All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT on your Fingertips 2025-2026 Edition >
All Questions
All questions of MCQ Corner for NEET Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A flower which can be divided into equal vertical halves by more than one plane of division is
- A:
Cyclic
- B:
Zygomorphic
- C:
Actinomorphic
- D:
Heteromorphic
The answer is c.
A flower which can be divided into equal vertical halves by more than one plane of division is
Cyclic
Zygomorphic
Actinomorphic
Heteromorphic

|
Trisha Vashisht answered |
Actinomorphic flowers are radially symmetrical, they are able to be divided into similar halves in more than one vertical plane.
Zygomorphic flowers are bilaterally symmetrical,they can be divided into similar halves in only one plane.
Cyclic is a type of floral organ arrangement, the floral organs are arranged in regular whorls at the node of the thalamus.
Heteromorphic is a type of incompatibilty, same species produce more than one morphological type of flower.
So the correct answer is C
Zygomorphic flowers are bilaterally symmetrical,they can be divided into similar halves in only one plane.
Cyclic is a type of floral organ arrangement, the floral organs are arranged in regular whorls at the node of the thalamus.
Heteromorphic is a type of incompatibilty, same species produce more than one morphological type of flower.
So the correct answer is C
Rhizome of ginger is a modification of stem because:
- a)It bears Adventitious roots
- b)It bears nodes and internodes
- c)It is underground
- d)It stores food material
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rhizome of ginger is a modification of stem because:
a)
It bears Adventitious roots
b)
It bears nodes and internodes
c)
It is underground
d)
It stores food material
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
To differentiate between underground stems and modified roots,standard morphological character considered is presence an absence of nodes and internodes.
Flowers in which only one set of essential organs is present are said to be- a)Polygamous
- b)Bisexual
- c)Dioecious
- d)Unisexual
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Flowers in which only one set of essential organs is present are said to be
a)
Polygamous
b)
Bisexual
c)
Dioecious
d)
Unisexual
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
POLYGAMY ⇒ The condition of bearing some flowers with stamens only, some with pistils only, and some with both, on the same or different plants.
BISEXUAL ⇒ The flower having both male and female reproductive organ on the same plant.
DIOECIOUS ⇒ Both male and female plants may have flowers, but one will have "male" flowers and the other "female" flowers.
UNISEXTUAL ⇒ The flower which has only one essential worl either male or female.
Stem developes from______.
- a)Plumule
- b)Radicle
- c)Both 1 & 2
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stem developes from______.
a)
Plumule
b)
Radicle
c)
Both 1 & 2
d)
None of the above
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The stem is the ascending part of the axis bearing branches, leaves, flowers and fruits. It develops from the plumule of the embryo of a germinating seed. It bears nodes and internodes.
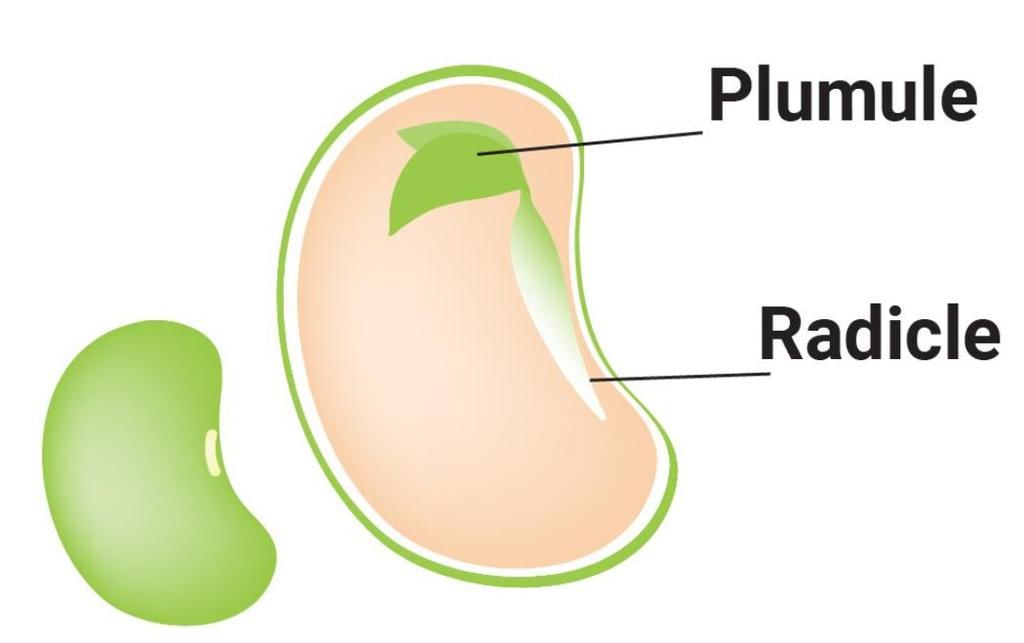
Pulses which we use for daily purpose belong to the family- a)Malvaceae
- b)Liliaceae
- c)Solanaceae
- d)Fabaceae
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pulses which we use for daily purpose belong to the family
a)
Malvaceae
b)
Liliaceae
c)
Solanaceae
d)
Fabaceae

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
Fabaceae are the sources of pulses such as gram, arhar,sem, moong, soyabean.
A scar on the seed coat through which the developing seed is attached to the fruit is- a)Hypocotyl
- b)Coleorhiza
- c)Epicotyl
- d)Hilum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A scar on the seed coat through which the developing seed is attached to the fruit is
a)
Hypocotyl
b)
Coleorhiza
c)
Epicotyl
d)
Hilum
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The outer layer is called testa and the inner layer is called tegmen. There is a scar on the seed coat through which the developing seed was attached to the fruit. This scar is called hilum.
Bicarpellary, syncarpous ovary with axile placentation is seen in the plants of family_______.
- a)Malvaceae
- b)Asteraceae
- c)Solanaceae
- d)Caesalpiniaceae
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bicarpellary, syncarpous ovary with axile placentation is seen in the plants of family_______.
a)
Malvaceae
b)
Asteraceae
c)
Solanaceae
d)
Caesalpiniaceae
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Solanaceae or nightshades are an economically important family of flowering plants. The family ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, epiphytes, shrubs and trees.
In Solanaceae, the gynoecium is Bicarpellary, syncarpous, ovary superior, bilocular, axile placentation, placenta swollen, many ovules in each locule, ovary obliquely placed, style simple; stigma bifid or capitate.
So, the correct answer is 'Solanaceae'.
Placentation in a syncarpous, unilocular ovary bearing two or more placentae longitudinally along the wall is called- a)Apical
- b)Parietal
- c)Axile
- d)Marginal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Placentation in a syncarpous, unilocular ovary bearing two or more placentae longitudinally along the wall is called
a)
Apical
b)
Parietal
c)
Axile
d)
Marginal

|
Gowri Nair answered |
Placentation in a syncarpous, unilocular ovary bearing two or more placentae longitudinallyalong the wall is called parietal placentation.
The small lateral outgrowth of the leaf base which protect the young leaf and its axillary buds in young stage is called- a)Pulvinus
- b)Bracts
- c)Stipules
- d)Petiolate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The small lateral outgrowth of the leaf base which protect the young leaf and its axillary buds in young stage is called
a)
Pulvinus
b)
Bracts
c)
Stipules
d)
Petiolate

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
The leaf base bear two lateral small leaf like structures called stipules.
Testa of seed develops from- a)Hilum
- b)Ovary wall
- c)Outer integument
- d)Funicle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Testa of seed develops from
a)
Hilum
b)
Ovary wall
c)
Outer integument
d)
Funicle
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The outer seed coat (testa) of a seed is produced from outer integument of ovule. The inner integument forms tegmen (inner seed coat). Ovary wall forms pericarp (fruit wall).
Water is absorbed by______.
- a)Root hairs
- b)Root cap
- c)Root
- d)Root apex
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is absorbed by______.
a)
Root hairs
b)
Root cap
c)
Root
d)
Root apex
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Root hairs in plants have large surface area and is surrounded by water soil and nutrients and due to large surface area root hairs absorb water for the growth of plants.
A flower which can be divided into equal vertical halves by more than one plane of division is- a)Cyclic
- b)Zygomorphic
- c)Actinomorphic
- d)Heteromorphic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A flower which can be divided into equal vertical halves by more than one plane of division is
a)
Cyclic
b)
Zygomorphic
c)
Actinomorphic
d)
Heteromorphic
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
A actinomorphic flower is a type of flower that possesses radial symmetry. Any type of cut through the center will divide the flower into two equal parts.
Also known as "star-shaped", “regular”, “radial” or a “polysymmetric” flower, actinomorphic flowers can be bisected at any point and have two identical halves. Most flowers are actinomorphic. On a higher level, this is known as floral symmetry.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the Solanaceae family?- a)Taproot system
- b)Climbing stems
- c)Pinnately compound leaves
- d)Epipetalous anthers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the Solanaceae family?
a)
Taproot system
b)
Climbing stems
c)
Pinnately compound leaves
d)
Epipetalous anthers

|
Manohar Babu answered |
Ncert page 80 epipetalous for solanaceae (to be frank, epiphyllous is regarding to parianth but not to corolla)
Broad part of leaf is:
- a)Leaf base
- b)Petiole
- c)Lamina
- d)All
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Broad part of leaf is:
a)
Leaf base
b)
Petiole
c)
Lamina
d)
All
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Most leaves have two main parts:
(1) the blade and (2) the petiole, or leafstalk. The leaves of some kinds of plants also have a third part, called the stipules. The Blade, or lamina, is the broad, flat part of the leaf. Photosynthesis occurs in the blade, which has many green food-making cells.
(1) the blade and (2) the petiole, or leafstalk. The leaves of some kinds of plants also have a third part, called the stipules. The Blade, or lamina, is the broad, flat part of the leaf. Photosynthesis occurs in the blade, which has many green food-making cells.
If the margin of thalamus grows upward enclosing the ovary completely and getting fused with it, the other parts of flower arise above the ovary, the flower is said to be- a)Perigynous
- b)Hypogynous
- c)Epigynous
- d)Hypergynous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the margin of thalamus grows upward enclosing the ovary completely and getting fused with it, the other parts of flower arise above the ovary, the flower is said to be
a)
Perigynous
b)
Hypogynous
c)
Epigynous
d)
Hypergynous

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
In epigynous flowers, the margin of thalamus grows upward enclosing the ovary completely and getting fused with it, the other parts of flower arise above the ovary.
Which plant shows valvate aestivation?- a)China rose
- b)Pea
- c)Gulmohur
- d)Calotropis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which plant shows valvate aestivation?
a)
China rose
b)
Pea
c)
Gulmohur
d)
Calotropis

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
When sepals or petals in a whorl just touch one another at the margin, without overlapping, as in Calotropis, it is said to be valvate.
Which family is known for its plants with taproot system and includes herbs, shrubs, small trees, and climbers?- a)Solanaceae
- b)Fabaceae
- c)Liliaceae
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which family is known for its plants with taproot system and includes herbs, shrubs, small trees, and climbers?
a)
Solanaceae
b)
Fabaceae
c)
Liliaceae
d)
None of the above

|
Manohar Babu answered |
Ambiguity options fabaceae also show the same. hence both a and b is correct.
Monstera has- a)Adventitious roots
- b)Tap root system
- c)Fibrous root system
- d)Tertiary root
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Monstera has
a)
Adventitious roots
b)
Tap root system
c)
Fibrous root system
d)
Tertiary root
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
In some plants, like grass,Monsteraand the banyan tree, roots arisefrom parts of the plant other than theradicle and are called adventitious roots
The arrangement of leaves on a stem is called:
- a)Venation
- b)Inflorescence
- c)Phyllotaxy
- d)Aestivation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The arrangement of leaves on a stem is called:
a)
Venation
b)
Inflorescence
c)
Phyllotaxy
d)
Aestivation

|
Shalini Saha answered |
The arrangement of leaves on a stem is called phyllotaxy. There are three types of phyllotaxy
The root is covered at the apex by a thimble-like structure called- a)Region of maturation
- b)Root cap
- c)Region of meristematic activity
- d)Root hair
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The root is covered at the apex by a thimble-like structure called
a)
Region of maturation
b)
Root cap
c)
Region of meristematic activity
d)
Root hair

|
Arya Khanna answered |
The root is covered at the apex by a thimble-like structure called the root cap.
Inflorescence which shows indefinite growth and bears a number of flowers due to active growing point is called- a)Racemose
- b)Spike
- c)Corymb
- d)Cymose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Inflorescence which shows indefinite growth and bears a number of flowers due to active growing point is called
a)
Racemose
b)
Spike
c)
Corymb
d)
Cymose

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
In recemose inflorescence indefinite growth occurs and bears a number of flowers due to active growing point.
In which type of placentation, the ovary is unilocularwith a single ovule?- a)Axile placentation
- b)Marginal placentation
- c)Free central placentation
- d)Basal placentation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which type of placentation, the ovary is unilocularwith a single ovule?
a)
Axile placentation
b)
Marginal placentation
c)
Free central placentation
d)
Basal placentation

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
In basalplacentation, the placenta develops at the base of ovary and a single ovule is attached to it,
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds?
- a)They have a single cotyledon.
- b)The endosperm is well-developed and absorbs the cotyledons.
- c)The seed possesses two embryonic leaves or cotyledons
- d)The seed coat is absent.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds?
a)
They have a single cotyledon.
b)
The endosperm is well-developed and absorbs the cotyledons.
c)
The seed possesses two embryonic leaves or cotyledons
d)
The seed coat is absent.
|
|
Anu Saha answered |
**Characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds: The embryo possesses one seed leaf (cotyledon)**
Dicotyledonous seeds are seeds that come from angiosperms (flowering plants) belonging to the class Magnoliopsida. These seeds have several characteristic features, and one of the most distinctive features is that the embryo possesses one seed leaf or cotyledon.
**Explanation:**
1. **Cotyledons:** Cotyledons are the first leaves that emerge from the embryo of a seed. In dicotyledonous seeds, the embryo possesses two cotyledons. These cotyledons serve as a food source for the developing seedling until it becomes photosynthetically active. They are usually thick and fleshy in nature.
2. **Embryo:** The embryo is the tiny, undeveloped plant inside the seed. In dicotyledonous seeds, the embryo possesses two cotyledons. However, the statement in the question is incorrect as it states that the embryo possesses one cotyledon.
3. **Endosperm:** The endosperm is a tissue that provides nourishment to the developing embryo in some seeds. In dicotyledonous seeds, the endosperm is present but is usually not well-developed. Instead, the cotyledons take over the role of storing and supplying nutrients to the growing seedling.
4. **Seed coat:** The seed coat is the protective covering of the seed. It is formed from the outer layer of the ovule after fertilization. In dicotyledonous seeds, the seed coat is present and serves to protect the embryo and its food reserves from damage and desiccation.
In summary, the correct characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds is that the embryo possesses two seed leaves or cotyledons. This feature distinguishes them from monocotyledonous seeds, which have only one seed leaf. The endosperm in dicotyledonous seeds is usually not well-developed, and the seed coat is present for protection.
Dicotyledonous seeds are seeds that come from angiosperms (flowering plants) belonging to the class Magnoliopsida. These seeds have several characteristic features, and one of the most distinctive features is that the embryo possesses one seed leaf or cotyledon.
**Explanation:**
1. **Cotyledons:** Cotyledons are the first leaves that emerge from the embryo of a seed. In dicotyledonous seeds, the embryo possesses two cotyledons. These cotyledons serve as a food source for the developing seedling until it becomes photosynthetically active. They are usually thick and fleshy in nature.
2. **Embryo:** The embryo is the tiny, undeveloped plant inside the seed. In dicotyledonous seeds, the embryo possesses two cotyledons. However, the statement in the question is incorrect as it states that the embryo possesses one cotyledon.
3. **Endosperm:** The endosperm is a tissue that provides nourishment to the developing embryo in some seeds. In dicotyledonous seeds, the endosperm is present but is usually not well-developed. Instead, the cotyledons take over the role of storing and supplying nutrients to the growing seedling.
4. **Seed coat:** The seed coat is the protective covering of the seed. It is formed from the outer layer of the ovule after fertilization. In dicotyledonous seeds, the seed coat is present and serves to protect the embryo and its food reserves from damage and desiccation.
In summary, the correct characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds is that the embryo possesses two seed leaves or cotyledons. This feature distinguishes them from monocotyledonous seeds, which have only one seed leaf. The endosperm in dicotyledonous seeds is usually not well-developed, and the seed coat is present for protection.
Tobacco and Petunia belong to family- a)Solanaceae
- b)Poaceae
- c)Brassicaceae
- d)Fabaceae
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Tobacco and Petunia belong to family
a)
Solanaceae
b)
Poaceae
c)
Brassicaceae
d)
Fabaceae

|
Harihara Samavela answered |
Epiphyllous stamen, superior ovary with bicarpel synacarpous obliquely placed ovary characters are present in these plants
What is the characteristic floral formula of the Leguminosae (Fabaceae) family?- a)5 sepals, 5 petals, 6 stamens (5 long, 1 short), and a superior ovary
- b)5 sepals, 5 petals, numerous stamens, and a single compound ovary
- c)4 sepals, 4 petals, 6 stamens, and a superior ovary
- d)4 sepals, 4 petals, numerous stamens, and an inferior ovary
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
5 sepals, 5 petals, 6 stamens (5 long, 1 short), and a superior ovary
b)
5 sepals, 5 petals, numerous stamens, and a single compound ovary
c)
4 sepals, 4 petals, 6 stamens, and a superior ovary
d)
4 sepals, 4 petals, numerous stamens, and an inferior ovary
|
|
Amrita Khanna answered |
Floral Formula of Leguminosae (Fabaceae) Family
The Leguminosae family, also known as Fabaceae, is characterized by specific floral structures that play a crucial role in their reproductive strategies.
Key Features of the Floral Formula:
- 5 Sepals: The flowers typically have five sepals that form the calyx, providing protection to the developing flower.
- 5 Petals: The corolla consists of five petals, which can be differentiated into a banner (the largest petal), two wings, and a keel (formed by the two lower petals). This arrangement aids in attracting pollinators.
- Numerous Stamens: The floral structure includes numerous stamens, which are responsible for producing pollen. Often, they are arranged in a unique way, with some being longer than others. This arrangement is essential for effective pollination.
- Compound Ovary: The ovary is typically superior and is often compound, meaning it consists of multiple fused carpels. This structure leads to the formation of legumes, which are the characteristic fruit of this family.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct floral formula for the Leguminosae (Fabaceae) family is:
- 5 sepals, 5 petals, numerous stamens, and a single compound ovary.
This description aligns with option 'b', highlighting the intricate floral design that promotes efficient reproduction and adapts well to various pollinators. Understanding these features helps in recognizing the diversity and ecological significance of this plant family.
The Leguminosae family, also known as Fabaceae, is characterized by specific floral structures that play a crucial role in their reproductive strategies.
Key Features of the Floral Formula:
- 5 Sepals: The flowers typically have five sepals that form the calyx, providing protection to the developing flower.
- 5 Petals: The corolla consists of five petals, which can be differentiated into a banner (the largest petal), two wings, and a keel (formed by the two lower petals). This arrangement aids in attracting pollinators.
- Numerous Stamens: The floral structure includes numerous stamens, which are responsible for producing pollen. Often, they are arranged in a unique way, with some being longer than others. This arrangement is essential for effective pollination.
- Compound Ovary: The ovary is typically superior and is often compound, meaning it consists of multiple fused carpels. This structure leads to the formation of legumes, which are the characteristic fruit of this family.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct floral formula for the Leguminosae (Fabaceae) family is:
- 5 sepals, 5 petals, numerous stamens, and a single compound ovary.
This description aligns with option 'b', highlighting the intricate floral design that promotes efficient reproduction and adapts well to various pollinators. Understanding these features helps in recognizing the diversity and ecological significance of this plant family.
What does the presence of a '⊕' symbol in the floral formula signify?- a)The flower is zygomorphic.
- b)The flower is actinomorphic.
- c)The flower has free sepals and petals.
- d)The flower has a superior ovary.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The flower is zygomorphic.
b)
The flower is actinomorphic.
c)
The flower has free sepals and petals.
d)
The flower has a superior ovary.
|
|
Rohan Pillai answered |
Understanding the '⊕' Symbol in Floral Formula
The '⊕' symbol in a floral formula is crucial for identifying the symmetry of a flower. Here’s a detailed explanation of its significance:
1. Zygomorphic vs. Actinomorphic
- Zygomorphic Flowers: These flowers can be divided into two mirror-image halves along only one plane. They are often asymmetrical, and an example is the orchid family.
- Actinomorphic Flowers: These flowers can be divided into multiple symmetrical halves along several planes. They exhibit radial symmetry, like in daisies or hibiscus.
2. The Role of '⊕'
- The '⊕' symbol specifically indicates that the flower exhibits actinomorphic symmetry. This means the flower can be divided into equal halves in multiple ways, showcasing a more uniform appearance.
3. Other Options Explained
- Free Sepals and Petals: This feature is usually denoted by separate symbols (e.g., ‘(’) or ‘[’ rather than '⊕'.
- Superior Ovary: This characteristic is indicated by different symbols (like ‘O’ or ‘o’) and does not relate to the symmetry of the flower.
Conclusion
Thus, the presence of the '⊕' symbol in a floral formula indeed signifies that the flower is actinomorphic, meaning it has radial symmetry. Understanding these symbols helps in the identification and classification of flowering plants, which is essential for exams like NEET.
The '⊕' symbol in a floral formula is crucial for identifying the symmetry of a flower. Here’s a detailed explanation of its significance:
1. Zygomorphic vs. Actinomorphic
- Zygomorphic Flowers: These flowers can be divided into two mirror-image halves along only one plane. They are often asymmetrical, and an example is the orchid family.
- Actinomorphic Flowers: These flowers can be divided into multiple symmetrical halves along several planes. They exhibit radial symmetry, like in daisies or hibiscus.
2. The Role of '⊕'
- The '⊕' symbol specifically indicates that the flower exhibits actinomorphic symmetry. This means the flower can be divided into equal halves in multiple ways, showcasing a more uniform appearance.
3. Other Options Explained
- Free Sepals and Petals: This feature is usually denoted by separate symbols (e.g., ‘(’) or ‘[’ rather than '⊕'.
- Superior Ovary: This characteristic is indicated by different symbols (like ‘O’ or ‘o’) and does not relate to the symmetry of the flower.
Conclusion
Thus, the presence of the '⊕' symbol in a floral formula indeed signifies that the flower is actinomorphic, meaning it has radial symmetry. Understanding these symbols helps in the identification and classification of flowering plants, which is essential for exams like NEET.
The part that develops from the plumule of the embryo of a germinating seed is- a)Fruit
- b)Flower
- c)Stem
- d)Leaf
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The part that develops from the plumule of the embryo of a germinating seed is
a)
Fruit
b)
Flower
c)
Stem
d)
Leaf

|
Mahi Shah answered |
The stem develops from the plumule of the embryo of a germinating seed.
Which among the following is incorrect about phyllotaxy?- a)The arrangement of leaves in the plant is called phyllotaxy
- b)In alternate phyllotaxy, a single leaf is present at each node
- c)Opposite phyllotaxy is present in China rose
- d)In whorled phyllotaxy, multiple leaves are present at each node
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is incorrect about phyllotaxy?
a)
The arrangement of leaves in the plant is called phyllotaxy
b)
In alternate phyllotaxy, a single leaf is present at each node
c)
Opposite phyllotaxy is present in China rose
d)
In whorled phyllotaxy, multiple leaves are present at each node
|
|
Rithika Choudhury answered |
Phyllotaxy refers to the arrangement of leaves on the stem of a plant.
a) The arrangement of leaves in the plant is called phyllotaxy - This statement is correct.
b) In alternate phyllotaxy, a single leaf is present at each node - This statement is correct. In alternate phyllotaxy, a single leaf arises from each node in an alternate manner.
c) Opposite phyllotaxy is present in China rose - This statement is incorrect. China rose exhibits alternate phyllotaxy, not opposite phyllotaxy. Opposite phyllotaxy is seen in plants like guava, bougainvillea, and periwinkle, where two leaves arise from the same node in an opposite manner.
d) In whorled phyllotaxy, multiple leaves are present at each node - This statement is correct. In whorled phyllotaxy, three or more leaves arise from each node in a circular or whorled manner.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
a) The arrangement of leaves in the plant is called phyllotaxy - This statement is correct.
b) In alternate phyllotaxy, a single leaf is present at each node - This statement is correct. In alternate phyllotaxy, a single leaf arises from each node in an alternate manner.
c) Opposite phyllotaxy is present in China rose - This statement is incorrect. China rose exhibits alternate phyllotaxy, not opposite phyllotaxy. Opposite phyllotaxy is seen in plants like guava, bougainvillea, and periwinkle, where two leaves arise from the same node in an opposite manner.
d) In whorled phyllotaxy, multiple leaves are present at each node - This statement is correct. In whorled phyllotaxy, three or more leaves arise from each node in a circular or whorled manner.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
What is the primary function of the root cap in a plant's root system?- a)To absorb water and nutrients from the soil
- b)To protect the root's growing tip as it penetrates the soil
- c)To store food and energy for the plant
- d)To facilitate photosynthesis in the root region
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary function of the root cap in a plant's root system?
a)
To absorb water and nutrients from the soil
b)
To protect the root's growing tip as it penetrates the soil
c)
To store food and energy for the plant
d)
To facilitate photosynthesis in the root region
|
|
Dishani Menon answered |
Primary Function of the Root Cap
The root cap is a crucial structure at the tip of a plant's root system. Its primary function is to provide protection and support as the root grows and penetrates the soil.
Protection of the Growing Tip
- The root cap covers the delicate meristematic tissue, known as the root apical meristem.
- This tissue is responsible for the growth of the root, and it is particularly sensitive to physical damage.
Facilitating Soil Penetration
- As the root grows, it encounters various obstacles in the soil, such as rocks and compacted soil particles.
- The root cap helps the root to push through these materials by secreting mucilage, which lubricates the root and eases its passage.
Gravity Perception
- The root cap contains specialized cells that help the plant detect gravity, enabling the root to grow downward (positive gravitropism).
- This ensures that the plant establishes a stable foundation and effectively anchors itself in the soil.
Root Cap Shedding
- The root cap is constantly being worn away as it encounters soil, and it regularly sheds its outer cells.
- New cells are produced from the underlying meristem to replace those lost, maintaining the protective function.
In summary, the root cap plays an essential role in safeguarding the growing tip of the root as it navigates through the soil, facilitating healthy root development and stability for the plant.
The root cap is a crucial structure at the tip of a plant's root system. Its primary function is to provide protection and support as the root grows and penetrates the soil.
Protection of the Growing Tip
- The root cap covers the delicate meristematic tissue, known as the root apical meristem.
- This tissue is responsible for the growth of the root, and it is particularly sensitive to physical damage.
Facilitating Soil Penetration
- As the root grows, it encounters various obstacles in the soil, such as rocks and compacted soil particles.
- The root cap helps the root to push through these materials by secreting mucilage, which lubricates the root and eases its passage.
Gravity Perception
- The root cap contains specialized cells that help the plant detect gravity, enabling the root to grow downward (positive gravitropism).
- This ensures that the plant establishes a stable foundation and effectively anchors itself in the soil.
Root Cap Shedding
- The root cap is constantly being worn away as it encounters soil, and it regularly sheds its outer cells.
- New cells are produced from the underlying meristem to replace those lost, maintaining the protective function.
In summary, the root cap plays an essential role in safeguarding the growing tip of the root as it navigates through the soil, facilitating healthy root development and stability for the plant.
In the cymose type of inflorescence:
- a)Growth is limited and the flowers are borne in acropetal succession.
- b)The main axis continues to grow and the flowers are borne in basipetal succession.
- c)The main axis continues to grow, and the flowers are borne in acropetal succession.
- d)Growth is limited and the flowers are borne in basipetal succession.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the cymose type of inflorescence:
a)
Growth is limited and the flowers are borne in acropetal succession.
b)
The main axis continues to grow and the flowers are borne in basipetal succession.
c)
The main axis continues to grow, and the flowers are borne in acropetal succession.
d)
Growth is limited and the flowers are borne in basipetal succession.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- In a cymose inflorescence, growth is restricted, and the flowers develop in an acropetal arrangement.
- This means that the primary axis of the inflorescence ends with a flower, and subsequent flowers form in a basipetal (downward) order, with the youngest flowers at the top and the oldest at the bottom.
- The main axis growth is constrained, leading to a definite inflorescence pattern.
Which of the following is not a correct floral character of the members of the family Solanaceae?- a)Flower : Zygomorphic
- b)Calyx: Valvate aestivation
- c)Stamens: Epipetalous
- d)Fruit: Berry or capsule
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a correct floral character of the members of the family Solanaceae?
a)
Flower : Zygomorphic
b)
Calyx: Valvate aestivation
c)
Stamens: Epipetalous
d)
Fruit: Berry or capsule
|
|
Sinjini Das answered |
Answer:
The correct answer is option A) Flower: Zygomorphic.
Explanation:
The family Solanaceae, also known as the nightshade family, includes a wide variety of flowering plants. These plants have several distinct floral characteristics that help differentiate them from other families. Let's examine each of the given options to understand why option A is incorrect.
a) Flower: Zygomorphic:
Zygomorphic flowers are those that can be divided into symmetrical halves along only one plane. In Solanaceae, the flowers are typically actinomorphic, which means they are radially symmetrical and can be divided into similar halves along multiple planes. This feature allows for easier pollination by a wide range of pollinators. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
b) Calyx: Valvate aestivation:
Aestivation refers to the arrangement of floral parts in the bud. Valvate aestivation means that the sepals in the calyx overlap at the margins without any part being inside or outside the others. This is a correct floral character of Solanaceae. The sepals are usually green and fused at the base, forming a tubular or bell-shaped calyx.
c) Stamens: Epipetalous:
Epipetalous stamens are those that are attached to the petals. In Solanaceae, the stamens are often epipetalous, meaning they are attached to the corolla (petals) of the flower. This arrangement is common in many plants of the family and can be observed in flowers such as tomato, potato, and tobacco.
d) Fruit: Berry or capsule:
The fruit in Solanaceae can be either a berry or a capsule. A berry is a fleshy fruit with multiple seeds embedded in the pulp, such as tomatoes or peppers. On the other hand, a capsule is a dry fruit that opens to release its seeds, such as in the case of the genus Datura or Physalis. This is a correct floral character of Solanaceae.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option A) Flower: Zygomorphic, as the flowers of Solanaceae are typically actinomorphic rather than zygomorphic.
The correct answer is option A) Flower: Zygomorphic.
Explanation:
The family Solanaceae, also known as the nightshade family, includes a wide variety of flowering plants. These plants have several distinct floral characteristics that help differentiate them from other families. Let's examine each of the given options to understand why option A is incorrect.
a) Flower: Zygomorphic:
Zygomorphic flowers are those that can be divided into symmetrical halves along only one plane. In Solanaceae, the flowers are typically actinomorphic, which means they are radially symmetrical and can be divided into similar halves along multiple planes. This feature allows for easier pollination by a wide range of pollinators. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
b) Calyx: Valvate aestivation:
Aestivation refers to the arrangement of floral parts in the bud. Valvate aestivation means that the sepals in the calyx overlap at the margins without any part being inside or outside the others. This is a correct floral character of Solanaceae. The sepals are usually green and fused at the base, forming a tubular or bell-shaped calyx.
c) Stamens: Epipetalous:
Epipetalous stamens are those that are attached to the petals. In Solanaceae, the stamens are often epipetalous, meaning they are attached to the corolla (petals) of the flower. This arrangement is common in many plants of the family and can be observed in flowers such as tomato, potato, and tobacco.
d) Fruit: Berry or capsule:
The fruit in Solanaceae can be either a berry or a capsule. A berry is a fleshy fruit with multiple seeds embedded in the pulp, such as tomatoes or peppers. On the other hand, a capsule is a dry fruit that opens to release its seeds, such as in the case of the genus Datura or Physalis. This is a correct floral character of Solanaceae.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option A) Flower: Zygomorphic, as the flowers of Solanaceae are typically actinomorphic rather than zygomorphic.
The given figure represents vexillary aestivation. Select the suitable labels for P, Q and R .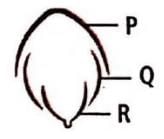
- a)Standard, Wing, Ala
- b)Standard, Carina, Ala
- c)Wing, Keel, Carina
- d)Standard, Keel, Wing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure represents vexillary aestivation. Select the suitable labels for P, Q and R .

a)
Standard, Wing, Ala
b)
Standard, Carina, Ala
c)
Wing, Keel, Carina
d)
Standard, Keel, Wing

|
Lead Academy answered |
In vexillary/descending imbricate aestivation, the posterior petal overlaps the two lateral petals and the latter overlap the two anterior petals. It is also called papilionaceous corolla and found in members of family Papilionaceae.
Which among the following statements is incorrect about stem?- a)The region of stem where buds arise is called a node
- b)The region between two consecutive nodes is called inter-node
- c)Stem system includes fruits, flowers, buds and leaves etc
- d)Stem helps in conduction of water and nutrients between root and shoot
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following statements is incorrect about stem?
a)
The region of stem where buds arise is called a node
b)
The region between two consecutive nodes is called inter-node
c)
Stem system includes fruits, flowers, buds and leaves etc
d)
Stem helps in conduction of water and nutrients between root and shoot

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- The region of stem where buds arise is called a node. The region between two consecutive nodes is called inter-node.
- Stem helps in conduction of water and nutrients between root and shoot. Shoot system includes fruits, flowers, buds and leaves etc.
Hence, the correct option is c
NCERT Reference: Topic “THE STEM” of chapter "Morphology of Flowering Plants" of NCERT.
A seed is made up of- a)Only cotyledons
- b)Only embryo
- c)Only seed coat
- d)A seed coat and an embryo
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A seed is made up of
a)
Only cotyledons
b)
Only embryo
c)
Only seed coat
d)
A seed coat and an embryo

|
Krish Patel answered |
A seed is made up of a seed coat and an embryo.
In Monocotyledonous seeds, the food is stored in the_______.- a)Cotyledons
- b)Endosperm
- c)Seed coat
- d)Embryo axis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Monocotyledonous seeds, the food is stored in the_______.
a)
Cotyledons
b)
Endosperm
c)
Seed coat
d)
Embryo axis
|
|
Mahesh Chaudhary answered |
Understanding Monocotyledonous Seeds
In monocotyledonous seeds, the primary storage of food occurs in the endosperm. Let's delve into the details to understand why this is the case.
Structure of Monocot Seeds
- Monocot seeds, such as those from grasses and cereals, typically have a single cotyledon.
- The seed comprises three main parts: the seed coat, the endosperm, and the embryo axis.
Role of Endosperm
- The endosperm is a tissue that nourishes the developing embryo.
- It is rich in starches, proteins, and oils, making it an ideal food source.
- The endosperm provides essential nutrients during germination, enabling the seedling to grow until it can photosynthesize.
Comparison with Cotyledons
- In monocots, the cotyledon is often not as prominent in food storage as in dicots.
- While dicot seeds store food in their cotyledons, monocots primarily rely on the endosperm.
- This adaptation supports their growth strategy, especially in environments where nutrient availability varies.
Importance of Endosperm in Germination
- During germination, enzymes break down the stored nutrients in the endosperm.
- These nutrients are then transported to the developing embryo to fuel its growth.
- The efficiency of this process is crucial for the survival and establishment of the plant.
In summary, the food stored in monocotyledonous seeds is primarily found in the endosperm, making it a vital component for the seed's development and germination.
In monocotyledonous seeds, the primary storage of food occurs in the endosperm. Let's delve into the details to understand why this is the case.
Structure of Monocot Seeds
- Monocot seeds, such as those from grasses and cereals, typically have a single cotyledon.
- The seed comprises three main parts: the seed coat, the endosperm, and the embryo axis.
Role of Endosperm
- The endosperm is a tissue that nourishes the developing embryo.
- It is rich in starches, proteins, and oils, making it an ideal food source.
- The endosperm provides essential nutrients during germination, enabling the seedling to grow until it can photosynthesize.
Comparison with Cotyledons
- In monocots, the cotyledon is often not as prominent in food storage as in dicots.
- While dicot seeds store food in their cotyledons, monocots primarily rely on the endosperm.
- This adaptation supports their growth strategy, especially in environments where nutrient availability varies.
Importance of Endosperm in Germination
- During germination, enzymes break down the stored nutrients in the endosperm.
- These nutrients are then transported to the developing embryo to fuel its growth.
- The efficiency of this process is crucial for the survival and establishment of the plant.
In summary, the food stored in monocotyledonous seeds is primarily found in the endosperm, making it a vital component for the seed's development and germination.
Which of the following is a key feature of the Gramineae (Poaceae) family regarding its inflorescence?- a)The inflorescence is a raceme, with pedicellate flowers
- b)The inflorescence is a capitulum with ray and disk florets
- c)The inflorescence is a spike or panicle composed of spikelets
- d)The inflorescence is a solitary flower, often large and showy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The inflorescence is a raceme, with pedicellate flowers
b)
The inflorescence is a capitulum with ray and disk florets
c)
The inflorescence is a spike or panicle composed of spikelets
d)
The inflorescence is a solitary flower, often large and showy
|
|
Amrita Khanna answered |
Key Features of Gramineae (Poaceae) Inflorescence
The Gramineae family, commonly known as Poaceae or the grass family, exhibits unique characteristics in its inflorescence, which is crucial for plant reproduction.
Inflorescence Structure
- The inflorescence of Gramineae is typically a spike or panicle.
- A spike consists of a central axis with flowers (spikelets) directly attached, while a panicle is a branched cluster of spikelets.
Spikelets Definition
- Spikelets are the basic units of the inflorescence, each containing one or more florets.
- Each spikelet is subtended by two bracts called glumes, which protect the developing flowers.
Reproductive Efficiency
- The structure of the inflorescence allows for efficient pollination, primarily by wind (anemophily).
- This adaptation is vital for the reproduction of grasses in various habitats.
Variability in Gramineae
- While the general form is a spike or panicle, some species may exhibit variations, yet they will still fall within these categories.
- This family includes important crops like wheat, rice, and corn, showcasing the economic significance of their inflorescence structure.
Conclusion
- In summary, the key feature of the Gramineae (Poaceae) family regarding its inflorescence is its formation of spikes or panicles composed of spikelets, facilitating reproduction and adaptation in diverse environments.
The Gramineae family, commonly known as Poaceae or the grass family, exhibits unique characteristics in its inflorescence, which is crucial for plant reproduction.
Inflorescence Structure
- The inflorescence of Gramineae is typically a spike or panicle.
- A spike consists of a central axis with flowers (spikelets) directly attached, while a panicle is a branched cluster of spikelets.
Spikelets Definition
- Spikelets are the basic units of the inflorescence, each containing one or more florets.
- Each spikelet is subtended by two bracts called glumes, which protect the developing flowers.
Reproductive Efficiency
- The structure of the inflorescence allows for efficient pollination, primarily by wind (anemophily).
- This adaptation is vital for the reproduction of grasses in various habitats.
Variability in Gramineae
- While the general form is a spike or panicle, some species may exhibit variations, yet they will still fall within these categories.
- This family includes important crops like wheat, rice, and corn, showcasing the economic significance of their inflorescence structure.
Conclusion
- In summary, the key feature of the Gramineae (Poaceae) family regarding its inflorescence is its formation of spikes or panicles composed of spikelets, facilitating reproduction and adaptation in diverse environments.
The part of the fruit that develops from the ovary wall is called__________.- a)Pericarp
- b)Seed coat
- c)Endosperm
- d)Cotyledon
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The part of the fruit that develops from the ovary wall is called__________.
a)
Pericarp
b)
Seed coat
c)
Endosperm
d)
Cotyledon
|
|
Arka Chopra answered |
Pericarp:
The term that describes the part of the fruit that develops from the ovary wall is known as the pericarp. The pericarp is the protective layer that surrounds the seeds within a fruit. It is derived from the ovary wall after fertilization.
Composition of Pericarp:
- The pericarp is typically made up of three layers: the exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp.
- The exocarp is the outermost layer of the pericarp, the mesocarp is the middle layer, and the endocarp is the innermost layer surrounding the seeds.
Functions of Pericarp:
- Protection: The pericarp protects the seeds from physical damage, pathogens, and environmental factors.
- Dispersal: It aids in the dispersal of seeds by attracting animals or facilitating wind or water dispersal.
- Nutrient storage: In some fruits, the pericarp stores nutrients that are essential for the growth of the developing seed.
Types of Pericarp:
- Dry pericarp: Examples include capsules, nuts, and achenes.
- Fleshy pericarp: Examples include berries, drupes, and pomes.
Importance of Understanding Pericarp:
Understanding the structure and function of the pericarp is essential for plant biologists, botanists, and agriculturists. It helps in the classification of fruits, understanding seed dispersal mechanisms, and studying the reproductive biology of plants. Additionally, knowledge of the pericarp is crucial in horticulture and agriculture for proper fruit production and storage.
The term that describes the part of the fruit that develops from the ovary wall is known as the pericarp. The pericarp is the protective layer that surrounds the seeds within a fruit. It is derived from the ovary wall after fertilization.
Composition of Pericarp:
- The pericarp is typically made up of three layers: the exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp.
- The exocarp is the outermost layer of the pericarp, the mesocarp is the middle layer, and the endocarp is the innermost layer surrounding the seeds.
Functions of Pericarp:
- Protection: The pericarp protects the seeds from physical damage, pathogens, and environmental factors.
- Dispersal: It aids in the dispersal of seeds by attracting animals or facilitating wind or water dispersal.
- Nutrient storage: In some fruits, the pericarp stores nutrients that are essential for the growth of the developing seed.
Types of Pericarp:
- Dry pericarp: Examples include capsules, nuts, and achenes.
- Fleshy pericarp: Examples include berries, drupes, and pomes.
Importance of Understanding Pericarp:
Understanding the structure and function of the pericarp is essential for plant biologists, botanists, and agriculturists. It helps in the classification of fruits, understanding seed dispersal mechanisms, and studying the reproductive biology of plants. Additionally, knowledge of the pericarp is crucial in horticulture and agriculture for proper fruit production and storage.
A leaf is a leaf in which veins of the same size, such as midribs, protrude from the petiole to the edge of the leaf to form a network.- a)Parallel pinnate
- b)Reticulate palmate
- c)Reticulate pinnate
- d)Parallel palmate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A leaf is a leaf in which veins of the same size, such as midribs, protrude from the petiole to the edge of the leaf to form a network.
a)
Parallel pinnate
b)
Reticulate palmate
c)
Reticulate pinnate
d)
Parallel palmate

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The type of leaf in which many equally strong veins arise from the petiole towards the margin of the leaf forming a network is called reticulate pinnate.
A scar on the seed coat through which the developing seeds were attached to the fruit is called- a)Tegmen
- b)Testa
- c)Micropyle
- d)Hilum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A scar on the seed coat through which the developing seeds were attached to the fruit is called
a)
Tegmen
b)
Testa
c)
Micropyle
d)
Hilum

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
The hilum is a scar on the seed coat through which the developing seeds were attached to the fruit.
The science that deals with the study of form, size, colour, structure and relative position of various parts of organism is called- a)Histology
- b)Anatomy
- c)Cytology
- d)Morphology
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The science that deals with the study of form, size, colour, structure and relative position of various parts of organism is called
a)
Histology
b)
Anatomy
c)
Cytology
d)
Morphology
|
|
Simran Patel answered |
Understanding Morphology
Morphology is a branch of biological science that focuses on the study of the form and structure of organisms. It encompasses various aspects of living beings, making it a fundamental area of study in biology.
Key Aspects of Morphology:
- Form and Size: Morphology examines the overall shape and dimensions of organisms, from microscopic structures to complete organisms.
- Color: Color analysis in morphology helps in understanding adaptations, species identification, and ecological interactions.
- Structure: This involves studying the arrangement and organization of different parts of an organism, including organs and tissues.
- Relative Position: Morphology also considers the spatial relationships between various parts, which is crucial for understanding function and evolution.
Comparison with Other Fields:
- Histology: Focuses on the microscopic structure of tissues. While important, it is a subset of morphology.
- Anatomy: Generally refers to the study of the structure of organisms, often used interchangeably with morphology, but morphology has a broader scope.
- Cytology: Deals specifically with cells and their internal structures, making it more specialized than morphology.
Importance in Biology:
Studying morphology is essential for various biological disciplines, including taxonomy, ecology, and evolutionary biology. Understanding the form and structure of organisms aids in species identification and understanding evolutionary relationships.
In summary, morphology is a comprehensive field that provides insights into the diversity and complexity of life forms, making it a vital area of study for anyone interested in biology.
Morphology is a branch of biological science that focuses on the study of the form and structure of organisms. It encompasses various aspects of living beings, making it a fundamental area of study in biology.
Key Aspects of Morphology:
- Form and Size: Morphology examines the overall shape and dimensions of organisms, from microscopic structures to complete organisms.
- Color: Color analysis in morphology helps in understanding adaptations, species identification, and ecological interactions.
- Structure: This involves studying the arrangement and organization of different parts of an organism, including organs and tissues.
- Relative Position: Morphology also considers the spatial relationships between various parts, which is crucial for understanding function and evolution.
Comparison with Other Fields:
- Histology: Focuses on the microscopic structure of tissues. While important, it is a subset of morphology.
- Anatomy: Generally refers to the study of the structure of organisms, often used interchangeably with morphology, but morphology has a broader scope.
- Cytology: Deals specifically with cells and their internal structures, making it more specialized than morphology.
Importance in Biology:
Studying morphology is essential for various biological disciplines, including taxonomy, ecology, and evolutionary biology. Understanding the form and structure of organisms aids in species identification and understanding evolutionary relationships.
In summary, morphology is a comprehensive field that provides insights into the diversity and complexity of life forms, making it a vital area of study for anyone interested in biology.
Locomotory organ of annelida is- a)Feet
- b)Pseudopodia
- c)Parapodia
- d)Sucker
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Locomotory organ of annelida is
a)
Feet
b)
Pseudopodia
c)
Parapodia
d)
Sucker

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Locomotory organ of annelia is parapodia. Parapodiumare in form of lateral fleshy protrusions on the body surface that help in movement and capturing food.
Find out the incorrect match.- a)Sterile stamen - Staminode
- b)Stamens attached to petals - Epipetalous
- c)Stamens attached to perianth - Episepalous
- d)Free stamens - Polyandrous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out the incorrect match.
a)
Sterile stamen - Staminode
b)
Stamens attached to petals - Epipetalous
c)
Stamens attached to perianth - Episepalous
d)
Free stamens - Polyandrous
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
When stamens are attached to the perianth, they are known as epiphyllous, e.g., Asparagus, lily.
Drupes are also called as stone fruits because- a) The seeds are stone like
- b) Endocarp is always hard and stony
- c) Pericarp is undifferentiated and sclerified
- d) The mesocarp is edible in most fruits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Drupes are also called as stone fruits because
a)
The seeds are stone like
b)
Endocarp is always hard and stony
c)
Pericarp is undifferentiated and sclerified
d)
The mesocarp is edible in most fruits

|
Lead Academy answered |
Drupes, also known as stone fruits, are characterized by having a hard and stony endocarp. The endocarp is the innermost layer of the fruit wall and is often hard and stony in drupes, enclosing the seed(s) within. Examples of drupes include fruits like peach, plum, cherry, and mango, where the endocarp is hard and stony, giving them the name "stone fruits".
In racemose inflorescence, flowers are borne in which sequence?- a)Basipetal succession
- b)Acropetal succession
- c)Spiral succession
- d)Random succession
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Basipetal succession
b)
Acropetal succession
c)
Spiral succession
d)
Random succession
|
|
Naveen Ghoshal answered |
Understanding Racemose Inflorescences
Racemose inflorescence is characterized by the arrangement of flowers along a central stem. The sequence in which they bloom is crucial for understanding plant reproductive strategies.
Acropetal Succession
- In racemose inflorescence, flowers are borne in acropetal succession. This means that the flowers develop from the lower part of the inflorescence towards the upper part.
- As the flowers at the base mature and shed their pollen or petals, new flowers at the top of the raceme are still in bud form, ensuring a continuous blooming period.
Why Acropetal Succession?
- Maximizes Pollination: By having older flowers at the bottom and newer ones at the top, the plant can attract pollinators efficiently. Pollinators are drawn to the mature flowers while still having access to the younger buds.
- Resource Allocation: This arrangement allows the plant to allocate resources effectively, ensuring that the flowers that are ready for fertilization are positioned in a way that maximizes reproductive success.
Examples of Racemose Inflorescence
- Common examples of plants with racemose inflorescences include mustard, snapdragon, and larkspur. These plants exhibit the acropetal pattern, which is evident in their flower arrangement.
Conclusion
Understanding the acropetal succession in racemose inflorescence is essential for appreciating how plants optimize their reproductive strategies, enhancing their chances of successful pollination and seed production.
Racemose inflorescence is characterized by the arrangement of flowers along a central stem. The sequence in which they bloom is crucial for understanding plant reproductive strategies.
Acropetal Succession
- In racemose inflorescence, flowers are borne in acropetal succession. This means that the flowers develop from the lower part of the inflorescence towards the upper part.
- As the flowers at the base mature and shed their pollen or petals, new flowers at the top of the raceme are still in bud form, ensuring a continuous blooming period.
Why Acropetal Succession?
- Maximizes Pollination: By having older flowers at the bottom and newer ones at the top, the plant can attract pollinators efficiently. Pollinators are drawn to the mature flowers while still having access to the younger buds.
- Resource Allocation: This arrangement allows the plant to allocate resources effectively, ensuring that the flowers that are ready for fertilization are positioned in a way that maximizes reproductive success.
Examples of Racemose Inflorescence
- Common examples of plants with racemose inflorescences include mustard, snapdragon, and larkspur. These plants exhibit the acropetal pattern, which is evident in their flower arrangement.
Conclusion
Understanding the acropetal succession in racemose inflorescence is essential for appreciating how plants optimize their reproductive strategies, enhancing their chances of successful pollination and seed production.
In which type of inflorescence does the main axis terminate in a flower?- a)Racemose
- b)Cymose
- c)Whorled
- d)Alternate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Racemose
b)
Cymose
c)
Whorled
d)
Alternate

|
Lead Academy answered |
In cymose inflorescence, the main axis terminates in a flower, making it limited in growth, and flowers are borne in a basipetal order.
When the stamens in a flower remain free, it is said to be
- a)Monoadelphous
- b)Polyadelphous
- c)Diadelphous
- d)Polyandrous
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When the stamens in a flower remain free, it is said to be
a)
Monoadelphous
b)
Polyadelphous
c)
Diadelphous
d)
Polyandrous

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
The correct option is D Polyandrous
Polyandrous flowers are flowers that have many stamens in them, all of which are free from each other.
Example: Flame lily
Monoadelphous stamens are where anthers are free but filaments are united to form a single tube.
Diadelphous stamens are united to form two groups whereas polyadelphous staments are united to form more than two groups.
Example: Flame lily
Monoadelphous stamens are where anthers are free but filaments are united to form a single tube.
Diadelphous stamens are united to form two groups whereas polyadelphous staments are united to form more than two groups.
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of the Malvaceae family that distinguishes it from other plant families?- a)The presence of a superior ovary with parietal placentation
- b)Monadelphous stamens surrounding the pistil
- c)A single carpel with basal placentation
- d)A four-petaled corolla in cruciform arrangement
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The presence of a superior ovary with parietal placentation
b)
Monadelphous stamens surrounding the pistil
c)
A single carpel with basal placentation
d)
A four-petaled corolla in cruciform arrangement
|
|
Amrita Khanna answered |
Characteristic Feature of Malvaceae
The Malvaceae family, commonly known as the mallow family, is distinguished by several unique traits, but one of the most prominent is the structure of its stamens.
Monadelphous Stamens
- Definition: The term "monadelphous" refers to a floral structure where the stamens are fused together in a single group or tube.
- Importance: This characteristic allows for efficient pollination mechanisms. The fusion of stamens aids in the transfer of pollen to pollinators, enhancing reproduction.
- Distinction: While other families may have stamens in various arrangements (e.g., diadelphous, where stamens are in two groups), the monadelphous arrangement is a defining feature of the Malvaceae family.
Other Options Explained
- Superior Ovary with Parietal Placentation: While some members of this family may exhibit this trait, it is not exclusive to Malvaceae and can be found in other families.
- Single Carpel with Basal Placentation: This is not typical for the Malvaceae. Members of this family often have multiple carpels.
- Four-Petaled Corolla in Cruciform Arrangement: This is characteristic of the Brassicaceae family (mustard family), not Malvaceae.
Conclusion
In summary, the characteristic feature that distinctly identifies the Malvaceae family is the presence of monadelphous stamens. This unique structure is critical for the reproductive success of these plants and sets them apart from other plant families.
The Malvaceae family, commonly known as the mallow family, is distinguished by several unique traits, but one of the most prominent is the structure of its stamens.
Monadelphous Stamens
- Definition: The term "monadelphous" refers to a floral structure where the stamens are fused together in a single group or tube.
- Importance: This characteristic allows for efficient pollination mechanisms. The fusion of stamens aids in the transfer of pollen to pollinators, enhancing reproduction.
- Distinction: While other families may have stamens in various arrangements (e.g., diadelphous, where stamens are in two groups), the monadelphous arrangement is a defining feature of the Malvaceae family.
Other Options Explained
- Superior Ovary with Parietal Placentation: While some members of this family may exhibit this trait, it is not exclusive to Malvaceae and can be found in other families.
- Single Carpel with Basal Placentation: This is not typical for the Malvaceae. Members of this family often have multiple carpels.
- Four-Petaled Corolla in Cruciform Arrangement: This is characteristic of the Brassicaceae family (mustard family), not Malvaceae.
Conclusion
In summary, the characteristic feature that distinctly identifies the Malvaceae family is the presence of monadelphous stamens. This unique structure is critical for the reproductive success of these plants and sets them apart from other plant families.
Which of the following correctly describes the floral formula of the Solanaceae family, commonly known as the 'potato family'?- a)⊕ K(5) C(5) A5 G(2)
- b)⊕ K5 C5 A5 G(2)
- c)⊕ K3 C3 A6 G3
- d)⊕ K(5) C(5) A3 G(3)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
⊕ K(5) C(5) A5 G(2)
b)
⊕ K5 C5 A5 G(2)
c)
⊕ K3 C3 A6 G3
d)
⊕ K(5) C(5) A3 G(3)
|
|
Nitya Shah answered |
Floral Formula of Solanaceae Family
The Solanaceae family, also known as the 'potato family', is characterized by specific floral structures. The correct floral formula is essential for identifying and classifying this family.
Understanding the Floral Formula
- ⊕: Indicates that the flower is actinomorphic (symmetrical).
- K5: Refers to the calyx, which consists of 5 fused or separate sepals.
- C5: Indicates the corolla made up of 5 petals, which may also be fused or separate.
- A5: Represents the five stamens present in the flower.
- G(2): Denotes the presence of a bicarpellary (two-carpel) ovary, which is superior.
Explanation of Option B
- Option B: ⊕ K5 C5 A5 G(2) is correct because:
- The actinomorphic nature of the flower allows for uniformity in petal arrangement.
- The 5 sepals (K5) and 5 petals (C5) are typical of many members in the Solanaceae family, including potatoes and tomatoes.
- The 5 stamens (A5) are consistently found in this family, contributing to their reproductive success.
- The bicarpellary ovary (G(2)) signifies a key reproductive characteristic of the family.
Importance in Botany
Understanding the floral formula helps in identifying and differentiating plants within the Solanaceae family, vital for studies in botany and agriculture, especially concerning crops like potatoes, tomatoes, and eggplants.
The Solanaceae family, also known as the 'potato family', is characterized by specific floral structures. The correct floral formula is essential for identifying and classifying this family.
Understanding the Floral Formula
- ⊕: Indicates that the flower is actinomorphic (symmetrical).
- K5: Refers to the calyx, which consists of 5 fused or separate sepals.
- C5: Indicates the corolla made up of 5 petals, which may also be fused or separate.
- A5: Represents the five stamens present in the flower.
- G(2): Denotes the presence of a bicarpellary (two-carpel) ovary, which is superior.
Explanation of Option B
- Option B: ⊕ K5 C5 A5 G(2) is correct because:
- The actinomorphic nature of the flower allows for uniformity in petal arrangement.
- The 5 sepals (K5) and 5 petals (C5) are typical of many members in the Solanaceae family, including potatoes and tomatoes.
- The 5 stamens (A5) are consistently found in this family, contributing to their reproductive success.
- The bicarpellary ovary (G(2)) signifies a key reproductive characteristic of the family.
Importance in Botany
Understanding the floral formula helps in identifying and differentiating plants within the Solanaceae family, vital for studies in botany and agriculture, especially concerning crops like potatoes, tomatoes, and eggplants.
In the Compositae (Asteraceae) family, what is the function of the pappus in the fruit?- a)It aids in pollination
- b)It protects the seed from desiccation
- c)It helps in seed dispersal by wind
- d)It attracts pollinators to the flower
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It aids in pollination
b)
It protects the seed from desiccation
c)
It helps in seed dispersal by wind
d)
It attracts pollinators to the flower

|
Top Rankers answered |
The pappus in Compositae fruits is a modified calyx that helps in wind dispersal of seeds, often resembling a tuft of hairs, bristles, or scales.
If the gynoecium is present in the top most position of the thalamus, the flower is referred to as- a)hypogynous
- b)perigynous
- c)epigynous
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the gynoecium is present in the top most position of the thalamus, the flower is referred to as
a)
hypogynous
b)
perigynous
c)
epigynous
d)
none of these
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In hypogynous condition of flowers, the thalamus is convex or conical. Gynoecium occupies the topmost (superior) position at the thalamus and other parts of flower are borne successively below. Androperianth or other floral organs are inferior, e.g, Hibiscus rosa sinensis, Ranunculus, etc.
Chapter doubts & questions for MCQ Corner - NCERT on your Fingertips 2025-2026 Edition 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of MCQ Corner - NCERT on your Fingertips 2025-2026 Edition in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









