All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Carbohydrates (OC, BC) for MCAT Exam
The compound which gives red colour with Fehling’s solution?- a)Cellulose
- b)Benzaldehyde
- c)Cane sugar
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound which gives red colour with Fehling’s solution?
a)
Cellulose
b)
Benzaldehyde
c)
Cane sugar
d)
Glucose

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Fehling's solution to make difference between carbohydrate and ketone functional grp and also used for differentiate reducing and non reducing sugar and as u know glucose is a reducing sugar so it will give red colour with fehling's solution (all monosachharides are reducing sugar).
Glucose + Tollen’s reagent → Silver mirror. The process shows:- a)The presence of -CHO group
- b)The presence of alkaline group
- c)The presence of acidic group
- d)The presence of keto group
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose + Tollen’s reagent → Silver mirror. The process shows:
a)
The presence of -CHO group
b)
The presence of alkaline group
c)
The presence of acidic group
d)
The presence of keto group
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Glucose gives silver mirror test with Tollens reagent. It shows the presence of aldehyde group.
Also, mild oxidation of glucose with bromine water gives gluconic acid which shows the presence of aldehyde group.
Also, mild oxidation of glucose with bromine water gives gluconic acid which shows the presence of aldehyde group.
Glucose and fructose are:- a)Position isomers
- b)Functional isomers
- c)Chain isomers
- d)Optical isomers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose and fructose are:
a)
Position isomers
b)
Functional isomers
c)
Chain isomers
d)
Optical isomers
|
|
Tanvi Bose answered |
Glucose and fructose are functional isomers of each other Because they have same molecular formula that is C6H12O6 But different functional group in their chemical formula. Glucose has aldehyde group while fructose has ketone as functional group.
Which of the following carbohydrate is an example of an oligosaccharide?- a)Cellulose
- b)Lactose
- c)Mannose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrate is an example of an oligosaccharide?
a)
Cellulose
b)
Lactose
c)
Mannose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Lactose intolerance is the inability to break down a type of natural sugar called lactose. Lactose is commonly found in dairy products, such as milk and yogurt. A person becomes lactose intolerant when his or her small intestine stops making enough of the enzyme lactase to digest and break down the lactose.
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called:- a)Hydration
- b)Inversion
- c)Esterification
- d)Saponification
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called:
a)
Hydration
b)
Inversion
c)
Esterification
d)
Saponification

|
Sahana Savalagi answered |
Hydrolysis of sucrose is inversion because the angle of specific rotation of the plane polarized light changes from positive to negative value due to the presence of optical isomers of mixture of glucose and fructose sugar...
Glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to form:- a)Monoacetate
- b)Diacetate
- c)Pentaacetate
- d) Hexaacetate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to form:
a)
Monoacetate
b)
Diacetate
c)
Pentaacetate
d)
Hexaacetate
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
It forms glucose pentaacetate. The acetic anhydride esterifies with all the alcohol groups on the glucose ring.
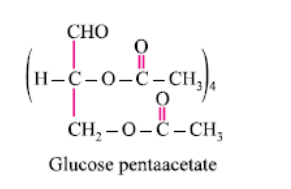

The oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule when two monosaccharides are joined together through oxygen atom is called:- a)Carboxylic linkage
- b)Carbonyl linkage
- c)Peptide linkage
- d)Glycosidic linkage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule when two monosaccharides are joined together through oxygen atom is called:
a)
Carboxylic linkage
b)
Carbonyl linkage
c)
Peptide linkage
d)
Glycosidic linkage

|
Aleena Mathew answered |
All sacchrides /carbohydrates form glycosidic bond by eliminating water molecule
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because:- a)The -CHO group of glucose is not involved in glycosidic bond formation.
- b)Two monosaccharide units are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose.
- c)On hydrolysis, sucrose gives dextrorotatory and laevorotatory and the mixture is laevorotatory.
- d)Sucrose is dextrorotatory.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because:
a)
The -CHO group of glucose is not involved in glycosidic bond formation.
b)
Two monosaccharide units are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose.
c)
On hydrolysis, sucrose gives dextrorotatory and laevorotatory and the mixture is laevorotatory.
d)
Sucrose is dextrorotatory.
|
|
Gowri Menon answered |
Glucose and C2 of fructose, which does not have a free aldehyde or ketone group to undergo oxidation and reduction reactions.
c)Sucrose does not react with Benedict's reagent, which is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars.
d)Sucrose cannot be hydrolyzed by acid or enzyme into its constituent monosaccharides.
c)Sucrose does not react with Benedict's reagent, which is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars.
d)Sucrose cannot be hydrolyzed by acid or enzyme into its constituent monosaccharides.
The Molisch test is a chemical test that determines the presence of:- a)All carbohydrates
- b)Sucrose
- c)Fructose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Molisch test is a chemical test that determines the presence of:
a)
All carbohydrates
b)
Sucrose
c)
Fructose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The Molisch test uses concentrated sulphuric acid as the dehydrating acid. This acid dehydrates all carbohydrates, so the test is used to distinguish between carbohydrates and non-carbohydrates.
On hydrolysis maltose gives:- a)One molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose
- b)Two molecules of fructose
- c)One molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose
- d)Two molecules of glucose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
On hydrolysis maltose gives:
a)
One molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose
b)
Two molecules of fructose
c)
One molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose
d)
Two molecules of glucose
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
On hydrolysis, maltose gives glucose with the help of maltase enzyme which works as a catalysis of the hydrolysis of the glycoside bond.
Maltase is a disaccharide which will reduce sugar giving two molecules of glucose on hydrolysis.
It will give alpha-D-glucose and alpha-D-glucose.
What is the relation between the following pairs of monosaccharides?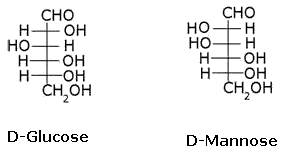
- a)Epimers
- b)Enatiomers
- c)Structural isomers
- d)Anomers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the relation between the following pairs of monosaccharides?
a)
Epimers
b)
Enatiomers
c)
Structural isomers
d)
Anomers

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The pairs of optical isomers which differ in configuration around any other C atom other than C1 atom are called epimers. D-glucose and D-mannose are C2 epimers.
Which of the following is an example of a complex carbohydrate?- a)Glucose
- b)Fructose
- c)Glycogen
- d)Sucrose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of a complex carbohydrate?
a)
Glucose
b)
Fructose
c)
Glycogen
d)
Sucrose
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Complex carbohydrates, also known as polysaccharides, are composed of long chains of monosaccharide units. Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate and serves as the main storage form of glucose in animals.
Which of the following nucleic acids is single-stranded?- a)DNA
- b)RNA
- c)mRNA
- d)tRNA
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following nucleic acids is single-stranded?
a)
DNA
b)
RNA
c)
mRNA
d)
tRNA
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a single-stranded nucleic acid that plays various roles in gene expression and protein synthesis. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is double-stranded.
Which among the following is a non-reducing sugar?- a)Sucrose
- b)Maltose
- c)Lactose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is a non-reducing sugar?
a)
Sucrose
b)
Maltose
c)
Lactose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Non-reducing sugars do not have an OH group attached to the anomeric carbon so they cannot reduce other compounds. All monosaccharides such as glucose are reducing sugars. A disaccharide can be a reducing sugar or a non-reducing sugar. Maltose and lactose are reducing sugars, while sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
The commonest disaccharide have the molecular formula:- a)C10H20O10
- b)C12H22O11
- c)C10H18O9
- d)C11H22O11
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The commonest disaccharide have the molecular formula:
a)
C10H20O10
b)
C12H22O11
c)
C10H18O9
d)
C11H22O11

|
Sanjeev Kumar answered |
Because it is in the ratio of 1:2:1
What does the following reaction shows about the structure of glucose?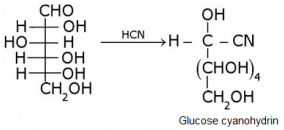
- a)It shows the presence of carbonyl group in glucose.
- b)It shows the presence of primary alcoholic group in glucose.
- c)It shows the presence of ring structure in glucose.
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the following reaction shows about the structure of glucose?
a)
It shows the presence of carbonyl group in glucose.
b)
It shows the presence of primary alcoholic group in glucose.
c)
It shows the presence of ring structure in glucose.
d)
none
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Glucose gets oxidized to cyanohydrin in reaction with HCN . This indicates that the carbonyl group is present as an aldehydic group.
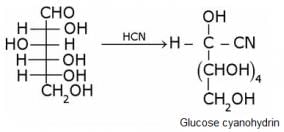
Glucose gets oxidized to cyanohydrin in reaction with HCN . This indicates that the carbonyl group is present as an aldehydic group.

Which of the following is a saturated fatty acid?- a)Oleic acid
- b)Linoleic acid
- c)Stearic acid
- d)Arachidonic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a saturated fatty acid?
a)
Oleic acid
b)
Linoleic acid
c)
Stearic acid
d)
Arachidonic acid
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds between carbon atoms and have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon chain. Stearic acid is an example of a saturated fatty acid.
The following is a reaction of glucose with Fehling’s reagent. What will happen in the reaction?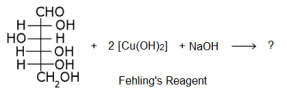
- a)Glucose will not react with Fehling’s reagent.
- b)Grey precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
- c)Red precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
- d)Saccharic acid will be formed when glucose will react with Fehling’s reagent.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The following is a reaction of glucose with Fehling’s reagent. What will happen in the reaction?
a)
Glucose will not react with Fehling’s reagent.
b)
Grey precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
c)
Red precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
d)
Saccharic acid will be formed when glucose will react with Fehling’s reagent.

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Because it is the chemical property of aliphatic aldehyde to give red precipitate with fehling solution.
RCHO + 2 CuO -----------> Cu2O. + RCOOH
Fehling reagents is aq. alkaline CuSO4 solution along with Rochelle salt Na-K tartrate.
And glucose molecule consists of aldehydic group at first position and hence it is also a aldehyde and thus give this characteristic test.
RCHO + 2 CuO -----------> Cu2O. + RCOOH
Fehling reagents is aq. alkaline CuSO4 solution along with Rochelle salt Na-K tartrate.
And glucose molecule consists of aldehydic group at first position and hence it is also a aldehyde and thus give this characteristic test.
Which of the following is a monosaccharide?- a)Glucose
- b)Starch
- c)Cellulose
- d)Glycogen
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a monosaccharide?
a)
Glucose
b)
Starch
c)
Cellulose
d)
Glycogen

|
Kowshika answered |
A)Glucose
Glucose is the simplest form of carbohydrates it is monosaccrides
Glucose is the simplest form of carbohydrates it is monosaccrides
Which of the following carbohydrates is called an invert sugar?- a)Sucrose
- b)Fructose
- c)Glucose
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrates is called an invert sugar?
a)
Sucrose
b)
Fructose
c)
Glucose
d)
Cellulose

|
Sanjeevini Angadi answered |
It is called invert sugar because the angle of the specific rotation of the plain polarized light changes from a positive to a negative value due to the presence of the optical isomers of the mixture of glucose and fructosesugars.
What does the following reaction of glucose with HI elucidates about the structure of glucose?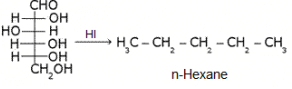
- a)Shows the presence of -CHO group
- b)Shows the presence of C=O group
- c)Shows the presence of six carbons linked linearly
- d)Shows the presence of ring structure of glucose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the following reaction of glucose with HI elucidates about the structure of glucose?
a)
Shows the presence of -CHO group
b)
Shows the presence of C=O group
c)
Shows the presence of six carbons linked linearly
d)
Shows the presence of ring structure of glucose
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
It shows that glucose exists as n-hexane...i.e. it has straight linear chain...
Which of the following is an example of a disaccharide?- a)Glucose
- b)Fructose
- c)Maltose
- d)Galactose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of a disaccharide?
a)
Glucose
b)
Fructose
c)
Maltose
d)
Galactose
|
|
Aurora Ross answered |
Understanding Disaccharides
Disaccharides are carbohydrates composed of two monosaccharide units linked together by a glycosidic bond. They serve as important energy sources and play various roles in biological processes.
Examples of Carbohydrates
- a) Glucose: A monosaccharide, also known as a simple sugar, which is a primary energy source for cells.
- b) Fructose: Another monosaccharide, commonly found in fruits. It is also a simple sugar.
- c) Maltose: This is the correct answer. Maltose consists of two glucose molecules linked together, making it a disaccharide. It is commonly found in malted foods and beverages.
- d) Galactose: A monosaccharide that, when combined with glucose, forms lactose, the sugar found in milk.
Why Maltose is a Disaccharide
- Composition: Maltose is formed by the condensation reaction of two glucose molecules.
- Bonding: The linkage between the two glucose units is through an alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond.
- Function: Maltose is important in the digestion of starch, as it is produced during the breakdown of starch by enzymes like amylase.
Conclusion
Among the options provided, maltose is the only disaccharide, as it is made of two monosaccharides (glucose) combined, while glucose, fructose, and galactose are all monosaccharides. Understanding these distinctions is essential for studying carbohydrate metabolism and nutrition.
Disaccharides are carbohydrates composed of two monosaccharide units linked together by a glycosidic bond. They serve as important energy sources and play various roles in biological processes.
Examples of Carbohydrates
- a) Glucose: A monosaccharide, also known as a simple sugar, which is a primary energy source for cells.
- b) Fructose: Another monosaccharide, commonly found in fruits. It is also a simple sugar.
- c) Maltose: This is the correct answer. Maltose consists of two glucose molecules linked together, making it a disaccharide. It is commonly found in malted foods and beverages.
- d) Galactose: A monosaccharide that, when combined with glucose, forms lactose, the sugar found in milk.
Why Maltose is a Disaccharide
- Composition: Maltose is formed by the condensation reaction of two glucose molecules.
- Bonding: The linkage between the two glucose units is through an alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond.
- Function: Maltose is important in the digestion of starch, as it is produced during the breakdown of starch by enzymes like amylase.
Conclusion
Among the options provided, maltose is the only disaccharide, as it is made of two monosaccharides (glucose) combined, while glucose, fructose, and galactose are all monosaccharides. Understanding these distinctions is essential for studying carbohydrate metabolism and nutrition.
Which of the following lipids is a major component of cell membranes?- a)Triglycerides
- b)Steroids
- c)Phospholipids
- d)Waxes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following lipids is a major component of cell membranes?
a)
Triglycerides
b)
Steroids
c)
Phospholipids
d)
Waxes
|
|
Samuel Lewis answered |
Role of Phospholipids in Cell Membranes
Phospholipids are a crucial component of cell membranes, primarily due to their unique structure and properties. Here’s an overview of why they are essential:
Structure of Phospholipids
- Amphipathic Nature: Phospholipids possess both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) regions. This dual nature facilitates their ability to form bilayers in aqueous environments.
- Bilayer Formation: When exposed to water, phospholipids arrange themselves into a bilayer, with hydrophilic heads facing outward towards the water and hydrophobic tails tucked inward. This arrangement creates a semi-permeable membrane that is vital for cellular function.
Functions of Phospholipids in Cell Membranes
- Barrier to Free Diffusion: The phospholipid bilayer acts as a barrier, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This selective permeability is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Fluidity and Flexibility: The presence of unsaturated fatty acids in some phospholipids contributes to membrane fluidity, allowing for the movement of proteins and lipids within the membrane. This fluidity is crucial for various cellular processes, including signaling and cell division.
Comparison with Other Lipids
- Triglycerides: Primarily used for energy storage, they do not play a role in cell membrane structure.
- Steroids: While they can be part of membranes (like cholesterol), they do not form the membrane structure itself.
- Waxes: Typically serve protective roles in plants and animals, rather than structural roles in membranes.
In summary, phospholipids are fundamental to the structure and function of cell membranes, enabling essential processes for life.
Phospholipids are a crucial component of cell membranes, primarily due to their unique structure and properties. Here’s an overview of why they are essential:
Structure of Phospholipids
- Amphipathic Nature: Phospholipids possess both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) regions. This dual nature facilitates their ability to form bilayers in aqueous environments.
- Bilayer Formation: When exposed to water, phospholipids arrange themselves into a bilayer, with hydrophilic heads facing outward towards the water and hydrophobic tails tucked inward. This arrangement creates a semi-permeable membrane that is vital for cellular function.
Functions of Phospholipids in Cell Membranes
- Barrier to Free Diffusion: The phospholipid bilayer acts as a barrier, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This selective permeability is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Fluidity and Flexibility: The presence of unsaturated fatty acids in some phospholipids contributes to membrane fluidity, allowing for the movement of proteins and lipids within the membrane. This fluidity is crucial for various cellular processes, including signaling and cell division.
Comparison with Other Lipids
- Triglycerides: Primarily used for energy storage, they do not play a role in cell membrane structure.
- Steroids: While they can be part of membranes (like cholesterol), they do not form the membrane structure itself.
- Waxes: Typically serve protective roles in plants and animals, rather than structural roles in membranes.
In summary, phospholipids are fundamental to the structure and function of cell membranes, enabling essential processes for life.
Which of the following reactions would produce the compound below?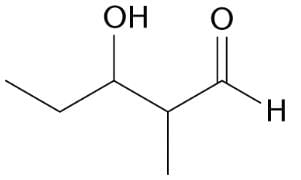
- a)CH3CHO + CH3CH2CH2CHO →
- b)CH3COCH3 + CH3CH2CH2CHO →
- c)CH3CH2COCH3 + CH3CHO →
- d)CH3CH2CHO + CH3CH2CHO →
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions would produce the compound below?

a)
CH3CHO + CH3CH2CH2CHO →
b)
CH3COCH3 + CH3CH2CH2CHO →
c)
CH3CH2COCH3 + CH3CHO →
d)
CH3CH2CHO + CH3CH2CHO →
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The reactions listed in the answer choices are examples of aldol condensations. In the presence of a base, the α-hydrogen is abstracted from an aldehyde, forming an enolate ion, [CH3CHCHO]–. This enolate ion then attacks the carbonyl group of the other aldehyde molecule, CH3CH2CHO, forming the pictured aldol.
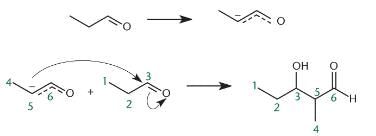

In polysaccharides, the linkage connecting monosaccharide is called:- a)peptide linkage
- b)glycogen linkage
- c)nucleosidic linkage
- d)glycosidic linkage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In polysaccharides, the linkage connecting monosaccharide is called:
a)
peptide linkage
b)
glycogen linkage
c)
nucleosidic linkage
d)
glycosidic linkage
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Monosaccharides such as glucose can be linked together in condensation reactions. For example, sucrose (table sugar) is formed from one molecule of glucose and one of fructose, as shown below. Molecules composed of two monosaccharides are called disaccharides.
Which of the following is a characteristic of nucleic acids?- a)Insoluble in water
- b)Composed of amino acids
- c)Store and transmit genetic information
- d)Primarily serve as structural components of cell membranes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a characteristic of nucleic acids?
a)
Insoluble in water
b)
Composed of amino acids
c)
Store and transmit genetic information
d)
Primarily serve as structural components of cell membranes
|
|
Andrew King answered |
Characteristic of Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are essential biomolecules found in all living organisms. Their primary roles are crucial for the storage and transmission of genetic information.
Key Functions of Nucleic Acids:
- Genetic Information Storage:
Nucleic acids, particularly DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), store the genetic blueprint of an organism. The sequence of nucleotides (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) in DNA encodes the instructions needed for the development and functioning of living organisms.
- Transmission of Genetic Information:
During reproduction and cell division, nucleic acids ensure that genetic information is accurately copied and passed on to the next generation. This is accomplished through processes like DNA replication and transcription.
- Role of RNA:
RNA (ribonucleic acid) plays a vital role in expressing this genetic information. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized. Other forms of RNA, such as tRNA and rRNA, are also crucial for protein synthesis and regulation.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
- Insoluble in Water:
Nucleic acids are generally soluble in water due to their polar backbone, which allows them to interact with the aqueous environment of cells.
- Composed of Amino Acids:
Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides, not amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
- Structural Components of Cell Membranes:
While nucleic acids are vital for genetic functions, they do not primarily serve as structural components of cell membranes. That role is fulfilled by lipids and proteins.
In summary, option 'C' accurately describes nucleic acids as key molecules that store and transmit genetic information, highlighting their fundamental role in biology.
Nucleic acids are essential biomolecules found in all living organisms. Their primary roles are crucial for the storage and transmission of genetic information.
Key Functions of Nucleic Acids:
- Genetic Information Storage:
Nucleic acids, particularly DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), store the genetic blueprint of an organism. The sequence of nucleotides (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) in DNA encodes the instructions needed for the development and functioning of living organisms.
- Transmission of Genetic Information:
During reproduction and cell division, nucleic acids ensure that genetic information is accurately copied and passed on to the next generation. This is accomplished through processes like DNA replication and transcription.
- Role of RNA:
RNA (ribonucleic acid) plays a vital role in expressing this genetic information. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized. Other forms of RNA, such as tRNA and rRNA, are also crucial for protein synthesis and regulation.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
- Insoluble in Water:
Nucleic acids are generally soluble in water due to their polar backbone, which allows them to interact with the aqueous environment of cells.
- Composed of Amino Acids:
Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides, not amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
- Structural Components of Cell Membranes:
While nucleic acids are vital for genetic functions, they do not primarily serve as structural components of cell membranes. That role is fulfilled by lipids and proteins.
In summary, option 'C' accurately describes nucleic acids as key molecules that store and transmit genetic information, highlighting their fundamental role in biology.
Which of the following carbohydrates is called milk sugar?- a)Glucose
- b)Galactose
- c)Lactose
- d)Maltose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrates is called milk sugar?
a)
Glucose
b)
Galactose
c)
Lactose
d)
Maltose

|
Nidhi Yadav answered |
Lactose is the carbohydrate that is commonly known as milk sugar. It is a disaccharide composed of two sugar molecules, galactose and glucose, linked together by a β-glycosidic bond. Lactose is found in the milk of mammals, including humans, and is an important source of energy for infants.
Here is a detailed explanation of why lactose is called milk sugar:
Lactose in Milk:
- Lactose is primarily found in the milk of mammals. It is the main carbohydrate present in milk, accounting for about 4-5% of its composition.
- It provides energy for the growing infant and is essential for their development.
- As mammals produce milk to nourish their young, lactose is present in varying amounts in the milk of different species, including humans.
Structure of Lactose:
- Lactose is a disaccharide, which means it is composed of two sugar molecules linked together.
- It consists of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose.
- The glucose and galactose molecules are joined by a β-glycosidic bond, which is a specific type of chemical bond between the two sugars.
Digestion of Lactose:
- Lactose is digested by the enzyme lactase, which is produced in the small intestine.
- Lactase breaks down lactose into its individual sugar components, glucose and galactose.
- These simple sugars can then be absorbed into the bloodstream and used as a source of energy by the body.
Intolerance to Lactose:
- Some individuals have a reduced ability to produce lactase, resulting in lactose intolerance.
- Lactose intolerance is characterized by symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming milk or dairy products.
- This occurs because undigested lactose reaches the large intestine, where it is fermented by bacteria, leading to the production of gas and other byproducts.
In conclusion, lactose is called milk sugar because it is the main carbohydrate found in milk. It consists of glucose and galactose linked together by a β-glycosidic bond. Lactose provides energy for infants and is digested by the enzyme lactase. Lactose intolerance can occur when there is a reduced ability to produce lactase, leading to digestive symptoms after consuming milk or dairy products.
Here is a detailed explanation of why lactose is called milk sugar:
Lactose in Milk:
- Lactose is primarily found in the milk of mammals. It is the main carbohydrate present in milk, accounting for about 4-5% of its composition.
- It provides energy for the growing infant and is essential for their development.
- As mammals produce milk to nourish their young, lactose is present in varying amounts in the milk of different species, including humans.
Structure of Lactose:
- Lactose is a disaccharide, which means it is composed of two sugar molecules linked together.
- It consists of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose.
- The glucose and galactose molecules are joined by a β-glycosidic bond, which is a specific type of chemical bond between the two sugars.
Digestion of Lactose:
- Lactose is digested by the enzyme lactase, which is produced in the small intestine.
- Lactase breaks down lactose into its individual sugar components, glucose and galactose.
- These simple sugars can then be absorbed into the bloodstream and used as a source of energy by the body.
Intolerance to Lactose:
- Some individuals have a reduced ability to produce lactase, resulting in lactose intolerance.
- Lactose intolerance is characterized by symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming milk or dairy products.
- This occurs because undigested lactose reaches the large intestine, where it is fermented by bacteria, leading to the production of gas and other byproducts.
In conclusion, lactose is called milk sugar because it is the main carbohydrate found in milk. It consists of glucose and galactose linked together by a β-glycosidic bond. Lactose provides energy for infants and is digested by the enzyme lactase. Lactose intolerance can occur when there is a reduced ability to produce lactase, leading to digestive symptoms after consuming milk or dairy products.
Which of the following lipids function as long-term energy storage in animals?- a)Triglycerides
- b)Phospholipids
- c)Cholesterol
- d)Steroids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following lipids function as long-term energy storage in animals?
a)
Triglycerides
b)
Phospholipids
c)
Cholesterol
d)
Steroids
|
|
Nathan Wood answered |
Triglycerides are the lipids that function as long-term energy storage in animals.
Triglycerides are a type of lipid molecule composed of a glycerol backbone and three fatty acid chains. They are the most abundant type of lipid in the body and serve as a highly efficient form of energy storage.
Here is a detailed explanation of why triglycerides are the primary lipid involved in long-term energy storage in animals:
1. Structure of Triglycerides:
- Triglycerides consist of a glycerol molecule and three fatty acid chains.
- The fatty acid chains can vary in length and degree of saturation, which affects their physical properties.
2. Storage in Adipose Tissue:
- Triglycerides are primarily stored in specialized cells called adipocytes, which make up adipose tissue.
- Adipose tissue is found throughout the body, with larger deposits in regions such as the abdomen and thighs.
- When excess energy is consumed, it is converted into triglycerides and stored in adipose tissue.
3. Energy Storage and Release:
- Triglycerides serve as an efficient way to store energy because they are highly concentrated and have a low water content, allowing for compact storage.
- When the body needs energy, triglycerides can be broken down through a process called lipolysis.
- Lipolysis involves the hydrolysis of triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids, which can then be used as fuel by cells.
- This process primarily occurs in adipose tissue and is regulated by hormones such as glucagon and adrenaline.
4. High Energy Yield:
- Triglycerides provide a high yield of energy when compared to other molecules.
- When triglycerides are metabolized, they release more than twice the amount of energy as carbohydrates or proteins.
- This makes triglycerides an efficient and long-lasting source of energy, especially during periods of fasting or prolonged exercise.
In summary, triglycerides function as the primary long-term energy storage in animals due to their structure, storage in adipose tissue, efficient energy storage and release, and high energy yield.
Triglycerides are a type of lipid molecule composed of a glycerol backbone and three fatty acid chains. They are the most abundant type of lipid in the body and serve as a highly efficient form of energy storage.
Here is a detailed explanation of why triglycerides are the primary lipid involved in long-term energy storage in animals:
1. Structure of Triglycerides:
- Triglycerides consist of a glycerol molecule and three fatty acid chains.
- The fatty acid chains can vary in length and degree of saturation, which affects their physical properties.
2. Storage in Adipose Tissue:
- Triglycerides are primarily stored in specialized cells called adipocytes, which make up adipose tissue.
- Adipose tissue is found throughout the body, with larger deposits in regions such as the abdomen and thighs.
- When excess energy is consumed, it is converted into triglycerides and stored in adipose tissue.
3. Energy Storage and Release:
- Triglycerides serve as an efficient way to store energy because they are highly concentrated and have a low water content, allowing for compact storage.
- When the body needs energy, triglycerides can be broken down through a process called lipolysis.
- Lipolysis involves the hydrolysis of triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids, which can then be used as fuel by cells.
- This process primarily occurs in adipose tissue and is regulated by hormones such as glucagon and adrenaline.
4. High Energy Yield:
- Triglycerides provide a high yield of energy when compared to other molecules.
- When triglycerides are metabolized, they release more than twice the amount of energy as carbohydrates or proteins.
- This makes triglycerides an efficient and long-lasting source of energy, especially during periods of fasting or prolonged exercise.
In summary, triglycerides function as the primary long-term energy storage in animals due to their structure, storage in adipose tissue, efficient energy storage and release, and high energy yield.
Which of the following nucleotides is found only in RNA?- a)Adenine (A)
- b)Guanine (G)
- c)Thymine (T)
- d)Uracil (U)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following nucleotides is found only in RNA?
a)
Adenine (A)
b)
Guanine (G)
c)
Thymine (T)
d)
Uracil (U)
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Uracil (U) is a nitrogenous base found in RNA, whereas thymine (T) is found in DNA. Adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) are common to both RNA and DNA.
The reaction below is an example of:
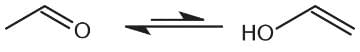
- a)esterification.
- b)tautomerization.
- c)elimination.
- d)dehydration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction below is an example of:


a)
esterification.
b)
tautomerization.
c)
elimination.
d)
dehydration
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
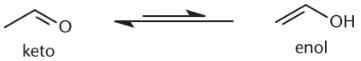
Tautomerization is the interconversion of two isomers in which a hydrogen and a double bond are moved. The keto and enol tautomers of aldehydes and ketones are common examples of tautomers seen on Test Day. Note that the equilibrium lies to the left because the keto form is more stable. Esterification, choice (A), is the formation of esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols. Elimination, choice (C), is a reaction in which a part of a reactant is lost and a new multiple bond is introduced. Dehydration, choice (D), is a reaction in which a molecule of water is eliminated.
In a hemiacetal, the central carbon is bound to:- a)–OH, –OR, –H and –R.
- b)–H, –OR, –OR, and –R.
- c)–OH, –OR, –R, and –R.
- d)–OR, –OR, –R, and –R.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a hemiacetal, the central carbon is bound to:
a)
–OH, –OR, –H and –R.
b)
–H, –OR, –OR, and –R.
c)
–OH, –OR, –R, and –R.
d)
–OR, –OR, –R, and –R.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
A hemiacetal is a molecule in which one equivalent alcohol has been added to a carbonyl (–OR) and the carbonyl oxygen has been protonated (–OH). Otherwise, there is the same alkyl group (–R) and hydrogen atom (–H) as the parent aldehyde. Choice (B) describes an acetal, choice (C) a hemiketal, and choice (D) a ketal.
Why does the equilibrium between keto and enol tautomers lie far to the keto side?
I. The keto form is more thermodynamically stable.
II. The enol form is lower energy.
III. The enol form is more thermodynamically stable.- a)I only
- b)III only
- c)I and II only
- d)II and III only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Why does the equilibrium between keto and enol tautomers lie far to the keto side?
I. The keto form is more thermodynamically stable.
II. The enol form is lower energy.
III. The enol form is more thermodynamically stable.
I. The keto form is more thermodynamically stable.
II. The enol form is lower energy.
III. The enol form is more thermodynamically stable.
a)
I only
b)
III only
c)
I and II only
d)
II and III only
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The keto–enol equilibrium lies far to the keto side because the keto form is significantly more thermodynamically stable than the enol form. This thermodynamic stability stems from the fact that the oxygen is more electronegative than the carbon, and the keto tautomer puts more electron density around the oxygen than the enol tautomer. If the enol tautomer is less thermodynamically stable, it is also higher energy than the keto tautomer.
Identify the following compound: 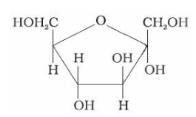
- a)β – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
- b)α – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
- c)α – D – (+) – Glucopyranose
- d)β – D – (+) – Glucopyranose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the following compound:

a)
β – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
b)
α – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
c)
α – D – (+) – Glucopyranose
d)
β – D – (+) – Glucopyranose

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The given compound is a five-membered ring with:
- An oxygen atom in the ring → furanose ring
- Two –CH₂OH groups (on carbon-1 and carbon-4)
- Multiple –OH groups on the ring
This matches the structure of β-D-fructofuranose, the cyclic form of fructose.
Hemiacetals and hemiketals usually keep reacting to form acetals and ketals. Why is it difficult to isolate hemiacetals and hemiketals?
I. These molecules are unstable.
II. The hydroxyl group is rapidly protonated and lost as water under acidic conditions, leaving behind a reactive carbocation.
III. The molecules are extremely basic and react rapidly with one another.- a)I only
- b)I and II only
- c)II and III only
- d)I, II, and III
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hemiacetals and hemiketals usually keep reacting to form acetals and ketals. Why is it difficult to isolate hemiacetals and hemiketals?
I. These molecules are unstable.
II. The hydroxyl group is rapidly protonated and lost as water under acidic conditions, leaving behind a reactive carbocation.
III. The molecules are extremely basic and react rapidly with one another.
I. These molecules are unstable.
II. The hydroxyl group is rapidly protonated and lost as water under acidic conditions, leaving behind a reactive carbocation.
III. The molecules are extremely basic and react rapidly with one another.
a)
I only
b)
I and II only
c)
II and III only
d)
I, II, and III
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Hemiacetals and hemiketals are usually short-lived because the –OH group will rapidly become protonated in acidic conditions and is lost as water, leaving behind a carbocation that is very susceptible to attack by an alcohol. Once the alcohol has been added, the acetal or ketal becomes more stable because the newly added group is less likely to become protonated and leave as compared to –OH.
When reacted with ammonia (NH3) at 200°C, which enolate of a carbonyl-containing compound would predominate?- a)Kinetic enolate
- b)Thermodynamic enolate
- c)Neither enolate; they would be present in roughly equal proportions
- d)Neither enolate; these reaction conditions would not form either enolate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When reacted with ammonia (NH3) at 200°C, which enolate of a carbonyl-containing compound would predominate?
a)
Kinetic enolate
b)
Thermodynamic enolate
c)
Neither enolate; they would be present in roughly equal proportions
d)
Neither enolate; these reaction conditions would not form either enolate
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
At high temperatures and with a weak base like NH3, the thermodynamic enolate will be favored. The reaction proceeds slowly with the weak base, giving the kinetic enolate time to interconvert to the more stable thermodynamic enolate.
Order the following compounds by increasing boiling point: butane, butanol, butanone- a)Butanol < butane < butanone
- b)Butane < butanone < butanol
- c)Butanone < butane < butanol
- d)Butane < butanol < butanone
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Order the following compounds by increasing boiling point: butane, butanol, butanone
a)
Butanol < butane < butanone
b)
Butane < butanone < butanol
c)
Butanone < butane < butanol
d)
Butane < butanol < butanone
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Assuming the length of the carbon chain remains the same, the alkane consistently has the lowest boiling point. The boiling point of the ketone is elevated by the dipole in the carbonyl. The boiling point of the alcohol is elevated further by hydrogen bonding.
What is the product of the reaction below?- a)
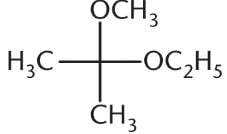
- b)
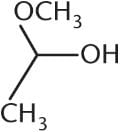
- c)
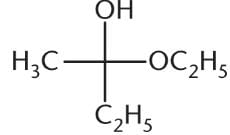
- d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the product of the reaction below?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The reaction between a ketone and one equivalent of alcohol produces a hemiketal. This has an –OR group, an –OH group, and two alkyl groups attached at the same carbon. Choice (A) is a ketal, with two –OR groups and two –R groups. Choice (B) is a hemiacetal, with an –OH group, an –OR group, one R group, and a hydrogen atom. Choice (D) is a ketone. Note that a hemiketal is a very unstable compound, and will react rapidly with a second equivalent of alcohol to form a ketal in acidic conditions.
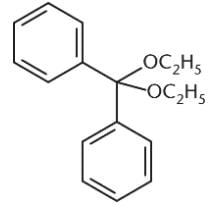
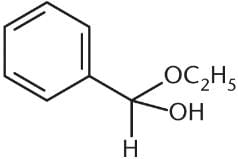
What is the product of the reaction between benzaldehyde and an excess of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) in the presence of anhydrous HCl?- a)
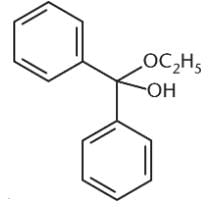
- b)
- c)
- d)
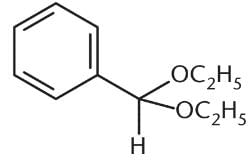
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the product of the reaction between benzaldehyde and an excess of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) in the presence of anhydrous HCl?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Because an excess of ethanol is present, the product of the reaction between this aldehyde and ethanol will be an acetal. The benzaldehyde will first be converted to a hemiacetal, shown in choice (C), but will then proceed to completion as an acetal. Choices (A) and (B) are incorrect because they show the presence of two benzene rings in the final product.
When succinaldehyde is treated with lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), it:
I. becomes more nucleophilic.
II. becomes less nucleophilic.
III. generates a carbanion.- a)I only
- b)II only
- c)I and III only
- d)II and III only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When succinaldehyde is treated with lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), it:
I. becomes more nucleophilic.
II. becomes less nucleophilic.
III. generates a carbanion.
I. becomes more nucleophilic.
II. becomes less nucleophilic.
III. generates a carbanion.
a)
I only
b)
II only
c)
I and III only
d)
II and III only
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
When succinaldehyde (or any aldehyde or ketone with α-hydrogens) is treated with a strong base like lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), it forms the more nucleophilic enolate carbanion.
The aldol condensation is an example of which reaction type(s)?
I. Dehydration
II. Cleavage
III. Nucleophilic addition- a)I only
- b)I and III only
- c)II and III only
- d)I, II, and III
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The aldol condensation is an example of which reaction type(s)?
I. Dehydration
II. Cleavage
III. Nucleophilic addition
I. Dehydration
II. Cleavage
III. Nucleophilic addition
a)
I only
b)
I and III only
c)
II and III only
d)
I, II, and III
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The aldol condensation is both a dehydration reaction because a molecule of water is lost, and a nucleophilic addition reaction because the nucleophilic enolate attacks and binds to the carbonyl carbon.
α-hydrogens of a ketone are acidic due to:
I. resonance stabilization.
II. the electron-withdrawing properties of the alkyl groups.
III. the electronegative carbonyl oxygen.- a)I only
- b)I and III only
- c)II and III only
- d)I, II, and III
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
α-hydrogens of a ketone are acidic due to:
I. resonance stabilization.
II. the electron-withdrawing properties of the alkyl groups.
III. the electronegative carbonyl oxygen.
I. resonance stabilization.
II. the electron-withdrawing properties of the alkyl groups.
III. the electronegative carbonyl oxygen.
a)
I only
b)
I and III only
c)
II and III only
d)
I, II, and III
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
When α-carbons are deprotonated, the negative charge is resonance stabilized in part by the electronegative carbonyl oxygen, which is electron-withdrawing. Alkyl groups are actually electron-donating, which destabilizes carbanion intermediates; this invalidates statement II.
Which of the following is a function of carbohydrates in living organisms?- a)Regulation of body temperature
- b)Energy storage and release
- c)Transmission of nerve impulses
- d)Formation of antibodies
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a function of carbohydrates in living organisms?
a)
Regulation of body temperature
b)
Energy storage and release
c)
Transmission of nerve impulses
d)
Formation of antibodies
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Carbohydrates serve as a primary source of energy for living organisms. They are broken down into glucose, which can be utilized for various metabolic processes and energy production.
Imines naturally tautomerize to form:- a)oximes.
- b)hydrazones.
- c)semicarbazones.
- d)enamines.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Imines naturally tautomerize to form:
a)
oximes.
b)
hydrazones.
c)
semicarbazones.
d)
enamines.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
During tautomerization, the double bond between the carbon and nitrogen in an imine is moved to lie between two carbons. This results in an enamine—a compound with a double bond and an amine.
Which of the following describe(s) pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)?
I. An oxidant that can form aldehydes from primary alcohols
II. An oxidant that can form carboxylic acids from primary alcohols
III. An oxidant that can completely oxidize secondary alcohols to ketones- a)I only
- b)I and II only
- c)I and III only
- d)I, II, and III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following describe(s) pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)?
I. An oxidant that can form aldehydes from primary alcohols
II. An oxidant that can form carboxylic acids from primary alcohols
III. An oxidant that can completely oxidize secondary alcohols to ketones
I. An oxidant that can form aldehydes from primary alcohols
II. An oxidant that can form carboxylic acids from primary alcohols
III. An oxidant that can completely oxidize secondary alcohols to ketones
a)
I only
b)
I and II only
c)
I and III only
d)
I, II, and III
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
PCC is a mild anhydrous oxidant that can oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes, and secondary alcohols to ketones. It is not strong enough to oxidize alcohols or aldehydes to carboxylic acids.
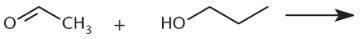
What is the product of the reaction below?
- a)
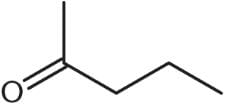
- b)
- c)
- d)
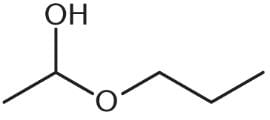
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the product of the reaction below?


a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
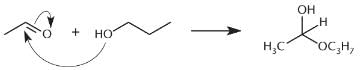
One mole of aldehyde reacts with one mole of alcohol via a nucleophilic addition reaction to form a product called a hemiacetal. In a hemiacetal, an –OH group, an –OR group, a hydrogen atom, and an –R group are attached to the same carbon atom.
The catalytic production of dihydroxyacetone and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (2-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl dihydrogen phosphate) from fructose-1,6-bisphosphate ({[(2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}phosphonic acid) is what type of reaction?- a)Aldol condensation
- b)Retro-aldol reaction
- c)Dehydration
- d)Nucleophilic attack
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The catalytic production of dihydroxyacetone and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (2-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl dihydrogen phosphate) from fructose-1,6-bisphosphate ({[(2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}phosphonic acid) is what type of reaction?
a)
Aldol condensation
b)
Retro-aldol reaction
c)
Dehydration
d)
Nucleophilic attack
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The nomenclature in this question is well above what one needs to be able to draw on the MCAT; however, we can discern that we are forming a ketone and an aldehyde from a single molecule. The hallmark of a reverse aldol reaction is the breakage of a carbon–carbon bond, forming two aldehydes, two ketones, or one of each. In an aldol condensation, choice (A), we would expect to form a single product by combining two aldehydes, two ketones, or one of each. A dehydration reaction, choice (C), should release a water molecule, rather than breaking apart a large organic molecule into two smaller molecules. A nucleophilic attack, choice (D), should feature the formation of a bond between a nucleophile and an electrophile; again, we would not expect to break apart a large organic molecule into two smaller molecules. Note that simply noting how many reactants and products are present in the reaction is sufficient to determine the answer.
What is the product of the reaction below?

- a)C3H7OH
- b)C2H5COOH
- c)C3H6CHO
- d)CH3COOH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the product of the reaction below?


a)
C3H7OH
b)
C2H5COOH
c)
C3H6CHO
d)
CH3COOH
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Aldehydes are easily oxidized to the corresponding carboxylic acids by KMnO4. In choice (A), the aldehyde has been reduced to an alcohol. In choice (C), the molecule has not reacted. In choice (D), the aldehyde has been oxidized, but a –CH2– group has been removed.
All of the following are true with respect to carbonyls EXCEPT:- a)the carbonyl carbon is electrophilic.
- b)the carbonyl oxygen is electron-withdrawing.
- c)a resonance structure of functional group places a positive charge on the carbonyl carbon.
- d)the π electrons are mobile and are pulled toward the carbonyl carbon.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
All of the following are true with respect to carbonyls EXCEPT:
a)
the carbonyl carbon is electrophilic.
b)
the carbonyl oxygen is electron-withdrawing.
c)
a resonance structure of functional group places a positive charge on the carbonyl carbon.
d)
the π electrons are mobile and are pulled toward the carbonyl carbon.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The reactivity of the carbonyl can be attributed to the difference in electronegativity between the carbon and oxygen atoms. The more electronegative oxygen atom attracts the bonding electrons and is therefore electron-withdrawing. Thus, the carbonyl carbon is electrophilic, and the carbonyl oxygen is nucleophilic. One resonance structure of the carbonyl pushes the π electrons onto the oxygen, resulting in a positively charged carbonyl carbon.
When benzaldehyde is reacted with acetone, which will act as the nucleophile?- a)Benzaldehyde, after addition of strong acid
- b)Benzaldehyde, after reaction with strong base
- c)Acetone, after addition of strong acid
- d)Acetone, after reaction with strong base
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When benzaldehyde is reacted with acetone, which will act as the nucleophile?
a)
Benzaldehyde, after addition of strong acid
b)
Benzaldehyde, after reaction with strong base
c)
Acetone, after addition of strong acid
d)
Acetone, after reaction with strong base
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Because benzaldehyde lacks an α-proton, it cannot be reacted with base to form the nucleophilic enolate carbanion. Therefore, acetone will act as our nucleophile, and both choices (A) and (B) can be eliminated. In order to perform this reaction, which is an aldol condensation, acetone will be reacted with a strong base—not a strong acid—in order to extract the α-hydrogen and form the enolate anion, which will act as a nucleophile.
In a reaction between ammonia and glutaraldehyde, what is the major product?- a)An imine
- b)A cyanohydrin
- c)An aldehyde with a substituted ring
- d)An alcohol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a reaction between ammonia and glutaraldehyde, what is the major product?
a)
An imine
b)
A cyanohydrin
c)
An aldehyde with a substituted ring
d)
An alcohol
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Ammonia, or NH3, will react with an aldehyde like glutaraldehyde to form an imine. This is a condensation and a substitution reaction, as the C=O of the carbonyl will be replaced with a C=N bond.
Chapter doubts & questions for Carbohydrates (OC, BC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Carbohydrates (OC, BC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations
336 videos|223 docs|109 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









