All Exams >
NEET >
Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Biotechnology: Principles and Processes for NEET Exam
The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non recombinant bacteria because of :
[NEET 2013]
- a)Insertional inactivation of α-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
- b)Non-recombinant bacteria containing β-galactosidease
- c)Inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non recombinant bacteria because of :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Insertional inactivation of α-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
b)
Non-recombinant bacteria containing β-galactosidease
c)
Inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria
d)
None of these
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The blue-white screen is a screening technique that allows for the rapid and convenient detection of recombinant bacteria . This technique is based on the insertional inactivation of the β-galactosidase gene.
Cells transformed with vector containing the recombinant DNA contain an inactive form of the β-galactosidase gene and hence produce white colonies.
cells transformed with non-recombinant plasmid i.e. only the vector, have an active β-galactosidase gene and thus produce blue colonies.
Cells transformed with vector containing the recombinant DNA contain an inactive form of the β-galactosidase gene and hence produce white colonies.
cells transformed with non-recombinant plasmid i.e. only the vector, have an active β-galactosidase gene and thus produce blue colonies.
Biolistics (gene-gun) is suitable for[2012M]a)DNA finger printing.b)Disarming pathogen vectors.c)Constructing recombinant DNA by joining with vectors.d)Transformation of plant cells.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
A gene gun or a biolistic particle delivery system, originally designed for plant transformation, is a device for delivering exogenous DNA (transgenes) to cells. The payload is an elemental particle of a heavy metal coated with DNA (typically plasmid DNA). This technique is often simply referred to as biolistics.
Polyethylene glycol method is used for[2009]- a)biodiesel production
- b)seedless fruit production
- c)energy production from sewage
- d)gene transfer without a vector
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Polyethylene glycol method is used for
[2009]
a)
biodiesel production
b)
seedless fruit production
c)
energy production from sewage
d)
gene transfer without a vector

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
Direct gene transfer is the transfer of naked. DNA into plant cells but the presence of rigid plant cell wall acts as a barrier to uptake. Therefore protoplasts are the favoured target for direct gene transfer. Polyethylene glycol mediated DNA uptake is a direct gene transfer method that utilizes the interaction between polyethylene glycol, naked DNA, salts and the protoplast membrane to effect transport of the DNA into the cytoplasm.
In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used[2012M]- a)as selectable markers.
- b)to select healthy vectors.
- c)to keep the cultures free of infection.
- d)as sequences from where replication starts.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used
[2012M]
a)
as selectable markers.
b)
to select healthy vectors.
c)
to keep the cultures free of infection.
d)
as sequences from where replication starts.

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
Antibiotics are powerful medicines that fight bacterial infections. They either kill bacteria or keep them from reproducing. In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used as selectable markers.
Which one is a true statement regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR[2012]- a)It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cell
- b)It serves as a selectable marker
- c)It is isolated from a virus
- d)It remains active at high temperature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is a true statement regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR
[2012]
a)
It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cell
b)
It serves as a selectable marker
c)
It is isolated from a virus
d)
It remains active at high temperature

|
Rohan Unni answered |
The name of this DNA polymerase is Taq polymerase extracted from a thermophilic bacterial.
The figure below is the diagrammatic representation of the E.Coli vector pBR 322. Which one of the given options correctly identifies its certain component (s) ?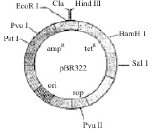 [2012]
[2012] - a)ori - original restriction enzyme
- b)rop-reduced osmotic pressure
- c)Hind III, EcoRI - selectable markers
- d)ampR, tetR - antibiotic resistance genes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure below is the diagrammatic representation of the E.Coli vector pBR 322. Which one of the given options correctly identifies its certain component (s) ?

[2012]
a)
ori - original restriction enzyme
b)
rop-reduced osmotic pressure
c)
Hind III, EcoRI - selectable markers
d)
ampR, tetR - antibiotic resistance genes

|
Palak Khanna answered |
In pBR 322
ori - represents site of originor replication rop-represents those proteins that take part in replication of plasmid. Hind III, EcoRI- Recoginition sites of Restriction endonucleases ampR and tetR - They are antibiotic resistant gene part
PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism are the methods for :[2012]- a)Study of enzymes
- b)Genetic transformation
- c)DNA sequencing
- d)Genetic Fingerprinting
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism are the methods for :
[2012]
a)
Study of enzymes
b)
Genetic transformation
c)
DNA sequencing
d)
Genetic Fingerprinting
|
|
Avantika Roy answered |
PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) are the methods used for Genetic Fingerprinting.
Genetic Fingerprinting:
Genetic Fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on differences in their DNA sequences. It is also known as DNA fingerprinting, DNA profiling or DNA typing. Genetic fingerprinting is used in forensic investigations, paternity testing, and studying genetic relationships between individuals.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction):
PCR is a technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA. It is a three-step process that involves denaturation, annealing, and extension. PCR is used to create a large amount of DNA from a small amount of starting material, such as a single hair or a drop of blood.
RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism):
RFLP is a technique used to analyze differences in DNA sequences. It involves cutting DNA with a restriction enzyme and separating the resulting fragments by gel electrophoresis. RFLP is used to identify genetic variations between individuals.
PCR and RFLP are used together in genetic fingerprinting to create a unique DNA profile for an individual. PCR is used to amplify specific regions of DNA, and RFLP is used to analyze the resulting fragments to identify differences between individuals. These differences are then used to create a DNA profile that can be used for identification purposes.
Genetic Fingerprinting:
Genetic Fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on differences in their DNA sequences. It is also known as DNA fingerprinting, DNA profiling or DNA typing. Genetic fingerprinting is used in forensic investigations, paternity testing, and studying genetic relationships between individuals.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction):
PCR is a technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA. It is a three-step process that involves denaturation, annealing, and extension. PCR is used to create a large amount of DNA from a small amount of starting material, such as a single hair or a drop of blood.
RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism):
RFLP is a technique used to analyze differences in DNA sequences. It involves cutting DNA with a restriction enzyme and separating the resulting fragments by gel electrophoresis. RFLP is used to identify genetic variations between individuals.
PCR and RFLP are used together in genetic fingerprinting to create a unique DNA profile for an individual. PCR is used to amplify specific regions of DNA, and RFLP is used to analyze the resulting fragments to identify differences between individuals. These differences are then used to create a DNA profile that can be used for identification purposes.
There is a restriction endonuclease called EcoRI. What does .co. part in it stand for ?[2011]- a)colon
- b)coelom
- c)coenzyme
- d)coli
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
There is a restriction endonuclease called EcoRI. What does .co. part in it stand for ?
[2011]
a)
colon
b)
coelom
c)
coenzyme
d)
coli

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
EcoRI is an endonuclease enzyme isolated from strains of E.coli and a part of restriction modified system. So co part stands for coli.
Genes of interest can be selected from a genomic library by using[NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Restriction enzymes
- b)Cloning vectors
- c)DNA probes
- d)Gene targets
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Genes of interest can be selected from a genomic library by using
[NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Restriction enzymes
b)
Cloning vectors
c)
DNA probes
d)
Gene targets

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
A hybridization probe is a fragment of DNA of variable length which is used in DNA samples to detect the presence of nucleotide sequence (the DNA target) that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. The probe hybridize to single–stranded DNA whose base sequence allow probe target base-pairing due to complementary between the probe and target.
DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by :[NEET 2013]- a)Polymerase chain reaction
- b)Electrophoresis
- c)Restriction mapping
- d)Centrifugation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Polymerase chain reaction
b)
Electrophoresis
c)
Restriction mapping
d)
Centrifugation

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
DNA fragments generated by restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by gel electrophoresis. Since DNA fragments are negatively charged molecules they can be separated by forcing them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium/matrix. The DNA fragments separate according to their size through sieving effect provided by matrix.
Introduction of food plants developed by genetic engineering is not desirable because[2002]- a)economy of developing countries may suffer
- b)these products are less tasty as compared to the already existing products
- c)this method is costly
- d)there is danger of entry of viruses and toxins with introduced crop
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Introduction of food plants developed by genetic engineering is not desirable because
[2002]
a)
economy of developing countries may suffer
b)
these products are less tasty as compared to the already existing products
c)
this method is costly
d)
there is danger of entry of viruses and toxins with introduced crop

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Plants developed by genetic engineering are called transgenic plants or genetically modified crops from which genetically modified food is produced. For their production micro-organisms (bacteria, virus) are used. So, by consuming them there is a danger of entry of viruses and toxins causing differ types of allergies and other health hazards to human beings.
DNA strands on a gel stained with ethidium bromide when viewed under UV radiation, appear as: [NEET 2021]- a)Dark red bands
- b)Bright blue bands
- c)Yellow bands
- d)Bright orange bands
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA strands on a gel stained with ethidium bromide when viewed under UV radiation, appear as: [NEET 2021]
a)
Dark red bands
b)
Bright blue bands
c)
Yellow bands
d)
Bright orange bands
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The separated DNA fragments can be visualised only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation (you cannot see pure DNA fragments in the visible light and without staining). You can see bright orange coloured bands of DNA in a ethidium bromide stained gel exposed to UV light.

The figure below shows three steps (A, B, C) of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Select the option giving correct identification together with what it represents?
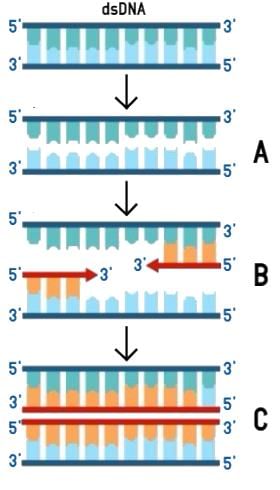 [2012M]
[2012M]
- a)C - Extension in the presence of heat stable DNA polymerase.
- b)A - Denaturation at a temperature of about 50°C.
- c)A - Denaturation at a temperature of about 98°C separating the two DNA strands.
- d)B - Annealing with two sets of primers.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure below shows three steps (A, B, C) of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Select the option giving correct identification together with what it represents?

[2012M]
a)
C - Extension in the presence of heat stable DNA polymerase.
b)
A - Denaturation at a temperature of about 50°C.
c)
A - Denaturation at a temperature of about 98°C separating the two DNA strands.
d)
B - Annealing with two sets of primers.

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
PCR or polymerase chain reaction is the technique employed for the amplification of the gene of interest. The image shows 3 steps of the PCR cycle, namely denaturation, annealing, and extension. Part A represents the step of denaturation, where the dsDNA is divided into two ssDNA under high temperature. For denaturation to occur, an approximate temperature of 90-92oC is required.
Whereas, part B represents the attachment of short oligonucleotide sequences called primer by a process called annealing and part C represents the extension of the DNA segment by the addition of nucleotides by the action of the thermostable polymerase called Taq polymerase.
A single strand of nucleic acid tagged with a radioactive molecule is called :[2012]- a)Vector
- b)Selectablemarker
- c)Plasmid
- d)Probe
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A single strand of nucleic acid tagged with a radioactive molecule is called :
[2012]
a)
Vector
b)
Selectablemarker
c)
Plasmid
d)
Probe

|
Soumya Ahuja answered |
A single strand DNA or RNA tagged with radioactive molecule that is used in of hybridization of DNA or RNA is called probe.
Restriction endonucleases are enzymes which[2010]- a)make cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule
- b)recognize a specific nucleotide sequence for binding of DNA ligase
- c)restrict the action of the enzyme DNA polymerase
- d)remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA molecule
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Restriction endonucleases are enzymes which
[2010]
a)
make cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule
b)
recognize a specific nucleotide sequence for binding of DNA ligase
c)
restrict the action of the enzyme DNA polymerase
d)
remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA molecule

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
Restriction endonucleases are enzymes that makes cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule. They acts as molecular scissors. They recognise specific base sequence at palindrome sites in DNA duplex and cut its strands.
Bacillus thuringiensis forms protein crystals which contain insecticidal protein. [2011M]- a)binds with epithelial cells of midgut of the insect pest ultimately killing it
- b)is coded by several genes including the gene cry
- c)is activated by acid pH of the foregut of the insect pest.
- d)does not kill the carrier bacterium which is itself resistant to this toxin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bacillus thuringiensis forms protein crystals which contain insecticidal protein.
[2011M]
a)
binds with epithelial cells of midgut of the insect pest ultimately killing it
b)
is coded by several genes including the gene cry
c)
is activated by acid pH of the foregut of the insect pest.
d)
does not kill the carrier bacterium which is itself resistant to this toxin

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
Bacillus thuringiensis produces a large amount of crystalline protein during sporulation. In the cell toxins are formed along with the spore and are referred to as parasporal body. The bacteria are capable of entering the insect’s blood and using the host insect to reproduce. The proteins from ingested spores are activated by gut, high pH and the polypeptide toxins destroy gut epithelial cells and kill the pest.
Gel electrophoresis is used for- a)cutting of DNA into fragments
- b)separation of DNA fragments according to their size
- c)construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors
- d)isolation of DNA molecule
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Gel electrophoresis is used for
a)
cutting of DNA into fragments
b)
separation of DNA fragments according to their size
c)
construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors
d)
isolation of DNA molecule

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Gel electrophoresis is a technique to separation of DNA fragments according to their size. DNA is negatively charged so in gel tank when electric passed, DNA move towards positive electrode.
The linking of antibiotic resistance gene with the plasmid vector became possible with[2008]- a)DNA ligase
- b)Endonucleases
- c)DNA polymerase
- d)Exonucleases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The linking of antibiotic resistance gene with the plasmid vector became possible with
[2008]
a)
DNA ligase
b)
Endonucleases
c)
DNA polymerase
d)
Exonucleases

|
Tejas Chavan answered |
The linking of antibiotic resistance gene with the plasmid vector became possible with DNA ligase. DNA ligase is an enzyme that is able to join together two portions of DNA and therefore plays an important role in DNA repair. DNA ligase is also used in recombinant DNA technology as it ensures that the foreign DNA is bound to the plasmid into which it is incorporated.
Which one of the following represents a palindromic sequence in DNA?[2012M]- a)5' - GAATTC - 3'
3' - CTTAAG - 5' - b)5' - CCAATG - 3'
3' - GAATCC - 5' - c)5' - CATTAG - 3'
3' - GATAAC - 5' - d)5' - GATACC - 3'
3' - CCTAAG - 5'
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following represents a palindromic sequence in DNA?
[2012M]
a)
5' - GAATTC - 3'
3' - CTTAAG - 5'
3' - CTTAAG - 5'
b)
5' - CCAATG - 3'
3' - GAATCC - 5'
3' - GAATCC - 5'
c)
5' - CATTAG - 3'
3' - GATAAC - 5'
3' - GATAAC - 5'
d)
5' - GATACC - 3'
3' - CCTAAG - 5'
3' - CCTAAG - 5'

|
Rajat Roy answered |
A palindromic sequence is a nucleic acid sequence (DNA or RNA) that is the same whether read 5' (five-prime) to 3' (three prime) on one strand or 5' to 3' on the complementary strand with which it forms a double helix.
5. - GAATTC - 3.
3. - CTTAAG - 5.
It is a palindromic sequence of DNA cut by restriction enzyme ECORI.
5. - GAATTC - 3.
3. - CTTAAG - 5.
It is a palindromic sequence of DNA cut by restriction enzyme ECORI.
Which one of the following palindromic base sequences in DNA can be easily cut at about the middle by some particular restriction enzyme?[2010]- a)5'.............CGTTCG.............3'
3'.............ATGGTA.............5' - b)5'.............GATATG.............3'
3'.............CTACTA.............5' - c)5'.............GAATTC.............3'
3'.............CTTAAG.............5' - d)5'.............CACGTA.............3'
3'.............CTCAGT.............5'
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following palindromic base sequences in DNA can be easily cut at about the middle by some particular restriction enzyme?
[2010]
a)
5'.............CGTTCG.............3'
3'.............ATGGTA.............5'
3'.............ATGGTA.............5'
b)
5'.............GATATG.............3'
3'.............CTACTA.............5'
3'.............CTACTA.............5'
c)
5'.............GAATTC.............3'
3'.............CTTAAG.............5'
3'.............CTTAAG.............5'
d)
5'.............CACGTA.............3'
3'.............CTCAGT.............5'
3'.............CTCAGT.............5'

|
Rohan Unni answered |
Palindromic sequences in DNA molecule are group of bases that forms the same sequence when read in both forward and backward direction. In the given question, only option (c) represent a palindromic sequence.
For transformation, micro-particles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of :[2012]- a)Silver or Platinum
- b)Platinum or Zinc
- c)Silicon or Platinum
- d)Gold or Tungsten
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For transformation, micro-particles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of :
[2012]
a)
Silver or Platinum
b)
Platinum or Zinc
c)
Silicon or Platinum
d)
Gold or Tungsten

|
Tejas Chavan answered |
For gene transfer in to the host cell without using vector microparticles made of tungsten and Gold coated with foregin DNA are bombarded into target cells at a very high velocity.
DNA or RNA segment tagged with a radioactive molecule is called[2010]- a)Vector
- b)Probe
- c)Clone
- d)Plasmid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA or RNA segment tagged with a radioactive molecule is called
[2010]
a)
Vector
b)
Probe
c)
Clone
d)
Plasmid

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
DNA or RNA segment tagged with a radioactive molecule is called Probe. They are used to detect the presence of complementary sequences in nucleic acid samples. Probes are used for identification and isolation of DNA and RNA.
Agarose extracted from sea weeds finds use in :[2011]- a)Spectrophotometry
- b)Tissue culture
- c)PCR
- d)Gel electrophoresis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Agarose extracted from sea weeds finds use in :
[2011]
a)
Spectrophotometry
b)
Tissue culture
c)
PCR
d)
Gel electrophoresis

|
Rajat Roy answered |
In gel electrophoresis agarose extracted from sea weed used as gel garose, made of 0.7% gel show good resolution of large DNA and 2% gel will show good resolution of small fragments.
Which one of the following is used as vector for cloning genes into higher organisms? [2010]- a)Baculovirus
- b)Salmonella typhimurium
- c)Rhizopus nigricans
- d)Retrovirus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is used as vector for cloning genes into higher organisms?
[2010]
a)
Baculovirus
b)
Salmonella typhimurium
c)
Rhizopus nigricans
d)
Retrovirus

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Retrovirus as has the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells. Hence, it can used as a vector for cloning desirable genes into animal cells.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biotechnology: Principles and Processes - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biotechnology: Principles and Processes - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









