicate with system memory without CPU intervention, enhancing efficiency. In Cycle Stealing Mode, the DMA device transfers data one byte at a time while the CPU executes its instructions.
Calculating DMA Transfer Rate
To determine the DMA Data Transfer Rate, consider the following:
- DMA Clock Frequency: 2 MHz (or 2,000,000 Hz)
- DMA Cycle Duration: Each DMA cycle takes 6 clock states.
Step 1: Determine DMA Cycle Time
- Cycle Time = 1 / DMA Clock Frequency = 1 / 2,000,000 = 0.5 μs (or 500 ns).
- Total DMA Cycle Time = 6 clock states * 0.5 μs = 3 μs.
Step 2: Calculate Total Time for Data Transfer
Since the CPU machine cycle takes 2 μs, the DMA can only steal cycles when the CPU is idle. Thus, for every DMA operation, the effective time for each transfer is:
- Effective Transfer Time = CPU Cycle Time + DMA Cycle Time = 2 μs + 3 μs = 5 μs.
Step 3: Determine Transfers per Second
From the effective transfer time:
- Transfers per Second = 1 / Effective Transfer Time = 1 / 5 μs = 200,000 transfers/sec.
Step 4: Calculate Data Transfer Rate
Since the DMA device transfers 1 byte (8 bits) per cycle:
- Data Transfer Rate = Transfers per Second * Bytes per Transfer = 200,000 * 1 = 200,000 bytes/sec.
To convert to Kbytes/sec:
- Data Transfer Rate in Kbytes/sec = 200,000 bytes/sec / 1024 = 195.31 Kbytes/sec, which can be approximated to 200 Kbytes/sec for practical purposes.
Conclusion
Thus, the DMA Data Transfer Rate in Cycle Stealing Mode is approximately 200 Kbytes/sec.
Improve the bracketed part of the sentence. My car (broke off) on my way to the office.- a)broke out
- b)broke in
- c)broke down
- d)No improvement
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Improve the bracketed part of the sentence. My car (broke off) on my way to the office.
a)
broke out
b)
broke in
c)
broke down
d)
No improvement
|
|
Milan Chavan answered |
Let's understand the meanings of each phrasal verb given in the options:
Broke off = became separated/detached
Broke out = started/began suddenly
Broke in = force entry to a building
Broke down = suddenly ceased or stopped to function (of a machine or motor vehicle)
As per the context of the sentence, the correct phrasal verb is "broke down".
A priority queue is implemented as a Max-Heap. Initially, it has 5 elements. The level-order traversal of the heap is: 10, 8, 5, 3, 2. Two new elements 1 and 7 are inserted into the heap in that order. The level-order traversal of the heap after the insertion of the elements is __________.- a) 10, 8, 7, 3, 2, 1, 5
- b) 10, 8, 7, 2, 3, 1, 5
- c) 10, 8, 7, 1, 2, 3, 5
- d) 10, 8, 7, 5, 3, 2, 1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A priority queue is implemented as a Max-Heap. Initially, it has 5 elements. The level-order traversal of the heap is: 10, 8, 5, 3, 2. Two new elements 1 and 7 are inserted into the heap in that order. The level-order traversal of the heap after the insertion of the elements is __________.
a)
10, 8, 7, 3, 2, 1, 5
b)
10, 8, 7, 2, 3, 1, 5
c)
10, 8, 7, 1, 2, 3, 5
d)
10, 8, 7, 5, 3, 2, 1
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
Max heap: Root node value should be greater than child nodes.
Whenever we insert the new element in the heap, we will insert it at the last level of the heap.
After inserting the element if the max heap doesn't follow the property then we will apply heapify algorithm until we get the max heap.
Whenever insertion will be done in heap, it will always be inserted in the last level from left to right. So, we insert '1' and '7' as a child of node 5 now, we perform heapify algorithm until the heap property will satisfied and then we get the heap whose level order traversal is 10, 8, 7, 3, 2, 1, 5.
Initially heap has 10, 8, 5, 3, 2.
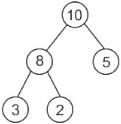
After insertion of 1:
No need to heapify as 5 is greater than 1.
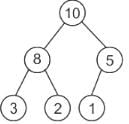
After insertion of 7:
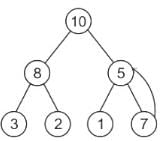
Heapify 5 as 7 is greater than 5.
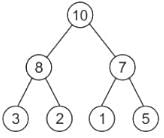
No need to heapify any further as 10 is greater than 7:
Hence, the correct option is (A).
TCP/IP was included by a _______ operating system .- a)UNIX
- b)DARPAN
- c)ACP
- d)NCP
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
TCP/IP was included by a _______ operating system .
a)
UNIX
b)
DARPAN
c)
ACP
d)
NCP
|
|
Kritika Sengupta answered |
TCP/IP was included by a version of UNIX operating system.
Let G be a complete undirected graph of six vertices. If the vertices of G are labelled, then the number of distinct cycles of length 4 in G is
Correct answer is '45'. Can you explain this answer?
Let G be a complete undirected graph of six vertices. If the vertices of G are labelled, then the number of distinct cycles of length 4 in G is
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
There can be total 6C4 ways to pick four vertices from six. The value of 6C4 is 15.
Note that the given graph is complete, so any four vertices can form a cycle.
There can be six different cycles with four vertices. For example, consider four vertices a, b, c and d.
(a, b, c, d, a)
(a, b, d, c, a)
(a, c, b, d, a)
(a, c, d, b, a)
(a, d, b, c, a)
(a, d, c, b, a)
And (a, b, c, d, a) and (a, d, c, b, a); (a, b, d, c, a) and (a, c, d, b, a); and (a, c, b, d, a) and (a, d, b, c, a) are same cycles.
So, total number of distinct cycles = (15 x 3) = 45
Note that the given graph is complete, so any four vertices can form a cycle.
There can be six different cycles with four vertices. For example, consider four vertices a, b, c and d.
(a, b, c, d, a)
(a, b, d, c, a)
(a, c, b, d, a)
(a, c, d, b, a)
(a, d, b, c, a)
(a, d, c, b, a)
And (a, b, c, d, a) and (a, d, c, b, a); (a, b, d, c, a) and (a, c, d, b, a); and (a, c, b, d, a) and (a, d, b, c, a) are same cycles.
So, total number of distinct cycles = (15 x 3) = 45
Consider the relation schema as follows.
Employee (employee-name, sheet, city)
Works (employee-name, company-name, salary)
Company (Company-name, city)
Manages (Employee-name, manager-name)
Write a SQL query that gives the names of the employee who works in the same city and having salary greater than equal to 17000 and less than equal to 35500.
- a)SELECT employee-name
FROM employee, works, company
WHERE salary between 17000 and 35500
- b)SELECT employee-name
FROM employee, works, company
GROUP BY city having salary between 17000 and 35500
- c)SELECT employee-name
FROM employee, works, company
GROUP BY company, city having salary between 17000 and 35500
- d)SELECT employee-name
FROM employee, works, company
GROUP BY city having salary > = 17000 and 35500 salary ≤ 35500
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the relation schema as follows.
Employee (employee-name, sheet, city)
Works (employee-name, company-name, salary)
Company (Company-name, city)
Manages (Employee-name, manager-name)
Works (employee-name, company-name, salary)
Company (Company-name, city)
Manages (Employee-name, manager-name)
Write a SQL query that gives the names of the employee who works in the same city and having salary greater than equal to 17000 and less than equal to 35500.
a)
SELECT employee-name
FROM employee, works, company
WHERE salary between 17000 and 35500
FROM employee, works, company
WHERE salary between 17000 and 35500
b)
SELECT employee-name
FROM employee, works, company
GROUP BY city having salary between 17000 and 35500
FROM employee, works, company
GROUP BY city having salary between 17000 and 35500
c)
SELECT employee-name
FROM employee, works, company
GROUP BY company, city having salary between 17000 and 35500
FROM employee, works, company
GROUP BY company, city having salary between 17000 and 35500
d)
SELECT employee-name
FROM employee, works, company
GROUP BY city having salary > = 17000 and 35500 salary ≤ 35500
FROM employee, works, company
GROUP BY city having salary > = 17000 and 35500 salary ≤ 35500
|
|
Priyanka Ahuja answered |
Between 17000 and 35500
Which of the following sorting algorithms has the lowest worst-case complexity?- a)Merge sort
- b)Bubble sort
- c)Quick sort
- d)Selection sort
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following sorting algorithms has the lowest worst-case complexity?
a)
Merge sort
b)
Bubble sort
c)
Quick sort
d)
Selection sort
|
|
Kunal Sen answered |
Merge Sort
Merge sort is an efficient, stable, and comparison-based sorting algorithm that divides the unsorted list into smaller sublists, sorts those sublists, and then merges them to obtain a sorted list. It has a worst-case complexity of O(n log n).
Bubble Sort
Bubble sort is a simple and inefficient sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through the list, compares adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. It has a worst-case complexity of O(n^2).
Quick Sort
Quick sort is an efficient, comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses a divide-and-conquer strategy. It selects a pivot element and partitions the other elements into two sub-arrays, according to whether they are less than or greater than the pivot. It then recursively sorts the sub-arrays. Quick sort has a worst-case complexity of O(n^2), but on average it has a complexity of O(n log n).
Selection Sort
Selection sort is a simple and inefficient sorting algorithm that repeatedly finds the minimum element from the unsorted part of the list and puts it at the beginning. It has a worst-case complexity of O(n^2).
Comparison of Worst-Case Complexities:
- Merge sort: O(n log n)
- Bubble sort: O(n^2)
- Quick sort: O(n^2)
- Selection sort: O(n^2)
Conclusion:
Among the given sorting algorithms, Merge sort has the lowest worst-case complexity of O(n log n). This means that it performs better than the other algorithms when dealing with larger input sizes. Merge sort's divide-and-conquer approach ensures that it consistently achieves this efficiency, regardless of the initial order of the elements. On the other hand, bubble sort, quick sort, and selection sort all have worst-case complexities of O(n^2), making them less efficient for large-scale sorting tasks.
Merge sort is an efficient, stable, and comparison-based sorting algorithm that divides the unsorted list into smaller sublists, sorts those sublists, and then merges them to obtain a sorted list. It has a worst-case complexity of O(n log n).
Bubble Sort
Bubble sort is a simple and inefficient sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through the list, compares adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. It has a worst-case complexity of O(n^2).
Quick Sort
Quick sort is an efficient, comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses a divide-and-conquer strategy. It selects a pivot element and partitions the other elements into two sub-arrays, according to whether they are less than or greater than the pivot. It then recursively sorts the sub-arrays. Quick sort has a worst-case complexity of O(n^2), but on average it has a complexity of O(n log n).
Selection Sort
Selection sort is a simple and inefficient sorting algorithm that repeatedly finds the minimum element from the unsorted part of the list and puts it at the beginning. It has a worst-case complexity of O(n^2).
Comparison of Worst-Case Complexities:
- Merge sort: O(n log n)
- Bubble sort: O(n^2)
- Quick sort: O(n^2)
- Selection sort: O(n^2)
Conclusion:
Among the given sorting algorithms, Merge sort has the lowest worst-case complexity of O(n log n). This means that it performs better than the other algorithms when dealing with larger input sizes. Merge sort's divide-and-conquer approach ensures that it consistently achieves this efficiency, regardless of the initial order of the elements. On the other hand, bubble sort, quick sort, and selection sort all have worst-case complexities of O(n^2), making them less efficient for large-scale sorting tasks.
Find minimum number of tables required for converting the following entity relationship diagram into relational database?
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Find minimum number of tables required for converting the following entity relationship diagram into relational database?


|
Riverdale Learning Institute answered |
Rules for finding a minimum number of tables required for an ER diagram:
1. A strong entity with single or composite attributes requires one table.
2. A strong entity with multivalued attributes requires two tables.
3. In the case of many to many relations between two entities, 3 tables are required.
There is one to many relationships between R1 and R2.
So, two tables are required for two entities. But, entity R1 contains multivalued attribute B, due to which one table for this is also needed.
Here we have 1 to Many relation so we requires two tables.
Attribute B being multi-valued, we need to remove the multi-valued attribute B to convert the given entity-relationship diagram into a relational database.
As relational database do not allow multi-valued attributes. We have to introduce a new table.
So, the number of tables is as below:
R1
R1 2R2
A table for B (Multi-valued attribute).
So, a total of 3 tables are required for the given entity relational diagram.
Hence, the correct answer is 3.
Which among the following is incorrect about DMA?- a) The controller performs I/O operations.
- b) First register in interface stores address.
- c) The controller gives special access to main memory.
- d) DMA interface carries status in second register.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is incorrect about DMA?
a)
The controller performs I/O operations.
b)
First register in interface stores address.
c)
The controller gives special access to main memory.
d)
DMA interface carries status in second register.
|
|
Arka Dasgupta answered |
Incorrect Statement about DMA:
The incorrect statement about DMA is option 'D': DMA interface carries status in the second register.
Explanation:
DMA (Direct Memory Access) is a technique in computer systems that allows data to be transferred between peripheral devices and main memory without the need for CPU intervention. DMA controllers are responsible for managing these data transfers.
Let's analyze each option to understand why option 'D' is incorrect.
a) The controller performs I/O operations:
- This statement is correct. The DMA controller is responsible for managing data transfers between peripheral devices and main memory, effectively performing I/O operations.
b) First register in the interface stores address:
- This statement is correct. The DMA controller uses registers to store the memory addresses of the source and destination locations for data transfer. The first register in the interface is typically used to store the address of the source or destination.
c) The controller gives special access to main memory:
- This statement is correct. DMA controllers have direct access to the main memory and can transfer data to or from it without CPU intervention. This allows for faster data transfer rates and efficient utilization of CPU resources.
d) DMA interface carries status in the second register:
- This statement is incorrect. The DMA interface does not carry the status in the second register. The status of DMA operations is typically stored in a separate status register or a set of status bits within the DMA controller. These status bits indicate the progress, completion, or any error conditions during the data transfer.
Conclusion:
The incorrect statement about DMA is option 'D' because DMA interface does not carry the status in the second register. The status of DMA operations is usually stored in a separate status register or status bits within the DMA controller.
The incorrect statement about DMA is option 'D': DMA interface carries status in the second register.
Explanation:
DMA (Direct Memory Access) is a technique in computer systems that allows data to be transferred between peripheral devices and main memory without the need for CPU intervention. DMA controllers are responsible for managing these data transfers.
Let's analyze each option to understand why option 'D' is incorrect.
a) The controller performs I/O operations:
- This statement is correct. The DMA controller is responsible for managing data transfers between peripheral devices and main memory, effectively performing I/O operations.
b) First register in the interface stores address:
- This statement is correct. The DMA controller uses registers to store the memory addresses of the source and destination locations for data transfer. The first register in the interface is typically used to store the address of the source or destination.
c) The controller gives special access to main memory:
- This statement is correct. DMA controllers have direct access to the main memory and can transfer data to or from it without CPU intervention. This allows for faster data transfer rates and efficient utilization of CPU resources.
d) DMA interface carries status in the second register:
- This statement is incorrect. The DMA interface does not carry the status in the second register. The status of DMA operations is typically stored in a separate status register or a set of status bits within the DMA controller. These status bits indicate the progress, completion, or any error conditions during the data transfer.
Conclusion:
The incorrect statement about DMA is option 'D' because DMA interface does not carry the status in the second register. The status of DMA operations is usually stored in a separate status register or status bits within the DMA controller.
Consider the options about process state transitions for a system using pre-emptive scheduling:Which of the below-given statements is/are TRUE?- a) A running process can move to ready state.
- b) A blocked process can move to running state.
- c) A ready process can move to running state.
- d) A blocked process can move to ready state.
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the options about process state transitions for a system using pre-emptive scheduling:
Which of the below-given statements is/are TRUE?
a)
A running process can move to ready state.
b)
A blocked process can move to running state.
c)
A ready process can move to running state.
d)
A blocked process can move to ready state.

|
Riverdale Learning Institute answered |
A process state diagram for pre-emptive scheduling is:
Statement I: TRUE
A process can move from running state to ready state on interrupt or when priority expires, that is, when it is pre-empted.
Statement II: TRUE
A ready process moves to running process when it is dispatched.
Statement III: FALSE
A blocked process that is in a waiting state can never move directly to a running state. It must go to the ready queue first.
Statement IV: TRUE
A blocked or waiting process can move to a ready state.
Important Point:
The transition from running to ready state is possible only in pre-emptive scheduling. It cannot happen in non-pre-emptive scheduling.
Hence, the correct options are (A), (B) and (D).
Directions: Choose the sentence that best combines the given sentences.The federal government has diversity of jobs and geographic locations. The federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.- a)In spite of its diversity of jobs and geographic locations, the federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.
- b)No matter its diversity of jobs and geographic locations, the federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.
- c)Because of its diversity of jobs and geographic locations, the federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.
- d)The federal government has diversity of jobs and geographic locations, so it offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Choose the sentence that best combines the given sentences.
The federal government has diversity of jobs and geographic locations. The federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.
a)
In spite of its diversity of jobs and geographic locations, the federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.
b)
No matter its diversity of jobs and geographic locations, the federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.
c)
Because of its diversity of jobs and geographic locations, the federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.
d)
The federal government has diversity of jobs and geographic locations, so it offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector.
|
|
Nisha Ahuja answered |
Explanation of the Correct Answer
The correct answer is option 'C': "Because of its diversity of jobs and geographic locations, the federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector." This sentence effectively combines the two original sentences by establishing a clear causal relationship between the diversity of jobs and the flexibility of job opportunities provided by the federal government.
Key Points of Option C
- Causal Connection: The phrase "Because of" indicates that the diversity in jobs and locations directly contributes to the flexibility in job opportunities. This makes a logical connection between the two ideas, showing that one is a result of the other.
- Clarity and Coherence: The sentence flows well and presents the information in a coherent manner. It clearly communicates that the federal government’s variety of job options leads to unmatched flexibility, making it easy for readers to understand the relationship.
- Focus on Benefits: This option highlights the advantages of working in the federal government, emphasizing that the diversity is not just a characteristic but a reason for the flexibility in job opportunities.
Comparison with Other Options
- Option A: "In spite of" suggests a contradiction rather than a connection, which misrepresents the relationship.
- Option B: "No matter" also implies a disregard for the diversity, failing to establish a causal link.
- Option D: "So it offers" implies a consequence but lacks the clarity of a direct causal relationship.
In conclusion, option 'C' is the best choice as it effectively combines the ideas while maintaining clarity and logical flow.
The correct answer is option 'C': "Because of its diversity of jobs and geographic locations, the federal government offers flexibility in job opportunities that is unmatched in the private sector." This sentence effectively combines the two original sentences by establishing a clear causal relationship between the diversity of jobs and the flexibility of job opportunities provided by the federal government.
Key Points of Option C
- Causal Connection: The phrase "Because of" indicates that the diversity in jobs and locations directly contributes to the flexibility in job opportunities. This makes a logical connection between the two ideas, showing that one is a result of the other.
- Clarity and Coherence: The sentence flows well and presents the information in a coherent manner. It clearly communicates that the federal government’s variety of job options leads to unmatched flexibility, making it easy for readers to understand the relationship.
- Focus on Benefits: This option highlights the advantages of working in the federal government, emphasizing that the diversity is not just a characteristic but a reason for the flexibility in job opportunities.
Comparison with Other Options
- Option A: "In spite of" suggests a contradiction rather than a connection, which misrepresents the relationship.
- Option B: "No matter" also implies a disregard for the diversity, failing to establish a causal link.
- Option D: "So it offers" implies a consequence but lacks the clarity of a direct causal relationship.
In conclusion, option 'C' is the best choice as it effectively combines the ideas while maintaining clarity and logical flow.
Some keys define a relation in a unique manner. The relation is named as Emp dtl. The attributes given to this relation are:
empcode (unique), name, street, city, state and pincode.In this relation, there is a unique city and state for each pincode. Also, for any particular street, state and city, there exists only one pincode. Emp dtl is a relation in (regarding normalisation)- a)1 NF only
- b)2 NF and also in 1 NF
- c)3 NF and also in 2 NF and 1 NF
- d)BCNF and also in 3 NF, 2 NF and 1 NF
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Some keys define a relation in a unique manner. The relation is named as Emp dtl. The attributes given to this relation are:
empcode (unique), name, street, city, state and pincode.
empcode (unique), name, street, city, state and pincode.
In this relation, there is a unique city and state for each pincode. Also, for any particular street, state and city, there exists only one pincode. Emp dtl is a relation in (regarding normalisation)
a)
1 NF only
b)
2 NF and also in 1 NF
c)
3 NF and also in 2 NF and 1 NF
d)
BCNF and also in 3 NF, 2 NF and 1 NF
|
|
Deepika Choudhary answered |
Understanding the Relation: Emp dtl
The relation Emp dtl consists of the following attributes: empcode, name, street, city, state, and pincode. To analyze its normalization, let's break it down.
1NF (First Normal Form)
- The relation is in 1NF since all attributes contain atomic values.
- Each column contains indivisible values, and there are no repeating groups of data.
2NF (Second Normal Form)
- For the relation to be in 2NF, it must first be in 1NF, which it is.
- However, there are partial dependencies present. For instance, the pincode determines the city and state, and the street, city, and state together determine the pincode.
- Since not all non-key attributes are fully functionally dependent on the primary key (empcode), it fails to meet the requirements for 2NF.
3NF (Third Normal Form)
- The relation cannot be in 3NF because it is not in 2NF.
- 3NF requires that there are no transitive dependencies, meaning non-key attributes should not depend on other non-key attributes. Here, pincode depends on street, city, and state.
BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form)
- Similar to 3NF, the relation cannot be in BCNF due to its failure to meet the criteria of 3NF.
Conclusion
Given the above analysis, the relation Emp dtl is only in 1NF, as it does not satisfy the conditions for 2NF or higher levels of normalization. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.
The relation Emp dtl consists of the following attributes: empcode, name, street, city, state, and pincode. To analyze its normalization, let's break it down.
1NF (First Normal Form)
- The relation is in 1NF since all attributes contain atomic values.
- Each column contains indivisible values, and there are no repeating groups of data.
2NF (Second Normal Form)
- For the relation to be in 2NF, it must first be in 1NF, which it is.
- However, there are partial dependencies present. For instance, the pincode determines the city and state, and the street, city, and state together determine the pincode.
- Since not all non-key attributes are fully functionally dependent on the primary key (empcode), it fails to meet the requirements for 2NF.
3NF (Third Normal Form)
- The relation cannot be in 3NF because it is not in 2NF.
- 3NF requires that there are no transitive dependencies, meaning non-key attributes should not depend on other non-key attributes. Here, pincode depends on street, city, and state.
BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form)
- Similar to 3NF, the relation cannot be in BCNF due to its failure to meet the criteria of 3NF.
Conclusion
Given the above analysis, the relation Emp dtl is only in 1NF, as it does not satisfy the conditions for 2NF or higher levels of normalization. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.
Choose the correct option to fill the empty blanks in below statement :If variables are declared previously, then __________ is responsible for generation of symbol table but if variables are not declared then symbol table will be generated by __________.- a)Lexical Analyzer, Semantic Analyzer
- b)Semantic Analyzer, Lexical Analyzer
- c)Lexical Analyzer, Syntax Analyzer
- d)Syntax Analyzer, Semantic Analyzer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct option to fill the empty blanks in below statement :If variables are declared previously, then __________ is responsible for generation of symbol table but if variables are not declared then symbol table will be generated by __________.
a)
Lexical Analyzer, Semantic Analyzer
b)
Semantic Analyzer, Lexical Analyzer
c)
Lexical Analyzer, Syntax Analyzer
d)
Syntax Analyzer, Semantic Analyzer
|
|
Partho Yadav answered |
If variables are declared previously, then semantic analyzer is responsible for generation of symbol table.
If variables are not declared, then lexical analyzer will generate the symbol table.
Hence option b is correct.
Consider the following problems L(G) denotes the language generated by a grammar G.L(M) denotes the language accepted by a machine M.(I) For an unrestricted grammar G and a string w, where w = L(G).(II) Given a Turing Machine M, whether L(M) is regular.(III) Given two grammars G1 and G2 whether L(G1) = L(G2).(IV) Given an NFA N, whether there is a deterministic PDA P such that N and P accept the same language.Which one of the following statements is correct?- a)(I) is undecidable
- b)(II) is undecidable
- c)(III) is undecidable
- d)(IV) is undecidable
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following problems L(G) denotes the language generated by a grammar G.L(M) denotes the language accepted by a machine M.
(I) For an unrestricted grammar G and a string w, where w = L(G).
(II) Given a Turing Machine M, whether L(M) is regular.
(III) Given two grammars G1 and G2 whether L(G1) = L(G2).
(IV) Given an NFA N, whether there is a deterministic PDA P such that N and P accept the same language.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
a)
(I) is undecidable
b)
(II) is undecidable
c)
(III) is undecidable
d)
(IV) is undecidable
|
|
Shruti Tiwari answered |
Understanding the Problems
The problems presented involve different types of grammars and machines in formal language theory. Let's analyze each one to understand why they are undecidable.
Problem I: Unrestricted Grammar Membership
- Statement: For an unrestricted grammar G and a string w, whether w is in L(G).
- Undecidability: This problem is undecidable because it can be reduced from the Halting Problem. There is no algorithm that can determine if a given string belongs to the language generated by an unrestricted grammar.
Problem II: Regular Language Acceptance by Turing Machines
- Statement: Given a Turing Machine M, whether L(M) is regular.
- Undecidability: This is also undecidable. There is no effective method to ascertain if the language accepted by a Turing Machine is regular, as it involves understanding the intricacies of the language generated beyond regular capabilities.
Problem III: Equivalence of Two Grammars
- Statement: Given two grammars G1 and G2, whether L(G1) = L(G2).
- Undecidability: This problem is undecidable for unrestricted grammars. The equivalence of context-free grammars is known to be undecidable, thus extending to unrestricted grammars.
Problem IV: NFA and PDA Language Acceptance
- Statement: Given an NFA N, whether there exists a deterministic PDA P such that N and P accept the same language.
- Decidability: This problem is decidable, as NFAs and PDAs can be transformed into equivalent forms with clear language acceptance criteria.
Conclusion
- As a result, options A, B, and C are correct as they pertain to undecidable problems, while option D is incorrect because it addresses a decidable scenario.
The problems presented involve different types of grammars and machines in formal language theory. Let's analyze each one to understand why they are undecidable.
Problem I: Unrestricted Grammar Membership
- Statement: For an unrestricted grammar G and a string w, whether w is in L(G).
- Undecidability: This problem is undecidable because it can be reduced from the Halting Problem. There is no algorithm that can determine if a given string belongs to the language generated by an unrestricted grammar.
Problem II: Regular Language Acceptance by Turing Machines
- Statement: Given a Turing Machine M, whether L(M) is regular.
- Undecidability: This is also undecidable. There is no effective method to ascertain if the language accepted by a Turing Machine is regular, as it involves understanding the intricacies of the language generated beyond regular capabilities.
Problem III: Equivalence of Two Grammars
- Statement: Given two grammars G1 and G2, whether L(G1) = L(G2).
- Undecidability: This problem is undecidable for unrestricted grammars. The equivalence of context-free grammars is known to be undecidable, thus extending to unrestricted grammars.
Problem IV: NFA and PDA Language Acceptance
- Statement: Given an NFA N, whether there exists a deterministic PDA P such that N and P accept the same language.
- Decidability: This problem is decidable, as NFAs and PDAs can be transformed into equivalent forms with clear language acceptance criteria.
Conclusion
- As a result, options A, B, and C are correct as they pertain to undecidable problems, while option D is incorrect because it addresses a decidable scenario.
The range of signed decimal numbers that can be represented by 6-bit 1's complement number is:- a)-31 to +31
- b)-63 to +63
- c)-64 to +63
- d)-32 to +31
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The range of signed decimal numbers that can be represented by 6-bit 1's complement number is:
a)
-31 to +31
b)
-63 to +63
c)
-64 to +63
d)
-32 to +31
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
The 1's complement number is a 6-bit number. We have to find the maximum and minimum number which can be represented by it.
When the number is negative, then the maximum value can be 111111, i.e. -(26 - 1) = (-31)10.
Here, MSB is for sign.
Maximum positive number is 0 11111, i.e. + (26- 1) = (+ 31)10.
Hence, the range of signed decimal numbers that can be represented by 6-bit 1's complement number is: -31 to +31.
When the number is negative, then the maximum value can be 111111, i.e. -(26 - 1) = (-31)10.
Here, MSB is for sign.
Maximum positive number is 0 11111, i.e. + (26- 1) = (+ 31)10.
Hence, the range of signed decimal numbers that can be represented by 6-bit 1's complement number is: -31 to +31.
What is the maximum number of Binary Search Trees possible with 6 nodes?- a)130
- b)132
- c)135
- d)137
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the maximum number of Binary Search Trees possible with 6 nodes?
a)
130
b)
132
c)
135
d)
137
|
|
Yashvi Chavan answered |
Number of BST with ‘n’ nodes is given by 2nCn/(n+1)
=>12C6/7 =132.
There are 60 students in a class. The students are divided into three groups A, B and C of 15, 20 and 25 students, respectively. The groups A and C are combined to form group D. What is the average weight of the students in group D?- a)More than the average weight of students in group A
- b)More than the average weight of students in group C
- c)Less than the average weight of students in group C
- d)Cannot be determined
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
There are 60 students in a class. The students are divided into three groups A, B and C of 15, 20 and 25 students, respectively. The groups A and C are combined to form group D. What is the average weight of the students in group D?
a)
More than the average weight of students in group A
b)
More than the average weight of students in group C
c)
Less than the average weight of students in group C
d)
Cannot be determined
|
|
Arka Chauhan answered |
Given information:
- Total number of students in the class = 60
- Number of students in group A = 15
- Number of students in group B = 20
- Number of students in group C = 25
Combining groups A and C to form group D:
- Number of students in group D = 15 + 25 = 40
We are not given any information about the weights of the students in each group. Therefore, we cannot determine the average weight of students in group D.
Hence, the correct answer is option D - Cannot be determined.
- Total number of students in the class = 60
- Number of students in group A = 15
- Number of students in group B = 20
- Number of students in group C = 25
Combining groups A and C to form group D:
- Number of students in group D = 15 + 25 = 40
We are not given any information about the weights of the students in each group. Therefore, we cannot determine the average weight of students in group D.
Hence, the correct answer is option D - Cannot be determined.
Which of the following is used for the purpose of link editing?- a)Compiler
- b)Assembler
- c)Loader
- d)Preprocessor
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is used for the purpose of link editing?
a)
Compiler
b)
Assembler
c)
Loader
d)
Preprocessor
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
Loader is a program which performs the functions of:
(1) Loading
(2) Link editing
Link editing is used to create a single program from several files of relocatable machine code.
(1) Loading
(2) Link editing
Link editing is used to create a single program from several files of relocatable machine code.
Which of the following approach can be used to implement lexical analyser?- a)Use a lexical analyzer generator.
- b)Write the lexical analyzer in a conventional systems-programming language
- c)Write the lexical analyzer in assembly language.
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following approach can be used to implement lexical analyser?
a)
Use a lexical analyzer generator.
b)
Write the lexical analyzer in a conventional systems-programming language
c)
Write the lexical analyzer in assembly language.
d)
All of these
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
Lexical Analysis is the first phase of the compiler also known as a scanner. It converts the High-level input program into a sequence of tokens. The following approach can be used to implement a lexical analyzer are:
- Use a lexical analyzer generator such as a lex compiler to produce a lexical analyzer from a regular expression-based specification.
- Write the lexical analyzer in a conventional systems-programming language using the I/O facilities of that language to read the input.
- Write the lexical analyzer in assembly language in assembly language and explicitly manage the reading of input.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Chapter doubts & questions for Syllabus & Full Mock Tests - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Syllabus & Full Mock Tests - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE in English & Hindi are available as part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE
459 videos|1398 docs|786 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









