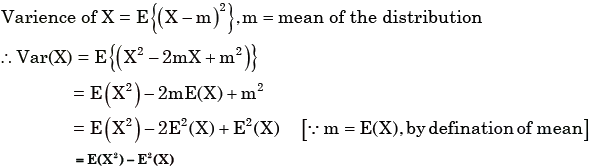All Exams >
Mathematics >
Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics >
All Questions
All questions of Probability for Mathematics Exam
The probability of a defective piece produced in a manufacturing process is 0.01. The probability that out of 5 successive pieces, only one is defective, is- a)(0.99)2 (0.01)
- b)(0.99) (0.01)4
- c)5 x (0.99)(0.01)4
- d)5x(0.99)4(0.01)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The probability of a defective piece produced in a manufacturing process is 0.01. The probability that out of 5 successive pieces, only one is defective, is
a)
(0.99)2 (0.01)
b)
(0.99) (0.01)4
c)
5 x (0.99)(0.01)4
d)
5x(0.99)4(0.01)
|
|
Aditya Sharma answered |
Probability of having exactly one defective piece out of 5
- The probability of having a defective piece is 0.01, which means the probability of having a non-defective piece is 0.99.
- To find the probability of having exactly one defective piece out of 5 successive pieces, we need to use the binomial probability formula: P(X = k) = nCk * p^k * (1-p)^(n-k), where n is the number of trials, k is the number of successes, p is the probability of success, and (1-p) is the probability of failure.
- In this case, n = 5, k = 1, p = 0.01, and (1-p) = 0.99.
- Plugging these values into the formula, we get: P(X = 1) = 5C1 * (0.01)^1 * (0.99)^(5-1) = 5 * 0.01 * (0.99)^4
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D': 5 * (0.99)^4 * (0.01)
An examination consists of two papers, Paper 1 and Paper 2. The probability of failing in Paper 1 is 0.3 and that in Paper 2 is 0.2. Given that a student has failed in Paper 2, the probability of failing in Paper 1 is 0.6. The probability of a student failing in both the papers is- a)0.5
- b)0.18
- c)0.12
- d)0.06
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An examination consists of two papers, Paper 1 and Paper 2. The probability of failing in Paper 1 is 0.3 and that in Paper 2 is 0.2. Given that a student has failed in Paper 2, the probability of failing in Paper 1 is 0.6. The probability of a student failing in both the papers is
a)
0.5
b)
0.18
c)
0.12
d)
0.06
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Let A be the event that 'faied in paper 1'.
B be the event that 'failed in paper 2'.
Given P(A) = 0.3, P(B) = 0.2.
And also given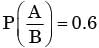
we know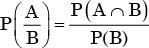
⇒ P(A∩B) = 0.6 x 0.2 = 0.12
B be the event that 'failed in paper 2'.
Given P(A) = 0.3, P(B) = 0.2.
And also given
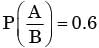
we know
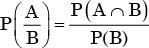
⇒ P(A∩B) = 0.6 x 0.2 = 0.12
A box contains 5 black and 5 red balls. Two balls are randomly picked one after another from the box, without replacement. The probability for both balls being red is- a)1/90
- b)1/2
- c)19/90
- d)2/9
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A box contains 5 black and 5 red balls. Two balls are randomly picked one after another from the box, without replacement. The probability for both balls being red is
a)
1/90
b)
1/2
c)
19/90
d)
2/9

|
Veda Institute answered |
The probability of drawing two red balls without replacement
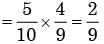
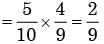
A fair coin is tossed 10 times. What is the probability that ONLY the first two tosses will yield heads? - a)(1/2)2
- b)10C2 (1/2)3
- c)(1/2)10
- d)10C2 (1/2)10
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A fair coin is tossed 10 times. What is the probability that ONLY the first two tosses will yield heads?
a)
(1/2)2
b)
10C2 (1/2)3
c)
(1/2)10
d)
10C2 (1/2)10
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Let A be the event that first toss is head
And B be the event that second toss is head.
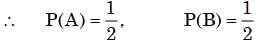
By the given condition rest all 8 tosses should be tail
∴ The probability of getting head in first two cases
=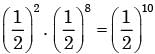
And B be the event that second toss is head.
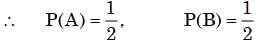
By the given condition rest all 8 tosses should be tail
∴ The probability of getting head in first two cases
=
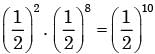
A fair dice is rolled twice. The probability that an odd number will follow an even number is - a)1/2
- b)1/6
- c)1/3
- d)1/4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A fair dice is rolled twice. The probability that an odd number will follow an even number is
a)
1/2
b)
1/6
c)
1/3
d)
1/4
|
|
Arjun Mehta answered |
Understanding the Problem:
We are given that a fair dice is rolled twice and we need to find the probability that an odd number will follow an even number.
Approach:
To solve this problem, we can use the concept of conditional probability. We know that the probability of an event A occurring given that event B has already occurred is given by P(A|B) = P(A ∩ B) / P(B), where P(A ∩ B) represents the probability of both events A and B occurring together, and P(B) represents the probability of event B occurring.
Calculating the Probability:
Let's consider event A as the occurrence of an odd number and event B as the occurrence of an even number in the first roll.
We know that the probability of rolling an odd number on a fair dice is 3/6 = 1/2 (since there are 3 odd numbers out of 6 possible outcomes). Similarly, the probability of rolling an even number on a fair dice is also 1/2 (since there are 3 even numbers out of 6 possible outcomes).
Now, let's calculate the probability of both events A and B occurring together (P(A ∩ B)). Since the outcomes of the two rolls are independent, the probability of both events occurring together is equal to the product of their individual probabilities. Therefore, P(A ∩ B) = P(A) * P(B) = (1/2) * (1/2) = 1/4.
Next, let's calculate the probability of event B occurring (P(B)), which is the probability of rolling an even number on the first roll. As mentioned earlier, this probability is 1/2.
Finally, we can use the formula for conditional probability to find the probability of event A occurring given that event B has already occurred. Using the formula P(A|B) = P(A ∩ B) / P(B), we have P(A|B) = (1/4) / (1/2) = 1/2.
Therefore, the probability that an odd number will follow an even number is 1/2, which corresponds to option 'D' in the given choices.
We are given that a fair dice is rolled twice and we need to find the probability that an odd number will follow an even number.
Approach:
To solve this problem, we can use the concept of conditional probability. We know that the probability of an event A occurring given that event B has already occurred is given by P(A|B) = P(A ∩ B) / P(B), where P(A ∩ B) represents the probability of both events A and B occurring together, and P(B) represents the probability of event B occurring.
Calculating the Probability:
Let's consider event A as the occurrence of an odd number and event B as the occurrence of an even number in the first roll.
We know that the probability of rolling an odd number on a fair dice is 3/6 = 1/2 (since there are 3 odd numbers out of 6 possible outcomes). Similarly, the probability of rolling an even number on a fair dice is also 1/2 (since there are 3 even numbers out of 6 possible outcomes).
Now, let's calculate the probability of both events A and B occurring together (P(A ∩ B)). Since the outcomes of the two rolls are independent, the probability of both events occurring together is equal to the product of their individual probabilities. Therefore, P(A ∩ B) = P(A) * P(B) = (1/2) * (1/2) = 1/4.
Next, let's calculate the probability of event B occurring (P(B)), which is the probability of rolling an even number on the first roll. As mentioned earlier, this probability is 1/2.
Finally, we can use the formula for conditional probability to find the probability of event A occurring given that event B has already occurred. Using the formula P(A|B) = P(A ∩ B) / P(B), we have P(A|B) = (1/4) / (1/2) = 1/2.
Therefore, the probability that an odd number will follow an even number is 1/2, which corresponds to option 'D' in the given choices.
Three values of x and y are to be fitted in a straight line in the form y = a + bx by the method of least squares. Given ∑x = 6, ∑y = 21, ∑x2 = 14 and ∑xy = 46, the values of a and b are respectively.- a)2 and 3
- b)1 and 2
- c)2 and 1
- d)3 and 2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Three values of x and y are to be fitted in a straight line in the form y = a + bx by the method of least squares. Given ∑x = 6, ∑y = 21, ∑x2 = 14 and ∑xy = 46, the values of a and b are respectively.
a)
2 and 3
b)
1 and 2
c)
2 and 1
d)
3 and 2
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
y = a + bx
Given
n = 3, Σx = 6, Σy = 21, Σx2 = 14
And
Σxy = 46
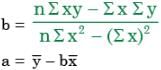
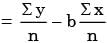
Substituting, we get
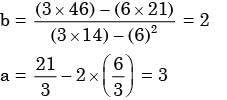
∴ a = 3 and b = 2
Given
n = 3, Σx = 6, Σy = 21, Σx2 = 14
And
Σxy = 46
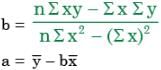
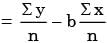
Substituting, we get
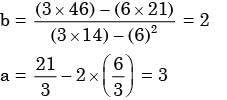
∴ a = 3 and b = 2
A hydraulic structure has four gates which operate independently. The probability of failure off each gate is 0.2. Given that gate 1 has failed, the probability that both gates 2 and 3 will fail is- a)0.240
- b)0.200
- c)0.040
- d)0.008
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydraulic structure has four gates which operate independently. The probability of failure off each gate is 0.2. Given that gate 1 has failed, the probability that both gates 2 and 3 will fail is
a)
0.240
b)
0.200
c)
0.040
d)
0.008

|
Veda Institute answered |
P(gate to and gate 3/gate 1 failed)
= P(gate 2 and gate 3)
[∴ all three gates are independent corresponding to each other]

= P(gate 2 and gate 3)
[∴ all three gates are independent corresponding to each other]

From a pack of regular from a playing cards, two cards are drawn at random. What is the probability that both cards will be Kings, if first card in NOT replaced- a)1/26
- b)1/52
- c)1/169
- d)1/221
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
From a pack of regular from a playing cards, two cards are drawn at random. What is the probability that both cards will be Kings, if first card in NOT replaced
a)
1/26
b)
1/52
c)
1/169
d)
1/221
|
|
Hetal Shah answered |
Understanding the Problem
When drawing two cards from a standard deck of 52 playing cards without replacement, we need to find the probability that both cards drawn are Kings.
Step 1: Total Number of Kings
- A standard deck has 4 Kings (one from each suit: hearts, diamonds, clubs, spades).
Step 2: Drawing the First Card
- The probability of drawing a King first:
- There are 4 Kings in a deck of 52 cards.
- Probability of drawing the first King = 4/52 = 1/13.
Step 3: Drawing the Second Card
- After drawing the first King, there are now:
- 3 Kings left in the deck.
- 51 cards remaining in total.
- The probability of drawing a second King:
- Probability of drawing the second King = 3/51.
Step 4: Calculating the Combined Probability
- To find the overall probability of both events (drawing two Kings):
- Multiply the probabilities of each event:
Probability = (Probability of first King) * (Probability of second King)
= (4/52) * (3/51)
= (1/13) * (1/17)
= 4/663.
Step 5: Simplifying the Probability
- To express 4/663 in a more useful manner:
- 4/663 simplifies and leads to the probability of drawing two Kings with no replacement being 1/221.
Final Answer
Thus, the correct answer is option 'D' (1/221), which illustrates the probability of drawing two Kings consecutively from a deck without replacement.
When drawing two cards from a standard deck of 52 playing cards without replacement, we need to find the probability that both cards drawn are Kings.
Step 1: Total Number of Kings
- A standard deck has 4 Kings (one from each suit: hearts, diamonds, clubs, spades).
Step 2: Drawing the First Card
- The probability of drawing a King first:
- There are 4 Kings in a deck of 52 cards.
- Probability of drawing the first King = 4/52 = 1/13.
Step 3: Drawing the Second Card
- After drawing the first King, there are now:
- 3 Kings left in the deck.
- 51 cards remaining in total.
- The probability of drawing a second King:
- Probability of drawing the second King = 3/51.
Step 4: Calculating the Combined Probability
- To find the overall probability of both events (drawing two Kings):
- Multiply the probabilities of each event:
Probability = (Probability of first King) * (Probability of second King)
= (4/52) * (3/51)
= (1/13) * (1/17)
= 4/663.
Step 5: Simplifying the Probability
- To express 4/663 in a more useful manner:
- 4/663 simplifies and leads to the probability of drawing two Kings with no replacement being 1/221.
Final Answer
Thus, the correct answer is option 'D' (1/221), which illustrates the probability of drawing two Kings consecutively from a deck without replacement.
A box contains 2 washers, 3 nuts and 4 bolts. Items are drawn from the box at random one at a time without replacement. The probability of drawing 2 washers first followed by 3 nuts and subsequently the 4 bolts is- a)2/315
- b)1/630
- c)1/1260
- d)1/2520
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A box contains 2 washers, 3 nuts and 4 bolts. Items are drawn from the box at random one at a time without replacement. The probability of drawing 2 washers first followed by 3 nuts and subsequently the 4 bolts is
a)
2/315
b)
1/630
c)
1/1260
d)
1/2520

|
Veda Institute answered |
Here sample space = 9
The required probability of drawing 2 washers, 3 nuts and 4 bolts respectively without replacement
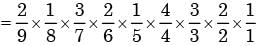
= 1/1260
The required probability of drawing 2 washers, 3 nuts and 4 bolts respectively without replacement
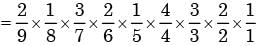
= 1/1260
A box contains 5 block balls and 3 red balls. A total of three balls are picked from the box one after another, without replacing them back. The probability of getting two black balls and one red ball is- a)3/8
- b)2/15
- c)15/28
- d)1/2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A box contains 5 block balls and 3 red balls. A total of three balls are picked from the box one after another, without replacing them back. The probability of getting two black balls and one red ball is
a)
3/8
b)
2/15
c)
15/28
d)
1/2
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Here the possible combination of picking up three balls without replacement is BBR, BRB, RBB
(B = Black ball, R = Red balls)
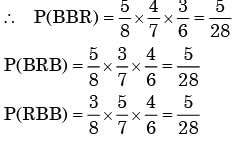
∴ Probability of getting two black balls and one red ball is 15/28.
(B = Black ball, R = Red balls)
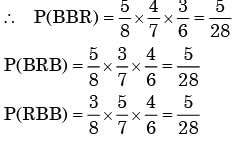
∴ Probability of getting two black balls and one red ball is 15/28.
A person on a trip has a choice between private car and public transport. The probability of using a private car is 0.45. While using the public transport, further choices available are bus and metro, out of which the probability of commuting by a bus is 0.55. In such a situation, the probability (rounded up to two decimals) of using a car, bus and metro, respectively would be- a)0.45, 0.30 and 0.25
- b)0.45, 0.25 and 0.30
- c)0.45, 0.55 and 0.00
- d)0.45, 0.35 and
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A person on a trip has a choice between private car and public transport. The probability of using a private car is 0.45. While using the public transport, further choices available are bus and metro, out of which the probability of commuting by a bus is 0.55. In such a situation, the probability (rounded up to two decimals) of using a car, bus and metro, respectively would be
a)
0.45, 0.30 and 0.25
b)
0.45, 0.25 and 0.30
c)
0.45, 0.55 and 0.00
d)
0.45, 0.35 and
|
|
Gaurav Bhatia answered |
Explanation:
To find the probability of using a car, bus, and metro, we need to consider the different scenarios and calculate their probabilities.
Scenario 1: Using a private car
Given that the probability of using a private car is 0.45, the probability of using a car is 0.45.
Scenario 2: Using public transport
If the person decides to use public transport, there are two options available: bus and metro.
Scenario 2.1: Using a bus
Given that the probability of using a bus is 0.55, the probability of using a bus is 0.45 * 0.55 = 0.2475 (rounded to two decimal places).
Scenario 2.2: Using a metro
Since the person has already decided to use public transport and the only options left are bus and metro, the probability of using a metro is 1 - probability of using a bus = 1 - 0.2475 = 0.7525 (rounded to two decimal places).
Therefore, the probability of using a car, bus, and metro would be:
- Car: 0.45
- Bus: 0.2475 (rounded to two decimal places)
- Metro: 0.7525 (rounded to two decimal places)
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': 0.45, 0.30, and 0.25.
To find the probability of using a car, bus, and metro, we need to consider the different scenarios and calculate their probabilities.
Scenario 1: Using a private car
Given that the probability of using a private car is 0.45, the probability of using a car is 0.45.
Scenario 2: Using public transport
If the person decides to use public transport, there are two options available: bus and metro.
Scenario 2.1: Using a bus
Given that the probability of using a bus is 0.55, the probability of using a bus is 0.45 * 0.55 = 0.2475 (rounded to two decimal places).
Scenario 2.2: Using a metro
Since the person has already decided to use public transport and the only options left are bus and metro, the probability of using a metro is 1 - probability of using a bus = 1 - 0.2475 = 0.7525 (rounded to two decimal places).
Therefore, the probability of using a car, bus, and metro would be:
- Car: 0.45
- Bus: 0.2475 (rounded to two decimal places)
- Metro: 0.7525 (rounded to two decimal places)
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': 0.45, 0.30, and 0.25.
A coin is tossed 4 times. What is the probability of getting heads exactly 3 times?- a)1/4
- b)3/8
- c)1/2
- d)3/4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A coin is tossed 4 times. What is the probability of getting heads exactly 3 times?
a)
1/4
b)
3/8
c)
1/2
d)
3/4

|
Veda Institute answered |
Probability of getting exactly three heads
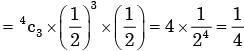
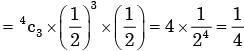
In a manufacturing plant, the probability of making a defective bolt is 0.1. The mean and standard deviation of defective bolts in a total of 900 bolts are respectively- a)90 and 9
- b)9 and 90
- c)0.9 and 90
- d)90 and 0.9
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a manufacturing plant, the probability of making a defective bolt is 0.1. The mean and standard deviation of defective bolts in a total of 900 bolts are respectively
a)
90 and 9
b)
9 and 90
c)
0.9 and 90
d)
90 and 0.9

|
Veda Institute answered |
It’s a poission distribution. Here n = 900, p = 0.1
∴ mean (m)= np = 900 × 0.1 = 90
Standard deviat ion (σ)=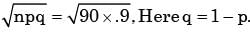
= √81 = 9 (∵ σ > 0).,
∴ mean (m)= np = 900 × 0.1 = 90
Standard deviat ion (σ)=
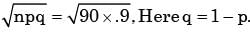
= √81 = 9 (∵ σ > 0).,
A fair coin is tossed independently four times. The probability of the event "the number of time heads shown up is more than the number of times tails shown up" is- a)1/16
- b)1/8
- c)1/4
- d)5/16
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A fair coin is tossed independently four times. The probability of the event "the number of time heads shown up is more than the number of times tails shown up" is
a)
1/16
b)
1/8
c)
1/4
d)
5/16
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Here we have to find
P(H,H,H,T) + P(H,H,H,H)
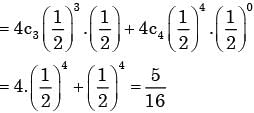
P(H,H,H,T) + P(H,H,H,H)
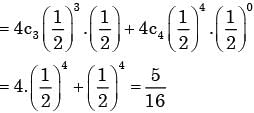
A box contains 20 defective items and 80 non-defective items. If two items are selected at random without replacement, what will be the probability that both items are defective?- a)1/5
- b)1/25
- c)20/99
- d)11/495
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A box contains 20 defective items and 80 non-defective items. If two items are selected at random without replacement, what will be the probability that both items are defective?
a)
1/5
b)
1/25
c)
20/99
d)
11/495

|
Veda Institute answered |
The probability of defective items = 20/100.
Therefore the probability of first two defective items without replacement
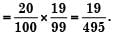
Therefore the probability of first two defective items without replacement
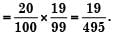
The standard deviation of a uniformly distributed random variable between 0 and 1 is- a)1/√12
- b)1/√3
- c)5/√12
- d)7/√12
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard deviation of a uniformly distributed random variable between 0 and 1 is
a)
1/√12
b)
1/√3
c)
5/√12
d)
7/√12

|
Veda Institute answered |
Here p.d.f is f(x) = 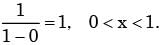
∴ mean(m) = E(x) =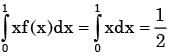
∴ Var (x) =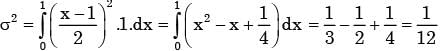
∴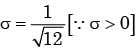
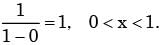
∴ mean(m) = E(x) =
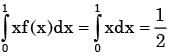
∴ Var (x) =
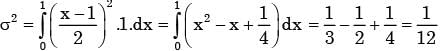
∴
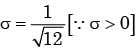
Which one of the following statements is NOT true?- a)The measure of skewness is dependent upon the amount of dispersion
- b)In a symmetric distribution, the values of mean, mode and median are the same
- c)In a positively skewed distribution; mean > median > mode
- d)In a negatively skewed distribution; mode > mean > median
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is NOT true?
a)
The measure of skewness is dependent upon the amount of dispersion
b)
In a symmetric distribution, the values of mean, mode and median are the same
c)
In a positively skewed distribution; mean > median > mode
d)
In a negatively skewed distribution; mode > mean > median
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
is not true since in a negatively skewed distribution, mode > median > mean
A box contains 10 screws, 3 of which are defective. Two screws are drawn at random with replacement. The probability that none of the two screws is defective will be- a)100%
- b)50%
- c)49%
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A box contains 10 screws, 3 of which are defective. Two screws are drawn at random with replacement. The probability that none of the two screws is defective will be
a)
100%
b)
50%
c)
49%
d)
None of these
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Non defective screws = 7
∴ Probability of the two screws are non defective
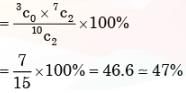
∴ Probability of the two screws are non defective
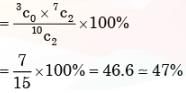
A class of first year B. Tech. Students is composed of four batches A, B, C and D, each consisting of 30 students. It is found that the sessional marks of students in Engineering Drawing in batch C have a mean of 6.6 and standard deviation of 2.3. The mean and standard deviation of the marks for the entire class are 5.5 and 4.2, respectively. It is decided by the course instructor to normalize the marks of the students of all batches to have the same mean and standard deviation as that of the entire class. Due to this, the marks of a student in batch C are changed from 8.5 to- a)6.0
- b)7.0
- c)8. 0
- d)9.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A class of first year B. Tech. Students is composed of four batches A, B, C and D, each consisting of 30 students. It is found that the sessional marks of students in Engineering Drawing in batch C have a mean of 6.6 and standard deviation of 2.3. The mean and standard deviation of the marks for the entire class are 5.5 and 4.2, respectively. It is decided by the course instructor to normalize the marks of the students of all batches to have the same mean and standard deviation as that of the entire class. Due to this, the marks of a student in batch C are changed from 8.5 to
a)
6.0
b)
7.0
c)
8. 0
d)
9.0
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Let mean and stander deviation of batch C be μc and σc respectively and mean and standard deviation of entire class of 1st year students be μ and σ respectively.
Given μc = 6.6 and σc = 2.3
and μ = 5.5 and σ = 4.2
In order to normalize batch F to entire class, the normalized score must be equated
Since
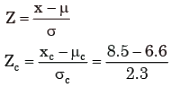
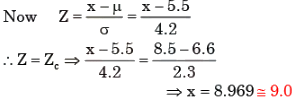
Given μc = 6.6 and σc = 2.3
and μ = 5.5 and σ = 4.2
In order to normalize batch F to entire class, the normalized score must be equated
Since
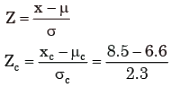
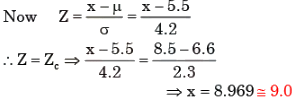
Four arbitrary point (x1,y1), (x2,y2),(x3,y3), (x4,y4), are given in the x, y - Plane Using the method of least squares, if, regressing y upon x gives the fitted line y = ax + b; and regressing y upon x given the fitted line x = cy + d then- a)The two fitted lines must coincide
- b)The two fitted lines need not coincide
- c)It is possible that ac = 0
- d)A must be 1/c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Four arbitrary point (x1,y1), (x2,y2),(x3,y3), (x4,y4), are given in the x, y - Plane Using the method of least squares, if, regressing y upon x gives the fitted line y = ax + b; and regressing y upon x given the fitted line x = cy + d then
a)
The two fitted lines must coincide
b)
The two fitted lines need not coincide
c)
It is possible that ac = 0
d)
A must be 1/c
|
|
Anand Srinivasan answered |
Explanation:
To understand why option D is the correct answer, let's analyze the given information and use the method of least squares to find the regression lines.
1. Fitted line y = ax + b:
We are given that the fitted line when regressing y upon x is given by y = ax + b. This means that we are trying to find a linear relationship between the variables x and y, where a is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept.
2. Fitted line x = cy + d:
We are also given that the fitted line when regressing x upon y is given by x = cy + d. In this case, we are trying to find a linear relationship between the variables y and x, where c is the slope of the line and d is the y-intercept.
Now, let's consider the relationship between these two lines:
- The slope of the first line, y = ax + b, is a.
- The slope of the second line, x = cy + d, is 1/c.
Since we are given that a is the slope of the first line, and the slope of the second line is 1/c, we can conclude that a must be equal to 1/c. Therefore, option D is correct.
Summary:
Based on the given information and the method of least squares, we can conclude that the slope of the fitted line when regressing y upon x (a) is equal to the reciprocal of the slope of the fitted line when regressing x upon y (1/c), which is represented by option D.
To understand why option D is the correct answer, let's analyze the given information and use the method of least squares to find the regression lines.
1. Fitted line y = ax + b:
We are given that the fitted line when regressing y upon x is given by y = ax + b. This means that we are trying to find a linear relationship between the variables x and y, where a is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept.
2. Fitted line x = cy + d:
We are also given that the fitted line when regressing x upon y is given by x = cy + d. In this case, we are trying to find a linear relationship between the variables y and x, where c is the slope of the line and d is the y-intercept.
Now, let's consider the relationship between these two lines:
- The slope of the first line, y = ax + b, is a.
- The slope of the second line, x = cy + d, is 1/c.
Since we are given that a is the slope of the first line, and the slope of the second line is 1/c, we can conclude that a must be equal to 1/c. Therefore, option D is correct.
Summary:
Based on the given information and the method of least squares, we can conclude that the slope of the fitted line when regressing y upon x (a) is equal to the reciprocal of the slope of the fitted line when regressing x upon y (1/c), which is represented by option D.
Two dice are thrown. What is the probability that is the sum of the numbers on the two dice is eight?- a)5/36
- b)5/18
- c)¼
- d)1/3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two dice are thrown. What is the probability that is the sum of the numbers on the two dice is eight?
a)
5/36
b)
5/18
c)
¼
d)
1/3
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Here sample space = 6 × 6 = 36
Here, there are five such points whose sum is 8. They are (2,6), (3,5), (4,4), (5,3), (6,2).
∴ Requireprobability = 5/36
Here, there are five such points whose sum is 8. They are (2,6), (3,5), (4,4), (5,3), (6,2).
∴ Requireprobability = 5/36
The probability that two friends share the same birth-month is- a)1/6
- b)1/12
- c)1/144
- d)1/24
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The probability that two friends share the same birth-month is
a)
1/6
b)
1/12
c)
1/144
d)
1/24

|
Veda Institute answered |
Let A = the event that the birth month of first friend
And B= that of second friend.
∴ P( A )= 1, as 1st friend can born in any month
and P(B) = 1/12, by the condition.
∴ Probability of two friends share same birth-month is 1 x 1/12 = 1/12
And B= that of second friend.
∴ P( A )= 1, as 1st friend can born in any month
and P(B) = 1/12, by the condition.
∴ Probability of two friends share same birth-month is 1 x 1/12 = 1/12
If three coins are tossed simultaneously, the probability of getting at least one head is- a)1/8
- b)3/8
- c)1/2
- d)7/8
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If three coins are tossed simultaneously, the probability of getting at least one head is
a)
1/8
b)
3/8
c)
1/2
d)
7/8

|
Veda Institute answered |
Here the sample space = S = 23 = 8.
No. of ways to get all tails = 1.
∴ probability to get all tails = 1/8
∴ Probability to get at least one head is = 1 - 1/8 = 7/8
No. of ways to get all tails = 1.
∴ probability to get all tails = 1/8
∴ Probability to get at least one head is = 1 - 1/8 = 7/8
If the standard deviation of the spot speed of vehicles in a highway is 8.8 kmph and the mean speed of the vehicles is 33 kmph, the coefficient of variation in speed is- a)0.1517
- b)0.1867
- c)0.2666
- d)0.3645
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the standard deviation of the spot speed of vehicles in a highway is 8.8 kmph and the mean speed of the vehicles is 33 kmph, the coefficient of variation in speed is
a)
0.1517
b)
0.1867
c)
0.2666
d)
0.3645
|
|
Mahi Sharma answered |
Coefficient of Variation (CV) is a measure of relative variability. It is used to compare the standard deviation of different datasets when the means are significantly different. It is calculated by dividing the standard deviation by the mean.
Given:
Standard deviation (σ) = 8.8 kmph
Mean (μ) = 33 kmph
To find the coefficient of variation, we use the formula:
CV = (σ / μ) * 100
Calculating the Coefficient of Variation:
CV = (8.8 / 33) * 100
CV = 0.2666 * 100
CV = 26.66
Since the coefficient of variation is expressed as a percentage, we can convert it to a decimal by dividing by 100:
CV = 26.66 / 100
CV = 0.2666
Therefore, the coefficient of variation in speed is 0.2666, which is option (c).
Explanation:
The coefficient of variation is a measure of the relative variability of a dataset. In this case, it is used to compare the standard deviation of the spot speeds of vehicles on the highway to the mean speed of the vehicles.
A lower coefficient of variation indicates that the dataset has less relative variability, while a higher coefficient of variation indicates greater relative variability.
In this case, the standard deviation is 8.8 kmph, which means that the spot speeds of vehicles on the highway vary by an average of 8.8 kmph from the mean speed of 33 kmph. Dividing the standard deviation by the mean gives us the coefficient of variation of 0.2666.
Option (c) is the correct answer.
Given:
Standard deviation (σ) = 8.8 kmph
Mean (μ) = 33 kmph
To find the coefficient of variation, we use the formula:
CV = (σ / μ) * 100
Calculating the Coefficient of Variation:
CV = (8.8 / 33) * 100
CV = 0.2666 * 100
CV = 26.66
Since the coefficient of variation is expressed as a percentage, we can convert it to a decimal by dividing by 100:
CV = 26.66 / 100
CV = 0.2666
Therefore, the coefficient of variation in speed is 0.2666, which is option (c).
Explanation:
The coefficient of variation is a measure of the relative variability of a dataset. In this case, it is used to compare the standard deviation of the spot speeds of vehicles on the highway to the mean speed of the vehicles.
A lower coefficient of variation indicates that the dataset has less relative variability, while a higher coefficient of variation indicates greater relative variability.
In this case, the standard deviation is 8.8 kmph, which means that the spot speeds of vehicles on the highway vary by an average of 8.8 kmph from the mean speed of 33 kmph. Dividing the standard deviation by the mean gives us the coefficient of variation of 0.2666.
Option (c) is the correct answer.
If probability density functions of a random variable X is f(x) = x2 for -1 ≤ x ≤ 1, and = for any other value of x
Then, the percentage probability 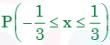 is
is- a)0.247
- b)2.47
- c)24.7
- d)247
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If probability density functions of a random variable X is f(x) = x2 for -1 ≤ x ≤ 1, and = for any other value of x
Then, the percentage probability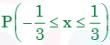 is
is
Then, the percentage probability
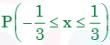 is
isa)
0.247
b)
2.47
c)
24.7
d)
247

|
Veda Institute answered |
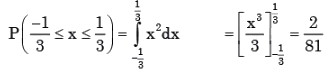
∴ Percentage probability = 2/81 x 100 = 2.47%
Px(x) = M exp(–2|x|) – N exp(–3 |x|) is the probability density function for the real random variable X, over the entire x axis. M and N are both positive real numbers. The equation relating M and N is- a)
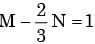
- b)
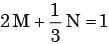
- c)M + N = 1
- d)M + N = 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Px(x) = M exp(–2|x|) – N exp(–3 |x|) is the probability density function for the real random variable X, over the entire x axis. M and N are both positive real numbers. The equation relating M and N is
a)
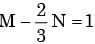
b)
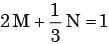
c)
M + N = 1
d)
M + N = 3
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Given Px (x ) is the probability density function for the random variable X.
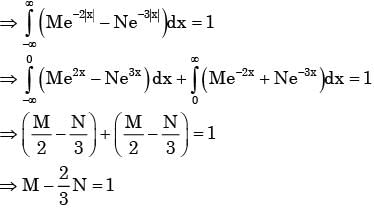
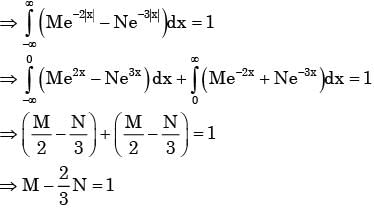
A single die is thrown twice. What is the sum is neither 8 nor 9?- a)1/9
- b)5/36
- c)1/4
- d)3/4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A single die is thrown twice. What is the sum is neither 8 nor 9?
a)
1/9
b)
5/36
c)
1/4
d)
3/4
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Here sample space = 36
Total No. of way in which sum is either 8 or 9 are (2,6), (3,5),(3,6),(4,4),(4,5),(5,3),(5,4),(6,2),(6,3)
So probability of getting sum 8 or 9 = 9/36 = 1/4
So the probability of not getting sum 8 or 9
Total No. of way in which sum is either 8 or 9 are (2,6), (3,5),(3,6),(4,4),(4,5),(5,3),(5,4),(6,2),(6,3)
So probability of getting sum 8 or 9 = 9/36 = 1/4
So the probability of not getting sum 8 or 9
A lot has 10% defective items. Ten items are chosen randomly from this lot. The probability that exactly 2 of the chosen items are defective is - a)0.0036
- b)0.1937
- c)0.2234
- d)0.3874
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A lot has 10% defective items. Ten items are chosen randomly from this lot. The probability that exactly 2 of the chosen items are defective is
a)
0.0036
b)
0.1937
c)
0.2234
d)
0.3874

|
Veda Institute answered |
Let A be the event that items are defective and B be the event that items are non-defective.
∴ P(A) = 0.1 and P(B) = 0.9
∴ Probability that exactly two of those items are defective
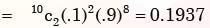
∴ P(A) = 0.1 and P(B) = 0.9
∴ Probability that exactly two of those items are defective
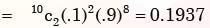
A probability density function is of the form
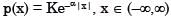
The value of K is - a)0.5
- b)1
- c)0.5 α
- d)α
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A probability density function is of the form
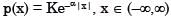
The value of K is
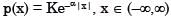
The value of K is
a)
0.5
b)
1
c)
0.5 α
d)
α
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
As (x) is a probability density funciton
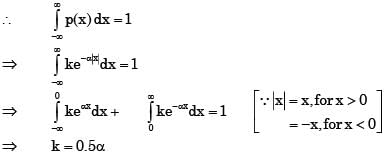
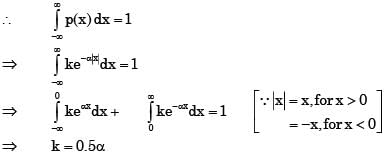
If 20 per cent managers are technocrats, the probability that a random committee of 5 managers consists of exactly 2 technocrats is- a)0.2048
- b)0.4000
- c)0.4096
- d)0.9421
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If 20 per cent managers are technocrats, the probability that a random committee of 5 managers consists of exactly 2 technocrats is
a)
0.2048
b)
0.4000
c)
0.4096
d)
0.9421
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The probability of technocrats manager = 20/100
= 1/5
∴ Probability of non technocrats manager = 4/5
Now the require probability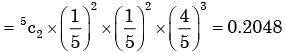
= 1/5
∴ Probability of non technocrats manager = 4/5
Now the require probability
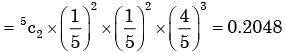
Consider the continuous random variable with probability density function
f(t) = 1 + t for -1 ≤ t ≤ 0
= 1 - t for 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
The standard deviation of the random variables is - a)1/√3
- b)1/√6
- c)1/3
- d)1/6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the continuous random variable with probability density function
f(t) = 1 + t for -1 ≤ t ≤ 0
= 1 - t for 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
The standard deviation of the random variables is
f(t) = 1 + t for -1 ≤ t ≤ 0
= 1 - t for 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
The standard deviation of the random variables is
a)
1/√3
b)
1/√6
c)
1/3
d)
1/6
|
|
Devansh Choudhary answered |
The probability density function (PDF) given is:
f(t) = 1/t for -1 < t="" />< />
To determine the cumulative distribution function (CDF) F(t) for this continuous random variable, we need to integrate the PDF over the given range:
F(t) = ∫[from -∞ to t] f(u) du
For -1 < t="" />< 1,="" we="" />
F(t) = ∫[from -∞ to t] (1/u) du
To evaluate this integral, we need to split it into two parts:
F(t) = ∫[from -∞ to 0] (1/u) du + ∫[from 0 to t] (1/u) du
The first integral from -∞ to 0 is undefined because the PDF is not defined for negative values. Therefore, we can ignore this part.
For the second integral from 0 to t, we have:
F(t) = ∫[from 0 to t] (1/u) du
Now, to evaluate this integral, we can use the natural logarithm function:
F(t) = ln|u| [from 0 to t]
F(t) = ln|t| - ln|0|
Since ln|0| is undefined, we cannot evaluate it. However, as t approaches 0 from the positive side, ln|t| approaches -∞. Therefore, we can write:
F(t) = ln|t| for 0 ≤ t < />
So, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) for the given continuous random variable is:
F(t) = ln|t| for 0 ≤ t < 1="" />
f(t) = 1/t for -1 < t="" />< />
To determine the cumulative distribution function (CDF) F(t) for this continuous random variable, we need to integrate the PDF over the given range:
F(t) = ∫[from -∞ to t] f(u) du
For -1 < t="" />< 1,="" we="" />
F(t) = ∫[from -∞ to t] (1/u) du
To evaluate this integral, we need to split it into two parts:
F(t) = ∫[from -∞ to 0] (1/u) du + ∫[from 0 to t] (1/u) du
The first integral from -∞ to 0 is undefined because the PDF is not defined for negative values. Therefore, we can ignore this part.
For the second integral from 0 to t, we have:
F(t) = ∫[from 0 to t] (1/u) du
Now, to evaluate this integral, we can use the natural logarithm function:
F(t) = ln|u| [from 0 to t]
F(t) = ln|t| - ln|0|
Since ln|0| is undefined, we cannot evaluate it. However, as t approaches 0 from the positive side, ln|t| approaches -∞. Therefore, we can write:
F(t) = ln|t| for 0 ≤ t < />
So, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) for the given continuous random variable is:
F(t) = ln|t| for 0 ≤ t < 1="" />
There are 25 calculators in a box. Two of them are defective. Suppose 5 calculators are randomly picked for inspection (i.e., each has the same chance of being selected), what is the probability that only one of the defective calculators will be included in the inspection?- a)1/2
- b)1/3
- c)1/4
- d)1/5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There are 25 calculators in a box. Two of them are defective. Suppose 5 calculators are randomly picked for inspection (i.e., each has the same chance of being selected), what is the probability that only one of the defective calculators will be included in the inspection?
a)
1/2
b)
1/3
c)
1/4
d)
1/5

|
Scholars Academy answered |
To arrive at the answer, first note that there are C(2,1) = 2 ways to choose one defective calculator out of the 2 available.
Next, there are C(23,4) ways to choose 4 non-defective calculators from the 23 good ones.
Since the total number of ways to pick any 5 calculators from 25 is C(25,5),
the probability that exactly one defective calculator is chosen is given by [C(2,1) × C(23,4)] / C(25,5).
the probability simplifies to 1/3.
Analysis of variance is concerned with:- a)Determining change in a dependent variable per unit change in an independent variable
- b)Determining whether a qualitative factor affects the mean of an output variable
- c)Determining whether significant correlation exists between an output variable and an input variable.
- d)Determining whether variance in two or more populations are significantly different.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Analysis of variance is concerned with:
a)
Determining change in a dependent variable per unit change in an independent variable
b)
Determining whether a qualitative factor affects the mean of an output variable
c)
Determining whether significant correlation exists between an output variable and an input variable.
d)
Determining whether variance in two or more populations are significantly different.
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Analysis of variance is used in comparing two or more populations, e.g. Different types of manures for yelding a single crop.
Manish has to travel from A to D changing buses at stops B and C enroute. The maximum waiting time at either stop can be 8 minutes each, but any time of waiting up to 8 minutes is equally likely at both places. He can afford up to 13 minutes of total waiting time if he is to arrive at D on time. What is the probability that Manish will arrive late at D?- a)8/13
- b)13/64
- c)119/128
- d)9/128
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Manish has to travel from A to D changing buses at stops B and C enroute. The maximum waiting time at either stop can be 8 minutes each, but any time of waiting up to 8 minutes is equally likely at both places. He can afford up to 13 minutes of total waiting time if he is to arrive at D on time. What is the probability that Manish will arrive late at D?
a)
8/13
b)
13/64
c)
119/128
d)
9/128
|
|
Yashvi Bhatia answered |
Understanding the Problem
Manish has a maximum waiting time of 8 minutes at each of the two stops (B and C) and he can afford a total waiting time of 13 minutes. This means:
- Waiting at Stop B: X (0 to 8 minutes)
- Waiting at Stop C: Y (0 to 8 minutes)
The total waiting time is given by the equation:
X + Y > 13
We need to find the probability that Manish arrives late at D.
Setting Up the Scenario
- Both X and Y are uniformly distributed between 0 and 8.
- The total possible waiting time combinations (X, Y) form a square region in the XY-plane with vertices (0,0), (8,0), (0,8), and (8,8). The area of this square is 64 (8*8).
Finding the Area of Interest
1. Late Arrival Condition:
- The condition X + Y > 13 represents a line on the XY-plane.
2. Identifying the Intersection:
- The line intersects the boundaries of the square at points (5,8) and (8,5).
3. Calculating the Area Above the Line:
- The triangle formed by these points and the origin (0,0) has vertices (5,8), (8,5), and (8,8).
Calculating Areas
- Area of the triangle:
- Base = 8 - 5 = 3
- Height = 8 - 5 = 3
- Area = 0.5 * base * height = 0.5 * 3 * 3 = 4.5
- Total area above the line = Area of the square - Area of the triangle = 64 - 4.5 = 59.5
Probability Calculation
- Probability of arriving late (X + Y > 13):
P = Area above the line / Total area of the square = (64 - 4.5) / 64 = 59.5 / 64 = 8/13
Conclusion
Thus, the probability that Manish will arrive late at D is 8/13, making option 'A' the correct answer.
Manish has a maximum waiting time of 8 minutes at each of the two stops (B and C) and he can afford a total waiting time of 13 minutes. This means:
- Waiting at Stop B: X (0 to 8 minutes)
- Waiting at Stop C: Y (0 to 8 minutes)
The total waiting time is given by the equation:
X + Y > 13
We need to find the probability that Manish arrives late at D.
Setting Up the Scenario
- Both X and Y are uniformly distributed between 0 and 8.
- The total possible waiting time combinations (X, Y) form a square region in the XY-plane with vertices (0,0), (8,0), (0,8), and (8,8). The area of this square is 64 (8*8).
Finding the Area of Interest
1. Late Arrival Condition:
- The condition X + Y > 13 represents a line on the XY-plane.
2. Identifying the Intersection:
- The line intersects the boundaries of the square at points (5,8) and (8,5).
3. Calculating the Area Above the Line:
- The triangle formed by these points and the origin (0,0) has vertices (5,8), (8,5), and (8,8).
Calculating Areas
- Area of the triangle:
- Base = 8 - 5 = 3
- Height = 8 - 5 = 3
- Area = 0.5 * base * height = 0.5 * 3 * 3 = 4.5
- Total area above the line = Area of the square - Area of the triangle = 64 - 4.5 = 59.5
Probability Calculation
- Probability of arriving late (X + Y > 13):
P = Area above the line / Total area of the square = (64 - 4.5) / 64 = 59.5 / 64 = 8/13
Conclusion
Thus, the probability that Manish will arrive late at D is 8/13, making option 'A' the correct answer.
Chapter doubts & questions for Probability - Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics 2025 is part of Mathematics exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mathematics exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mathematics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Probability - Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics in English & Hindi are available as part of Mathematics exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mathematics Exam by signing up for free.
Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics
2 videos|44 docs|4 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily