All Exams >
NEET >
Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Chemical Coordination and Regulation for NEET Exam
Oxytocin helps in [1999]- a)lactation
- b)child birth
- c)ovulation
- d)implantation of the embryo
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxytocin helps in [1999]
a)
lactation
b)
child birth
c)
ovulation
d)
implantation of the embryo
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
"Oxytocin is a peptide produced in the brain that was first recognized for its role in the birth process, and also in nursing," said Larry Young, a behavioral neuroscientist at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia. The hormone causes uterine contractions during labor and helps shrink the uterus after delivery.
The most important component of the oral contraceptive pill is [1998]- a)growth hormone
- b)thyroxine
- c)luteinizing hormone
- d)progesterone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most important component of the oral contraceptive pill is [1998]
a)
growth hormone
b)
thyroxine
c)
luteinizing hormone
d)
progesterone

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
Use of contraceptive pills is a wide spread form of birth control. contraceptive pills contain estrogen and progesterone. The production of the pituitary hormones FSH & LH in the normal sexual cycle of a female is shut down by these hormones. In the absence of FSH, the ovarian follicles do not ripe and ovulation does not occur in the absence of LH.
Norepinephrine : [NEET Kar. 2013]
(1) Is released by sympathetic fibres
(2) Is released by parasympathetic fibres
(3) Increases the heart rate
(4) Decreases blood pressure
Which of the above said statements are correct?- a)(1) and (4)
- b)(1) and (3)
- c)(2) and (3)
- d)(2) and (4)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Norepinephrine : [NEET Kar. 2013]
(1) Is released by sympathetic fibres
(2) Is released by parasympathetic fibres
(3) Increases the heart rate
(4) Decreases blood pressure
Which of the above said statements are correct?
(1) Is released by sympathetic fibres
(2) Is released by parasympathetic fibres
(3) Increases the heart rate
(4) Decreases blood pressure
Which of the above said statements are correct?
a)
(1) and (4)
b)
(1) and (3)
c)
(2) and (3)
d)
(2) and (4)

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
Norepinephrine is released by sympathetic fibres i.e, rapidly secreted in response to stress of any kind and during emergency situations. It increases the heart beat, the strength of heart contraction and the rate of respiration.
Which one of the following pairs is incorrectly matched? [2010]- a)Glucagon - Beta cells (source)
- b)Somatostatin - Delta cells (source)
- c)Corpus luteum - Relaxin (secretion)
- d)Insulin - Diabetes mellitus (disease)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs is incorrectly matched? [2010]
a)
Glucagon - Beta cells (source)
b)
Somatostatin - Delta cells (source)
c)
Corpus luteum - Relaxin (secretion)
d)
Insulin - Diabetes mellitus (disease)

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Glucagon is secreted by a-cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. It increases the concentration of glucose in the blood by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen.
A health disorder that results from the deficiency of thyroxine in adults and characterised by (i) a low metabolic rate, (ii) increase in body weight and (iii) tendency to retain water in tissues is: [2009]- a)simple goitre
- b)myxoedema
- c)cretinism
- d)hypothyroidism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A health disorder that results from the deficiency of thyroxine in adults and characterised by (i) a low metabolic rate, (ii) increase in body weight and (iii) tendency to retain water in tissues is: [2009]
a)
simple goitre
b)
myxoedema
c)
cretinism
d)
hypothyroidism

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
Myxoedema is caused by deficiency of thyroid hormone or thyroxine in adults. It is characterised by increase in body weight, puffy appearance, low metabolic rate, and tendency to retain water in tissues.
Which of the following is an accumulation and release centre of neurohormones ? [2006]- a)Intermediate lobe of the pituitary
- b)Hypothalamus
- c)Anterior pituitary lobe
- d)Posterior pituitary lobe
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an accumulation and release centre of neurohormones ? [2006]
a)
Intermediate lobe of the pituitary
b)
Hypothalamus
c)
Anterior pituitary lobe
d)
Posterior pituitary lobe

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
Neurohormones are actually secreted by the neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus. They are circulated to the posterior part of the pituitary gland through the blood & stored there and released when required.
Which hormone possesses anti-insulin effect?[1988]- a)Cortisol
- b)Calcitonin
- c)Oxytocin
- d)Aldosterone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which hormone possesses anti-insulin effect?[1988]
a)
Cortisol
b)
Calcitonin
c)
Oxytocin
d)
Aldosterone

|
Maitri Mukherjee answered |
Cortisol is secreted by the middle region of adrenal cortex. It increases the blood glucose level (which is anti-insulin effect) by converting proteins & fats into glucose.
Acromegaly is caused by [2002]- a)excess of G.H.
- b)excess of thyroxin
- c)deficiency of thyroxin
- d)excess of adrenalin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Acromegaly is caused by [2002]
a)
excess of G.H.
b)
excess of thyroxin
c)
deficiency of thyroxin
d)
excess of adrenalin

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Deficiency of thyroxin causes cretinism in infants and myxoedema in adults. Excess of adrenalin does not cause any disorder. Acromegaly is caused by over secretion of STH or somatotrophic hormone (Growth hormone).
Which one of the following pairs of organs includes only the endocrine glands? [2008]- a)Parathyroid and Adrenal
- b)Pancreas and Parathyroid
- c)Thymus and Testes
- d)Adrenal and Ovary
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of organs includes only the endocrine glands? [2008]
a)
Parathyroid and Adrenal
b)
Pancreas and Parathyroid
c)
Thymus and Testes
d)
Adrenal and Ovary

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
Parathyroid and adrenal are the endocrine glands. Adrenal glands are the pairs of endocrine glands situated immediately above the kidneys. Hence they are also known as suprarenal glands. Parathyroid glands are the two pairs of endocrine glands -situated behind or embedded within, the thyroid gland in higher vertebrates. They produce parathyroid hormone, which controls the amount of calcium in the blood.
The mammalian corpus luteum produces [1995]- a)estrogen
- b)progesterone
- c)luteotropic hormone
- d)luteinizing hormone
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mammalian corpus luteum produces [1995]
a)
estrogen
b)
progesterone
c)
luteotropic hormone
d)
luteinizing hormone

|
Anu Bajaj answered |
Mammalian corpus luteum produces progesterone. It is essential for the continuation of pregnancy and it also stimulates acini glands.
MSH of pars intermedia of middle pituitary is responsible for [1988]
- a)darkening of skin in lower vertebrates
- b)Light colouration of skin in lower vertebrates
- c)Both A and B
- d)Darkening of skin in human beings
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
MSH of pars intermedia of middle pituitary is responsible for [1988]
a)
darkening of skin in lower vertebrates
b)
Light colouration of skin in lower vertebrates
c)
Both A and B
d)
Darkening of skin in human beings

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) or Melanotropin is secreted by the intermediate lobe of adenohypophysis (pars intermedia) of pituitary gland in mammals (other than man) so named ‘intermedin’. In lower vertebrates, it targets chromatophores & does wider distribution of the melanin grannules in chromatophores, so that the skin colour darkens. In birds & human beings and other mammals its role is uncertain but in man it is probably responsible for bronzing of skin, moles etc.
Injury to adrenal cortex is not likely to affect the secretion of which one of the following? [2010]- a)Aldosterone
- b)Both Androstenedione and Dehydroepiandrosterone
- c)Adrenaline
- d)Cortisol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Injury to adrenal cortex is not likely to affect the secretion of which one of the following? [2010]
a)
Aldosterone
b)
Both Androstenedione and Dehydroepiandrosterone
c)
Adrenaline
d)
Cortisol

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
Adrenal gland has two parts-cortex and medulla. The medulla is stimulated by sympathetic nervous tissue to produce adrenaline and non-adrenaline while the cortex is stimulated by pituitary hormone to release cortisol, aldosterone and estrogens. Thus injury to adrenal cortex is not likely to affect the secretion of adrenaline
Sertoli cells are regulated by the pituitary hormone known as [2006]- a)GH
- b)Prolactin
- c)LH
- d)FSH
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sertoli cells are regulated by the pituitary hormone known as [2006]
a)
GH
b)
Prolactin
c)
LH
d)
FSH
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
Sertoli cells are the cells that line the seminiferous tubules in the testis. These cells protect the spermatids and convey nutrients to both the developing and mature spermatozoa. Sertoli cells are regulated by FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)which is secreted by the anterior pituitary. FSH stimulates Sertoli cells to produce androgen-binding protein and inhibin and together with testosterone, promotes the proliferation of Sertoli cells. So, the correct answer is option 'D'.
Which one of the following statement is correct? [2006]- a)Endrocrine glands regulate neural activity, and nervous system regulates endocrine glands
- b)Neither hormones control neural activity nor the neurons control endocrine activity
- c)Endocrine glands regulate neural activity, but not vice versa
- d)Neurons regulate endocrine activity, but not vice versa
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statement is correct? [2006]
a)
Endrocrine glands regulate neural activity, and nervous system regulates endocrine glands
b)
Neither hormones control neural activity nor the neurons control endocrine activity
c)
Endocrine glands regulate neural activity, but not vice versa
d)
Neurons regulate endocrine activity, but not vice versa

|
Pankaj Kulkarni answered |
Endocrine glands regulate neural activity as endocrine glands secrete epinephrine & norepinephrine which have their effects on neuron activity. On the other hand neuron also controls the activity of endocrine glands by secreting neurohormones which regulate the activity of many endocrine glands.
Low Ca++ in the body fluid may be the cause of:[2010]- a)tetany
- b)anaemia
- c)angina pectoris
- d)gout
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Low Ca++ in the body fluid may be the cause of:[2010]
a)
tetany
b)
anaemia
c)
angina pectoris
d)
gout

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
Tetany is caused by reduction in the calcium level due to underactive parathyroid hormone.
Which of the following statements is correct in relation to the endocrine system? [NEET 2013]- a)Organs in the body like gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidney and liver do not produce any hormones.
- b)Non-nutrient chemicals produced by the body in trace amount that act as intercellular messenger are known as hormones.
- c)Releasing and inhibitory hormones are produced by the pituitary gland .
- d)Adenohypophysis is under direct neural regulation of the hypothalamus.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct in relation to the endocrine system? [NEET 2013]
a)
Organs in the body like gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidney and liver do not produce any hormones.
b)
Non-nutrient chemicals produced by the body in trace amount that act as intercellular messenger are known as hormones.
c)
Releasing and inhibitory hormones are produced by the pituitary gland .
d)
Adenohypophysis is under direct neural regulation of the hypothalamus.

|
Pankaj Kulkarni answered |
Hormones are non-nutrient chemicals which act as intercellular messengers and are produced in trace amounts.
Gastrointestinal tracts secretes four major peptide hormones – gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin (CCK) and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) while juxtaglomerular cells of kidney secretes erythropoietin, a peptide hormone. Releasing and inhibitory hormones are produced by hypothalamus. Neurohypophysis or posterior pituitary is under direct neural regulation of the hypothalamus.
Gastrointestinal tracts secretes four major peptide hormones – gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin (CCK) and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) while juxtaglomerular cells of kidney secretes erythropoietin, a peptide hormone. Releasing and inhibitory hormones are produced by hypothalamus. Neurohypophysis or posterior pituitary is under direct neural regulation of the hypothalamus.
Which hormone causes dilation of blood vessels, increased oxygen consumption and glucogenesis? [2006]- a)Insulin
- b)Adrenaline
- c)Glucagon
- d)ACTH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which hormone causes dilation of blood vessels, increased oxygen consumption and glucogenesis? [2006]
a)
Insulin
b)
Adrenaline
c)
Glucagon
d)
ACTH

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
Adrenaline (called Frieght-Flight-Fight hormone) in responsible for the dilation of blood vessels, increased oxygen consumption by tissues & glucogenesis to prepare the body for emergency reactions under the threatening conditions.
Which one of the following pairs correctly matches a hormone with a disease resulting from its deficiency ? [2003]- a)Insulin – Diabetes insipidus
- b)Relaxin – Gigantism
- c)Prolactin – Cretinism
- d)Parathyroid hormone – Tetany
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs correctly matches a hormone with a disease resulting from its deficiency ? [2003]
a)
Insulin – Diabetes insipidus
b)
Relaxin – Gigantism
c)
Prolactin – Cretinism
d)
Parathyroid hormone – Tetany

|
Ayush Sengupta answered |
Deficiency of parathyroid hormone causes tetany. The disease causes sustained contraction of muscles of larynx, face, hands and feet.
When both ovaries are removed from rat then which hormone is decreased in blood? [2002]- a)Oxytocin
- b)Prolactin
- c)Estrogen
- d)Gonadotropin releasing factor
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When both ovaries are removed from rat then which hormone is decreased in blood? [2002]
a)
Oxytocin
b)
Prolactin
c)
Estrogen
d)
Gonadotropin releasing factor

|
Krish Khanna answered |
Estrogen is released from the ovarian follicles. Oxytocin is secreted by posterior pituitary and prolactin is released by anterior pituitary. Gonadotropin releasing factor is produced by hypothalamus.
Calcitonin is a thyroid hormone which [1998]- a)lowers calcium level in blood
- b)elevates calcium level in blood
- c)has no effect on calcium
- d)elevates potassium level in blood
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calcitonin is a thyroid hormone which [1998]
a)
lowers calcium level in blood
b)
elevates calcium level in blood
c)
has no effect on calcium
d)
elevates potassium level in blood

|
Krish Khanna answered |
Calcitonin is a polypeptide hormone which lowers calcium and phosphate level of plasma by inhibiting bone degradation and stimulating their uptake by bone parathyroid harmone elevates calcium level in blood.
Progesterone, the component of the oral contraceptive pills, prevents pregnancy by [2000]- a)preventing the cleavage of the fertilized egg
- b)preventing the formation of ova
- c)blocking ovulation
- d)creating unfavourable chemical environment for the sperms to survive in the female reproductive tract
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Progesterone, the component of the oral contraceptive pills, prevents pregnancy by [2000]
a)
preventing the cleavage of the fertilized egg
b)
preventing the formation of ova
c)
blocking ovulation
d)
creating unfavourable chemical environment for the sperms to survive in the female reproductive tract

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Contraceptive pills have estrogen and progesterone. Progesterone suppresses ovulation and production of LH while estrogen suppresses the production of FSH.
A person is having problems with calcium and phosphorus metabolism in his body. Which one of following glands may not be functioning properly ? [2007]- a)Parotid
- b)Pancreas
- c)Thyroid
- d)Parathyroid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A person is having problems with calcium and phosphorus metabolism in his body. Which one of following glands may not be functioning properly ? [2007]
a)
Parotid
b)
Pancreas
c)
Thyroid
d)
Parathyroid

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
Parathyroid disorders : It causes the lowering of blood calcium level. This increases the excitability of nerves and muscles causing cramps and convulsions.
Mainly which type of hormones control the menstrual cycle in human beings? [2002]- a)FSH
- b)LH
- c)FSH, LH, estrogen
- d)Progesteron
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mainly which type of hormones control the menstrual cycle in human beings? [2002]
a)
FSH
b)
LH
c)
FSH, LH, estrogen
d)
Progesteron

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Estrogens are steroid hormones secreted by growing ovarian follicles. During menstrual cycle a negative feedback prevents the over secretion of estrogen. FSH stimulates maturation of Graafian follicles. LH stimulates ovulation and development of corpus luteum.
Hormones, thyroxine, adrenaline and the pigment melanin are formed from [1997]- a)tryptophan
- b)glycine
- c)tyrosine
- d)proline
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormones, thyroxine, adrenaline and the pigment melanin are formed from [1997]
a)
tryptophan
b)
glycine
c)
tyrosine
d)
proline

|
Snehal Shah answered |
The amino acid glycine forms porphyrin ring in chlorophyll and haeme proteins like haemoglobin. Tryptophan gives rise to plant hormone indole- 3 - acetic acid.
Nicotine acts as a stimulant, because it mimics the effect of [1995]- a)thyroxine
- b)acetylcholine
- c)testosterone
- d)dopamine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Nicotine acts as a stimulant, because it mimics the effect of [1995]
a)
thyroxine
b)
acetylcholine
c)
testosterone
d)
dopamine
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Nicotine initially stimulates and subsequently in high doses inhibits neural impulses at autonomic ganglia and the neuromuscular junction.
Parathormone deficiency produces muscle ramps or tetany as a result of [1999]- a)lowered blood Ca2+
- b)enhanced blood Na+
- c)enhanced blood glucose
- d)enhanced blood Ca2+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Parathormone deficiency produces muscle ramps or tetany as a result of [1999]
a)
lowered blood Ca2+
b)
enhanced blood Na+
c)
enhanced blood glucose
d)
enhanced blood Ca2+

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Parathormone released by the parathyroid gland elevates the level of Ca2+ in blood. The deficiency of this hormone lowers blood Ca2+. As a result, the excitability of muscles and nerves increases producing tetany -sustained contraction.
A candidate vaccine for male contraception is based on [1999]- a)follicle stimulating hormone
- b)progesterone
- c)testosterone
- d)luteinizing hormone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A candidate vaccine for male contraception is based on [1999]
a)
follicle stimulating hormone
b)
progesterone
c)
testosterone
d)
luteinizing hormone

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
Progesterone is a steroid hormone secreted by corpus luteum and causes routine temporary changes in the endometrial lining of uterus. Follicle stimulating hormone secreted by anterior pituitary lobe stimulates spermatogenesis in testes of males. Luteinizing hormone activates Leydig’s cells of testes to secrete testosterones.
Which one of the following pairs of hormones are the examples of those that can easily pass through the cell membrane of the target cell and bind to a receptor inside it (Mostly in the nucleus) [2012]- a)Insulin, glucagon
- b)Thyroxin, insulin
- c)Somatostain, oxytocin
- d)Cortisol, testosterone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of hormones are the examples of those that can easily pass through the cell membrane of the target cell and bind to a receptor inside it (Mostly in the nucleus) [2012]
a)
Insulin, glucagon
b)
Thyroxin, insulin
c)
Somatostain, oxytocin
d)
Cortisol, testosterone

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Cor tisol and testosterone are steroid hormones which are lipid soluble and easily pass through the cell membrane of a target cell and bind to specific intracellular receptor.
Select the correct statement. [2020]- a)Insulin acts on pancreatic cells and adipocytes.
- b)Insulin is associated with hyperglycemia.
- c)Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenesis.
- d)Glucagon is associated with hypoglycemia.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement. [2020]
a)
Insulin acts on pancreatic cells and adipocytes.
b)
Insulin is associated with hyperglycemia.
c)
Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenesis.
d)
Glucagon is associated with hypoglycemia.
|
|
Gaurav Majumdar answered |
Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenesis
Glucocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal glands. One of the main functions of glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, is to regulate metabolism. One way they do this is by stimulating the process of gluconeogenesis, which is the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like amino acids and glycerol.
Role of Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is an important metabolic pathway that helps maintain blood glucose levels during fasting or prolonged exercise. By increasing gluconeogenesis, glucocorticoids ensure that there is a steady supply of glucose available for the body to use as energy.
Regulation of Gluconeogenesis
Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenesis by upregulating the expression of key enzymes involved in the pathway, such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase. This leads to an increase in the production of glucose from precursors in the liver.
Impact on Blood Glucose Levels
Due to their role in stimulating gluconeogenesis, glucocorticoids can lead to an increase in blood glucose levels. This is why glucocorticoid medications, such as prednisone, are associated with side effects like hyperglycemia in some individuals.
In conclusion, glucocorticoids play a crucial role in the regulation of metabolism, particularly by stimulating gluconeogenesis to ensure a constant supply of glucose for the body's energy needs.
Glucocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal glands. One of the main functions of glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, is to regulate metabolism. One way they do this is by stimulating the process of gluconeogenesis, which is the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like amino acids and glycerol.
Role of Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is an important metabolic pathway that helps maintain blood glucose levels during fasting or prolonged exercise. By increasing gluconeogenesis, glucocorticoids ensure that there is a steady supply of glucose available for the body to use as energy.
Regulation of Gluconeogenesis
Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenesis by upregulating the expression of key enzymes involved in the pathway, such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase. This leads to an increase in the production of glucose from precursors in the liver.
Impact on Blood Glucose Levels
Due to their role in stimulating gluconeogenesis, glucocorticoids can lead to an increase in blood glucose levels. This is why glucocorticoid medications, such as prednisone, are associated with side effects like hyperglycemia in some individuals.
In conclusion, glucocorticoids play a crucial role in the regulation of metabolism, particularly by stimulating gluconeogenesis to ensure a constant supply of glucose for the body's energy needs.
Insulin is [1990]- a)vitamin
- b)lipid
- c)hormone
- d)enzyme
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Insulin is [1990]
a)
vitamin
b)
lipid
c)
hormone
d)
enzyme

|
Shalini Saha answered |
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the b-cells of pancreas and it controls the sugar level in blood
Which one of the following hormone stimulates the “let-down” (release) of milk from the mother’s breasts when the baby is sucking ? [1996]- a)Progesterone
- b)Oxytocin
- c)Prolactin
- d)Relaxin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following hormone stimulates the “let-down” (release) of milk from the mother’s breasts when the baby is sucking ? [1996]
a)
Progesterone
b)
Oxytocin
c)
Prolactin
d)
Relaxin

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
Prolactin is a proteinaceous hormone released by anterior lobe of pituitary. Prolactin supplements the action of gonadal hormones in stimulating the growth and activity of female mammary gland during pregnancy and lactation. Oxytocin released by the posterior lobe of pituitary gland, is important for the mechanism of ejection of milk from the mammary glands due to sucking of breasts by infant. Progesterone, released by corpus luteum brings about pregnancy changes such as uterine growth, implantation of embryo etc. Relaxin is a proteinaceous hormone secreted by corpus luteum towards the end of gestation period for loosening and softening of pelvic ligaments, relaxing of uterus for easing parturition.
Which part of ovary in mammals acts as an endocrine gland after ovulation ? [2007]- a)Stroma
- b)Germinal epithelium
- c)Vetelline membrane
- d)Graafian follicle.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of ovary in mammals acts as an endocrine gland after ovulation ? [2007]
a)
Stroma
b)
Germinal epithelium
c)
Vetelline membrane
d)
Graafian follicle.

|
Anand Jain answered |
Graafian follicle – the ovarian medulla contains many rounded or oval bodies, called ovarian, or grafian follicles, at various stages of development. Each follicle contains a large ovum surrounded by many layers of follicle cells.
A pregnant female deliver a baby who suffers from stunted growth, mental retardation/low intelligence quotient and abnormal skin. This is the result of : [NEET 2013]- a)Low secretion of growth hormone
- b)Cancer of the thyroid gland
- c)Over secretion of pars distalis
- d)Deficiency of iodine in diet
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A pregnant female deliver a baby who suffers from stunted growth, mental retardation/low intelligence quotient and abnormal skin. This is the result of : [NEET 2013]
a)
Low secretion of growth hormone
b)
Cancer of the thyroid gland
c)
Over secretion of pars distalis
d)
Deficiency of iodine in diet
|
|
Yashvi Malik answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option D, i.e., deficiency of iodine in diet. Iodine is an essential micronutrient required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. During pregnancy, the demand for iodine increases, and if the maternal diet lacks iodine, it can lead to several fetal abnormalities, including stunted growth, mental retardation/low intelligence quotient, and abnormal skin. This condition is known as cretinism or congenital hypothyroidism.
Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can lead to the following consequences:
1. Stunted growth: Iodine is required for the development of bones and muscles in the fetus. In the absence of iodine, the growth of the fetus is impaired, leading to stunted growth.
2. Mental retardation/low intelligence quotient: Iodine is crucial for the development of the nervous system, including the brain. Inadequate iodine intake during pregnancy can lead to irreversible damage to the developing brain, resulting in mental retardation and low intelligence quotient.
3. Abnormal skin: Iodine deficiency can lead to dry and scaly skin, which is a characteristic feature of cretinism.
Prevention:
Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can be prevented by ensuring an adequate intake of iodine through the diet or iodine supplements. Foods rich in iodine include iodized salt, seafood, dairy products, and eggs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, iodine deficiency during pregnancy can have severe consequences on fetal growth and development, leading to stunted growth, mental retardation/low intelligence quotient, and abnormal skin. It is essential to ensure an adequate intake of iodine during pregnancy to prevent these complications.
The correct answer is option D, i.e., deficiency of iodine in diet. Iodine is an essential micronutrient required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. During pregnancy, the demand for iodine increases, and if the maternal diet lacks iodine, it can lead to several fetal abnormalities, including stunted growth, mental retardation/low intelligence quotient, and abnormal skin. This condition is known as cretinism or congenital hypothyroidism.
Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can lead to the following consequences:
1. Stunted growth: Iodine is required for the development of bones and muscles in the fetus. In the absence of iodine, the growth of the fetus is impaired, leading to stunted growth.
2. Mental retardation/low intelligence quotient: Iodine is crucial for the development of the nervous system, including the brain. Inadequate iodine intake during pregnancy can lead to irreversible damage to the developing brain, resulting in mental retardation and low intelligence quotient.
3. Abnormal skin: Iodine deficiency can lead to dry and scaly skin, which is a characteristic feature of cretinism.
Prevention:
Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can be prevented by ensuring an adequate intake of iodine through the diet or iodine supplements. Foods rich in iodine include iodized salt, seafood, dairy products, and eggs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, iodine deficiency during pregnancy can have severe consequences on fetal growth and development, leading to stunted growth, mental retardation/low intelligence quotient, and abnormal skin. It is essential to ensure an adequate intake of iodine during pregnancy to prevent these complications.
Parkinson’s disease (characterized by tremors and progressive rigidity of limbs) is caused by degeneration of brain neurons that are involved in movement control and make use of neurotransmitter [2005]- a)acetylcholine
- b)norepinephrine
- c)dopamine
- d)GABA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Parkinson’s disease (characterized by tremors and progressive rigidity of limbs) is caused by degeneration of brain neurons that are involved in movement control and make use of neurotransmitter [2005]
a)
acetylcholine
b)
norepinephrine
c)
dopamine
d)
GABA

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
Parkinson’s disease (Paralysis agitans) (i) It develops due to deficiency of neuro transmitter, dopamine. The dopamine is not produced due to gradual destruction of neurons in the substantia nigra. (ii) It produces muscle tremors so called shaking palsy. (iii) There is lack of control and coordination of movements resulting in expression less face and stooping posture which gradually produces physical disability.
Which one of the following does not act as a neurotransmitter ? [2006]- a)Epinephrine
- b)Norepinephrine
- c)Cortisone
- d)Acetylcholine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following does not act as a neurotransmitter ? [2006]
a)
Epinephrine
b)
Norepinephrine
c)
Cortisone
d)
Acetylcholine

|
Naveen Menon answered |
Epinephrine or adrenaline, norepinephrine or noradrenaline and acetylchloline are the neurotransmitters. These are released by the nerve fibres to transmit the impulse to the next neurone. Cortisone is not the neurotransmitter.
Adrenaline directly affects on [2002]- a)S. A. node
- b)b-cells of Langerhans
- c)dorsal root of spinal cord
- d)epithelial cells of stomach
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Adrenaline directly affects on [2002]
a)
S. A. node
b)
b-cells of Langerhans
c)
dorsal root of spinal cord
d)
epithelial cells of stomach
|
|
Dhruba Sharma answered |
Effect of Adrenaline on the S. A. Node
Adrenaline directly affects the S. A. (sinoatrial) node, which is often referred to as the heart's natural pacemaker. The S. A. node is a cluster of cells located in the right atrium of the heart that initiates the electrical impulses responsible for coordinating the heart's contractions.
Stimulation of the S. A. Node
When adrenaline binds to its receptors on the S. A. node cells, it leads to an increase in the heart rate. This occurs because adrenaline stimulates the S. A. node to generate electrical impulses at a faster rate, causing the heart to beat more rapidly. This response is part of the body's fight or flight response, preparing the body for action by increasing blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Effects on Heart Function
The stimulation of the S. A. node by adrenaline results in an increase in both heart rate and the force of heart contractions. This leads to an overall increase in cardiac output, allowing more blood to be pumped to the body's tissues and organs.
Regulation of Heart Rate
The effects of adrenaline on the S. A. node play a crucial role in regulating heart rate in response to stress or physical activity. By increasing heart rate and cardiac output, adrenaline helps to ensure that the body can meet the increased demand for oxygen and nutrients during times of exertion or danger.
In conclusion, adrenaline directly affects the S. A. node in the heart, leading to an increase in heart rate and cardiac output. This response is essential for the body's ability to respond to stress and physical activity.
How does steroid hormone influence the cellular activities? [2019]- a)Using aquaporin channels ‘as second messenger'
- b)Changing the permeability of the cell membrane
- c)Binding to DNA and forming a gene- hormone complex
- d)Activating cyclic AMP located on the cell membrane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How does steroid hormone influence the cellular activities? [2019]
a)
Using aquaporin channels ‘as second messenger'
b)
Changing the permeability of the cell membrane
c)
Binding to DNA and forming a gene- hormone complex
d)
Activating cyclic AMP located on the cell membrane
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Steroid hormones are lipid-soluble and easily pass through the cell membrane of a target cell into the cytoplasm where they bind to specific intracellular receptors (proteins) to form a hormone receptor complex that enters the nucleus. In the nucleus, hormone which interact with intracellular receptors mostly regulate gene expression or chromosome function by the interaction of hormone-receptor complex with the genome. Biochemical actions result in physiological and developmental effects.
A steroid hormone which regulates glucose metabolism is- a)corticosterone
- b)11- deoxycorticosterone
- c)cortisone
- d)cortisol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A steroid hormone which regulates glucose metabolism is
a)
corticosterone
b)
11- deoxycorticosterone
c)
cortisone
d)
cortisol

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Cortisole is the steroid hormone secreted by adrenal cortex and plays an important role in carbohydrate metabolism. It retards the glucose consumption & hence level of glucose in blood increases & blood pressure increases.
What is correct to say about the hormone action in humans [2012]- a)Glucagon is secreted by β -cells of islets of Langerhans and stimulates glycogenolysis
- b)Secretion of thymosins is stimulated with ageing
- c)In females FSH first binds with specific receptors on ovarian cell membrane
- d)FSH stimulates the secretion of estrogen and progesterone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is correct to say about the hormone action in humans [2012]
a)
Glucagon is secreted by β -cells of islets of Langerhans and stimulates glycogenolysis
b)
Secretion of thymosins is stimulated with ageing
c)
In females FSH first binds with specific receptors on ovarian cell membrane
d)
FSH stimulates the secretion of estrogen and progesterone

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
Glucagon is secreted by α cells of islets of langerhans and stimulate glycogenolysis i.e. breakdown of glycogen into glucose Thymosin hormone secreted from thymus gland stimulates the development of certain kinds of white blood cells involved in producing immunity. It also hostens attainment of sexual maturity.
Match the source gland with respective hormone as well as the function correctly. [2011]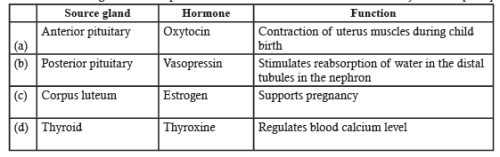
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the source gland with respective hormone as well as the function correctly. [2011]

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Krish Patel answered |
Posterior pituitary releases vasopressin which stimulates reabsorption of water in the distal tubules in nephron.
Insulin differs from growth hormone in that it- a)stimulates lipoprotein lipase in vicinity of fat cells [1999]
- b)increases the transport of amino acids across the cell membranes of muscles
- c)increases mRNA/ribosome acitivity
- d)stimulates hormone sensitive lipase in fat cells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Insulin differs from growth hormone in that it
a)
stimulates lipoprotein lipase in vicinity of fat cells [1999]
b)
increases the transport of amino acids across the cell membranes of muscles
c)
increases mRNA/ribosome acitivity
d)
stimulates hormone sensitive lipase in fat cells

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
Insulin is released from the pancreas it helps in conversion of glucose to fatty acids. It increases fat synthesis in adipose tissues.
Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) is produced by [2000]- a)parathyroid
- b)pars intermedia of pituitary
- c)anterior pituitary
- d)posterior pituitary
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) is produced by [2000]
a)
parathyroid
b)
pars intermedia of pituitary
c)
anterior pituitary
d)
posterior pituitary

|
Ayush Sengupta answered |
Parathyroid gland secretes parathormone which regulates Ca2+ level in blood. Anterior lobe of pituitary secretes the following hormones growth hormone, ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH. Posterior pituitary secretes vasopressin and oxytocin.
The intermediate lobe (pars intermedium) of the pitutary gland secretes MSH which causes dispersal of pigment granules in the pigment cells which give colour to the skin
The intermediate lobe (pars intermedium) of the pitutary gland secretes MSH which causes dispersal of pigment granules in the pigment cells which give colour to the skin
Feeling the tremors of an earthquake a scared resident of seventh floor of a multistored building starts climbing down the stairs rapidly. Which hormone initiated this action ? [2007]- a)adrenaline
- b)glucagon
- c)gastrin
- d)thyroxine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Feeling the tremors of an earthquake a scared resident of seventh floor of a multistored building starts climbing down the stairs rapidly. Which hormone initiated this action ? [2007]
a)
adrenaline
b)
glucagon
c)
gastrin
d)
thyroxine

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
It is commonly called as ‘emergency hormone’ or 3F – hormone (For fear, fight & flight). Its secretion is regulated by SNS, and not by pituitary as in case of adrenal cortex. It stimulates sweating, heart beat and breathing rate. It causes the dilation of coronary artery (supplying blood to the heart muscles), bronchioles (for increasing inspiratory volume) and pupil (for better vision).
Melatonin is produced by [2000]- a)thymus
- b)skin
- c)pituitary
- d)pineal gland
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Melatonin is produced by [2000]
a)
thymus
b)
skin
c)
pituitary
d)
pineal gland

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Melatonin is secreted by pineal gland present between the cerebral hemispheres. Melatonin concentration in blood follows a diurnal cycle, it rises in the evening and drops at noon. Melatonin lightens skin colour in certain animals and regulates working of gonads.
Which one of the following hormones is a modified amino acid? [2004]- a)Epinephrine
- b)Progesterone
- c)Prostaglandin
- d)Estrogen
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following hormones is a modified amino acid? [2004]
a)
Epinephrine
b)
Progesterone
c)
Prostaglandin
d)
Estrogen

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Epinephrine is synthesized from amino acid tyrosine. While estrogen and progesterone are modified steroids and prostaglandins are basically fat.
Toxic agents present in food which interfere with thyroxine synthesis lead to the development of: [2010]- a)toxic goitre
- b)cretinism
- c)simple goitre
- d)thyrotoxicosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Toxic agents present in food which interfere with thyroxine synthesis lead to the development of: [2010]
a)
toxic goitre
b)
cretinism
c)
simple goitre
d)
thyrotoxicosis

|
Shounak Nair answered |
Goitre is caused by deficiency of iodine in diet. Iodine is needed for the synthesis of thyroxine. Toxic agents present in food interfere with thyroxine synthesis and lead to goitre.
Erythropoietin hormone which stimulates R.B.C. formation is produced by: [2021]- a)The cells of bone marrow
- b)Juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney
- c)Alpha cells of the pancreas
- d)The cells of the rostral adenohypophysis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Erythropoietin hormone which stimulates R.B.C. formation is produced by: [2021]
a)
The cells of bone marrow
b)
Juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney
c)
Alpha cells of the pancreas
d)
The cells of the rostral adenohypophysis
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The juxtaglomerular cells of kidney produce a peptide hormone called erythropoietin which stimulates erythropoiesis (formation of RBC).
Ovulation is stimulated by [1994]- a)LH
- b)FSH
- c)estrogen
- d)progesterone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ovulation is stimulated by [1994]
a)
LH
b)
FSH
c)
estrogen
d)
progesterone

|
Srishti Sen answered |
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) induces the Leideyg’s cells in males to produce testesterone and in female it causes ovulation and secretion of female sex hormone estrogen from mature ovarian follicle & progesterone by corpus luteum.
According to the “immunity theory” of ageing, the process starts with the gradual atrophy and disappearance of [1996]- a)thyroid
- b)parthyroid
- c)thymus
- d) islets of Langerhans
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the “immunity theory” of ageing, the process starts with the gradual atrophy and disappearance of [1996]
a)
thyroid
b)
parthyroid
c)
thymus
d)
islets of Langerhans

|
Nayanika Dasgupta answered |
According to the immunity theory ageing occurs due to the loss of power of defence against the invasion of germs and pathogens. The process starts with the gradual atrophy and disappearance of the thymus gland during middle age.
Chapter doubts & questions for Chemical Coordination and Regulation - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Chemical Coordination and Regulation - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










