All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Stoichiometry (GC) for MCAT Exam
The molar mass of ZnSO4 is- a)161.47 g
- b)136.4g
- c)166.4g
- d)156.4g
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The molar mass of ZnSO4 is
a)
161.47 g
b)
136.4g
c)
166.4g
d)
156.4g
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Chemical Formula: ZnSO4
Molar Mass: 161.47 g/mol (anhydrous)
Molar Mass: 161.47 g/mol (anhydrous)
For the reaction 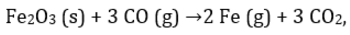 224 g of CO is available to react with 400 g Fe2O3, the yield of iron and CO2, are:
224 g of CO is available to react with 400 g Fe2O3, the yield of iron and CO2, are:- a)225 and 279
- b)280 and 330 g
- c)210 and 290
- d)210 and 279 g
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction
224 g of CO is available to react with 400 g Fe2O3, the yield of iron and CO2, are:
a)
225 and 279
b)
280 and 330 g
c)
210 and 290
d)
210 and 279 g
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Moles of CO =8 moles Moles of Fe2O3= 2.5 moles.
3 moles of CO is needed for 1 mole of Fe2O3 so 8 moles of CO will require 2.66 mole of Fe2O3 so Fe2O3 is limiting reagent.
1 mole of Fe2O3 produce 2 mole of Fe so 2.5 mole of Fe2O3will produce 5 mole of Fe = 280g of Fe.
Also 1 mole of Fe2O3 also produce 3 mole of CO2 so 2.5 mole of Fe2O3 will produce 7.5 mole of CO2=330g.
How many atoms of hydrogen are in 67.2 L of H2 at STP?
- a)5.612 × 1024
- b)2.612 × 1024
- c)4.612 × 1024
- d)3.6132 × 1024
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many atoms of hydrogen are in 67.2 L of H2 at STP?
a)
5.612 × 1024
b)
2.612 × 1024
c)
4.612 × 1024
d)
3.6132 × 1024
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) is defined as 0 degrees Celsius and 1 atmosphere of pressure. At STP, 1 mole of any gas occupies 22.4 liters.
First, calculate the number of moles of hydrogen gas (H2) in 67.2 liters:
67.2 L / 22.4 L/mole = 3 moles of H2
Each molecule of H2 contains 2 atoms of hydrogen. Therefore, 3 moles of H2 contains:
3 moles * (6.022 x 10^23 molecules/mole) * 2 atoms/molecule = 3.6132 x 10^24 atoms of hydrogen.
First, calculate the number of moles of hydrogen gas (H2) in 67.2 liters:
67.2 L / 22.4 L/mole = 3 moles of H2
Each molecule of H2 contains 2 atoms of hydrogen. Therefore, 3 moles of H2 contains:
3 moles * (6.022 x 10^23 molecules/mole) * 2 atoms/molecule = 3.6132 x 10^24 atoms of hydrogen.
A measured temperature is 100 0F on Fahrenheit scale, then what is this reading be on Celsius scale :- a)11.2 0C
- b)78 0C
- c)102.7 0C
- d)37.8 0C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A measured temperature is 100 0F on Fahrenheit scale, then what is this reading be on Celsius scale :
a)
11.2 0C
b)
78 0C
c)
102.7 0C
d)
37.8 0C
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
C-0/100-0 = F-32/180.
C/5= F-32/9.
C/5= 100-32/9.
C/5= 68/9.
C= 68×5/9.
C= 340/9.
C= 37.77.
C= 37.8
C/5= F-32/9.
C/5= 100-32/9.
C/5= 68/9.
C= 68×5/9.
C= 340/9.
C= 37.77.
C= 37.8
Chemistry does not play a major role in- a)Design and synthesis new materials having specific magnetic, electric and optical properties.
- b)Large scale production of a variety of fertilizers
- c)Explaining superconductivity
- d)Explaining ozone depletion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Chemistry does not play a major role in
a)
Design and synthesis new materials having specific magnetic, electric and optical properties.
b)
Large scale production of a variety of fertilizers
c)
Explaining superconductivity
d)
Explaining ozone depletion
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Chemistry does not deal in explaining superconductivity.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:How many atoms of Oxygen are there in 18g of water? (Hint: Avagadro’s Number = 6.02 x 1023 atoms/mol)- a:8.02 x 1023
- b:6.02 x 1023
- c:5 .02 x 1023
- d:7.02 x 1023
Correct answer is 'b'.
How many atoms of Oxygen are there in 18g of water? (Hint: Avagadro’s Number = 6.02 x 1023 atoms/mol)
a:
8.02 x 1023
b:
6.02 x 1023
c:
5 .02 x 1023
d:
7.02 x 1023
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
18g H2O = 1mol water = 6.02 x 1023 molecules of water = 6.02 x 1023 atoms of oxygen.
The molar mass of Al2O3 is- a)112
- b)82
- c)102
- d)92
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The molar mass of Al2O3 is
a)
112
b)
82
c)
102
d)
92
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Molar mass = 2(27) +3 (16) = 102g.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Choose the most appropriate answer amongst the options given below for the statement. A solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting- a:solution of known higher concentration
- b:solution of known lower concentration
- c:from a serially diluted solution
- d:stock solution.
Correct answer is 'd'.
Choose the most appropriate answer amongst the options given below for the statement. A solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting
a:
solution of known higher concentration
b:
solution of known lower concentration
c:
from a serially diluted solution
d:
stock solution.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Stock solution is diluted to prepare the solution of desired concentration.
The molar mass of AgNO3 is- a)169.87 g
- b)189.9
- c)179.9
- d)159.9
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The molar mass of AgNO3 is
a)
169.87 g
b)
189.9
c)
179.9
d)
159.9
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Molar mass of AgNO3 = mass of Ag + N + O3 = 107.87 + 14 + 3* 16 = 107. 87 + 14 + 48 = 169.87 g
There are ____ in 12.0 ml?- a)0.12 L
- b)120 L
- c)0.012 L
- d)12000 L
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are ____ in 12.0 ml?
a)
0.12 L
b)
120 L
c)
0.012 L
d)
12000 L
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Since we know that 1litre -1000ml 1ml-1\1000litre So,12ml-1/1000×12=12/1000 =0.012
SI unit of density is
- a)kg−1m3
- b)kg m−2
- c)kg m3
- d)kg m−3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
SI unit of density is
a)
kg−1m3
b)
kg m−2
c)
kg m3
d)
kg m−3

|
Kunal Patel answered |
density = mass/volume. SI unit of mass is kg and that of volume is m3
If a matter has definite volume and definite shape, then it is :- a)Solid
- b)Liquid
- c)Gas
- d)All of the Above
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a matter has definite volume and definite shape, then it is :
a)
Solid
b)
Liquid
c)
Gas
d)
All of the Above
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Solid
Holds shape
Fixed Volume
Liquid
Shape of Container
Free Surface
Fixed Volume
Gas
Shape Of Container
Volume of Container
Explanation:
Solid is the only state of matter that has a definite shape and definite volume.
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to oxygen atom in- a)superoxides
- b)when oxygen is bonded to fluorine
- c)when oxygen is bonded to metals
- d)peroxidesperoxides
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to oxygen atom in
a)
superoxides
b)
when oxygen is bonded to fluorine
c)
when oxygen is bonded to metals
d)
peroxidesperoxides
|
|
Arka Desai answered |
The oxidation number is a concept used in chemistry to keep track of the distribution of electrons in a compound or molecule. It is a measure of the charge that an atom would have if all the shared electrons were assigned to the more electronegative atom in a bond.
In the case of oxygen, its most common oxidation number is -2. However, in certain compounds, such as superoxides and peroxides, the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides. Superoxides are a class of compounds that contain the superoxide ion, O2-. In this ion, each oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -1/2. This is because the oxygen-oxygen bond in the superoxide ion is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. Therefore, each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1/2 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
In the case of peroxides, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. In peroxides, the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1. Each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to fluorine, the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and therefore, it attracts the shared electrons in the bond more strongly than oxygen. As a result, oxygen is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the unequal distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to metals, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -2. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as in certain metal peroxides or superoxides, where the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
In summary, the oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides, where the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. In other compounds, such as peroxides, fluorides, and most metal oxides, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -1 or -2.
In the case of oxygen, its most common oxidation number is -2. However, in certain compounds, such as superoxides and peroxides, the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides. Superoxides are a class of compounds that contain the superoxide ion, O2-. In this ion, each oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -1/2. This is because the oxygen-oxygen bond in the superoxide ion is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. Therefore, each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1/2 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
In the case of peroxides, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. In peroxides, the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1. Each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to fluorine, the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and therefore, it attracts the shared electrons in the bond more strongly than oxygen. As a result, oxygen is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the unequal distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to metals, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -2. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as in certain metal peroxides or superoxides, where the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
In summary, the oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides, where the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. In other compounds, such as peroxides, fluorides, and most metal oxides, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -1 or -2.
In scientific notation for such numbers, any number can be represented in the form N × 10n where- a)n is an exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary from 10 to 100
- b)n is an exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary from 0 to 1
- c)n is an exponent having positive values only and N can vary from 1 to 10
- d)n is an exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary from 1 to 10
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In scientific notation for such numbers, any number can be represented in the form N × 10n where
a)
n is an exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary from 10 to 100
b)
n is an exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary from 0 to 1
c)
n is an exponent having positive values only and N can vary from 1 to 10
d)
n is an exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary from 1 to 10
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Scientific notation and Significant Figures. It is exponential notation in which any number can be represented in the form N X 10n where n is an exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary between 1 to 10.
The molar mass of CaCO3 is- a)120
- b)70
- c)100
- d)90
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The molar mass of CaCO3 is
a)
120
b)
70
c)
100
d)
90
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Molar Mass
Molar mass relates the mass of a substance to the moles of the substance (g/mol). The mole in chemistry is sometimes called the chemist's ''dozen'' because it's a counting unit like a dozen. Just like there are 12 donuts in a dozen, there is 6.02 x 1023 atoms or molecules in a mole. Molar mass tells chemists how many grams of a substance are needed for 6.02 x 1023 atoms or molecules.
The molar mass of calcium carbonate is 100.086g/mol.
The first step of determining the molar mass is to determine the chemical formula of calcium carbonate, which is CaCO3. Then, multiply the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms in the formula. You can find the atomic mass on the periodic table.
1 Ca: 1 x 40.078 g/mol = 40.078 g/mol
1 C: 1 x 12.011 g/mol = 12.011 g/mol
3 O: 3 x 15.999 g/mol = 47.997 g/mol
Add all the atomic masses to determine the molar mass.
40.078 g/mol + 12.011 g/mol + 47.997 g/mol = 100.086 g/mol
Hydrogen is prepared from H2O by adding- a)Ag, which acts as reducing agent
- b)Ca, which acts as reducing agent
- c)Au, which acts as oxidising agent
- d)AI, which acts as oxidising agent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen is prepared from H2O by adding
a)
Ag, which acts as reducing agent
b)
Ca, which acts as reducing agent
c)
Au, which acts as oxidising agent
d)
AI, which acts as oxidising agent
|
|
Saumya Dey answered |
Preparation of Hydrogen from Water
- Hydrogen gas can be prepared from water by using a reducing agent, which reduces water to hydrogen gas and also gets oxidized in the process.
- Calcium (Ca) is a good reducing agent and can be used to prepare hydrogen gas from water.
- When calcium is added to water, it reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
- Calcium has a strong affinity for oxygen and readily reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide, liberating hydrogen gas.
- This reaction is exothermic and produces a considerable amount of heat, which can be used to heat water or other substances.
- The liberated hydrogen gas can be collected by upward displacement of air or by using a gas syringe or gas jar.
- The purity of hydrogen gas prepared by this method is relatively low, as it may contain impurities like calcium hydroxide, unreacted water, and other gases like nitrogen and oxygen.
- Therefore, additional purification steps may be required to obtain pure hydrogen gas.
Advantages of using Calcium as a reducing agent
- Calcium is a readily available and inexpensive reducing agent.
- It reacts readily with water, producing a large amount of hydrogen gas.
- The reaction is exothermic and produces heat, which can be utilized in other processes.
- Calcium is a relatively safe reducing agent, as it does not react violently with water or other substances.
- The by-products of the reaction, calcium hydroxide, and hydrogen gas, are non-toxic and can be disposed of safely.
- Hydrogen gas can be prepared from water by using a reducing agent, which reduces water to hydrogen gas and also gets oxidized in the process.
- Calcium (Ca) is a good reducing agent and can be used to prepare hydrogen gas from water.
- When calcium is added to water, it reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
- Calcium has a strong affinity for oxygen and readily reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide, liberating hydrogen gas.
- This reaction is exothermic and produces a considerable amount of heat, which can be used to heat water or other substances.
- The liberated hydrogen gas can be collected by upward displacement of air or by using a gas syringe or gas jar.
- The purity of hydrogen gas prepared by this method is relatively low, as it may contain impurities like calcium hydroxide, unreacted water, and other gases like nitrogen and oxygen.
- Therefore, additional purification steps may be required to obtain pure hydrogen gas.
Advantages of using Calcium as a reducing agent
- Calcium is a readily available and inexpensive reducing agent.
- It reacts readily with water, producing a large amount of hydrogen gas.
- The reaction is exothermic and produces heat, which can be utilized in other processes.
- Calcium is a relatively safe reducing agent, as it does not react violently with water or other substances.
- The by-products of the reaction, calcium hydroxide, and hydrogen gas, are non-toxic and can be disposed of safely.
Choose the most appropriate answer amongst the options given below for the statement. A solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting- a)solution of known higher concentration
- b)solution of known lower concentration
- c)from a serially diluted solution
- d)stock solution.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the most appropriate answer amongst the options given below for the statement. A solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting
a)
solution of known higher concentration
b)
solution of known lower concentration
c)
from a serially diluted solution
d)
stock solution.

|
Atharva Pillai answered |
Preparing Stock Solutions
A stock solution is prepared by weighing out an appropriate portion of a pure solid or by measuring out an appropriate volume of a pure liquid and diluting to a known volume. Exactly how this is done depends on the required concentration unit. For example, to prepare a solution with a desired molarity you weigh out an appropriate mass of the reagent, dissolve it in a portion of solvent, and bring to the desired volume. To prepare a solution where the solute’s concentration is a volume percent, you measure out an appropriate volume of solute and add sufficient solvent to obtain the desired total volume.
There are ____ in 0.05 ml?- a)50 liters
- b)0.00005 liters
- c)5 liters
- d)0.0005 liters
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There are ____ in 0.05 ml?
a)
50 liters
b)
0.00005 liters
c)
5 liters
d)
0.0005 liters

|
Arnav Kulkarni answered |
1L=1000mL so 0.00005L=0.05mL.
Suppose that an industrial chemist wishes to obtain calcium chloride (CaCl2) by reacting calcium metal with chlorine gas. For safety reasons, she wishes to design the reaction to ensure that all of the chlorine gas is used in synthesis. Which of the following methods will ensure that the minimum amount of chlorine remains after the reaction?- a)The amount of chlorine used is independent of the relative ratios of reagents
- b)Adding less calcium in deficit of that required by stoichiometry
- c)Adding additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry
- d)Adding the exact amount of calcium required by stoichiometry
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose that an industrial chemist wishes to obtain calcium chloride (CaCl2) by reacting calcium metal with chlorine gas. For safety reasons, she wishes to design the reaction to ensure that all of the chlorine gas is used in synthesis. Which of the following methods will ensure that the minimum amount of chlorine remains after the reaction?
a)
The amount of chlorine used is independent of the relative ratios of reagents
b)
Adding less calcium in deficit of that required by stoichiometry
c)
Adding additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry
d)
Adding the exact amount of calcium required by stoichiometry
|
|
Avery Hernandez answered |
Explanation:
To ensure that the minimum amount of chlorine remains after the reaction, the industrial chemist should add additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry. This is because the reaction between calcium metal and chlorine gas is a redox reaction, where calcium is oxidized and chlorine is reduced. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
Ca(s) + Cl2(g) → CaCl2(s)
The stoichiometry of the reaction tells us that one mole of calcium reacts with one mole of chlorine gas to form one mole of calcium chloride. Therefore, adding additional calcium in excess will ensure that all of the chlorine is consumed in the reaction.
Reasoning:
1. Stoichiometry of the Reaction:
The stoichiometry of the reaction determines the molar ratios of the reactants and products involved. In this case, the stoichiometry tells us that one mole of calcium reacts with one mole of chlorine gas to form one mole of calcium chloride. Therefore, the amount of chlorine used is dependent on the amount of calcium present.
2. Excess Calcium:
By adding additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry, the industrial chemist ensures that all of the chlorine gas is consumed in the reaction. Any remaining calcium will not react with the chlorine, as there is no more chlorine available. This allows for the complete utilization of the chlorine and minimizes the amount of chlorine that remains after the reaction.
Conclusion:
Adding additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry is the method that will ensure that the minimum amount of chlorine remains after the reaction. This approach allows for the complete utilization of the chlorine gas, ensuring that none of it is wasted or left unused.
To ensure that the minimum amount of chlorine remains after the reaction, the industrial chemist should add additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry. This is because the reaction between calcium metal and chlorine gas is a redox reaction, where calcium is oxidized and chlorine is reduced. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
Ca(s) + Cl2(g) → CaCl2(s)
The stoichiometry of the reaction tells us that one mole of calcium reacts with one mole of chlorine gas to form one mole of calcium chloride. Therefore, adding additional calcium in excess will ensure that all of the chlorine is consumed in the reaction.
Reasoning:
1. Stoichiometry of the Reaction:
The stoichiometry of the reaction determines the molar ratios of the reactants and products involved. In this case, the stoichiometry tells us that one mole of calcium reacts with one mole of chlorine gas to form one mole of calcium chloride. Therefore, the amount of chlorine used is dependent on the amount of calcium present.
2. Excess Calcium:
By adding additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry, the industrial chemist ensures that all of the chlorine gas is consumed in the reaction. Any remaining calcium will not react with the chlorine, as there is no more chlorine available. This allows for the complete utilization of the chlorine and minimizes the amount of chlorine that remains after the reaction.
Conclusion:
Adding additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry is the method that will ensure that the minimum amount of chlorine remains after the reaction. This approach allows for the complete utilization of the chlorine gas, ensuring that none of it is wasted or left unused.
The molar mass of C6H10O5 is- a)182
- b)152
- c)162
- d)172
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The molar mass of C6H10O5 is
a)
182
b)
152
c)
162
d)
172

|
Advait Chakraborty answered |
Molar mass = 6(12)+10(1)+5(16)=162g
Assign oxidation number to P in NaH2PO4- a)+6
- b)+1
- c)+4
- d)5.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assign oxidation number to P in NaH2PO4
a)
+6
b)
+1
c)
+4
d)
5.0

|
Raksha Nambiar answered |
Oxidation state of P in NaH2PO4
Suppose 1 mol of H2 completely reacts with 1 mol of O2 to form water. How many mols of water will result from the reaction?- a)2 mol
- b)4 mol
- c)1 mol
- d).5 mol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose 1 mol of H2 completely reacts with 1 mol of O2 to form water. How many mols of water will result from the reaction?
a)
2 mol
b)
4 mol
c)
1 mol
d)
.5 mol
|
|
Abigail Rodriguez answered |
Understanding the Reaction
When hydrogen gas (H2) reacts with oxygen gas (O2), they combine to form water (H2O). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
This equation indicates that:
- 2 moles of H2 react with 1 mole of O2 to produce 2 moles of H2O.
Reaction Stoichiometry
In this scenario, you start with:
- 1 mole of H2
- 1 mole of O2
According to the stoichiometry of the balanced equation:
- 1 mole of H2 would need 0.5 moles of O2 to react completely (since 2 moles of H2 require 1 mole of O2).
Since you have 1 mole of O2 available, it is in excess. The limiting reactant here is H2.
Water Production
From the stoichiometric ratios in the reaction:
- 1 mole of H2 produces 1 mole of H2O (as 2 moles of H2 yield 2 moles of H2O, 1 mole of H2 yields 1 mole of H2O).
Therefore, when 1 mole of H2 reacts completely with 1 mole of O2, it results in:
- 1 mole of water (H2O) produced.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is:
- 1 mole of water will result from the reaction (option C).
This understanding of stoichiometry is essential in chemistry for predicting the outcomes of reactions.
When hydrogen gas (H2) reacts with oxygen gas (O2), they combine to form water (H2O). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
This equation indicates that:
- 2 moles of H2 react with 1 mole of O2 to produce 2 moles of H2O.
Reaction Stoichiometry
In this scenario, you start with:
- 1 mole of H2
- 1 mole of O2
According to the stoichiometry of the balanced equation:
- 1 mole of H2 would need 0.5 moles of O2 to react completely (since 2 moles of H2 require 1 mole of O2).
Since you have 1 mole of O2 available, it is in excess. The limiting reactant here is H2.
Water Production
From the stoichiometric ratios in the reaction:
- 1 mole of H2 produces 1 mole of H2O (as 2 moles of H2 yield 2 moles of H2O, 1 mole of H2 yields 1 mole of H2O).
Therefore, when 1 mole of H2 reacts completely with 1 mole of O2, it results in:
- 1 mole of water (H2O) produced.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is:
- 1 mole of water will result from the reaction (option C).
This understanding of stoichiometry is essential in chemistry for predicting the outcomes of reactions.
Suppose 12 × 1023, atoms of sodium metal react stoichiometrically with chlorine gas. How many grams of sodium chloride will result if the molar mass of sodium chloride is 60 g/mol?- a)100 g
- b)120 g
- c)60 g
- d)10 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose 12 × 1023, atoms of sodium metal react stoichiometrically with chlorine gas. How many grams of sodium chloride will result if the molar mass of sodium chloride is 60 g/mol?
a)
100 g
b)
120 g
c)
60 g
d)
10 g
|
|
Violet Flores answered |
Suppose 12 is the number of students in a class.
Intensity of blue colour increases gradually when _________________- a)copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution
- b)silver rod is dipped in copper nitrate solution
- c)zinc rod is dipped in silver solution
- d)copper rod is dipped in zinc rod solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Intensity of blue colour increases gradually when _________________
a)
copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution
b)
silver rod is dipped in copper nitrate solution
c)
zinc rod is dipped in silver solution
d)
copper rod is dipped in zinc rod solution

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When a copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution, a redox reaction occurs between Copper and an aqueous solution of silver nitrate.
- So the intensity of blue colour increases gradually as silver deposits on the rod.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:How many atoms of Oxygen are there in 18g of water? (Hint: Avagadro’s Number = 6.02 x 1023 atoms/mol)
- A:
8.02 x 1023
- B:
6.02 x 1023
- C:
5 .02 x 1023
- D:
7.02 x 1023
The answer is b.
How many atoms of Oxygen are there in 18g of water? (Hint: Avagadro’s Number = 6.02 x 1023 atoms/mol)
8.02 x 1023
6.02 x 1023
5 .02 x 1023
7.02 x 1023

|
Krithika Kulkarni answered |
18g H2O = 1mol water = 6.02 x 1023 molecules of water = 6.02 x 1023 atoms of oxygen.
Physical properties are those properties which ______ measured or observed ______ changing the identity or the composition of the substance- a)cannot be ,without
- b)can be ,without
- c)cannot be ,even by
- d)can be, after
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Physical properties are those properties which ______ measured or observed ______ changing the identity or the composition of the substance
a)
cannot be ,without
b)
can be ,without
c)
cannot be ,even by
d)
can be, after
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Properties that can be determined/observed without changing the composition of a substance are referred to as physical properties.
Characteristics such as melting point, boiling point, density, solubility, color, odor, etc. are physical properties.
The oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is- a)-3
- b)1
- c)4
- d)-2.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is
a)
-3
b)
1
c)
4
d)
-2.0
|
|
Niharika Nair answered |
Oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is -2.
Explanation:
- Oxidation number is the number assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or loss/gain of electrons.
- Oxygen is a highly electronegative element, meaning it has a strong tendency to attract electrons.
- In most compounds, oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 because it tends to gain electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration (8 valence electrons).
- For example, in water (H2O), each hydrogen atom has an oxidation number of +1 and the oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -2, which balances out the charge to zero.
- There are some exceptions to this rule, such as in peroxides where oxygen has an oxidation number of -1, and in compounds with more electronegative elements where oxygen may have a positive oxidation number.
- Overall, the oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is -2.
Explanation:
- Oxidation number is the number assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or loss/gain of electrons.
- Oxygen is a highly electronegative element, meaning it has a strong tendency to attract electrons.
- In most compounds, oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 because it tends to gain electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration (8 valence electrons).
- For example, in water (H2O), each hydrogen atom has an oxidation number of +1 and the oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -2, which balances out the charge to zero.
- There are some exceptions to this rule, such as in peroxides where oxygen has an oxidation number of -1, and in compounds with more electronegative elements where oxygen may have a positive oxidation number.
- Overall, the oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is -2.
Avogadro’s law states that one mole of an ideal gas takes up around 22 liters at standard temperature and pressure. Assuming all reagents can be treated as ideal gases, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced in the complete reaction of 44 liters of butane (C4H10), with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide (at STP)?- a)44 g
- b)350 g
- c)10 g
- d)4400 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Avogadro’s law states that one mole of an ideal gas takes up around 22 liters at standard temperature and pressure. Assuming all reagents can be treated as ideal gases, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced in the complete reaction of 44 liters of butane (C4H10), with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide (at STP)?
a)
44 g
b)
350 g
c)
10 g
d)
4400 g
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The first step is to determine the balanced combustion reaction.
The correct reaction is 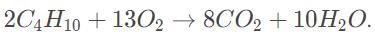
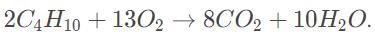
From Avogadro’s law, 44 liters of butane is 2 mol, which would produce 8 mol of carbon dioxide.
The molar mass of carbon dioxide is 12 + 2 × 16 = 44 g/mol, suggesting that 8 × 44 = 350 grams of carbon dioxide is released during the reaction.
One type of anaerobic respiration converts glucose (C6H12O6) to ethanol (C2H5OH) and carbon dioxide. If the molecular weight of glucose is 180 grams/mol and the molar mass of ethanol is 46 g/mol, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced when 1 mol of glucose is digested via respiration?- a)88 grams
- b)0 grams
- c)40 grams
- d)100 grams
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One type of anaerobic respiration converts glucose (C6H12O6) to ethanol (C2H5OH) and carbon dioxide. If the molecular weight of glucose is 180 grams/mol and the molar mass of ethanol is 46 g/mol, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced when 1 mol of glucose is digested via respiration?
a)
88 grams
b)
0 grams
c)
40 grams
d)
100 grams
|
|
Sofia Hall answered |
Calculation:
- First, calculate the molar mass of carbon dioxide (CO2):
- The molar mass of carbon (C) is 12g/mol, and the molar mass of oxygen (O) is 16g/mol.
- Therefore, the molar mass of CO2 = 12g/mol (C) + 2(16g/mol) (O) = 44g/mol.
- Next, determine the stoichiometry of the reaction:
- From the given information, 1 mol of glucose produces 2 mol of ethanol and 2 mol of CO2.
- Calculate the amount of CO2 produced from 1 mol of glucose:
- Since 1 mol of glucose produces 2 mol of CO2, the total mass of CO2 produced is 2 x 44g = 88g.
Therefore, when 1 mol of glucose is digested via anaerobic respiration, 88 grams of carbon dioxide are produced.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A' (88 grams).
- First, calculate the molar mass of carbon dioxide (CO2):
- The molar mass of carbon (C) is 12g/mol, and the molar mass of oxygen (O) is 16g/mol.
- Therefore, the molar mass of CO2 = 12g/mol (C) + 2(16g/mol) (O) = 44g/mol.
- Next, determine the stoichiometry of the reaction:
- From the given information, 1 mol of glucose produces 2 mol of ethanol and 2 mol of CO2.
- Calculate the amount of CO2 produced from 1 mol of glucose:
- Since 1 mol of glucose produces 2 mol of CO2, the total mass of CO2 produced is 2 x 44g = 88g.
Therefore, when 1 mol of glucose is digested via anaerobic respiration, 88 grams of carbon dioxide are produced.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A' (88 grams).
When a zinc rod is kept in a copper nitrate solution what happens?- a)zinc is deposited on copper
- b)copper is deposited in the beaker
- c)zinc is deposited in the beaker
- d)copper is deposited on zinc
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When a zinc rod is kept in a copper nitrate solution what happens?
a)
zinc is deposited on copper
b)
copper is deposited in the beaker
c)
zinc is deposited in the beaker
d)
copper is deposited on zinc

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When zinc is placed in copper nitrate solution the intensity of the blue colour is produced and copper iron is deposited on zinc.
- This is a Redox reaction between zinc and an aqueous solution of copper nitrate occurring in a beaker.
Consider the elements: Cs, Ne, I and F. Identify the element(s) that exhibits only negative oxidation state- a)F
- b)I
- c)s
- d)Cs and F
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the elements: Cs, Ne, I and F. Identify the element(s) that exhibits only negative oxidation state
a)
F
b)
I
c)
s
d)
Cs and F

|
Sinjini Datta answered |
F has negative oxidation state as it is very electro negative.
The correct order of N-compounds in its decreasing order of oxidation states is- a)HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
- b)HNO3, NO, NH4Cl, N2
- c)HNO3, NH4Cl, NO, N2
- d)NH4Cl, N2, NO, HN03
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of N-compounds in its decreasing order of oxidation states is
a)
HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
b)
HNO3, NO, NH4Cl, N2
c)
HNO3, NH4Cl, NO, N2
d)
NH4Cl, N2, NO, HN03

|
Infinity Academy answered |
To determine the decreasing order of oxidation states of nitrogen in the given compounds, we need to find the oxidation state of nitrogen in each compound:
- HNO3 (Nitric acid): Oxidation state of nitrogen: +5
- NO (Nitric oxide): Oxidation state of nitrogen: +2
- N2 (Dinitrogen): Oxidation state of nitrogen: 0
- NH4Cl (Ammonium chloride): Oxidation state of nitrogen: -3
Now, let's arrange these compounds in decreasing order of oxidation states:
- HNO3: +5
- NO: +2
- N2: 0
- NH4Cl: -3
So, the correct order in decreasing oxidation state is:
HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
Which of the following is true as per metal activity series?- a)Zn>Cu>Ag
- b)Zn<Cu<Ag
- c)Zn>Ag>Cu
- d)Zn<Ag<Cu
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true as per metal activity series?
a)
Zn>Cu>Ag
b)
Zn<Cu<Ag
c)
Zn>Ag>Cu
d)
Zn<Ag<Cu

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Metal activity series or electrochemical series is a series in the decreasing order of metals which are active during a chemical reaction comparatively with each other.
- Here, Zinc’s activity is greater than Copper’s activity and Copper’s activity is greater than that of silver.
The more positive the value of E0, the greater is the tendency of the species to get reduced. Using the standard electrode potential of redox couples given below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent. E0values : Fe3 + / Fe2+ = +0.77; I2(s)/l- = +0.54; cu2+/ Cu = +0.34; Ag+ / Ag = +0.80V- a)Ag+
- b)Fe3+
- c)I2 (s)
- d)Cu2+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The more positive the value of E0, the greater is the tendency of the species to get reduced. Using the standard electrode potential of redox couples given below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
E0values : Fe3 + / Fe2+ = +0.77; I2(s)/l- = +0.54; cu2+/ Cu = +0.34; Ag+ / Ag = +0.80V
a)
Ag+
b)
Fe3+
c)
I2 (s)
d)
Cu2+

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Oxidation number of H is not always +1 . It can be -1 , 0.
In an unknown compound, the molar ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen is found to be, respectively, 1:2:1. The molar mass is separately found to be 180 grams/mol. Which of the following gives the molecular formula of the compound?- a)C1H2O1
- b)C6H12O6
- c)C6H1O8
- d)C8H8O2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In an unknown compound, the molar ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen is found to be, respectively, 1:2:1. The molar mass is separately found to be 180 grams/mol. Which of the following gives the molecular formula of the compound?
a)
C1H2O1
b)
C6H12O6
c)
C6H1O8
d)
C8H8O2
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The molecular formula gives the actual chemical structure, rather than just the minimum molar ratio given by the empirical formula.
The empirical formula, based on the mol ratio, is C1H2O1.This can be converted to a molar mass.
The empirical formula, based on the mol ratio, is C1H2O1.This can be converted to a molar mass.
The molar mass if the molecular formula was the same as the empirical formula would be (1mol × 12g/mol) + (2mol x 1g/mol) + (1mol x 16g/mol) = 30g/mol
The actual molar mass is six times the molar mass of the empirical formula; thus the molecular formula is C6H12O6
The kelvin scale is related to celsius scale by- a)K = °C + 212
- b)K = °C + 100
- c)K = °C + 32
- d)K = °C + 273.15
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The kelvin scale is related to celsius scale by
a)
K = °C + 212
b)
K = °C + 100
c)
K = °C + 32
d)
K = °C + 273.15
|
|
Sparsh Datta answered |
Understanding the Kelvin Scale
The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale used primarily in scientific contexts. It provides a direct representation of thermal energy.
Relationship Between Kelvin and Celsius
The Kelvin and Celsius scales are related through a simple linear equation:
- K = C + 273.15
This means that to convert a temperature from Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273.15 to the Celsius temperature.
Key Points of the Kelvin Scale
- Absolute Zero: The Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, which is 0 K. This is the theoretical point where molecular motion ceases.
- Celsius to Kelvin Conversion:
- For example, 0 degrees Celsius (the freezing point of water) is equivalent to 273.15 K.
- Therefore, to find the Kelvin value for any Celsius temperature, simply add 273.15.
Why Option D is Correct
- Options Explained:
- a) K = C + 212: Incorrect; this relates to Fahrenheit.
- b) K = C + 100: Incorrect; does not correspond to any known conversion.
- c) K = C + 32: Incorrect; this is the conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
- d) K = C + 273.15: Correct; accurately represents the relationship between Celsius and Kelvin.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between these temperature scales is crucial in scientific calculations, ensuring clarity and precision in thermal measurements. The Kelvin scale is fundamental in fields like physics and chemistry, emphasizing the importance of absolute temperature in experiments.
The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale used primarily in scientific contexts. It provides a direct representation of thermal energy.
Relationship Between Kelvin and Celsius
The Kelvin and Celsius scales are related through a simple linear equation:
- K = C + 273.15
This means that to convert a temperature from Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273.15 to the Celsius temperature.
Key Points of the Kelvin Scale
- Absolute Zero: The Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, which is 0 K. This is the theoretical point where molecular motion ceases.
- Celsius to Kelvin Conversion:
- For example, 0 degrees Celsius (the freezing point of water) is equivalent to 273.15 K.
- Therefore, to find the Kelvin value for any Celsius temperature, simply add 273.15.
Why Option D is Correct
- Options Explained:
- a) K = C + 212: Incorrect; this relates to Fahrenheit.
- b) K = C + 100: Incorrect; does not correspond to any known conversion.
- c) K = C + 32: Incorrect; this is the conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
- d) K = C + 273.15: Correct; accurately represents the relationship between Celsius and Kelvin.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between these temperature scales is crucial in scientific calculations, ensuring clarity and precision in thermal measurements. The Kelvin scale is fundamental in fields like physics and chemistry, emphasizing the importance of absolute temperature in experiments.
In the reaction of metallic cobalt placed in nickel sulphate solution, therein is a competition for release of electrons At equilibrium, chemical tests reveal that both Ni+2 (aq) and Co+2 (aq) are present at moderate concentrations. The result is that:
- a)Only one reactant and one product is greatly favoured.
- b)Only [Co(s) and Ni+2 (aq)] are favoured
- c)Only Co+2 (aq) and Ni (s)] are favoured
- d)neither the reactants nor the products [are greatly favoured.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the reaction of metallic cobalt placed in nickel sulphate solution, therein is a competition for release of electrons At equilibrium, chemical tests reveal that both Ni+2 (aq) and Co+2 (aq) are present at moderate concentrations. The result is that:
a)
Only one reactant and one product is greatly favoured.
b)
Only [Co(s) and Ni+2 (aq)] are favoured
c)
Only Co+2 (aq) and Ni (s)] are favoured
d)
neither the reactants nor the products [are greatly favoured.

|
Arya Reddy answered |
The reaction of metallic cobalt in a nickel sulfate solution involves a competition for the release of electrons. This means that the cobalt metal can react with the nickel ions in the solution, or the nickel can deposit on the cobalt metal.
At equilibrium, the reaction has balanced out with no net change in the concentration of the reactants and products. The fact that both Ni+2 (aq) and Co+2 (aq) are present at moderate concentrations at equilibrium signifies that neither forward nor reverse reactions are greatly favoured.
- A: This option is incorrect because both reactants and products are present in moderate concentrations, indicating that neither is greatly favoured.
- B: This statement is not correct either. Even though Co (s) and Ni+2 (aq) are part of the reaction, the fact that Co+2 (aq) is also present at moderate concentrations shows that they are not the only favoured species.
- C: This option is also incorrect. Even though Co+2 (aq) and Ni (s) are part of the reaction, the fact that Ni+2 (aq) is also present at moderate concentrations shows that they are not the only favoured species.
- D: This is the correct answer. When a reaction is at equilibrium, it means that the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. Therefore, neither the reactants nor the products are greatly favoured. In other words, the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant over time
The highest value of oxidation number changes from 1 to 7- a)in the atoms of transition elements
- b)the first three groups
- c)In alkaline earth metals
- d)across the third period in the periodic table
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The highest value of oxidation number changes from 1 to 7
a)
in the atoms of transition elements
b)
the first three groups
c)
In alkaline earth metals
d)
across the third period in the periodic table

|
Sai Mishra answered |
the highest value of oxidation number changes from 1 to 7.
A metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state. Which metal is a better reducing agent in such a case?
- a)Better reducing agent is the one that looses more electrons
- b)Better reducing agent is the one that looses less electrons
- c)Both are same in reducing capacity
- d)The reduced metal is a better reducing agent than the reducing metal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state. Which metal is a better reducing agent in such a case?
a)
Better reducing agent is the one that looses more electrons
b)
Better reducing agent is the one that looses less electrons
c)
Both are same in reducing capacity
d)
The reduced metal is a better reducing agent than the reducing metal

|
Bhavana Chavan answered |
Concept of Reducing Agent:
A reducing agent is a substance that loses or "donates" an electron to another substance in a redox chemical reaction. Therefore, a good reducing agent is the one that gets oxidized easily, or in other words, the one that can easily lose electrons.
Characteristics of a Good Reducing Agent:
A reducing agent is a substance that loses or "donates" an electron to another substance in a redox chemical reaction. Therefore, a good reducing agent is the one that gets oxidized easily, or in other words, the one that can easily lose electrons.
Characteristics of a Good Reducing Agent:
- Electron Loss: A better reducing agent is the one that loses more electrons. This is because by losing electrons, the reducing agent gets oxidized and in turn reduces the other substance. This is the basic principle of a redox reaction.
- Reactivity: The reactivity of the metal also determines its capacity as a reducing agent. Metals that are high in the reactivity series are good reducing agents. This is because they can easily lose electrons and get oxidized.
- Stability: Metals that are less stable are better reducing agents because they can easily lose electrons to attain a stable state.
Hence, Option A is the correct answer - a better reducing agent is the one that loses more electrons.
The oxidation number of an element in a compound is evaluated on the basis of certain rules. Which of the following rules is not correct in this respect?- a)The algebraic sum of all the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero.
- b)In all its compounds, the oxidation number of fluorine is – 1.
- c)An element in the free or the uncombined state bears oxidation number zero.
- d)The oxidation number of hydrogen is always +1.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation number of an element in a compound is evaluated on the basis of certain rules. Which of the following rules is not correct in this respect?
a)
The algebraic sum of all the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero.
b)
In all its compounds, the oxidation number of fluorine is – 1.
c)
An element in the free or the uncombined state bears oxidation number zero.
d)
The oxidation number of hydrogen is always +1.

|
Ishani Mehta answered |
as oxygen is more electronegative than Cl,Br and I. So they have positive oxidation state.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion: In laboratory, a solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting a stock solution.
Reason: Stock solution is the solution of higher concentration.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
- c)Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
- d)Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion: In laboratory, a solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting a stock solution.
Reason: Stock solution is the solution of higher concentration.
Assertion: In laboratory, a solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting a stock solution.
Reason: Stock solution is the solution of higher concentration.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
c)
Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
d)
Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
|
|
Sagar Jain answered |
Explanation:
Assertion: In the laboratory, a solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting a stock solution.
Reason: Stock solution is the solution of higher concentration.
The correct answer is option 'A' - Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
Explanation:
To understand the given assertion and reason, let's break it down into two parts:
1. Assertion: In the laboratory, a solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting a stock solution.
In a laboratory, when a solution of a specific concentration is required, it is prepared by diluting a stock solution. Dilution involves adding a solvent (usually water) to the stock solution to decrease its concentration.
2. Reason: Stock solution is the solution of higher concentration.
A stock solution refers to a solution that has a higher concentration compared to the desired concentration. It is typically a concentrated solution that is used as a source for preparing solutions of lower concentration.
Explanation of the Assertion and Reason:
The given assertion and reason are both correct and are interrelated. A stock solution is prepared to have a higher concentration so that it can be diluted to obtain solutions with different desired concentrations.
When a solution of a desired concentration needs to be prepared in the laboratory, the stock solution is used as a starting point. By diluting the stock solution with a suitable solvent, the desired concentration can be achieved.
Conclusion:
The given assertion and reason are logically correct and are connected to each other. The stock solution is prepared to have a higher concentration, and from that, solutions of desired concentrations are obtained by dilution. Therefore, option 'A' - Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion is the correct answer.
Assertion: In the laboratory, a solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting a stock solution.
Reason: Stock solution is the solution of higher concentration.
The correct answer is option 'A' - Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
Explanation:
To understand the given assertion and reason, let's break it down into two parts:
1. Assertion: In the laboratory, a solution of a desired concentration is prepared by diluting a stock solution.
In a laboratory, when a solution of a specific concentration is required, it is prepared by diluting a stock solution. Dilution involves adding a solvent (usually water) to the stock solution to decrease its concentration.
2. Reason: Stock solution is the solution of higher concentration.
A stock solution refers to a solution that has a higher concentration compared to the desired concentration. It is typically a concentrated solution that is used as a source for preparing solutions of lower concentration.
Explanation of the Assertion and Reason:
The given assertion and reason are both correct and are interrelated. A stock solution is prepared to have a higher concentration so that it can be diluted to obtain solutions with different desired concentrations.
When a solution of a desired concentration needs to be prepared in the laboratory, the stock solution is used as a starting point. By diluting the stock solution with a suitable solvent, the desired concentration can be achieved.
Conclusion:
The given assertion and reason are logically correct and are connected to each other. The stock solution is prepared to have a higher concentration, and from that, solutions of desired concentrations are obtained by dilution. Therefore, option 'A' - Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion is the correct answer.
According to the law of conservation of mass, a balanced chemical equation has- a)the same number of electrons of each element on both sides of the equation
- b)the same number of protons of each element on both sides of the equation
- c)the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation
- d)the same ratio of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the law of conservation of mass, a balanced chemical equation has
a)
the same number of electrons of each element on both sides of the equation
b)
the same number of protons of each element on both sides of the equation
c)
the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation
d)
the same ratio of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation

|
Gaurav Saini answered |
according to this total mass of reactants = total mass of product so no. of atoms of each element in reactant is equal to no. of atoms of that element in product
Molarity is defined as- a)the number of moles of the solute in 1 m3 of the solution
- b)the number of moles of the solvent in 1 litre of the solution
- c)the number of moles of the solute in 1 litre of the solution
- d)the number of grams of the solute in 1 litre of the solution
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Molarity is defined as
a)
the number of moles of the solute in 1 m3 of the solution
b)
the number of moles of the solvent in 1 litre of the solution
c)
the number of moles of the solute in 1 litre of the solution
d)
the number of grams of the solute in 1 litre of the solution
|
|
Pranav Datta answered |
Molarity is a unit of concentration used in chemistry to describe the amount of solute in a given volume of solution. It is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
Explanation:
Molarity is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the volume of the solution in liters. It is expressed in moles per liter (mol/L) or Molar (M). The formula for molarity is:
Molarity (M) = Moles of Solute / Volume of Solution (in liters)
Let's understand the options given in the question:
a) The number of moles of the solute in 1 m3 of the solution
This option is incorrect because molarity is expressed in liters, not cubic meters. The molarity is calculated based on the volume of the solution in liters.
b) The number of moles of the solvent in 1 litre of the solution
This option is also incorrect because molarity is a measure of the concentration of the solute, not the solvent. It is the amount of solute present in a given volume of solution.
c) The number of moles of the solute in 1 litre of the solution (Correct answer)
This option is correct. Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It tells us how many moles of solute are present in each liter of the solution. This is the most commonly used definition of molarity.
d) The number of grams of the solute in 1 litre of the solution
This option is incorrect because molarity is a measure of concentration in moles, not grams. The mass of the solute can be used to calculate molarity, but it is not the definition of molarity itself.
In conclusion, molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute present in one liter of the solution. It is a measure of concentration and is expressed in moles per liter (M) or mol/L.
Explanation:
Molarity is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the volume of the solution in liters. It is expressed in moles per liter (mol/L) or Molar (M). The formula for molarity is:
Molarity (M) = Moles of Solute / Volume of Solution (in liters)
Let's understand the options given in the question:
a) The number of moles of the solute in 1 m3 of the solution
This option is incorrect because molarity is expressed in liters, not cubic meters. The molarity is calculated based on the volume of the solution in liters.
b) The number of moles of the solvent in 1 litre of the solution
This option is also incorrect because molarity is a measure of the concentration of the solute, not the solvent. It is the amount of solute present in a given volume of solution.
c) The number of moles of the solute in 1 litre of the solution (Correct answer)
This option is correct. Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It tells us how many moles of solute are present in each liter of the solution. This is the most commonly used definition of molarity.
d) The number of grams of the solute in 1 litre of the solution
This option is incorrect because molarity is a measure of concentration in moles, not grams. The mass of the solute can be used to calculate molarity, but it is not the definition of molarity itself.
In conclusion, molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute present in one liter of the solution. It is a measure of concentration and is expressed in moles per liter (M) or mol/L.
Measurements of a compound reveal that it is 36% carbon, 6% hydrogen, and 48% oxygen, with systematic error accounting for the remaining 10%. Which of the following is the most accurate empirical formula for this compound?- a)C1H1O1
- b)C1H2O1
- c)C6H12O8
- d)C6H1O8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Measurements of a compound reveal that it is 36% carbon, 6% hydrogen, and 48% oxygen, with systematic error accounting for the remaining 10%. Which of the following is the most accurate empirical formula for this compound?
a)
C1H1O1
b)
C1H2O1
c)
C6H12O8
d)
C6H1O8
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Pick an arbitrary initial mass of 100 grams. The given analysis would suggest that this contains 36 g carbon, 6 g hydrogen, and 48 g oxygen.
Convert these masses into mols by dividing them by the known molar masses of the various elements: 36/12 = 3 mol carbon, 6/1 = 6 mol hydrogen, 48/16 = 3 mol oxygen
Divide the three mol counts by their greatest common denominator to obtain the empirical formula: C1H2O1
When an antacid tablet is used, calcium hydroxide interacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach to form inert calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water. If the molar mass of (Ca(OH)2 is 75 grams/mol, how many mols of HCl are required to fully react with 150 g of Ca(OH)2?- a)4 mol
- b)1 mol
- c)8 mol
- d)2 mol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When an antacid tablet is used, calcium hydroxide interacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach to form inert calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water. If the molar mass of (Ca(OH)2 is 75 grams/mol, how many mols of HCl are required to fully react with 150 g of Ca(OH)2?
a)
4 mol
b)
1 mol
c)
8 mol
d)
2 mol
|
|
Aurora Cooper answered |
Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach to form calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water. We are given the molar mass of Ca(OH)2 as 75 grams/mol and we need to determine the number of moles of HCl required to fully react with 150g of Ca(OH)2.
To solve this problem, we can use the concept of stoichiometry, which relates the number of moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
1. Calculate the number of moles of Ca(OH)2:
Given mass of Ca(OH)2 = 150g
Molar mass of Ca(OH)2 = 75g/mol
Number of moles of Ca(OH)2 = Mass of Ca(OH)2 / Molar mass of Ca(OH)2
= 150g / 75g/mol
= 2 mol
2. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction:
Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + 2H2O
From the balanced equation, we can see that 1 mole of Ca(OH)2 reacts with 2 moles of HCl.
3. Determine the number of moles of HCl required:
Number of moles of HCl = Number of moles of Ca(OH)2 × (2 moles of HCl / 1 mole of Ca(OH)2)
= 2 mol × (2 mol HCl / 1 mol Ca(OH)2)
= 4 mol HCl
Therefore, 4 moles of HCl are required to fully react with 150g of Ca(OH)2. The correct answer is option A.
To solve this problem, we can use the concept of stoichiometry, which relates the number of moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
1. Calculate the number of moles of Ca(OH)2:
Given mass of Ca(OH)2 = 150g
Molar mass of Ca(OH)2 = 75g/mol
Number of moles of Ca(OH)2 = Mass of Ca(OH)2 / Molar mass of Ca(OH)2
= 150g / 75g/mol
= 2 mol
2. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction:
Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + 2H2O
From the balanced equation, we can see that 1 mole of Ca(OH)2 reacts with 2 moles of HCl.
3. Determine the number of moles of HCl required:
Number of moles of HCl = Number of moles of Ca(OH)2 × (2 moles of HCl / 1 mole of Ca(OH)2)
= 2 mol × (2 mol HCl / 1 mol Ca(OH)2)
= 4 mol HCl
Therefore, 4 moles of HCl are required to fully react with 150g of Ca(OH)2. The correct answer is option A.
The general form of a synthesis reaction is αX + bY→ cZ, where capital letters denote reactants and lowercase letters denote balanced coefficients, a < b. Which of the following formulas gives the number of Z molecules produced when 4 mols of Y react completely? N is Avogadro’s number- a)
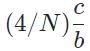
- b)
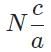
- c)
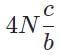
- d)
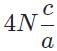
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The general form of a synthesis reaction is αX + bY→ cZ, where capital letters denote reactants and lowercase letters denote balanced coefficients, a < b. Which of the following formulas gives the number of Z molecules produced when 4 mols of Y react completely? N is Avogadro’s number
a)
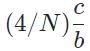
b)
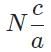
c)
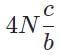
d)
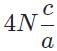

|
Orion Classes answered |
If all 4 mols of Y react completly, then X is in excess because a < b. Thus only b matters for determining the reaction yield.
The ratios of coefficients in a balanced reaction gives the ratio of moles of each reagent and product required in a perfectly stoichiometric reaction.
The number of moles of product can be converted to the number of molecules by multiplying by Avogadro’s number
The correct formula is 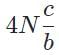
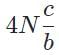
Chapter doubts & questions for Stoichiometry (GC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Stoichiometry (GC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations
336 videos|223 docs|109 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup