All Exams >
Class 4 >
Science Olympiad Class 4 >
All Questions
All questions of Plants for Class 4 Exam
An example of a fruit containing seeds that is edible to humans is a:- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of a fruit containing seeds that is edible to humans is a:
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ipsit Raj answered |
Because potato, mushroom and banana do not contain seeds. Also tomato contains seed and is edible to humans too.
Look at the following picture of leaves and identify the plant or tree name:

- a)Gulmohar
- b)Pine
- c)Neem
- d)Mango
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Look at the following picture of leaves and identify the plant or tree name:


a)
Gulmohar
b)
Pine
c)
Neem
d)
Mango
|
|
Manognya .banerji answered |
It is pine tree as only pine has a fish- bone pattern. So correct option is 'B'.
Anish and his friends set up an experiment as shown below:
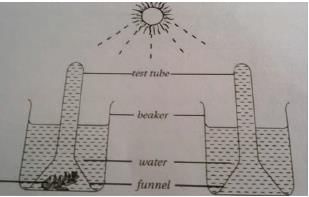
Hydrilla
They left the set-up in bright sunlight for four hours.Q. What would they observe at the end of the four hours?- a)A gas would collect in test tube A and B
- b)A gas would collect in the entire set-up
- c)A gas would collect in test tube A but not in test tube B
- d)Nothing will happen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Anish and his friends set up an experiment as shown below:

Hydrilla
They left the set-up in bright sunlight for four hours.

Hydrilla
They left the set-up in bright sunlight for four hours.
Q. What would they observe at the end of the four hours?
a)
A gas would collect in test tube A and B
b)
A gas would collect in the entire set-up
c)
A gas would collect in test tube A but not in test tube B
d)
Nothing will happen
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
The correct option is Option C.
The given experiment demonstrates that oxygen is evolved during the process of photosynthesis. In this experiment, the aquatic plant-like Hydrilla is used. The aspect is the light reaction of photosynthesis. This is the process in which the plants with the help of chloroplast captures light energy. They can use the carbon dioxide from the air to produce carbohydrates in the form of sugar and starch. There is a splitting of water to fill the gap created by the electron in the photosystem. The product which is formed is oxygen which is liberated during this process.
Since, test tube B does not contain hydrilla in it, it will not form any gas.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert:- a)Sugar and sunlight into oxygen
- b)Sugar and oxygen into carbon dioxide and energy
- c)Carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen
- d)Sunlight into oxygen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert:
a)
Sugar and sunlight into oxygen
b)
Sugar and oxygen into carbon dioxide and energy
c)
Carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen
d)
Sunlight into oxygen
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
Plants are autotrophs, which means they produce their own food. They use the process of photosynthesis to transform water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide into oxygen, and simple sugars that the plant uses as fuel.
The main purpose of flowers is to provide:- a)Support
- b)Food
- c)Water
- d)Seed
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The main purpose of flowers is to provide:
a)
Support
b)
Food
c)
Water
d)
Seed
|
|
Sharada singhania answered |
The main purpose of flowers is to produce seeds for reproduction (Option D is correct). Flowers also have other functions such as attracting pollinators and providing food and nectar for animals, but the primary purpose is reproduction.
This plant is found in Australia. It has very few leaves. Local people put a thin pipe into the trunk of this tree to drink water. This tree is:- a)Spinifex
- b)Oak
- c)Cactus
- d)Bamboo
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
This plant is found in Australia. It has very few leaves. Local people put a thin pipe into the trunk of this tree to drink water. This tree is:
a)
Spinifex
b)
Oak
c)
Cactus
d)
Bamboo
|
|
Sounak Chakraborty answered |
Answer:
Introduction:
The plant found in Australia with very few leaves and local people put a thin pipe into the trunk of this tree to drink water is the Oak tree.
About Oak tree:
The Oak tree is a large, strong and long-lived tree. It is a native of the Northern hemisphere and can be found in most parts of the world. In Australia, the Oak tree is known as the Flooded Gum or River Gum. It is found in the eastern half of the country, along the coastal regions and in the drier areas of the interior.
Appearance:
The Oak tree can grow up to 45 meters high and can have a trunk diameter of up to 3 meters. It has a thick, rough bark that is greyish-brown in color. The leaves of the Oak tree are long and narrow, with a dark green color on top and a lighter green underneath. The leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern along the branches.
Adaptation:
The Oak tree has adapted to the Australian climate by having very few leaves. This helps the tree to conserve water in the dry conditions of the Australian landscape. The Oak tree is also able to store water in its trunk, which is why local people can put a thin pipe into the trunk to drink water.
Uses:
The Oak tree has many uses, including being used for timber, firewood, and shade. The timber from the Oak tree is strong and durable, making it ideal for construction and furniture. The Oak tree also provides a habitat for many animals, including birds and insects.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the plant found in Australia with very few leaves and local people put a thin pipe into the trunk of this tree to drink water is the Oak tree. The Oak tree is a large, strong and long-lived tree that has adapted to the Australian climate by having very few leaves and being able to store water in its trunk. The Oak tree has many uses, including being used for timber, firewood, and shade, and provides a habitat for many animals.
Introduction:
The plant found in Australia with very few leaves and local people put a thin pipe into the trunk of this tree to drink water is the Oak tree.
About Oak tree:
The Oak tree is a large, strong and long-lived tree. It is a native of the Northern hemisphere and can be found in most parts of the world. In Australia, the Oak tree is known as the Flooded Gum or River Gum. It is found in the eastern half of the country, along the coastal regions and in the drier areas of the interior.
Appearance:
The Oak tree can grow up to 45 meters high and can have a trunk diameter of up to 3 meters. It has a thick, rough bark that is greyish-brown in color. The leaves of the Oak tree are long and narrow, with a dark green color on top and a lighter green underneath. The leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern along the branches.
Adaptation:
The Oak tree has adapted to the Australian climate by having very few leaves. This helps the tree to conserve water in the dry conditions of the Australian landscape. The Oak tree is also able to store water in its trunk, which is why local people can put a thin pipe into the trunk to drink water.
Uses:
The Oak tree has many uses, including being used for timber, firewood, and shade. The timber from the Oak tree is strong and durable, making it ideal for construction and furniture. The Oak tree also provides a habitat for many animals, including birds and insects.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the plant found in Australia with very few leaves and local people put a thin pipe into the trunk of this tree to drink water is the Oak tree. The Oak tree is a large, strong and long-lived tree that has adapted to the Australian climate by having very few leaves and being able to store water in its trunk. The Oak tree has many uses, including being used for timber, firewood, and shade, and provides a habitat for many animals.
In the carrot, food is stored in the:- a)Stem
- b)Leaves
- c)Flowers
- d)Roots
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the carrot, food is stored in the:
a)
Stem
b)
Leaves
c)
Flowers
d)
Roots
|
|
Sparsh Singh answered |
carrots store food in its roots and live on it all winter and in summers a new plant grows from these roots. When they have extra food they store it in their seeds and when the seed grows it gets it's food from the plant until the plant is able to photosynthesis and produce its food.
Saumya performed an activity as follows:She took a plant with many leaves. Then she covered a healthy leaf of that plant completely with some black paper and left the plant in the open for three days. Finally she performed starch test on both the leaves.Q. What would happen?- a) Covered leaves would turn blue
- b) Uncovered leaves would turn blue
- c) Nothing will happen
- d) All leaves, covered and uncovered, would turn blue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Saumya performed an activity as follows:
She took a plant with many leaves. Then she covered a healthy leaf of that plant completely with some black paper and left the plant in the open for three days. Finally she performed starch test on both the leaves.
Q. What would happen?
a)
Covered leaves would turn blue
b)
Uncovered leaves would turn blue
c)
Nothing will happen
d)
All leaves, covered and uncovered, would turn blue
|
|
Rajesh Saini answered |
one of them will turn blue-black and the other will be reddish-brown. Iodine is an indicator that turns blue-black in the presence of starch. The leaf that was in the light turns blue-black, which demonstrates that the leaf has been performing photosynthesis and producing starch.
The tiny pores present on the leaves of plants are called:- a)Chlorophyll
- b)Cells
- c)Grains
- d)Stomata
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The tiny pores present on the leaves of plants are called:
a)
Chlorophyll
b)
Cells
c)
Grains
d)
Stomata

|
Learning Education answered |
Stomata are the tiny pores or openings found on the surface of plant leaves (and some other plant parts). They are like small mouths or windows that allow for the exchange of gases and water vapor between the plant and its surroundings.
Stomata play an essential role in the life of a plant. They allow carbon dioxide, which is needed for photosynthesis, to enter the leaf. At the same time, they release oxygen, which is produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis, and excess water vapor through the process of transpiration.
Roots and stems carry:- a)Sunlight and sugar
- b)Nutrients and water
- c)Carbon dioxide and sugar
- d)Oxygen and nutrients
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Roots and stems carry:
a)
Sunlight and sugar
b)
Nutrients and water
c)
Carbon dioxide and sugar
d)
Oxygen and nutrients
|
|
Kajal Reddy answered |
The correct answer is b
The stem is the stalk or trunk of a plant. They pass the water and minerals onto xylem, which is a tissue that transports the water and minerals through the plant. We find xylem in both the roots and the stems of plants. This is also true of phloem, which is a tissue that transports food through the plant
Which of the following structures of plant exchange gases?- a)Flower
- b)Leaves
- c)Buds
- d)Fruits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following structures of plant exchange gases?
a)
Flower
b)
Leaves
c)
Buds
d)
Fruits
|
|
Mehul Unni answered |
**Leaves**
Leaves are the primary structures in plants that exchange gases, specifically carbon dioxide and oxygen, through tiny openings called stomata. The process of gas exchange in leaves is known as respiration.
**Structure of Leaves**
Leaves are flat, thin, and typically green structures that emerge from stems. They are attached to the stem by a petiole and have a blade-like structure. The blade is the main part of the leaf, and it contains several important components for gas exchange.
**Stomata**
Stomata are small openings found on the surface of leaves. They are surrounded by specialized cells called guard cells, which control their opening and closing. Stomata are vital for gas exchange as they allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaf and oxygen to exit.
**Photosynthesis and Respiration**
Leaves not only exchange gases but also play a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, leaves absorb sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen. This process occurs in specialized structures within the leaf called chloroplasts.
On the other hand, during respiration, plants use oxygen and glucose to release energy. Respiration occurs in all living cells, including the cells found in leaves. Oxygen is taken in through the stomata, and carbon dioxide, a waste product of respiration, is released through the same openings.
**Conclusion**
In conclusion, leaves are the structures in plants that primarily exchange gases. They have stomata that allow for the entry of carbon dioxide and the exit of oxygen. Leaves also play a vital role in photosynthesis and respiration, which are essential processes for plant growth and survival.
Leaves are the primary structures in plants that exchange gases, specifically carbon dioxide and oxygen, through tiny openings called stomata. The process of gas exchange in leaves is known as respiration.
**Structure of Leaves**
Leaves are flat, thin, and typically green structures that emerge from stems. They are attached to the stem by a petiole and have a blade-like structure. The blade is the main part of the leaf, and it contains several important components for gas exchange.
**Stomata**
Stomata are small openings found on the surface of leaves. They are surrounded by specialized cells called guard cells, which control their opening and closing. Stomata are vital for gas exchange as they allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaf and oxygen to exit.
**Photosynthesis and Respiration**
Leaves not only exchange gases but also play a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, leaves absorb sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen. This process occurs in specialized structures within the leaf called chloroplasts.
On the other hand, during respiration, plants use oxygen and glucose to release energy. Respiration occurs in all living cells, including the cells found in leaves. Oxygen is taken in through the stomata, and carbon dioxide, a waste product of respiration, is released through the same openings.
**Conclusion**
In conclusion, leaves are the structures in plants that primarily exchange gases. They have stomata that allow for the entry of carbon dioxide and the exit of oxygen. Leaves also play a vital role in photosynthesis and respiration, which are essential processes for plant growth and survival.
Water is taken from the surroundings into the plant through the:- a)Leaves
- b)Roots
- c)Stems
- d)Flower
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is taken from the surroundings into the plant through the:
a)
Leaves
b)
Roots
c)
Stems
d)
Flower
|
|
Swara Roy answered |
Water Uptake in Plants
Plants are remarkable organisms that require water for various vital processes. The primary way they absorb water from their surroundings is through their roots.
Role of Roots
- The roots are specialized structures that anchor the plant in the soil.
- They have tiny root hairs that increase the surface area for absorption, allowing them to take in more water and nutrients.
- Water enters the roots through a process called osmosis, where water moves from an area of higher concentration in the soil to an area of lower concentration in the root cells.
Importance of Water
- Water is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into food.
- It helps transport nutrients from the soil throughout the plant.
- Water also provides structural support to plant cells, helping them maintain their shape.
Other Parts of the Plant
- While leaves, stems, and flowers play crucial roles in the plant's life, they do not absorb water directly from the environment.
- Leaves are primarily responsible for photosynthesis and gas exchange.
- Stems serve as conduits for transporting water and nutrients between the roots and leaves.
- Flowers are involved in reproduction and attracting pollinators.
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' because roots are specifically designed to absorb water from the soil, making them essential for a plant's survival and growth.
Plants are remarkable organisms that require water for various vital processes. The primary way they absorb water from their surroundings is through their roots.
Role of Roots
- The roots are specialized structures that anchor the plant in the soil.
- They have tiny root hairs that increase the surface area for absorption, allowing them to take in more water and nutrients.
- Water enters the roots through a process called osmosis, where water moves from an area of higher concentration in the soil to an area of lower concentration in the root cells.
Importance of Water
- Water is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into food.
- It helps transport nutrients from the soil throughout the plant.
- Water also provides structural support to plant cells, helping them maintain their shape.
Other Parts of the Plant
- While leaves, stems, and flowers play crucial roles in the plant's life, they do not absorb water directly from the environment.
- Leaves are primarily responsible for photosynthesis and gas exchange.
- Stems serve as conduits for transporting water and nutrients between the roots and leaves.
- Flowers are involved in reproduction and attracting pollinators.
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' because roots are specifically designed to absorb water from the soil, making them essential for a plant's survival and growth.
Leaves provide the surface area necessary for:- a)Absorption of sunlight, which begins the process of photosynthesis
- b)Absorption of carbon dioxide, which begins the process of photosynthesis
- c)Absorption of water, which begins the process of photosynthesis
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Leaves provide the surface area necessary for:
a)
Absorption of sunlight, which begins the process of photosynthesis
b)
Absorption of carbon dioxide, which begins the process of photosynthesis
c)
Absorption of water, which begins the process of photosynthesis
d)
None of the above
|
|
Maulik Chaudhary answered |
Leaves provide the surface area necessary for absorbing sunlight, which begins the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen. This process is essential for the survival of plants and the production of oxygen in the atmosphere.
1. Importance of sunlight for photosynthesis:
Sunlight is the primary source of energy for photosynthesis. The leaves of plants contain a pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight. This absorbed sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Therefore, leaves need to have a large surface area to maximize their exposure to sunlight.
2. Leaf structure and surface area:
Leaves are flat and thin, providing a large surface area for sunlight absorption. They are typically broad and have a large number of interconnected cells. The upper surface of the leaf is exposed to sunlight, while the lower surface allows for gas exchange. The arrangement of cells and structures like chloroplasts within the leaf further increases the surface area available for sunlight absorption.
3. Role of chlorophyll:
Chlorophyll, the green pigment found in chloroplasts, is responsible for capturing sunlight. It is located in specialized cells called mesophyll cells, which are found in the middle layer of the leaf. The chlorophyll pigments absorb light energy, primarily from the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and transfer it to the chloroplasts. This energy is then used to fuel the process of photosynthesis.
4. Other functions of leaves:
In addition to absorbing sunlight, leaves also play a vital role in the exchange of gases. Through tiny openings called stomata, leaves absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, which is necessary for photosynthesis. The stomata also allow for the release of oxygen (O2) produced during photosynthesis and the exchange of water vapor.
Conclusion:
Leaves provide the surface area necessary for the absorption of sunlight, which initiates the process of photosynthesis. Through the presence of chlorophyll and the structure of their cells, leaves maximize their exposure to sunlight and optimize the energy capture needed for photosynthesis. While leaves also absorb carbon dioxide and water, these processes are not the primary purpose of their large surface area.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen. This process is essential for the survival of plants and the production of oxygen in the atmosphere.
1. Importance of sunlight for photosynthesis:
Sunlight is the primary source of energy for photosynthesis. The leaves of plants contain a pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight. This absorbed sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Therefore, leaves need to have a large surface area to maximize their exposure to sunlight.
2. Leaf structure and surface area:
Leaves are flat and thin, providing a large surface area for sunlight absorption. They are typically broad and have a large number of interconnected cells. The upper surface of the leaf is exposed to sunlight, while the lower surface allows for gas exchange. The arrangement of cells and structures like chloroplasts within the leaf further increases the surface area available for sunlight absorption.
3. Role of chlorophyll:
Chlorophyll, the green pigment found in chloroplasts, is responsible for capturing sunlight. It is located in specialized cells called mesophyll cells, which are found in the middle layer of the leaf. The chlorophyll pigments absorb light energy, primarily from the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and transfer it to the chloroplasts. This energy is then used to fuel the process of photosynthesis.
4. Other functions of leaves:
In addition to absorbing sunlight, leaves also play a vital role in the exchange of gases. Through tiny openings called stomata, leaves absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, which is necessary for photosynthesis. The stomata also allow for the release of oxygen (O2) produced during photosynthesis and the exchange of water vapor.
Conclusion:
Leaves provide the surface area necessary for the absorption of sunlight, which initiates the process of photosynthesis. Through the presence of chlorophyll and the structure of their cells, leaves maximize their exposure to sunlight and optimize the energy capture needed for photosynthesis. While leaves also absorb carbon dioxide and water, these processes are not the primary purpose of their large surface area.
Plants store extra food in the form of:- a)Carbon dioxide
- b)Starch
- c)Oxygen
- d)Chlorophyll
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Plants store extra food in the form of:
a)
Carbon dioxide
b)
Starch
c)
Oxygen
d)
Chlorophyll
|
|
Nisha Choudhury answered |
- Plants have a remarkable ability to produce their own food through a process called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide from the air, and water from the soil to create glucose, which is a type of sugar. Glucose is the primary source of energy for plants.
- However, plants often produce more glucose than they immediately need for energy. To save this extra food for later use, plants convert the glucose into a different substance called starch. Starch is a complex carbohydrate that serves as a storage form of energy in plants.
- Similar to how we save extra food in a pantry or refrigerator for later consumption, plants store their extra food in the form of starch. The starch is stored in different parts of the plant, such as roots, stems, and leaves, and can be used when the plant needs energy but is unable to perform photosynthesis, such as during the night or in winter when there is less sunlight available.
The stomata are the pores in the leaf. Their function is to take in:- a)Carbon dioxide for photosynthesis
- b)Oxygen for photosynthesis
- c)Carbon dioxide for respiration
- d)Oxygen for respiration
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The stomata are the pores in the leaf. Their function is to take in:
a)
Carbon dioxide for photosynthesis
b)
Oxygen for photosynthesis
c)
Carbon dioxide for respiration
d)
Oxygen for respiration
|
|
Nisha Choudhury answered |
- Stomata are tiny openings or pores found on the surface of leaves. They play an important role in the process of photosynthesis, which is how plants make their food.
- Stomata allow gases to enter and exit the leaf. One of their main functions is to take in carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air. Carbon dioxide is an essential raw material for photosynthesis.
- Inside the leaf, with the help of sunlight and chlorophyll, carbon dioxide combines with water to produce glucose (sugar) and release oxygen as a byproduct.
So, the correct answer is option A) Carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
Mushroom gets its food from:- a)The water we pour near it
- b)Dead and decaying plants
- c)Photosynthesis
- d)Eating small insects that come near it
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mushroom gets its food from:
a)
The water we pour near it
b)
Dead and decaying plants
c)
Photosynthesis
d)
Eating small insects that come near it
|
|
Sounak Kulkarni answered |
Mushroom gets its food from:
Dead and decaying plants
Mushrooms are fungi that belong to a separate kingdom called Fungi. Unlike plants, they do not have chlorophyll and cannot carry out photosynthesis to produce their own food. Instead, mushrooms obtain their nutrition from organic matter in their environment, particularly dead and decaying plants.
Decomposers:
Mushrooms are decomposers, which means they play an important role in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients in ecosystems. When plants die, their organic material starts to decompose, and mushrooms are one of the organisms that help in this process. They secrete enzymes that break down complex organic compounds present in dead plants into simpler forms that they can absorb and use as food.
Nutrient Absorption:
Mushrooms have a network of fine, thread-like structures called mycelium that spread through the soil or other substrates. The mycelium acts as the feeding structure of the mushroom and is responsible for absorbing nutrients. It grows through the decaying organic matter, releasing enzymes that break down complex molecules into smaller molecules that can be absorbed. The mycelium then takes up these nutrients and transports them to the mushroom's fruiting body, which is the visible part of the mushroom that we usually see.
Role in Ecosystems:
Mushrooms are not only important decomposers, but they also have a symbiotic relationship with plants. Some mushrooms form mycorrhizal associations with the roots of plants, where they exchange nutrients with the plant. In this mutualistic relationship, the mushrooms provide the plant with essential nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, while the plant provides the mushrooms with carbohydrates produced through photosynthesis.
Conclusion:
In summary, mushrooms obtain their food by decomposing dead and decaying plants. They secrete enzymes to break down organic matter, absorb the nutrients through their mycelium, and transport them to their fruiting bodies. Mushrooms are vital for nutrient cycling in ecosystems and have a symbiotic relationship with plants.
Dead and decaying plants
Mushrooms are fungi that belong to a separate kingdom called Fungi. Unlike plants, they do not have chlorophyll and cannot carry out photosynthesis to produce their own food. Instead, mushrooms obtain their nutrition from organic matter in their environment, particularly dead and decaying plants.
Decomposers:
Mushrooms are decomposers, which means they play an important role in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients in ecosystems. When plants die, their organic material starts to decompose, and mushrooms are one of the organisms that help in this process. They secrete enzymes that break down complex organic compounds present in dead plants into simpler forms that they can absorb and use as food.
Nutrient Absorption:
Mushrooms have a network of fine, thread-like structures called mycelium that spread through the soil or other substrates. The mycelium acts as the feeding structure of the mushroom and is responsible for absorbing nutrients. It grows through the decaying organic matter, releasing enzymes that break down complex molecules into smaller molecules that can be absorbed. The mycelium then takes up these nutrients and transports them to the mushroom's fruiting body, which is the visible part of the mushroom that we usually see.
Role in Ecosystems:
Mushrooms are not only important decomposers, but they also have a symbiotic relationship with plants. Some mushrooms form mycorrhizal associations with the roots of plants, where they exchange nutrients with the plant. In this mutualistic relationship, the mushrooms provide the plant with essential nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, while the plant provides the mushrooms with carbohydrates produced through photosynthesis.
Conclusion:
In summary, mushrooms obtain their food by decomposing dead and decaying plants. They secrete enzymes to break down organic matter, absorb the nutrients through their mycelium, and transport them to their fruiting bodies. Mushrooms are vital for nutrient cycling in ecosystems and have a symbiotic relationship with plants.
Which part of a sugarcane plant contains food?- a)Fruit
- b)Stem
- c)Root
- d)Leaf
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of a sugarcane plant contains food?
a)
Fruit
b)
Stem
c)
Root
d)
Leaf
|
|
Gourav joshi answered |
The part of a sugarcane plant that contains food is the stem. The stem of a sugarcane plant is a long, thick, cylindrical structure that grows vertically upwards from the ground. It is made up of a series of joints, or nodes, that are separated by internodes. The stem is the main source of food for the plant and stores a large amount of sugars and other nutrients.
The other parts of a sugarcane plant (fruit, root, and leaf) do not contain food. The fruit of a sugarcane plant is a small, round, greenish structure that is produced at the end of the stem. The root system of a sugarcane plant consists of a main taproot and numerous lateral roots that anchor the plant to the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. The leaves of a sugarcane plant are long, narrow, and pointed, and are used by the plant to produce food through photosynthesis.
Therefore, the correct answer is b) stem.
Which of the following instruments is used to examine the cells of a leaf?- a)Telescope
- b)Magnifying glass
- c)Camera
- d)Microscope
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following instruments is used to examine the cells of a leaf?
a)
Telescope
b)
Magnifying glass
c)
Camera
d)
Microscope
|
|
Saikat Kapoor answered |
Introduction:
The instrument used to examine the cells of a leaf is a microscope. A microscope is an essential tool for scientists and researchers as it allows them to observe tiny objects and structures that cannot be seen with the naked eye. By using a microscope, we can study the intricate details of cells and understand their functions and characteristics.
Explanation:
Here's a detailed explanation of why a microscope is the correct instrument for examining leaf cells:
1. Magnification:
- A microscope is designed to magnify objects, allowing us to view them in much greater detail.
- Leaf cells are very small, and their structures cannot be seen clearly without magnification.
- The microscope's lenses and eyepiece work together to increase the size of the cells, making them visible to the observer.
2. Resolving Power:
- The resolving power of a microscope refers to its ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects.
- Leaf cells have various components, such as chloroplasts, nucleus, and cell walls, that need to be observed separately.
- A microscope with high resolving power can distinguish between these structures and provide clear images of individual cells.
3. Types of Microscopes:
- There are different types of microscopes used for examining cells, including light microscopes and electron microscopes.
- Light microscopes use visible light to illuminate the specimen, while electron microscopes use beams of electrons.
- Both types of microscopes can be used to study leaf cells, depending on the level of detail required.
4. Preparation of Leaf Cells:
- Before examining leaf cells under a microscope, they need to be prepared for observation.
- This usually involves obtaining a thin section of the leaf and placing it on a glass slide.
- Staining techniques may also be used to enhance the visibility of certain cell structures.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a microscope is the instrument used to examine the cells of a leaf. It provides the necessary magnification and resolving power to observe the intricate details of leaf cells. By using a microscope, scientists can study the structure and function of cells, contributing to our understanding of plant biology.
The instrument used to examine the cells of a leaf is a microscope. A microscope is an essential tool for scientists and researchers as it allows them to observe tiny objects and structures that cannot be seen with the naked eye. By using a microscope, we can study the intricate details of cells and understand their functions and characteristics.
Explanation:
Here's a detailed explanation of why a microscope is the correct instrument for examining leaf cells:
1. Magnification:
- A microscope is designed to magnify objects, allowing us to view them in much greater detail.
- Leaf cells are very small, and their structures cannot be seen clearly without magnification.
- The microscope's lenses and eyepiece work together to increase the size of the cells, making them visible to the observer.
2. Resolving Power:
- The resolving power of a microscope refers to its ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects.
- Leaf cells have various components, such as chloroplasts, nucleus, and cell walls, that need to be observed separately.
- A microscope with high resolving power can distinguish between these structures and provide clear images of individual cells.
3. Types of Microscopes:
- There are different types of microscopes used for examining cells, including light microscopes and electron microscopes.
- Light microscopes use visible light to illuminate the specimen, while electron microscopes use beams of electrons.
- Both types of microscopes can be used to study leaf cells, depending on the level of detail required.
4. Preparation of Leaf Cells:
- Before examining leaf cells under a microscope, they need to be prepared for observation.
- This usually involves obtaining a thin section of the leaf and placing it on a glass slide.
- Staining techniques may also be used to enhance the visibility of certain cell structures.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a microscope is the instrument used to examine the cells of a leaf. It provides the necessary magnification and resolving power to observe the intricate details of leaf cells. By using a microscope, scientists can study the structure and function of cells, contributing to our understanding of plant biology.
The loss of water through the leaves of a plant is called:- a)Inspiration
- b)Expiration
- c)Transpiration
- d)Photosynthesis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The loss of water through the leaves of a plant is called:
a)
Inspiration
b)
Expiration
c)
Transpiration
d)
Photosynthesis
|
|
Shivam Mehra answered |
Transpiration is the correct answer.
Explanation:
Transpiration is the process of loss of water through the leaves of a plant. It is an important process in the water cycle, as it helps to maintain the water balance in the environment.
When the water is absorbed by the roots of the plant, it travels up to the leaves through the stem. The water is then released into the air through tiny pores called stomata present on the leaves. This process of water loss through the leaves is called transpiration.
Transpiration plays an important role in regulating the temperature of the plant. As the water is released into the air, it cools down the plant. It also helps in the absorption of nutrients and minerals from the soil by creating a negative pressure in the roots that pulls the water and nutrients up through the plant.
Transpiration also helps in the upward movement of water in the xylem vessels of the plant. This movement of water is essential for the survival of the plant as it helps in the transport of nutrients, minerals, and other essential substances throughout the plant.
In summary, transpiration is the process of loss of water through the leaves of a plant, which helps in regulating the temperature of the plant, absorption of nutrients, and upward movement of water in the plant.
Explanation:
Transpiration is the process of loss of water through the leaves of a plant. It is an important process in the water cycle, as it helps to maintain the water balance in the environment.
When the water is absorbed by the roots of the plant, it travels up to the leaves through the stem. The water is then released into the air through tiny pores called stomata present on the leaves. This process of water loss through the leaves is called transpiration.
Transpiration plays an important role in regulating the temperature of the plant. As the water is released into the air, it cools down the plant. It also helps in the absorption of nutrients and minerals from the soil by creating a negative pressure in the roots that pulls the water and nutrients up through the plant.
Transpiration also helps in the upward movement of water in the xylem vessels of the plant. This movement of water is essential for the survival of the plant as it helps in the transport of nutrients, minerals, and other essential substances throughout the plant.
In summary, transpiration is the process of loss of water through the leaves of a plant, which helps in regulating the temperature of the plant, absorption of nutrients, and upward movement of water in the plant.
The secondary stems grow out from the main stem, and these stems have:- a)Thistles
- b)Flowers
- c)Leaves
- d)Stems
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The secondary stems grow out from the main stem, and these stems have:
a)
Thistles
b)
Flowers
c)
Leaves
d)
Stems
|
|
Kalyan Singh answered |
Main Stem - Holds up the plant and carries water throughout the plant. Secondary Stem - A stem that grows out from the main stem and holds the leaves. Chlorophyll - The green matter that is needed to make food for the plant.
One day when Ananya was holding her sunflower plant, the stem of the plant accidentally broke. Her plant died two days later. Why?
1. The plant could not transport food made by the leaves to the rest of the plant
2. The plant lost too much water through the break in the stem
3. The plant could not transport water from the roots to the leaves- a)1
- b)3
- c)1 and 3
- d)2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One day when Ananya was holding her sunflower plant, the stem of the plant accidentally broke. Her plant died two days later. Why?
1. The plant could not transport food made by the leaves to the rest of the plant
2. The plant lost too much water through the break in the stem
3. The plant could not transport water from the roots to the leaves
1. The plant could not transport food made by the leaves to the rest of the plant
2. The plant lost too much water through the break in the stem
3. The plant could not transport water from the roots to the leaves
a)
1
b)
3
c)
1 and 3
d)
2 and 3
|
|
Kavya Desai answered |
The Correct Answer is Option 'C' (1 and 3)
Explanation:
When the stem of the sunflower plant broke, it caused two major problems for the plant, leading to its death.
1. The plant could not transport food made by the leaves to the rest of the plant:
- The stem of a plant is responsible for transporting food made by the leaves to other parts of the plant.
- This food is produced through a process called photosynthesis, where the leaves use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food in the form of glucose.
- The food produced in the leaves is transported to different parts of the plant through a tissue called 'phloem' present in the stem.
- However, when the stem breaks, the phloem tissue gets damaged, and the transportation of food is disrupted.
- As a result, the plant cannot get the necessary nutrients and energy to survive and eventually dies.
2. The plant could not transport water from the roots to the leaves:
- The stem also plays a crucial role in transporting water from the roots to the leaves of the plant.
- Water is essential for the plant's growth and survival as it helps in carrying nutrients from the soil to different parts of the plant.
- The stem contains a tissue called 'xylem' that is responsible for upward movement of water.
- However, when the stem breaks, the xylem tissue gets damaged, and the transportation of water is hindered.
- Without a continuous supply of water, the plant's leaves cannot perform photosynthesis effectively, and the plant eventually withers and dies.
In conclusion, when the stem of the sunflower plant broke, it disrupted the transportation of both food and water within the plant. Without a supply of nutrients and water, the plant was unable to survive, leading to its death. Therefore, both option 1 and 3 are correct.
Explanation:
When the stem of the sunflower plant broke, it caused two major problems for the plant, leading to its death.
1. The plant could not transport food made by the leaves to the rest of the plant:
- The stem of a plant is responsible for transporting food made by the leaves to other parts of the plant.
- This food is produced through a process called photosynthesis, where the leaves use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food in the form of glucose.
- The food produced in the leaves is transported to different parts of the plant through a tissue called 'phloem' present in the stem.
- However, when the stem breaks, the phloem tissue gets damaged, and the transportation of food is disrupted.
- As a result, the plant cannot get the necessary nutrients and energy to survive and eventually dies.
2. The plant could not transport water from the roots to the leaves:
- The stem also plays a crucial role in transporting water from the roots to the leaves of the plant.
- Water is essential for the plant's growth and survival as it helps in carrying nutrients from the soil to different parts of the plant.
- The stem contains a tissue called 'xylem' that is responsible for upward movement of water.
- However, when the stem breaks, the xylem tissue gets damaged, and the transportation of water is hindered.
- Without a continuous supply of water, the plant's leaves cannot perform photosynthesis effectively, and the plant eventually withers and dies.
In conclusion, when the stem of the sunflower plant broke, it disrupted the transportation of both food and water within the plant. Without a supply of nutrients and water, the plant was unable to survive, leading to its death. Therefore, both option 1 and 3 are correct.
Which of the following is an example of a fixed aquatic plant?- a)Water Hyacinth
- b)Duckweed
- c)Lotus
- d)Water Lettuce
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of a fixed aquatic plant?
a)
Water Hyacinth
b)
Duckweed
c)
Lotus
d)
Water Lettuce

|
Kds Coaching answered |
Lotus and water lily are examples of fixed aquatic plants. These plants are attached to the bed of the water body and have broad leaves. In contrast, water hyacinth, duckweed, and water lettuce are free-floating aquatic plants that float on water without being attached to the surface.
There are four plants:
Coconut tree
Cactus
Mushroom
Mimosa
Among those four, mushroom should be categorized differently because:
1. The mushroom feeds on decaying things while the rest do not
2. The mushroom is a plant while the rest are not
3. The mushroom is a fungus while the rest are not
4. The mushroom cannot make its own food while the rest can- a)1 and 2
- b)1, 3, and 4
- c)2 and 3
- d)Only 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There are four plants:
Coconut tree
Cactus
Mushroom
Mimosa
Among those four, mushroom should be categorized differently because:
1. The mushroom feeds on decaying things while the rest do not
2. The mushroom is a plant while the rest are not
3. The mushroom is a fungus while the rest are not
4. The mushroom cannot make its own food while the rest can
Coconut tree
Cactus
Mushroom
Mimosa
Among those four, mushroom should be categorized differently because:
1. The mushroom feeds on decaying things while the rest do not
2. The mushroom is a plant while the rest are not
3. The mushroom is a fungus while the rest are not
4. The mushroom cannot make its own food while the rest can
a)
1 and 2
b)
1, 3, and 4
c)
2 and 3
d)
Only 4
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is B: 1, 3, and 4.
Reasons:
1. The mushroom feeds on decaying things while the rest do not:
- Mushroom is a decomposer and obtains its nutrients by breaking down dead organic matter. This is known as saprophytic nutrition.
- Coconut tree, cactus, and mimosa are autotrophs that can produce their own food through photosynthesis.
2. The mushroom is a fungus while the rest are not:
- Mushroom belongs to the kingdom Fungi, which is a distinct biological group separate from plants.
- Coconut tree, cactus, and mimosa are all plants belonging to the kingdom Plantae.
3. The mushroom cannot make its own food while the rest can:
- Mushroom lacks chlorophyll, a pigment necessary for photosynthesis, so it cannot make its own food.
- Coconut tree, cactus, and mimosa possess chlorophyll and are capable of photosynthesis to synthesize their own food.
Therefore, mushroom should be categorized differently from the other plants because it feeds on decaying matter, is a fungus, and cannot produce its own food through photosynthesis.
The correct answer is B: 1, 3, and 4.
Reasons:
1. The mushroom feeds on decaying things while the rest do not:
- Mushroom is a decomposer and obtains its nutrients by breaking down dead organic matter. This is known as saprophytic nutrition.
- Coconut tree, cactus, and mimosa are autotrophs that can produce their own food through photosynthesis.
2. The mushroom is a fungus while the rest are not:
- Mushroom belongs to the kingdom Fungi, which is a distinct biological group separate from plants.
- Coconut tree, cactus, and mimosa are all plants belonging to the kingdom Plantae.
3. The mushroom cannot make its own food while the rest can:
- Mushroom lacks chlorophyll, a pigment necessary for photosynthesis, so it cannot make its own food.
- Coconut tree, cactus, and mimosa possess chlorophyll and are capable of photosynthesis to synthesize their own food.
Therefore, mushroom should be categorized differently from the other plants because it feeds on decaying matter, is a fungus, and cannot produce its own food through photosynthesis.
Chapter doubts & questions for Plants - Science Olympiad Class 4 2025 is part of Class 4 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 4 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 4 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Plants - Science Olympiad Class 4 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 4 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 4 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Olympiad Class 4
52 videos|70 docs|53 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









