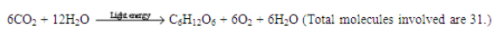All Exams >
NEET >
Biology Class 11 >
All Questions
All questions of Photosynthesis in Higher Plants for NEET Exam
The splitting of water molecule is take place inside
a)Outer membraneb)Lumenc)Stromad)Inner membrane Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vibhor Goyal answered |
Splitting of water takes place near PS II, located in the inner side of the thylakoid membrane.
Splitting of water releases oxygen in the atmosphere and generates a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
The splitting of water molecules is associated with- a)PS II
- b)PS I
- c)Cyclic phosphorylation
- d)Non-cyclic phosphorylation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The splitting of water molecules is associated with
a)
PS II
b)
PS I
c)
Cyclic phosphorylation
d)
Non-cyclic phosphorylation
|
|
Swara Sarkar answered |
This is achieved by electrons available due to splitting of water. The splitting of water is associated with the PS II; water is split into H+, [O] and electrons.
In the half-leaf experiment of photosynthesis, KOH solution is used because- a)It provides O2 to the leaf.
- b)It provides moisture to the leaf.
- c)It helps in CO2 fixation.
- d)It absorbs CO2.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the half-leaf experiment of photosynthesis, KOH solution is used because
a)
It provides O2 to the leaf.
b)
It provides moisture to the leaf.
c)
It helps in CO2 fixation.
d)
It absorbs CO2.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
KOH (Potassium Hydroxide) absorbs carbon dioxide. The leaf inside the bottle containing KOH solution does not become blue-black when compared with the leaf which is exposed to atmospheric air. This shows that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis.
The dark reaction in photosynthesis is called so because- a)It does not depend on light energy.
- b)It can occur in dark also.
- c)It cannot occur during day light.
- d)It occurs more rapidly at night.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dark reaction in photosynthesis is called so because
a)
It does not depend on light energy.
b)
It can occur in dark also.
c)
It cannot occur during day light.
d)
It occurs more rapidly at night.
|
|
Mansi Ahuja answered |
Explanation:
Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll pigment. The process of photosynthesis is divided into two parts - light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions.
The light reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and involve the absorption of light energy by the pigments like chlorophyll and the conversion of that energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. The dark reactions, on the other hand, occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts and are also known as the Calvin cycle.
Dark reactions in photosynthesis:
The dark reactions or the light-independent reactions in photosynthesis are so called because they do not require the presence of light energy to occur. These reactions can occur in the absence of light, but they do require the products of the light-dependent reactions, i.e., ATP and NADPH, to proceed. The dark reactions involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules like glucose, which can be used as a source of energy by the plant.
The dark reactions also involve the enzyme RuBisCO, which is responsible for catalyzing the reaction between carbon dioxide and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP). The reaction produces two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate, which is then converted into other organic molecules like glucose and other carbohydrates.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the dark reactions in photosynthesis are called so because they do not depend on light energy to occur. They can occur in the absence of light, but they do require the products of the light-dependent reactions to proceed. The dark reactions involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules and are essential for the synthesis of glucose and other carbohydrates, which serve as a source of energy for the plant.
Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll pigment. The process of photosynthesis is divided into two parts - light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions.
The light reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and involve the absorption of light energy by the pigments like chlorophyll and the conversion of that energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. The dark reactions, on the other hand, occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts and are also known as the Calvin cycle.
Dark reactions in photosynthesis:
The dark reactions or the light-independent reactions in photosynthesis are so called because they do not require the presence of light energy to occur. These reactions can occur in the absence of light, but they do require the products of the light-dependent reactions, i.e., ATP and NADPH, to proceed. The dark reactions involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules like glucose, which can be used as a source of energy by the plant.
The dark reactions also involve the enzyme RuBisCO, which is responsible for catalyzing the reaction between carbon dioxide and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP). The reaction produces two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate, which is then converted into other organic molecules like glucose and other carbohydrates.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the dark reactions in photosynthesis are called so because they do not depend on light energy to occur. They can occur in the absence of light, but they do require the products of the light-dependent reactions to proceed. The dark reactions involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules and are essential for the synthesis of glucose and other carbohydrates, which serve as a source of energy for the plant.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which range of wavelength (in nm) is called photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)?
- A:
400-700
- B:
760-10,000
- C:
100-390
- D:
390-430
The answer is a.
Which range of wavelength (in nm) is called photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)?
400-700
760-10,000
100-390
390-430
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Photosynthetically active radiation. Photosynthetically active radiation, often abbreviated PAR, designates the spectral range (wave band) of solar radiation from 400 to 700 nanometers that photosynthetic organisms are able to use in the process of photosynthesis.
The C4 plants show higher rate of photosynthesis in- a)Optimum temperature
- b)High temperature
- c)Absence of temperature
- d)Low temperature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The C4 plants show higher rate of photosynthesis in
a)
Optimum temperature
b)
High temperature
c)
Absence of temperature
d)
Low temperature

|
Shreya Saini answered |
C4 planets show higher rate of photosynthesis in higher temperatures because there is no energy loss in photorespiration in these plants, i.e.at high temperature they show full efficiency of production.
During photochemical reaction of photosynthesis –- a)liberation of O2 takes place
- b)Formation of ATP and NADPH2 take place
- c)Liberation of O2, formation of ATP, and NADPH2 takes place
- d)Assimilation of CO2 takes place
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During photochemical reaction of photosynthesis –
a)
liberation of O2 takes place
b)
Formation of ATP and NADPH2 take place
c)
Liberation of O2, formation of ATP, and NADPH2 takes place
d)
Assimilation of CO2 takes place
|
|
Momin Anam answered |
C is correct
The by product of photosynthesis is- a)CO2
- b)Oxygen
- c)Energy
- d)Sugar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The by product of photosynthesis is
a)
CO2
b)
Oxygen
c)
Energy
d)
Sugar

|
Rajni Kokate answered |
6(CO2) + 12(H2O) ----------> C6H12O6 +6(O2) + 6H2O
In photosynthesis phototrophs synthesize glucose and water and evolve O2 as by product
In photosynthesis phototrophs synthesize glucose and water and evolve O2 as by product
In higher plants, the shape of the chloroplast is- a)Reticulate
- b)Girdle-shaped
- c)Discoid
- d)Cup-shaped
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In higher plants, the shape of the chloroplast is
a)
Reticulate
b)
Girdle-shaped
c)
Discoid
d)
Cup-shaped

|
EduRev JEE answered |
Chloroplasts are the green plastids which take part in photosynthesis and temporary or permanent storage of starch. These are discoid (disc-shaped) in higher plants with diameter of 4-6 μm and thickness of 2-4.μm.
The Calvin cycle leads to reduction of- a)RUBP
- b)RUMP
- c)O2
- d)CO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Calvin cycle leads to reduction of
a)
RUBP
b)
RUMP
c)
O2
d)
CO2
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
In fixation, the first stage of the Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions are initiated; CO2 is fixed from an inorganic to an organic molecule. In the second stage, ATP and NADPH are used to reduce 3-PGA into G3P; then ATP and NADPH are converted to ADP and NADP+, respectively.
Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in- a)Grana
- b)Pyrenoid
- c)Stroma
- d)Both grana and stroma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in
a)
Grana
b)
Pyrenoid
c)
Stroma
d)
Both grana and stroma
|
|
Gulzar Ahmad answered |
Grana are the stakes of thylakoids which possess green pigment called chlorophyll...
Who described the first action spectrum for photosynthesis?- a)T. W. Engelmann
- b)Cornelius van Niel
- c)Joseph Priestley
- d)Julius von Sachs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who described the first action spectrum for photosynthesis?
a)
T. W. Engelmann
b)
Cornelius van Niel
c)
Joseph Priestley
d)
Julius von Sachs
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Engelmann used a prism to split light into its spectral components, and then illuminated a green alga, Cladophora, placed in a suspension of aerobic bacteria. The bacteria were used to detect the sites of oxygen evolution.
He observed that bacteria mainly accumulated in the region of blue and red light of the split spectrum, thus giving the first action spectrum of photosynthesis.
Element which helps in electron transport in the process of photosynthesis is- a)Zinc
- b)Molybdenum
- c)Boron
- d)Mangnese
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Element which helps in electron transport in the process of photosynthesis is
a)
Zinc
b)
Molybdenum
c)
Boron
d)
Mangnese
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
During noncyclic electron flow the electron hole in P-680 is filled by electrons obtained by photolysis of water. As a result, there is an evolution of oxygen and the electron move through Mn-protein bound to PS II. In this transport Mn++ is oxidised to Mn+++ and then reduced to Mn++ in a cyclic manner. The manganese thus transfers electrons from water to photosystem II and thus plays an important role in electron transport in the process of photosynthesis.
Select the incorrectly matched pair with regard to the C4 cycle.- a)Primary CO2 fixation product – PGA
- b)C4 plant – Maize
- c)Primary CO2 acceptor – PEP
- d)Site of initial carboxylation – Mesophyll cells
- e)Location of enzyme RuBisCO – Bundle sheath cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrectly matched pair with regard to the C4 cycle.
a)
Primary CO2 fixation product – PGA
b)
C4 plant – Maize
c)
Primary CO2 acceptor – PEP
d)
Site of initial carboxylation – Mesophyll cells
e)
Location of enzyme RuBisCO – Bundle sheath cells
|
|
Vignesh answered |
The primary CO
2
fixation product in C
4
plants is oxaloacetic acid, which is converted to malic acid or aspartic acid that is transported to the bundle sheath cells where the acid is decarboxylated and the CO
2
thus released enters the Calvin cycle.
Which one of the following is wrong in relation to photorespiration?- a)It occurs in daytime only.
- b)It occurs in chloroplast.
- c)It is characteristic of C3 plants.
- d)It is characteristic of C4 plants.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is wrong in relation to photorespiration?
a)
It occurs in daytime only.
b)
It occurs in chloroplast.
c)
It is characteristic of C3 plants.
d)
It is characteristic of C4 plants.

|
Virat answered |
C4 plant does not show photorespiration.
Which pigment system ultimately donates e– for the reduction of NADP.- a)PS II
- b)PS I
- c)CO2
- d)Plastoquinone
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which pigment system ultimately donates e– for the reduction of NADP.
a)
PS II
b)
PS I
c)
CO2
d)
Plastoquinone

|
Navya Sengupta answered |
Ans.
The electrons from PS I may also pass onto an electron carrier and then combine with the hydrogen ions (from the water) to reduce NADP to NADPH. This reduced NADP is used in the next series of reactions.
ADP + iP = ATP in grana is called :–- a)Phosphorylation
- b)Oxidative phosphorylation
- c)Photophosphorylation
- d)Photolysis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
ADP + iP = ATP in grana is called :–
a)
Phosphorylation
b)
Oxidative phosphorylation
c)
Photophosphorylation
d)
Photolysis

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Photophosphorylation is the conversion of ADP to ATP using the energy of sunlight by activation of PSII. This involves the splitting of the water molecule in oxygen and hydrogen protons (H+), a process known as photolysis.
In PSI, the reaction centre the chlorophyll a has an absorption peak at- a)780nm
- b)700nm
- c)680nm
- d)800nm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In PSI, the reaction centre the chlorophyll a has an absorption peak at
a)
780nm
b)
700nm
c)
680nm
d)
800nm
|
|
Vartika Shukla (NEET Aspirant) answered |
In PS-I, the reaction centre chlorophyll a has an absorption peak at 700 nm, hence, is called P 700 while in PS-H, it has absorption maxima at 680 nm, so is called P 680.
so the correct answer is b) 700nm
so the correct answer is b) 700nm
The first step in photosynthesis is- a)Joining of three carbon atoms to from glucose
- b)Formation of ATP
- c)Ionization of water
- d)Excitement of an electron of chlorophyll by a photon of light.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The first step in photosynthesis is
a)
Joining of three carbon atoms to from glucose
b)
Formation of ATP
c)
Ionization of water
d)
Excitement of an electron of chlorophyll by a photon of light.
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The energy from the sun, raises an energy level in the chlorophyll molecule, causing electrons to leave the molecule and travel along the electron transport chain (ETC) in a series of oxidation and reductions. In doing so it releases energy converting ADP+Pi into ATP. Photolysis (splitting of water) occurs, and the electrons produced, replace those lost. This is the Light Dependant stage as it relies on light energy
In photosynthesis, hydrogen is transferred from the light reactions to dark reactions by :–- a)DPN
- b)DNA
- c)ATP
- d)NADP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In photosynthesis, hydrogen is transferred from the light reactions to dark reactions by :–
a)
DPN
b)
DNA
c)
ATP
d)
NADP

|
Bs Academy answered |
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages, light reaction, and dark reaction. During the light reaction reduced NADPH2 and ATP are synthesized. These products are used subsequently to reduce carbon dioxide into sugars. The purpose of ATP in photosynthesis is to transfer energy from light reaction to dark reaction. The purpose of NADP is to transfer hydrogen from light reaction to dark reaction in the form of reduced NADPH2.
For fixing one molecule of CO2 in Calvin cycle, required- a)3ATP+2NADPH2
- b)3ATP+1NADPH2
- c)2ATP+3NADPH2
- d)3ATP+3NADPH2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For fixing one molecule of CO2 in Calvin cycle, required
a)
3ATP+2NADPH2
b)
3ATP+1NADPH2
c)
2ATP+3NADPH2
d)
3ATP+3NADPH2

|
Aashna Mukherjee answered |
Fixing of one molecule of carbon dioxide in Calvin cycle require 3 ATP and 2 NADPH2 as the source of energy. One NADPH2 molecule produce 3 molecules of ATP.
Solarisation is- a)Effect of solar light
- b)Destruction of chlorophyll
- c)Formation of chlorophyll
- d)Utilisation of sunlight
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Solarisation is
a)
Effect of solar light
b)
Destruction of chlorophyll
c)
Formation of chlorophyll
d)
Utilisation of sunlight
|
|
Muskaan Dasgupta answered |
Solarisation is the process of destruction of chlorophyll due to prolonged exposure to sunlight. This phenomenon is commonly observed in plants that grow in areas with high solar radiation. Here is a detailed explanation of the process:
Explanation:
Chlorophyll is the green pigment present in the leaves of plants. It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. However, prolonged exposure to sunlight can damage the chlorophyll molecules, leading to their destruction. This process is known as solarisation.
Solarisation occurs due to the following reasons:
1. High intensity of sunlight: Plants that grow in areas with high solar radiation are more prone to solarisation. This is because the intensity of sunlight in these areas is much higher than in other regions.
2. Extended exposure to sunlight: The longer a plant is exposed to sunlight, the greater the damage to its chlorophyll molecules. This is why solarisation is more common during the summer months, when the days are longer and the sun is more intense.
Effects of solarisation:
1. Reduced photosynthesis: Solarisation damages the chlorophyll molecules, which reduces the plant's ability to carry out photosynthesis. This can lead to stunted growth and reduced yield.
2. Loss of colour: As the chlorophyll molecules are destroyed, the leaves of the plant lose their green colour and turn yellow or brown.
3. Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases: Plants that have been solarised are more susceptible to pests and diseases, as their weakened state makes them more vulnerable to attack.
Prevention of solarisation:
1. Shade: Providing shade to the plants can reduce their exposure to sunlight and prevent solarisation. This can be done by using shade cloth or by planting the crops under trees.
2. Watering: Regular watering can help cool down the plants and reduce the damage caused by solarisation.
3. Timely harvesting: Harvesting the crops before they are fully mature can reduce their exposure to sunlight and prevent solarisation.
In conclusion, solarisation is the process of destruction of chlorophyll due to prolonged exposure to sunlight. It can have a negative impact on plant growth and yield, and can be prevented by providing shade, regular watering, and timely harvesting.
Explanation:
Chlorophyll is the green pigment present in the leaves of plants. It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. However, prolonged exposure to sunlight can damage the chlorophyll molecules, leading to their destruction. This process is known as solarisation.
Solarisation occurs due to the following reasons:
1. High intensity of sunlight: Plants that grow in areas with high solar radiation are more prone to solarisation. This is because the intensity of sunlight in these areas is much higher than in other regions.
2. Extended exposure to sunlight: The longer a plant is exposed to sunlight, the greater the damage to its chlorophyll molecules. This is why solarisation is more common during the summer months, when the days are longer and the sun is more intense.
Effects of solarisation:
1. Reduced photosynthesis: Solarisation damages the chlorophyll molecules, which reduces the plant's ability to carry out photosynthesis. This can lead to stunted growth and reduced yield.
2. Loss of colour: As the chlorophyll molecules are destroyed, the leaves of the plant lose their green colour and turn yellow or brown.
3. Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases: Plants that have been solarised are more susceptible to pests and diseases, as their weakened state makes them more vulnerable to attack.
Prevention of solarisation:
1. Shade: Providing shade to the plants can reduce their exposure to sunlight and prevent solarisation. This can be done by using shade cloth or by planting the crops under trees.
2. Watering: Regular watering can help cool down the plants and reduce the damage caused by solarisation.
3. Timely harvesting: Harvesting the crops before they are fully mature can reduce their exposure to sunlight and prevent solarisation.
In conclusion, solarisation is the process of destruction of chlorophyll due to prolonged exposure to sunlight. It can have a negative impact on plant growth and yield, and can be prevented by providing shade, regular watering, and timely harvesting.
Photosynthesis take place in- a)Roots
- b)Leaves
- c)Stem
- d)Flowers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Photosynthesis take place in
a)
Roots
b)
Leaves
c)
Stem
d)
Flowers

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
Photosynthesis takes place only in the green parts of the plants, mainly the leaves.
Internally, the chloroplast is divided into two parts – the membrane system and the fluid portion called stroma. Labour is equally divided between the two parts with each responsible for a particular function of photosynthesis leading to the formation of sugars. Which part(s) is/are involved in the synthesis of ATP and NADPH?
- a)Both membrane system and stroma
- b)Stroma
- c)Neither membrane system nor stroma
- d)Membrane system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Internally, the chloroplast is divided into two parts – the membrane system and the fluid portion called stroma. Labour is equally divided between the two parts with each responsible for a particular function of photosynthesis leading to the formation of sugars. Which part(s) is/are involved in the synthesis of ATP and NADPH?
a)
Both membrane system and stroma
b)
Stroma
c)
Neither membrane system nor stroma
d)
Membrane system
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
There is clear division of labour within the chloroplast. the membrane system is responsible for the light reaction ( trapping light energy and synthesis of ATP and NADPH) while dark reaction i.e., enzymatic reactions for the reduction of carbon dioxide into sugar using ATP and NADPH take place in the stroma.
The photosystem II has reaction centre 680nm absorbs- a)Violet light
- b)Blue light
- c)Red light
- d)Green light
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The photosystem II has reaction centre 680nm absorbs
a)
Violet light
b)
Blue light
c)
Red light
d)
Green light

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
While PS II has a P680 reaction centre that absorbs red light at 680 nm
Which occurs during the light reaction of photosynthesis- a)Chlorophyll is produced
- b)Water splits to form 2H+ & O2
- c)CO2 is given off as a waste
- d)Sugar is formed from CO2 and water
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which occurs during the light reaction of photosynthesis
a)
Chlorophyll is produced
b)
Water splits to form 2H+ & O2
c)
CO2 is given off as a waste
d)
Sugar is formed from CO2 and water
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The chlorophyll pigments which are excited give up their electrons and to compensate for the loss of electrons, water is split to release four H+ ions and four electrons and O2. The electrons that are lost from the PSII enter into an electron transfer chain or ETC.
Who demonstrated the importance of sunlight for the process of photosynthesis?- a)Robert Hill
- b)Engelmann
- c)Jan Ingenhousz
- d)Joseph Priestley
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who demonstrated the importance of sunlight for the process of photosynthesis?
a)
Robert Hill
b)
Engelmann
c)
Jan Ingenhousz
d)
Joseph Priestley
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Jan Ingenhousz is best known for his discovery of photosynthesis, the process by which green plants absorb carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight and release oxygen. Through an ingenious series of experiments, Ingenhousz proved that plant leaves need sunlight rather than heat in order to produce oxygen.
Photorespiration does not occur in- a)C4 plants
- b)C3 plants
- c)Algae
- d)Bacteria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Photorespiration does not occur in
a)
C4 plants
b)
C3 plants
c)
Algae
d)
Bacteria
|
|
Awantika Gupta answered |
Photorespiration is a wastefull process because it doesn't synthesis ATP.
but in new ncert it is mentioned that the requirements of photorespiration is not known yet.
but in new ncert it is mentioned that the requirements of photorespiration is not known yet.
Which pigment absorbs the red and far red light?- a)Cytochrome
- b)Phytochrome
- c)Carotenoids
- d)Chlorophyll
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which pigment absorbs the red and far red light?
a)
Cytochrome
b)
Phytochrome
c)
Carotenoids
d)
Chlorophyll
|
|
Srishti Shah answered |
**Phytochrome**
Phytochrome is a pigment that plays a crucial role in plant growth and development. It is a photoreceptor protein that absorbs red and far-red light wavelengths. This pigment helps plants sense and respond to changes in light conditions, such as the length of the day and the quality of light.
**Structure and Absorption Spectrum**
Phytochrome exists in two interconvertible forms: the red-light absorbing form (Pr) and the far-red-light absorbing form (Pfr). When Pr absorbs red light, it is converted into Pfr, and when Pfr absorbs far-red light, it is converted back to Pr.
The absorption spectrum of phytochrome shows two peaks: one in the red region (around 660 nm) and another in the far-red region (around 730 nm). These absorption peaks allow phytochrome to efficiently absorb red and far-red light, making it the primary pigment responsible for these light wavelengths in plants.
**Functions of Phytochrome**
1. Seed Germination: Phytochrome controls the germination of seeds by sensing and responding to the presence of light. When seeds are exposed to red light, the conversion of Pr to Pfr triggers the germination process.
2. Photomorphogenesis: Phytochrome regulates various aspects of plant development, including stem elongation, leaf expansion, and branching. In the presence of red light, Pfr promotes growth and development, while in the presence of far-red light, the conversion of Pfr to Pr inhibits growth.
3. Photoperiodism: Phytochrome also plays a crucial role in regulating flowering and flowering time in plants. The ratio of red to far-red light is used by plants to determine the length of the day, which in turn affects the flowering process.
4. Shade Avoidance: Plants can detect changes in light quality and quantity and adjust their growth patterns accordingly. Phytochrome helps plants respond to shade by promoting elongation of stems and leaves, allowing them to reach for more available light.
In conclusion, phytochrome is the pigment that absorbs red and far-red light in plants. This pigment plays a vital role in various physiological processes, including seed germination, photomorphogenesis, photoperiodism, and shade avoidance. By sensing and responding to changes in light conditions, phytochrome helps plants optimize their growth and development.
Phytochrome is a pigment that plays a crucial role in plant growth and development. It is a photoreceptor protein that absorbs red and far-red light wavelengths. This pigment helps plants sense and respond to changes in light conditions, such as the length of the day and the quality of light.
**Structure and Absorption Spectrum**
Phytochrome exists in two interconvertible forms: the red-light absorbing form (Pr) and the far-red-light absorbing form (Pfr). When Pr absorbs red light, it is converted into Pfr, and when Pfr absorbs far-red light, it is converted back to Pr.
The absorption spectrum of phytochrome shows two peaks: one in the red region (around 660 nm) and another in the far-red region (around 730 nm). These absorption peaks allow phytochrome to efficiently absorb red and far-red light, making it the primary pigment responsible for these light wavelengths in plants.
**Functions of Phytochrome**
1. Seed Germination: Phytochrome controls the germination of seeds by sensing and responding to the presence of light. When seeds are exposed to red light, the conversion of Pr to Pfr triggers the germination process.
2. Photomorphogenesis: Phytochrome regulates various aspects of plant development, including stem elongation, leaf expansion, and branching. In the presence of red light, Pfr promotes growth and development, while in the presence of far-red light, the conversion of Pfr to Pr inhibits growth.
3. Photoperiodism: Phytochrome also plays a crucial role in regulating flowering and flowering time in plants. The ratio of red to far-red light is used by plants to determine the length of the day, which in turn affects the flowering process.
4. Shade Avoidance: Plants can detect changes in light quality and quantity and adjust their growth patterns accordingly. Phytochrome helps plants respond to shade by promoting elongation of stems and leaves, allowing them to reach for more available light.
In conclusion, phytochrome is the pigment that absorbs red and far-red light in plants. This pigment plays a vital role in various physiological processes, including seed germination, photomorphogenesis, photoperiodism, and shade avoidance. By sensing and responding to changes in light conditions, phytochrome helps plants optimize their growth and development.
The site in chloroplast which is responsible for trapping for light energy is- a)Grana
- b)Stroma
- c)Ribosomes
- d)Stromal lamellae
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The site in chloroplast which is responsible for trapping for light energy is
a)
Grana
b)
Stroma
c)
Ribosomes
d)
Stromal lamellae

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
In chloroplast there is the membranous system consisting of grana, the stroma lamellae, and the fluid stroma. There is a clear division of labour within the chloroplast. The granum is responsible for trapping the light energy.
Photosynthesis is maximum in- a)Very high light
- b)Red light
- c)Green light
- d)Continuous light
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Photosynthesis is maximum in
a)
Very high light
b)
Red light
c)
Green light
d)
Continuous light
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
For the process of photosynthesis, light is abosorbed by Photosystem II which are membrane bound. Photosystem II aborbs infrared and red light (540nm-630nm) and it is for this reason that photosynthesis is highest under red light. Though blue light maybe absorbed the highest it does not activate photosynthesis, red light is.
Which of the following stages of calvin cycle are in correct order?- a)Carboxylation, reduction, regeneration
- b)Regeneration,carboxylation, reduction
- c)Regeneration,reduction,carboxylation
- d)Carboxylation,regeneration,reduction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following stages of calvin cycle are in correct order?
a)
Carboxylation, reduction, regeneration
b)
Regeneration,carboxylation, reduction
c)
Regeneration,reduction,carboxylation
d)
Carboxylation,regeneration,reduction
|
|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
##ncert refer kro yrr... directly Diya hua h..
Dark fixation of CO2 in CAM plants is called ocification because it produces- a)Tartaric acid
- b)Oxaloacetic acid
- c)Malic acid
- d)Formic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dark fixation of CO2 in CAM plants is called ocification because it produces
a)
Tartaric acid
b)
Oxaloacetic acid
c)
Malic acid
d)
Formic acid
|
|
Gopikas S answered |
The principal metabolic feature of CAM plants is assimilation of CO2 at night into malic acid which is stored in the vacuole. Malate is generated in the reaction catalyzed by PEP carboxylase and PEP is, in turn, generated by degradation of starch or soluble sugars. During the day, malate is released from the vacuole and is decarboxylated to provide CO2 for fixation in the Benson–Calvin cycle behind closed stomata. Starch and sugars are then resynthesized .
The number of Oxygen molecules released per photon or quantum of light is called- a)Quantosome
- b)Net Yield
- c)Quantum Yield
- d)Quantum number
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of Oxygen molecules released per photon or quantum of light is called
a)
Quantosome
b)
Net Yield
c)
Quantum Yield
d)
Quantum number

|
Anand Jain answered |
Quantum yield is the number of Oxygen molecules released per photon or quantum of light. During light reaction of photosynthesis oxygen molecules are release during photolysis.
Fixation of 1 CO2 requires :–- a)6NADPH2 & 3ATP
- b)2NADP.H2 & 3ATP
- c)4 NADP.H2 & 3ATP
- d)5 NADP.H2 & 3ATP
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Fixation of 1 CO2 requires :–
a)
6NADPH2 & 3ATP
b)
2NADP.H2 & 3ATP
c)
4 NADP.H2 & 3ATP
d)
5 NADP.H2 & 3ATP
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The Calvin cycle has three stages.
1)carbon fixation
2)reduction
3)regeneration.
At the end of each Calvin cycle net gain is 9ATP and 6 NADPH2.In each Calvin cycle, 3 CO2 molecules are fixed with RuBP to form 2 molecules of 3PGA in the first step. Later two molecules of 3PGA through a series of reactions regenerate 2RuBP in the third stage. So, for the fixation of one CO2 carbon dioxide molecule through the Calvin cycle requires 3ATP and 2NADPH2.
So, the correct answer is 'option B'.
1)carbon fixation
2)reduction
3)regeneration.
At the end of each Calvin cycle net gain is 9ATP and 6 NADPH2.In each Calvin cycle, 3 CO2 molecules are fixed with RuBP to form 2 molecules of 3PGA in the first step. Later two molecules of 3PGA through a series of reactions regenerate 2RuBP in the third stage. So, for the fixation of one CO2 carbon dioxide molecule through the Calvin cycle requires 3ATP and 2NADPH2.
So, the correct answer is 'option B'.
Photophosphorylation is the process in which- a)CO2 and O2 unite
- b)Phosphoglyceric acid is produced
- c)Aspartic acid is formed
- d)Light energy is converted in to chemical energy by production of ATP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Photophosphorylation is the process in which
a)
CO2 and O2 unite
b)
Phosphoglyceric acid is produced
c)
Aspartic acid is formed
d)
Light energy is converted in to chemical energy by production of ATP
|
|
Vartika shukla answered |
Phosphorylation: A biochemical process that involves the addition of phosphate to an organic compound. Examples include the addition of phosphate to glucose to produce glucose monophosphate and the addition of phosphate to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to form adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Phosphorylation is carried out through the action of enzymes known as phosphotransferases or kinases.
The electron ejected by P680 in light reaction is initially accepted by- a)Plastoquinone
- b)ATP
- c)Ferredoxin
- d)P-700
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The electron ejected by P680 in light reaction is initially accepted by
a)
Plastoquinone
b)
ATP
c)
Ferredoxin
d)
P-700

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
During the light reaction, the path of the electron has been elucidated in the Z-scheme. It is named so because of its shape and was first proposed by Hill and Bendall in 1960. The electron released by reaction center of photosystem II i.e., P680 moves uphill and reduces pheophytin, a nonmagnesium chlorophyll a molecule. From pheophytin, electrons are accepted by plastoquinone which requires two electrons for complete reduction. It also accepts two protons from the stromal side of thylakoid membrane and becomes reduced to PQH2 after accepting 2 electrons and 2 protons. It is the only carrier in the photosynthetic electron transport chain, which can bind both electrons and protons.
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was discovered in photosynthesis of- a)Angiosperm
- b)Bryophytes
- c)Algae
- d)Gymnosperm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was discovered in photosynthesis of
a)
Angiosperm
b)
Bryophytes
c)
Algae
d)
Gymnosperm
|
|
Abhiram Basu answered |
Photosynthesis and CO2 fixation
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into organic compounds and oxygen. This process is essential for life on earth as it produces the oxygen that we breathe and provides food for organisms that cannot produce their own.
CO2 fixation is the process by which carbon dioxide is transformed into an organic molecule that can be used by living organisms. This process is important because carbon dioxide is an essential component of the atmosphere, but it is not readily available to most organisms in its gaseous form.
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product
PGA (phosphoglyceric acid) is the first stable product of CO2 fixation in photosynthesis. It is formed when carbon dioxide combines with a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme Rubisco (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase).
Discovery of PGA
The discovery of PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was made by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1940s. They used radioactive carbon-14 to trace the movement of carbon through the photosynthetic process and discovered that PGA was the first stable product of CO2 fixation.
Source of PGA
PGA is produced in the stroma of the chloroplasts in plant cells. It is then used to make glucose and other organic compounds through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions known as the Calvin cycle.
Role of algae in PGA discovery
Algae played a crucial role in the discovery of PGA as the first CO2 fixation product. Algae are photosynthetic organisms that are capable of fixing carbon dioxide in a similar way to plants. They were used by Calvin and his colleagues as a model system to study photosynthesis and CO2 fixation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PGA was discovered as the first CO2 fixation product in photosynthesis by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1940s. This discovery was made using algae as a model system and has since been confirmed in plants and other photosynthetic organisms.
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into organic compounds and oxygen. This process is essential for life on earth as it produces the oxygen that we breathe and provides food for organisms that cannot produce their own.
CO2 fixation is the process by which carbon dioxide is transformed into an organic molecule that can be used by living organisms. This process is important because carbon dioxide is an essential component of the atmosphere, but it is not readily available to most organisms in its gaseous form.
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product
PGA (phosphoglyceric acid) is the first stable product of CO2 fixation in photosynthesis. It is formed when carbon dioxide combines with a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme Rubisco (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase).
Discovery of PGA
The discovery of PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was made by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1940s. They used radioactive carbon-14 to trace the movement of carbon through the photosynthetic process and discovered that PGA was the first stable product of CO2 fixation.
Source of PGA
PGA is produced in the stroma of the chloroplasts in plant cells. It is then used to make glucose and other organic compounds through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions known as the Calvin cycle.
Role of algae in PGA discovery
Algae played a crucial role in the discovery of PGA as the first CO2 fixation product. Algae are photosynthetic organisms that are capable of fixing carbon dioxide in a similar way to plants. They were used by Calvin and his colleagues as a model system to study photosynthesis and CO2 fixation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PGA was discovered as the first CO2 fixation product in photosynthesis by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1940s. This discovery was made using algae as a model system and has since been confirmed in plants and other photosynthetic organisms.
In sugarcane, CO2 is fixed in malic acid with the help of enzyme- a)Ribulose phosphate kinase
- b)RuBP carboxylase
- c)Fructose phosphotase
- d)PEP carboxylase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In sugarcane, CO2 is fixed in malic acid with the help of enzyme
a)
Ribulose phosphate kinase
b)
RuBP carboxylase
c)
Fructose phosphotase
d)
PEP carboxylase
|
|
Jay Kumar answered |
In C4 plants, Carbon dioxide is fixed in malic acid with the help of enzyme phosphoenel pyruvate (PEP). Malic acid is a four carbon compound that later change into oxyloacetic acid.
The chief pigment associated in process of photosynthesis is- a)Chlorophyll m
- b)Chlorophyll c
- c)Chlorophyll b
- d)Chlorophyll a
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The chief pigment associated in process of photosynthesis is
a)
Chlorophyll m
b)
Chlorophyll c
c)
Chlorophyll b
d)
Chlorophyll a
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Chlorophyll a, shows higher rate of photosynthesis. Hence, it is conclude that chlorophyll a is the chief pigment associated with photosynthesis.
In photorespiration, the cell organelles involved are- a)Chloroplast and mitochondrion
- b)Chloroplast, mitochondrion and ribosome
- c)Chloroplast only
- d)Chloroplast, mitochondrion and peroxisome
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In photorespiration, the cell organelles involved are
a)
Chloroplast and mitochondrion
b)
Chloroplast, mitochondrion and ribosome
c)
Chloroplast only
d)
Chloroplast, mitochondrion and peroxisome

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
This process occurs when the concentration of oxygen increase and carbon dioxide decrease and its substrate is glycolate. RubisCO, catalase (CAT) and GOX, and GDC are the main enzymes in chloroplasts, leaf peroxisomes, and mitochondria from mature leaves, respectively, and support the major role of the photorespiratory C2 cycle in leaf metabolism.
So the correct option is 'Mitochondria, peroxisomes and chloroplasts'.
So the correct option is 'Mitochondria, peroxisomes and chloroplasts'.
The carbon in CO2 is radioactively labelled. The product in which this radioactive carbon can be found in C3 plants is
a) PGAL
b) RuBP
c) PGA
d) PEP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pankaj Singh answered |
**Explanation:**
**C3 Plants:**
C3 plants are a type of plants that undergo the Calvin cycle during photosynthesis. In this cycle, the first stable compound formed is a three-carbon molecule called phosphoglycerate (PGA). C3 plants include many common crops such as wheat, rice, and soybeans.
**Radioactive Carbon in CO2:**
When carbon dioxide (CO2) is radioactively labeled, it means that one or more of the carbon atoms in the molecule have been replaced with a radioactive isotope of carbon, such as carbon-14 (^14C). This labeling allows scientists to track the movement and transformation of carbon within a biological system.
**Product of Radioactive Carbon in C3 Plants:**
In C3 plants, the product in which the radioactive carbon can be found is phosphoglycerate (PGA). This is because during the Calvin cycle, CO2 is fixed by the enzyme RuBisCo (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) to form an unstable six-carbon compound called RuBP (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate). This compound then breaks down into two molecules of PGA, each containing three carbon atoms.
**Explanation of Options:**
a) PGAL (phosphoglyceraldehyde): PGAL is an intermediate molecule formed during the Calvin cycle and is a product of PGA. However, it does not directly contain the radioactive carbon from CO2.
b) RuBP (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate): RuBP is the initial compound that reacts with CO2 during the Calvin cycle, but it is not a direct product of radioactive carbon in CO2.
c) PGA (phosphoglycerate): PGA is the first stable product formed during the Calvin cycle and contains the radioactive carbon from CO2. Therefore, this is the correct answer.
d) PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate): PEP is a molecule involved in the formation of glucose during gluconeogenesis, which is not directly related to the Calvin cycle or the fixation of CO2.
**Conclusion:**
The radioactive carbon from CO2 can be found in the product phosphoglycerate (PGA) in C3 plants. This is the first stable compound formed during the Calvin cycle and contains the radioactive carbon.
**C3 Plants:**
C3 plants are a type of plants that undergo the Calvin cycle during photosynthesis. In this cycle, the first stable compound formed is a three-carbon molecule called phosphoglycerate (PGA). C3 plants include many common crops such as wheat, rice, and soybeans.
**Radioactive Carbon in CO2:**
When carbon dioxide (CO2) is radioactively labeled, it means that one or more of the carbon atoms in the molecule have been replaced with a radioactive isotope of carbon, such as carbon-14 (^14C). This labeling allows scientists to track the movement and transformation of carbon within a biological system.
**Product of Radioactive Carbon in C3 Plants:**
In C3 plants, the product in which the radioactive carbon can be found is phosphoglycerate (PGA). This is because during the Calvin cycle, CO2 is fixed by the enzyme RuBisCo (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) to form an unstable six-carbon compound called RuBP (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate). This compound then breaks down into two molecules of PGA, each containing three carbon atoms.
**Explanation of Options:**
a) PGAL (phosphoglyceraldehyde): PGAL is an intermediate molecule formed during the Calvin cycle and is a product of PGA. However, it does not directly contain the radioactive carbon from CO2.
b) RuBP (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate): RuBP is the initial compound that reacts with CO2 during the Calvin cycle, but it is not a direct product of radioactive carbon in CO2.
c) PGA (phosphoglycerate): PGA is the first stable product formed during the Calvin cycle and contains the radioactive carbon from CO2. Therefore, this is the correct answer.
d) PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate): PEP is a molecule involved in the formation of glucose during gluconeogenesis, which is not directly related to the Calvin cycle or the fixation of CO2.
**Conclusion:**
The radioactive carbon from CO2 can be found in the product phosphoglycerate (PGA) in C3 plants. This is the first stable compound formed during the Calvin cycle and contains the radioactive carbon.
In photosynthesis, photolysis of water is used in
- a)None of the below options
- b)Oxidation of FAD
- c)Oxidation of NADP
- d)Reduction of NADP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In photosynthesis, photolysis of water is used in
a)
None of the below options
b)
Oxidation of FAD
c)
Oxidation of NADP
d)
Reduction of NADP

|
Arya Khanna answered |
Breaking down of water molecules in presence of sunlight during photosynthesis is called photolysis of water. During photolysis of water reduction of NADP+ into NADPH takes place.
Chapter doubts & questions for Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Biology Class 11 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Biology Class 11 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily