All Exams >
Humanities/Arts >
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities >
All Questions
All questions of Geography for Humanities/Arts Exam
Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:Available water resources are degrading rapidly. The major rivers of the country generally retain better water quality in less densely populated upper stretches in hilly areas. In plains, river water is used intensively for irrigation, drinking, domestic and industrial purposes. The drains carrying agricultural (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic (solid and liquid wastes), and industrial effluents join the rivers. The concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season when flow of water is low. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in collaboration with State Pollution Control Boards has been monitoring water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continues to be the main source of pollution in rivers. The Yamuna river is the most polluted river in the country between Delhi and Etawah. Other severely polluted rivers are: the Sabarmati at Ahmedabad, the Gomti at Lucknow, the Kali, the Adyar, the Cooum (entire stretches), the Vaigai at Madurai and the Musi of Hyderabad and the Ganga at Kanpur and Varanasi. Ground water pollution has occurred due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride and nitrates at different parts of the country. Q. When was the CPCB established?- a)1964
- b)1974
- c)1984
- d)1994
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:
Available water resources are degrading rapidly. The major rivers of the country generally retain better water quality in less densely populated upper stretches in hilly areas. In plains, river water is used intensively for irrigation, drinking, domestic and industrial purposes. The drains carrying agricultural (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic (solid and liquid wastes), and industrial effluents join the rivers. The concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season when flow of water is low. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in collaboration with State Pollution Control Boards has been monitoring water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continues to be the main source of pollution in rivers. The Yamuna river is the most polluted river in the country between Delhi and Etawah. Other severely polluted rivers are: the Sabarmati at Ahmedabad, the Gomti at Lucknow, the Kali, the Adyar, the Cooum (entire stretches), the Vaigai at Madurai and the Musi of Hyderabad and the Ganga at Kanpur and Varanasi. Ground water pollution has occurred due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride and nitrates at different parts of the country.
Q. When was the CPCB established?
a)
1964
b)
1974
c)
1984
d)
1994
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), statutory organisation, was constituted in September, 1974.
Which one of the following concepts is related to Naturalization of Humans?- a)Environmental Determinism
- b)Possiblism
- c)Humanism
- d)Neo-Determinism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following concepts is related to Naturalization of Humans?
a)
Environmental Determinism
b)
Possiblism
c)
Humanism
d)
Neo-Determinism
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The environmental determinism suggests that humans are not a product of their environment, rather they possess the skills necessary to change their environment to satisfy human needs.
OR
The humans were dictated by nature and its forces. Thus, humans were naturalised because they were afraid of nature and worshipped it. This is known as naturalisation of humans. This naturalisation of humans is termed as environmental determinism.
OR
The humans were dictated by nature and its forces. Thus, humans were naturalised because they were afraid of nature and worshipped it. This is known as naturalisation of humans. This naturalisation of humans is termed as environmental determinism.
Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:Available water resources are degrading rapidly. The major rivers of the country generally retain better water quality in less densely populated upper stretches in hilly areas. In plains, river water is used intensively for irrigation, drinking, domestic and industrial purposes. The drains carrying agricultural (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic (solid and liquid wastes), and industrial effluents join the rivers. The concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season when flow of water is low. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in collaboration with State Pollution Control Boards has been monitoring water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continues to be the main source of pollution in rivers. The Yamuna river is the most polluted river in the country between Delhi and Etawah. Other severely polluted rivers are: the Sabarmati at Ahmedabad, the Gomti at Lucknow, the Kali, the Adyar, the Cooum (entire stretches), the Vaigai at Madurai and the Musi of Hyderabad and the Ganga at Kanpur and Varanasi. Ground water pollution has occurred due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride and nitrates at different parts of the country. Q. Why the available water resources are degrading rapidly?- a)Border conflicts
- b)Concentration of pollutants is very high
- c)Drying up of water bodies
- d)None of the Above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:
Available water resources are degrading rapidly. The major rivers of the country generally retain better water quality in less densely populated upper stretches in hilly areas. In plains, river water is used intensively for irrigation, drinking, domestic and industrial purposes. The drains carrying agricultural (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic (solid and liquid wastes), and industrial effluents join the rivers. The concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season when flow of water is low. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in collaboration with State Pollution Control Boards has been monitoring water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continues to be the main source of pollution in rivers. The Yamuna river is the most polluted river in the country between Delhi and Etawah. Other severely polluted rivers are: the Sabarmati at Ahmedabad, the Gomti at Lucknow, the Kali, the Adyar, the Cooum (entire stretches), the Vaigai at Madurai and the Musi of Hyderabad and the Ganga at Kanpur and Varanasi. Ground water pollution has occurred due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride and nitrates at different parts of the country.
Q. Why the available water resources are degrading rapidly?
a)
Border conflicts
b)
Concentration of pollutants is very high
c)
Drying up of water bodies
d)
None of the Above
|
|
Rajesh Chauhan answered |
Reasons for the rapid degradation of available water resources:
- Concentration of pollutants is very high: The major reason for the rapid degradation of available water resources is the high concentration of pollutants in rivers. These pollutants come from various sources such as agricultural runoff (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic waste (solid and liquid waste), and industrial effluents. During the summer season when the flow of water is low, the concentration of pollutants in rivers increases significantly, leading to water quality degradation.
- Intensive use of river water: In the plains, river water is used intensively for various purposes including irrigation, drinking, domestic, and industrial uses. This intensive use puts pressure on the rivers and contributes to their degradation.
- Groundwater pollution: Groundwater pollution has also occurred in various parts of the country due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride, and nitrates. This further adds to the degradation of available water resources.
- Monitoring and data: The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards have been monitoring the water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continue to be the main sources of pollution in rivers.
In conclusion, the degradation of available water resources is primarily due to the high concentration of pollutants in rivers, intensive use of river water, groundwater pollution, and lack of effective management and monitoring. Addressing these issues through better pollution control measures and sustainable water management practices is essential to prevent further degradation of water resources.
- Concentration of pollutants is very high: The major reason for the rapid degradation of available water resources is the high concentration of pollutants in rivers. These pollutants come from various sources such as agricultural runoff (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic waste (solid and liquid waste), and industrial effluents. During the summer season when the flow of water is low, the concentration of pollutants in rivers increases significantly, leading to water quality degradation.
- Intensive use of river water: In the plains, river water is used intensively for various purposes including irrigation, drinking, domestic, and industrial uses. This intensive use puts pressure on the rivers and contributes to their degradation.
- Groundwater pollution: Groundwater pollution has also occurred in various parts of the country due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride, and nitrates. This further adds to the degradation of available water resources.
- Monitoring and data: The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards have been monitoring the water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continue to be the main sources of pollution in rivers.
In conclusion, the degradation of available water resources is primarily due to the high concentration of pollutants in rivers, intensive use of river water, groundwater pollution, and lack of effective management and monitoring. Addressing these issues through better pollution control measures and sustainable water management practices is essential to prevent further degradation of water resources.
predominate the rural-to-urban stream of inter-state migration due to economic reasons.- a)Children
- b)Women
- c)Men
- d)Government
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
predominate the rural-to-urban stream of inter-state migration due to economic reasons.
a)
Children
b)
Women
c)
Men
d)
Government
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
During the distribution of male and female migrants in different streams of intra-state and inter-state migration, females predominate the streams of short distance rural to rural migration in both types of migration.
Consider the following and choose the correct answer from the given optionsI. Work participation rate tend to be higher in the areas of lower levels of economic development.
II. Number of manual workers are needed to perform the subsistence or near subsistence economic activities- a)Only statement I is correct
- b)Both statements are correct and statement II correctly explains statement I
- c)Only statement II is correct
- d)Both the statements are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following and choose the correct answer from the given options
I. Work participation rate tend to be higher in the areas of lower levels of economic development.
II. Number of manual workers are needed to perform the subsistence or near subsistence economic activities
II. Number of manual workers are needed to perform the subsistence or near subsistence economic activities
a)
Only statement I is correct
b)
Both statements are correct and statement II correctly explains statement I
c)
Only statement II is correct
d)
Both the statements are incorrect

|
Gauri Sharma answered |
Explanation:
Statement I: Work participation rate tends to be higher in the areas of lower levels of economic development.
This statement is correct. In areas with lower levels of economic development, there are often limited job opportunities and a lack of alternative sources of income. As a result, a higher proportion of the population needs to participate in the workforce to sustain their livelihoods. This can be due to factors such as limited access to education and skill development, limited availability of industries or businesses, and a reliance on traditional or subsistence economic activities.
Statement II: Number of manual workers are needed to perform the subsistence or near subsistence economic activities.
This statement is also correct. Subsistence or near subsistence economic activities refer to activities where individuals produce goods or services primarily for their own consumption or for meeting their basic needs. These activities often require manual labor, as they are typically labor-intensive and involve tasks such as farming, fishing, and handicraft production. Since these activities are usually small-scale and lack mechanization, a greater number of manual workers are needed to carry out the necessary tasks.
Explanation of the relationship between the two statements:
Both statements are correct and statement II correctly explains statement I. The higher work participation rate in areas with lower levels of economic development can be attributed to the need for a larger number of manual workers to perform subsistence or near subsistence economic activities. The lack of alternative employment opportunities and the reliance on traditional labor-intensive activities lead to a higher proportion of the population engaging in work to sustain their livelihoods.
In areas with higher levels of economic development, there is often a greater availability of non-manual or white-collar jobs, technological advancements, and more diversified economic activities. This can result in a lower work participation rate as individuals have more options for employment and may not need to rely solely on manual labor for their livelihoods.
Therefore, both statements I and II are correct, and statement II provides a valid explanation for statement I.
Statement I: Work participation rate tends to be higher in the areas of lower levels of economic development.
This statement is correct. In areas with lower levels of economic development, there are often limited job opportunities and a lack of alternative sources of income. As a result, a higher proportion of the population needs to participate in the workforce to sustain their livelihoods. This can be due to factors such as limited access to education and skill development, limited availability of industries or businesses, and a reliance on traditional or subsistence economic activities.
Statement II: Number of manual workers are needed to perform the subsistence or near subsistence economic activities.
This statement is also correct. Subsistence or near subsistence economic activities refer to activities where individuals produce goods or services primarily for their own consumption or for meeting their basic needs. These activities often require manual labor, as they are typically labor-intensive and involve tasks such as farming, fishing, and handicraft production. Since these activities are usually small-scale and lack mechanization, a greater number of manual workers are needed to carry out the necessary tasks.
Explanation of the relationship between the two statements:
Both statements are correct and statement II correctly explains statement I. The higher work participation rate in areas with lower levels of economic development can be attributed to the need for a larger number of manual workers to perform subsistence or near subsistence economic activities. The lack of alternative employment opportunities and the reliance on traditional labor-intensive activities lead to a higher proportion of the population engaging in work to sustain their livelihoods.
In areas with higher levels of economic development, there is often a greater availability of non-manual or white-collar jobs, technological advancements, and more diversified economic activities. This can result in a lower work participation rate as individuals have more options for employment and may not need to rely solely on manual labor for their livelihoods.
Therefore, both statements I and II are correct, and statement II provides a valid explanation for statement I.
According to Census of India, migration is enumerated on which of the following basis?- a)Place of Origin
- b)Place of residence
- c)Place of Origin as well as Place of Residence
- d)Place of Birth
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Census of India, migration is enumerated on which of the following basis?
a)
Place of Origin
b)
Place of residence
c)
Place of Origin as well as Place of Residence
d)
Place of Birth

|
Rahul Desai answered |
Migration is enumerated on the basis of Place of Origin as well as Place of Residence according to the Census of India.
Explanation:
Migration is the movement of individuals or groups from one place to another with the intention of settling permanently or temporarily in the new location. The Census of India is conducted every ten years to collect demographic and socio-economic data of the country's population. Migration is an important aspect of the census as it provides valuable insights into the patterns and trends of population movement.
The census enumerates migration on the basis of two main factors - Place of Origin and Place of Residence. Let's understand each of these factors in detail:
1. Place of Origin: This refers to the place where a person originally belongs or comes from. It captures information about the birthplace or the place of origin of an individual. This data helps in understanding the regional distribution of the population and the extent of migration within the country.
2. Place of Residence: This refers to the place where a person currently resides or lives. It captures information about the current address or location of an individual. This data helps in analyzing the distribution of population across different regions and urban-rural areas.
By considering both Place of Origin and Place of Residence, the census provides a comprehensive picture of migration patterns. It allows for the identification of migrants who have moved from one place to another and provides information about their current place of residence as well as their original place of origin.
This information is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and planners to understand the demographic and socio-economic characteristics of migrants, their settlement patterns, and the impact of migration on regional development. It helps in formulating targeted policies and programs to address the needs and challenges of migrants and ensure their social and economic integration into their new place of residence.
In conclusion, the Census of India enumerates migration on the basis of both Place of Origin and Place of Residence, providing valuable insights into population movement and facilitating evidence-based decision-making.
Explanation:
Migration is the movement of individuals or groups from one place to another with the intention of settling permanently or temporarily in the new location. The Census of India is conducted every ten years to collect demographic and socio-economic data of the country's population. Migration is an important aspect of the census as it provides valuable insights into the patterns and trends of population movement.
The census enumerates migration on the basis of two main factors - Place of Origin and Place of Residence. Let's understand each of these factors in detail:
1. Place of Origin: This refers to the place where a person originally belongs or comes from. It captures information about the birthplace or the place of origin of an individual. This data helps in understanding the regional distribution of the population and the extent of migration within the country.
2. Place of Residence: This refers to the place where a person currently resides or lives. It captures information about the current address or location of an individual. This data helps in analyzing the distribution of population across different regions and urban-rural areas.
By considering both Place of Origin and Place of Residence, the census provides a comprehensive picture of migration patterns. It allows for the identification of migrants who have moved from one place to another and provides information about their current place of residence as well as their original place of origin.
This information is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and planners to understand the demographic and socio-economic characteristics of migrants, their settlement patterns, and the impact of migration on regional development. It helps in formulating targeted policies and programs to address the needs and challenges of migrants and ensure their social and economic integration into their new place of residence.
In conclusion, the Census of India enumerates migration on the basis of both Place of Origin and Place of Residence, providing valuable insights into population movement and facilitating evidence-based decision-making.
Who among the following has introduced the concept of Neo-determinism?- a)Ratzel
- b)Griffith Taylor
- c)Allen c.Semple
- d)Paul Vidal de la Blache
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who among the following has introduced the concept of Neo-determinism?
a)
Ratzel
b)
Griffith Taylor
c)
Allen c.Semple
d)
Paul Vidal de la Blache
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
Griffith Taylor introduced the concept of Neo- determinism which reflects a middle path between the two ideas of environmental determinism and possibilism.
Development means:- a)a qualitative change which is always value positive.
- b)a qualitative change which is always value negative.
- c)a quantitative change which is always value positive.
- d)None of the Above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Development means:
a)
a qualitative change which is always value positive.
b)
a qualitative change which is always value negative.
c)
a quantitative change which is always value positive.
d)
None of the Above

|
Ritika Kulkarni answered |
Development
Development refers to a qualitative change that is always value positive. Let's break down the concept further:
Qualitative Change
Development involves a qualitative change, which means a change in the nature or essence of something. It is not just about increasing quantity but also improving the quality of life or a certain aspect.
Value Positive
When we talk about development being value positive, it means that the change is perceived as beneficial or desirable. It leads to improvements in various aspects of life such as living standards, education, healthcare, infrastructure, and overall well-being.
Examples
- Improving access to education for all individuals
- Enhancing healthcare services to reduce mortality rates
- Building better infrastructure to support economic growth
- Promoting gender equality and social inclusion
In conclusion, development signifies a positive qualitative change that brings about improvements and progress in society. It focuses on enhancing the well-being and quality of life for individuals and communities.
In which of the following streams of migration, females pre-dominate in both intra-state and inter-state migration?- a)Urban to rural
- b)Urban to urban
- c)Rural to rural
- d)Rural to urban
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following streams of migration, females pre-dominate in both intra-state and inter-state migration?
a)
Urban to rural
b)
Urban to urban
c)
Rural to rural
d)
Rural to urban
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
The females predominate the streams of short distance rural to rural migration in both types of migration. The most common reason for migration in India is marriage.
Several countries of Africa and few of south America and Asia have over fifty per cent of the earnings from_________ alone.- a)labour
- b)migrant money
- c)minerals
- d)dairy farming
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Several countries of Africa and few of south America and Asia have over fifty per cent of the earnings from_________ alone.
a)
labour
b)
migrant money
c)
minerals
d)
dairy farming
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Several countries of Africa, few of South America and Asia extracts an immense wealth of minerals, of which its mineral fuels— coal, petroleum, and natural gas—are of greatest value. These areas are rich in minerals.
Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:Available water resources are degrading rapidly. The major rivers of the country generally retain better water quality in less densely populated upper stretches in hilly areas. In plains, river water is used intensively for irrigation, drinking, domestic and industrial purposes. The drains carrying agricultural (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic (solid and liquid wastes), and industrial effluents join the rivers. The concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season when flow of water is low. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in collaboration with State Pollution Control Boards has been monitoring water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continues to be the main source of pollution in rivers. The Yamuna river is the most polluted river in the country between Delhi and Etawah. Other severely polluted rivers are: the Sabarmati at Ahmedabad, the Gomti at Lucknow, the Kali, the Adyar, the Cooum (entire stretches), the Vaigai at Madurai and the Musi of Hyderabad and the Ganga at Kanpur and Varanasi. Ground water pollution has occurred due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride and nitrates at different parts of the country. Q. What is the main role of CPCB?- a)Environmental assessments and research
- b)Maintaining national standards under a variety of environmental laws
- c)Conduct monitoring of water quality
- d)All of the Above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:
Available water resources are degrading rapidly. The major rivers of the country generally retain better water quality in less densely populated upper stretches in hilly areas. In plains, river water is used intensively for irrigation, drinking, domestic and industrial purposes. The drains carrying agricultural (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic (solid and liquid wastes), and industrial effluents join the rivers. The concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season when flow of water is low. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in collaboration with State Pollution Control Boards has been monitoring water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continues to be the main source of pollution in rivers. The Yamuna river is the most polluted river in the country between Delhi and Etawah. Other severely polluted rivers are: the Sabarmati at Ahmedabad, the Gomti at Lucknow, the Kali, the Adyar, the Cooum (entire stretches), the Vaigai at Madurai and the Musi of Hyderabad and the Ganga at Kanpur and Varanasi. Ground water pollution has occurred due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride and nitrates at different parts of the country.
Q. What is the main role of CPCB?
a)
Environmental assessments and research
b)
Maintaining national standards under a variety of environmental laws
c)
Conduct monitoring of water quality
d)
All of the Above
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The primary objective/ goal of the CPCB is to promote cleanliness and restore wholesomeness of water in wells and streams .
Arrange the following agglomeration in the sequence of their ranks i.e., 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th.(i) Delhi(ii) Chennai(iii) Greater Mumbai(iv) Kolkata- a)iii, iv, i, ii
- b)i, ii, iii, iv
- c)iv, ii, i, iii
- d)ii, i, iv, iii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following agglomeration in the sequence of their ranks i.e., 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th.
(i) Delhi
(ii) Chennai
(iii) Greater Mumbai
(iv) Kolkata
a)
iii, iv, i, ii
b)
i, ii, iii, iv
c)
iv, ii, i, iii
d)
ii, i, iv, iii
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
An urban agglomeration is identified and ranked according to its size, population, occupations and economic activities.
In the year 2015, a policy was formulated for the adolescents to give them proper guidance and the better development of their talent. Select the correct answer.- a)Skill development and entrepreneurship
- b)Universalisation of education
- c)Rejuvenation of schools
- d)National Youth Policy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the year 2015, a policy was formulated for the adolescents to give them proper guidance and the better development of their talent. Select the correct answer.
a)
Skill development and entrepreneurship
b)
Universalisation of education
c)
Rejuvenation of schools
d)
National Youth Policy
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In 2015, Prime Minister Narender Modi, launched Skill India Programme on World Youth Skill Day. This paved a way for formulation of the National Policy on Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, 2015. The objective of the National Policy on Skill Development and Entrepreneurship was to meet the challenge of skilling at scale with speed and standard (quality). This policy linked skills development to improved employability and productivity.
Arrange the countries from highest HDI to lowest HDI.(i) Norway(ii) Ireland(iii) Switzerland(iv) Hong kong- a)i, ii, iii, iv
- b)ii, iii, i, iv
- c)iv, i, ii, iii
- d)iii, iv, ii, i
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the countries from highest HDI to lowest HDI.
(i) Norway
(ii) Ireland
(iii) Switzerland
(iv) Hong kong
a)
i, ii, iii, iv
b)
ii, iii, i, iv
c)
iv, i, ii, iii
d)
iii, iv, ii, i

|
Lekshmi Bose answered |
Highest HDI to Lowest HDI:
(i) Norway
(ii) Ireland
(iii) Switzerland
(iv) Hong Kong
Explanation:
HDI, or Human Development Index, is a measure of a country's overall development and well-being, taking into account factors such as life expectancy, education, and income. A higher HDI indicates a higher level of human development.
(i) Norway:
Norway consistently ranks at the top of the HDI rankings due to its high standard of living, excellent healthcare system, and quality education. The country has a strong economy, low unemployment rate, and a high life expectancy. Norway's commitment to social welfare and sustainable development has contributed to its high HDI score.
(ii) Ireland:
Ireland also ranks high on the HDI scale, primarily due to its high standard of living and well-developed education system. The country has experienced significant economic growth over the past few decades, attracting multinational companies and creating job opportunities. Ireland's investment in education and healthcare has improved the overall well-being of its population.
(iii) Switzerland:
Switzerland is known for its high quality of life, strong economy, and well-functioning healthcare system. The country has a high HDI score due to its high life expectancy, high standard of education, and high average income. Switzerland's political stability and commitment to innovation have contributed to its overall development.
(iv) Hong Kong:
Although Hong Kong is not a country, it is included in the HDI rankings as a Special Administrative Region of China. It has a relatively high HDI score, primarily due to its high life expectancy and high average income. Hong Kong has a developed economy and offers a high standard of living. However, it is worth noting that the HDI for Hong Kong may not accurately reflect the overall well-being and development of its population, as it is a small region with unique political and economic circumstances.
In summary, Norway has the highest HDI among the given countries, followed by Ireland, Switzerland, and Hong Kong. These countries demonstrate a high level of overall development and well-being, with a focus on factors such as education, healthcare, and income.
(i) Norway
(ii) Ireland
(iii) Switzerland
(iv) Hong Kong
Explanation:
HDI, or Human Development Index, is a measure of a country's overall development and well-being, taking into account factors such as life expectancy, education, and income. A higher HDI indicates a higher level of human development.
(i) Norway:
Norway consistently ranks at the top of the HDI rankings due to its high standard of living, excellent healthcare system, and quality education. The country has a strong economy, low unemployment rate, and a high life expectancy. Norway's commitment to social welfare and sustainable development has contributed to its high HDI score.
(ii) Ireland:
Ireland also ranks high on the HDI scale, primarily due to its high standard of living and well-developed education system. The country has experienced significant economic growth over the past few decades, attracting multinational companies and creating job opportunities. Ireland's investment in education and healthcare has improved the overall well-being of its population.
(iii) Switzerland:
Switzerland is known for its high quality of life, strong economy, and well-functioning healthcare system. The country has a high HDI score due to its high life expectancy, high standard of education, and high average income. Switzerland's political stability and commitment to innovation have contributed to its overall development.
(iv) Hong Kong:
Although Hong Kong is not a country, it is included in the HDI rankings as a Special Administrative Region of China. It has a relatively high HDI score, primarily due to its high life expectancy and high average income. Hong Kong has a developed economy and offers a high standard of living. However, it is worth noting that the HDI for Hong Kong may not accurately reflect the overall well-being and development of its population, as it is a small region with unique political and economic circumstances.
In summary, Norway has the highest HDI among the given countries, followed by Ireland, Switzerland, and Hong Kong. These countries demonstrate a high level of overall development and well-being, with a focus on factors such as education, healthcare, and income.
Coffee Plantations in Brazil are known as:- a)Downs
- b)Campos
- c)Fazendas
- d)Pampas
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Coffee Plantations in Brazil are known as:
a)
Downs
b)
Campos
c)
Fazendas
d)
Pampas
|
|
Nandita Ahuja answered |
Coffee Plantations in Brazil
Brazil is one of the largest producers of coffee in the world, and the plantations where coffee is cultivated are known as "fazendas."
What is a Fazenda?
- A "fazenda" is a Portuguese term that translates to "farm" or "plantation" in English.
- These large estates typically consist of vast areas dedicated to the cultivation of crops, including coffee.
Importance of Fazendas in Coffee Production
- Scale of Production: Fazendas can cover extensive land areas, allowing for the large-scale production of coffee beans.
- Variety of Coffee: Many fazendas grow different varieties of coffee, including Arabica and Robusta, catering to various market preferences.
Geographical Distribution
- Regions: Coffee fazendas are primarily located in regions of Brazil such as Minas Gerais, São Paulo, and Espírito Santo.
- Climate: The climate in these areas is ideal for coffee growth, with rich soil and appropriate rainfall.
Economic Impact
- Employment: Fazendas provide employment opportunities for thousands of workers, contributing significantly to the local economy.
- Exports: Coffee produced on these plantations contributes heavily to Brazil's export economy, making it a vital agricultural product.
In summary, the correct answer to the question regarding coffee plantations in Brazil is "fazendas" due to their significant role in the cultivation, production, and economic impact of coffee in the country.
Brazil is one of the largest producers of coffee in the world, and the plantations where coffee is cultivated are known as "fazendas."
What is a Fazenda?
- A "fazenda" is a Portuguese term that translates to "farm" or "plantation" in English.
- These large estates typically consist of vast areas dedicated to the cultivation of crops, including coffee.
Importance of Fazendas in Coffee Production
- Scale of Production: Fazendas can cover extensive land areas, allowing for the large-scale production of coffee beans.
- Variety of Coffee: Many fazendas grow different varieties of coffee, including Arabica and Robusta, catering to various market preferences.
Geographical Distribution
- Regions: Coffee fazendas are primarily located in regions of Brazil such as Minas Gerais, São Paulo, and Espírito Santo.
- Climate: The climate in these areas is ideal for coffee growth, with rich soil and appropriate rainfall.
Economic Impact
- Employment: Fazendas provide employment opportunities for thousands of workers, contributing significantly to the local economy.
- Exports: Coffee produced on these plantations contributes heavily to Brazil's export economy, making it a vital agricultural product.
In summary, the correct answer to the question regarding coffee plantations in Brazil is "fazendas" due to their significant role in the cultivation, production, and economic impact of coffee in the country.
Which of the following sectors has used the highest percentage of total water in India?- a)Domestic
- b)Commerce
- c)Agriculture
- d)Industry
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following sectors has used the highest percentage of total water in India?
a)
Domestic
b)
Commerce
c)
Agriculture
d)
Industry
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
The share of agricultural sector in total water utilisation is much higher than other sectors. Agriculture accounts for most of the surface and groundwater utilisation. Agriculture accounts for 89 per cent of the surface water and 92 per cent of the groundwater utilisation.
Which of the following colonial super power had monopoly over sugarcane plantation in Indonesia?- a)British
- b)French
- c)Dutch
- d)Americans
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following colonial super power had monopoly over sugarcane plantation in Indonesia?
a)
British
b)
French
c)
Dutch
d)
Americans

|
Rashi Bose answered |
Colonial Super Power with Monopoly over Sugarcane Plantation in Indonesia: Dutch
Indonesia was a colony of the Dutch East India Company, which later became the Dutch colonial empire. The Dutch had a significant impact on the economy of Indonesia, particularly in the sugar industry. Here's why the Dutch had a monopoly over sugarcane plantation in Indonesia:
Historical Background:
- The Dutch East India Company (VOC) was instrumental in establishing sugarcane plantations in Indonesia during the 17th and 18th centuries.
- The Dutch introduced advanced agricultural techniques and technology, including irrigation systems, to maximize sugarcane production.
Monopoly Control:
- The Dutch implemented a system of forced cultivation, known as the "Cultuurstelsel," which required farmers to allocate a portion of their land to grow cash crops like sugarcane for export.
- The Dutch government granted concessions to European planters, giving them exclusive rights to cultivate sugarcane in certain regions of Indonesia.
- The Dutch also controlled the transportation and export of sugarcane, ensuring that they maintained a monopoly over the industry.
Impact on Indonesia:
- The Dutch monopoly over sugarcane production in Indonesia led to the exploitation of local farmers and the concentration of wealth in the hands of European planters.
- The cultivation of sugarcane for export deprived local communities of food crops and led to widespread poverty and hunger.
- The Dutch colonial administration profited immensely from the sugarcane industry, using the revenue to fund further expansion and development in Indonesia.
In conclusion, the Dutch colonial empire had a monopoly over sugarcane plantation in Indonesia, which had far-reaching economic and social consequences for the local population.
Through which of the following, functional relations establish between rural and urban areas?- a)Through the means of transport and communications
- b)Through the supply of raw material
- c)Through the exchange of finished products in rural areas
- d)Through the consumption of products produced in rural areas
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Through which of the following, functional relations establish between rural and urban areas?
a)
Through the means of transport and communications
b)
Through the supply of raw material
c)
Through the exchange of finished products in rural areas
d)
Through the consumption of products produced in rural areas
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
Urban centres have factories which process the raw materials obtained from the surrounding rural areas or buy goods in bulk from importers and sell them to rural dwellers. On the other hand, rural settlements offer the market for the products manufactured, produced or purchased in bulk by the urban centres.
The practice of nurturing the animals for food and for other human uses is known as:- a)Professional livestock rearing
- b)Commercial livestock rearing
- c)Social livestock rearing
- d)Subsistence Gathering
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The practice of nurturing the animals for food and for other human uses is known as:
a)
Professional livestock rearing
b)
Commercial livestock rearing
c)
Social livestock rearing
d)
Subsistence Gathering

|
Akshay Sharma answered |
Commercial Livestock Rearing
Livestock rearing is the practice of raising animals for food, fiber, labor, or other human uses. Commercial livestock rearing specifically refers to the practice of nurturing animals on a large scale for the purpose of generating profit. Here are some key points to explain the concept of commercial livestock rearing:
Definition:
- Commercial livestock rearing involves the breeding, feeding, and management of animals such as cattle, poultry, pigs, and sheep with the intention of selling products like meat, milk, eggs, and wool for profit.
Scale of Operation:
- Commercial livestock rearing is typically carried out on a larger scale compared to subsistence or social livestock rearing. It often involves specialized facilities, equipment, and techniques to maximize production efficiency.
Market Orientation:
- The primary objective of commercial livestock rearing is to meet market demands for animal products. Farmers may focus on specific breeds or species that are in high demand to maximize profitability.
Management Practices:
- Commercial livestock rearing requires careful planning and management to ensure the health, welfare, and productivity of the animals. This may involve the use of modern technologies, veterinary services, and nutritional programs.
Economic Impact:
- Commercial livestock rearing plays a significant role in the economy by providing employment opportunities, contributing to agricultural output, and supplying essential food products to consumers.
In conclusion, commercial livestock rearing is a vital component of the agricultural industry, providing a sustainable source of animal products for human consumption while also contributing to economic growth and development.
Livestock rearing is the practice of raising animals for food, fiber, labor, or other human uses. Commercial livestock rearing specifically refers to the practice of nurturing animals on a large scale for the purpose of generating profit. Here are some key points to explain the concept of commercial livestock rearing:
Definition:
- Commercial livestock rearing involves the breeding, feeding, and management of animals such as cattle, poultry, pigs, and sheep with the intention of selling products like meat, milk, eggs, and wool for profit.
Scale of Operation:
- Commercial livestock rearing is typically carried out on a larger scale compared to subsistence or social livestock rearing. It often involves specialized facilities, equipment, and techniques to maximize production efficiency.
Market Orientation:
- The primary objective of commercial livestock rearing is to meet market demands for animal products. Farmers may focus on specific breeds or species that are in high demand to maximize profitability.
Management Practices:
- Commercial livestock rearing requires careful planning and management to ensure the health, welfare, and productivity of the animals. This may involve the use of modern technologies, veterinary services, and nutritional programs.
Economic Impact:
- Commercial livestock rearing plays a significant role in the economy by providing employment opportunities, contributing to agricultural output, and supplying essential food products to consumers.
In conclusion, commercial livestock rearing is a vital component of the agricultural industry, providing a sustainable source of animal products for human consumption while also contributing to economic growth and development.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option for the same:I. Grape cultivation is the speciality of the Mediterranean agriculture.
II. Wines are produced from high quality grapes and the inferior grapes are dried into raisins and Currants.- a)Only 1 is correct
- b)Both 1 and 2 are correct
- c)Only 2 is correct
- d)Both are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option for the same:
I. Grape cultivation is the speciality of the Mediterranean agriculture.
II. Wines are produced from high quality grapes and the inferior grapes are dried into raisins and Currants.
II. Wines are produced from high quality grapes and the inferior grapes are dried into raisins and Currants.
a)
Only 1 is correct
b)
Both 1 and 2 are correct
c)
Only 2 is correct
d)
Both are incorrect
|
|
Subhankar Choudhary answered |
Overview of Mediterranean Agriculture
Mediterranean agriculture is characterized by its unique climatic conditions, which are ideal for specific crops. Among these, grape cultivation stands out as a primary specialty.
Statement I: Grape Cultivation
- Grape cultivation is indeed a hallmark of Mediterranean agriculture.
- The region’s warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters provide an optimal environment for growing various grape varieties.
- The Mediterranean climate is known for producing high-quality grapes that are essential for winemaking.
Statement II: Wine Production and Dried Grapes
- Wines are primarily produced from high-quality grapes.
- The inferior or overripe grapes are often dried to create raisins and currants, which are popular in many cuisines.
- This practice not only maximizes the use of the grape harvest but also diversifies the products derived from grape cultivation.
Conclusion
Both statements are accurate, confirming that:
- Grape cultivation is indeed a specialty of Mediterranean agriculture.
- The production of wines from high-quality grapes and the drying of inferior grapes into raisins and currants are both established practices in the region.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B': Both 1 and 2 are correct. This reflects the significance of grapes in Mediterranean agriculture, emphasizing their dual purpose in winemaking and producing dried fruits.
Mediterranean agriculture is characterized by its unique climatic conditions, which are ideal for specific crops. Among these, grape cultivation stands out as a primary specialty.
Statement I: Grape Cultivation
- Grape cultivation is indeed a hallmark of Mediterranean agriculture.
- The region’s warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters provide an optimal environment for growing various grape varieties.
- The Mediterranean climate is known for producing high-quality grapes that are essential for winemaking.
Statement II: Wine Production and Dried Grapes
- Wines are primarily produced from high-quality grapes.
- The inferior or overripe grapes are often dried to create raisins and currants, which are popular in many cuisines.
- This practice not only maximizes the use of the grape harvest but also diversifies the products derived from grape cultivation.
Conclusion
Both statements are accurate, confirming that:
- Grape cultivation is indeed a specialty of Mediterranean agriculture.
- The production of wines from high-quality grapes and the drying of inferior grapes into raisins and currants are both established practices in the region.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B': Both 1 and 2 are correct. This reflects the significance of grapes in Mediterranean agriculture, emphasizing their dual purpose in winemaking and producing dried fruits.
Which of the following is a good example of Fort town?- a)Jaipur
- b)Banaras
- c)Mathura
- d)Rameshwaram
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a good example of Fort town?
a)
Jaipur
b)
Banaras
c)
Mathura
d)
Rameshwaram
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Famous forts in Jaipur are Amer Fort, Nahargarh Fort and Jaigarh Fort .
The river basin which makes the maximum utilisation of groundwater is :- a)Ganga
- b)Brahmaputra
- c)Satluj
- d)Indus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The river basin which makes the maximum utilisation of groundwater is :
a)
Ganga
b)
Brahmaputra
c)
Satluj
d)
Indus

|
Bhavya Joshi answered |
The river basin which makes the maximum utilization of groundwater is the Brahmaputra river basin. The Brahmaputra river is one of the major rivers in Asia, flowing through China, India, and Bangladesh. It is known for its vast basin area and high water discharge.
Here is a detailed explanation of why the Brahmaputra river basin makes the maximum utilization of groundwater:
1. Geographical Factors:
- The Brahmaputra river basin covers a large area in Northeast India, including parts of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and Meghalaya. These regions have favorable geological conditions for groundwater storage and recharge.
- The basin is surrounded by the Eastern Himalayas, which receive significant rainfall. This abundant rainfall contributes to the recharge of groundwater reservoirs.
2. Alluvial Soil:
- The Brahmaputra river carries a huge amount of sediment from the Himalayas, depositing it in the basin. This sediment consists of alluvial soil, which is highly permeable and ideal for groundwater storage.
- Alluvial soil has high porosity, allowing water to percolate easily and replenish the underground aquifers.
3. Groundwater Extraction:
- The agricultural activities in the Brahmaputra river basin heavily rely on groundwater irrigation. Farmers extract groundwater through wells and tube wells to meet their water requirements for irrigation.
- The fertile alluvial soil and availability of groundwater make the basin suitable for extensive agriculture, leading to high groundwater utilization.
4. River Water Availability:
- The Brahmaputra river has a substantial water discharge, especially during the monsoon season. This abundant river water supply allows for significant recharge of groundwater reservoirs.
- The river water also helps maintain a favorable water table, ensuring the availability of groundwater throughout the year.
5. Economic Importance:
- The Brahmaputra river basin is economically significant, supporting various industries and hydropower projects. The availability of groundwater plays a crucial role in sustaining these economic activities.
In conclusion, the Brahmaputra river basin makes the maximum utilization of groundwater due to its favorable geographical factors, alluvial soil, extensive agriculture, abundant river water availability, and economic importance. The combination of these factors makes it a prime region for groundwater utilization in comparison to other river basins like Ganga, Satluj, and Indus.
Here is a detailed explanation of why the Brahmaputra river basin makes the maximum utilization of groundwater:
1. Geographical Factors:
- The Brahmaputra river basin covers a large area in Northeast India, including parts of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and Meghalaya. These regions have favorable geological conditions for groundwater storage and recharge.
- The basin is surrounded by the Eastern Himalayas, which receive significant rainfall. This abundant rainfall contributes to the recharge of groundwater reservoirs.
2. Alluvial Soil:
- The Brahmaputra river carries a huge amount of sediment from the Himalayas, depositing it in the basin. This sediment consists of alluvial soil, which is highly permeable and ideal for groundwater storage.
- Alluvial soil has high porosity, allowing water to percolate easily and replenish the underground aquifers.
3. Groundwater Extraction:
- The agricultural activities in the Brahmaputra river basin heavily rely on groundwater irrigation. Farmers extract groundwater through wells and tube wells to meet their water requirements for irrigation.
- The fertile alluvial soil and availability of groundwater make the basin suitable for extensive agriculture, leading to high groundwater utilization.
4. River Water Availability:
- The Brahmaputra river has a substantial water discharge, especially during the monsoon season. This abundant river water supply allows for significant recharge of groundwater reservoirs.
- The river water also helps maintain a favorable water table, ensuring the availability of groundwater throughout the year.
5. Economic Importance:
- The Brahmaputra river basin is economically significant, supporting various industries and hydropower projects. The availability of groundwater plays a crucial role in sustaining these economic activities.
In conclusion, the Brahmaputra river basin makes the maximum utilization of groundwater due to its favorable geographical factors, alluvial soil, extensive agriculture, abundant river water availability, and economic importance. The combination of these factors makes it a prime region for groundwater utilization in comparison to other river basins like Ganga, Satluj, and Indus.
The state with the highest population in India is:- a)West Bengal
- b)Kerala
- c)Uttar Pradesh
- d)Odisha
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The state with the highest population in India is:
a)
West Bengal
b)
Kerala
c)
Uttar Pradesh
d)
Odisha
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The population of Uttar Pradesh continues to grow at a high rate. Because of that high growth rate and a substantial reduction in infant mortality in the 20th century, there has been a significant increase in the proportion of young adults and children.
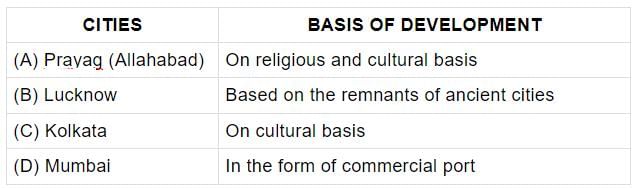
Which of the following pairs is not matched correctly?
- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs is not matched correctly?


a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Kolkata developed as a major port city.
Study the data based carefully and answer the following questions:India – Trends of Urbanisation 1901-2011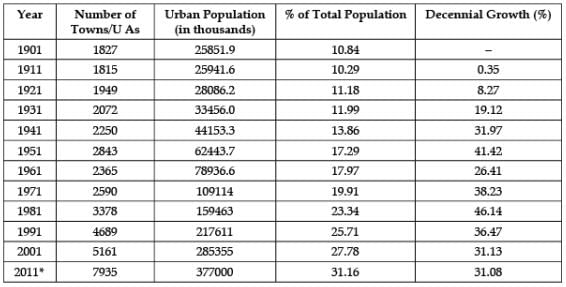 Why are the number of towns growing in India ?
Why are the number of towns growing in India ?- a)Growth of urban agglomeration
- b)Migration to other countries
- c)Increase in awareness
- d)Increased political pressure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the data based carefully and answer the following questions:
India – Trends of Urbanisation 1901-2011

Why are the number of towns growing in India ?
a)
Growth of urban agglomeration
b)
Migration to other countries
c)
Increase in awareness
d)
Increased political pressure
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The perceived boundaries of certain cities, known as urban agglomeration that includes densely built-up areas outside the official municipal boundary is expanding at a fast pace. This has led to the fast growth of cities in India.
Study the data based carefully and answer the following questions:India – Trends of Urbanisation 1901-2011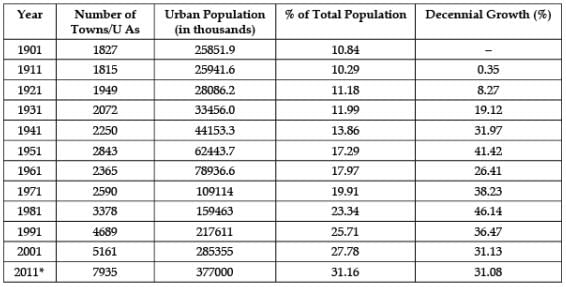 In which decade the growth rate of urban population was lowest in the country?
In which decade the growth rate of urban population was lowest in the country?- a)1901
- b)1911
- c)1921
- d)1931
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the data based carefully and answer the following questions:
India – Trends of Urbanisation 1901-2011

In which decade the growth rate of urban population was lowest in the country?
a)
1901
b)
1911
c)
1921
d)
1931
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The growth rate was low due to the high mortality during this period and this was because of large scale abnormal deaths due to epidemics of influenza, plague, small pox, cholera, etc.
Study the data based carefully and answer the following questions:India – Trends of Urbanisation 1901-2011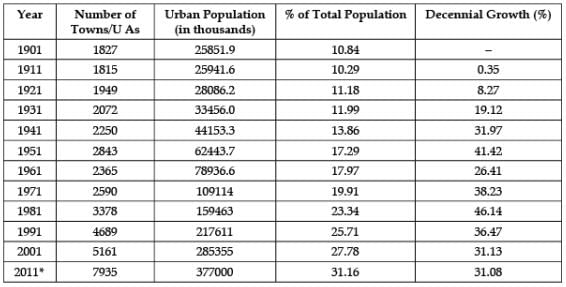 In which year the decennial growth rate of urban population was the highest?
In which year the decennial growth rate of urban population was the highest?- a)2011
- b)2001
- c)1991
- d)1981
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the data based carefully and answer the following questions:
India – Trends of Urbanisation 1901-2011

In which year the decennial growth rate of urban population was the highest?
a)
2011
b)
2001
c)
1991
d)
1981
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
There are many reasons for increased urban growth in 1981. The employment opportunities were greater within urban areas, better paid jobs in the cities, an expected higher standard of living, etc all collectively lead to increased urban population.
Larger settlements which are specialising in secondary and tertiary activities are known as :- a)rural settlements
- b)urban settlements
- c)sub-urbans
- d)rented settlements
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Larger settlements which are specialising in secondary and tertiary activities are known as :
a)
rural settlements
b)
urban settlements
c)
sub-urbans
d)
rented settlements
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Urban settlement often has a large population size and high population density.
Study the data based carefully and answer the following questions:India – Trends of Urbanisation 1901-2011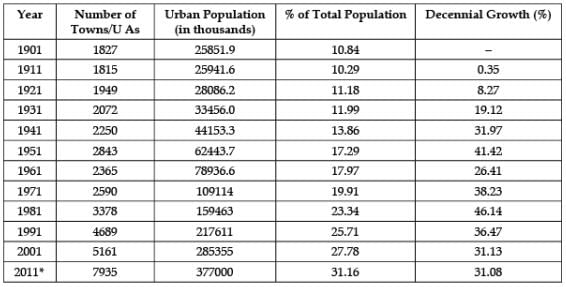 What does decennial growth rate mean?
What does decennial growth rate mean?- a)Increase in population rate of an area calculated in five years
- b)Increase in population rate of an area calculated in ten years
- c)Stagnation in population rate of an area in five years
- d)None of the Above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the data based carefully and answer the following questions:
India – Trends of Urbanisation 1901-2011

What does decennial growth rate mean?
a)
Increase in population rate of an area calculated in five years
b)
Increase in population rate of an area calculated in ten years
c)
Stagnation in population rate of an area in five years
d)
None of the Above
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The decennial growth rate gives an overview of the total population growth in a particular decade. This is simple growth rate calculation between two population observations that are 10 years apart.
Nomadic herding or pastoral nomadism is a:- a)primitive subsistence activity
- b)secondary subsistence activity
- c)non- existent subsistence activity
- d)tertiary activity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nomadic herding or pastoral nomadism is a:
a)
primitive subsistence activity
b)
secondary subsistence activity
c)
non- existent subsistence activity
d)
tertiary activity
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Nomadic herding or pastoral nomadism is a primitive subsistence activity, in which the herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. They move from one place to another along with their livestock, depending on the amount and quality of pastures and water.
Which one of the following is the main feature of rural settlement?- a)Derive economic needs from primary activities
- b)Derive economic needs from secondary activities
- c)Derive economic needs from tertiary activities
- d)Derive economic needs from quaternary activities
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the main feature of rural settlement?
a)
Derive economic needs from primary activities
b)
Derive economic needs from secondary activities
c)
Derive economic needs from tertiary activities
d)
Derive economic needs from quaternary activities
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The rural settlements derive their life support or basic economic needs from land based primary economic activities. Communities living in rural settlement are predominantly involved in primary activities such as farming, lumbering and mining.
This age was marked by use of computers and sophisticated statistical tools. Laws of physics were often applied to map and analyze. Select the correct option.- a)Regional analysis
- b)Quantitative revolution
- c)Areal Differentiation
- d)Spatial organization
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
This age was marked by use of computers and sophisticated statistical tools. Laws of physics were often applied to map and analyze. Select the correct option.
a)
Regional analysis
b)
Quantitative revolution
c)
Areal Differentiation
d)
Spatial organization
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Spatial organization, as one of the basic themes of geography, focuses on how to recognize and organize geographic space in which human activities occur, giving rise to spatial structures.
Who among the following is related to ‘capability approach’?- a)Dr Mahbub-ul-haq
- b)Prof Amartya Sen
- c)Malthus
- d)Ratzel
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who among the following is related to ‘capability approach’?
a)
Dr Mahbub-ul-haq
b)
Prof Amartya Sen
c)
Malthus
d)
Ratzel
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The economist and philosopher Amartya Sen, who is associated with the 'capability approach' provide the philosophical basis of human development. The Sen capability approach is a moral framework. It proposes that social arrangements should be evaluated primarily according to the extent of freedom people have to promote as well as achieve functions they value.
The clustered rural settlement is:- a)closely built up houses
- b)scattered houses
- c)sparsely built up houses
- d)unplanned houses
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The clustered rural settlement is:
a)
closely built up houses
b)
scattered houses
c)
sparsely built up houses
d)
unplanned houses
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
A clustered rural settlement is a rural settlement where a number of families live in close proximity to each other.
Consider the following features and choose the correct title after associating them.1. More often such a pattern may also result from segregation or fragmentation of large compact village.2. The land- owning and dominant community occupies the central part of the main village whereas people of lower strata of society and menial workers settle on the outer flanks of the village.3. They are found in Gujarat plains and some parts of Rajasthan.- a)Hamleted Settlement
- b)Semi-clustered or fragmented
- c)Clustered Settlements
- d)Isolated Settlements
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following features and choose the correct title after associating them.
1. More often such a pattern may also result from segregation or fragmentation of large compact village.
2. The land- owning and dominant community occupies the central part of the main village whereas people of lower strata of society and menial workers settle on the outer flanks of the village.
3. They are found in Gujarat plains and some parts of Rajasthan.
a)
Hamleted Settlement
b)
Semi-clustered or fragmented
c)
Clustered Settlements
d)
Isolated Settlements
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Semi-clustered settlements result from the tendency of clustering in a limited region associated with a dispersed settlement. More often such a pattern may also result from segregation or fragmentation of a large compact village.
Who among the following pioneered the concept of ‘human development’?- a)Ellen C. Musk
- b)Dr Mahbub-ul-haq
- c)Arundhati Roy
- d)Thomas Edison
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who among the following pioneered the concept of ‘human development’?
a)
Ellen C. Musk
b)
Dr Mahbub-ul-haq
c)
Arundhati Roy
d)
Thomas Edison
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Mahbub-ul-Haq was the pioneer in developing the concept of human development. He not only articulated the human development philosophy for making economic development plans but he also provided the world with a statistical measure to quantify the indicators of economic growth with human development.
Cities having more than 10 million population are known as :- a)Hyper city
- b)Metropolitan city
- c)Mega city
- d)Super city
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cities having more than 10 million population are known as :
a)
Hyper city
b)
Metropolitan city
c)
Mega city
d)
Super city
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
Mega city refers to metropolitan areas with a total population of more than 10 million people.
Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:Available water resources are degrading rapidly. The major rivers of the country generally retain better water quality in less densely populated upper stretches in hilly areas. In plains, river water is used intensively for irrigation, drinking, domestic and industrial purposes. The drains carrying agricultural (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic (solid and liquid wastes), and industrial effluents join the rivers. The concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season when flow of water is low. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in collaboration with State Pollution Control Boards has been monitoring water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continues to be the main source of pollution in rivers. The Yamuna river is the most polluted river in the country between Delhi and Etawah. Other severely polluted rivers are: the Sabarmati at Ahmedabad, the Gomti at Lucknow, the Kali, the Adyar, the Cooum (entire stretches), the Vaigai at Madurai and the Musi of Hyderabad and the Ganga at Kanpur and Varanasi. Ground water pollution has occurred due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride and nitrates at different parts of the country. Q. Why does the concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season?- a)Due to high flow of water
- b)Due to high precipitation level
- c)Due to low flow of water
- d)Due to increased industrial use
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the case study given below and answer the questions that follow:
Available water resources are degrading rapidly. The major rivers of the country generally retain better water quality in less densely populated upper stretches in hilly areas. In plains, river water is used intensively for irrigation, drinking, domestic and industrial purposes. The drains carrying agricultural (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic (solid and liquid wastes), and industrial effluents join the rivers. The concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season when flow of water is low. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in collaboration with State Pollution Control Boards has been monitoring water quality of national aquatic resources at 507 stations. The data obtained from these stations show that organic and bacterial contamination continues to be the main source of pollution in rivers. The Yamuna river is the most polluted river in the country between Delhi and Etawah. Other severely polluted rivers are: the Sabarmati at Ahmedabad, the Gomti at Lucknow, the Kali, the Adyar, the Cooum (entire stretches), the Vaigai at Madurai and the Musi of Hyderabad and the Ganga at Kanpur and Varanasi. Ground water pollution has occurred due to high concentrations of heavy/toxic metals, fluoride and nitrates at different parts of the country.
Q. Why does the concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season?
a)
Due to high flow of water
b)
Due to high precipitation level
c)
Due to low flow of water
d)
Due to increased industrial use
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The drains carrying agricultural (fertilizers and insecticides), domestic (solid and liquid wastes), and industrial effluents join the rivers. The concentration of pollutants in rivers, especially remains very high during the summer season when flow of water is low.
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following questions: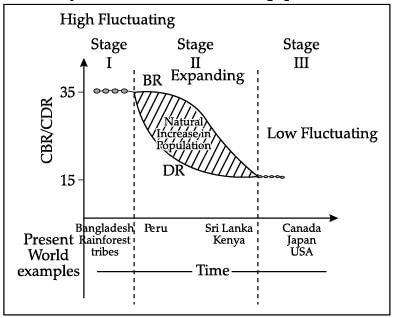 How does the natural increase in population occur, as per the graph?
How does the natural increase in population occur, as per the graph?- a)Birth Rate – Death Rate
- b)Death Rate + Birth Rate
- c)Growth Rate – Birth Rate
- d)Birth Rate + Migration
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following questions:

How does the natural increase in population occur, as per the graph?
a)
Birth Rate – Death Rate
b)
Death Rate + Birth Rate
c)
Growth Rate – Birth Rate
d)
Birth Rate + Migration
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The difference between the birth rate and the death rate of a country or place causes the natural increase.
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following questions: In which stage of Demographic Transition, population explosion took place–
In which stage of Demographic Transition, population explosion took place–- a)Stage I
- b)Stage II
- c)Stage III
- d)Post Stage III
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following questions:

In which stage of Demographic Transition, population explosion took place–
a)
Stage I
b)
Stage II
c)
Stage III
d)
Post Stage III
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Stage II is characterized by a rapid decrease in a country's death rate while the birth rate remains high. The fall in the death rate is due to drastic improvement in the medical facilities, vaccinations, etc.
Traditional ________ in rural areas is done by using surface storage bodies like lakes, ponds, irrigation tanks.- a)rain water harvesting
- b)ground water preservation
- c)watershed management
- d)storage management
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Traditional ________ in rural areas is done by using surface storage bodies like lakes, ponds, irrigation tanks.
a)
rain water harvesting
b)
ground water preservation
c)
watershed management
d)
storage management
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Rainwater harvesting is the collection and storage of rain, rather than allowing it to run off.
Which of the following column is not matched correctly?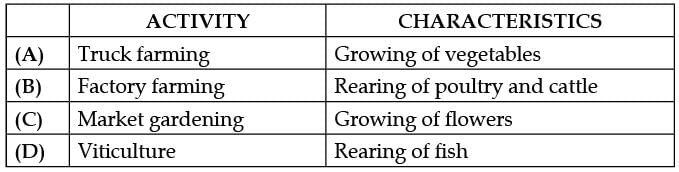
- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following column is not matched correctly?

a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Viticulture is the scientific study of grapes, most often with a focus on growth and production.
Which of the following areas of our country are deficient in rainfall and are drought prone?- a)North- eastern states
- b)Deccan Plateau
- c)Gangetic Plain
- d)Brahmaputra valley
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following areas of our country are deficient in rainfall and are drought prone?
a)
North- eastern states
b)
Deccan Plateau
c)
Gangetic Plain
d)
Brahmaputra valley
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The Deccan plateau is a large triangular region that covers about 43% of India, and spans eight states – Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana. The highest frequency of the severe droughts are observed in the Deccan region.
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following questions: From the given graph, what condition can you infer about the developing countries?
From the given graph, what condition can you infer about the developing countries?- a)High Birth Rate and High Death Rate
- b)Low Birth rate and Low Death rate
- c)High Birth Rate and Low Death Rate
- d)Low Birth Rate and High Death Rate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following questions:

From the given graph, what condition can you infer about the developing countries?
a)
High Birth Rate and High Death Rate
b)
Low Birth rate and Low Death rate
c)
High Birth Rate and Low Death Rate
d)
Low Birth Rate and High Death Rate
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The social structure, religious beliefs, economic prosperity and urbanisation within each country leads to high birth rates and low death rates in developing countries.
Chapter doubts & questions for Geography - CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities 2025 is part of Humanities/Arts exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Humanities/Arts exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Humanities/Arts 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Geography - CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities in English & Hindi are available as part of Humanities/Arts exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Humanities/Arts Exam by signing up for free.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities
145 docs|4 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









