All Exams >
UPSC >
Old & New NCERTs for IAS Preparation (Must Read) >
All Questions
All questions of NCERT Based Tests for UPSC CSE Exam
Amrita Devi Bishnoi National Award is given in which of the following fields?
- a)In the soil conservation
- b)In the field of wildlife conservation
- c)In the field of women empowerment
- d)In science
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Amrita Devi Bishnoi National Award is given in which of the following fields?
a)
In the soil conservation
b)
In the field of wildlife conservation
c)
In the field of women empowerment
d)
In science
|
|
Sanjay Rana answered |
The Government of India instituted an ‘Amrita Devi Bishnoi National Award for Wildlife Conservation’ in the memory of Amrita Devi Bishnoi, who in 1731 sacrificed her life along with 363 others for the protection of ‘khejri’ trees in Khejarli village near Jodhpur in Rajasthan.
Consider the following:1. Cotton2. PET3. PlasticWhich of the above is/are example(s) of natural polymers?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) 1 and 2 Only
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following:
1. Cotton
2. PET
3. Plastic
Which of the above is/are example(s) of natural polymers?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
1 and 2 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Dhruv Yadav answered |
Introduction:
In the given options, we are asked to identify the natural polymers among cotton, PET, and plastic. To determine this, we need to understand what natural polymers are and how they differ from synthetic polymers.
Natural Polymers:
Natural polymers are large molecules composed of repeating subunits found in nature. These polymers are typically derived from living organisms and can be extracted or synthesized from natural sources. Unlike synthetic polymers, natural polymers have a complex molecular structure and are biodegradable.
Analysis of the Options:
Let's analyze each option to determine if it is a natural polymer:
1. Cotton: Cotton is a natural polymer. It is composed of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate, which is a natural polymer found in the cell walls of plants. Cotton fibers are made up of long chains of cellulose molecules, making it a natural polymer.
2. PET (Polyethylene terephthalate): PET is a synthetic polymer and not a natural polymer. It is a thermoplastic polymer that is derived from petroleum. PET is commonly used in the production of bottles, containers, and polyester fibers.
3. Plastic: The term "plastic" is a broad category that includes both natural and synthetic polymers. However, in the context of the given options, it is unclear which specific type of plastic is being referred to. Some plastics, such as polypropylene and polyethylene, are derived from petroleum and are synthetic polymers. On the other hand, there are certain types of natural polymers, such as natural rubber and shellac, that can be considered as plastics. Without further information, we cannot definitively categorize "plastic" as a natural polymer.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, it can be concluded that cotton (option 1) is the only example of a natural polymer among the given options. PET (option 2) is a synthetic polymer, and the categorization of "plastic" (option 3) as a natural polymer is ambiguous without additional information. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - 1 only.
In the given options, we are asked to identify the natural polymers among cotton, PET, and plastic. To determine this, we need to understand what natural polymers are and how they differ from synthetic polymers.
Natural Polymers:
Natural polymers are large molecules composed of repeating subunits found in nature. These polymers are typically derived from living organisms and can be extracted or synthesized from natural sources. Unlike synthetic polymers, natural polymers have a complex molecular structure and are biodegradable.
Analysis of the Options:
Let's analyze each option to determine if it is a natural polymer:
1. Cotton: Cotton is a natural polymer. It is composed of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate, which is a natural polymer found in the cell walls of plants. Cotton fibers are made up of long chains of cellulose molecules, making it a natural polymer.
2. PET (Polyethylene terephthalate): PET is a synthetic polymer and not a natural polymer. It is a thermoplastic polymer that is derived from petroleum. PET is commonly used in the production of bottles, containers, and polyester fibers.
3. Plastic: The term "plastic" is a broad category that includes both natural and synthetic polymers. However, in the context of the given options, it is unclear which specific type of plastic is being referred to. Some plastics, such as polypropylene and polyethylene, are derived from petroleum and are synthetic polymers. On the other hand, there are certain types of natural polymers, such as natural rubber and shellac, that can be considered as plastics. Without further information, we cannot definitively categorize "plastic" as a natural polymer.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, it can be concluded that cotton (option 1) is the only example of a natural polymer among the given options. PET (option 2) is a synthetic polymer, and the categorization of "plastic" (option 3) as a natural polymer is ambiguous without additional information. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - 1 only.
Which of the following statements is incorrect about the structure of an atom?1. The whole mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus2. The atom is an indivisible particle3. The atom as a whole is neutral4. All the atoms are stable in their basic stateChoose the right option among the following:- a) 1 and 3 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) 2 and 4 only
- d) None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect about the structure of an atom?
1. The whole mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus
2. The atom is an indivisible particle
3. The atom as a whole is neutral
4. All the atoms are stable in their basic state
Choose the right option among the following:
a)
1 and 3 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
2 and 4 only
d)
None of the above

|
Rajesh Kumar answered |
When 6 gram of carbon is 16 gram oxygen bicycle of carbon dioxide is produced if 6 gram of carbon is burn this gram of oxygen then the carbon dioxide used below answer
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. The earth attracts the moon with a force that is:- a) More than that exerted by the moon
- b) Same as that exerted by the moon
- c) Less than that exerted by the moon
- d) Not related to that exerted by the moon
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. The earth attracts the moon with a force that is:
a)
More than that exerted by the moon
b)
Same as that exerted by the moon
c)
Less than that exerted by the moon
d)
Not related to that exerted by the moon
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
- Gravitational attraction is caused by the mass of an object. Since Earth is far more massive than the Moon, the gravitational force exerted on the Moon is far greater than that of the Moon on the Earth.
- An example of the difference: while the Moon causes tides on the Earth, the Earth has the Moon locked so that the same face (minus some wobbling) is always visible from the Earth.
In a rocket, a large volume of gases produced by ... morethe combustion of fuel is allowed to escape through its tail nozzle in the downward direction with the tremendous speed and makes the rocket move upward.
Which principle is followed in this take off of the rocket?
a) Moment of inertia
b) Conservation of momentum
c) Newton’s first law of motion
d) Newton’s law of gravitationCorrect answer is option 'B'.
Can you explain this answer?
Can you explain this answer?

|
UPSC Achievers answered |
Rocket Propulsion follow these two principles:
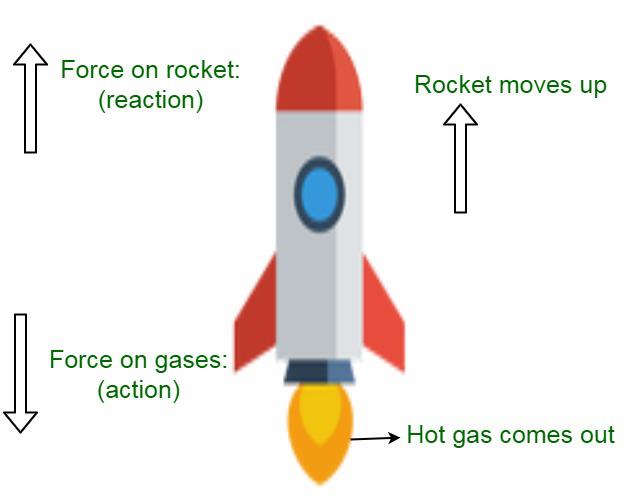
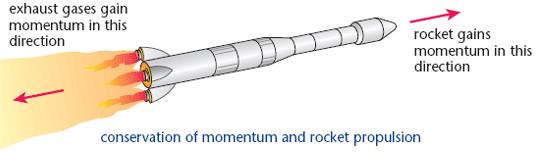
and can cover all the important aspects relevant from UPSC point of view through it.
1) Newton’s Third Law
2) Principle of Conservation of Momentum
Here’s the detailed explanation:
Newton's Third Law of Motion and Rocket Propulsion:
• Newton's Third Law of Motion: The principle of rocket propulsion works on the 'Newton's Third Law of Motion'. It states that, 'to every action, there is always an equal and opposite reaction'.
• Application: In the case of a rocket, the engine emits hot burning gases in the downward direction. These gases apply an equal and opposite reaction force to the rocket in the upward direction.
Principle of conservation of momentum and Rocket Propulsion:
• The principle of conservation of momentum: It states that whenever two bodies collide or get separated, then their total momentum before collision or separation is equal to their total momentum after collision or separation.
• Application: Since the gases of the rocket and the rocket are stationery at the start, their total momentum is zero. After the gases start burning, the momentum imparted to the rocket is equal and opposite to that of the gases. Hence their total momentum is zero.
Hence, Correct Answer is B
You can go through the course of Science & Technology for UPSC CSE:
Which of the following is not a physical change?- a) Boiling of water to give water vapour
- b) Melting of ice to give water
- c) Dissolution of salt in water
- d) Combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a physical change?
a)
Boiling of water to give water vapour
b)
Melting of ice to give water
c)
Dissolution of salt in water
d)
Combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
A physical change involves only change in physical state whereas a chemical change results in the formation of new substances. Boiling of water, melting of ice and dissolution of salt are physical changes as no new products are formed.
With regard to organic manure, consider the following statements: 1. It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.2. It makes the soil loose and porous.3. It enhances the number of friendly microbes.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 1 and 2 Only
- c) 2 and 3 Only
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
With regard to organic manure, consider the following statements:
1. It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
2. It makes the soil loose and porous.
3. It enhances the number of friendly microbes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
2 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Saptarshi Chakraborty answered |
The correct answer is option 'D' - 1, 2 and 3. Let's understand why each statement is correct:
1. It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil:
Organic manure, such as compost or animal manure, contains organic matter that improves the water holding capacity of the soil. When organic matter decomposes, it forms humus, which acts as a sponge, holding water in the soil. This helps to prevent water runoff and allows the soil to retain moisture for a longer period. As a result, the soil becomes more capable of sustaining plant growth, especially during dry periods.
2. It makes the soil loose and porous:
Organic manure contains organic matter that enriches the soil and improves its structure. The organic matter helps to break up compacted soil, making it loose and porous. This improves the soil's ability to hold air and water, facilitating better root growth and nutrient uptake by plants. The increased porosity also enhances soil drainage, preventing waterlogging and reducing the risk of root rot.
3. It enhances the number of friendly microbes:
Organic manure provides a food source for beneficial microorganisms in the soil. These microbes break down organic matter and release essential nutrients in a form that plants can absorb. The presence of organic manure in the soil promotes the growth and multiplication of these beneficial microbes, such as bacteria, fungi, and earthworms. These microbes help in nutrient cycling, soil aeration, and the suppression of harmful pathogens, thus creating a healthier soil ecosystem.
In conclusion, organic manure has several positive effects on soil health. It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil, making it more resilient to drought conditions. It also improves soil structure, making it loose and porous, which aids in root growth and nutrient availability. Additionally, organic manure promotes the growth of friendly microbes that contribute to nutrient cycling and soil health. Therefore, all three statements are correct.
1. It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil:
Organic manure, such as compost or animal manure, contains organic matter that improves the water holding capacity of the soil. When organic matter decomposes, it forms humus, which acts as a sponge, holding water in the soil. This helps to prevent water runoff and allows the soil to retain moisture for a longer period. As a result, the soil becomes more capable of sustaining plant growth, especially during dry periods.
2. It makes the soil loose and porous:
Organic manure contains organic matter that enriches the soil and improves its structure. The organic matter helps to break up compacted soil, making it loose and porous. This improves the soil's ability to hold air and water, facilitating better root growth and nutrient uptake by plants. The increased porosity also enhances soil drainage, preventing waterlogging and reducing the risk of root rot.
3. It enhances the number of friendly microbes:
Organic manure provides a food source for beneficial microorganisms in the soil. These microbes break down organic matter and release essential nutrients in a form that plants can absorb. The presence of organic manure in the soil promotes the growth and multiplication of these beneficial microbes, such as bacteria, fungi, and earthworms. These microbes help in nutrient cycling, soil aeration, and the suppression of harmful pathogens, thus creating a healthier soil ecosystem.
In conclusion, organic manure has several positive effects on soil health. It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil, making it more resilient to drought conditions. It also improves soil structure, making it loose and porous, which aids in root growth and nutrient availability. Additionally, organic manure promotes the growth of friendly microbes that contribute to nutrient cycling and soil health. Therefore, all three statements are correct.
Which is the Indian breed of high milk-yielding variety of cow?- a) Jersey
- b) Ongole
- c) Sahiwal
- d) Red sindhi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the Indian breed of high milk-yielding variety of cow?
a)
Jersey
b)
Ongole
c)
Sahiwal
d)
Red sindhi
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Sahiwal is a breed of 'Zebu cattle' and is considered to be one of the best milch cattle breeds in India. The breed has derived its name from the Sahiwal area in Montgomery district of Punjab in Pakistan.
Regarding the lens, consider the following statements: 1. A transparent material bound by two surfaces, of which one or both surfaces are spherical, forms a lens.2. A lens, either a convex lens or a concave lens, has two spherical surfaces.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Regarding the lens, consider the following statements:
1. A transparent material bound by two surfaces, of which one or both surfaces are spherical, forms a lens.
2. A lens, either a convex lens or a concave lens, has two spherical surfaces.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
- A transparent material bound by two surfaces, of which one or both surfaces are spherical, forms a lens. This means that a lens is bound by at least one spherical surface. In such lenses, the other surface would be plane. A lens may have two spherical surfaces, bulging outwards. Such a lens is called a double convex lens. It is simply called a convex lens. It is thicker at the middle as compared to the edges.
- Similarly, a double concave lens is bounded by two spherical surfaces, curved inwards. It is thicker at the edges than at the middle. A double concave lens is simply called a concave lens.A lens, either a convex lens or a concave lens, has two spherical surfaces. Each of these surfaces forms a part of a sphere.
Regarding the female reproductive system, consider the following statements: 1. Fertilization takes place in the female's Uterus.2. The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta.Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Regarding the female reproductive system, consider the following statements:
1. Fertilization takes place in the female's Uterus.
2. The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Kavita Mehta answered |
- The ovary gets produced in the ovaries in the female. The fertilization of gametes takes place in the fallopian tube. The fertilised egg, the zygote, gets implanted in the lining of the uterus, and starts dividing. The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta.
- This is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side are blood spaces, which surround the villi.
Due to which phenomena sound is heard at longer distances in nights than in day?- a) Reflection
- b) Refraction
- c) Interference of sound
- d) Diffraction of sound
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Due to which phenomena sound is heard at longer distances in nights than in day?
a)
Reflection
b)
Refraction
c)
Interference of sound
d)
Diffraction of sound
|
|
Om Basu answered |
Refraction of Sound: Explanation
Introduction:
Sound is a form of energy that travels in the form of waves through different mediums. The speed of sound varies depending on various factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind conditions. One of the phenomena that affect the propagation of sound is refraction.
Definition of Refraction:
Refraction is the bending of sound waves as they pass from one medium to another due to a change in their speed. When sound waves enter a medium with a different density or temperature, they change their direction.
Refraction of Sound in the Atmosphere:
During the day, the temperature of the Earth's surface increases, leading to the heating of the air closest to the surface. This causes the air near the surface to be less dense compared to the higher layers of the atmosphere. As a result, the speed of sound in the lower layers of the atmosphere is lower than the speed of sound in the upper layers.
Explanation:
The phenomenon of refraction causes sound waves to bend towards the region of higher speed as they travel from one medium to another. In the case of sound traveling through the atmosphere, the sound waves tend to bend away from the surface of the Earth during the day.
This bending of sound waves away from the surface of the Earth during the day prevents the sound from reaching longer distances. The sound waves get reflected back towards the ground due to the change in medium and the bending effect. Hence, the sound is heard at shorter distances during the day.
However, during the night, the surface of the Earth cools down, causing the air near the surface to become denser. This leads to a reversal in the density gradient of the atmosphere. As a result, the sound waves tend to bend towards the surface of the Earth during the night.
Implication:
This bending effect allows sound waves to travel longer distances during the night. The sound waves refract towards the ground and follow a curved path, allowing them to reach distant locations. This is why sound is heard at longer distances during the night compared to the day.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the phenomenon of refraction plays a significant role in the propagation of sound waves. During the day, the bending of sound waves away from the surface of the Earth limits the distance over which the sound can be heard. However, during the night, the bending of sound waves towards the surface of the Earth allows them to travel longer distances, resulting in sound being heard at greater distances.
Introduction:
Sound is a form of energy that travels in the form of waves through different mediums. The speed of sound varies depending on various factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind conditions. One of the phenomena that affect the propagation of sound is refraction.
Definition of Refraction:
Refraction is the bending of sound waves as they pass from one medium to another due to a change in their speed. When sound waves enter a medium with a different density or temperature, they change their direction.
Refraction of Sound in the Atmosphere:
During the day, the temperature of the Earth's surface increases, leading to the heating of the air closest to the surface. This causes the air near the surface to be less dense compared to the higher layers of the atmosphere. As a result, the speed of sound in the lower layers of the atmosphere is lower than the speed of sound in the upper layers.
Explanation:
The phenomenon of refraction causes sound waves to bend towards the region of higher speed as they travel from one medium to another. In the case of sound traveling through the atmosphere, the sound waves tend to bend away from the surface of the Earth during the day.
This bending of sound waves away from the surface of the Earth during the day prevents the sound from reaching longer distances. The sound waves get reflected back towards the ground due to the change in medium and the bending effect. Hence, the sound is heard at shorter distances during the day.
However, during the night, the surface of the Earth cools down, causing the air near the surface to become denser. This leads to a reversal in the density gradient of the atmosphere. As a result, the sound waves tend to bend towards the surface of the Earth during the night.
Implication:
This bending effect allows sound waves to travel longer distances during the night. The sound waves refract towards the ground and follow a curved path, allowing them to reach distant locations. This is why sound is heard at longer distances during the night compared to the day.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the phenomenon of refraction plays a significant role in the propagation of sound waves. During the day, the bending of sound waves away from the surface of the Earth limits the distance over which the sound can be heard. However, during the night, the bending of sound waves towards the surface of the Earth allows them to travel longer distances, resulting in sound being heard at greater distances.
Children are vaccinated against polio because- a) Vaccination kills polio causing microbes
- b) Prevents the entry of polio causing organisms
- c) It creates immunity against the virus
- d) All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Children are vaccinated against polio because
a)
Vaccination kills polio causing microbes
b)
Prevents the entry of polio causing organisms
c)
It creates immunity against the virus
d)
All of the above

|
Anish answered |
Vaccination doesn't kill polio causing microbes.
Also it cannot prevent the entry of polio causing viruses.
It only creates immunity against the virus.
Also it cannot prevent the entry of polio causing viruses.
It only creates immunity against the virus.
Which one of the following crops does not require nitrogenous fertiliser?- a) Wheat
- b) Millet
- c) Beans
- d) Paddy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following crops does not require nitrogenous fertiliser?
a)
Wheat
b)
Millet
c)
Beans
d)
Paddy

|
Tanishq Roy answered |
Introduction:
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient required by plants for their growth and development. It is a major component of proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll. Most plants obtain nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrates or ammonium ions. However, some crops have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen with the help of symbiotic bacteria.
Explanation:
Among the given options, beans (option C) do not require nitrogenous fertilizer. Let's understand why.
Nitrogen Fixation:
Some plants have a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which are capable of converting atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for plants. This process is called nitrogen fixation. These bacteria reside in root nodules of leguminous plants, such as beans, peas, and lentils. The bacteria take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into ammonia, which is then used by the plants for their growth. Therefore, leguminous crops like beans do not require nitrogenous fertilizers as they can obtain nitrogen through biological fixation.
Other Crops:
1. Wheat (option A): Wheat is not capable of nitrogen fixation and relies on the availability of nitrogen in the soil. Therefore, wheat crops require nitrogenous fertilizers to meet their nitrogen requirements.
2. Millet (option B): Similar to wheat, millet crops do not have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen. Hence, they need nitrogenous fertilizers to fulfill their nitrogen needs.
3. Paddy (option D): Paddy, also known as rice, does not have the ability to fix nitrogen either. It requires nitrogenous fertilizers to meet its nitrogen demands.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, among the given options, beans do not require nitrogenous fertilizers as they have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen with the help of symbiotic bacteria present in their root nodules. On the other hand, crops like wheat, millet, and paddy rely on nitrogenous fertilizers to meet their nitrogen requirements.
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient required by plants for their growth and development. It is a major component of proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll. Most plants obtain nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrates or ammonium ions. However, some crops have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen with the help of symbiotic bacteria.
Explanation:
Among the given options, beans (option C) do not require nitrogenous fertilizer. Let's understand why.
Nitrogen Fixation:
Some plants have a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which are capable of converting atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for plants. This process is called nitrogen fixation. These bacteria reside in root nodules of leguminous plants, such as beans, peas, and lentils. The bacteria take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into ammonia, which is then used by the plants for their growth. Therefore, leguminous crops like beans do not require nitrogenous fertilizers as they can obtain nitrogen through biological fixation.
Other Crops:
1. Wheat (option A): Wheat is not capable of nitrogen fixation and relies on the availability of nitrogen in the soil. Therefore, wheat crops require nitrogenous fertilizers to meet their nitrogen requirements.
2. Millet (option B): Similar to wheat, millet crops do not have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen. Hence, they need nitrogenous fertilizers to fulfill their nitrogen needs.
3. Paddy (option D): Paddy, also known as rice, does not have the ability to fix nitrogen either. It requires nitrogenous fertilizers to meet its nitrogen demands.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, among the given options, beans do not require nitrogenous fertilizers as they have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen with the help of symbiotic bacteria present in their root nodules. On the other hand, crops like wheat, millet, and paddy rely on nitrogenous fertilizers to meet their nitrogen requirements.
Which of the following statements best describes the term ecosystem?- a) A community of people interacting with each other (organism).
- b) The part of the Earth that is inhabited by living organisms.
- c) The interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment.
- d) Flora and fauna of a geographical area.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements best describes the term ecosystem?
a)
A community of people interacting with each other (organism).
b)
The part of the Earth that is inhabited by living organisms.
c)
The interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment.
d)
Flora and fauna of a geographical area.
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
All the Biotic Components in an area together with the abiotic constituents of the environment form an ecosystem. Biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals
Which of the following laws states that- the electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V, across its ends, provided its temperature remains the same?- a) Faraday's law
- b) Charles’s law
- c) Ohm’s law
- d) Fleming's law
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following laws states that- the electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V, across its ends, provided its temperature remains the same?
a)
Faraday's law
b)
Charles’s law
c)
Ohm’s law
d)
Fleming's law
|
|
Eshaan Kapoor answered |
- In 1827, a German physicist Georg Simon Ohm (1787–1854) found out the relationship between the current I, flowing in a metallic wire and the potential difference across its terminals.
- He stated that the electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V, across its ends provided its temperature remains the same. This is called Ohm’s law.
Which of the following statements is not correct?- a) Like charges attract each other.
- b) Electric charge obtained by rubbing materials against each other is static.
- c) Electricity is generated by the movement of charge.
- d) The charge from any charged object is sent to the earth by earthing.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct?
a)
Like charges attract each other.
b)
Electric charge obtained by rubbing materials against each other is static.
c)
Electricity is generated by the movement of charge.
d)
The charge from any charged object is sent to the earth by earthing.
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
- Like charges repel each other, while unlike charges attract each other.Charge is generated by rubbing objects against each other. It is a convention to call the charge acquired by a glass rod when it is rubbed with silk as positive.
- The other kind of charge is called negative.When charge moves, electricity is generated.The process of sending the extra charge from a charged object is called earthing.
Consider the following statements:1. The chemical process of the purification of drinking water is called chlorination.2. To protect the Ganges from pollution, Ganga Action Plan was started in the year 1985.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. The chemical process of the purification of drinking water is called chlorination.
2. To protect the Ganges from pollution, Ganga Action Plan was started in the year 1985.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Kritika Basak answered |
Explanation:
1. Chlorination for Drinking Water Purification:
- The statement that the chemical process of purifying drinking water is called chlorination is correct.
- Chlorination is a common method used to disinfect water by adding chlorine or chlorine compounds to the water.
- Chlorine kills bacteria and other microorganisms present in the water, making it safe for consumption.
- It is a crucial step in ensuring the safety of drinking water and preventing waterborne diseases.
2. Ganga Action Plan (GAP) for Ganges Pollution:
- The statement mentioning the Ganga Action Plan (GAP) being initiated in 1985 to protect the Ganges from pollution is also correct.
- The Ganga Action Plan was launched by the Government of India in 1985 with the aim of reducing pollution and improving the water quality of the Ganga River.
- The plan focused on the interception, diversion, and treatment of domestic sewage and industrial effluents flowing into the Ganges.
- It was one of the first major initiatives to clean up a polluted river in India and has since been followed by other similar projects for different rivers in the country.
Therefore, both statements are correct as chlorination is indeed used for water purification, and the Ganga Action Plan was indeed started in 1985 to address pollution in the Ganges.
1. Chlorination for Drinking Water Purification:
- The statement that the chemical process of purifying drinking water is called chlorination is correct.
- Chlorination is a common method used to disinfect water by adding chlorine or chlorine compounds to the water.
- Chlorine kills bacteria and other microorganisms present in the water, making it safe for consumption.
- It is a crucial step in ensuring the safety of drinking water and preventing waterborne diseases.
2. Ganga Action Plan (GAP) for Ganges Pollution:
- The statement mentioning the Ganga Action Plan (GAP) being initiated in 1985 to protect the Ganges from pollution is also correct.
- The Ganga Action Plan was launched by the Government of India in 1985 with the aim of reducing pollution and improving the water quality of the Ganga River.
- The plan focused on the interception, diversion, and treatment of domestic sewage and industrial effluents flowing into the Ganges.
- It was one of the first major initiatives to clean up a polluted river in India and has since been followed by other similar projects for different rivers in the country.
Therefore, both statements are correct as chlorination is indeed used for water purification, and the Ganga Action Plan was indeed started in 1985 to address pollution in the Ganges.
Consider the following statements regarding food preservatives.1. Sodium Benzoate and Sodium Metabisulfite are common food preservatives.2. Salt, sugar, edible oil and vinegar are used as food preservatives.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding food preservatives.
1. Sodium Benzoate and Sodium Metabisulfite are common food preservatives.
2. Salt, sugar, edible oil and vinegar are used as food preservatives.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Sanjana Roy answered |
Food Preservatives
Sodium Benzoate and Sodium Metabisulfite are indeed common food preservatives.
- Sodium Benzoate: It is a chemical compound that has antimicrobial properties. It is commonly used in acidic foods such as carbonated drinks, pickles, and sauces to inhibit the growth of bacteria, yeasts, and molds. It works by reducing the pH level of the food, making it acidic and preventing the growth of microorganisms.
- Sodium Metabisulfite: It is a compound that is often used as a preservative in foods and beverages. It acts as an antioxidant and helps to prevent the oxidation of food, which can lead to spoilage. It is commonly used in wine, dried fruits, and processed meats.
Therefore, Statement 1 is correct.
Salt, sugar, edible oil, and vinegar are commonly used as food preservatives.
- Salt: Salt has been used as a preservative for centuries. It works by drawing out moisture from food, creating an environment that is inhospitable to bacteria and other microorganisms. It is commonly used in curing meats, pickling vegetables, and preserving fish.
- Sugar: Sugar acts as a preservative by reducing the water activity in foods, making it difficult for microorganisms to survive and reproduce. It is commonly used in jams, jellies, and syrups to prevent spoilage.
- Edible oil: Certain edible oils, such as olive oil and coconut oil, have antimicrobial properties and can help to inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi. They are often used in marinades and dressings to preserve the freshness of food.
- Vinegar: Vinegar is acidic in nature and can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms. It is commonly used in pickling vegetables, preserving fruits, and making sauces and condiments.
Therefore, Statement 2 is also correct.
Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are correct. Sodium Benzoate and Sodium Metabisulfite are common food preservatives, and salt, sugar, edible oil, and vinegar are also widely used as food preservatives. These preservatives help to extend the shelf life of food products by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms and preventing spoilage.
Statement 1: Sodium Benzoate and Sodium Metabisulfite are common food preservatives.
Sodium Benzoate and Sodium Metabisulfite are indeed common food preservatives.
- Sodium Benzoate: It is a chemical compound that has antimicrobial properties. It is commonly used in acidic foods such as carbonated drinks, pickles, and sauces to inhibit the growth of bacteria, yeasts, and molds. It works by reducing the pH level of the food, making it acidic and preventing the growth of microorganisms.
- Sodium Metabisulfite: It is a compound that is often used as a preservative in foods and beverages. It acts as an antioxidant and helps to prevent the oxidation of food, which can lead to spoilage. It is commonly used in wine, dried fruits, and processed meats.
Therefore, Statement 1 is correct.
Statement 2: Salt, sugar, edible oil, and vinegar are used as food preservatives.
Salt, sugar, edible oil, and vinegar are commonly used as food preservatives.
- Salt: Salt has been used as a preservative for centuries. It works by drawing out moisture from food, creating an environment that is inhospitable to bacteria and other microorganisms. It is commonly used in curing meats, pickling vegetables, and preserving fish.
- Sugar: Sugar acts as a preservative by reducing the water activity in foods, making it difficult for microorganisms to survive and reproduce. It is commonly used in jams, jellies, and syrups to prevent spoilage.
- Edible oil: Certain edible oils, such as olive oil and coconut oil, have antimicrobial properties and can help to inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi. They are often used in marinades and dressings to preserve the freshness of food.
- Vinegar: Vinegar is acidic in nature and can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms. It is commonly used in pickling vegetables, preserving fruits, and making sauces and condiments.
Therefore, Statement 2 is also correct.
Conclusion
Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are correct. Sodium Benzoate and Sodium Metabisulfite are common food preservatives, and salt, sugar, edible oil, and vinegar are also widely used as food preservatives. These preservatives help to extend the shelf life of food products by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms and preventing spoilage.
Puberty age in males is- a) 10-12
- b) 12-16
- c) 8-10
- d) More than 14 years
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Puberty age in males is
a)
10-12
b)
12-16
c)
8-10
d)
More than 14 years
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Puberty usually occurs in girls between the ages of 10 and 14, while in boys it generally occurs later, between the ages of 12 and 16. In some African-American girls, puberty begins earlier, at about age 9, meaning that puberty occurs from ages 9 to 14.
Consider the following statements regarding the moon. 1. The moon completes one rotation on its axis as it completes one revolution around the Earth.2. The day on which the whole disc of the moon is visible is known as the full moon day. The time period between two consecutive full moons is a little less than 29 days.3. Neil Armstrong landed on the moon for the first time followed by Edwin Aldrin.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 1 and 3 Only
- c) 2 and 3 Only
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding the moon.
1. The moon completes one rotation on its axis as it completes one revolution around the Earth.
2. The day on which the whole disc of the moon is visible is known as the full moon day. The time period between two consecutive full moons is a little less than 29 days.
3. Neil Armstrong landed on the moon for the first time followed by Edwin Aldrin.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 3 Only
c)
2 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Anita Desai answered |
- The moon completes one rotation on its axis as it completes one revolution around the Earth. The day of the appearance of the full disc of the moon is called full moon day, but the time period between two consecutive full moons is a little more than 29 days. In many calendars, this is the period of a month.
- The day on which the whole disc of the moon is visible is known as the full moon day. Thereafter, every night the size of the bright part of the moon appears to become thinner and thinner.
- On the fifteenth day the moon is not visible. This day is known as the new moon day. The next day, only a small portion of the moon appears in the sky. This is known as the crescent moon.
- Then again the moon grows larger every day. On the fifteenth day once again we get a full view of the moon. On July 21, 1969 the American astronaut Neil Armstrong landed on the moon for the first time followed by Edwin Aldrin.
Which of the following are the three primary nutrients needed for plant growth?- a) Calcium, sulphur and magnesium.
- b) Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
- c) Zinc, boron and copper.
- d) Calcium/zinc/copper.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are the three primary nutrients needed for plant growth?
a)
Calcium, sulphur and magnesium.
b)
Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
c)
Zinc, boron and copper.
d)
Calcium/zinc/copper.
|
|
Sounak Menon answered |
The Three Primary Nutrients for Plant Growth
The three primary nutrients needed for plant growth are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These nutrients are often referred to as macronutrients because plants require them in relatively large quantities compared to other essential elements.
Nitrogen (N)
- Nitrogen is essential for the growth and development of plants.
- It is a major component of amino acids, proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll.
- Nitrogen is responsible for promoting leaf and stem growth.
- It helps in the production of healthy, lush foliage and enhances photosynthesis.
- Lack of nitrogen can result in stunted growth, yellowing of leaves (chlorosis), and poor overall plant health.
Phosphorus (P)
- Phosphorus plays a crucial role in energy transfer and storage within plants.
- It is necessary for the formation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary energy currency in cells.
- Phosphorus is involved in DNA and RNA synthesis, as well as the development of roots, flowers, and fruits.
- It aids in early root growth and establishment.
- Insufficient phosphorus can lead to poor root development, delayed flowering, and reduced fruit production.
Potassium (K)
- Potassium is vital for various physiological processes in plants.
- It helps in the activation of enzymes involved in photosynthesis and respiration.
- Potassium regulates water uptake and retention, enhancing the plant's ability to withstand drought and stress.
- It promotes strong stems and improves disease resistance.
- Lack of potassium can result in weakened plants, reduced fruit quality, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Conclusion
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are the three primary nutrients essential for plant growth. These macronutrients play crucial roles in various physiological processes and are necessary for the development of healthy and productive plants. By providing plants with adequate amounts of these nutrients, gardeners and farmers can ensure optimal growth, productivity, and overall plant health.
The three primary nutrients needed for plant growth are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These nutrients are often referred to as macronutrients because plants require them in relatively large quantities compared to other essential elements.
Nitrogen (N)
- Nitrogen is essential for the growth and development of plants.
- It is a major component of amino acids, proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll.
- Nitrogen is responsible for promoting leaf and stem growth.
- It helps in the production of healthy, lush foliage and enhances photosynthesis.
- Lack of nitrogen can result in stunted growth, yellowing of leaves (chlorosis), and poor overall plant health.
Phosphorus (P)
- Phosphorus plays a crucial role in energy transfer and storage within plants.
- It is necessary for the formation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary energy currency in cells.
- Phosphorus is involved in DNA and RNA synthesis, as well as the development of roots, flowers, and fruits.
- It aids in early root growth and establishment.
- Insufficient phosphorus can lead to poor root development, delayed flowering, and reduced fruit production.
Potassium (K)
- Potassium is vital for various physiological processes in plants.
- It helps in the activation of enzymes involved in photosynthesis and respiration.
- Potassium regulates water uptake and retention, enhancing the plant's ability to withstand drought and stress.
- It promotes strong stems and improves disease resistance.
- Lack of potassium can result in weakened plants, reduced fruit quality, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Conclusion
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are the three primary nutrients essential for plant growth. These macronutrients play crucial roles in various physiological processes and are necessary for the development of healthy and productive plants. By providing plants with adequate amounts of these nutrients, gardeners and farmers can ensure optimal growth, productivity, and overall plant health.
Consider the following assertions :1. The heat flows from a hotter object to a colder object.2. The mode of heat transfer that continues till the whole water gets heated is known as convection.3. The process by which heat is transferred from the hotter end to the colder end of an object is known as the conduction.Which of the above assertions is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) 2 and 3 only
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following assertions :
1. The heat flows from a hotter object to a colder object.
2. The mode of heat transfer that continues till the whole water gets heated is known as convection.
3. The process by which heat is transferred from the hotter end to the colder end of an object is known as the conduction.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Rahul Mehta answered |
- Heat Transfer: The movement of heat from a warmer object to a colder one – when two substances at different temperatures are mixed together, heat flows from the warmer body to the cooler body until they reach the same temperature (Zeroth Law of
- Thermodynamics – Thermal Equilibrium). Part of the heat lost by the warmer body is transferred to the cooler body and part is lost to the surrounding object or the air.
- Convection is the process of heat transfer by the bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids. The initial heat transfer between the object and the fluid takes place through conduction, but the bulk heat transfer happens due to the motion of the fluid.• Convection is the process of heat transfer in fluids by the actual motion of matter.• It happens in liquids and gases.• It may be natural or forced.• It involves a bulk transfer of portions of the fluid.
- Conduction is the transfer of energy in the form of heat or electricity from one atom to another within an object by direct contact. Conduction occurs in solids, liquids, and gases. However, solids transfer energy most efficiently since the molecules in solids are most tightly packed, and the molecules are closer together, as shown in this figure. For liquids and gases, the density of the particles are generally lower than those of solids and the particles are farther apart, so the energy transfer is less efficient.
The process of loosening and turning the soil is called:- a) Ploughing
- b) Levelling
- c) Manuring
- d) All the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of loosening and turning the soil is called:
a)
Ploughing
b)
Levelling
c)
Manuring
d)
All the above
|
|
Tejas Datta answered |
Introduction:
The process of loosening and turning the soil is called ploughing. It is an important agricultural practice that helps prepare the soil for planting crops. Ploughing involves breaking up the soil, turning it over, and creating furrows for planting seeds.
Explanation:
Ploughing is an essential step in the cultivation of crops as it helps improve soil structure and fertility. It provides several benefits to the soil and the crops grown on it. Let's discuss these benefits in detail:
1. Loosening the soil:
Ploughing helps in loosening the compacted soil, which is necessary for the growth of plant roots. This process allows air, water, and nutrients to penetrate the soil more easily, promoting healthy root development.
2. Weed control:
Ploughing helps control weeds by uprooting and burying them deep into the soil. This prevents weed growth and competition with the cultivated crops. Turning the soil also exposes weed seeds to sunlight, which can inhibit their germination.
3. Enhancing soil aeration:
By breaking up the soil, ploughing improves soil aeration. This allows oxygen to reach the root zone, facilitating the respiration process of the plants. Adequate oxygen availability promotes healthy root growth and overall plant development.
4. Mixing organic matter:
During ploughing, organic matter such as crop residues or manure can be incorporated into the soil. This improves the soil's nutrient content, organic matter content, and overall fertility. Organic matter acts as a source of nutrients for the plants and also enhances the soil's water-holding capacity.
5. Pest and disease management:
Ploughing can help manage pests and diseases by burying crop residues and pathogens deep into the soil. This reduces the survival and spread of pests and diseases, minimizing their impact on subsequent crops.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, ploughing is the process of loosening and turning the soil, which is crucial for successful crop cultivation. It improves soil structure, enhances nutrient availability, controls weeds, and manages pests and diseases. Ploughing is an integral part of sustainable agricultural practices and plays a vital role in ensuring high crop yields.
The process of loosening and turning the soil is called ploughing. It is an important agricultural practice that helps prepare the soil for planting crops. Ploughing involves breaking up the soil, turning it over, and creating furrows for planting seeds.
Explanation:
Ploughing is an essential step in the cultivation of crops as it helps improve soil structure and fertility. It provides several benefits to the soil and the crops grown on it. Let's discuss these benefits in detail:
1. Loosening the soil:
Ploughing helps in loosening the compacted soil, which is necessary for the growth of plant roots. This process allows air, water, and nutrients to penetrate the soil more easily, promoting healthy root development.
2. Weed control:
Ploughing helps control weeds by uprooting and burying them deep into the soil. This prevents weed growth and competition with the cultivated crops. Turning the soil also exposes weed seeds to sunlight, which can inhibit their germination.
3. Enhancing soil aeration:
By breaking up the soil, ploughing improves soil aeration. This allows oxygen to reach the root zone, facilitating the respiration process of the plants. Adequate oxygen availability promotes healthy root growth and overall plant development.
4. Mixing organic matter:
During ploughing, organic matter such as crop residues or manure can be incorporated into the soil. This improves the soil's nutrient content, organic matter content, and overall fertility. Organic matter acts as a source of nutrients for the plants and also enhances the soil's water-holding capacity.
5. Pest and disease management:
Ploughing can help manage pests and diseases by burying crop residues and pathogens deep into the soil. This reduces the survival and spread of pests and diseases, minimizing their impact on subsequent crops.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, ploughing is the process of loosening and turning the soil, which is crucial for successful crop cultivation. It improves soil structure, enhances nutrient availability, controls weeds, and manages pests and diseases. Ploughing is an integral part of sustainable agricultural practices and plays a vital role in ensuring high crop yields.
What is the unit of loudness?- a) Bel
- b) Phon
- c) Decibel
- d) All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the unit of loudness?
a)
Bel
b)
Phon
c)
Decibel
d)
All of the above
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
The sensation of a sound perceived in an ear is measured by another term called loudness which depends on intensity of sound and sensitiveness of the ear. Unit of loudness is bel. A practical unit of loudness is decibel (dB) which is 1/10th of bel. Another unit of loudness is phon.
Regarding the modern periodic table, consider the following statements: 1. Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.2. There are 7 groups and 18 periods.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Regarding the modern periodic table, consider the following statements:
1. Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
2. There are 7 groups and 18 periods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2

|
Hiral Singh answered |
Properties of elements
- The first statement is correct. Properties of elements are indeed a periodic function of their atomic number. This is the fundamental principle behind the organization of the modern periodic table.
- The periodic table is arranged in such a way that elements with similar properties are placed in the same group/column. This periodic repetition of properties is directly related to the atomic number of the elements.
Groups and Periods
- The second statement is incorrect. There are actually 18 groups and 7 periods in the modern periodic table.
- Groups are the vertical columns on the periodic table, and there are 18 groups in total. Each group has elements with similar chemical properties.
- Periods are the horizontal rows on the periodic table, and there are 7 periods in total. Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
- Therefore, the correct number of groups and periods in the modern periodic table are 18 and 7, respectively.
In conclusion, statement 1 is correct while statement 2 is incorrect. Properties of elements are indeed a periodic function of their atomic number, and there are 7 periods and 18 groups in the modern periodic table.
- The first statement is correct. Properties of elements are indeed a periodic function of their atomic number. This is the fundamental principle behind the organization of the modern periodic table.
- The periodic table is arranged in such a way that elements with similar properties are placed in the same group/column. This periodic repetition of properties is directly related to the atomic number of the elements.
Groups and Periods
- The second statement is incorrect. There are actually 18 groups and 7 periods in the modern periodic table.
- Groups are the vertical columns on the periodic table, and there are 18 groups in total. Each group has elements with similar chemical properties.
- Periods are the horizontal rows on the periodic table, and there are 7 periods in total. Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
- Therefore, the correct number of groups and periods in the modern periodic table are 18 and 7, respectively.
In conclusion, statement 1 is correct while statement 2 is incorrect. Properties of elements are indeed a periodic function of their atomic number, and there are 7 periods and 18 groups in the modern periodic table.
Sex hormones are secreted by endocrine glands. Consider the following statements regarding the same.1. Estrogen and testosterone are sex hormones. These are responsible for the secondary sexual characters in the human body.2. Estrogen is the male hormone, while testosterone is the female hormone.3. The secretion of these hormones is regulated by a separate hormone, secreted by the pituitary.Which of the above given statements/statements is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) 1 and 3 Only
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Sex hormones are secreted by endocrine glands. Consider the following statements regarding the same.
1. Estrogen and testosterone are sex hormones. These are responsible for the secondary sexual characters in the human body.
2. Estrogen is the male hormone, while testosterone is the female hormone.
3. The secretion of these hormones is regulated by a separate hormone, secreted by the pituitary.
Which of the above given statements/statements is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Devansh Mukherjee answered |
Introduction
Understanding sex hormones and their roles is essential in human biology. Let’s analyze the statements provided regarding sex hormones, particularly estrogen and testosterone.
Statement 1: Correct
- Estrogen and testosterone are indeed sex hormones.
- They play crucial roles in the development of secondary sexual characteristics:
- **Estrogen**: Promotes breast development, wider hips, and menstrual cycle regulation in females.
- **Testosterone**: Responsible for muscle mass, voice deepening, and facial hair growth in males.
Statement 2: Incorrect
- This statement incorrectly identifies the hormones:
- **Estrogen** is primarily a female hormone associated with female characteristics.
- **Testosterone** is primarily a male hormone associated with male characteristics.
- Therefore, the characterization in this statement is reversed.
Statement 3: Correct
- The secretion of estrogen and testosterone is regulated by hormones from the pituitary gland:
- **Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)** and **Luteinizing hormone (LH)** are secreted by the anterior pituitary.
- These hormones stimulate the gonads (ovaries in females and testes in males) to produce sex hormones.
Conclusion
- Based on the analysis:
- **Correct Statements**: 1 and 3
- **Incorrect Statement**: 2
- Hence, the correct answer is **option 'C': 1 and 3 only**.
Understanding sex hormones and their roles is essential in human biology. Let’s analyze the statements provided regarding sex hormones, particularly estrogen and testosterone.
Statement 1: Correct
- Estrogen and testosterone are indeed sex hormones.
- They play crucial roles in the development of secondary sexual characteristics:
- **Estrogen**: Promotes breast development, wider hips, and menstrual cycle regulation in females.
- **Testosterone**: Responsible for muscle mass, voice deepening, and facial hair growth in males.
Statement 2: Incorrect
- This statement incorrectly identifies the hormones:
- **Estrogen** is primarily a female hormone associated with female characteristics.
- **Testosterone** is primarily a male hormone associated with male characteristics.
- Therefore, the characterization in this statement is reversed.
Statement 3: Correct
- The secretion of estrogen and testosterone is regulated by hormones from the pituitary gland:
- **Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)** and **Luteinizing hormone (LH)** are secreted by the anterior pituitary.
- These hormones stimulate the gonads (ovaries in females and testes in males) to produce sex hormones.
Conclusion
- Based on the analysis:
- **Correct Statements**: 1 and 3
- **Incorrect Statement**: 2
- Hence, the correct answer is **option 'C': 1 and 3 only**.
Which leaves are used to protect stored grains from insects and microorganisms?- a) Mango leaves
- b) Peepal leaves
- c) Banana leaves
- d) Neem leaves
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which leaves are used to protect stored grains from insects and microorganisms?
a)
Mango leaves
b)
Peepal leaves
c)
Banana leaves
d)
Neem leaves
|
|
Megha Sharma answered |
Neem leaves are used to protect stored grains from insects and microorganisms. Neem, also known as Azadirachta indica, is a tree native to the Indian subcontinent. Its leaves have been traditionally used in various applications due to their medicinal and insecticidal properties.
The use of neem leaves for grain protection can be attributed to the following factors:
1. Insecticidal properties:
- Neem leaves contain various bioactive compounds such as azadirachtin, nimbin, and salannin, which exhibit strong insecticidal properties.
- These compounds disrupt the feeding, growth, and reproduction of insects, making them effective in controlling pest infestation in stored grains.
- Neem leaves act as a natural insecticide, preventing the growth and spread of insects that can damage stored grains.
2. Antimicrobial properties:
- Neem leaves possess antimicrobial properties that inhibit the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi.
- The bioactive compounds present in neem leaves, such as nimbin and gedunin, have been found to exhibit antimicrobial activity.
- By inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, neem leaves help in preventing the spoilage of stored grains and maintaining their quality.
3. Safe and eco-friendly:
- Neem leaves are a natural and safe option for grain protection as they do not pose any health hazards to humans or animals.
- Unlike synthetic chemical pesticides, neem leaves are biodegradable and do not contribute to environmental pollution.
- The use of neem leaves for grain protection aligns with sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural practices.
In conclusion, neem leaves are used to protect stored grains from insects and microorganisms due to their insecticidal and antimicrobial properties. The bioactive compounds present in neem leaves act as natural pesticides, effectively controlling pest infestation and preventing spoilage of stored grains. Additionally, the use of neem leaves is safe and environmentally friendly, making it a preferred choice for grain protection.
The use of neem leaves for grain protection can be attributed to the following factors:
1. Insecticidal properties:
- Neem leaves contain various bioactive compounds such as azadirachtin, nimbin, and salannin, which exhibit strong insecticidal properties.
- These compounds disrupt the feeding, growth, and reproduction of insects, making them effective in controlling pest infestation in stored grains.
- Neem leaves act as a natural insecticide, preventing the growth and spread of insects that can damage stored grains.
2. Antimicrobial properties:
- Neem leaves possess antimicrobial properties that inhibit the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi.
- The bioactive compounds present in neem leaves, such as nimbin and gedunin, have been found to exhibit antimicrobial activity.
- By inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, neem leaves help in preventing the spoilage of stored grains and maintaining their quality.
3. Safe and eco-friendly:
- Neem leaves are a natural and safe option for grain protection as they do not pose any health hazards to humans or animals.
- Unlike synthetic chemical pesticides, neem leaves are biodegradable and do not contribute to environmental pollution.
- The use of neem leaves for grain protection aligns with sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural practices.
In conclusion, neem leaves are used to protect stored grains from insects and microorganisms due to their insecticidal and antimicrobial properties. The bioactive compounds present in neem leaves act as natural pesticides, effectively controlling pest infestation and preventing spoilage of stored grains. Additionally, the use of neem leaves is safe and environmentally friendly, making it a preferred choice for grain protection.
Hydrogen bomb is based on which of the following reactions?- a) Controlled fusion reaction
- b) Thermonuclear fusion reaction
- c) Controlled fission reaction
- d) Thermonuclear fission reaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bomb is based on which of the following reactions?
a)
Controlled fusion reaction
b)
Thermonuclear fusion reaction
c)
Controlled fission reaction
d)
Thermonuclear fission reaction

|
Shraddha Mukherjee answered |
Understanding the Hydrogen Bomb
The hydrogen bomb, also known as a thermonuclear bomb, operates on the principle of thermonuclear fusion. This process involves the merging of light atomic nuclei to form heavier nuclei, releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the process.
Key Features of Thermonuclear Fusion
- Fusion Reaction: In a hydrogen bomb, isotopes of hydrogen, specifically deuterium and tritium, are fused together under extreme temperatures and pressures. This is similar to the processes that occur in the core of stars, including our Sun.
- Energy Release: The fusion of these hydrogen isotopes releases energy exponentially greater than that from traditional chemical explosives or fission reactions. This is due to the substantial binding energy that is released when nucleons combine into a more stable nucleus.
- Temperature and Pressure: The conditions necessary for fusion require temperatures in the order of millions of degrees Celsius, which is achieved through an initial fission explosion. This fission reaction acts as a trigger for the subsequent fusion process.
Why Not Controlled Fusion or Fission?
- Controlled Fusion Reaction: While research into controlled fusion (like that in fusion reactors) aims to harness energy from fusion safely, hydrogen bombs do not employ this method, as they are designed for explosive power rather than energy generation.
- Fission: Controlled fission reactions, as found in nuclear reactors, involve splitting heavy nuclei (like uranium or plutonium) and do not produce the same energy levels or mechanisms involved in the hydrogen bomb's operation.
In conclusion, the hydrogen bomb is fundamentally based on thermonuclear fusion reactions, making option 'B' the correct choice.
The hydrogen bomb, also known as a thermonuclear bomb, operates on the principle of thermonuclear fusion. This process involves the merging of light atomic nuclei to form heavier nuclei, releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the process.
Key Features of Thermonuclear Fusion
- Fusion Reaction: In a hydrogen bomb, isotopes of hydrogen, specifically deuterium and tritium, are fused together under extreme temperatures and pressures. This is similar to the processes that occur in the core of stars, including our Sun.
- Energy Release: The fusion of these hydrogen isotopes releases energy exponentially greater than that from traditional chemical explosives or fission reactions. This is due to the substantial binding energy that is released when nucleons combine into a more stable nucleus.
- Temperature and Pressure: The conditions necessary for fusion require temperatures in the order of millions of degrees Celsius, which is achieved through an initial fission explosion. This fission reaction acts as a trigger for the subsequent fusion process.
Why Not Controlled Fusion or Fission?
- Controlled Fusion Reaction: While research into controlled fusion (like that in fusion reactors) aims to harness energy from fusion safely, hydrogen bombs do not employ this method, as they are designed for explosive power rather than energy generation.
- Fission: Controlled fission reactions, as found in nuclear reactors, involve splitting heavy nuclei (like uranium or plutonium) and do not produce the same energy levels or mechanisms involved in the hydrogen bomb's operation.
In conclusion, the hydrogen bomb is fundamentally based on thermonuclear fusion reactions, making option 'B' the correct choice.
Plants take in air during respiration. What do the plants do in the next step?- a) Utilise carbon dioxide and give out oxygen into the atmosphere.
- b) Utilise oxygen and give out carbon dioxide.
- c) Utilise both carbon dioxide and oxygen.
- d) Give out both oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Plants take in air during respiration. What do the plants do in the next step?
a)
Utilise carbon dioxide and give out oxygen into the atmosphere.
b)
Utilise oxygen and give out carbon dioxide.
c)
Utilise both carbon dioxide and oxygen.
d)
Give out both oxygen and carbon dioxide.
|
|
Sakshi Pillai answered |
Respiration in Plants
Plants undergo respiration just like animals do. During respiration, plants take in air through small pores called stomata present on their leaves. The air contains oxygen and carbon dioxide. The process of respiration occurs in two stages:
1. Glycolysis - In this stage, glucose is broken down into pyruvate molecules. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of the plant cell and does not require oxygen.
2. Aerobic Respiration - In this stage, the pyruvate molecules produced in glycolysis are further broken down in the presence of oxygen. This process occurs in the mitochondria of the plant cell.
What Happens Next?
After taking in air during respiration, the plants utilize oxygen and give out carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This is because during the second stage of respiration, the pyruvate molecules combine with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
The equation for respiration in plants is:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option B, i.e., plants utilize oxygen and give out carbon dioxide during respiration.
Plants undergo respiration just like animals do. During respiration, plants take in air through small pores called stomata present on their leaves. The air contains oxygen and carbon dioxide. The process of respiration occurs in two stages:
1. Glycolysis - In this stage, glucose is broken down into pyruvate molecules. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of the plant cell and does not require oxygen.
2. Aerobic Respiration - In this stage, the pyruvate molecules produced in glycolysis are further broken down in the presence of oxygen. This process occurs in the mitochondria of the plant cell.
What Happens Next?
After taking in air during respiration, the plants utilize oxygen and give out carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This is because during the second stage of respiration, the pyruvate molecules combine with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
The equation for respiration in plants is:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option B, i.e., plants utilize oxygen and give out carbon dioxide during respiration.
Select the chain that contains primary consumers:- a) Bird, rabbit, elephant
- b) Grass, parrot, snake
- c) Snake, hawk, tiger
- d) Bacteria, fungi, viruses
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the chain that contains primary consumers:
a)
Bird, rabbit, elephant
b)
Grass, parrot, snake
c)
Snake, hawk, tiger
d)
Bacteria, fungi, viruses
|
|
Siddharth Nair answered |
Primary consumers are organisms that directly consume producers (plants or algae) as their source of energy. They are herbivores that feed on plants or plant-based materials.
The correct answer is option 'A' - Bird, rabbit, elephant. Let's break down the chain to understand why it contains primary consumers:
1. Bird: Birds are primary consumers because they consume plants and seeds as their primary source of energy. They may feed on fruits, nuts, and grains.
2. Rabbit: Rabbits are also primary consumers as they mainly feed on plant material such as grass, leaves, and vegetables.
3. Elephant: Elephants are primary consumers because they are herbivores that primarily feed on plants, including grass, leaves, bark, and fruits.
In this chain, each organism directly consumes plants or plant-based materials, making them primary consumers in the food chain.
Let's compare the other options to see why they are not correct:
- Option 'B' - Grass, parrot, snake:
Grass is a producer, but parrots are not primary consumers. They are secondary consumers as they feed on seeds, fruits, and sometimes insects. Snakes are also not primary consumers as they are carnivores that feed on other animals, including birds and rodents.
- Option 'C' - Snake, hawk, tiger:
Snakes are not primary consumers as mentioned earlier. Hawks are secondary consumers as they prey on small mammals and birds. Tigers are tertiary consumers as they are top predators that feed on herbivores and other carnivores.
- Option 'D' - Bacteria, fungi, viruses:
Bacteria, fungi, and viruses are not considered primary consumers as they are decomposers or pathogens that break down organic matter or cause diseases. They do not directly consume producers.
In summary, the chain that contains primary consumers is option 'A' - Bird, rabbit, elephant.
The correct answer is option 'A' - Bird, rabbit, elephant. Let's break down the chain to understand why it contains primary consumers:
1. Bird: Birds are primary consumers because they consume plants and seeds as their primary source of energy. They may feed on fruits, nuts, and grains.
2. Rabbit: Rabbits are also primary consumers as they mainly feed on plant material such as grass, leaves, and vegetables.
3. Elephant: Elephants are primary consumers because they are herbivores that primarily feed on plants, including grass, leaves, bark, and fruits.
In this chain, each organism directly consumes plants or plant-based materials, making them primary consumers in the food chain.
Let's compare the other options to see why they are not correct:
- Option 'B' - Grass, parrot, snake:
Grass is a producer, but parrots are not primary consumers. They are secondary consumers as they feed on seeds, fruits, and sometimes insects. Snakes are also not primary consumers as they are carnivores that feed on other animals, including birds and rodents.
- Option 'C' - Snake, hawk, tiger:
Snakes are not primary consumers as mentioned earlier. Hawks are secondary consumers as they prey on small mammals and birds. Tigers are tertiary consumers as they are top predators that feed on herbivores and other carnivores.
- Option 'D' - Bacteria, fungi, viruses:
Bacteria, fungi, and viruses are not considered primary consumers as they are decomposers or pathogens that break down organic matter or cause diseases. They do not directly consume producers.
In summary, the chain that contains primary consumers is option 'A' - Bird, rabbit, elephant.
An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C. The heat will- a) flow from iron ball to water.
- b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
- c) flow from water to iron ball.
- d) increase the temperature of both.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C. The heat will
a)
flow from iron ball to water.
b)
not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
c)
flow from water to iron ball.
d)
increase the temperature of both.
|
|
Devanshi Saha answered |
Heat transfer between an iron ball and water
Introduction:
When two objects at different temperatures come into contact with each other, heat transfer occurs between them. The direction of heat transfer depends on the temperature difference between the objects. In this scenario, an iron ball at 40°C is dropped into a mug containing water also at 40°C. Let's analyze the possible heat transfer between the iron ball and water.
Explanation:
- When the iron ball is dropped into the water, the molecules of the iron ball and the water come into contact with each other.
- Heat transfer occurs due to the temperature difference between the iron ball and water.
- However, since both the iron ball and water are at the same temperature of 40°C, there is no temperature difference between them.
- According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat transfer occurs only when there is a temperature gradient (difference in temperature).
- In this case, as there is no temperature difference between the iron ball and water, heat will not flow from the iron ball to the water or from the water to the iron ball.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - heat will not flow from the iron ball to the water or from the water to the iron ball.
Conclusion:
In the given scenario, since the iron ball and water are at the same temperature, there is no temperature difference between them. As a result, heat transfer does not occur between the iron ball and water.
Introduction:
When two objects at different temperatures come into contact with each other, heat transfer occurs between them. The direction of heat transfer depends on the temperature difference between the objects. In this scenario, an iron ball at 40°C is dropped into a mug containing water also at 40°C. Let's analyze the possible heat transfer between the iron ball and water.
Explanation:
- When the iron ball is dropped into the water, the molecules of the iron ball and the water come into contact with each other.
- Heat transfer occurs due to the temperature difference between the iron ball and water.
- However, since both the iron ball and water are at the same temperature of 40°C, there is no temperature difference between them.
- According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat transfer occurs only when there is a temperature gradient (difference in temperature).
- In this case, as there is no temperature difference between the iron ball and water, heat will not flow from the iron ball to the water or from the water to the iron ball.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - heat will not flow from the iron ball to the water or from the water to the iron ball.
Conclusion:
In the given scenario, since the iron ball and water are at the same temperature, there is no temperature difference between them. As a result, heat transfer does not occur between the iron ball and water.
Meristematic tissues are those which help in increasing the length and girth of the plan.Which of the following statements given below is correct about the meristematic tissue?- a) It is made up of cells that are incapable of cell division
- b) It is made up of cells that are capable of cell division
- c) It is composed of single type of cells
- d) It is composed of more than one type of cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Meristematic tissues are those which help in increasing the length and girth of the plan.
Which of the following statements given below is correct about the meristematic tissue?
a)
It is made up of cells that are incapable of cell division
b)
It is made up of cells that are capable of cell division
c)
It is composed of single type of cells
d)
It is composed of more than one type of cells
|
|
Rahul Choudhury answered |
Meristematic Tissue: They are the group of young cells, which consists of actively dividing cells and leads to increase in length and thickness of the plant. There are different types of meristematic tissues, which are classified on the basis of positions, functions, plane of divisions, origin and development. The three main types of meristematic tissues depending on the occurrence of the meristematic tissue on the plant body are
1. Apical Meristem.
2. Lateral Meristem.
3. Intercalary Meristem.
Functions of Meristematic Tissue
1. It is responsible for the growth of the new organs.
2. Involved in the movement of water and nutrition within the plants.
3. These tissues are responsible for both primary and secondary growth of the plant.
4. It is the outermost tissue, functions by providing protection from mechanical injury.
5. It gives rise to the epidermis layer, cortex, endodermis, ground tissue and vascular tissue.
Why was Thomson's Model of an atom failed? 1. It could not explain the screening of negative charges from that of positive2. It did not tell about the presence of electrons3. It did not give an idea about the discrete energy levels4. It explained the atom as a whole to be electrically neutralChoose the correct option from the following:- a) 3 Only
- b) 1 and 3 Only
- c) 1 Only
- d) 2 and 4 only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why was Thomson's Model of an atom failed?
1. It could not explain the screening of negative charges from that of positive
2. It did not tell about the presence of electrons
3. It did not give an idea about the discrete energy levels
4. It explained the atom as a whole to be electrically neutral
Choose the correct option from the following:
a)
3 Only
b)
1 and 3 Only
c)
1 Only
d)
2 and 4 only
|
|
Rajiv Reddy answered |
- Thomson atomic model was proposed by William Thomson in the year 1900. This model explained the description of an inner structure of the atom theoretically. It was strongly supported by Sir Joseph Thomson, who had discovered the electron earlier. During a cathode ray tube experiment, a negatively charged particle was discovered by J.J. Thomson. This experiment took place in the year 1897.
- Cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube. The negative particle was called an electron. Thomson assumed that an electron is two thousand times lighter than a proton and believed that an atom is made up of thousands of electrons.
- In this atomic structure model, he considered atoms surrounded by a cloud having positive as well as negative charges. The demonstration of the ionization of air by X-ray was also done by him together with Rutherford.
- They were the first to demonstrate it. Thomson’s model of an atom is similar to a plum pudding. Postulates of Thomson’s atomic model: Postulate 1: An atom consists of a positively charged sphere with electrons embedded in it Postulate 2: An atom as a whole is electrically neutral because the negative and positive charges are equal in magnitude Thomson atomic model is compared to watermelon.
Molecular mass is defined as the:- a) Mass of one molecule of any substance compared with the mass of one atom of C – 12
- b) Mass of one atom compared with the mass of one atom of hydrogen
- c) Mass of one atom compared with the mass of one molecule
- d) None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Molecular mass is defined as the:
a)
Mass of one molecule of any substance compared with the mass of one atom of C – 12
b)
Mass of one atom compared with the mass of one atom of hydrogen
c)
Mass of one atom compared with the mass of one molecule
d)
None of the above
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
- Molecular mass is a number equal to the sum of the atomic masses of the atoms in a molecule. The molecular mass gives the mass of a molecule relative to that of the 12C atom, which is taken to have a mass of 12.
- Molecular mass is a dimensionless quantity, but it is given the unit Dalton or atomic mass unit as a means of indicating the mass is relative to 1/12th the mass of a single atom of carbon-12.
Among the following choose the correct option that best describes the characteristics of spirogyra.- a) Multicellular, autotrophic, root like rhizoids.
- b) Cytoplasmic strands, autotrophic, presence of rhizome.
- c) Presence of male cones, nonvascular, filaments.
- d) Filamentous, presence of Cytoplasmic strands, presence of pyrenoids.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following choose the correct option that best describes the characteristics of spirogyra.
a)
Multicellular, autotrophic, root like rhizoids.
b)
Cytoplasmic strands, autotrophic, presence of rhizome.
c)
Presence of male cones, nonvascular, filaments.
d)
Filamentous, presence of Cytoplasmic strands, presence of pyrenoids.
|
|
Rahul Choudhury answered |
The important characteristics of spirogyra are
1. It is an unbranched, filamentous green algae occurring in the stagnant water so known as pond scum.
2. A mucilaginous covering or sheath is present which makes the surface slimy hence known as pond silk.
3. A double layered cell wall is present in which the outer wall is made of pectin and inner wall of cellulose.
4. A spirally coiled or ribbon shaped chloroplast with a number of pyrenoids is present.
5. Reproduction occurs both in vegetative and sexual methods.
6. Vegetative reproduction is by fragmentation.
7. Sexual reproduction takes place by conjugation.
8. Three types of conjugation are found in spirogyra.
They are
i. scalariform conjugation,
ii. Lateral conjugation,
iii. Self conjugation.
9. The lifecycle of the spirogyra is haplobiontic.
With reference to nuclear fusion, consider the following statements:
1. During the nuclear fusion reaction two lighter nuclei are joined to make a heavier nucleus.
2. Nuclear fusion reactions take place in the Sun and Star. It takes considerable energy to force the nuclei to fuse.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- a)1 Only
- b)2 only
- c)1 and 2 Only
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
With reference to nuclear fusion, consider the following statements:
1. During the nuclear fusion reaction two lighter nuclei are joined to make a heavier nucleus.
2. Nuclear fusion reactions take place in the Sun and Star. It takes considerable energy to force the nuclei to fuse.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 only
c)
1 and 2 Only
d)
None of these
|
|
Sanjay Rana answered |
-
Fusion means joining lighter nuclei to make a heavier nucleus, most commonly hydrogen isotopes are added together to create Helium. It releases a tremendous amount of energy, according to the Einstein equation, as the mass of the product is little less than the sum of the masses of the original individual nuclei.
-
Such nuclear fusion reactions are the source of energy in the Sun and other stars. It takes considerable energy to force the nuclei to fuse. The conditions needed for this process are extreme – millions of degrees of temperature and millions of pascals of pressure.
Epithelial tissue always has an exposed outer surface and an inner surface anchored to connective tissue by a thin, non- cellular structure called the- a) Non-stratified layer
- b) Stratified layer
- c) Basement membrane
- d) Fibroblast
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Epithelial tissue always has an exposed outer surface and an inner surface anchored to connective tissue by a thin, non- cellular structure called the
a)
Non-stratified layer
b)
Stratified layer
c)
Basement membrane
d)
Fibroblast
|
|
Arun Khatri answered |
Epithelial Tissue: They are formed by cells which cover the external parts of the body organs and line the organ surfaces such as the surface of the skin, the reproductive tract, the airways, and the inner lining of the digestive tract. Functions of Epithelial Tissue
1. Play a major role in sensory reception, excretion, filtration and other metabolic activities.
2. Provide mechanical strength and resistance to the underlying cells and tissue.
3. It is involved in the movement of materials through the process of filtration, diffusion and secretion.
4. Protects the internal organs against the invasions of pathogens, toxins, physical trauma, radiation, etc. Epithelial tissues are also involved in secreting hormones, enzymes, mucus and other products from ducts and transporting it to the circulatory system.
The seat belts are provided in the cars so that if the car stops suddenly due to an emergency braking, the persons sitting on the front seats are not thrown forward violently and saved from getting injured. Can you guess the law due to which a person falls in forward direction on the sudden stopping of the car?- a) Newton’s first law of motion
- b) Newton’s second law of motion
- c) Newton’s third law of motion
- d) Newton’s law of gravitation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The seat belts are provided in the cars so that if the car stops suddenly due to an emergency braking, the persons sitting on the front seats are not thrown forward violently and saved from getting injured. Can you guess the law due to which a person falls in forward direction on the sudden stopping of the car?
a)
Newton’s first law of motion
b)
Newton’s second law of motion
c)
Newton’s third law of motion
d)
Newton’s law of gravitation
|
|
Pranjal Kumar answered |
Explanation:
Newton’s first law of motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net external force. This is also known as the law of inertia.
When a car is in motion, the passengers inside the car are also in motion. When the car stops suddenly due to an emergency braking, the passengers inside the car tend to continue their motion in the same direction due to the law of inertia. This means that the passengers tend to move forward in the direction of the car’s motion before it stopped suddenly. This is the reason why a person falls forward on sudden stopping of the car.
The seat belts are designed to prevent this forward motion of the passengers. When a car stops suddenly, the seat belt applies a force on the passenger in the opposite direction to their motion, which helps to slow down their forward motion and bring them to a stop. This prevents the passengers from getting injured due to the sudden stop.
Conclusion:
Therefore, it can be concluded that a person falls in forward direction on the sudden stopping of the car due to Newton’s first law of motion, which is the law of inertia. The seat belts in the cars are designed to prevent this forward motion of the passengers and protect them from getting injured.
Newton’s first law of motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net external force. This is also known as the law of inertia.
When a car is in motion, the passengers inside the car are also in motion. When the car stops suddenly due to an emergency braking, the passengers inside the car tend to continue their motion in the same direction due to the law of inertia. This means that the passengers tend to move forward in the direction of the car’s motion before it stopped suddenly. This is the reason why a person falls forward on sudden stopping of the car.
The seat belts are designed to prevent this forward motion of the passengers. When a car stops suddenly, the seat belt applies a force on the passenger in the opposite direction to their motion, which helps to slow down their forward motion and bring them to a stop. This prevents the passengers from getting injured due to the sudden stop.
Conclusion:
Therefore, it can be concluded that a person falls in forward direction on the sudden stopping of the car due to Newton’s first law of motion, which is the law of inertia. The seat belts in the cars are designed to prevent this forward motion of the passengers and protect them from getting injured.
Osmosis is a process by which molecules of a solvent tend to pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one. Can you pick out the option among the following which does not belong to this process?- a) The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane is affected by the amount of substances dissolved in it.
- b) Membranes are made of organic molecules such as proteins and lipids.
- c) Molecules soluble in organic solvents can easily pass through the membrane.
- d) Plasma membranes contain chitin sugar in plants.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Osmosis is a process by which molecules of a solvent tend to pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one. Can you pick out the option among the following which does not belong to this process?
a)
The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane is affected by the amount of substances dissolved in it.
b)
Membranes are made of organic molecules such as proteins and lipids.
c)
Molecules soluble in organic solvents can easily pass through the membrane.
d)
Plasma membranes contain chitin sugar in plants.
|
|
Rajiv Reddy answered |
- Osmosis is the diffusion of a solvent through a differentially permeable membrane. In biological systems, the solvent will usually be water.
- Osmosis will occur whenever the water concentrations are different on either side of a differentially permeable membrane. Osmosis can be defined as the movement of water molecules from a higher water concentration area to the area of less water concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
- In other words, it can be defined as the diffusion of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane. It is a special case of diffusion of water (High to low). For example, water in the roots of plants is transported through osmosis.
Consider the following statements with respect to sound: 1. It can travel through solids, liquids, gases and vacuum.2. The intensity of sound is measured in decibels (dB).3. For the human ear, the range of audible frequencies is roughly from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 and 3 Only
- c) 3 only
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements with respect to sound:
1. It can travel through solids, liquids, gases and vacuum.
2. The intensity of sound is measured in decibels (dB).
3. For the human ear, the range of audible frequencies is roughly from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 and 3 Only
c)
3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Krithika Chavan answered |
The correct answer is option 'B': 2 and 3 Only.
Explanation:
1. It can travel through solids, liquids, gases, and vacuum.
This statement is incorrect. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum because it requires a medium to propagate. Sound is a mechanical wave that travels by compressing and decompressing particles in a medium, such as air, water, or solids. In a vacuum, there are no particles to vibrate, so sound cannot travel.
2. The intensity of sound is measured in decibels (dB).
This statement is correct. The intensity of sound refers to the amount of energy carried by sound waves. It is measured in a unit called decibels (dB). The decibel scale is logarithmic, which means that a small change in decibel value represents a large change in sound intensity. The decibel scale is commonly used to measure the loudness of sounds.
3. For the human ear, the range of audible frequencies is roughly from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
This statement is correct. The human ear can perceive sound waves within a certain range of frequencies. This range is commonly referred to as the audible frequency range. For most individuals, the range of audible frequencies is approximately from 20 Hz (low-pitched sounds) to 20,000 Hz (high-pitched sounds). However, the exact range can vary slightly from person to person.
In summary, statement 1 is incorrect as sound cannot travel through a vacuum. Statement 2 is correct as the intensity of sound is measured in decibels. Statement 3 is correct as the range of audible frequencies for the human ear is roughly from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B': 2 and 3 Only.
Explanation:
1. It can travel through solids, liquids, gases, and vacuum.
This statement is incorrect. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum because it requires a medium to propagate. Sound is a mechanical wave that travels by compressing and decompressing particles in a medium, such as air, water, or solids. In a vacuum, there are no particles to vibrate, so sound cannot travel.
2. The intensity of sound is measured in decibels (dB).
This statement is correct. The intensity of sound refers to the amount of energy carried by sound waves. It is measured in a unit called decibels (dB). The decibel scale is logarithmic, which means that a small change in decibel value represents a large change in sound intensity. The decibel scale is commonly used to measure the loudness of sounds.
3. For the human ear, the range of audible frequencies is roughly from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
This statement is correct. The human ear can perceive sound waves within a certain range of frequencies. This range is commonly referred to as the audible frequency range. For most individuals, the range of audible frequencies is approximately from 20 Hz (low-pitched sounds) to 20,000 Hz (high-pitched sounds). However, the exact range can vary slightly from person to person.
In summary, statement 1 is incorrect as sound cannot travel through a vacuum. Statement 2 is correct as the intensity of sound is measured in decibels. Statement 3 is correct as the range of audible frequencies for the human ear is roughly from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B': 2 and 3 Only.
Which of the following statements is not correct about deforestation?- a) Deforestation increases the temperature on the earth.
- b) Ground water level gets lowered.
- c) The soil properties remain unaffected.
- d) The water holding capacity of soil is lowered.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct about deforestation?
a)
Deforestation increases the temperature on the earth.
b)
Ground water level gets lowered.
c)
The soil properties remain unaffected.
d)
The water holding capacity of soil is lowered.
|
|
Kavita Mehta answered |
- Deforestation means that less carbon dioxide will be taken up by the plants, resulting in an increase in its amount in the atmosphere.
- This will lead to global warming as carbon dioxide traps the heat rays reflected by the earth. Deforestation also lowers the ground water level. The major reason behind the changes of soil properties is deforestation. This causes soil erosion. Soil erosion lowers the content of humus in soil and soil fertility also declines. Soil erosion also causes desertification.
- Deforestation adversely affects the water holding capacity of the soil. The movement of water from the soil surface into the ground (infiltration rate) is reduced. This is responsible for floods.
The school bags are generally provided with the broad strips because:- a) It will spread the force of the bag over the large area of the shoulder of the child producing large pressure
- b) It will spread the force of the bag over the large area of the shoulder of the child producing less pressure
- c) It has become a trend among the students to carry the bags with wide strips
- d) It will spread the force of the bag over the small area of the shoulder of the child producing less pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The school bags are generally provided with the broad strips because:
a)
It will spread the force of the bag over the large area of the shoulder of the child producing large pressure
b)
It will spread the force of the bag over the large area of the shoulder of the child producing less pressure
c)
It has become a trend among the students to carry the bags with wide strips
d)
It will spread the force of the bag over the small area of the shoulder of the child producing less pressure
|
|
Ameya Malik answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option B: It will spread the force of the bag over the large area of the shoulder of the child producing less pressure.
Reasoning:
When designing school bags, it is important to consider the well-being and comfort of the students who will be carrying them. Broad strips on school bags serve a specific purpose, which is to distribute the force exerted by the bag over a larger surface area of the shoulder. This helps in reducing the pressure exerted on the shoulder and provides a more comfortable carrying experience for the child.
Advantages of Broad Strips:
1. Force Distribution: Broad strips on school bags help in spreading the force exerted by the bag over a larger area of the shoulder. This means that the weight of the bag is distributed more evenly, reducing the pressure on a specific point on the shoulder. This is especially important when students have to carry heavy books and other items in their bags.
2. Less Pressure: By distributing the force over a larger area, the pressure exerted on the shoulder is reduced. This can help prevent shoulder pain, discomfort, and even potential injuries that may arise from carrying heavy bags with narrow straps.
3. Improved Comfort: The use of broad straps on school bags enhances the overall comfort of carrying the bag. The broader straps provide better support and stability to the bag, allowing the child to carry it with ease for extended periods of time.
4. Prevention of Shoulder Strain: Carrying heavy bags with narrow straps can lead to strain on the shoulders, neck, and back. Broad straps help in minimizing this strain by evenly distributing the weight, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal issues.
5. Longevity of the Bag: By spreading the force over a larger area, the pressure on the straps themselves is reduced. This helps in preventing wear and tear on the straps, increasing the overall durability and longevity of the bag.
In conclusion, the provision of broad strips on school bags is beneficial as it spreads the force of the bag over a larger area of the shoulder, resulting in less pressure and improved comfort for the child.
The correct answer is option B: It will spread the force of the bag over the large area of the shoulder of the child producing less pressure.
Reasoning:
When designing school bags, it is important to consider the well-being and comfort of the students who will be carrying them. Broad strips on school bags serve a specific purpose, which is to distribute the force exerted by the bag over a larger surface area of the shoulder. This helps in reducing the pressure exerted on the shoulder and provides a more comfortable carrying experience for the child.
Advantages of Broad Strips:
1. Force Distribution: Broad strips on school bags help in spreading the force exerted by the bag over a larger area of the shoulder. This means that the weight of the bag is distributed more evenly, reducing the pressure on a specific point on the shoulder. This is especially important when students have to carry heavy books and other items in their bags.
2. Less Pressure: By distributing the force over a larger area, the pressure exerted on the shoulder is reduced. This can help prevent shoulder pain, discomfort, and even potential injuries that may arise from carrying heavy bags with narrow straps.
3. Improved Comfort: The use of broad straps on school bags enhances the overall comfort of carrying the bag. The broader straps provide better support and stability to the bag, allowing the child to carry it with ease for extended periods of time.
4. Prevention of Shoulder Strain: Carrying heavy bags with narrow straps can lead to strain on the shoulders, neck, and back. Broad straps help in minimizing this strain by evenly distributing the weight, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal issues.
5. Longevity of the Bag: By spreading the force over a larger area, the pressure on the straps themselves is reduced. This helps in preventing wear and tear on the straps, increasing the overall durability and longevity of the bag.
In conclusion, the provision of broad strips on school bags is beneficial as it spreads the force of the bag over a larger area of the shoulder, resulting in less pressure and improved comfort for the child.
Animals have eyes shaped in different ways, and have various specialities. Consider the following statements regarding these specialities: 1. Eyes of a crab are quite small but they enable the crab to look all around him.2. Butterflies have large eyes that seem to be made up of thousands of little eyes.3. The Owl has a large cornea and a large pupil to allow more light in its eye.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 and 2 only
- b) 2 and 3 Only
- c) 3 Only
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Animals have eyes shaped in different ways, and have various specialities. Consider the following statements regarding these specialities:
1. Eyes of a crab are quite small but they enable the crab to look all around him.
2. Butterflies have large eyes that seem to be made up of thousands of little eyes.
3. The Owl has a large cornea and a large pupil to allow more light in its eye.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
2 and 3 Only
c)
3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Rhea Mishra answered |
Statement 1: Eyes of a crab are quite small but they enable the crab to look all around him.
Explanation:
- Crabs have compound eyes, which are made up of thousands of tiny lenses called ommatidia.
- Each ommatidium captures a small portion of the visual field, and the crab's brain combines all the information to create a complete image.
- The small size of the crab's eyes allows them to be positioned all around its body, providing a wide field of vision.
- This enables the crab to detect potential threats or prey from multiple directions, increasing its chances of survival.
- Therefore, statement 1 is correct.
Statement 2: Butterflies have large eyes that seem to be made up of thousands of little eyes.
Explanation:
- Butterflies also have compound eyes composed of numerous ommatidia.
- These ommatidia work together to provide a wide field of vision, allowing butterflies to detect movement in their surroundings.
- The large size of their eyes helps them gather more light, which is essential for their visual perception.
- Each ommatidium captures a small portion of the visual field, and the butterfly's brain processes this information to create a composite image.
- Therefore, statement 2 is correct.
Statement 3: The owl has a large cornea and a large pupil to allow more light into its eye.
Explanation:
- Owls are nocturnal birds and have adapted to hunting in low light conditions.
- To maximize light intake, their eyes have a large cornea, which is the transparent front part of the eye that allows light to enter.
- The large pupil of owls also helps in gathering more light. The pupil dilates in low light conditions, allowing more light to reach the retina.
- The retina of owls has a higher number of rod cells, which are specialized for low-light vision.
- These adaptations enable owls to have excellent night vision and hunt effectively in the dark.
- Therefore, statement 3 is correct.
Conclusion:
- All three statements are correct as they accurately describe the eye specializations of different animals.
- Hence, the correct answer is option D) 1, 2, and 3.
Explanation:
- Crabs have compound eyes, which are made up of thousands of tiny lenses called ommatidia.
- Each ommatidium captures a small portion of the visual field, and the crab's brain combines all the information to create a complete image.
- The small size of the crab's eyes allows them to be positioned all around its body, providing a wide field of vision.
- This enables the crab to detect potential threats or prey from multiple directions, increasing its chances of survival.
- Therefore, statement 1 is correct.
Statement 2: Butterflies have large eyes that seem to be made up of thousands of little eyes.
Explanation:
- Butterflies also have compound eyes composed of numerous ommatidia.
- These ommatidia work together to provide a wide field of vision, allowing butterflies to detect movement in their surroundings.
- The large size of their eyes helps them gather more light, which is essential for their visual perception.
- Each ommatidium captures a small portion of the visual field, and the butterfly's brain processes this information to create a composite image.
- Therefore, statement 2 is correct.
Statement 3: The owl has a large cornea and a large pupil to allow more light into its eye.
Explanation:
- Owls are nocturnal birds and have adapted to hunting in low light conditions.
- To maximize light intake, their eyes have a large cornea, which is the transparent front part of the eye that allows light to enter.
- The large pupil of owls also helps in gathering more light. The pupil dilates in low light conditions, allowing more light to reach the retina.
- The retina of owls has a higher number of rod cells, which are specialized for low-light vision.
- These adaptations enable owls to have excellent night vision and hunt effectively in the dark.
- Therefore, statement 3 is correct.
Conclusion:
- All three statements are correct as they accurately describe the eye specializations of different animals.
- Hence, the correct answer is option D) 1, 2, and 3.
In the context of lenses, consider the following assertions —1. The image formed by a convex lens is real, inverted and larger in size than the object.2. The image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, erect, and smaller in size than the object.Which of the above assertions is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the context of lenses, consider the following assertions —
1. The image formed by a convex lens is real, inverted and larger in size than the object.
2. The image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, erect, and smaller in size than the object.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Mahi Das answered |
Explanation:
2 Only
- Assertion 1 is incorrect as the image formed by a convex lens can be real or virtual, depending on the object distance. It can also be erect or inverted, and the size of the image can be larger, smaller, or the same as the object.
- Assertion 2 is correct. The image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, erect, and smaller in size than the object. This is a fundamental property of concave lenses due to their diverging nature.
Therefore, only assertion 2 is correct in this case.
2 Only
- Assertion 1 is incorrect as the image formed by a convex lens can be real or virtual, depending on the object distance. It can also be erect or inverted, and the size of the image can be larger, smaller, or the same as the object.
- Assertion 2 is correct. The image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, erect, and smaller in size than the object. This is a fundamental property of concave lenses due to their diverging nature.
Therefore, only assertion 2 is correct in this case.
Consider the following statements: 1. The fuels which are produced by plants and animals are called biomass.2. The main Constituent of Biogas is Methane.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 Only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. The fuels which are produced by plants and animals are called biomass.
2. The main Constituent of Biogas is Methane.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Eshaan Kapoor answered |
- Cow dung cakes serve as a steady source of fuel. Since, these fuels are derived from plants and animals hence they constitute – Biomass.
- These fuels, however, do not produce much heat on burning but a lot of smoke is given out when they are burnt. Cow-dung, various plant materials like crops residue, vegetable waste and sewage are decomposed in the absence of oxygen to give Biogas. Since the starting material is mainly cow-dung, it is popularly known as ‘gobar-gas’.
- Bio-gas is produced in a dome-shaped plant. Bio-gas is an excellent fuel as it contains up to 75% methane. It burns without smoke, leaves no residue like ash in wood, charcoal and coal burning. Its heating capacity is high.
Consider the following:1. Algae: Spirogyra2. Protozoa: Chlamydomonas3. Fungi: Rhizopus (bread mould)Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?- a) 1 Only
- b) 1 and 3 Only
- c) 3 Only
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following:
1. Algae: Spirogyra
2. Protozoa: Chlamydomonas
3. Fungi: Rhizopus (bread mould)
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 3 Only
c)
3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
- Of the given microorganisms, Spirogyra and Chlamydomonas are examples of algae. Common examples of protozoa are amoeba and paramecium.
- Rhizopus (bread mould), Penicillium and Aspergillus are examples of fungi. Microorganisms can be unicellular, like bacteria; some are multicellular, like algae and fungi.
- Some microorganisms are dependent on other microorganisms (parasitic), while some are not (free living). Microorganisms like amoeba live alone (solitary) while fungi live in groups (colonial).
Aluminium is used for making cooking utensils. Which of the following properties of aluminium are responsible for the same? 1. Good thermal conductivity2. Good electrical conductivity3. Ductility4. High melting point- a) 1 and 2 only
- b) 1 and 3 Only
- c) 2 and 3 only
- d) 1 and 4 only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Aluminium is used for making cooking utensils. Which of the following properties of aluminium are responsible for the same?
1. Good thermal conductivity
2. Good electrical conductivity
3. Ductility
4. High melting point
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
1 and 3 Only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1 and 4 only
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
Some of the most common properties of Aluminium are good thermal conductivity, malleability, light weight and high melting point which make it useful for making cooking utensils.
Assertion (A): In India, 98% of the coal is found in Gondwana rocks of the Moran region.Reason (R): The main regions of Gondwana rocks are found in West Bengal, Jharkhand and Odisha.Codes:- a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b) Both A and R are true but R is not a correct explanation of A
- c) A is true but R is false
- d) Both A & R is not true
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): In India, 98% of the coal is found in Gondwana rocks of the Moran region.
Reason (R): The main regions of Gondwana rocks are found in West Bengal, Jharkhand and Odisha.
Codes:
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is not a correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
Both A & R is not true
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
- Around 67 % of total commercial energy produced in India and 98% of India's total account is found in Gondwana rocks of the Moran region.
- The main regions of Gondwana rocks are found in West Bengal, Jharkhand and Odisha. There are four types of coal found in India: Anthracite (Best quality of coal found only in Jammu & Kashmir); Bituminous (Second best quality of coal); Lignite (Found in Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Jammu & Kashmir).
- Coal accounts for approx. 67 % of total commercial energy produced in India and 98% of India’s total account is found in Gondwana rocks of Moran region.
If the current through the wire increases, the magnitude of the magnetic field produced at a given point:- a) Increases
- b) Decreases
- c) Firstly increases and then decreases
- d) Can’t comment anything
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the current through the wire increases, the magnitude of the magnetic field produced at a given point:
a)
Increases
b)
Decreases
c)
Firstly increases and then decreases
d)
Can’t comment anything
|
|
Kavita Mehta answered |
The current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to magnetic field. As the electric current through the wire increases, the magnitude of the magnetic field produced at a given point increases.
Chapter doubts & questions for NCERT Based Tests - Old & New NCERTs for IAS Preparation (Must Read) 2025 is part of UPSC CSE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UPSC CSE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UPSC CSE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of NCERT Based Tests - Old & New NCERTs for IAS Preparation (Must Read) in English & Hindi are available as part of UPSC CSE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC CSE Exam by signing up for free.
Old & New NCERTs for IAS Preparation (Must Read)
3 videos|704 docs|515 tests
|
Related UPSC CSE Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup