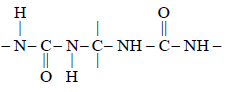All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Biomolecules for NEET Exam
In DNA, the complimentary bases are: [2008]- a)Adenine and thymine; guanine andcytosine
- b)Adenine and thymine ; guanine and uracil
- c)Adenine and guanine; thymine andcytosine
- d)Uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In DNA, the complimentary bases are: [2008]
a)
Adenine and thymine; guanine andcytosine
b)
Adenine and thymine ; guanine and uracil
c)
Adenine and guanine; thymine andcytosine
d)
Uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
In DNA the complimentary base are
Adenine and thymine.
Guanine and cytosine
The genetic information for cell is contained
in the sequence of bases A, T, G and C in
DNA molecule.
Adenine and thymine.
Guanine and cytosine
The genetic information for cell is contained
in the sequence of bases A, T, G and C in
DNA molecule.
Which one of the following does not exhibit thephenomenon of mutarotation ? [2010]- a)(+) – Sucrose
- b)(+) – Lactose
- c)(+) – Maltose
- d)(–) – Fructose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following does not exhibit thephenomenon of mutarotation ? [2010]
a)
(+) – Sucrose
b)
(+) – Lactose
c)
(+) – Maltose
d)
(–) – Fructose

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Sucrose does not have free — CHO or
CO group, hence it does not undergo
mutarotation.
CO group, hence it does not undergo
mutarotation.
The cell membranes are mainly composed of [2005]- a)fats
- b)proteins
- c)phospholipids
- d)carbohydrates
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell membranes are mainly composed of [2005]
a)
fats
b)
proteins
c)
phospholipids
d)
carbohydrates

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
Cell membranes (Plasma membranes) constitutes bilayer of phospholipid with embedded proteins. In humans, lipids accounts for upto 79% of cell membrance.
The segment of DNA which acts as theinstrumental manual for the synthesis of the protein is: [2009]- a)ribose
- b)gene
- c)nucleoside
- d)nucleotide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The segment of DNA which acts as theinstrumental manual for the synthesis of the protein is: [2009]
a)
ribose
b)
gene
c)
nucleoside
d)
nucleotide

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
The DNA sequence that codes for a specific
protein is called a Gene and thus every
protein in a cell has a corrosponding gene.
protein is called a Gene and thus every
protein in a cell has a corrosponding gene.
Chargaff's rule states that in an organism [2003]- a)Amounts of all bases are equal
- b)Amount of adenine (A) is equal to that ofthymine (T) and the amount of guanine (G)is equal to that of cytosine (C)
- c)Amount of adenine (A) is equal to that ofguanine (G) and the amount of thymine (T)is equal to that of cytosine (C)
- d)Amount of adenine (A) is equal to that ofcytosine (C) and rthe amount of thymine (T)is equal to that of guanine (G)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Chargaff's rule states that in an organism [2003]
a)
Amounts of all bases are equal
b)
Amount of adenine (A) is equal to that ofthymine (T) and the amount of guanine (G)is equal to that of cytosine (C)
c)
Amount of adenine (A) is equal to that ofguanine (G) and the amount of thymine (T)is equal to that of cytosine (C)
d)
Amount of adenine (A) is equal to that ofcytosine (C) and rthe amount of thymine (T)is equal to that of guanine (G)

|
Surbhi Das answered |
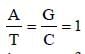
Amount of A = T and that of G = C.
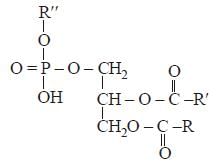
Phospholipids are esters of glycerol with [2003]- a)Three phosphate groups
- b)Three carboxylic acid residues
- c)Two carboxylic acid residues and onephosphate group
- d)One carboxylic acid residue and twophosphate groups
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Phospholipids are esters of glycerol with [2003]
a)
Three phosphate groups
b)
Three carboxylic acid residues
c)
Two carboxylic acid residues and onephosphate group
d)
One carboxylic acid residue and twophosphate groups

|
Pankaj Kulkarni answered |
Phospholipids are derivatives of glycerol in
which two of the hydroxyl groups are
esterified with fatty acids while the third is
esterified with some derivative of phosphoric
acid with some alcohol such as choline,
ethanolamine, serine or inositol.
which two of the hydroxyl groups are
esterified with fatty acids while the third is
esterified with some derivative of phosphoric
acid with some alcohol such as choline,
ethanolamine, serine or inositol.
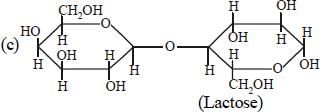
Which one of the following statements is nottrue regarding (+) Lactose ? [2011]- a)On hydrolysis (+) Lactose gives equalamount of D(+) glucose and D(+) galactose.
- b)(+) Lactose is a β-glycoside formed by theunion of a molecule of D(+) glucose and amolecule of D(+) galactose.
- c)(+) Lactose is a reducing sugar and doesnot exhibit mutarotation.
- d)(+) Lactose, C12H22O11 contains 8-OHgroups.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is nottrue regarding (+) Lactose ? [2011]
a)
On hydrolysis (+) Lactose gives equalamount of D(+) glucose and D(+) galactose.
b)
(+) Lactose is a β-glycoside formed by theunion of a molecule of D(+) glucose and amolecule of D(+) galactose.
c)
(+) Lactose is a reducing sugar and doesnot exhibit mutarotation.
d)
(+) Lactose, C12H22O11 contains 8-OHgroups.

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
The enzyme which hydrolyses triglycerides tofatty acids and glycerol is called [2004]- a)Maltase
- b)Lipase
- c)Zymase
- d)Pepsin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme which hydrolyses triglycerides tofatty acids and glycerol is called [2004]
a)
Maltase
b)
Lipase
c)
Zymase
d)
Pepsin

|
Swara Desai answered |
Triglycerides are lipids, hence these are
hydrolysed by lipases to glycerol and fatty
acids.
hydrolysed by lipases to glycerol and fatty
acids.
The correct statement in respect of protein haemoglobin is that it [2004]- a)functions as a catalyst for biologicalreactions
- b)maintains blood sugar level
- c)acts as an oxygen carrier in the blood
- d)forms antibodies and offers resistance todieases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement in respect of protein haemoglobin is that it [2004]
a)
functions as a catalyst for biologicalreactions
b)
maintains blood sugar level
c)
acts as an oxygen carrier in the blood
d)
forms antibodies and offers resistance todieases

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Haemoglobin acts as an oxygen carrier in
the blood since it reacts with oxygen to form
unstable oxyhaemoglobin which easily
breaks to give back haemoglobin and
oxygen.
the blood since it reacts with oxygen to form
unstable oxyhaemoglobin which easily
breaks to give back haemoglobin and
oxygen.
Cellulose is a polymer of [2002]- a)Glucose
- b)Fructose
- c)Ribose
- d)Sucrose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cellulose is a polymer of [2002]
a)
Glucose
b)
Fructose
c)
Ribose
d)
Sucrose

|
Yash Saha answered |
We know that cellulose (C6H12O6 )n is the
chief constituent of cell walls of plants. It is
the most abundant organic substance found
in nature. It is a polymer of glucose with
3500 repeat units in a chain.
chief constituent of cell walls of plants. It is
the most abundant organic substance found
in nature. It is a polymer of glucose with
3500 repeat units in a chain.
RNA and DNA are chiral molecules, their chiralityis due to [2007]- a)chiral bases
- b)chiral phosphate ester units
- c)D-sugar component
- d)L-sugar component.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
RNA and DNA are chiral molecules, their chiralityis due to [2007]
a)
chiral bases
b)
chiral phosphate ester units
c)
D-sugar component
d)
L-sugar component.

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
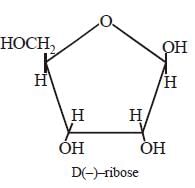
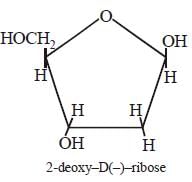
Each nucleic acid consists of a pentose
sugar a heterocyclic base, and phosphoric
acid. The sugar present in DNA is 2-deoxy
-D (–) ribose and the sugar present in RNA
is D (–)- ribose. The chirality of DNA and
RNA molecules are due to the presence of
sugar components.
sugar a heterocyclic base, and phosphoric
acid. The sugar present in DNA is 2-deoxy
-D (–) ribose and the sugar present in RNA
is D (–)- ribose. The chirality of DNA and
RNA molecules are due to the presence of
sugar components.
The helical structure of protein is stabilized by [2004]- a)dipeptide bonds
- b)hydrogen bonds
- c)ether bonds
- d)peptide bonds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The helical structure of protein is stabilized by [2004]
a)
dipeptide bonds
b)
hydrogen bonds
c)
ether bonds
d)
peptide bonds

|
Nabanita Basu answered |
Stabilization of Helical Structure in Proteins
The helical structure of proteins is a fundamental aspect of their secondary structure, primarily found in alpha helices. This structure is crucial for the overall shape and function of proteins.
Role of Hydrogen Bonds
- Hydrogen bonds play a vital role in stabilizing the helical structure of proteins.
- In an alpha helix, the carbonyl oxygen (C=O) of one amino acid forms a hydrogen bond with the amide hydrogen (N-H) of another amino acid located four residues down the chain.
- These hydrogen bonds create a regular pattern that promotes the coiling of the polypeptide chain into a helical formation.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonding
- The consistent formation of hydrogen bonds along the length of the helix gives it stability and makes it resilient to environmental changes.
- Hydrogen bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent bonds, but their cumulative effect in a long helix can provide significant structural integrity.
- This stabilization is crucial for the protein's overall folding and functional conformation.
Other Bonds in Proteins
- While dipeptide bonds and peptide bonds are essential for linking amino acids together to form proteins, they do not contribute to the helical structure itself.
- Ether bonds are not typically found in proteins and do not have a role in stabilizing protein structures.
Conclusion
In summary, the helical structure of proteins is primarily stabilized by hydrogen bonds, which enable the formation of alpha helices, essential for the protein's stability and functionality.
The helical structure of proteins is a fundamental aspect of their secondary structure, primarily found in alpha helices. This structure is crucial for the overall shape and function of proteins.
Role of Hydrogen Bonds
- Hydrogen bonds play a vital role in stabilizing the helical structure of proteins.
- In an alpha helix, the carbonyl oxygen (C=O) of one amino acid forms a hydrogen bond with the amide hydrogen (N-H) of another amino acid located four residues down the chain.
- These hydrogen bonds create a regular pattern that promotes the coiling of the polypeptide chain into a helical formation.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonding
- The consistent formation of hydrogen bonds along the length of the helix gives it stability and makes it resilient to environmental changes.
- Hydrogen bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent bonds, but their cumulative effect in a long helix can provide significant structural integrity.
- This stabilization is crucial for the protein's overall folding and functional conformation.
Other Bonds in Proteins
- While dipeptide bonds and peptide bonds are essential for linking amino acids together to form proteins, they do not contribute to the helical structure itself.
- Ether bonds are not typically found in proteins and do not have a role in stabilizing protein structures.
Conclusion
In summary, the helical structure of proteins is primarily stabilized by hydrogen bonds, which enable the formation of alpha helices, essential for the protein's stability and functionality.
Which of the statements about "Denaturation" given below are correct ? [2011 M]
(a) Denaturation of proteins causes loss of secondary and tertiary structures of the protein.
(b) Denturation leads to the conversion of double strand of DNA into single strand
(c) Denaturation affects primary strucrture which gets distorted- a)(b) and (c)
- b)(a) and (c)
- c)(a) and (b)
- d)(a), (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the statements about "Denaturation" given below are correct ? [2011 M]
(a) Denaturation of proteins causes loss of secondary and tertiary structures of the protein.
(b) Denturation leads to the conversion of double strand of DNA into single strand
(c) Denaturation affects primary strucrture which gets distorted
(a) Denaturation of proteins causes loss of secondary and tertiary structures of the protein.
(b) Denturation leads to the conversion of double strand of DNA into single strand
(c) Denaturation affects primary strucrture which gets distorted
a)
(b) and (c)
b)
(a) and (c)
c)
(a) and (b)
d)
(a), (b) and (c)

|
Anu Bajaj answered |
When the proteins are subjected to the
action of heat, mineral acids or alkali, the
water soluble form of globular protein
changes to water insoluble fibrous protein.
This is called denaturation of proteins.
During denaturation secondary and tertiary
structures of protein destroyed but primary
structures remains intact.
action of heat, mineral acids or alkali, the
water soluble form of globular protein
changes to water insoluble fibrous protein.
This is called denaturation of proteins.
During denaturation secondary and tertiary
structures of protein destroyed but primary
structures remains intact.
A sequence of how many nucleotides inmessenger RNA makes a codon for an amino acid? [2004]- a)Three
- b)Four
- c)One
- d)Two
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A sequence of how many nucleotides inmessenger RNA makes a codon for an amino acid? [2004]
a)
Three
b)
Four
c)
One
d)
Two

|
Krish Patel answered |
The bond formed between two amino acids
by the elimination of a water molecule is
called a peptide linkage or bond. The peptide
bond is simply another name for amide bond.
by the elimination of a water molecule is
called a peptide linkage or bond. The peptide
bond is simply another name for amide bond.
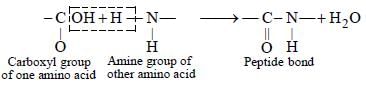
The product formed by linking amino acid
molecules through peptide linkages. —
CO—NH—, is called a peptide
molecules through peptide linkages. —
CO—NH—, is called a peptide
Which is not a true statement? [2002]- a)α-Carbon of α-amino acid is asymmetric
- b)All proteins are found in L-form
- c)Human body can synthesize all proteins theyneed
- d)At pH = 7 both amino and carboxylic groupsexist in ionised form
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not a true statement? [2002]
a)
α-Carbon of α-amino acid is asymmetric
b)
All proteins are found in L-form
c)
Human body can synthesize all proteins theyneed
d)
At pH = 7 both amino and carboxylic groupsexist in ionised form

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
All proteins are not found in L-form but they
may be present in form of D or L
may be present in form of D or L
Which one of the following is a peptide hormone ? [2006]- a)Testosterone
- b)Thyroxin
- c)Adrenaline
- d)Glucagon
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a peptide hormone ? [2006]
a)
Testosterone
b)
Thyroxin
c)
Adrenaline
d)
Glucagon

|
Subham Chavan answered |
Testorterone and Adrenaline are steroid
harmone, Thyroxin is non-steroided harmone
glucagon is peptide harmone.
harmone, Thyroxin is non-steroided harmone
glucagon is peptide harmone.
Which one of the following, statements isincorrect about enzyme catalysis? [2012]- a)Enzymes are mostly proteinous in nature.
- b)Enzyme action is specific.
- c)Enzymes are denaturated by ultraviolet raysand at high temperature.
- d)Enzymes are least reactive at optimumtemperature.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following, statements isincorrect about enzyme catalysis? [2012]
a)
Enzymes are mostly proteinous in nature.
b)
Enzyme action is specific.
c)
Enzymes are denaturated by ultraviolet raysand at high temperature.
d)
Enzymes are least reactive at optimumtemperature.

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
Enzymes are most reactive at optimum
temperature. The optimum temperature for
enzyme activity lies between 40°C to 60°C.
temperature. The optimum temperature for
enzyme activity lies between 40°C to 60°C.
Glycolysis is [2003]- a)conversion of glucose to haem
- b)oxidation of glucose to glutamate
- c)conversion of pyruvate to citrate
- d)oxidation of glucose to pyruvate
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Glycolysis is [2003]
a)
conversion of glucose to haem
b)
oxidation of glucose to glutamate
c)
conversion of pyruvate to citrate
d)
oxidation of glucose to pyruvate

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
It is a common pathway for both the aerobic
& anaerobic respiration in which 1 glucose
molecule is converted to 2 molecules of
pyruvate.
& anaerobic respiration in which 1 glucose
molecule is converted to 2 molecules of
pyruvate.
In DNA the linkages between differentnitrogenous bases are: [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)peptide linkage
- b)phosphate linkage
- c)H-bonding
- d)glycosidic linkage
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In DNA the linkages between differentnitrogenous bases are: [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
peptide linkage
b)
phosphate linkage
c)
H-bonding
d)
glycosidic linkage

|
Arya Nair answered |
The base pairs of the two strands of DNA
are linked together through H-bonds.
are linked together through H-bonds.
Which functional group participates indisulphide bond formation in proteins? [2005]- a)Thioester
- b)Thioether
- c)Thiol
- d)Thiolactone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which functional group participates indisulphide bond formation in proteins? [2005]
a)
Thioester
b)
Thioether
c)
Thiol
d)
Thiolactone
|
|
Madhurima Mishra answered |
Thiol group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins
Disulphide bonds play a crucial role in stabilizing the tertiary structure of proteins by covalently linking different parts of the polypeptide chain. The formation of disulphide bonds involves the oxidation of two thiol groups (-SH) to form a covalent bond between the sulfur atoms.
Thiol group
- Thiol group, also known as sulfhydryl group, is a functional group containing a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom.
- In proteins, cysteine residues contain thiol groups that can participate in disulphide bond formation.
Disulphide bond formation
- The process of disulphide bond formation involves the oxidation of two thiol groups to form a covalent bond between the sulfur atoms.
- This process is often catalyzed by enzymes known as disulphide bond isomerases.
Importance of disulphide bonds
- Disulphide bonds play a crucial role in stabilizing the tertiary structure of proteins.
- They can help maintain the structural integrity of proteins in various environments.
In conclusion, the thiol group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins by undergoing oxidation to form covalent bonds between sulfur atoms. This process is essential for maintaining the structural stability of proteins.
Which of the following hormones containsiodine? [2009]- a)Testosterone
- b)Adrenaline
- c)Thyroxine
- d)Insulin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following hormones containsiodine? [2009]
a)
Testosterone
b)
Adrenaline
c)
Thyroxine
d)
Insulin

|
Sonal Kulkarni answered |
Thyroxine is the only hormone among the
given choices that contains iodine. Its
structure is as follows:
given choices that contains iodine. Its
structure is as follows:

Fructose reduces Tollen’s reagent due to:[2010]- a)enolisation of fructose followed byconversion to glucose (having aldehydicgroup) by the base present in Tollen’sreagent
- b)asymmetric carbons
- c)primary alcoholic group
- d)secondary alcoholic group
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Fructose reduces Tollen’s reagent due to:[2010]
a)
enolisation of fructose followed byconversion to glucose (having aldehydicgroup) by the base present in Tollen’sreagent
b)
asymmetric carbons
c)
primary alcoholic group
d)
secondary alcoholic group

|
Veerendra Kuruva answered |
Fructose which is another form of starch.
having an aldehydic group which reacts with Fehlingsoln and reduces it.
having an aldehydic group which reacts with Fehlingsoln and reduces it.
The hormone that helps in the conversion ofglucose to glycogen is [2004]- a)Cortisone
- b)Bile acids
- c)Adrenaline
- d)Insulin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The hormone that helps in the conversion ofglucose to glycogen is [2004]
a)
Cortisone
b)
Bile acids
c)
Adrenaline
d)
Insulin

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Insulin helps in converting glucose to
glycogen
glycogen
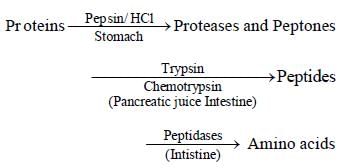
During the process of digestion, the proteins present in food materials are hydrolysed to amino acids. The two enzymes involved in the process  are respectively [2006]
are respectively [2006]
- a)Diastase and Lipase
- b)Pepsin and Trypsin
- c)Invertase and Zymase
- d)Amylase and Maltase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During the process of digestion, the proteins present in food materials are hydrolysed to amino acids. The two enzymes involved in the process
 are respectively [2006]
are respectively [2006]a)
Diastase and Lipase
b)
Pepsin and Trypsin
c)
Invertase and Zymase
d)
Amylase and Maltase

|
Anu Bajaj answered |
Pepsin and Trypsin are two enzymes
involved in the process (hydrolysis of
proteins)
involved in the process (hydrolysis of
proteins)
Which one of the following sets of monosaccharidesforms sucrose? [2012]- a)α–D-Galactopyranose and α–D-Glucopyranose
- b)α–D-Glucopyranose and β–D-Fructofuranose
- c)β–D-Glucopyranose and α–D- Fructofuranose
- d)α–D-Glucopyranose and β–D-Fructopyranose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following sets of monosaccharidesforms sucrose? [2012]
a)
α–D-Galactopyranose and α–D-Glucopyranose
b)
α–D-Glucopyranose and β–D-Fructofuranose
c)
β–D-Glucopyranose and α–D- Fructofuranose
d)
α–D-Glucopyranose and β–D-Fructopyranose

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
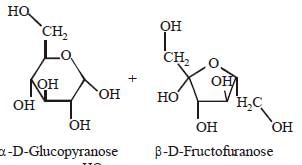
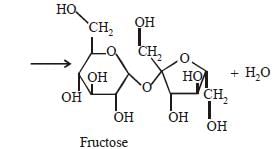
Sucrose is a disaccharide of α–DGlucopyranose
and β–D-Fructofuranose.
and β–D-Fructofuranose.
Enzymes are made up of [2002]- a)Edible proteins
- b)Proteins with specific structure
- c)Nitrogen containing carbohydrates
- d)Carbohydrates
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes are made up of [2002]
a)
Edible proteins
b)
Proteins with specific structure
c)
Nitrogen containing carbohydrates
d)
Carbohydrates

|
Nayanika Dasgupta answered |
Enzymes are made up of protein with specific
structure.
structure.
The human body does not produce [2006]- a)Vitamins
- b)Hormones
- c)Enzymes
- d)DNA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The human body does not produce [2006]
a)
Vitamins
b)
Hormones
c)
Enzymes
d)
DNA

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Vitamins are organic substances which does
not provide energy but are essential for
healthy growth and proper functioning of
body. Vitamins are not synthesized inside
human body but they are essential part of
our diet.
not provide energy but are essential for
healthy growth and proper functioning of
body. Vitamins are not synthesized inside
human body but they are essential part of
our diet.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biomolecules - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biomolecules - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup