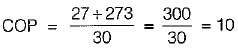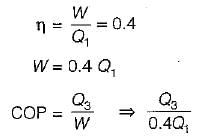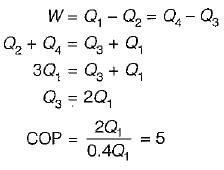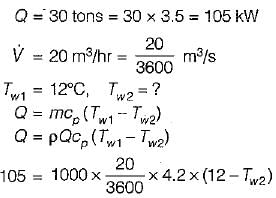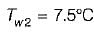All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering >
All Questions
All questions of Refrigeration & Air Conditioning for Mechanical Engineering Exam
In a domestic refrigerator, a capillary tube controls the flow of refrigerant from the- a)expansion valve to the evaporator
- b)evaporator to the thermostat
- c)condenser to the expansion valve
- d)condenser to the evaporator
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a domestic refrigerator, a capillary tube controls the flow of refrigerant from the
a)
expansion valve to the evaporator
b)
evaporator to the thermostat
c)
condenser to the expansion valve
d)
condenser to the evaporator
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
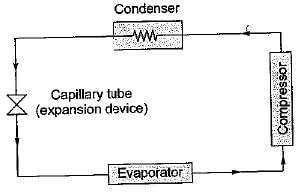
Hence capillary tube is placed between condenser and evaporator.
Pure dehumidification can be achieved by passing air through the spray water maintained at- a)DBT
- b)WBT
- c)Dew point temperature
- d)Any of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pure dehumidification can be achieved by passing air through the spray water maintained at
a)
DBT
b)
WBT
c)
Dew point temperature
d)
Any of the above
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Pure dehumidification is achieved by passing air through the spray water which is maintained at dew point temperature. By doing this, excess moisture condenses and temperature remains constant.
Which of the following is considered comfort conditions in air-conditioning?- a)10°C DBT and 50% RH
- b)15°C DBT and 40% RH
- c)20°C DBT and 60% RH
- d)25°C DBT and 70% RH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is considered comfort conditions in air-conditioning?
a)
10°C DBT and 50% RH
b)
15°C DBT and 40% RH
c)
20°C DBT and 60% RH
d)
25°C DBT and 70% RH
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
A human body feels comfortable when the air is at 21°C DBT with 56% RH. In general, for summer air conditioning, the RH should not be less than 60% whereas for winter air conditioning it should not be more than 40%.
One tonne refrigerator machine means that- a)one tonne is the total mass of machine.
- b)one tonne of refrigerator is used.
- c)one tonne of water can be converted onto ice.
- d)one tonne of ice when melts from and at 0°C in 24 hours, the refrigerating effect produced is equivalent to 210 kJ/min.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One tonne refrigerator machine means that
a)
one tonne is the total mass of machine.
b)
one tonne of refrigerator is used.
c)
one tonne of water can be converted onto ice.
d)
one tonne of ice when melts from and at 0°C in 24 hours, the refrigerating effect produced is equivalent to 210 kJ/min.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
1 tonne of refrigeration is the rate of heat removal required to freeze a metric ton (1000 kg) of water at 0°C in 24 hours. Based on the heat of fusion being 333.55 kJ/kg, 1 tonne of refrigeration = 13,898 kJ/h = 3.861 kW
In refrigeration system refrigerant gains heat at- a)compressor
- b)evaporator
- c)condenser
- d)expansion valve
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In refrigeration system refrigerant gains heat at
a)
compressor
b)
evaporator
c)
condenser
d)
expansion valve

|
Garima Kulkarni answered |
In refrigeration system, heat is absorbed at evaporator and rejected at condenser.
Which of the following is not true in respect of an ideal refrigerant?- a)High latent heat of vaporization and specific heat.
- b)Critical pressure and temperature well above the maximum operating pressure and temperature limits.
- c)Low value of specific volume.
- d)High value of thermal conductivity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not true in respect of an ideal refrigerant?
a)
High latent heat of vaporization and specific heat.
b)
Critical pressure and temperature well above the maximum operating pressure and temperature limits.
c)
Low value of specific volume.
d)
High value of thermal conductivity
|
|
Niharika Iyer answered |
Desirable properties of an ideal refrigerant:
-Low boiling point
- High critical temperature
- High latent heat of vaporization
- Low specific heat of liquid
- Low specific volume of vapour
- Non-corrosive to metal
- Non-flammable and non-explosive
- Non-toxic
- Low cost
- Easy to liquify at moderate pressure and temperature
- Easy of locating leaks by odour or suitable indicator
- Mixes well with oil
-Low boiling point
- High critical temperature
- High latent heat of vaporization
- Low specific heat of liquid
- Low specific volume of vapour
- Non-corrosive to metal
- Non-flammable and non-explosive
- Non-toxic
- Low cost
- Easy to liquify at moderate pressure and temperature
- Easy of locating leaks by odour or suitable indicator
- Mixes well with oil
In on-off control refrigeration system, which one of the following expansion devices is used?- a)Capillary tube
- b)Thermostat
- c)Automatic expansion valve
- d)Float valve
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In on-off control refrigeration system, which one of the following expansion devices is used?
a)
Capillary tube
b)
Thermostat
c)
Automatic expansion valve
d)
Float valve
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
On-off control is done by thermostat. In the On- off control of the air-handling unit, the fan motor is operated intermittently by the room thermostat the bulb of which is installed in the return air.
Dry ice is suitable for ____ temperature refrigeration.- a)low
- b)high
- c)all range of
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Dry ice is suitable for ____ temperature refrigeration.
a)
low
b)
high
c)
all range of
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Dry ice when exposed to atmosphere sublimates by absorbing latent heat of sublimation.
The best capacity control method suitable for domestic refrigerant compressor is- a)On and Off control
- b)Holding the valves open
- c)Hot gas bypass
- d)Using multiple unit
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The best capacity control method suitable for domestic refrigerant compressor is
a)
On and Off control
b)
Holding the valves open
c)
Hot gas bypass
d)
Using multiple unit

|
Tanishq Rane answered |
The best capacity control method suitable for domestic refrigerant compressor is On and Off control.
Explanation:
On and Off control is the most suitable capacity control method for domestic refrigerant compressors. This method involves turning the compressor on and off to maintain the desired temperature in the refrigeration system. Here are the reasons why On and Off control is the best option:
1. Simplicity:
On and Off control is a simple and straightforward method. It does not require any complex control mechanisms or additional components. The compressor is either running at full capacity or completely turned off, making it easy to implement and understand.
2. Energy Efficiency:
In domestic refrigeration systems, the load demand can vary significantly throughout the day. On and Off control allows the compressor to operate only when cooling is required. This helps in conserving energy by reducing the runtime of the compressor when it is not needed.
3. Cost-effectiveness:
Since On and Off control does not involve any additional control components, it is a cost-effective solution for domestic refrigeration systems. The simplicity of this method reduces the overall system cost and maintenance requirements.
4. Reliability:
On and Off control is a reliable method as it does not rely on complex control mechanisms that can fail or malfunction. The compressor operates at full capacity when it is on, providing efficient cooling performance.
5. Temperature Control:
On and Off control allows for precise temperature control in the refrigeration system. When the desired temperature is reached, the compressor turns off, and when the temperature rises above the set point, the compressor turns on again. This ensures that the temperature is maintained within the desired range.
In conclusion, On and Off control is the best capacity control method for domestic refrigerant compressors due to its simplicity, energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, reliability, and temperature control capabilities.
Explanation:
On and Off control is the most suitable capacity control method for domestic refrigerant compressors. This method involves turning the compressor on and off to maintain the desired temperature in the refrigeration system. Here are the reasons why On and Off control is the best option:
1. Simplicity:
On and Off control is a simple and straightforward method. It does not require any complex control mechanisms or additional components. The compressor is either running at full capacity or completely turned off, making it easy to implement and understand.
2. Energy Efficiency:
In domestic refrigeration systems, the load demand can vary significantly throughout the day. On and Off control allows the compressor to operate only when cooling is required. This helps in conserving energy by reducing the runtime of the compressor when it is not needed.
3. Cost-effectiveness:
Since On and Off control does not involve any additional control components, it is a cost-effective solution for domestic refrigeration systems. The simplicity of this method reduces the overall system cost and maintenance requirements.
4. Reliability:
On and Off control is a reliable method as it does not rely on complex control mechanisms that can fail or malfunction. The compressor operates at full capacity when it is on, providing efficient cooling performance.
5. Temperature Control:
On and Off control allows for precise temperature control in the refrigeration system. When the desired temperature is reached, the compressor turns off, and when the temperature rises above the set point, the compressor turns on again. This ensures that the temperature is maintained within the desired range.
In conclusion, On and Off control is the best capacity control method for domestic refrigerant compressors due to its simplicity, energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, reliability, and temperature control capabilities.
One tonnes of refrigeration is equal to- a)210 kJ/min
- b)3.5 kJ/min
- c)105 kJ/min
- d)250 kJ/min
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One tonnes of refrigeration is equal to
a)
210 kJ/min
b)
3.5 kJ/min
c)
105 kJ/min
d)
250 kJ/min
|
|
Ashutosh Sharma answered |
One Tonnes of Refrigeration (TR) is equal to 210 kJ/min.
Explanation:
- One Tonnes of Refrigeration (TR) is a unit of power used in refrigeration and air conditioning industries.
- It is defined as the amount of cooling required to freeze one metric tonne (1000 kg) of water from 0°C to -1°C in 24 hours.
- TR is commonly used to rate the capacity of refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
- The conversion factor from TR to kJ/min is 210.
- Therefore, one TR is equal to 210 kJ/min.
Formula:
- The formula to calculate the cooling capacity in TR is given as: Q = m × Cp × ΔT / 24
- Where Q is the cooling capacity in TR, m is the mass of water to be frozen (in kg), Cp is the specific heat of water (4.18 kJ/kg°C), and ΔT is the temperature difference (in °C) between the initial and final temperatures of water.
- For example, if we want to freeze 1000 kg of water from 0°C to -1°C in 24 hours, the cooling capacity required will be:
Q = 1000 × 4.18 × (0-(-1)) / 24 = 34.9 kJ/min
- To convert this cooling capacity in TR, we need to divide it by 211. That is:
Q(TR) = 34.9 / 210 = 0.166 TR
Conclusion:
- One Tonnes of Refrigeration (TR) is equal to 210 kJ/min.
- It is used to rate the capacity of refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
- The formula to calculate the cooling capacity in TR is Q = m × Cp × ΔT / 24.
- To convert the cooling capacity in TR to kJ/min, we need to multiply it by 210.
Explanation:
- One Tonnes of Refrigeration (TR) is a unit of power used in refrigeration and air conditioning industries.
- It is defined as the amount of cooling required to freeze one metric tonne (1000 kg) of water from 0°C to -1°C in 24 hours.
- TR is commonly used to rate the capacity of refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
- The conversion factor from TR to kJ/min is 210.
- Therefore, one TR is equal to 210 kJ/min.
Formula:
- The formula to calculate the cooling capacity in TR is given as: Q = m × Cp × ΔT / 24
- Where Q is the cooling capacity in TR, m is the mass of water to be frozen (in kg), Cp is the specific heat of water (4.18 kJ/kg°C), and ΔT is the temperature difference (in °C) between the initial and final temperatures of water.
- For example, if we want to freeze 1000 kg of water from 0°C to -1°C in 24 hours, the cooling capacity required will be:
Q = 1000 × 4.18 × (0-(-1)) / 24 = 34.9 kJ/min
- To convert this cooling capacity in TR, we need to divide it by 211. That is:
Q(TR) = 34.9 / 210 = 0.166 TR
Conclusion:
- One Tonnes of Refrigeration (TR) is equal to 210 kJ/min.
- It is used to rate the capacity of refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
- The formula to calculate the cooling capacity in TR is Q = m × Cp × ΔT / 24.
- To convert the cooling capacity in TR to kJ/min, we need to multiply it by 210.
The by-pass factor of a cooling coil decreases with - a)decrease in fin spacing and increase in number of rows.
- b)increase in fin spacing and increase in number of rows. .
- c)increase in fin spacing and decrease in number of rows.
- d)decrease in fin spacing and decrease in number of rows.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The by-pass factor of a cooling coil decreases with
a)
decrease in fin spacing and increase in number of rows.
b)
increase in fin spacing and increase in number of rows. .
c)
increase in fin spacing and decrease in number of rows.
d)
decrease in fin spacing and decrease in number of rows.

|
Harshad Iyer answered |
The BPF depends upon the following factors:
1. The number of fins provided in a unit length i.e. the pitch of the cooling coil fins.
2. The number of rows in a coil in the direction of flow.
3. The velocity of flow of air.
1. The number of fins provided in a unit length i.e. the pitch of the cooling coil fins.
2. The number of rows in a coil in the direction of flow.
3. The velocity of flow of air.
The static regain method of designing the ducts as compared to equal friction method- a)increases balancing problems
- b)decreases balancing problems
- c)increases cost of sheet metal of duct
- d)decrases cost of sheet metal of duct
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The static regain method of designing the ducts as compared to equal friction method
a)
increases balancing problems
b)
decreases balancing problems
c)
increases cost of sheet metal of duct
d)
decrases cost of sheet metal of duct
|
|
Devansh Sengupta answered |
in static regain method, the size of duct is decided to give equal pressure at all outlets for perfect balancing of the air duct layout system. This method allows for balancing but reducing velocity increases duct size and it should not be taken beyond the economic limit.
Match List-I with List-ll and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Milk Chilling plant
B. Textile Mills
C. Biological process industry
List-ll
1. Strict control of temperature and humidity
2. Strict control of humidity
3. Strict control of temperature
Codes:
A B C
(a) 3 2 1
(b) 1 2 3
(c) 2 3 1
(d) 2 1 3- a)(a)
- b)(b)
- c)(c)
- d)(d)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-I with List-ll and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Milk Chilling plant
B. Textile Mills
C. Biological process industry
List-ll
1. Strict control of temperature and humidity
2. Strict control of humidity
3. Strict control of temperature
Codes:
A B C
(a) 3 2 1
(b) 1 2 3
(c) 2 3 1
(d) 2 1 3
List-I
A. Milk Chilling plant
B. Textile Mills
C. Biological process industry
List-ll
1. Strict control of temperature and humidity
2. Strict control of humidity
3. Strict control of temperature
Codes:
A B C
(a) 3 2 1
(b) 1 2 3
(c) 2 3 1
(d) 2 1 3
a)
(a)
b)
(b)
c)
(c)
d)
(d)

|
Saptarshi Khanna answered |
- Strict control of temperature metrological laboratories, precision m/c shops, computer centres etc.
- Relative humidity control-paper and textile mills.
- Strict control of both-chemical and biological industries.
The correct nomenclature for ethylene is- a)R 150
- b)R 740
- c)R 1150
- d)R 12
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct nomenclature for ethylene is
a)
R 150
b)
R 740
c)
R 1150
d)
R 12

|
Tanishq Rane answered |
Correct nomenclature for ethylene is R 150
Explanation:
The nomenclature system used for naming refrigerants is called the "Refrigerant Numbering System" or the "R-number system". This system was developed by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) and is widely used in the industry.
Refrigerant R 150:
R 150 is the correct nomenclature for ethylene. Ethylene is a hydrocarbon compound with the chemical formula C2H4. It is a colorless gas with a sweet odor and is commonly used as a refrigerant in low-temperature applications.
Significance of R-number:
The R-number assigned to a refrigerant provides important information about its chemical composition, thermodynamic properties, and environmental impact. The R-number system helps in identifying and categorizing different refrigerants based on their characteristics.
Other options:
- R 740: This nomenclature is not correct for ethylene. R 740 refers to carbon dioxide (CO2), which is another commonly used refrigerant.
- R 1150: This nomenclature is not correct for ethylene. R 1150 refers to ethane (C2H6), which is also a hydrocarbon compound but has different properties compared to ethylene.
- R 12: This nomenclature is not correct for ethylene. R 12 refers to dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2), which is an ozone-depleting refrigerant commonly known as Freon-12.
Conclusion:
The correct nomenclature for ethylene is R 150. It is important to use the correct nomenclature when working with refrigerants to ensure proper identification and handling.
Explanation:
The nomenclature system used for naming refrigerants is called the "Refrigerant Numbering System" or the "R-number system". This system was developed by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) and is widely used in the industry.
Refrigerant R 150:
R 150 is the correct nomenclature for ethylene. Ethylene is a hydrocarbon compound with the chemical formula C2H4. It is a colorless gas with a sweet odor and is commonly used as a refrigerant in low-temperature applications.
Significance of R-number:
The R-number assigned to a refrigerant provides important information about its chemical composition, thermodynamic properties, and environmental impact. The R-number system helps in identifying and categorizing different refrigerants based on their characteristics.
Other options:
- R 740: This nomenclature is not correct for ethylene. R 740 refers to carbon dioxide (CO2), which is another commonly used refrigerant.
- R 1150: This nomenclature is not correct for ethylene. R 1150 refers to ethane (C2H6), which is also a hydrocarbon compound but has different properties compared to ethylene.
- R 12: This nomenclature is not correct for ethylene. R 12 refers to dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2), which is an ozone-depleting refrigerant commonly known as Freon-12.
Conclusion:
The correct nomenclature for ethylene is R 150. It is important to use the correct nomenclature when working with refrigerants to ensure proper identification and handling.
The solution circuit in vapour-absorption cycle comprises of- a)Absorber
- b)Absorber + pump
- c)Generator + valve + absorber + pump
- d)Generator + absorber + pump
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The solution circuit in vapour-absorption cycle comprises of
a)
Absorber
b)
Absorber + pump
c)
Generator + valve + absorber + pump
d)
Generator + absorber + pump
|
|
Samarth Chaudhary answered |
In vapour-absorption cycle, the system formed by the generator-valve-absorber-pump may be considered to represent the heat engine part of the cycle. In this part, only the refrigerant- absorbent solution circulates. This part is known as solution circuit.
COP of a domestic refrigerator in comparison to domestic air conditioner will be- a)more
- b)less
- c)same
- d)depends on other factors
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
COP of a domestic refrigerator in comparison to domestic air conditioner will be
a)
more
b)
less
c)
same
d)
depends on other factors

|
Simran Dasgupta answered |
Due to low temperature in domestic refrigerator COP of domestic refrigerator < COP of domestic air-conditioner.
Which of the following evaporators use surge tank as a accumulator?- a)Flooded evaporators
- b)Shell and coil evaporator
- c)Double tube evaporators
- d)Frosting evaporator
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following evaporators use surge tank as a accumulator?
a)
Flooded evaporators
b)
Shell and coil evaporator
c)
Double tube evaporators
d)
Frosting evaporator
|
|
Nitin Joshi answered |
Flooded evaporators use surge tanks as accumulators.
Explanation:
Evaporators are heat exchangers that are used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems to remove heat from a substance, typically a liquid, and convert it into a vapor. This process is achieved by transferring heat from the substance to a refrigerant, which evaporates and carries the heat away.
Accumulators are devices used in refrigeration systems to store excess refrigerant and prevent it from entering the compressor. They help to separate the liquid and vapor phases of the refrigerant, ensuring that only vapor enters the compressor, which is more efficient and prevents damage to the compressor.
Flooded evaporators are a type of evaporator where the entire heat exchanger is completely filled with liquid refrigerant. The refrigerant enters the evaporator as a liquid and is completely evaporated before leaving the evaporator as a vapor. This type of evaporator is often used in large-scale industrial refrigeration systems.
Surge tanks, also known as surge drums or flash drums, are vessels that are connected to the evaporator and act as accumulators. They are used to store excess refrigerant that is not immediately evaporated and prevent it from entering the compressor. The surge tank helps to maintain a steady flow of refrigerant to the evaporator and prevent any liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor, which could cause damage.
In the case of flooded evaporators, the surge tank serves as an accumulator by collecting any excess liquid refrigerant and separating it from the vapor before it is sent to the compressor. The surge tank allows the liquid refrigerant to settle and be returned to the evaporator as needed, while only allowing vapor to enter the compressor. This helps to ensure the efficiency and longevity of the refrigeration system.
In summary, flooded evaporators use surge tanks as accumulators to store excess liquid refrigerant and prevent it from entering the compressor. This helps to maintain the efficiency and reliability of the refrigeration system.
Explanation:
Evaporators are heat exchangers that are used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems to remove heat from a substance, typically a liquid, and convert it into a vapor. This process is achieved by transferring heat from the substance to a refrigerant, which evaporates and carries the heat away.
Accumulators are devices used in refrigeration systems to store excess refrigerant and prevent it from entering the compressor. They help to separate the liquid and vapor phases of the refrigerant, ensuring that only vapor enters the compressor, which is more efficient and prevents damage to the compressor.
Flooded evaporators are a type of evaporator where the entire heat exchanger is completely filled with liquid refrigerant. The refrigerant enters the evaporator as a liquid and is completely evaporated before leaving the evaporator as a vapor. This type of evaporator is often used in large-scale industrial refrigeration systems.
Surge tanks, also known as surge drums or flash drums, are vessels that are connected to the evaporator and act as accumulators. They are used to store excess refrigerant that is not immediately evaporated and prevent it from entering the compressor. The surge tank helps to maintain a steady flow of refrigerant to the evaporator and prevent any liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor, which could cause damage.
In the case of flooded evaporators, the surge tank serves as an accumulator by collecting any excess liquid refrigerant and separating it from the vapor before it is sent to the compressor. The surge tank allows the liquid refrigerant to settle and be returned to the evaporator as needed, while only allowing vapor to enter the compressor. This helps to ensure the efficiency and longevity of the refrigeration system.
In summary, flooded evaporators use surge tanks as accumulators to store excess liquid refrigerant and prevent it from entering the compressor. This helps to maintain the efficiency and reliability of the refrigeration system.
The domestic refrigerator operating on vapour compression cycle uses the following device for expansion- a)thermostatic valve
- b)thermostat
- c)capillary tube
- d)throttling valve
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The domestic refrigerator operating on vapour compression cycle uses the following device for expansion
a)
thermostatic valve
b)
thermostat
c)
capillary tube
d)
throttling valve

|
Pallabi Chavan answered |
Capillary tube is used as an expansion device in small capacity hermetic sealed refrigeration units such as in domestic refrigerators, water coolers, room air-conditioners and freezers.
The bank of tubes at the back of a domestic refrigerator of vapour compression type are- a)condenser tubes
- b)evaporator tubes
- c)capillary tubes
- d)tubes carrying electric wires
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The bank of tubes at the back of a domestic refrigerator of vapour compression type are
a)
condenser tubes
b)
evaporator tubes
c)
capillary tubes
d)
tubes carrying electric wires

|
Manasa Sen answered |
These tubes are air-cooled condenser which are used only in small capacity machines, such as refrigerators and small water coolers which use vertical wire and tube or plate and tube construction with natural circulation, and window type and packaged air conditioners which have tubes with 5-7 fins per cm and use forced circulation of air.
In a vapour compression refrigeration system, a throttle valve is used in place of expander because- a)it leads to significant cost reduction
- b)it considerably reduces the system work
- c)positive work in isentropic expansion of liquid is very small
- d)improves COP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a vapour compression refrigeration system, a throttle valve is used in place of expander because
a)
it leads to significant cost reduction
b)
it considerably reduces the system work
c)
positive work in isentropic expansion of liquid is very small
d)
improves COP
|
|
Kirti Bose answered |
There are practical difficulties in smoothly expanding a liquid of a highly wet vapour in an expander. As vg → vf, the positive work of isentropic expansion is seldom large enough to justify the cost of an expander. The the rmodynamic and friction losses of an expander if employed, may even exceed the gain in work. Accordingly, the isentropic expansion process may be replaced by the use of an expansion device such as a throttle valve or a capillary tube.
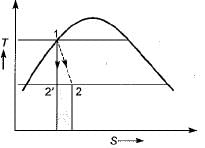

For cooling and dehumidification of unsaturated moist air, it must be passed over a coil at a temperature- a)of adiabatic saturation of incoming steam
- b)which is lower than the dew point of incoming stream
- c)which lies between dry bulb and wet bulb temperature
- d)which lies between wet bulb and dew point temperature of incoming stream
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For cooling and dehumidification of unsaturated moist air, it must be passed over a coil at a temperature
a)
of adiabatic saturation of incoming steam
b)
which is lower than the dew point of incoming stream
c)
which lies between dry bulb and wet bulb temperature
d)
which lies between wet bulb and dew point temperature of incoming stream
|
|
Sinjini Nambiar answered |
Cooling and dehumidification : The dehumidification of air is only possible when the effective surface temperature of the cooling coil is less than the dew point temperature of the air entering the coil.
Atmospheric air at DBT of 15°C enters a heating coil whose surface temperature is maintained at 40°C. The air leaves the heating coil at 25°C. What will be the by-pass factor of heating coil?- a)0.376
- b)0.4
- c)0.6
- d)0.67
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Atmospheric air at DBT of 15°C enters a heating coil whose surface temperature is maintained at 40°C. The air leaves the heating coil at 25°C. What will be the by-pass factor of heating coil?
a)
0.376
b)
0.4
c)
0.6
d)
0.67

|
Raghavendra Goyal answered |
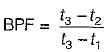
Where
t3 = temperature of heating coil = 40°C
t2 = exit temperature of air = 25°C
t1 = temperature of air at inlet = 15°C
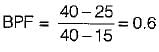
Solid CO2 is produced by- a)vapour absorption method
- b)simple vapour compression cycle
- c)vapour compression cycle with compounding of compressor
- d)pressure snow chamber method
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Solid CO2 is produced by
a)
vapour absorption method
b)
simple vapour compression cycle
c)
vapour compression cycle with compounding of compressor
d)
pressure snow chamber method

|
Pallabi Chavan answered |
There are two method of manufacturing of solid CO2
1. Simple vapour compression cycle
2. Pressure snow chamber method
Power requirement for the simple vapour compression cycle is of the order of 400-500 J-hr per ton of solid CO2; one of the main reason for such high power consumption is the high pressure ratio that is nearly equal to 70.
Another problem in the process of manufacture is the blocking of expansion device by the formation of dry ice due to these difficulties, snow chamber method is most commonly used.
1. Simple vapour compression cycle
2. Pressure snow chamber method
Power requirement for the simple vapour compression cycle is of the order of 400-500 J-hr per ton of solid CO2; one of the main reason for such high power consumption is the high pressure ratio that is nearly equal to 70.
Another problem in the process of manufacture is the blocking of expansion device by the formation of dry ice due to these difficulties, snow chamber method is most commonly used.
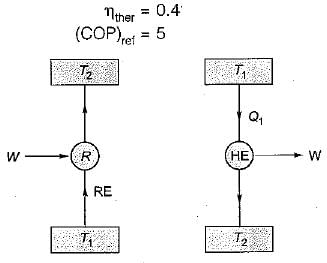
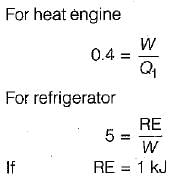
If an engine of 40% thermal efficiency drives a refrigerator having a coefficient of performance of 5, then the heat input to engine for each kJ of heat removed from the cold body of the refrigerator is- a)0.50 kJ
- b)0.75 kJ
- c)1 kJ
- d)1.25 k
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If an engine of 40% thermal efficiency drives a refrigerator having a coefficient of performance of 5, then the heat input to engine for each kJ of heat removed from the cold body of the refrigerator is
a)
0.50 kJ
b)
0.75 kJ
c)
1 kJ
d)
1.25 k

|
Navya Saha answered |
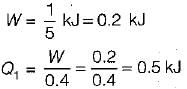
The comfort chart is drawn between- a)DBT and RH
- b)DRT and WDT
- c)WBT and DBT
- d)WBT, RH and Air velocity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The comfort chart is drawn between
a)
DBT and RH
b)
DRT and WDT
c)
WBT and DBT
d)
WBT, RH and Air velocity
|
|
Rajat Basu answered |
Comfort chart is drawn between DBT-in x-axis and WBT-in y-axis.
For small installations of refrigeration systems (up to 35 kW), which type of condenser is used?- a)shell and tube type
- b)shell and coil type
- c)double tube type
- d)air cooled type
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For small installations of refrigeration systems (up to 35 kW), which type of condenser is used?
a)
shell and tube type
b)
shell and coil type
c)
double tube type
d)
air cooled type
|
|
Vaibhav Khanna answered |
Air-cooled condensers used only in small capacity machines. Air cooled condensers are seldom made in sizes over 5 TR because of high head pressure, excessive power consumption and objectionable fan noise. In air-cooled condensers, heat is removed by air using either natural or forced circulation.
The aspect ratio, for rectangular ducts, should not be greater than .... in any case- a)8
- b)10
- c)12
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The aspect ratio, for rectangular ducts, should not be greater than .... in any case
a)
8
b)
10
c)
12
d)
16

|
Sharmila Gupta answered |
The aspect ratio of a rectangular duct is defined as the ratio of its width to its height. In other words, it represents the shape of the duct, specifically how elongated or squarish it is. The aspect ratio is an important parameter to consider in duct design as it directly affects the airflow characteristics and pressure drop.
The correct answer to the given question is option 'A' which states that the aspect ratio should not be greater than 8 in any case. Let's understand why this is the case.
1. Definition of Aspect Ratio:
- The aspect ratio is defined as the width (W) divided by the height (H) of the rectangular duct.
- Mathematically, Aspect Ratio = W/H.
2. Importance of Aspect Ratio:
- The aspect ratio has a significant impact on the airflow characteristics inside the duct.
- For low aspect ratios (more squarish shape), the airflow is more uniform and evenly distributed across the cross-section of the duct.
- Higher aspect ratios (elongated shape) can cause uneven airflow distribution, leading to higher pressure drop and potential flow disturbances.
3. Ideal Aspect Ratio Range:
- In general, an aspect ratio between 1 to 4 is considered desirable for rectangular ducts.
- This range ensures relatively uniform airflow distribution and minimizes pressure drop.
- Aspect ratios outside this range can lead to flow separation, increased turbulence, and pressure losses.
4. Limitation of Aspect Ratio:
- The given question states that the aspect ratio should not be greater than 8 in any case.
- This limitation is based on practical considerations and engineering experience.
- Aspect ratios greater than 8 result in highly elongated ducts, which can cause severe flow disturbances, increased pressure drop, and potential structural issues.
5. Safety and Efficiency:
- Ensuring that the aspect ratio does not exceed 8 helps maintain the safety and efficiency of the duct system.
- It ensures that the airflow remains relatively uniform, reducing the risk of flow separation and associated problems.
- Additionally, it helps minimize pressure losses, optimizing the energy efficiency of the system.
In conclusion, the aspect ratio of rectangular ducts should not be greater than 8 in any case. This limitation is based on the need for uniform airflow distribution, reduced pressure drop, and overall system efficiency.
The correct answer to the given question is option 'A' which states that the aspect ratio should not be greater than 8 in any case. Let's understand why this is the case.
1. Definition of Aspect Ratio:
- The aspect ratio is defined as the width (W) divided by the height (H) of the rectangular duct.
- Mathematically, Aspect Ratio = W/H.
2. Importance of Aspect Ratio:
- The aspect ratio has a significant impact on the airflow characteristics inside the duct.
- For low aspect ratios (more squarish shape), the airflow is more uniform and evenly distributed across the cross-section of the duct.
- Higher aspect ratios (elongated shape) can cause uneven airflow distribution, leading to higher pressure drop and potential flow disturbances.
3. Ideal Aspect Ratio Range:
- In general, an aspect ratio between 1 to 4 is considered desirable for rectangular ducts.
- This range ensures relatively uniform airflow distribution and minimizes pressure drop.
- Aspect ratios outside this range can lead to flow separation, increased turbulence, and pressure losses.
4. Limitation of Aspect Ratio:
- The given question states that the aspect ratio should not be greater than 8 in any case.
- This limitation is based on practical considerations and engineering experience.
- Aspect ratios greater than 8 result in highly elongated ducts, which can cause severe flow disturbances, increased pressure drop, and potential structural issues.
5. Safety and Efficiency:
- Ensuring that the aspect ratio does not exceed 8 helps maintain the safety and efficiency of the duct system.
- It ensures that the airflow remains relatively uniform, reducing the risk of flow separation and associated problems.
- Additionally, it helps minimize pressure losses, optimizing the energy efficiency of the system.
In conclusion, the aspect ratio of rectangular ducts should not be greater than 8 in any case. This limitation is based on the need for uniform airflow distribution, reduced pressure drop, and overall system efficiency.
The refrigerant circuit in vapour-absorption cycle consists of
- a)condenser + expansion device
- b)condenser + expansion device + evaporator
- c)condenser + expansion device + absorber
- d)condenser + absorber + pump
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The refrigerant circuit in vapour-absorption cycle consists of
a)
condenser + expansion device
b)
condenser + expansion device + evaporator
c)
condenser + expansion device + absorber
d)
condenser + absorber + pump
|
|
Anuj Chauhan answered |
The refrigerant circuit in a vapor-absorption cycle consists of:
- Condenser
- Expansion Device
- Evaporator
- Absorber
Explanation:
The vapor-absorption cycle is a type of refrigeration cycle that uses a combination of a refrigerant and an absorbent to achieve cooling. It is commonly used in large-scale refrigeration systems and is known for its low power consumption.
The refrigerant circuit in a vapor-absorption cycle includes the following components:
1. Condenser:
The condenser is the component where the hot refrigerant vapor coming from the evaporator is cooled and condensed into a liquid. It transfers heat from the refrigerant to the cooling medium (usually air or water) and allows the refrigerant to change phase from a vapor to a liquid.
2. Expansion Device:
The expansion device is located between the condenser and the evaporator. It is responsible for reducing the pressure of the condensed refrigerant liquid, thereby causing it to expand and evaporate. This expansion results in a drop in temperature, which is necessary for the refrigeration process.
3. Evaporator:
The evaporator is where the low-pressure refrigerant vapor absorbs heat from the surroundings, such as the air or water being cooled. As the refrigerant evaporates, it absorbs heat energy, causing the surroundings to cool down. This is the part of the cycle where cooling is achieved.
4. Absorber:
The absorber is the component where the refrigerant vapor, after leaving the evaporator, is absorbed by the absorbent. The absorbent is a substance that has a high affinity for the refrigerant and helps to separate it from the vapor mixture. This allows the refrigerant to be recycled back into the cycle.
By following this circuit, the vapor-absorption cycle can continuously remove heat from a space or process, providing cooling effects. The cycle is driven by the absorption of the refrigerant vapor by the absorbent and the subsequent release of the refrigerant by heating the absorbent. This allows the refrigerant to be effectively recycled and used for cooling purposes.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - condenser, expansion device, and evaporator.
- Condenser
- Expansion Device
- Evaporator
- Absorber
Explanation:
The vapor-absorption cycle is a type of refrigeration cycle that uses a combination of a refrigerant and an absorbent to achieve cooling. It is commonly used in large-scale refrigeration systems and is known for its low power consumption.
The refrigerant circuit in a vapor-absorption cycle includes the following components:
1. Condenser:
The condenser is the component where the hot refrigerant vapor coming from the evaporator is cooled and condensed into a liquid. It transfers heat from the refrigerant to the cooling medium (usually air or water) and allows the refrigerant to change phase from a vapor to a liquid.
2. Expansion Device:
The expansion device is located between the condenser and the evaporator. It is responsible for reducing the pressure of the condensed refrigerant liquid, thereby causing it to expand and evaporate. This expansion results in a drop in temperature, which is necessary for the refrigeration process.
3. Evaporator:
The evaporator is where the low-pressure refrigerant vapor absorbs heat from the surroundings, such as the air or water being cooled. As the refrigerant evaporates, it absorbs heat energy, causing the surroundings to cool down. This is the part of the cycle where cooling is achieved.
4. Absorber:
The absorber is the component where the refrigerant vapor, after leaving the evaporator, is absorbed by the absorbent. The absorbent is a substance that has a high affinity for the refrigerant and helps to separate it from the vapor mixture. This allows the refrigerant to be recycled back into the cycle.
By following this circuit, the vapor-absorption cycle can continuously remove heat from a space or process, providing cooling effects. The cycle is driven by the absorption of the refrigerant vapor by the absorbent and the subsequent release of the refrigerant by heating the absorbent. This allows the refrigerant to be effectively recycled and used for cooling purposes.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - condenser, expansion device, and evaporator.
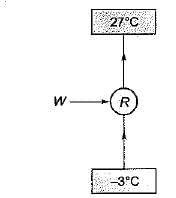
If COP of a refrigerator is 5 and efficiency of a heat engine of the same temperature limit is 50%. Then what is the ratio of heat supplied to engine to heat absorbed by the refrigerator from the space- a)2.5
- b)0.4
- c)4
- d)0.25
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If COP of a refrigerator is 5 and efficiency of a heat engine of the same temperature limit is 50%. Then what is the ratio of heat supplied to engine to heat absorbed by the refrigerator from the space
a)
2.5
b)
0.4
c)
4
d)
0.25

|
Gauri Roy answered |
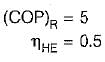
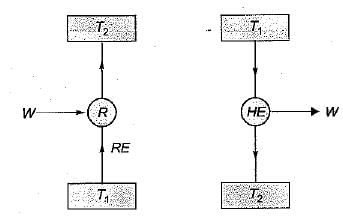
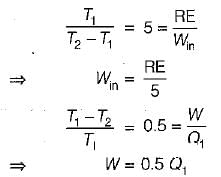
By equating, we get
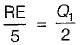
⇒
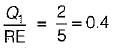
Absorbent in a vapour absorption refrigerator system separates from the refrigerant only when it- a)is sufficiently heated
- b)is sprayed on cooling water
- c)is cooled
- d)reacts with refrigerant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Absorbent in a vapour absorption refrigerator system separates from the refrigerant only when it
a)
is sufficiently heated
b)
is sprayed on cooling water
c)
is cooled
d)
reacts with refrigerant

|
Bhargavi Sarkar answered |
When the mixture of absorbent and refrigerant is heated sufficiently in the generator they get separate and refrigerant vapour is send to condenser and absorbent is sent back to the absorber.
The domestic refrigerator has.a refrigeration load of the order of- a)less than 0.25 ton
- b)between 0.5 and 1 ton
- c)more than 1 ton
- d)more than 5 ton
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The domestic refrigerator has.a refrigeration load of the order of
a)
less than 0.25 ton
b)
between 0.5 and 1 ton
c)
more than 1 ton
d)
more than 5 ton
|
|
Dipika Bose answered |
Refrigeration Load of Domestic Refrigerator
Definition of Refrigeration Load
Refrigeration load is defined as the amount of heat that needs to be removed from a space or substance in order to achieve a desired temperature.
Refrigeration Load of Domestic Refrigerator
The refrigeration load of a domestic refrigerator is the amount of heat that needs to be removed from the interior of the refrigerator in order to keep the temperature low enough to preserve food and beverages.
Calculation of Refrigeration Load
The refrigeration load of a domestic refrigerator can be calculated by determining the heat gain into the refrigerator and then calculating the amount of heat that needs to be removed to maintain the desired temperature. Factors that contribute to the heat gain into the refrigerator include:
- Ambient temperature
- Insulation quality
- Door opening frequency
- Type and quantity of food stored
Answer Explanation
The refrigeration load of a domestic refrigerator is typically less than 0.25 ton. This is because the size of a domestic refrigerator is relatively small compared to commercial refrigeration systems, and the amount of heat gain into the refrigerator is relatively low due to the insulation quality and infrequent door opening. Therefore, the amount of heat that needs to be removed is also relatively low.
Definition of Refrigeration Load
Refrigeration load is defined as the amount of heat that needs to be removed from a space or substance in order to achieve a desired temperature.
Refrigeration Load of Domestic Refrigerator
The refrigeration load of a domestic refrigerator is the amount of heat that needs to be removed from the interior of the refrigerator in order to keep the temperature low enough to preserve food and beverages.
Calculation of Refrigeration Load
The refrigeration load of a domestic refrigerator can be calculated by determining the heat gain into the refrigerator and then calculating the amount of heat that needs to be removed to maintain the desired temperature. Factors that contribute to the heat gain into the refrigerator include:
- Ambient temperature
- Insulation quality
- Door opening frequency
- Type and quantity of food stored
Answer Explanation
The refrigeration load of a domestic refrigerator is typically less than 0.25 ton. This is because the size of a domestic refrigerator is relatively small compared to commercial refrigeration systems, and the amount of heat gain into the refrigerator is relatively low due to the insulation quality and infrequent door opening. Therefore, the amount of heat that needs to be removed is also relatively low.
The wet bulb depression is zero, when relative humidity is equal to- a)zero
- b)0.5
- c)0.75
- d)1.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The wet bulb depression is zero, when relative humidity is equal to
a)
zero
b)
0.5
c)
0.75
d)
1.0
|
|
Sandeep Sengupta answered |
Explanation:
The wet bulb depression is a measure of the difference between the dry bulb temperature and the wet bulb temperature. It represents the cooling effect of evaporation on the wet bulb temperature.
The wet bulb depression is zero when the relative humidity is equal to 1.0 or 100%. This means that the air is saturated with moisture and cannot hold any more water vapor. When the air is saturated, the wet bulb temperature is equal to the dry bulb temperature.
Why is the wet bulb depression zero when the relative humidity is 1.0?
When the relative humidity is 1.0, it means that the air is holding the maximum amount of water vapor it can at a given temperature. The air is saturated with moisture, and any additional water vapor will condense into liquid water.
In this saturated condition, there is no evaporation occurring from the wet bulb. Evaporation is a cooling process, and it lowers the temperature of the wet bulb. However, when the air is already holding as much moisture as it can, there is no more room for evaporation to take place. As a result, the wet bulb temperature is equal to the dry bulb temperature, and the wet bulb depression is zero.
Significance of wet bulb depression:
The wet bulb depression is an important parameter in determining the comfort level and heat stress in a given environment. It provides an indication of the cooling effect of evaporation and the potential for heat transfer through sweating.
When the wet bulb depression is high, it means that there is a significant difference between the dry and wet bulb temperatures. This indicates that evaporation is occurring and the air has the potential to provide cooling. This is desirable in hot and humid conditions as it helps in dissipating heat from the body.
On the other hand, when the wet bulb depression is low or zero, it indicates that the air is already saturated with moisture and evaporation is not occurring. This can lead to discomfort and heat stress as the body's ability to cool down through sweating is limited.
In conclusion, the wet bulb depression is zero when the relative humidity is equal to 1.0 or 100%. This means that the air is saturated with moisture and there is no room for evaporation. Understanding the wet bulb depression is important in assessing the comfort level and heat stress in a given environment.
The wet bulb depression is a measure of the difference between the dry bulb temperature and the wet bulb temperature. It represents the cooling effect of evaporation on the wet bulb temperature.
The wet bulb depression is zero when the relative humidity is equal to 1.0 or 100%. This means that the air is saturated with moisture and cannot hold any more water vapor. When the air is saturated, the wet bulb temperature is equal to the dry bulb temperature.
Why is the wet bulb depression zero when the relative humidity is 1.0?
When the relative humidity is 1.0, it means that the air is holding the maximum amount of water vapor it can at a given temperature. The air is saturated with moisture, and any additional water vapor will condense into liquid water.
In this saturated condition, there is no evaporation occurring from the wet bulb. Evaporation is a cooling process, and it lowers the temperature of the wet bulb. However, when the air is already holding as much moisture as it can, there is no more room for evaporation to take place. As a result, the wet bulb temperature is equal to the dry bulb temperature, and the wet bulb depression is zero.
Significance of wet bulb depression:
The wet bulb depression is an important parameter in determining the comfort level and heat stress in a given environment. It provides an indication of the cooling effect of evaporation and the potential for heat transfer through sweating.
When the wet bulb depression is high, it means that there is a significant difference between the dry and wet bulb temperatures. This indicates that evaporation is occurring and the air has the potential to provide cooling. This is desirable in hot and humid conditions as it helps in dissipating heat from the body.
On the other hand, when the wet bulb depression is low or zero, it indicates that the air is already saturated with moisture and evaporation is not occurring. This can lead to discomfort and heat stress as the body's ability to cool down through sweating is limited.
In conclusion, the wet bulb depression is zero when the relative humidity is equal to 1.0 or 100%. This means that the air is saturated with moisture and there is no room for evaporation. Understanding the wet bulb depression is important in assessing the comfort level and heat stress in a given environment.
An ideal vapour compression refrigerator operates between a condenser pressure P1 and an evaporator pressure P2. Which of the following changes would increase its COP?- a)Increasing P1 by Δ P and keeping P2 constant
- b)Decreasing P2 by Δ P and keeping P1 constant
- c)Adopting wet compression
- d)Subcooling the refrigerant
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An ideal vapour compression refrigerator operates between a condenser pressure P1 and an evaporator pressure P2. Which of the following changes would increase its COP?
a)
Increasing P1 by Δ P and keeping P2 constant
b)
Decreasing P2 by Δ P and keeping P1 constant
c)
Adopting wet compression
d)
Subcooling the refrigerant

|
Aniket Mehta answered |
COP decreases both with decreasing evaporator and increasing condenser pressures. The COP increases by installing a subcooler between the condenser and the expansion valve. The subcooling reduces flashing of the liquid during expansion and increases refrigerating effect.
For air with a relative humidity of 80%- a)the dry bulb temperature is less than the wet bulb temperature
- b)the dew point temperature is less than wet bulb temperature
- c)the dew point and wet bulb temperatures are equal
- d)the dry bulb and dew point temperatures are equai
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For air with a relative humidity of 80%
a)
the dry bulb temperature is less than the wet bulb temperature
b)
the dew point temperature is less than wet bulb temperature
c)
the dew point and wet bulb temperatures are equal
d)
the dry bulb and dew point temperatures are equai

|
Jaideep Malik answered |
For unsaturated air
DBT > WBT > DPT
DBT > WBT > DPT
Which of the following machines can be used to obtain refrigeration at the place where there is no electric power?- a)Air refrigeration
- b)Steam jet refrigeration
- c)Vapour compression refrigeration
- d)Vapour absorption refrigeration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following machines can be used to obtain refrigeration at the place where there is no electric power?
a)
Air refrigeration
b)
Steam jet refrigeration
c)
Vapour compression refrigeration
d)
Vapour absorption refrigeration

|
Aditi Sarkar answered |
Vapour absorption refrigeration is heat operated refrigeration system and can operate by taking heat from the solar system.
Heating of air without changing its moisture content takes place on Psychrometric chart along- a)rising line
- b)a horizontal line of the constant dew point
- c)a vertical line of constant dry bulb temperature
- d)curved line
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Heating of air without changing its moisture content takes place on Psychrometric chart along
a)
rising line
b)
a horizontal line of the constant dew point
c)
a vertical line of constant dry bulb temperature
d)
curved line
|
|
Siddharth Menon answered |
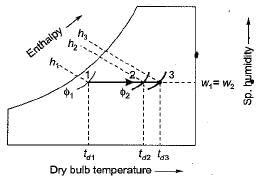
Where
td1 = dry bulb temperature of air entering to the coil
td2 = dry bulb temperature of air living the coil
td3 = dry bulb temperature of coil
Degree of saturation or percentage humidity is- a)the mass of water vapour present in 1 m3 of dry air
- b)the mass of water vapour present in 1 kg of dry air
- c)the ratio of the actual mass of water vapour in a unit mass of dry air to the mass of water vapour in the same mass of dry air when it is saturated at the same temperature and pressure
- d)the ratio of actual mass of water vapour in a given volume of moist air to the mass of water vapour in the same volume of saturated air at the same temperature and pressure
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Degree of saturation or percentage humidity is
a)
the mass of water vapour present in 1 m3 of dry air
b)
the mass of water vapour present in 1 kg of dry air
c)
the ratio of the actual mass of water vapour in a unit mass of dry air to the mass of water vapour in the same mass of dry air when it is saturated at the same temperature and pressure
d)
the ratio of actual mass of water vapour in a given volume of moist air to the mass of water vapour in the same volume of saturated air at the same temperature and pressure
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Degree of saturation is the ratio of actual specific humidity to the specific humidity under saturated condition.
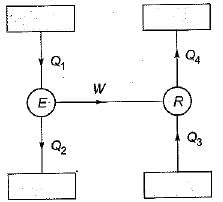
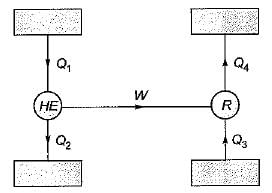
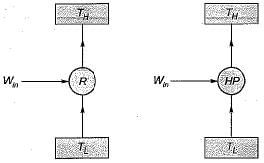
Which one of the following is correct relation between (COP)HP and (COP)R- a)(COP)HP-(COP)R - 1
- b)(COP)R - (COP)HP = 1
- c)(COP)Hp + (COP)R = 1
- d)(COP)HP + (COP)H = 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is correct relation between (COP)HP and (COP)R
a)
(COP)HP-(COP)R - 1
b)
(COP)R - (COP)HP = 1
c)
(COP)Hp + (COP)R = 1
d)
(COP)HP + (COP)H = 0

|
Shail Rane answered |
Relation between coefficient of performance of heat pump and refrigerator:



In a boot-strap air evaporative cooling system, the evaporator is provided- a)between the combustion chauber and the first heat exchanger.
- b)between the first heat exchanger and the secondary compressor.
- c)between the secondary compressor and the second heat exchanger.
- d)between the second heat exchanger and the cooling turbine.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a boot-strap air evaporative cooling system, the evaporator is provided
a)
between the combustion chauber and the first heat exchanger.
b)
between the first heat exchanger and the secondary compressor.
c)
between the secondary compressor and the second heat exchanger.
d)
between the second heat exchanger and the cooling turbine.

|
Nayanika Joshi answered |
Boot-strap air evaporative cooling system is similar to boot-strap air cycle system except that the addition of an evaporator between the second heat exchanger and the cooling turbine.
The number of hydrogen atoms in the refrigerant R-12 is- a)4
- b)2
- c)1
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of hydrogen atoms in the refrigerant R-12 is
a)
4
b)
2
c)
1
d)
0

|
Subham Unni answered |
R - 012
By comparing R-(m - 1)(n + 1) P
m - 1 = 0 ⇒ m = 1
n + 1 = 1 ⇒ n = 0
P = 2
where, n = number of hydrogen atom
m = number of carbon atom
By comparing R-(m - 1)(n + 1) P
m - 1 = 0 ⇒ m = 1
n + 1 = 1 ⇒ n = 0
P = 2
where, n = number of hydrogen atom
m = number of carbon atom
Consider the following statements: In a chemical dehumidification process,
1. DPT decreases
2. WBT decreases
3. DBT decreasesQ. Which of these are correct?- a)1,2 and 3
- b)1 and 2
- c)1 and 3
- d)2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements: In a chemical dehumidification process,
1. DPT decreases
2. WBT decreases
3. DBT decreases
1. DPT decreases
2. WBT decreases
3. DBT decreases
Q. Which of these are correct?
a)
1,2 and 3
b)
1 and 2
c)
1 and 3
d)
2 and 3

|
Naina Das answered |
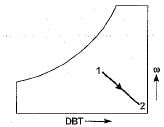
1→2 : Chemical dehumidication so, DBT increases
Which of the following expansion valve is most suitable for application in air conditioning and refrigerant plants?- a)Automatic expansion valve
- b)T-X valve
- c)Cross-charged expansion valve
- d)Gas charged valves
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following expansion valve is most suitable for application in air conditioning and refrigerant plants?
a)
Automatic expansion valve
b)
T-X valve
c)
Cross-charged expansion valve
d)
Gas charged valves
|
|
Shreya Choudhury answered |
Overview of Expansion Valves
Expansion valves are crucial components in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, controlling refrigerant flow and maintaining optimal performance. Among various types, the Thermostatic Expansion Valve (T-X valve) stands out for several reasons.
Functionality of T-X Valve
- Temperature Regulation: The T-X valve adjusts the flow of refrigerant based on the temperature at the evaporator outlet, ensuring the system operates efficiently.
- Pressure Differential: It maintains the necessary pressure difference between the high-pressure and low-pressure sides, preventing liquid refrigerant from returning to the compressor.
Advantages of T-X Valves
- Versatility: Suitable for various refrigerants and adaptable to different operational conditions, making it ideal for diverse air conditioning applications.
- Energy Efficiency: By optimizing refrigerant flow, T-X valves enhance system efficiency, leading to lower energy consumption and operational costs.
- Reliable Performance: They provide stable performance across varying loads and conditions, reducing the risk of system failure.
Comparison with Other Valves
- Automatic Expansion Valve: Primarily suited for constant load applications; it lacks the adaptability required for varying conditions.
- Cross-Charged Expansion Valve: Less common and often not as efficient in managing refrigerant flow compared to T-X valves.
- Gas Charged Valves: While functional, they may not provide the same level of precise control as T-X valves.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the T-X valve is the most suitable expansion valve for air conditioning and refrigerant plants due to its versatility, energy efficiency, and reliable temperature regulation. Its capability to adapt to varying loads makes it the preferred choice in modern HVAC applications.
Expansion valves are crucial components in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, controlling refrigerant flow and maintaining optimal performance. Among various types, the Thermostatic Expansion Valve (T-X valve) stands out for several reasons.
Functionality of T-X Valve
- Temperature Regulation: The T-X valve adjusts the flow of refrigerant based on the temperature at the evaporator outlet, ensuring the system operates efficiently.
- Pressure Differential: It maintains the necessary pressure difference between the high-pressure and low-pressure sides, preventing liquid refrigerant from returning to the compressor.
Advantages of T-X Valves
- Versatility: Suitable for various refrigerants and adaptable to different operational conditions, making it ideal for diverse air conditioning applications.
- Energy Efficiency: By optimizing refrigerant flow, T-X valves enhance system efficiency, leading to lower energy consumption and operational costs.
- Reliable Performance: They provide stable performance across varying loads and conditions, reducing the risk of system failure.
Comparison with Other Valves
- Automatic Expansion Valve: Primarily suited for constant load applications; it lacks the adaptability required for varying conditions.
- Cross-Charged Expansion Valve: Less common and often not as efficient in managing refrigerant flow compared to T-X valves.
- Gas Charged Valves: While functional, they may not provide the same level of precise control as T-X valves.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the T-X valve is the most suitable expansion valve for air conditioning and refrigerant plants due to its versatility, energy efficiency, and reliable temperature regulation. Its capability to adapt to varying loads makes it the preferred choice in modern HVAC applications.
The main supply air duct of an air-conditioning system is 100 cm x 90 cm in cross-section and carries 10 m3/s of air. It branches off into two ducts, one 80 cm x 80 cm and the other 80 cm x 60 cm. If the mean velocity in the larger branch is 9 m/s, what is the mean velocity in smaller branch?- a)11.1 m/s
- b)10 m/s
- c)8.83 m/s
- d)9 m/s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The main supply air duct of an air-conditioning system is 100 cm x 90 cm in cross-section and carries 10 m3/s of air. It branches off into two ducts, one 80 cm x 80 cm and the other 80 cm x 60 cm. If the mean velocity in the larger branch is 9 m/s, what is the mean velocity in smaller branch?
a)
11.1 m/s
b)
10 m/s
c)
8.83 m/s
d)
9 m/s
|
|
Kritika Joshi answered |
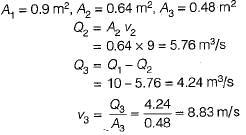
The heat load from the occupants in air conditioning load calculation is a source of- a)Sensible heat only
- b)Latent heat only
- c)Both sensible and latent heat
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The heat load from the occupants in air conditioning load calculation is a source of
a)
Sensible heat only
b)
Latent heat only
c)
Both sensible and latent heat
d)
None of these

|
Abhay Banerjee answered |
Sensible heat load is due to following:
1. The heat flowing into the building by conduction through exterior walls, floors, ceilings, doors and windows due to temperature difference
2. Heat received by solar radiation through glass of window, ventilations
3. Heat gained by lightnings, machineries, cooking operations, industrial processes etc.
Latent heat load is due to following:
1. Heat gain due to moisture in the outside air entering by infiltration.
2. Heat gain due to condensation of moisture from occupants.
3. Heat gain due to condensation of moisture from any process such as cooking.
1. The heat flowing into the building by conduction through exterior walls, floors, ceilings, doors and windows due to temperature difference
2. Heat received by solar radiation through glass of window, ventilations
3. Heat gained by lightnings, machineries, cooking operations, industrial processes etc.
Latent heat load is due to following:
1. Heat gain due to moisture in the outside air entering by infiltration.
2. Heat gain due to condensation of moisture from occupants.
3. Heat gain due to condensation of moisture from any process such as cooking.
Chapter doubts & questions for Refrigeration & Air Conditioning - Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Refrigeration & Air Conditioning - Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering
45 videos|314 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup