All Exams >
NEET >
Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Ecosystem for NEET Exam
More than 70% of world’s freshwater is contained in:[2005]- a)polar ice
- b)glaciers and mountains
- c)antarctica
- d)greenland
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
More than 70% of world’s freshwater is contained in:
[2005]
a)
polar ice
b)
glaciers and mountains
c)
antarctica
d)
greenland

|
Devansh Mehra answered |
Three fourth surface of earth is covered by oceans which contain 97.5% of total water. It is marine water with about 3.5% salt content only 2.5% is fresh water which occurs on land. Most of this water (1.97%) occurs as frozen ice caps and glaciers, 0.5% fresh water occurs as ground water. Rivers and lakes contain 0.02%, soil 0.01% while atmosphere possesses 0.001% of water as vapours.
Pneumatophores are characteristic of plants growing in[2000]- a)saline soils
- b)sandy soils
- c)marshy places and salt lakes
- d)dryland regions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pneumatophores are characteristic of plants growing in
[2000]
a)
saline soils
b)
sandy soils
c)
marshy places and salt lakes
d)
dryland regions

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Some plants growing in salty marshes develop special roots for respiration, called pneumatophores. They are (–) vely geotropic.
Mass of living matter at a trophic level in an area at any time is called[2011]- a)standing crop
- b)deteritus
- c)humus
- d)standing state
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mass of living matter at a trophic level in an area at any time is called
[2011]
a)
standing crop
b)
deteritus
c)
humus
d)
standing state

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
A standing crop is the quantity or total weight or energy content of the organism, which are in a particular location at a particular time.
The rate at which light energy is converted to the chemical energy of organic molecules is the ecosystem’s[1998]- a)net primary productivity
- b)gross primary productivity
- c)net secondary productivity
- d)gross secondary productivity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The rate at which light energy is converted to the chemical energy of organic molecules is the ecosystem’s
[1998]
a)
net primary productivity
b)
gross primary productivity
c)
net secondary productivity
d)
gross secondary productivity

|
Subhankar Datta answered |
The rate at which organic molecules are formed in a green plant is called gross productivity.
Bamboo plant is growing in a fir forest then what will be the trophic level of it?[2002]- a)First trophic level (T1)
- b)Second trophic level (T2)
- c)Third trophic level (T3)
- d)Fourth trophic level (T4)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bamboo plant is growing in a fir forest then what will be the trophic level of it?
[2002]
a)
First trophic level (T1)
b)
Second trophic level (T2)
c)
Third trophic level (T3)
d)
Fourth trophic level (T4)

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
First trophic level is occupied by producers. Second trophic level is occupied by primary consumers. Third trophic level is occupied by the secondary consumers.
Upper part of sea / aquaticeco system contains[1988]- a)plankton
- b)nekton
- c)plankton and nekton
- d)benthos
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Upper part of sea / aquaticeco system contains
[1988]
a)
plankton
b)
nekton
c)
plankton and nekton
d)
benthos

|
Gowri Nair answered |
Plankton → Organisms passively floating in upper water.
Nekton → Actively swimming Benthos → Lead sedentary life upon the sea bottom
Nekton → Actively swimming Benthos → Lead sedentary life upon the sea bottom
Approximately how much of the solar energy that falls on the leaves of a plant is converted to chemical energy by photosynthesis?- a)Less than 1%
- b)2-10%
- c)30%
- d)50%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Approximately how much of the solar energy that falls on the leaves of a plant is converted to chemical energy by photosynthesis?
a)
Less than 1%
b)
2-10%
c)
30%
d)
50%
|
|
Sadiya Siddique answered |
Of the total solar energy, only 50%is PAR( photosynthetically active radiation) of which plants utilise only 2-10% fr photosynthesis. thus,op B.
Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in a biotic community is known as:[2015 RS]- a)Stratification
- b)Zonation
- c)Pyramid
- d)Divergence
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in a biotic community is known as:
[2015 RS]
a)
Stratification
b)
Zonation
c)
Pyramid
d)
Divergence

|
Shalini Saha answered |
(a) Stratification is the occurrence of vertical zonation in the ecosystem & indicates the presence of favorable environmental conditions, for e.g., trees occupy top vertical strata or layer of a forest, shrubs the second. Herbs & grasses occupy the bottom layers. It is absent or poor where environmental conditions are unfavorable, e.g. desert ecosystems have very few trees & shrubs.
Sudden mass killing of fishes is likely in[1999]- a)mesotrophic lake
- b)oligotrophic lake
- c)salt lake
- d)eutrophic lake
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sudden mass killing of fishes is likely in
[1999]
a)
mesotrophic lake
b)
oligotrophic lake
c)
salt lake
d)
eutrophic lake

|
Snehal Shah answered |
Organic pollutants provide nutrients for stimulating growth of algae and other plants. Algal bloom reduces availability of light to submerged plants which get killed. The dead submerged plants consume more oxygen in decomposition. This reduces availability of oxygen to other life forms leading to death of organisms. This is known as eutrophication.
In an ecosystem the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis is termed as:[2015 RS]- a)Gross primary productivity
- b)Secondary productivity
- c)Net productivity
- d)Net primary productivity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In an ecosystem the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis is termed as:
[2015 RS]
a)
Gross primary productivity
b)
Secondary productivity
c)
Net productivity
d)
Net primary productivity

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
(a) Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) is the rate of production of biomass or accumulation of energy by green plants per unit area per unit time. GPP depends on the chlorophyll content.
In an ecosystem, which one shows one-way passage[1988]- a)free energy
- b)carbon
- c)nitrogen
- d)potassium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In an ecosystem, which one shows one-way passage
[1988]
a)
free energy
b)
carbon
c)
nitrogen
d)
potassium

|
Devansh Mehra answered |
Energy f low takes place only in one direction i.e., producers → herbivores → carnivores whereas, nutrients use carbon, nitrogen and potassium shows cyclic flow.
The greatest biomass of autotrophs in the oceans is that of[2000]- a)sea grasses and slime moulds
- b)free floating microalgae, cyanobacteria and nanoplankton
- c)benthic brown algae,coastal red algae and daphnids
- d)benthic diatoms and marine viruses
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The greatest biomass of autotrophs in the oceans is that of
[2000]
a)
sea grasses and slime moulds
b)
free floating microalgae, cyanobacteria and nanoplankton
c)
benthic brown algae,coastal red algae and daphnids
d)
benthic diatoms and marine viruses

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
The greatest biomass of autotrophs in the oceans is that of free floating microalgae, cyanobacteria and nanoplankton.
The biomass available for consumption by the herbivores and the decomposers is called:[2010]- a)net primary productivity
- b)secondary productivity
- c)standing crop
- d)gross primary productivity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The biomass available for consumption by the herbivores and the decomposers is called:
[2010]
a)
net primary productivity
b)
secondary productivity
c)
standing crop
d)
gross primary productivity

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
The biomass available for consumption by the herbivores and the decomposers is called net primary productivity. It is equal to the rate of organic matter created by photosynthesis minus the rate of respiration and other losses.
If by radiation all nitrogenase enzymes are inactivated, then there will be no[2004]- a)fixation of nitrogen in legumes
- b)fixation of atmospheric nitrogen
- c)conversion from nitrate to nitrite in legumes
- d)conversion from ammonium to nitrate in soil
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If by radiation all nitrogenase enzymes are inactivated, then there will be no
[2004]
a)
fixation of nitrogen in legumes
b)
fixation of atmospheric nitrogen
c)
conversion from nitrate to nitrite in legumes
d)
conversion from ammonium to nitrate in soil

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
Nitrogenase is an enzyme involved in biological nitrogen fixation. Enzyme nitrate reductase is involved in conversion of nitrate to nitrite. Conversion of ammonia to nitrate is carried out by Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter.
Which one of the following types of organisms occupy more than one trophic level in a pond ecosystem?[2009]- a)Fish
- b)Zooplankton
- c)Frog
- d)Phytoplankton
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following types of organisms occupy more than one trophic level in a pond ecosystem?
[2009]
a)
Fish
b)
Zooplankton
c)
Frog
d)
Phytoplankton

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
A pond ecosystem is a delicate balance of fish, plants and other animals. Fish occupy more than one tropic level in pond ecosystem. Small fishes act as secondary consumer. They feed on primary consumer. Large fishes act as tertiary consumer. They feed on smaller fish.
The slow rate of decomposition of fallen logs in nature is due to their[2008]- a) low cellulose content
- b)poor nitrogen content
- c)anaerobic environment around them
- d)low moisture content
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The slow rate of decomposition of fallen logs in nature is due to their
[2008]
a)
low cellulose content
b)
poor nitrogen content
c)
anaerobic environment around them
d)
low moisture content
|
|
Harshitha Basak answered |
The microorganisms breakdown the complex compounds of dead protoplasm of producers and consumers absorb some of the decomposition products and release simple substances. The slow rate of decomposition of fallen logs in nature is due to their low moisture content The cellulose is in high amount in fallen logs.
During adverse season, therophytes survive by[1997]- a)bulbs
- b)corms
- c)rhizomes
- d)seeds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During adverse season, therophytes survive by
[1997]
a)
bulbs
b)
corms
c)
rhizomes
d)
seeds

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Therophytes are those plants which survive the adverse season like winter as a seed and complete their life cycle between spring and autumn.
About 70% of total global carbon is found in[2008]- a)grasslands
- b)agroecosystems
- c)oceans
- d)forests
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
About 70% of total global carbon is found in
[2008]
a)
grasslands
b)
agroecosystems
c)
oceans
d)
forests

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
About 70% oftotal global carbon is found in oceans. This oceanic reservoir regulates the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Atmosphere contains only about one percent of total global carbon.
Which one of the following ecosystem types has the highest annual net primary productivity?[2007]- a)tropical deciduous forest
- b)temperate evergreen forest
- c)temperate deciduous forest
- d)tropical rain forest.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following ecosystem types has the highest annual net primary productivity?
[2007]
a)
tropical deciduous forest
b)
temperate evergreen forest
c)
temperate deciduous forest
d)
tropical rain forest.
|
|
Jyoti Desai answered |
<b>Introduction</b>
Net primary productivity (NPP) is the amount of energy that is converted into organic matter through photosynthesis in plants, minus the energy that is used by the plants for their own respiration. It is an important measure of the productivity and biomass production in an ecosystem. In this question, we are asked to determine which ecosystem type has the highest annual NPP among the given options.
<b>Explanation</b>
To determine which ecosystem type has the highest annual NPP, we need to consider the characteristics of each ecosystem and how they influence primary productivity.
<b>Tropical deciduous forest</b>
- Tropical deciduous forests are found in regions with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- These forests have a high diversity of plant species.
- During the wet season, these forests experience high rates of photosynthesis and growth.
- However, during the dry season, many of the trees shed their leaves and the productivity decreases.
- Therefore, the annual NPP of tropical deciduous forests is relatively lower compared to other ecosystem types.
<b>Temperate evergreen forest</b>
- Temperate evergreen forests are found in regions with moderate temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year.
- These forests are dominated by evergreen trees that maintain their leaves year-round.
- The constant availability of water and sunlight allows for continuous photosynthesis and growth.
- Therefore, temperate evergreen forests have a relatively high annual NPP.
<b>Temperate deciduous forest</b>
- Temperate deciduous forests are found in regions with distinct seasons, including a cold winter.
- These forests are characterized by deciduous trees that lose their leaves during the winter.
- The productivity of these forests is highest during the growing season when the trees have leaves.
- However, the productivity decreases during the winter when the trees are bare.
- As a result, the annual NPP of temperate deciduous forests is lower compared to temperate evergreen forests.
<b>Tropical rainforest</b>
- Tropical rainforests are found in regions near the equator with consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall.
- These forests have the highest biodiversity and are dominated by tall, evergreen trees.
- The combination of high temperature, abundant water, and sunlight results in high rates of photosynthesis and growth throughout the year.
- Therefore, tropical rainforests have the highest annual NPP among the given options.
<b>Conclusion</b>
Among the given options, the tropical rainforest has the highest annual net primary productivity due to its consistently high temperature, abundant rainfall, and high biodiversity.
Net primary productivity (NPP) is the amount of energy that is converted into organic matter through photosynthesis in plants, minus the energy that is used by the plants for their own respiration. It is an important measure of the productivity and biomass production in an ecosystem. In this question, we are asked to determine which ecosystem type has the highest annual NPP among the given options.
<b>Explanation</b>
To determine which ecosystem type has the highest annual NPP, we need to consider the characteristics of each ecosystem and how they influence primary productivity.
<b>Tropical deciduous forest</b>
- Tropical deciduous forests are found in regions with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- These forests have a high diversity of plant species.
- During the wet season, these forests experience high rates of photosynthesis and growth.
- However, during the dry season, many of the trees shed their leaves and the productivity decreases.
- Therefore, the annual NPP of tropical deciduous forests is relatively lower compared to other ecosystem types.
<b>Temperate evergreen forest</b>
- Temperate evergreen forests are found in regions with moderate temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year.
- These forests are dominated by evergreen trees that maintain their leaves year-round.
- The constant availability of water and sunlight allows for continuous photosynthesis and growth.
- Therefore, temperate evergreen forests have a relatively high annual NPP.
<b>Temperate deciduous forest</b>
- Temperate deciduous forests are found in regions with distinct seasons, including a cold winter.
- These forests are characterized by deciduous trees that lose their leaves during the winter.
- The productivity of these forests is highest during the growing season when the trees have leaves.
- However, the productivity decreases during the winter when the trees are bare.
- As a result, the annual NPP of temperate deciduous forests is lower compared to temperate evergreen forests.
<b>Tropical rainforest</b>
- Tropical rainforests are found in regions near the equator with consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall.
- These forests have the highest biodiversity and are dominated by tall, evergreen trees.
- The combination of high temperature, abundant water, and sunlight results in high rates of photosynthesis and growth throughout the year.
- Therefore, tropical rainforests have the highest annual NPP among the given options.
<b>Conclusion</b>
Among the given options, the tropical rainforest has the highest annual net primary productivity due to its consistently high temperature, abundant rainfall, and high biodiversity.
Given below are two statements
Statement I: The rate of decomposition is not related to chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors.
Statement II: In a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is faster if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are True
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are False
- c)Statement I is True but Statement II is False
- d)Statement I is False but Statement II is True
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are two statements
Statement I: The rate of decomposition is not related to chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors.
Statement II: In a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is faster if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Statement I: The rate of decomposition is not related to chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors.
Statement II: In a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is faster if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are True
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are False
c)
Statement I is True but Statement II is False
d)
Statement I is False but Statement II is True
|
|
Bhavana Khanna answered |
Understanding the Statements
The two statements pertain to the process of decomposition in ecological systems. Let's analyze each statement:
Statement I: The rate of decomposition is not related to chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors.
- This statement is False.
- Decomposition is significantly influenced by the chemical composition of detritus (organic matter) and various climatic factors such as temperature, moisture, and humidity.
- For instance, materials rich in cellulose decompose faster than those rich in lignin due to their chemical structure.
Statement II: In a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is faster if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin.
- This statement is also False.
- Lignin is known to be more resistant to decomposition compared to other organic compounds. Chitin, found in the exoskeletons of arthropods, also decomposes slowly.
- Therefore, detritus that is rich in these compounds typically decomposes at a slower rate, contrary to what is stated.
Conclusion
Since both statements are incorrect, the correct answer is option b) Both Statement I and Statement II are False.
Understanding the dynamics of decomposition is crucial in ecology, as it affects nutrient cycling and energy flow within ecosystems.
The two statements pertain to the process of decomposition in ecological systems. Let's analyze each statement:
Statement I: The rate of decomposition is not related to chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors.
- This statement is False.
- Decomposition is significantly influenced by the chemical composition of detritus (organic matter) and various climatic factors such as temperature, moisture, and humidity.
- For instance, materials rich in cellulose decompose faster than those rich in lignin due to their chemical structure.
Statement II: In a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is faster if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin.
- This statement is also False.
- Lignin is known to be more resistant to decomposition compared to other organic compounds. Chitin, found in the exoskeletons of arthropods, also decomposes slowly.
- Therefore, detritus that is rich in these compounds typically decomposes at a slower rate, contrary to what is stated.
Conclusion
Since both statements are incorrect, the correct answer is option b) Both Statement I and Statement II are False.
Understanding the dynamics of decomposition is crucial in ecology, as it affects nutrient cycling and energy flow within ecosystems.
What is true of ecosystem?[1988]- a)Primary consumers are least dependent upon producers
- b)Primary consumers out - number producers
- c)Producers are more than primary consumers
- d)Secondary consumers are the largest and most powerful
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true of ecosystem?
[1988]
a)
Primary consumers are least dependent upon producers
b)
Primary consumers out - number producers
c)
Producers are more than primary consumers
d)
Secondary consumers are the largest and most powerful

|
Ayush Sengupta answered |
In an ecosystem producers (green plants) are always more than consumers (herbivores, carnivores etc.)
An ecosystem which can be easily damaged but can recover after some time if damaging effect stops will be having[2004]- a)low stability and high resilience
- b)high stability and low resilience
- c)low stability and low resilience
- d)high stability and high resilience
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An ecosystem which can be easily damaged but can recover after some time if damaging effect stops will be having
[2004]
a)
low stability and high resilience
b)
high stability and low resilience
c)
low stability and low resilience
d)
high stability and high resilience

|
Mahi Shah answered |
An ecosystem having low stability can be easily damaged. An ecosystem having high resilience will take less time to recover.
The mass of living material at a trophic level at a particular time is called :[2015 RS]- a)Standing state
- b)Net primary productivity
- c)Standing crop
- d)Gross primary productivity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass of living material at a trophic level at a particular time is called :
[2015 RS]
a)
Standing state
b)
Net primary productivity
c)
Standing crop
d)
Gross primary productivity

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
(c) Standing crop is the amount of living biomass in an ecosystem. It indicates theproductivity & luxuriance of growth. It is expressed in the form of number or biomass of organisms per unit area
In relation to Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity of an ecosystem. Which one of the following statements is correct? [2020]- a)Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity are one and same.
- b)There is no relationship between Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity
- c)Gross primary productivity is always less than Net primary productivity.
- d)Gross primary productivity is always more than Net primary productivity.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In relation to Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity of an ecosystem. Which one of the following statements is correct? [2020]
a)
Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity are one and same.
b)
There is no relationship between Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity
c)
Gross primary productivity is always less than Net primary productivity.
d)
Gross primary productivity is always more than Net primary productivity.
|
|
Yashvi Khanna answered |
Understanding Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) and Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) refers to the total amount of organic matter, or biomass, produced by photosynthetic organisms in an ecosystem within a specific time frame. This includes all the energy captured by plants through photosynthesis.
Net Primary Productivity (NPP), on the other hand, is the energy or biomass available to the next trophic levels, which is calculated by subtracting the energy used by plants for respiration from GPP.
Key Differences Between GPP and NPP:
- GPP represents total energy capture.
- NPP represents the energy available for consumption by herbivores and decomposers.
Why GPP is Always Greater than NPP:
- Respiration Losses: A portion of the energy captured by plants is utilized for their own metabolic processes, such as respiration. This energy loss means that NPP will always be less than GPP.
- Formula Representation: Mathematically, NPP = GPP - Respiration. Since respiration is always a positive value, NPP is always less than GPP.
- Ecological Implications: The difference between GPP and NPP highlights how much energy is available for the food web. A higher GPP indicates a productive ecosystem, but the NPP is crucial for supporting herbivores and, subsequently, carnivores.
Conclusion:
In summary, option 'D' is correct because Gross Primary Productivity is always more than Net Primary Productivity due to the energy lost during respiration processes in plants. Understanding this relationship is essential for grasping ecosystem productivity dynamics in ecological studies.
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) refers to the total amount of organic matter, or biomass, produced by photosynthetic organisms in an ecosystem within a specific time frame. This includes all the energy captured by plants through photosynthesis.
Net Primary Productivity (NPP), on the other hand, is the energy or biomass available to the next trophic levels, which is calculated by subtracting the energy used by plants for respiration from GPP.
Key Differences Between GPP and NPP:
- GPP represents total energy capture.
- NPP represents the energy available for consumption by herbivores and decomposers.
Why GPP is Always Greater than NPP:
- Respiration Losses: A portion of the energy captured by plants is utilized for their own metabolic processes, such as respiration. This energy loss means that NPP will always be less than GPP.
- Formula Representation: Mathematically, NPP = GPP - Respiration. Since respiration is always a positive value, NPP is always less than GPP.
- Ecological Implications: The difference between GPP and NPP highlights how much energy is available for the food web. A higher GPP indicates a productive ecosystem, but the NPP is crucial for supporting herbivores and, subsequently, carnivores.
Conclusion:
In summary, option 'D' is correct because Gross Primary Productivity is always more than Net Primary Productivity due to the energy lost during respiration processes in plants. Understanding this relationship is essential for grasping ecosystem productivity dynamics in ecological studies.
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)Statement I: Decomposition is a process in which the detritus is degraded into simpler substances by microbes. Statement II: Decomposition is faster if the detritus is rich in lignin and chitin In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below: - a)Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
- b)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- c)Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
- d)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Statement I: Decomposition is a process in which the detritus is degraded into simpler substances by microbes.
Statement II: Decomposition is faster if the detritus is rich in lignin and chitin
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
b)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
c)
Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
d)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- Decomposition is the process by which decomposers breakdown complex organic matter into inorganic substances.
- The rate of decomposition is controlled by chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors. Decomposition is slower if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin and quicker, if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water soluble substances like sugars.
Topic in NCERT: Decomposition
Line in NCERT: "decomposition is largely an oxygen-requiring process. the rate of decomposition is controlled by chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors. in a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is slower if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin, and quicker, if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water-soluble substances like sugars."
Identify the correct statements: (NEET 2023)A. Detrivores perform fragmentation.
B. The humus is further degraded by some microbes during mineralization.
C. Water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil and get precipitated by a process called leaching.
D. The detritus food chain begins with living organisms.
E. Earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles by a process called catabolism.Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- a)B, C, D only
- b) C, D, E only
- c) D, E, A only
- d) A, B, C only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct statements: (NEET 2023)
A. Detrivores perform fragmentation.
B. The humus is further degraded by some microbes during mineralization.
C. Water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil and get precipitated by a process called leaching.
D. The detritus food chain begins with living organisms.
E. Earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles by a process called catabolism.
B. The humus is further degraded by some microbes during mineralization.
C. Water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil and get precipitated by a process called leaching.
D. The detritus food chain begins with living organisms.
E. Earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles by a process called catabolism.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
B, C, D only
b)
C, D, E only
c)
D, E, A only
d)
A, B, C only

|
Bs Academy answered |
Let's evaluate each statement:
A. Detrivores perform fragmentation.
This statement is true. Detrivores, such as earthworms and beetles, break down detritus (dead organic material) into smaller pieces in a process called fragmentation.
A. Detrivores perform fragmentation.
This statement is true. Detrivores, such as earthworms and beetles, break down detritus (dead organic material) into smaller pieces in a process called fragmentation.
B. The humus is further degraded by some microbes during mineralization.
This statement is true. Microbes, including bacteria and fungi, break down humus into inorganic nutrients in a process called mineralization.
This statement is true. Microbes, including bacteria and fungi, break down humus into inorganic nutrients in a process called mineralization.
C. Water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil and get precipitated by a process called leaching.
This statement is true. Leaching refers to the process where nutrients are washed away from the soil into lower layers or into bodies of water.
This statement is true. Leaching refers to the process where nutrients are washed away from the soil into lower layers or into bodies of water.
D. The detritus food chain begins with living organisms.
This statement is false. The detritus food chain begins with dead organic material or detritus, not living organisms.
This statement is false. The detritus food chain begins with dead organic material or detritus, not living organisms.
E. Earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles by a process called catabolism.
This statement is false. The process by which earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles is called fragmentation, not catabolism. Catabolism refers to the breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones, along with the release of energy.
This statement is false. The process by which earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles is called fragmentation, not catabolism. Catabolism refers to the breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones, along with the release of energy.
Therefore, the correct answer is : Option D : A, B, C only.
Which one of the following is not used for construction of ecological pyramids?[2006]- a)Number of individuals
- b)Rate of energy flow
- c)Fresh weight
- d)Dry weight
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not used for construction of ecological pyramids?
[2006]
a)
Number of individuals
b)
Rate of energy flow
c)
Fresh weight
d)
Dry weight
|
|
Shivam Kapoor answered |
Ecological Pyramids
Ecological pyramids are graphical representations of the trophic structure and energy flow within an ecosystem. They provide a visual representation of the relative amounts of energy or biomass at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
There are three types of ecological pyramids:
1. Pyramid of numbers: It represents the number of individuals at each trophic level.
2. Pyramid of biomass: It represents the total dry weight of organisms at each trophic level.
3. Pyramid of energy: It represents the total amount of energy present at each trophic level.
Construction of Ecological Pyramids
To construct ecological pyramids, various factors and parameters are taken into consideration. These include:
- Number of individuals
- Rate of energy flow
- Fresh weight
- Dry weight
Explanation of the Answer
The answer to the given question is option 'C' - Fresh weight. Fresh weight is not used for the construction of ecological pyramids.
Reasoning
Fresh weight refers to the weight of an organism or its parts when they are freshly harvested or collected. However, fresh weight is not a reliable measure for constructing ecological pyramids because it includes the weight of water content in the organism. Since water content can vary greatly between organisms and can change over time, it does not provide an accurate representation of the biomass or energy present at each trophic level.
Importance of Dry Weight
Dry weight, on the other hand, is the weight of an organism or its parts after all the water content has been removed. It provides a more accurate measure of the biomass and energy present in an organism. Dry weight is used to construct the pyramid of biomass, which represents the total dry weight of organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
Conclusion
In summary, the construction of ecological pyramids involves considering factors such as the number of individuals, rate of energy flow, and dry weight. Fresh weight, which includes the weight of water content, is not used for constructing ecological pyramids as it does not provide an accurate representation of the biomass or energy present at each trophic level.
Ecological pyramids are graphical representations of the trophic structure and energy flow within an ecosystem. They provide a visual representation of the relative amounts of energy or biomass at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
There are three types of ecological pyramids:
1. Pyramid of numbers: It represents the number of individuals at each trophic level.
2. Pyramid of biomass: It represents the total dry weight of organisms at each trophic level.
3. Pyramid of energy: It represents the total amount of energy present at each trophic level.
Construction of Ecological Pyramids
To construct ecological pyramids, various factors and parameters are taken into consideration. These include:
- Number of individuals
- Rate of energy flow
- Fresh weight
- Dry weight
Explanation of the Answer
The answer to the given question is option 'C' - Fresh weight. Fresh weight is not used for the construction of ecological pyramids.
Reasoning
Fresh weight refers to the weight of an organism or its parts when they are freshly harvested or collected. However, fresh weight is not a reliable measure for constructing ecological pyramids because it includes the weight of water content in the organism. Since water content can vary greatly between organisms and can change over time, it does not provide an accurate representation of the biomass or energy present at each trophic level.
Importance of Dry Weight
Dry weight, on the other hand, is the weight of an organism or its parts after all the water content has been removed. It provides a more accurate measure of the biomass and energy present in an organism. Dry weight is used to construct the pyramid of biomass, which represents the total dry weight of organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
Conclusion
In summary, the construction of ecological pyramids involves considering factors such as the number of individuals, rate of energy flow, and dry weight. Fresh weight, which includes the weight of water content, is not used for constructing ecological pyramids as it does not provide an accurate representation of the biomass or energy present at each trophic level.
What type of ecological pyramid would be obtained with the following data? [2018)]
Secondary consumer : 120 g
Primary consumer : 60 g
Primary producer : 10 g- a)Inverted pyramid of biomass
- b)Pyramid of energy
- c)Upright pyramid of numbers
- d)Upright pyramid of biomass
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What type of ecological pyramid would be obtained with the following data? [2018)]
Secondary consumer : 120 g
Primary consumer : 60 g
Primary producer : 10 g
Secondary consumer : 120 g
Primary consumer : 60 g
Primary producer : 10 g
a)
Inverted pyramid of biomass
b)
Pyramid of energy
c)
Upright pyramid of numbers
d)
Upright pyramid of biomass
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The given data depicts the inverted pyramid of biomass, usually found in aquatic ecosystem. This can be understood by taking an example of a pond in which phytoplankton (10g) represents the producer. Small fishes (60g) feeding upon these phytoplankton represent primary consumers which are further eaten by the big fishes (120g) representing secondary consumers.
Study the four statements (a–d) given below and select the two correct ones out of them:
(i) A lion eating a deer and a spar row feeding on grain are ecologically similar in being consumers
(ii) Predator star fish Pisaster helps in maintaining species diversity of some invertebrates
(iii) Predators ultimately lead to the extinction of prey species
(iv) Production of chemicals such as nicotine, strychnine by the plants are metabolic disorders The two correct statements are:
[2010]
- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(i) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (ii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the four statements (a–d) given below and select the two correct ones out of them:
(i) A lion eating a deer and a spar row feeding on grain are ecologically similar in being consumers
(ii) Predator star fish Pisaster helps in maintaining species diversity of some invertebrates
(iii) Predators ultimately lead to the extinction of prey species
(iv) Production of chemicals such as nicotine, strychnine by the plants are metabolic disorders The two correct statements are:
(ii) Predator star fish Pisaster helps in maintaining species diversity of some invertebrates
(iii) Predators ultimately lead to the extinction of prey species
(iv) Production of chemicals such as nicotine, strychnine by the plants are metabolic disorders The two correct statements are:
[2010]
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(i) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (ii)
|
|
Sai Mehta answered |
, b, c, and d) below and determine which one is most likely to be true based on the given evidence:
a) All birds have feathers.
b) Penguins are birds.
c) Penguins are flightless.
d) All flightless animals are penguins.
Based on the evidence, the most likely true statement is:
c) Penguins are flightless.
a) All birds have feathers.
b) Penguins are birds.
c) Penguins are flightless.
d) All flightless animals are penguins.
Based on the evidence, the most likely true statement is:
c) Penguins are flightless.
Which of the following is expected to have the highest value (gm/m2/yr) in a grassland ecosystem?[2004]- a)Secondary Production
- b)Tertiary Production
- c)Gross Production (GP)
- d)Net Production (NP)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is expected to have the highest value (gm/m2/yr) in a grassland ecosystem?
[2004]
a)
Secondary Production
b)
Tertiary Production
c)
Gross Production (GP)
d)
Net Production (NP)
|
|
Nishanth Kumar answered |
Grassland Ecosystem and Production
Grassland ecosystems are characterized by a dominant vegetation of grasses and herbaceous plants. These ecosystems can be found in various regions around the world, including prairies, savannas, and steppes. They are known for their high productivity and support a diverse range of organisms.
Production in Ecosystems
Production in ecosystems refers to the process of converting solar energy into organic matter through photosynthesis. It can be divided into three categories: gross production (GP), net production (NP), and tertiary production.
1. Gross Production (GP):
Gross production (GP) is the total amount of organic matter produced by plants through photosynthesis in a given area within a specific time period. It represents the total energy captured by plants from the sun. GP includes both the energy used by plants for their own growth and maintenance (respiration) and the energy available for consumption by other organisms.
2. Net Production (NP):
Net production (NP) is the energy stored in plants' biomass that is available for consumption by herbivores. It is calculated by subtracting the energy lost through respiration (used for plant growth and maintenance) from the gross production. NP represents the energy available to support primary consumers in the food chain.
3. Tertiary Production:
Tertiary production refers to the energy stored in the biomass of higher trophic levels, such as carnivores and top predators. It represents the energy available to support secondary consumers and is derived from the consumption of primary consumers (herbivores).
Highest Value in a Grassland Ecosystem
In a grassland ecosystem, the highest value is expected for gross production (GP). This is because grasslands are highly productive ecosystems due to the abundance of grasses and herbaceous plants. These plants have adapted to a rapid growth strategy, allowing them to capture and utilize a significant amount of solar energy.
The high GP value indicates the total energy captured by plants through photosynthesis. It includes the energy used for plant growth and maintenance as well as the energy available for consumption by herbivores. Therefore, GP provides an estimate of the total energy available to support primary consumers and the subsequent trophic levels in the grassland ecosystem.
On the other hand, net production (NP) represents the energy available for consumption by herbivores after deducting the energy used for plant growth and maintenance. Tertiary production represents the energy stored in the biomass of higher trophic levels. While NP and tertiary production are important measures in the ecosystem, they are expected to have lower values compared to GP in a grassland ecosystem.
In conclusion, gross production (GP) is expected to have the highest value (gm/m2/yr) in a grassland ecosystem due to the high productivity of grasses and herbaceous plants in capturing solar energy through photosynthesis.
Grassland ecosystems are characterized by a dominant vegetation of grasses and herbaceous plants. These ecosystems can be found in various regions around the world, including prairies, savannas, and steppes. They are known for their high productivity and support a diverse range of organisms.
Production in Ecosystems
Production in ecosystems refers to the process of converting solar energy into organic matter through photosynthesis. It can be divided into three categories: gross production (GP), net production (NP), and tertiary production.
1. Gross Production (GP):
Gross production (GP) is the total amount of organic matter produced by plants through photosynthesis in a given area within a specific time period. It represents the total energy captured by plants from the sun. GP includes both the energy used by plants for their own growth and maintenance (respiration) and the energy available for consumption by other organisms.
2. Net Production (NP):
Net production (NP) is the energy stored in plants' biomass that is available for consumption by herbivores. It is calculated by subtracting the energy lost through respiration (used for plant growth and maintenance) from the gross production. NP represents the energy available to support primary consumers in the food chain.
3. Tertiary Production:
Tertiary production refers to the energy stored in the biomass of higher trophic levels, such as carnivores and top predators. It represents the energy available to support secondary consumers and is derived from the consumption of primary consumers (herbivores).
Highest Value in a Grassland Ecosystem
In a grassland ecosystem, the highest value is expected for gross production (GP). This is because grasslands are highly productive ecosystems due to the abundance of grasses and herbaceous plants. These plants have adapted to a rapid growth strategy, allowing them to capture and utilize a significant amount of solar energy.
The high GP value indicates the total energy captured by plants through photosynthesis. It includes the energy used for plant growth and maintenance as well as the energy available for consumption by herbivores. Therefore, GP provides an estimate of the total energy available to support primary consumers and the subsequent trophic levels in the grassland ecosystem.
On the other hand, net production (NP) represents the energy available for consumption by herbivores after deducting the energy used for plant growth and maintenance. Tertiary production represents the energy stored in the biomass of higher trophic levels. While NP and tertiary production are important measures in the ecosystem, they are expected to have lower values compared to GP in a grassland ecosystem.
In conclusion, gross production (GP) is expected to have the highest value (gm/m2/yr) in a grassland ecosystem due to the high productivity of grasses and herbaceous plants in capturing solar energy through photosynthesis.
Barophilic prokaryotes:[2005]- a)grow and multiply in very deep marine sediments
- b)occur in water containing high concentrations of barium hydroxide
- c)readily grow and divide in sea water enriched in any soluble salt of barium
- d)grow slowly in highly alkaline frozen lakes at high altitudes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Barophilic prokaryotes:
[2005]
a)
grow and multiply in very deep marine sediments
b)
occur in water containing high concentrations of barium hydroxide
c)
readily grow and divide in sea water enriched in any soluble salt of barium
d)
grow slowly in highly alkaline frozen lakes at high altitudes

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Barophiles are bacteria which live in high pressure environments. They are generally found on ocean floors, where pressure generally exceeds 380 atm (38 MPa). Some have been found at the bottom of the Pacific Ocean where the maximum pressure is roughly 117 MPa.
Match List-I with List-II: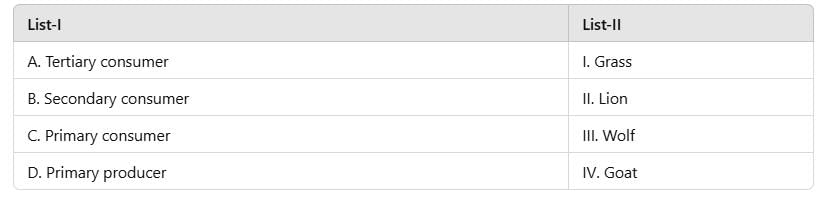
- a)A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
- b)A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
- c)A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
- d)A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-I with List-II:

a)
A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
b)
A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
c)
A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
d)
A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- A-II: Lion, a tertiary consumer.
- B-III: Wolf, as a secondary consumer.
- C-IV: Goat, a primary consumer.
- D-I: Grass, a primary producer.
Which ot the following ecological pyramids is generally inverted? [2019]- a)Pyramid of biomass in a sea
- b)Pyramid of numbers in grassland
- c)Pyramid of energy
- d)Pyramid of biomass in a forest
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which ot the following ecological pyramids is generally inverted? [2019]
a)
Pyramid of biomass in a sea
b)
Pyramid of numbers in grassland
c)
Pyramid of energy
d)
Pyramid of biomass in a forest
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Pyramid of biomass in an aquatic ecosystem (e.g., pond, sea) is usually inverted because the biomass of fishes exceeds the biomass of phytoplanktons.
The correct sequence of plants in a hydrosere is:[2009]- a)Volvox → Hydrilla → Pistia →Scirpus Lantana → Oak
- b)Pistia →Volvox →Scirpus →Hydrilla → Oak →Lantana
- c)Oak→Lantana →Volvox →Hydrilla → Pistia →Scirpus
- d)Oak →Lantana →Scirpus →Pistia → Hydrilla →Volvox
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence of plants in a hydrosere is:
[2009]
a)
Volvox → Hydrilla → Pistia →Scirpus Lantana → Oak
b)
Pistia →Volvox →Scirpus →Hydrilla → Oak →Lantana
c)
Oak→Lantana →Volvox →Hydrilla → Pistia →Scirpus
d)
Oak →Lantana →Scirpus →Pistia → Hydrilla →Volvox

|
Mahi Shah answered |
The cor rect sequence of plants in a hydrosere is Volvox, Hydrilla, Pistia, Scirpus, Lanatana and Oak. A hydrosere is a plant succession which occurs in a fresh water lake. In time, an area of open fresh water such as a lake will naturally dry out, ultimately becoming woodland. During this change, a range of different landtypes such as swamp and marsh will succeed each other. The succession from open water to climax woodland is likely to take at least two hundred years.
Consider the pyramid of energy of an ecosystem given below :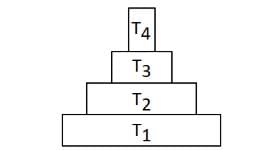 If T4 is equivalent to 1000 J, what is the value of T1?
If T4 is equivalent to 1000 J, what is the value of T1?- a)1000/10 J
- b)1000/10 x 4 J
- c)10,000J
- d)10,00,000J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the pyramid of energy of an ecosystem given below :

If T4 is equivalent to 1000 J, what is the value of T1?
a)
1000/10 J
b)
1000/10 x 4 J
c)
10,000J
d)
10,00,000J

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The pyramid of energy provided in the question represents how energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next in an ecosystem. Typically, there's an energy transfer efficiency of about 10% from one level to the next due to energy loss in the form of heat, metabolic processes, and other factors. This rule is often referred to as the 10% rule in ecology.
T4 = 1000J
T3= 10 x 1000 = 10,000J
T2= 10 x 10000 = 1,00,000J
T1 = 10 x 100000 = 10,00,000
T4 = 1000J
T3= 10 x 1000 = 10,000J
T2= 10 x 10000 = 1,00,000J
T1 = 10 x 100000 = 10,00,000
In an ecosystem if the Net Primary Productivity (NPP) of first trophic level is 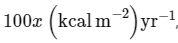 what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (2024)
what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (2024)- a)
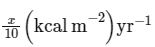
- b)
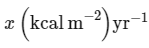
- c)
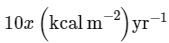
- d)
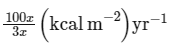
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an ecosystem if the Net Primary Productivity (NPP) of first trophic level is 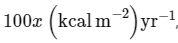 what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (2024)
what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (2024)
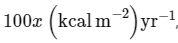 what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (2024)
what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (2024)a)
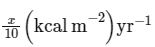
b)
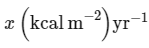
c)
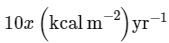
d)
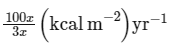

|
Bs Academy answered |
NPP at first trophic level would be the GPP for second trophic level. NPP at second trophic level would be GPP for third trophic level. Therefore, 100x(kcal/m2/yr) would be GPP at second trophic level and 100x * 10% (kcal/m2/yr) i.e 10x(kcal/m2/yr) energy would be GPP at third trophic level.
Topic in NCERT: Productivity
Line in NCERT: The rate of biomass production is called productivity. It is expressed in terms of gm–2 yr –1 or (kcal m–2 ) yr –1 to compare the productivity of different ecosystems. It can be divided into gross primary productivity (GPP) and net primary productivity (NPP)
Consider the following statements concerning food chains(a) removal of 80% tigers from an area resulted in greatly increased growth of vegetation
(b) removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of deers
(c) the length of food chains is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels due to energy loss
(d) the length of food chains may vary from 2 to 8 trophic levelsWhich two of the above statements are correct? [2008]- a)b and c
- b)c andd
- c)a and d
- d)a and b
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements concerning food chains
(a) removal of 80% tigers from an area resulted in greatly increased growth of vegetation
(b) removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of deers
(c) the length of food chains is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels due to energy loss
(d) the length of food chains may vary from 2 to 8 trophic levels
(b) removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of deers
(c) the length of food chains is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels due to energy loss
(d) the length of food chains may vary from 2 to 8 trophic levels
Which two of the above statements are correct?
[2008]
a)
b and c
b)
c andd
c)
a and d
d)
a and b

|
Gowri Nair answered |
Food chain is the transfer of energy from green plants (Primary producers), through a sequence of organisms occupies in a food chain is known as its trophic level. Therefore, statements b and c are correct.
Chapter doubts & questions for Ecosystem - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Ecosystem - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









