All Exams >
CA Foundation >
Business Economics for CA Foundation >
All Questions
All questions of Business Economics Test for CA Foundation Exam
Which of the following is/are the most important input cost(s) in service industry?- a)Material
- b)Labour
- c)Both material and labour
- d)Overheads
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are the most important input cost(s) in service industry?
a)
Material
b)
Labour
c)
Both material and labour
d)
Overheads

|
Srsps answered |
Answer: B. Labour
The most important input cost in the service industry is labour. This is because:
- Services are often people-intensive, requiring a significant amount of human interaction and expertise to deliver value to customers.
- Labour costs are typically higher in the service industry compared to other industries, as it involves skilled professionals and specialized knowledge.
- Unlike manufacturing industries, where material costs can be a significant portion of the overall costs, service industries generally have lower material costs, as they primarily deal with intangible products and offerings.
- While overheads such as rent, utilities, and equipment are important, they do not usually outweigh the significance of labour costs in the service industry.
Therefore, labour is the most important input cost in the service industry, as it has the most significant impact on the quality and delivery of services provided to customers.
The burden of tax lies more/equally on ______ in a regressive taxation system.- a)poor class
- b)rich class
- c)midddle class
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The burden of tax lies more/equally on ______ in a regressive taxation system.
a)
poor class
b)
rich class
c)
midddle class
d)
all of these
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Regressive Taxation System
- A regressive taxation system is one where the tax rate decreases as the taxable income increases.
- Under this system, the burden of tax is higher on lower-income groups, as they are required to pay a larger percentage of their income as taxes compared to higher-income groups.
The Burden of Tax in a Regressive Taxation System
- Poor class: The burden of tax lies more on the poor class in a regressive taxation system. This is because poor individuals pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes, which can lead to financial strain and limit their ability to meet basic needs.
- Rich class: The burden of tax is comparatively lower on the rich class, as they pay a smaller percentage of their income in taxes. This can lead to wealth accumulation and contribute to income inequality.
- Middle class: The burden of tax on the middle class is also relatively lower compared to the poor class but higher than the rich class. This can result in the middle class bearing a higher tax burden than they would under a progressive taxation system.
Conclusion
Under a regressive taxation system, the burden of tax lies more on the poor class, leading to negative impacts on their financial well-being and contributing to income inequality. In contrast, the rich class experiences a lower tax burden, allowing them to accumulate wealth more easily.
Till date, the Indian agriculture has been of ______ nature.- a)commercial
- b)advanced
- c)modern
- d)subsistence
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Till date, the Indian agriculture has been of ______ nature.
a)
commercial
b)
advanced
c)
modern
d)
subsistence
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Explanation:Indian agriculture has been of subsistence nature, which can be explained by the following points:1. Focus on meeting basic needs:- The primary objective of Indian agriculture has been to produce enough food to meet the needs of its large population.- Farmers grow crops mainly for their own consumption, and any surplus is sold in the market.2. Small and fragmented landholdings:- The majority of Indian farmers have small and fragmented landholdings, which makes it difficult to adopt modern and commercial farming techniques.- This results in low productivity and farmers mainly focus on producing enough to feed their families.3. Dependence on monsoons:- Indian agriculture is heavily dependent on monsoons, as a large percentage of the cultivated land is rainfed.- This makes agriculture vulnerable to the uncertainties of rainfall, leading to crop failures and low productivity.4. Limited use of modern technology:- Due to financial constraints and lack of awareness, many Indian farmers are still using traditional methods of farming.- The limited use of modern technology and agricultural practices contributes to the subsistence nature of Indian agriculture.5. Low level of commercialization:- The majority of Indian farmers are engaged in subsistence agriculture and produce mainly food crops.- The level of commercialization is low, with cash crops like cotton, jute, and sugarcane being produced on a relatively small scale.In conclusion, the Indian agriculture sector has been predominantly subsistence in nature due to its focus on meeting basic needs, small landholdings, dependence on monsoons, and limited use of modern technology. However, efforts are being made to transform Indian agriculture into a more modern and commercial sector through various government initiatives and the adoption of new technologies.
In _________ of estimation, national income is calculated by adding wages, rent, interest and profits.- a)product method
- b)income method
- c)expenditure method
- d)profit method
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In _________ of estimation, national income is calculated by adding wages, rent, interest and profits.
a)
product method
b)
income method
c)
expenditure method
d)
profit method
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The Income Method measures national income from the side of payments made to the primary factors of production in the form of rent, wages, interest and profit for their productive services in an accounting year.
Which Indian state has the lowest density of population?- a)West Bengal
- b)Delhi
- c)Arunachal Pradesh
- d)Mizoram
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which Indian state has the lowest density of population?
a)
West Bengal
b)
Delhi
c)
Arunachal Pradesh
d)
Mizoram
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Answer: C. Arunachal PradeshExplanation:- Arunachal Pradesh has the lowest population density among Indian states.- Population density refers to the number of people living per square kilometer of land area.- According to the 2011 Census of India, Arunachal Pradesh has a population density of only 17 people per square kilometer.- This low population density is attributed to the state's large forest cover, mountainous terrain, and limited urbanization, which make it difficult for people to settle in large numbers.- On the other hand, states like West Bengal and Delhi have much higher population densities, with 1,029 and 11,297 people per square kilometer, respectively.
Who among the followings is concerned with `welfare definition` of economics?- a)Prof. MarshallCorrect Answer
- b)Prof. Samuelson
- c)Adam Smith
- d)Lord Robbins
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who among the followings is concerned with `welfare definition` of economics?
a)
Prof. MarshallCorrect Answer
b)
Prof. Samuelson
c)
Adam Smith
d)
Lord Robbins

|
Charvi Roy answered |
The Concerned Economist:
- The question asks who among the given options is concerned with the `welfare definition` of economics.
- This suggests that the question is referring to the different definitions of economics - some of which may prioritize efficiency, while others may prioritize equity and welfare.
- Therefore, the answer must be someone who is known to have advocated for or emphasized the importance of welfare in economics.
Prof. Marshall:
- This option is the correct answer because Alfred Marshall is known for his welfare-oriented approach to economics.
- Marshall believed that economics should not just focus on maximizing individual utility or profit, but should also consider the social welfare implications of economic activity.
- He introduced the concept of consumer surplus, which measures the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what they actually pay, as a way to measure welfare gains from trade.
- Marshall also argued that economic policies should be evaluated based on their ability to improve social welfare, rather than just on their ability to promote economic growth or efficiency.
Prof. Samuelson:
- Although Paul Samuelson is a notable economist, he is not typically associated with the welfare definition of economics.
- Samuelson is known for his contributions to neoclassical economics, which emphasizes efficiency and rationality in economic decision-making.
- However, Samuelson did acknowledge the importance of welfare considerations in economics, particularly in his later work.
Adam Smith:
- Adam Smith is often considered the founder of modern economics, but his views on welfare are somewhat ambiguous.
- Smith believed that economic growth and efficiency were important goals, but he also recognized the importance of social welfare and justice.
- However, Smith's emphasis on the invisible hand and self-interest have led some to view him as a proponent of laissez-faire economics.
Lord Robbins:
- Lord Robbins is best known for his definition of economics as "the science which studies human behavior as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses."
- While this definition does not explicitly prioritize welfare, Robbins did acknowledge the importance of ethical considerations in economics.
- Robbins argued that economics should not just describe how people behave, but should also consider how they ought to behave in order to achieve social welfare.
- The question asks who among the given options is concerned with the `welfare definition` of economics.
- This suggests that the question is referring to the different definitions of economics - some of which may prioritize efficiency, while others may prioritize equity and welfare.
- Therefore, the answer must be someone who is known to have advocated for or emphasized the importance of welfare in economics.
Prof. Marshall:
- This option is the correct answer because Alfred Marshall is known for his welfare-oriented approach to economics.
- Marshall believed that economics should not just focus on maximizing individual utility or profit, but should also consider the social welfare implications of economic activity.
- He introduced the concept of consumer surplus, which measures the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what they actually pay, as a way to measure welfare gains from trade.
- Marshall also argued that economic policies should be evaluated based on their ability to improve social welfare, rather than just on their ability to promote economic growth or efficiency.
Prof. Samuelson:
- Although Paul Samuelson is a notable economist, he is not typically associated with the welfare definition of economics.
- Samuelson is known for his contributions to neoclassical economics, which emphasizes efficiency and rationality in economic decision-making.
- However, Samuelson did acknowledge the importance of welfare considerations in economics, particularly in his later work.
Adam Smith:
- Adam Smith is often considered the founder of modern economics, but his views on welfare are somewhat ambiguous.
- Smith believed that economic growth and efficiency were important goals, but he also recognized the importance of social welfare and justice.
- However, Smith's emphasis on the invisible hand and self-interest have led some to view him as a proponent of laissez-faire economics.
Lord Robbins:
- Lord Robbins is best known for his definition of economics as "the science which studies human behavior as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses."
- While this definition does not explicitly prioritize welfare, Robbins did acknowledge the importance of ethical considerations in economics.
- Robbins argued that economics should not just describe how people behave, but should also consider how they ought to behave in order to achieve social welfare.
When lesser quantity is demanded with a rise in price, it is called ________ of demand.- a)increase
- b)decrease
- c)expansion
- d)contraction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When lesser quantity is demanded with a rise in price, it is called ________ of demand.
a)
increase
b)
decrease
c)
expansion
d)
contraction
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Answer: D: ContractionExplanation:When lesser quantity is demanded with a rise in price, it is called contraction of demand. This concept is based on the law of demand, which states that the quantity demanded of a good or service is inversely related to its price.Key points to understand the contraction of demand:- Price increase: When the price of a good or service increases.- Lesser quantity demanded: The quantity demanded by consumers decreases due to the higher price.- Contraction: This decrease in quantity demanded is referred to as a contraction of demand.- Law of Demand: The contraction of demand is in line with the law of demand, which establishes a negative relationship between price and quantity demanded.
The agency functions of commercial banks do not include- a)collection of dividends
- b)providing loans
- c)collection of cheques and drafts
- d)acting as trustee or executor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The agency functions of commercial banks do not include
a)
collection of dividends
b)
providing loans
c)
collection of cheques and drafts
d)
acting as trustee or executor
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
The correct answer is B: providing loans.Explanation:Agency functions of commercial banks refer to the services that banks provide on behalf of their customers. These functions mainly involve assisting customers in managing their financial transactions and assets. Providing loans, however, is considered a primary function of commercial banks and not an agency function. Agency functions of commercial banks include:A: Collection of dividends- Commercial banks collect dividends on behalf of their customers from various investment sources such as stocks and bonds.C: Collection of cheques and drafts- Banks collect cheques and drafts for their customers, allowing them to receive payments from other parties.D: Acting as trustee or executor- Commercial banks can act as a trustee or executor for their customers by managing their estates, trusts, or other assets as per their instructions.In contrast, providing loans is a primary function of commercial banks, which involves lending money to customers for various purposes such as personal expenses, business investments, or buying property. This function is essential for the bank's profitability and does not fall under the category of agency functions.
Which of the following institutes is the apex body for rural credit and agricultural finance?- a)Reserve Bank of India
- b)Regional Rural Banks
- c)SIDBI
- d)NABARD
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following institutes is the apex body for rural credit and agricultural finance?
a)
Reserve Bank of India
b)
Regional Rural Banks
c)
SIDBI
d)
NABARD

|
Charvi Roy answered |
NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development) is the apex body for rural credit and agricultural finance in India. It was established in 1982 under the provisions of the NABARD Act of 1981. The main objective of NABARD is to promote sustainable and equitable agriculture and rural prosperity through effective credit support, related services, institutional development and other innovative initiatives.
Functions of NABARD:
1. Credit functions: NABARD provides credit facilities to farmers, rural artisans, entrepreneurs, and other rural individuals and institutions through various schemes.
2. Development functions: NABARD provides development assistance to various institutions for the promotion of agriculture and rural development. It also provides technical assistance and consultancy services to various agencies.
3. Supervisory functions: NABARD supervises and regulates the functioning of regional rural banks, cooperative banks, and other rural financial institutions.
4. Investment functions: NABARD invests in various development projects, such as irrigation, rural roads, and rural electrification, to promote rural development.
Importance of NABARD:
1. NABARD plays a crucial role in rural development by providing credit and other financial services to farmers and other rural individuals and institutions.
2. It helps in the promotion of sustainable and equitable agriculture and rural prosperity.
3. It acts as a catalyst for rural development by providing technical assistance, consultancy services, and other innovative initiatives.
4. It ensures the smooth functioning of rural financial institutions by supervising and regulating their operations.
In conclusion, NABARD is the apex body for rural credit and agricultural finance in India, and it plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable and equitable agriculture and rural prosperity through effective credit support, related services, institutional development and other innovative initiatives.
Functions of NABARD:
1. Credit functions: NABARD provides credit facilities to farmers, rural artisans, entrepreneurs, and other rural individuals and institutions through various schemes.
2. Development functions: NABARD provides development assistance to various institutions for the promotion of agriculture and rural development. It also provides technical assistance and consultancy services to various agencies.
3. Supervisory functions: NABARD supervises and regulates the functioning of regional rural banks, cooperative banks, and other rural financial institutions.
4. Investment functions: NABARD invests in various development projects, such as irrigation, rural roads, and rural electrification, to promote rural development.
Importance of NABARD:
1. NABARD plays a crucial role in rural development by providing credit and other financial services to farmers and other rural individuals and institutions.
2. It helps in the promotion of sustainable and equitable agriculture and rural prosperity.
3. It acts as a catalyst for rural development by providing technical assistance, consultancy services, and other innovative initiatives.
4. It ensures the smooth functioning of rural financial institutions by supervising and regulating their operations.
In conclusion, NABARD is the apex body for rural credit and agricultural finance in India, and it plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable and equitable agriculture and rural prosperity through effective credit support, related services, institutional development and other innovative initiatives.
The term 'deposits with banks with maturity over one year' comes under ___ definition of money.- a)M-1
- b)M-2
- c)M-3
- d)M-4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The term 'deposits with banks with maturity over one year' comes under ___ definition of money.
a)
M-1
b)
M-2
c)
M-3
d)
M-4

|
Freedom Institute answered |
The term 'deposits with banks with maturity over one year' comes under the M-3 definition of money. Explanation:There are four measures of money in the economy, commonly referred to as M-1, M-2, M-3, and M-4. Each measure includes different components of the money supply:M-1:- Currency in circulation (coins and notes)- Demand deposits (checking accounts)- Traveler's checksM-2:- All components of M-1- Savings deposits- Small denomination time deposits (certificates of deposit less than $100,000)- Money market deposit accountsM-3:- All components of M-2- Large denomination time deposits (certificates of deposit of $100,000 or more)- Institutional money market funds- Deposits with banks with maturity over one yearM-4:- All components of M-3- Other liquid assets, such as Treasury bills and commercial paperThe term 'deposits with banks with maturity over one year' falls under the M-3 definition of money because it includes large denomination time deposits and other less liquid assets in addition to the components of M-2.
Which of the following is/are the internal or domestic source(s) of fund mobilisation for the government?- a)Grants
- b)Loans
- c)Deficit financing
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are the internal or domestic source(s) of fund mobilisation for the government?
a)
Grants
b)
Loans
c)
Deficit financing
d)
All of these
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Deficit financing is the primary domestic source of fund mobilization for the government. Here is an explanation:Deficit Financing:- Deficit financing refers to the government's practice of borrowing money to cover the gap between its revenue and expenditure.- This can be done through various means, such as issuing government bonds, taking loans from domestic banks, or printing more currency.- Deficit financing allows the government to meet its short-term financial obligations and invest in long-term projects that can stimulate economic growth.- However, excessive deficit financing can lead to inflation and a rise in public debt, which could negatively impact the economy in the long run.While grants and loans can provide funds to the government, they are usually considered external sources of funding, as they typically come from foreign governments or international organizations.
Most of the unemployment in India is- a)voluntary
- b)frictional
- c)structural
- d)temporary
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the unemployment in India is
a)
voluntary
b)
frictional
c)
structural
d)
temporary
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Answer: C. StructuralExplanation:- Structural unemployment: This type of unemployment occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills that workers possess and the skills required for the available jobs. In India, a significant portion of the labor force is engaged in informal or unorganized sectors with limited skills and education, which makes it difficult for them to find appropriate jobs in the organized sector.- Reasons for structural unemployment in India: - Lack of quality education: Many people in India do not have access to quality education, which restricts their ability to acquire the skills needed for better employment opportunities. - Technological changes: Rapid technological advancements have led to a demand for skilled workers in various industries. Those who cannot adapt to these changes often find themselves unemployed. - Slow economic growth: India's economic growth has not been consistent, leading to fewer job opportunities in various sectors. - Rural-urban migration: Many people migrate from rural to urban areas in search of better job opportunities, but they often lack the necessary skills and education to find suitable employment.Other types of unemployment, such as voluntary, frictional, and temporary, do exist in India but are not as prevalent as structural unemployment. The primary focus needs to be on addressing the structural unemployment issue by investing in education and skill development programs, promoting industries and sectors with high employment potential, and creating a more inclusive labor market.
Directions: Use the table below to answer the question.
 Q. The average fixed cost of two units of output is
Q. The average fixed cost of two units of output is
- a)Rs. 80
- b)Rs. 85
- c)Rs. 120
- d)Rs. 205
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Use the table below to answer the question.


Q. The average fixed cost of two units of output is
a)
Rs. 80
b)
Rs. 85
c)
Rs. 120
d)
Rs. 205

|
Srsps answered |
Calculating Average Fixed Cost for Two Units of Output
- First, identify the fixed cost for producing two units of output from the table.
- From the table, find the total fixed cost for producing two units of output.
- Divide the total fixed cost by the number of units produced (in this case, 2) to calculate the average fixed cost per unit.
- According to the options provided, the average fixed cost of two units of output is Rs. 120
Price discrimination is the feature of which of the following competitions?- a)Perfect competition
- b)Oligopoly
- c)Monopoly
- d)Monopolistic competition
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Price discrimination is the feature of which of the following competitions?
a)
Perfect competition
b)
Oligopoly
c)
Monopoly
d)
Monopolistic competition

|
Dhruba Choudhary answered |
Price Discrimination in Monopoly Competition
Definition of Price Discrimination
Price discrimination is a strategy of charging different prices from different customers for the same product or service. It is a common phenomenon in monopolistic competition and monopoly where firms have market power.
Monopoly Competition
In a monopoly, there is only one seller of a product or service in the market. Due to the lack of competition, the monopolist has the power to set the price of the product or service. The monopolist can use this power to charge different prices from different customers.
Conditions for Price Discrimination
For price discrimination to be successful, the following conditions must be met:
- The monopolist must have market power.
- The monopolist must be able to distinguish between different customer groups.
- The monopolist must be able to prevent resale of the product or service.
Types of Price Discrimination
Price discrimination can be of the following types:
- First Degree Price Discrimination: This is when the monopolist charges each customer the maximum price they are willing to pay for the product or service. This type of price discrimination is rare.
- Second Degree Price Discrimination: This is when the monopolist charges different prices based on the quantity of the product or service bought. For example, a bulk discount.
- Third Degree Price Discrimination: This is when the monopolist charges different prices based on the characteristics of the customer group. For example, a student discount.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Price Discrimination
Advantages:
- Increases revenue for the monopolist.
- Allows the monopolist to reach a wider customer base.
- Can be used to price discriminate against price-sensitive customers.
Disadvantages:
- Can lead to customer dissatisfaction and loss of goodwill.
- Can lead to regulatory intervention and legal action.
- Can lead to a reduction in consumer surplus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, price discrimination is a common feature of monopoly competition due to the market power of the monopolist. Price discrimination can be of different types and has its advantages and disadvantages.
Definition of Price Discrimination
Price discrimination is a strategy of charging different prices from different customers for the same product or service. It is a common phenomenon in monopolistic competition and monopoly where firms have market power.
Monopoly Competition
In a monopoly, there is only one seller of a product or service in the market. Due to the lack of competition, the monopolist has the power to set the price of the product or service. The monopolist can use this power to charge different prices from different customers.
Conditions for Price Discrimination
For price discrimination to be successful, the following conditions must be met:
- The monopolist must have market power.
- The monopolist must be able to distinguish between different customer groups.
- The monopolist must be able to prevent resale of the product or service.
Types of Price Discrimination
Price discrimination can be of the following types:
- First Degree Price Discrimination: This is when the monopolist charges each customer the maximum price they are willing to pay for the product or service. This type of price discrimination is rare.
- Second Degree Price Discrimination: This is when the monopolist charges different prices based on the quantity of the product or service bought. For example, a bulk discount.
- Third Degree Price Discrimination: This is when the monopolist charges different prices based on the characteristics of the customer group. For example, a student discount.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Price Discrimination
Advantages:
- Increases revenue for the monopolist.
- Allows the monopolist to reach a wider customer base.
- Can be used to price discriminate against price-sensitive customers.
Disadvantages:
- Can lead to customer dissatisfaction and loss of goodwill.
- Can lead to regulatory intervention and legal action.
- Can lead to a reduction in consumer surplus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, price discrimination is a common feature of monopoly competition due to the market power of the monopolist. Price discrimination can be of different types and has its advantages and disadvantages.
Balance of payment includes- a)visible items of imports and exports
- b)invisible items of imports and exports
- c)capital account transactions
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Balance of payment includes
a)
visible items of imports and exports
b)
invisible items of imports and exports
c)
capital account transactions
d)
all of these

|
Muskaan Tiwari answered |
Balance of Payment (BOP) is a statement that records all transactions between a country and the rest of the world over a period of time. It includes both visible and invisible items of imports and exports, as well as capital account transactions.
Visible Items of Imports and Exports:
Visible items refer to tangible goods that are traded between countries. These include goods such as raw materials, finished products, machinery, and vehicles. The value of visible items is recorded in the current account of the BOP.
Invisible Items of Imports and Exports:
Invisible items refer to intangible goods and services that are traded between countries. These include services such as tourism, transportation, and software exports. The value of invisible items is also recorded in the current account of the BOP.
Capital Account Transactions:
Capital account transactions refer to the movement of capital between countries. This includes investments in stocks, bonds, and real estate, as well as foreign direct investments. The value of capital account transactions is recorded in the capital account of the BOP.
All of These:
The BOP statement records all transactions between a country and the rest of the world, including visible and invisible items of imports and exports, as well as capital account transactions. Therefore, option 'D' is the correct answer.
In conclusion, the BOP statement is an important economic tool that reflects a country's economic activity with the rest of the world. It is important for policymakers to monitor the BOP to ensure that a country's economy is in a healthy state and to identify areas that require attention.
Visible Items of Imports and Exports:
Visible items refer to tangible goods that are traded between countries. These include goods such as raw materials, finished products, machinery, and vehicles. The value of visible items is recorded in the current account of the BOP.
Invisible Items of Imports and Exports:
Invisible items refer to intangible goods and services that are traded between countries. These include services such as tourism, transportation, and software exports. The value of invisible items is also recorded in the current account of the BOP.
Capital Account Transactions:
Capital account transactions refer to the movement of capital between countries. This includes investments in stocks, bonds, and real estate, as well as foreign direct investments. The value of capital account transactions is recorded in the capital account of the BOP.
All of These:
The BOP statement records all transactions between a country and the rest of the world, including visible and invisible items of imports and exports, as well as capital account transactions. Therefore, option 'D' is the correct answer.
In conclusion, the BOP statement is an important economic tool that reflects a country's economic activity with the rest of the world. It is important for policymakers to monitor the BOP to ensure that a country's economy is in a healthy state and to identify areas that require attention.
According to Dr. Marshall, the ________ element has a great relevance in the determination of price.- a)supply
- b)demand
- c)time
- d)money
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Dr. Marshall, the ________ element has a great relevance in the determination of price.
a)
supply
b)
demand
c)
time
d)
money

|
Gaurav Chatterjee answered |
Understanding the Importance of Time in Pricing
In the context of pricing, time plays a pivotal role due to various reasons. Here’s an exploration of why time is essential in determining price:
Impact of Market Conditions
- Time influences market conditions which can change frequently due to various factors such as seasonality, economic cycles, and consumer trends.
- For example, demand for certain products may peak during holidays, leading to price increases.
Cost Considerations
- The cost of production can vary over time. Fluctuations in raw material prices, labor costs, and technological advancements can affect the overall cost structure, hence impacting pricing strategies.
- Companies may adjust prices based on long-term forecasts of these costs.
Consumer Behavior
- Consumer willingness to pay can change over time. Buyers may have different perceptions of value depending on current trends and their financial situation.
- Timing a product launch or sale strategically can maximize profit based on consumer readiness.
Pricing Strategies
- Businesses often employ time-based pricing strategies, such as dynamic pricing, which adjusts prices in real-time based on demand and supply conditions.
- Seasonal discounts or promotional periods are also time-sensitive approaches that can significantly affect pricing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the element of time is crucial in pricing decisions. It intertwines with supply and demand dynamics, cost fluctuations, and consumer behavior, making it a significant factor that businesses must consider for effective pricing strategies. Recognizing the relevance of time allows companies to optimize their pricing models for better profitability and market alignment.
In the context of pricing, time plays a pivotal role due to various reasons. Here’s an exploration of why time is essential in determining price:
Impact of Market Conditions
- Time influences market conditions which can change frequently due to various factors such as seasonality, economic cycles, and consumer trends.
- For example, demand for certain products may peak during holidays, leading to price increases.
Cost Considerations
- The cost of production can vary over time. Fluctuations in raw material prices, labor costs, and technological advancements can affect the overall cost structure, hence impacting pricing strategies.
- Companies may adjust prices based on long-term forecasts of these costs.
Consumer Behavior
- Consumer willingness to pay can change over time. Buyers may have different perceptions of value depending on current trends and their financial situation.
- Timing a product launch or sale strategically can maximize profit based on consumer readiness.
Pricing Strategies
- Businesses often employ time-based pricing strategies, such as dynamic pricing, which adjusts prices in real-time based on demand and supply conditions.
- Seasonal discounts or promotional periods are also time-sensitive approaches that can significantly affect pricing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the element of time is crucial in pricing decisions. It intertwines with supply and demand dynamics, cost fluctuations, and consumer behavior, making it a significant factor that businesses must consider for effective pricing strategies. Recognizing the relevance of time allows companies to optimize their pricing models for better profitability and market alignment.
Directions: In Econoville, there is one grocery shop, Ecoconvenience. It used to sell fresh milk at Rs. 20 per litre, at which price 400 litres of milk were sold per month. After some time, the price was raised to Rs. 30 per litre. Following the price rise:Only 200 litres of milk was sold every month.
The number of boxes of cereal customers bought went down from 280 to 240.
The number of packets of powered milk customers bought went up from 90 to 220 per month.The cross elasticity of monthly demand for powdered milk when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30 per litre is equal to- a)+ 1.05
- b)- 1.05
- c)- 2.09
- d)+ 2.09
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In Econoville, there is one grocery shop, Ecoconvenience. It used to sell fresh milk at Rs. 20 per litre, at which price 400 litres of milk were sold per month. After some time, the price was raised to Rs. 30 per litre. Following the price rise:
Only 200 litres of milk was sold every month.
The number of boxes of cereal customers bought went down from 280 to 240.
The number of packets of powered milk customers bought went up from 90 to 220 per month.
The number of boxes of cereal customers bought went down from 280 to 240.
The number of packets of powered milk customers bought went up from 90 to 220 per month.
The cross elasticity of monthly demand for powdered milk when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30 per litre is equal to
a)
+ 1.05
b)
- 1.05
c)
- 2.09
d)
+ 2.09

|
Pranav Gupta answered |
Cross Elasticity of Demand Calculation
The cross elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand for one good to changes in the price of another good. It is calculated using the following formula:
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (% Change in Quantity Demanded of Good A) / (% Change in Price of Good B)
Here, we need to calculate the cross elasticity of demand for powdered milk when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30 per litre.
Step 1: Calculate the percentage change in the quantity demanded of powdered milk.
Initial Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = 90 packets
New Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = 220 packets
% Change in Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = ((New Quantity Demanded - Initial Quantity Demanded) / Initial Quantity Demanded) x 100
% Change in Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = ((220 - 90) / 90) x 100
% Change in Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = 144.44%
Step 2: Calculate the percentage change in the price of fresh milk.
Initial Price of Fresh Milk = Rs. 20 per litre
New Price of Fresh Milk = Rs. 30 per litre
% Change in Price of Fresh Milk = ((New Price - Initial Price) / Initial Price) x 100
% Change in Price of Fresh Milk = ((30 - 20) / 20) x 100
% Change in Price of Fresh Milk = 50%
Step 3: Calculate the cross elasticity of demand.
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (% Change in Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk) / (% Change in Price of Fresh Milk)
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (144.44% / 50%)
Cross Elasticity of Demand = 2.89
Since the cross elasticity of demand is positive, we can conclude that powdered milk is a substitute for fresh milk. The correct answer is option 'D' (2.09), which may be a typo in the question.
The cross elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand for one good to changes in the price of another good. It is calculated using the following formula:
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (% Change in Quantity Demanded of Good A) / (% Change in Price of Good B)
Here, we need to calculate the cross elasticity of demand for powdered milk when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30 per litre.
Step 1: Calculate the percentage change in the quantity demanded of powdered milk.
Initial Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = 90 packets
New Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = 220 packets
% Change in Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = ((New Quantity Demanded - Initial Quantity Demanded) / Initial Quantity Demanded) x 100
% Change in Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = ((220 - 90) / 90) x 100
% Change in Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk = 144.44%
Step 2: Calculate the percentage change in the price of fresh milk.
Initial Price of Fresh Milk = Rs. 20 per litre
New Price of Fresh Milk = Rs. 30 per litre
% Change in Price of Fresh Milk = ((New Price - Initial Price) / Initial Price) x 100
% Change in Price of Fresh Milk = ((30 - 20) / 20) x 100
% Change in Price of Fresh Milk = 50%
Step 3: Calculate the cross elasticity of demand.
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (% Change in Quantity Demanded of Powdered Milk) / (% Change in Price of Fresh Milk)
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (144.44% / 50%)
Cross Elasticity of Demand = 2.89
Since the cross elasticity of demand is positive, we can conclude that powdered milk is a substitute for fresh milk. The correct answer is option 'D' (2.09), which may be a typo in the question.
If the railways are making losses on passenger traffic they should lower their fares. The suggested remedy would only work if the demand for rail travel had a price elasticity of- a)zero
- b)greater than one
- c)one
- d)greater than onegreater than zero but less than one
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the railways are making losses on passenger traffic they should lower their fares. The suggested remedy would only work if the demand for rail travel had a price elasticity of
a)
zero
b)
greater than one
c)
one
d)
greater than onegreater than zero but less than one
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
ANSWER
- b)greater than one
The 'suggested remedy' would only work if the 'demand for rail travel' had a 'price elasticity' of Greater than Zero and less than one. Explanation: If the railways decide to lower their fares their 'demand for rail' travel will
increaseIn case of perfect competition, the selling firm is- a)price taker
- b)price maker
- c)price leader
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of perfect competition, the selling firm is
a)
price taker
b)
price maker
c)
price leader
d)
none of these

|
Malavika Basak answered |
A perfectly competitive firm is a price taker, which means that it must accept the equilibrium price at which it sells goods. If a perfectly competitive firm attempts to charge even a tiny amount more than the market price, it will be unable to make any sales.
Giffen Paradox is applicable for- a)price demand
- b)income demand
- c)cross demand
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Giffen Paradox is applicable for
a)
price demand
b)
income demand
c)
cross demand
d)
all of these

|
Vaishnavi Joshi answered |
Giffen Paradox and its applicability to Income Demand
The Giffen Paradox is a phenomenon in which an increase in the price of a good leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of that good. This goes against the basic law of demand which states that the quantity demanded of a good decreases as the price increases. The paradox was first observed by Sir Robert Giffen, a Scottish economist.
Applicability to Income Demand
The Giffen Paradox is applicable to income demand, which refers to the relationship between the quantity demanded of a good and changes in income. In the case of a Giffen good, which is a product that has no close substitutes and is a significant portion of a consumer's budget, an increase in the price of the good leads to a decrease in the consumer's purchasing power. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded of all goods except for the Giffen good.
In the case of a Giffen good, the income effect dominates the substitution effect, which is the tendency of consumers to switch to substitute goods when the price of a good increases. As a result, an increase in the price of the Giffen good leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of the good, as consumers are forced to allocate more of their income to the good.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Giffen Paradox is applicable to income demand, and describes a situation where an increase in the price of a Giffen good leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of the good. This paradox is important in understanding consumer behavior and the relationship between price and demand.
The Giffen Paradox is a phenomenon in which an increase in the price of a good leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of that good. This goes against the basic law of demand which states that the quantity demanded of a good decreases as the price increases. The paradox was first observed by Sir Robert Giffen, a Scottish economist.
Applicability to Income Demand
The Giffen Paradox is applicable to income demand, which refers to the relationship between the quantity demanded of a good and changes in income. In the case of a Giffen good, which is a product that has no close substitutes and is a significant portion of a consumer's budget, an increase in the price of the good leads to a decrease in the consumer's purchasing power. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded of all goods except for the Giffen good.
In the case of a Giffen good, the income effect dominates the substitution effect, which is the tendency of consumers to switch to substitute goods when the price of a good increases. As a result, an increase in the price of the Giffen good leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of the good, as consumers are forced to allocate more of their income to the good.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Giffen Paradox is applicable to income demand, and describes a situation where an increase in the price of a Giffen good leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of the good. This paradox is important in understanding consumer behavior and the relationship between price and demand.
What is India`s rank in world population?
- a)Second
- b)First
- c)Third
- d)Fourth
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is India`s rank in world population?
a)
Second
b)
First
c)
Third
d)
Fourth

|
Rajveer Yadav answered |
India's Rank in World Population
India is the second-most populous country in the world after China. The country has a population of over 1.3 billion people, which is approximately 17.7% of the world's population.
Factors Contributing to India's Population
There are several factors contributing to India's high population growth, including:
1. High Fertility Rate: India has a high fertility rate, which is the average number of children born to a woman during her reproductive years. The fertility rate in India is around 2.2, which is higher than the global average of 1.7.
2. Lack of Awareness: There is a lack of awareness and access to family planning methods in many parts of the country. This leads to unplanned pregnancies and higher population growth.
3. Poverty: Poverty is a major factor contributing to high population growth in India. Many families believe that having more children will increase their chances of having a higher income in the future.
Impact of High Population on India
India's high population has several negative impacts on the country, including:
1. Strain on Resources: The high population puts a strain on the country's resources, including food, water, and energy.
2. Unemployment: The high population also contributes to high levels of unemployment in the country, as there are not enough jobs to support everyone.
3. Environmental Issues: The high population also leads to environmental issues, such as pollution and deforestation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, India is the second-most populous country in the world after China. The country's high population growth is due to several factors, including high fertility rates, lack of awareness, and poverty. The high population has several negative impacts on the country, including a strain on resources, high unemployment, and environmental issues.
India is the second-most populous country in the world after China. The country has a population of over 1.3 billion people, which is approximately 17.7% of the world's population.
Factors Contributing to India's Population
There are several factors contributing to India's high population growth, including:
1. High Fertility Rate: India has a high fertility rate, which is the average number of children born to a woman during her reproductive years. The fertility rate in India is around 2.2, which is higher than the global average of 1.7.
2. Lack of Awareness: There is a lack of awareness and access to family planning methods in many parts of the country. This leads to unplanned pregnancies and higher population growth.
3. Poverty: Poverty is a major factor contributing to high population growth in India. Many families believe that having more children will increase their chances of having a higher income in the future.
Impact of High Population on India
India's high population has several negative impacts on the country, including:
1. Strain on Resources: The high population puts a strain on the country's resources, including food, water, and energy.
2. Unemployment: The high population also contributes to high levels of unemployment in the country, as there are not enough jobs to support everyone.
3. Environmental Issues: The high population also leads to environmental issues, such as pollution and deforestation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, India is the second-most populous country in the world after China. The country's high population growth is due to several factors, including high fertility rates, lack of awareness, and poverty. The high population has several negative impacts on the country, including a strain on resources, high unemployment, and environmental issues.
Which of the following is/are not the quantitative measures of Central Bank?- a)Bank rate
- b)Open market operations
- c)Variable reserve ratios
- d)Rationing of credit
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are not the quantitative measures of Central Bank?
a)
Bank rate
b)
Open market operations
c)
Variable reserve ratios
d)
Rationing of credit

|
Arka Kaur answered |
Not Quantitative Measures of Central Bank
Rationing of Credit
Rationing of credit refers to the restriction of credit availability by the Central Bank. It is a qualitative measure of the Central Bank. The Central Bank may impose restrictions on the amount of credit that a commercial bank can lend to its customers. This is done to regulate the flow of credit and to prevent the economy from overheating.
Quantitative Measures of Central Bank
Bank Rate
Bank rate is the rate at which the Central Bank lends money to commercial banks. It is a quantitative measure of the Central Bank. The Central Bank uses the bank rate to control the money supply in the economy. An increase in the bank rate leads to a decrease in the money supply, and a decrease in the bank rate leads to an increase in the money supply.
Open Market Operations
Open market operations refer to the buying and selling of government securities by the Central Bank in the open market. It is a quantitative measure of the Central Bank. The Central Bank uses open market operations to control the money supply in the economy. If the Central Bank wants to decrease the money supply, it sells government securities in the open market, and if it wants to increase the money supply, it buys government securities in the open market.
Variable Reserve Ratios
Variable reserve ratios refer to the percentage of deposits that commercial banks are required to hold with the Central Bank. It is a quantitative measure of the Central Bank. The Central Bank uses variable reserve ratios to regulate the money supply in the economy. If the Central Bank wants to decrease the money supply, it increases the reserve ratio, and if it wants to increase the money supply, it decreases the reserve ratio.
Rationing of Credit
Rationing of credit refers to the restriction of credit availability by the Central Bank. It is a qualitative measure of the Central Bank. The Central Bank may impose restrictions on the amount of credit that a commercial bank can lend to its customers. This is done to regulate the flow of credit and to prevent the economy from overheating.
Quantitative Measures of Central Bank
Bank Rate
Bank rate is the rate at which the Central Bank lends money to commercial banks. It is a quantitative measure of the Central Bank. The Central Bank uses the bank rate to control the money supply in the economy. An increase in the bank rate leads to a decrease in the money supply, and a decrease in the bank rate leads to an increase in the money supply.
Open Market Operations
Open market operations refer to the buying and selling of government securities by the Central Bank in the open market. It is a quantitative measure of the Central Bank. The Central Bank uses open market operations to control the money supply in the economy. If the Central Bank wants to decrease the money supply, it sells government securities in the open market, and if it wants to increase the money supply, it buys government securities in the open market.
Variable Reserve Ratios
Variable reserve ratios refer to the percentage of deposits that commercial banks are required to hold with the Central Bank. It is a quantitative measure of the Central Bank. The Central Bank uses variable reserve ratios to regulate the money supply in the economy. If the Central Bank wants to decrease the money supply, it increases the reserve ratio, and if it wants to increase the money supply, it decreases the reserve ratio.
Directions: Use the table below to answer the question.
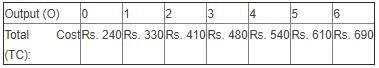 Q. The marginal cost of the sixth unit of output is
Q. The marginal cost of the sixth unit of output is- a)Rs. 133
- b)Rs. 75
- c)Rs. 80
- d)Rs. 450
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Use the table below to answer the question.


Q. The marginal cost of the sixth unit of output is
a)
Rs. 133
b)
Rs. 75
c)
Rs. 80
d)
Rs. 450

|
Lekshmi Mehta answered |
Correct Answer :- c
Explanation : In the above table,
MC = 690 - 610 = 80.
Which of the following is true about monopolistic competition?- a)AR < MR
- b)AR > MR
- c)AR = MR
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true about monopolistic competition?
a)
AR < MR
b)
AR > MR
c)
AR = MR
d)
None of these
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Answer: BExplanation:In monopolistic competition, the following is true:- AR > MR (Average Revenue is greater than Marginal Revenue)This situation occurs due to the following reasons:
- Downward Sloping Demand Curve: In monopolistic competition, there is a downward sloping demand curve. This means that in order to sell more units of a product, the firm has to lower the price. This results in a decrease in marginal revenue.
- Product Differentiation: Firms in monopolistic competition differentiate their products from their competitors'. This differentiation allows firms to have some degree of market power and charge a higher price than their marginal cost, resulting in a higher average revenue.
- Price Elasticity of Demand: In monopolistic competition, the demand for a firm's product is relatively elastic due to the presence of close substitutes. This means that a decrease in price leads to a proportionately larger increase in quantity demanded, resulting in a lower marginal revenue.
A discount store has a special offer on CDs. It reduces their price from Rs. 150 to Rs. 100. Suppose the store manager observes that the quantity demanded increases from 700 CDs to 1,300 CDs. What is the price elasticity of demand for CDs?(use arc elasticity)- a).8
- b)1.0
- c)1.25
- d)1.50
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A discount store has a special offer on CDs. It reduces their price from Rs. 150 to Rs. 100. Suppose the store manager observes that the quantity demanded increases from 700 CDs to 1,300 CDs. What is the price elasticity of demand for CDs?(use arc elasticity)
a)
.8
b)
1.0
c)
1.25
d)
1.50

|
Hrishikesh Mukherjee answered |
To calculate the price elasticity of demand using the arc elasticity formula, we need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Calculate the percentage change in quantity demanded.
Percentage change in quantity demanded = ((New quantity demanded - Old quantity demanded) / ((New quantity demanded + Old quantity demanded) / 2)) * 100
Given that the old quantity demanded is 700 CDs and the new quantity demanded is 1,300 CDs:
Percentage change in quantity demanded = ((1,300 - 700) / ((1,300 + 700) / 2)) * 100
Percentage change in quantity demanded = (600 / 1,000) * 100
Percentage change in quantity demanded = 60%
Step 2: Calculate the percentage change in price.
Percentage change in price = ((New price - Old price) / ((New price + Old price) / 2)) * 100
Given that the old price is Rs. 150 and the new price is Rs. 100:
Percentage change in price = ((100 - 150) / ((100 + 150) / 2)) * 100
Percentage change in price = (-50 / 125) * 100
Percentage change in price = -40%
Step 3: Calculate the price elasticity of demand.
Price elasticity of demand = (Percentage change in quantity demanded) / (Percentage change in price)
Price elasticity of demand = 60% / -40%
Price elasticity of demand = -1.5
Since price elasticity of demand is negative, we take the absolute value to get a positive elasticity value.
Price elasticity of demand = |-1.5| = 1.5
Therefore, the price elasticity of demand for CDs is 1.5.
The correct answer is option D) 1.50.
Step 1: Calculate the percentage change in quantity demanded.
Percentage change in quantity demanded = ((New quantity demanded - Old quantity demanded) / ((New quantity demanded + Old quantity demanded) / 2)) * 100
Given that the old quantity demanded is 700 CDs and the new quantity demanded is 1,300 CDs:
Percentage change in quantity demanded = ((1,300 - 700) / ((1,300 + 700) / 2)) * 100
Percentage change in quantity demanded = (600 / 1,000) * 100
Percentage change in quantity demanded = 60%
Step 2: Calculate the percentage change in price.
Percentage change in price = ((New price - Old price) / ((New price + Old price) / 2)) * 100
Given that the old price is Rs. 150 and the new price is Rs. 100:
Percentage change in price = ((100 - 150) / ((100 + 150) / 2)) * 100
Percentage change in price = (-50 / 125) * 100
Percentage change in price = -40%
Step 3: Calculate the price elasticity of demand.
Price elasticity of demand = (Percentage change in quantity demanded) / (Percentage change in price)
Price elasticity of demand = 60% / -40%
Price elasticity of demand = -1.5
Since price elasticity of demand is negative, we take the absolute value to get a positive elasticity value.
Price elasticity of demand = |-1.5| = 1.5
Therefore, the price elasticity of demand for CDs is 1.5.
The correct answer is option D) 1.50.
Which of the following concepts of budget deficit has become practically redundant in India?- a)Fiscal deficit
- b)Budgetary deficit
- c)Primary deficit
- d)Revenue deficit
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following concepts of budget deficit has become practically redundant in India?
a)
Fiscal deficit
b)
Budgetary deficit
c)
Primary deficit
d)
Revenue deficit

|
Anand Dasgupta answered |
Concepts of Budget Deficit in India
Budget deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue. In India, there are four concepts of budget deficit, which are as follows:
1. Fiscal Deficit:
Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue, excluding borrowings. In other words, it is the amount of money that the government needs to borrow to meet its expenditure. Fiscal deficit is an important indicator of the government's borrowing requirements and its ability to repay debts. It is the most widely used concept of budget deficit in India.
2. Budgetary Deficit:
Budgetary deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue, including borrowings. It is the amount of money that the government needs to borrow to meet its expenditure. Budgetary deficit was used in the past as the primary indicator of budget deficit in India.
3. Primary Deficit:
Primary deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue, excluding interest payments on past borrowings. It is used to measure the government's ability to repay debts without taking on new loans. Primary deficit is an important indicator of the government's fiscal discipline.
4. Revenue Deficit:
Revenue deficit is the difference between the government's revenue expenditure and its revenue receipts. It indicates that the government is not able to meet its day-to-day expenses from its own revenue sources and needs to borrow money for the same.
Redundant Concept of Budget Deficit in India
Among the four concepts of budget deficit in India, the concept of budgetary deficit has become practically redundant. This is because budgetary deficit includes borrowings, which are already included in fiscal deficit. Therefore, budgetary deficit does not provide any additional information beyond fiscal deficit. As a result, the government of India stopped using budgetary deficit as a measure of budget deficit in 2017-18 budget.
Budget deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue. In India, there are four concepts of budget deficit, which are as follows:
1. Fiscal Deficit:
Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue, excluding borrowings. In other words, it is the amount of money that the government needs to borrow to meet its expenditure. Fiscal deficit is an important indicator of the government's borrowing requirements and its ability to repay debts. It is the most widely used concept of budget deficit in India.
2. Budgetary Deficit:
Budgetary deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue, including borrowings. It is the amount of money that the government needs to borrow to meet its expenditure. Budgetary deficit was used in the past as the primary indicator of budget deficit in India.
3. Primary Deficit:
Primary deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue, excluding interest payments on past borrowings. It is used to measure the government's ability to repay debts without taking on new loans. Primary deficit is an important indicator of the government's fiscal discipline.
4. Revenue Deficit:
Revenue deficit is the difference between the government's revenue expenditure and its revenue receipts. It indicates that the government is not able to meet its day-to-day expenses from its own revenue sources and needs to borrow money for the same.
Redundant Concept of Budget Deficit in India
Among the four concepts of budget deficit in India, the concept of budgetary deficit has become practically redundant. This is because budgetary deficit includes borrowings, which are already included in fiscal deficit. Therefore, budgetary deficit does not provide any additional information beyond fiscal deficit. As a result, the government of India stopped using budgetary deficit as a measure of budget deficit in 2017-18 budget.
The demand of a product at the rate of 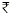 10 is 100 units. When the rate is decreased to
10 is 100 units. When the rate is decreased to 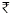 8 per unit, the demand rises to 130 units. What is the elasticity of demand according to the total expenditure method?
8 per unit, the demand rises to 130 units. What is the elasticity of demand according to the total expenditure method?- a)Unitary
- b)Less than unitary
- c)More than unitary
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The demand of a product at the rate of 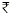 10 is 100 units. When the rate is decreased to
10 is 100 units. When the rate is decreased to 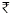 8 per unit, the demand rises to 130 units. What is the elasticity of demand according to the total expenditure method?
8 per unit, the demand rises to 130 units. What is the elasticity of demand according to the total expenditure method?
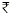 10 is 100 units. When the rate is decreased to
10 is 100 units. When the rate is decreased to 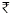 8 per unit, the demand rises to 130 units. What is the elasticity of demand according to the total expenditure method?
8 per unit, the demand rises to 130 units. What is the elasticity of demand according to the total expenditure method?a)
Unitary
b)
Less than unitary
c)
More than unitary
d)
None of these

|
Freedom Institute answered |
- The total expenditure method analyzes elasticity by comparing changes in total revenue (price × quantity) when price changes.
- Initially: (10 times 100 = 1000).
- New scenario: (8 times 130 = 1040).
- Total revenue increased from 1000 to 1040 when the price decreased, indicating demand is elastic.
- Elasticity greater than one implies consumers' demand is highly responsive to price changes.
- Therefore, the elasticity of demand is more than unitary, thus the correct answer is C: More than unitary.
- Initially: (10 times 100 = 1000).
- New scenario: (8 times 130 = 1040).
- Total revenue increased from 1000 to 1040 when the price decreased, indicating demand is elastic.
- Elasticity greater than one implies consumers' demand is highly responsive to price changes.
- Therefore, the elasticity of demand is more than unitary, thus the correct answer is C: More than unitary.
Which of the following costs can never be zero?- a)Variable
- b)Fixed
- c)Prime
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following costs can never be zero?
a)
Variable
b)
Fixed
c)
Prime
d)
All of these

|
Ronak Kothari answered |
B ) fixed cost is the cost that can never be zero, we can understand it by the example:
Suppose if u are a manufacturer and u had purchased a land and on that u r producing a good and every year u have to a pay a property tax for that land and it doesn't how much quantities of goods u r producing u have to property tax whether u produce 1 good or 100 goods u have to pay the cost and If u don't even produce a good still u have to pay the cost and these types of cost which u have pay no matter what are know as Fixed cost and these Fixed cost can never be zero
Suppose if u are a manufacturer and u had purchased a land and on that u r producing a good and every year u have to a pay a property tax for that land and it doesn't how much quantities of goods u r producing u have to property tax whether u produce 1 good or 100 goods u have to pay the cost and If u don't even produce a good still u have to pay the cost and these types of cost which u have pay no matter what are know as Fixed cost and these Fixed cost can never be zero
The elasticity of demand for perishable goods such as milk, vegetables etc. is generally- a)perfectly elastic
- b)relatively elastic
- c)relatively inelastic
- d)zero elastic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The elasticity of demand for perishable goods such as milk, vegetables etc. is generally
a)
perfectly elastic
b)
relatively elastic
c)
relatively inelastic
d)
zero elastic

|
Arka Kaur answered |
The Elasticity of Demand for Perishable Goods
The elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good or service to changes in its price. The elasticity of demand for perishable goods such as milk, vegetables, and fruits is generally relatively inelastic, which means that the quantity demanded does not change significantly when the price changes.
Reasons for Relatively Inelastic Demand for Perishable Goods
1. Necessity: Perishable goods are often considered essential items that consumers need to buy regardless of the price. For example, people need to buy milk, fruits, and vegetables to meet their nutritional needs.
2. Limited Substitutes: Perishable goods often have limited substitutes, especially in the short term. For example, if the price of milk increases, consumers may not be able to switch to other beverages like juice or soda immediately.
3. Time Constraint: Perishable goods have a limited shelf life, and consumers need to consume them before they spoil. Therefore, consumers may not have the luxury of waiting for the price to decrease before making a purchase.
Implications of Relatively Inelastic Demand for Perishable Goods
1. Price Changes: Producers of perishable goods have limited flexibility in increasing or decreasing prices because it may not significantly affect the quantity demanded.
2. Supply Chain Management: Producers of perishable goods need to manage their supply chain efficiently to reduce spoilage and waste. They need to ensure that the right quantity of goods is produced, transported, and stored to meet consumer demand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the elasticity of demand for perishable goods is generally relatively inelastic due to their necessity, limited substitutes, and time constraint. This has implications for pricing and supply chain management for producers of perishable goods.
The elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good or service to changes in its price. The elasticity of demand for perishable goods such as milk, vegetables, and fruits is generally relatively inelastic, which means that the quantity demanded does not change significantly when the price changes.
Reasons for Relatively Inelastic Demand for Perishable Goods
1. Necessity: Perishable goods are often considered essential items that consumers need to buy regardless of the price. For example, people need to buy milk, fruits, and vegetables to meet their nutritional needs.
2. Limited Substitutes: Perishable goods often have limited substitutes, especially in the short term. For example, if the price of milk increases, consumers may not be able to switch to other beverages like juice or soda immediately.
3. Time Constraint: Perishable goods have a limited shelf life, and consumers need to consume them before they spoil. Therefore, consumers may not have the luxury of waiting for the price to decrease before making a purchase.
Implications of Relatively Inelastic Demand for Perishable Goods
1. Price Changes: Producers of perishable goods have limited flexibility in increasing or decreasing prices because it may not significantly affect the quantity demanded.
2. Supply Chain Management: Producers of perishable goods need to manage their supply chain efficiently to reduce spoilage and waste. They need to ensure that the right quantity of goods is produced, transported, and stored to meet consumer demand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the elasticity of demand for perishable goods is generally relatively inelastic due to their necessity, limited substitutes, and time constraint. This has implications for pricing and supply chain management for producers of perishable goods.
The quantitative measures by the Central Bank are also known as
- a)qualitative measures
- b)general measures
- c)quota measures
- d)selective measures
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The quantitative measures by the Central Bank are also known as
a)
qualitative measures
b)
general measures
c)
quota measures
d)
selective measures

|
Moumita Bajaj answered |
Correct Answer :- a,d
Explanation : The methods used by the central bank to regulate the flows of credit into particular directions of the economy are called qualitative or selective methods of credit control. Unlike the quantitative methods, which affect the total volume of credit, the qualitative methods affect the types of credit, extended by the commercial banks; they affect the composition rather than the size of credit in the economy.
Which of the following industries has been excluded from the list of industries reserved for public sector?- a)Atomic energy
- b)Atomic minerals
- c)Railways
- d)Defense production
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following industries has been excluded from the list of industries reserved for public sector?
a)
Atomic energy
b)
Atomic minerals
c)
Railways
d)
Defense production

|
Lakshmi Kaur answered |
**Explanation:**
The list of industries reserved for the public sector in India is mentioned in the Industrial Policy Resolution, 1956. These industries are considered to be of strategic importance and are intended to be owned and operated by the government. However, over the years, there have been changes and certain industries have been excluded from this list.
The correct answer to the given question is option 'D' - Defense production. Defense production is no longer reserved for the public sector and can also be undertaken by private companies.
**Reason for Exclusion:**
The decision to exclude defense production from the list of industries reserved for the public sector was taken to encourage private sector participation, promote competition, and enhance efficiency and innovation in the defense industry. This move was aimed at attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) in defense manufacturing, modernizing the defense forces, and reducing the country's dependency on imports for defense equipment.
**Impact of the Decision:**
The exclusion of defense production from the list of reserved industries has led to the establishment of joint ventures, collaborations, and partnerships between Indian and foreign companies in the defense sector. This has resulted in the transfer of technology, knowledge sharing, and increased indigenous defense production capabilities.
Private companies are now able to participate in defense tenders, bid for defense contracts, and contribute to the development and production of defense equipment. This has not only boosted the growth of the private sector but has also created opportunities for employment and skill development in the defense industry.
The decision to allow private sector participation in defense production has also had a positive impact on the country's defense preparedness. It has led to the development and production of advanced defense equipment, weapons systems, and technology, thereby strengthening the country's defense capabilities.
In conclusion, defense production has been excluded from the list of industries reserved for the public sector in order to promote private sector participation, encourage competition, attract foreign investment, and enhance the country's defense preparedness.
The list of industries reserved for the public sector in India is mentioned in the Industrial Policy Resolution, 1956. These industries are considered to be of strategic importance and are intended to be owned and operated by the government. However, over the years, there have been changes and certain industries have been excluded from this list.
The correct answer to the given question is option 'D' - Defense production. Defense production is no longer reserved for the public sector and can also be undertaken by private companies.
**Reason for Exclusion:**
The decision to exclude defense production from the list of industries reserved for the public sector was taken to encourage private sector participation, promote competition, and enhance efficiency and innovation in the defense industry. This move was aimed at attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) in defense manufacturing, modernizing the defense forces, and reducing the country's dependency on imports for defense equipment.
**Impact of the Decision:**
The exclusion of defense production from the list of reserved industries has led to the establishment of joint ventures, collaborations, and partnerships between Indian and foreign companies in the defense sector. This has resulted in the transfer of technology, knowledge sharing, and increased indigenous defense production capabilities.
Private companies are now able to participate in defense tenders, bid for defense contracts, and contribute to the development and production of defense equipment. This has not only boosted the growth of the private sector but has also created opportunities for employment and skill development in the defense industry.
The decision to allow private sector participation in defense production has also had a positive impact on the country's defense preparedness. It has led to the development and production of advanced defense equipment, weapons systems, and technology, thereby strengthening the country's defense capabilities.
In conclusion, defense production has been excluded from the list of industries reserved for the public sector in order to promote private sector participation, encourage competition, attract foreign investment, and enhance the country's defense preparedness.
A tabular statement of price-quantity relationship is known as- a)demand
- b)demand curve
- c)demand schedule
- d)law of demand
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A tabular statement of price-quantity relationship is known as
a)
demand
b)
demand curve
c)
demand schedule
d)
law of demand

|
Freedom Institute answered |
The correct answer is C: Demand Schedule.Explanation:A demand schedule is a tabular statement that represents the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded by consumers. It is a way to display the information in a structured and organized manner. A demand schedule typically consists of:1. Price column: This column lists the various prices of a specific good or service. - The prices are usually listed in descending order, showing the highest price at the top and the lowest price at the bottom.2. Quantity demanded column: This column lists the corresponding quantities of the good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at each given price level. - The quantity demanded usually decreases as the price increases, which demonstrates the law of demand.A demand schedule can be used to create a demand curve, which is a graphical representation of the price-quantity relationship. The demand curve also demonstrates the law of demand, which states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa, all other factors remaining constant.
Directions: Use the table to answer the question.
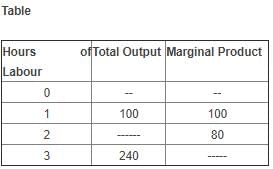 Q. What is the average product of the first three hours of labour?
Q. What is the average product of the first three hours of labour?- a)60
- b)80
- c)100
- d)240
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Use the table to answer the question.


Q. What is the average product of the first three hours of labour?
a)
60
b)
80
c)
100
d)
240
|
|
Lakshmi Sadhika Nagavara answered |
Answer is 80.Bcoz in 2hrs of labour TP is 160 bcoz mp is 80 we know MP=TP/hrs of labor
80=x/2 then TP=160
At 3hrs of labour
AP=TPn-TPn-1=240-160=80
80=x/2 then TP=160
At 3hrs of labour
AP=TPn-TPn-1=240-160=80
Marginal revenue will be negative if elasticity of demand is- a)less than one
- b)more than one
- c)equal to one
- d)equal to zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Marginal revenue will be negative if elasticity of demand is
a)
less than one
b)
more than one
c)
equal to one
d)
equal to zero

|
Mrinalini Iyer answered |
**Explanation:**
Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue that occurs when one additional unit of a product is sold. It is calculated by dividing the change in total revenue by the change in the quantity sold.
In order to understand why marginal revenue will be negative if elasticity of demand is less than one, we need to understand the concept of elasticity of demand.
**Elasticity of Demand:**
Elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
Elasticity of demand can be categorized into three types:
1. Elastic demand: If the absolute value of elasticity of demand is greater than 1, then demand is said to be elastic. This means that a change in price will result in a relatively larger change in quantity demanded. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 20%, the elasticity of demand would be -2.
2. Inelastic demand: If the absolute value of elasticity of demand is less than 1, then demand is said to be inelastic. This means that a change in price will result in a relatively smaller change in quantity demanded. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 5%, the elasticity of demand would be -0.5.
3. Unitary elastic demand: If the absolute value of elasticity of demand is equal to 1, then demand is said to be unitary elastic. This means that a change in price will result in an equal percentage change in quantity demanded. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 10%, the elasticity of demand would be -1.
**Impact on Marginal Revenue:**
The relationship between marginal revenue and elasticity of demand can be understood using the following formula:
Marginal Revenue = Price * (1 + 1/Elasticity of Demand)
Since elasticity of demand is a negative value, the marginal revenue will be positive if elasticity of demand is greater than 1 (elastic demand) and negative if elasticity of demand is less than 1 (inelastic demand).
This can be explained as follows:
- When demand is elastic (elasticity of demand > 1), a decrease in price will result in a relatively larger increase in quantity demanded. As a result, the change in total revenue will be positive, leading to a positive marginal revenue.
- When demand is inelastic (elasticity of demand < 1),="" a="" decrease="" in="" price="" will="" result="" in="" a="" relatively="" smaller="" increase="" in="" quantity="" demanded.="" as="" a="" result,="" the="" change="" in="" total="" revenue="" will="" be="" negative,="" leading="" to="" a="" negative="" marginal="" />
Therefore, if the elasticity of demand is less than one, the marginal revenue will be negative. This is because a decrease in price will lead to a decrease in total revenue, resulting in a negative change in total revenue.
Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue that occurs when one additional unit of a product is sold. It is calculated by dividing the change in total revenue by the change in the quantity sold.
In order to understand why marginal revenue will be negative if elasticity of demand is less than one, we need to understand the concept of elasticity of demand.
**Elasticity of Demand:**
Elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
Elasticity of demand can be categorized into three types:
1. Elastic demand: If the absolute value of elasticity of demand is greater than 1, then demand is said to be elastic. This means that a change in price will result in a relatively larger change in quantity demanded. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 20%, the elasticity of demand would be -2.
2. Inelastic demand: If the absolute value of elasticity of demand is less than 1, then demand is said to be inelastic. This means that a change in price will result in a relatively smaller change in quantity demanded. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 5%, the elasticity of demand would be -0.5.
3. Unitary elastic demand: If the absolute value of elasticity of demand is equal to 1, then demand is said to be unitary elastic. This means that a change in price will result in an equal percentage change in quantity demanded. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 10%, the elasticity of demand would be -1.
**Impact on Marginal Revenue:**
The relationship between marginal revenue and elasticity of demand can be understood using the following formula:
Marginal Revenue = Price * (1 + 1/Elasticity of Demand)
Since elasticity of demand is a negative value, the marginal revenue will be positive if elasticity of demand is greater than 1 (elastic demand) and negative if elasticity of demand is less than 1 (inelastic demand).
This can be explained as follows:
- When demand is elastic (elasticity of demand > 1), a decrease in price will result in a relatively larger increase in quantity demanded. As a result, the change in total revenue will be positive, leading to a positive marginal revenue.
- When demand is inelastic (elasticity of demand < 1),="" a="" decrease="" in="" price="" will="" result="" in="" a="" relatively="" smaller="" increase="" in="" quantity="" demanded.="" as="" a="" result,="" the="" change="" in="" total="" revenue="" will="" be="" negative,="" leading="" to="" a="" negative="" marginal="" />
Therefore, if the elasticity of demand is less than one, the marginal revenue will be negative. This is because a decrease in price will lead to a decrease in total revenue, resulting in a negative change in total revenue.
The period of the eleventh five year plan is/was - a)2002-2007
- b)2004-2009
- c)2007-2012
- d)2008-2013
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The period of the eleventh five year plan is/was
a)
2002-2007
b)
2004-2009
c)
2007-2012
d)
2008-2013

|
Aman Chaudhary answered |
The Period of the Eleventh Five Year Plan is/was 2007-2012
The Eleventh Five Year Plan in India was implemented by the Planning Commission, which is a body that formulates and implements five-year plans for the country's economic development. The plan period for the Eleventh Five Year Plan was from 2007 to 2012. Let's understand the reasons behind this answer in detail.
Introduction:
The five-year plans in India are comprehensive development blueprints that outline the country's economic and social priorities over a specific period of five years. These plans are designed to promote balanced regional development, reduce poverty, and achieve sustainable economic growth. The Eleventh Five Year Plan was no exception.
The Eleventh Five Year Plan:
The Eleventh Five Year Plan was implemented from 2007 to 2012. It aimed to achieve a high growth rate, inclusive development, and a reduction in poverty and unemployment. Some of the key objectives of this plan were:
1. Inclusive Growth: The Eleventh Five Year Plan aimed to ensure inclusive growth by focusing on sectors such as agriculture, rural development, health, education, and infrastructure development. It aimed to reduce regional disparities and promote social equity.
2. Infrastructure Development: The plan emphasized the need for infrastructure development in areas such as power, roads, railways, and telecommunications. The aim was to create a robust infrastructure network that would support economic growth and improve the quality of life for the people.
3. Human Resource Development: The plan recognized the importance of investing in human capital for sustainable development. It focused on improving the quality of education and healthcare services, enhancing skill development, and promoting employment generation.
4. Environmental Sustainability: The Eleventh Five Year Plan emphasized the need for sustainable development and environmental conservation. It aimed to promote renewable energy sources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and ensure the efficient use of resources.
5. Public-Private Partnerships: The plan encouraged public-private partnerships to mobilize resources and promote private sector participation in infrastructure development and other sectors.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the period of the Eleventh Five Year Plan in India was from 2007 to 2012. This plan aimed to achieve high economic growth, inclusive development, and reduction in poverty and unemployment. It focused on sectors such as agriculture, rural development, infrastructure, education, and healthcare. The plan also emphasized the importance of sustainable development and public-private partnerships.
The Eleventh Five Year Plan in India was implemented by the Planning Commission, which is a body that formulates and implements five-year plans for the country's economic development. The plan period for the Eleventh Five Year Plan was from 2007 to 2012. Let's understand the reasons behind this answer in detail.
Introduction:
The five-year plans in India are comprehensive development blueprints that outline the country's economic and social priorities over a specific period of five years. These plans are designed to promote balanced regional development, reduce poverty, and achieve sustainable economic growth. The Eleventh Five Year Plan was no exception.
The Eleventh Five Year Plan:
The Eleventh Five Year Plan was implemented from 2007 to 2012. It aimed to achieve a high growth rate, inclusive development, and a reduction in poverty and unemployment. Some of the key objectives of this plan were:
1. Inclusive Growth: The Eleventh Five Year Plan aimed to ensure inclusive growth by focusing on sectors such as agriculture, rural development, health, education, and infrastructure development. It aimed to reduce regional disparities and promote social equity.
2. Infrastructure Development: The plan emphasized the need for infrastructure development in areas such as power, roads, railways, and telecommunications. The aim was to create a robust infrastructure network that would support economic growth and improve the quality of life for the people.
3. Human Resource Development: The plan recognized the importance of investing in human capital for sustainable development. It focused on improving the quality of education and healthcare services, enhancing skill development, and promoting employment generation.
4. Environmental Sustainability: The Eleventh Five Year Plan emphasized the need for sustainable development and environmental conservation. It aimed to promote renewable energy sources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and ensure the efficient use of resources.
5. Public-Private Partnerships: The plan encouraged public-private partnerships to mobilize resources and promote private sector participation in infrastructure development and other sectors.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the period of the Eleventh Five Year Plan in India was from 2007 to 2012. This plan aimed to achieve high economic growth, inclusive development, and reduction in poverty and unemployment. It focused on sectors such as agriculture, rural development, infrastructure, education, and healthcare. The plan also emphasized the importance of sustainable development and public-private partnerships.
Directions: In Econoville, there is one grocery shop, Ecoconvenience. It used to sell fresh milk at Rs. 20 per litre, at which price 400 litres of milk was sold per month. After some time, the price was raised to Rs. 30 per litre.Following the price rise:
Only 200 litres of milk was sold every month.
The number of boxes of cereal customers bought went down from 280 to 240.
The number of packets of powered milk customers bought went up from 90 to 220 per month.The cross elasticity of monthly demand for cereal when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30 is equal to- a)-0.38
- b)+0.25
- c)-0.19
- d)+0.38
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In Econoville, there is one grocery shop, Ecoconvenience. It used to sell fresh milk at Rs. 20 per litre, at which price 400 litres of milk was sold per month. After some time, the price was raised to Rs. 30 per litre.
Following the price rise:
Only 200 litres of milk was sold every month.
The number of boxes of cereal customers bought went down from 280 to 240.
The number of packets of powered milk customers bought went up from 90 to 220 per month.
Only 200 litres of milk was sold every month.
The number of boxes of cereal customers bought went down from 280 to 240.
The number of packets of powered milk customers bought went up from 90 to 220 per month.
The cross elasticity of monthly demand for cereal when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30 is equal to
a)
-0.38
b)
+0.25
c)
-0.19
d)
+0.38

|
Sameer Basu answered |
Cross Elasticity of Demand
The cross elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand for one product to a change in the price of another product. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded of one product divided by the percentage change in price of another product.
Calculation
To calculate the cross elasticity of demand for cereal when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30, we need to use the following formula:
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded of Cereal) / (Percentage Change in Price of Fresh Milk)
Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded of Cereal = ((New Quantity Demanded - Old Quantity Demanded) / Old Quantity Demanded) x 100
= ((240 - 280) / 280) x 100
= -14.29%
Percentage Change in Price of Fresh Milk = ((New Price - Old Price) / Old Price) x 100
= ((30 - 20) / 20) x 100
= 50%
Substituting the values in the formula, we get:
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (-14.29% / 50%)
= -0.38
Therefore, the cross elasticity of demand for cereal when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30 is -0.38. This implies that cereal is an inferior good as the decrease in the demand for cereal is proportionately more than the increase in the price of fresh milk.
The cross elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand for one product to a change in the price of another product. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded of one product divided by the percentage change in price of another product.
Calculation
To calculate the cross elasticity of demand for cereal when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30, we need to use the following formula:
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded of Cereal) / (Percentage Change in Price of Fresh Milk)
Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded of Cereal = ((New Quantity Demanded - Old Quantity Demanded) / Old Quantity Demanded) x 100
= ((240 - 280) / 280) x 100
= -14.29%
Percentage Change in Price of Fresh Milk = ((New Price - Old Price) / Old Price) x 100
= ((30 - 20) / 20) x 100
= 50%
Substituting the values in the formula, we get:
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (-14.29% / 50%)
= -0.38
Therefore, the cross elasticity of demand for cereal when the price of fresh milk increases from Rs. 20 to Rs. 30 is -0.38. This implies that cereal is an inferior good as the decrease in the demand for cereal is proportionately more than the increase in the price of fresh milk.
In order to control credit- a)CRR should be increased and bank rate should be decreased
- b)CRR should be reduced and bank rate should be reduced
- c)CRR should be increased and bank rate should be increased
- d)CRR should be reduced and bank rate should be increased
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In order to control credit
a)
CRR should be increased and bank rate should be decreased
b)
CRR should be reduced and bank rate should be reduced
c)
CRR should be increased and bank rate should be increased
d)
CRR should be reduced and bank rate should be increased

|
Moumita Bajaj answered |
Understanding Credit Control
Credit control is a crucial part of monetary policy, primarily managed by a central bank, aimed at regulating the money supply and ensuring financial stability.
Key Terms Explained
- CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio): This is the percentage of a bank's total deposits that must be maintained as reserves with the central bank. A higher CRR reduces the available funds for banks to lend, thus tightening credit.
- Bank Rate: This is the rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks. An increase in the bank rate raises the cost of borrowing for banks, which is then passed on to consumers and businesses.
Why Option C is Correct
- Increased CRR: By increasing the CRR, the central bank restricts the amount of money that banks can use for lending. This leads to a contraction in credit availability, thereby controlling inflation and excessive borrowing.
- Increased Bank Rate: Raising the bank rate discourages banks from borrowing from the central bank. Consequently, banks will raise their lending rates to consumers, further reducing the demand for loans.
Combined Effect
- When both CRR and bank rate are increased, banks are compelled to reduce their lending activities. This effectively curtails credit growth in the economy, helping to stabilize prices and maintain economic equilibrium.
Conclusion
Thus, increasing CRR and the bank rate (Option C) is a robust strategy for controlling credit in the economy, ensuring that inflation is kept in check and financial stability is achieved.
Credit control is a crucial part of monetary policy, primarily managed by a central bank, aimed at regulating the money supply and ensuring financial stability.
Key Terms Explained
- CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio): This is the percentage of a bank's total deposits that must be maintained as reserves with the central bank. A higher CRR reduces the available funds for banks to lend, thus tightening credit.
- Bank Rate: This is the rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks. An increase in the bank rate raises the cost of borrowing for banks, which is then passed on to consumers and businesses.
Why Option C is Correct
- Increased CRR: By increasing the CRR, the central bank restricts the amount of money that banks can use for lending. This leads to a contraction in credit availability, thereby controlling inflation and excessive borrowing.
- Increased Bank Rate: Raising the bank rate discourages banks from borrowing from the central bank. Consequently, banks will raise their lending rates to consumers, further reducing the demand for loans.
Combined Effect
- When both CRR and bank rate are increased, banks are compelled to reduce their lending activities. This effectively curtails credit growth in the economy, helping to stabilize prices and maintain economic equilibrium.
Conclusion
Thus, increasing CRR and the bank rate (Option C) is a robust strategy for controlling credit in the economy, ensuring that inflation is kept in check and financial stability is achieved.
Which of the following is/are implicit cost(s) of production?- a)Wages of the labour
- b)Charges for electricity
- c)Interest on owned money capital
- d)Payment for raw material
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are implicit cost(s) of production?
a)
Wages of the labour
b)
Charges for electricity
c)
Interest on owned money capital
d)
Payment for raw material

|
Niharika Datta answered |
Implicit Costs of Production
Implicit costs are the opportunity costs of using resources in a particular manner. These costs do not involve any actual cash outflows but represent the foregone opportunities or benefits that could have been obtained by using the resources in an alternative way. In the context of production, implicit costs are the costs incurred by a firm when it uses its own resources instead of obtaining them from an external source.
Explanation:
Among the options given, the correct answer is option 'C' - Interest on owned money capital. Here's an explanation of why it is an implicit cost of production:
Definition of Implicit Costs:
Implicit costs are the costs that are not explicitly incurred by a firm but are still considered as costs because they represent the opportunity cost of using resources in a particular manner.
Explanation of Options:
a) Wages of the Labor:
Wages of labor are an explicit cost of production. They represent the actual cash outflows made by the firm to compensate the labor for their services. Therefore, wages of labor are not considered as implicit costs.
b) Charges for Electricity:
Charges for electricity are also an explicit cost of production. They represent the actual cash outflows made by the firm to pay for the electricity used in the production process. Therefore, charges for electricity are not considered as implicit costs.
c) Interest on owned money capital:
Interest on owned money capital is an implicit cost of production. It represents the opportunity cost of using the firm's own money capital in the production process instead of investing it elsewhere. The firm could have earned interest on its money capital if it had invested it in other ventures or financial instruments. Therefore, interest on owned money capital is considered as an implicit cost.
d) Payment for raw material:
Payment for raw material is an explicit cost of production. It represents the actual cash outflows made by the firm to purchase the raw materials used in the production process. Therefore, payment for raw material is not considered as an implicit cost.
Conclusion:
Among the options given, the only implicit cost of production is the interest on owned money capital (option 'C'). Implicit costs represent the opportunity costs of using resources in a particular manner and do not involve any actual cash outflows.
Implicit costs are the opportunity costs of using resources in a particular manner. These costs do not involve any actual cash outflows but represent the foregone opportunities or benefits that could have been obtained by using the resources in an alternative way. In the context of production, implicit costs are the costs incurred by a firm when it uses its own resources instead of obtaining them from an external source.
Explanation:
Among the options given, the correct answer is option 'C' - Interest on owned money capital. Here's an explanation of why it is an implicit cost of production:
Definition of Implicit Costs:
Implicit costs are the costs that are not explicitly incurred by a firm but are still considered as costs because they represent the opportunity cost of using resources in a particular manner.
Explanation of Options:
a) Wages of the Labor:
Wages of labor are an explicit cost of production. They represent the actual cash outflows made by the firm to compensate the labor for their services. Therefore, wages of labor are not considered as implicit costs.
b) Charges for Electricity:
Charges for electricity are also an explicit cost of production. They represent the actual cash outflows made by the firm to pay for the electricity used in the production process. Therefore, charges for electricity are not considered as implicit costs.
c) Interest on owned money capital:
Interest on owned money capital is an implicit cost of production. It represents the opportunity cost of using the firm's own money capital in the production process instead of investing it elsewhere. The firm could have earned interest on its money capital if it had invested it in other ventures or financial instruments. Therefore, interest on owned money capital is considered as an implicit cost.
d) Payment for raw material:
Payment for raw material is an explicit cost of production. It represents the actual cash outflows made by the firm to purchase the raw materials used in the production process. Therefore, payment for raw material is not considered as an implicit cost.
Conclusion:
Among the options given, the only implicit cost of production is the interest on owned money capital (option 'C'). Implicit costs represent the opportunity costs of using resources in a particular manner and do not involve any actual cash outflows.
Which of the following organisations has been concerned with the production and distribution of energy?- a)NTPC
- b)SEBI
- c)MMTC
- d)NHAI
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organisations has been concerned with the production and distribution of energy?
a)
NTPC
b)
SEBI
c)
MMTC
d)
NHAI

|
Sai Kulkarni answered |
NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation Limited) is the correct answer as it is an organization concerned with the production and distribution of energy. Let's understand why NTPC is involved in the energy sector.
NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation Limited):
- NTPC is a government-owned power generation company in India.
- It was established in 1975 with the aim of accelerating the power development in the country.
- NTPC is primarily engaged in generating electricity through various sources such as coal, gas, hydro, solar, and wind.
- The company operates many power plants across the country and has a total installed capacity of over 65,000 MW.
- NTPC is also involved in the transmission and distribution of electricity.
- It plays a crucial role in meeting the energy requirements of various industries, commercial establishments, and households in India.
Explanation:
- NTPC's main objective is to ensure reliable and affordable power supply to the nation.
- The organization utilizes various sources of energy to generate electricity, including coal, which is the primary source of power generation in India.
- NTPC has coal-based power plants in different parts of the country, which produce a significant portion of the total electricity consumed in India.
- The company also focuses on renewable energy sources like solar and wind, in line with the government's push for clean energy.
- NTPC has been actively involved in setting up solar power plants, wind farms, and other renewable energy projects to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote sustainable energy generation.
- Apart from generation, NTPC is also involved in the transmission and distribution of electricity. The company operates a vast network of transmission lines and substations to ensure power reaches the consumers efficiently.
- NTPC's role in the energy sector is crucial for the economic development of the country as it provides a reliable power supply for industrial, commercial, and domestic purposes.
- The organization follows strict environmental norms and invests in technologies to minimize the environmental impact of its operations.
- NTPC also provides training and consultancy services in the field of power generation and management, contributing to the overall growth of the energy sector in India.
Thus, NTPC is the correct option among the given organizations as it is primarily concerned with the production and distribution of energy in India.
NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation Limited):
- NTPC is a government-owned power generation company in India.
- It was established in 1975 with the aim of accelerating the power development in the country.
- NTPC is primarily engaged in generating electricity through various sources such as coal, gas, hydro, solar, and wind.
- The company operates many power plants across the country and has a total installed capacity of over 65,000 MW.
- NTPC is also involved in the transmission and distribution of electricity.
- It plays a crucial role in meeting the energy requirements of various industries, commercial establishments, and households in India.
Explanation:
- NTPC's main objective is to ensure reliable and affordable power supply to the nation.
- The organization utilizes various sources of energy to generate electricity, including coal, which is the primary source of power generation in India.
- NTPC has coal-based power plants in different parts of the country, which produce a significant portion of the total electricity consumed in India.
- The company also focuses on renewable energy sources like solar and wind, in line with the government's push for clean energy.
- NTPC has been actively involved in setting up solar power plants, wind farms, and other renewable energy projects to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote sustainable energy generation.
- Apart from generation, NTPC is also involved in the transmission and distribution of electricity. The company operates a vast network of transmission lines and substations to ensure power reaches the consumers efficiently.
- NTPC's role in the energy sector is crucial for the economic development of the country as it provides a reliable power supply for industrial, commercial, and domestic purposes.
- The organization follows strict environmental norms and invests in technologies to minimize the environmental impact of its operations.
- NTPC also provides training and consultancy services in the field of power generation and management, contributing to the overall growth of the energy sector in India.
Thus, NTPC is the correct option among the given organizations as it is primarily concerned with the production and distribution of energy in India.
Who expressed the view that "Economics should be neutral between ends"?- a)Robbins
- b)Marshall
- c)Pigou
- d)Adam Smith
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who expressed the view that "Economics should be neutral between ends"?
a)
Robbins
b)
Marshall
c)
Pigou
d)
Adam Smith

|
Saumya Khanna answered |
I'm sorry, but your question is incomplete. Please provide more information or context so I can better understand what you are asking.
Which of the following is an example of implicit cost?- a)Interest on bank loan
- b)Rent of building on hire
- c)Tax paid to government
- d)Interest on capital
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of implicit cost?
a)
Interest on bank loan
b)
Rent of building on hire
c)
Tax paid to government
d)
Interest on capital

|
Anu Sen answered |
Correct Answer :- d
Explanation : Implicit cost is the cost of self supplied factors of production. Hence Interest that could have been earned on retained earnings used by the firm to finance expansion is implicit cost.
____________ is the apex bank for agriculture credit.- a)RBI
- b)SIDBI
- c)NABARD
- d)ICICI
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
____________ is the apex bank for agriculture credit.
a)
RBI
b)
SIDBI
c)
NABARD
d)
ICICI

|
Disha Joshi answered |
NABARD, which stands for National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development, is the apex bank for agriculture credit in India. It was established in 1982 with the aim of promoting and developing agriculture and rural sectors in the country. NABARD functions as a development bank, providing financial and developmental support to the agricultural sector.
NABARD performs various functions to fulfill its objective of supporting agriculture and rural development. Some of its key functions include:
1. Refinancing Agricultural Institutions: NABARD provides refinancing facilities to various institutions involved in agricultural lending such as commercial banks, regional rural banks, and cooperative banks. It refinances these institutions for providing credit to farmers and other rural sectors.
2. Rural Infrastructure Development: NABARD plays a crucial role in financing and promoting rural infrastructure development. It provides loans and grants to projects related to irrigation, rural roads, bridges, warehouses, and other rural infrastructure facilities.
3. Development of Rural Financial Institutions: NABARD helps in the development and strengthening of rural financial institutions like cooperative banks and regional rural banks. It provides them with financial assistance, training programs, and technical support to enhance their capacity to serve the rural population.
4. Promotion of Agriculture and Rural Innovation: NABARD promotes agricultural and rural innovation by supporting research and development activities, technology transfer, and adoption of modern farming practices. It also encourages the use of renewable energy and sustainable farming methods.
5. Microfinance and Financial Inclusion: NABARD plays a vital role in promoting microfinance and financial inclusion in rural areas. It supports self-help groups (SHGs) and provides them with financial assistance and capacity-building initiatives to empower rural women and promote entrepreneurship.
In conclusion, NABARD serves as the apex bank for agriculture credit in India. It plays a crucial role in providing financial and developmental support to the agricultural and rural sectors. Through its various functions, NABARD contributes to the overall growth and development of agriculture and rural areas in the country.
Which is the most appropriate market for FMCG?- a)Perfect competition
- b)Oligopoly
- c)Monopoly
- d)Monopolistic competition
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the most appropriate market for FMCG?
a)
Perfect competition
b)
Oligopoly
c)
Monopoly
d)
Monopolistic competition

|
Dipika Kaur answered |
Understanding FMCG Market Structure
The Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) sector primarily operates under a market structure known as monopolistic competition. Here’s why this model is most appropriate:
Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition
- Product Differentiation: FMCG companies offer a wide array of products that, while similar, are differentiated through branding, packaging, and quality. This allows companies to create a niche and build brand loyalty.
- Many Sellers: The market is characterized by a large number of firms competing for market share. Each firm has a relatively small market share, preventing any single entity from dominating the market.
- Freedom of Entry and Exit: New companies can enter the market with relative ease, and existing companies can exit without substantial barriers. This encourages innovation and variety in product offerings.
Consumer Choices and Preferences
- Variety of Options: Consumers have numerous options to choose from, which is a hallmark of monopolistic competition. They can select from different brands and products, each with unique features.
- Price Flexibility: While firms have some control over pricing due to brand differentiation, prices are still influenced by competition. This results in a competitive pricing environment that benefits consumers.
Marketing and Advertising
- Emphasis on Promotion: Companies invest significantly in marketing and advertising to differentiate their products. This strategy is crucial in attracting consumers in a crowded marketplace.
- Brand Loyalty: Successful marketing leads to brand loyalty, where consumers consistently choose a particular brand over others, even if prices vary slightly.
In conclusion, the FMCG market thrives in a monopolistic competition environment, fostering innovation and providing consumers with diverse choices while maintaining competitive pricing structures.
The Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) sector primarily operates under a market structure known as monopolistic competition. Here’s why this model is most appropriate:
Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition
- Product Differentiation: FMCG companies offer a wide array of products that, while similar, are differentiated through branding, packaging, and quality. This allows companies to create a niche and build brand loyalty.
- Many Sellers: The market is characterized by a large number of firms competing for market share. Each firm has a relatively small market share, preventing any single entity from dominating the market.
- Freedom of Entry and Exit: New companies can enter the market with relative ease, and existing companies can exit without substantial barriers. This encourages innovation and variety in product offerings.
Consumer Choices and Preferences
- Variety of Options: Consumers have numerous options to choose from, which is a hallmark of monopolistic competition. They can select from different brands and products, each with unique features.
- Price Flexibility: While firms have some control over pricing due to brand differentiation, prices are still influenced by competition. This results in a competitive pricing environment that benefits consumers.
Marketing and Advertising
- Emphasis on Promotion: Companies invest significantly in marketing and advertising to differentiate their products. This strategy is crucial in attracting consumers in a crowded marketplace.
- Brand Loyalty: Successful marketing leads to brand loyalty, where consumers consistently choose a particular brand over others, even if prices vary slightly.
In conclusion, the FMCG market thrives in a monopolistic competition environment, fostering innovation and providing consumers with diverse choices while maintaining competitive pricing structures.
Which of the following demands has/have a direct relation?- a)Price demand
- b)Income demand
- c)Cross demand
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following demands has/have a direct relation?
a)
Price demand
b)
Income demand
c)
Cross demand
d)
All of these

|
Sahil Malik answered |
Income demand
Income demand refers to the relationship between the quantity demanded of a good and changes in consumer income. It measures how sensitive the demand for a product is to changes in income. When consumer income increases, the demand for normal goods typically also increases. On the other hand, the demand for inferior goods may decrease as consumer income rises.
Price demand
Price demand refers to the relationship between the quantity demanded of a good and changes in its price. It measures how sensitive the demand for a product is to changes in price. Generally, as the price of a product decreases, the quantity demanded increases, and vice versa. This is known as the law of demand.
Cross demand
Cross demand refers to the relationship between the quantity demanded of one good and changes in the price of another good. It measures the degree to which the demand for one good is affected by changes in the price of another good. If two goods are substitutes, an increase in the price of one good will lead to an increase in the demand for the other good. On the other hand, if two goods are complements, an increase in the price of one good will lead to a decrease in the demand for the other good.
Relation between the demands
Income demand, price demand, and cross demand are all different types of demand relationships. While price demand and cross demand are related to changes in price, income demand is related to changes in consumer income.
Direct relation
Among the given options, income demand is the only demand that has a direct relation to the other two demands. Both price demand and cross demand are influenced by changes in consumer income. When income increases, consumers may be willing to pay higher prices for certain goods or may have more disposable income to spend on substitute goods. Therefore, income demand has a direct relation to both price demand and cross demand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'B' - Income demand. It is the only demand that has a direct relation to both price demand and cross demand. Price demand and cross demand are related to changes in price, while income demand is related to changes in consumer income.
Income demand refers to the relationship between the quantity demanded of a good and changes in consumer income. It measures how sensitive the demand for a product is to changes in income. When consumer income increases, the demand for normal goods typically also increases. On the other hand, the demand for inferior goods may decrease as consumer income rises.
Price demand
Price demand refers to the relationship between the quantity demanded of a good and changes in its price. It measures how sensitive the demand for a product is to changes in price. Generally, as the price of a product decreases, the quantity demanded increases, and vice versa. This is known as the law of demand.
Cross demand
Cross demand refers to the relationship between the quantity demanded of one good and changes in the price of another good. It measures the degree to which the demand for one good is affected by changes in the price of another good. If two goods are substitutes, an increase in the price of one good will lead to an increase in the demand for the other good. On the other hand, if two goods are complements, an increase in the price of one good will lead to a decrease in the demand for the other good.
Relation between the demands
Income demand, price demand, and cross demand are all different types of demand relationships. While price demand and cross demand are related to changes in price, income demand is related to changes in consumer income.
Direct relation
Among the given options, income demand is the only demand that has a direct relation to the other two demands. Both price demand and cross demand are influenced by changes in consumer income. When income increases, consumers may be willing to pay higher prices for certain goods or may have more disposable income to spend on substitute goods. Therefore, income demand has a direct relation to both price demand and cross demand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'B' - Income demand. It is the only demand that has a direct relation to both price demand and cross demand. Price demand and cross demand are related to changes in price, while income demand is related to changes in consumer income.
Service sector accounted for nearly ______________ percent of exports (2004-05).- a)10 percent
- b)20 percent
- c)35 percent
- d)80 percent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Service sector accounted for nearly ______________ percent of exports (2004-05).
a)
10 percent
b)
20 percent
c)
35 percent
d)
80 percent

|
Palak Choudhary answered |
Service sector's contribution to exports in India
Introduction:
The service sector has emerged as the major contributor to India's GDP growth in the last decade. It includes sectors such as IT, banking, insurance, tourism, and healthcare, among others. The sector has also played a significant role in India's exports.
Export contribution:
According to the data from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the service sector accounted for nearly 35 percent of India's total exports in 2004-05. It was a significant increase from the earlier years when the contribution was much lower.
Reasons:
There are several reasons for the service sector's increasing contribution to exports in India. One of the primary reasons is the growth of the IT industry. India is considered a hub for IT services, and the sector has been growing at a rapid pace in recent years. Other factors that have contributed to the growth of the service sector include the liberalization of the economy, favorable government policies, and an increase in foreign investments.
Challenges:
The service sector also faces several challenges that need to be addressed. One of the major challenges is the lack of skilled manpower. The industry requires skilled workers with specific skill sets, and there is a shortage of such workers in the country. Another challenge is the lack of infrastructure, particularly in the tourism sector.
Conclusion:
Despite the challenges, the service sector's contribution to India's exports is significant and will continue to grow in the coming years. The government's focus on promoting the sector through various policies and initiatives will further boost its growth and contribution to the economy.
Introduction:
The service sector has emerged as the major contributor to India's GDP growth in the last decade. It includes sectors such as IT, banking, insurance, tourism, and healthcare, among others. The sector has also played a significant role in India's exports.
Export contribution:
According to the data from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the service sector accounted for nearly 35 percent of India's total exports in 2004-05. It was a significant increase from the earlier years when the contribution was much lower.
Reasons:
There are several reasons for the service sector's increasing contribution to exports in India. One of the primary reasons is the growth of the IT industry. India is considered a hub for IT services, and the sector has been growing at a rapid pace in recent years. Other factors that have contributed to the growth of the service sector include the liberalization of the economy, favorable government policies, and an increase in foreign investments.
Challenges:
The service sector also faces several challenges that need to be addressed. One of the major challenges is the lack of skilled manpower. The industry requires skilled workers with specific skill sets, and there is a shortage of such workers in the country. Another challenge is the lack of infrastructure, particularly in the tourism sector.
Conclusion:
Despite the challenges, the service sector's contribution to India's exports is significant and will continue to grow in the coming years. The government's focus on promoting the sector through various policies and initiatives will further boost its growth and contribution to the economy.
Directions: Study the given table and answer the following question.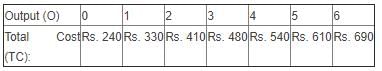 Q. Diminishing marginal returns start to occur between units
Q. Diminishing marginal returns start to occur between units- a)2 and 3 units
- b)3 and 4 units
- c)4 and 5 units
- d)5 and 6 units
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the given table and answer the following question.

Q. Diminishing marginal returns start to occur between units
a)
2 and 3 units
b)
3 and 4 units
c)
4 and 5 units
d)
5 and 6 units

|
Shravani T answered |
Can anyone say the answer for this question?
Who prepares the estimates of the national income in India?- a)RBI
- b)Planning Commission
- c)C.S.O.
- d)Ministry of Commerce
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who prepares the estimates of the national income in India?
a)
RBI
b)
Planning Commission
c)
C.S.O.
d)
Ministry of Commerce

|
Anuj Roy answered |
Estimates of National Income in India
Introduction:
National income is the sum of all the income earned in a country during a given period of time. It is an important measure of economic growth, development and welfare of a country. In India, the Central Statistical Office (CSO) is responsible for preparing the estimates of national income.
Central Statistical Office (CSO):
The Central Statistical Office (CSO) is a government agency under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. It is responsible for the collection, compilation, analysis and dissemination of statistical data related to the economy, social and demographic sectors.
Role in Preparing National Income Estimates:
The CSO prepares estimates of national income in India using the following methods:
1. Production Method:
The production method estimates national income by adding the value of all goods and services produced in the country during a given period of time. The CSO uses this method to estimate the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of India.
2. Income Method:
The income method estimates national income by adding up all the incomes earned by individuals and businesses in the country during a given period of time. The CSO uses this method to estimate the Gross National Income (GNI) of India.
3. Expenditure Method:
The expenditure method estimates national income by adding up all the expenditure made by individuals and businesses in the country during a given period of time. The CSO uses this method to estimate the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of India.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Central Statistical Office (CSO) is responsible for preparing the estimates of national income in India using different methods. These estimates are important in understanding the economic growth, development and welfare of the country.
Introduction:
National income is the sum of all the income earned in a country during a given period of time. It is an important measure of economic growth, development and welfare of a country. In India, the Central Statistical Office (CSO) is responsible for preparing the estimates of national income.
Central Statistical Office (CSO):
The Central Statistical Office (CSO) is a government agency under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. It is responsible for the collection, compilation, analysis and dissemination of statistical data related to the economy, social and demographic sectors.
Role in Preparing National Income Estimates:
The CSO prepares estimates of national income in India using the following methods:
1. Production Method:
The production method estimates national income by adding the value of all goods and services produced in the country during a given period of time. The CSO uses this method to estimate the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of India.
2. Income Method:
The income method estimates national income by adding up all the incomes earned by individuals and businesses in the country during a given period of time. The CSO uses this method to estimate the Gross National Income (GNI) of India.
3. Expenditure Method:
The expenditure method estimates national income by adding up all the expenditure made by individuals and businesses in the country during a given period of time. The CSO uses this method to estimate the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of India.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Central Statistical Office (CSO) is responsible for preparing the estimates of national income in India using different methods. These estimates are important in understanding the economic growth, development and welfare of the country.
Consider the following and decide which, if any, economy is without scarcity- a)the pre-independence Indian economy, where most people were farmers
- b)a mythical economy where everybody is a billionaire
- c)any economy where income is distributed equally among its people
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following and decide which, if any, economy is without scarcity
a)
the pre-independence Indian economy, where most people were farmers
b)
a mythical economy where everybody is a billionaire
c)
any economy where income is distributed equally among its people
d)
None of these

|
Sai Joshi answered |
Introduction:
Scarcity refers to the limited availability of resources in relation to unlimited wants and needs. It is a fundamental concept in economics as it necessitates the allocation of resources to satisfy the most pressing needs. In this context, we will analyze the given options to determine if any economy is without scarcity.
Analysis:
a) The pre-independence Indian economy, where most people were farmers:
In the pre-independence Indian economy, the majority of the population were engaged in agriculture as farmers. While they had access to land and resources for cultivation, scarcity still existed. Farmers faced limitations in terms of land, water, fertilizers, and other inputs necessary for agricultural production. Additionally, they also had limited access to markets and faced challenges in securing fair prices for their produce. Therefore, scarcity was prevalent in the pre-independence Indian economy.
b) A mythical economy where everybody is a billionaire:
In a mythical economy where everybody is a billionaire, scarcity may appear to be eliminated at first glance. However, scarcity is not solely determined by the availability of wealth. It is also influenced by the availability of resources and the allocation of goods and services. Even if everyone is a billionaire, there will still be a limited supply of resources such as land, labor, capital, and natural resources. Moreover, the allocation of goods and services will require choices and trade-offs, as individuals' wants and needs will still surpass the available resources. Therefore, even in such a mythical economy, scarcity would still exist.
c) Any economy where income is distributed equally among its people:
In an economy where income is distributed equally among its people, scarcity would still prevail. While equal distribution of income may contribute to reducing inequality, it does not eliminate the limited availability of resources. Scarce resources such as land, labor, and capital would still need to be allocated efficiently to meet the needs and wants of the population. Moreover, individuals' preferences and demands vary, which would require choices and trade-offs to be made in resource allocation. Consequently, scarcity would persist in any economy, irrespective of income distribution.
Conclusion:
After analyzing the given options, it is evident that none of the economies mentioned are without scarcity. Scarcity arises due to the limited availability of resources relative to unlimited wants and needs. It is a core economic concept that necessitates the allocation of resources to satisfy the most pressing needs. While different economic systems and income distributions can influence the degree of scarcity, it cannot be entirely eliminated.
Scarcity refers to the limited availability of resources in relation to unlimited wants and needs. It is a fundamental concept in economics as it necessitates the allocation of resources to satisfy the most pressing needs. In this context, we will analyze the given options to determine if any economy is without scarcity.
Analysis:
a) The pre-independence Indian economy, where most people were farmers:
In the pre-independence Indian economy, the majority of the population were engaged in agriculture as farmers. While they had access to land and resources for cultivation, scarcity still existed. Farmers faced limitations in terms of land, water, fertilizers, and other inputs necessary for agricultural production. Additionally, they also had limited access to markets and faced challenges in securing fair prices for their produce. Therefore, scarcity was prevalent in the pre-independence Indian economy.
b) A mythical economy where everybody is a billionaire:
In a mythical economy where everybody is a billionaire, scarcity may appear to be eliminated at first glance. However, scarcity is not solely determined by the availability of wealth. It is also influenced by the availability of resources and the allocation of goods and services. Even if everyone is a billionaire, there will still be a limited supply of resources such as land, labor, capital, and natural resources. Moreover, the allocation of goods and services will require choices and trade-offs, as individuals' wants and needs will still surpass the available resources. Therefore, even in such a mythical economy, scarcity would still exist.
c) Any economy where income is distributed equally among its people:
In an economy where income is distributed equally among its people, scarcity would still prevail. While equal distribution of income may contribute to reducing inequality, it does not eliminate the limited availability of resources. Scarce resources such as land, labor, and capital would still need to be allocated efficiently to meet the needs and wants of the population. Moreover, individuals' preferences and demands vary, which would require choices and trade-offs to be made in resource allocation. Consequently, scarcity would persist in any economy, irrespective of income distribution.
Conclusion:
After analyzing the given options, it is evident that none of the economies mentioned are without scarcity. Scarcity arises due to the limited availability of resources relative to unlimited wants and needs. It is a core economic concept that necessitates the allocation of resources to satisfy the most pressing needs. While different economic systems and income distributions can influence the degree of scarcity, it cannot be entirely eliminated.
Chapter doubts & questions for Business Economics Test - Business Economics for CA Foundation 2025 is part of CA Foundation exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Business Economics Test - Business Economics for CA Foundation in English & Hindi are available as part of CA Foundation exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CA Foundation Exam by signing up for free.
Business Economics for CA Foundation
86 videos|200 docs|58 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup

 30,000 and at 10,000 units level is
30,000 and at 10,000 units level is  55000. What will be the per unit variable cost?
55000. What will be the per unit variable cost? 3
3 2.50
2.50 5.50
5.50 2
2