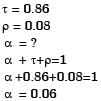All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
Additional Study Material for Mechanical Engineering >
All Questions
All questions of Tests for Mechanical Engineering Exam
The friction experienced by a body, when in motion, is known as- a)rolling friction
- b)dynamic friction
- c)limiting friction
- d)static friction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The friction experienced by a body, when in motion, is known as
a)
rolling friction
b)
dynamic friction
c)
limiting friction
d)
static friction

|
Anil Sharma answered |
Friction is categorized in two parts. Dynamics and static friction. Body is moving here so static friction will be eliminated. And not mention about rolling. so rolling friction also eliminated, no concern of force and reactions here so limiting friction is not playing vital role here. Only option remaining is DYNAMIC FRICTION. Or directly we can say wherever body is in motion dynamic friction are there.
Which of the following is an equation of linear motion?(where, u and v = Initial and final velocity of the body, a = Acceleration of the body, and s = Displacement of the body in time t seconds.)- a)v = u + a.t
- b)s = u.t + 1/2 a.t2
- c)v2 = u2+2a.s
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an equation of linear motion?(where, u and v = Initial and final velocity of the body, a = Acceleration of the body, and s = Displacement of the body in time t seconds.)
a)
v = u + a.t
b)
s = u.t + 1/2 a.t2
c)
v2 = u2+2a.s
d)
all of these

|
Ashwin Kulkarni answered |
Equation of Linear Motion
The equation of linear motion describes the motion of an object in a straight line with constant or variable acceleration. There are three basic variables involved in the equation of linear motion, which are initial velocity (u), final velocity (v), acceleration (a), and displacement (s).
The equation of linear motion can be represented in different forms, depending on the variables involved. The most common forms of the equation of linear motion are:
a) v = u + at
b) s = ut + 1/2at^2
c) v^2 = u^2 + 2as
All of these equations are interrelated and can be derived from one another.
Explanation of Options
a) v = u + at - This equation represents the final velocity (v) of an object in terms of its initial velocity (u) and acceleration (a) after time (t) seconds.
b) s = ut + 1/2at^2 - This equation represents the displacement (s) of an object in terms of its initial velocity (u), acceleration (a), and time (t) seconds.
c) v^2 = u^2 + 2as - This equation represents the final velocity (v) of an object in terms of its initial velocity (u), acceleration (a), and displacement (s).
d) all of these - This option is the correct answer as all three equations (a, b, and c) are equations of linear motion and are interrelated.
Conclusion
The equation of linear motion plays an important role in understanding the motion of objects in a straight line. These equations help us to calculate various parameters of motion such as velocity, acceleration, displacement, and time. The three common equations of linear motion are interrelated and one can be derived from another.
The equation of linear motion describes the motion of an object in a straight line with constant or variable acceleration. There are three basic variables involved in the equation of linear motion, which are initial velocity (u), final velocity (v), acceleration (a), and displacement (s).
The equation of linear motion can be represented in different forms, depending on the variables involved. The most common forms of the equation of linear motion are:
a) v = u + at
b) s = ut + 1/2at^2
c) v^2 = u^2 + 2as
All of these equations are interrelated and can be derived from one another.
Explanation of Options
a) v = u + at - This equation represents the final velocity (v) of an object in terms of its initial velocity (u) and acceleration (a) after time (t) seconds.
b) s = ut + 1/2at^2 - This equation represents the displacement (s) of an object in terms of its initial velocity (u), acceleration (a), and time (t) seconds.
c) v^2 = u^2 + 2as - This equation represents the final velocity (v) of an object in terms of its initial velocity (u), acceleration (a), and displacement (s).
d) all of these - This option is the correct answer as all three equations (a, b, and c) are equations of linear motion and are interrelated.
Conclusion
The equation of linear motion plays an important role in understanding the motion of objects in a straight line. These equations help us to calculate various parameters of motion such as velocity, acceleration, displacement, and time. The three common equations of linear motion are interrelated and one can be derived from another.
The range of a projectile is maximum, when the angle of projection is- a)30º
- b)45º
- c)60º
- d)90º
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The range of a projectile is maximum, when the angle of projection is
a)
30º
b)
45º
c)
60º
d)
90º
|
|
Aditi Saxena answered |
The range of projection can be found as:
R = u^2*sin2$/g ; where u = launch velocity ; $ : angle of projection from horizontal ; g : acceleration due to gravity.
Hence put $ = 45 degree.
Biot number signifies the ratio of[2014]- a)convective resistance in the fluid to conductive resistance in the solid
- b)conductive resistance in the solid to convective resistance in the fluid
- c)inertia force to viscous force in the fluid
- d)buoyancy force to viscous force in the fluid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Biot number signifies the ratio of
[2014]
a)
convective resistance in the fluid to conductive resistance in the solid
b)
conductive resistance in the solid to convective resistance in the fluid
c)
inertia force to viscous force in the fluid
d)
buoyancy force to viscous force in the fluid

|
Gate Funda answered |
Biot number provides a way to compare the conduction resistance within a solid body to the convection resistance external to the body (offered by the surrounding fluid) for heat transfer:

Where ‘s’ is a characteristic dimension of the solid
‘h’ is convective heat transfer coefficient
‘k’ is thermal conductivity of the body.

Where ‘s’ is a characteristic dimension of the solid
‘h’ is convective heat transfer coefficient
‘k’ is thermal conductivity of the body.
The Pascal law states that liquid at rest applies pressure at a point is ________ in all directions.- a)Same
- b)Un-same
- c)Not matching
- d)Matching but not equal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Pascal law states that liquid at rest applies pressure at a point is ________ in all directions.
a)
Same
b)
Un-same
c)
Not matching
d)
Matching but not equal
|
|
Neha Choudhury answered |
The Pascal law states that the liquid at rest applies pressure at a point is same in all directions. This means that the pressure is there in spite of the direction. And it is present in the same direction and is having same magnitude. Explanation: The liquid must be incompressible.
The bearing is subjected to a radial load of 4000N. Expected life for 90% bearings is 9000h and shaft is rotating at 1500rpm. Calculate the dynamic load capacity.- a)42.21kN
- b)37.29kN
- c)26.33kN
- d)35.22kN
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The bearing is subjected to a radial load of 4000N. Expected life for 90% bearings is 9000h and shaft is rotating at 1500rpm. Calculate the dynamic load capacity.
a)
42.21kN
b)
37.29kN
c)
26.33kN
d)
35.22kN
|
|
Prateek Mukherjee answered |
Explanation: C=4000x(810)⅓.
The pressure’of a gas in terms of its mean kinetic energy per unit volume E is equal to
- a) E/3
- b) E/2
- c) 3E/4
- d) 2E/3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure’of a gas in terms of its mean kinetic energy per unit volume E is equal to
a)
E/3 b)
E/2c)
3E/4 d)
2E/3|
|
Neha Choudhury answered |
Pressure in terms of kinetic energy per unit volume:- The pressure of a gas is equal to two-third of kinetic energy per unit volume of the gas.
P = 2E/3
Moment of inertia of a circular section about an axis perpendicular to the section is- a)πd3/16
- b)πd3/32
- c)πd4/32
- d)πd4/64
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Moment of inertia of a circular section about an axis perpendicular to the section is
a)
πd3/16
b)
πd3/32
c)
πd4/32
d)
πd4/64

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
BY PERPENDICULAR AXIS THEOREM,
Izz = Ixx+Iyy.
So about x&y nd^4/64.
Izz = nd^4/64+nd^4/64.
= nd^4/32.
The more effective way of increasing the efficiency of a carnot engine is to- a)increase higher temperature
- b)decrease higher temperature
- c)increase lower temperature
- d)decrease lower temperature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The more effective way of increasing the efficiency of a carnot engine is to
a)
increase higher temperature
b)
decrease higher temperature
c)
increase lower temperature
d)
decrease lower temperature
|
|
Neha Choudhury answered |
From the Carnot Efficiency formula, it can be inferred that a maximum of 64% of the fuel energy can go to generation. To make the Carnot efficiency as high as possible, either Thot should be increased or Tcold (temperature of heat rejection) should be decreased.
According to the Clausiu’s statement of the second law:
1. heat flows from cold surface to hot surface, unaided.
2. heat flows from hot surface to cold surface, unaided.
3. heat can flow from cold surface to hot surface with the aid of external work.
Which of the above statement is /are correct ?- a)2 only
- b)1 and 3
- c)2 and 3
- d)3 only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the Clausiu’s statement of the second law:
1. heat flows from cold surface to hot surface, unaided.
2. heat flows from hot surface to cold surface, unaided.
3. heat can flow from cold surface to hot surface with the aid of external work.
Which of the above statement is /are correct ?
1. heat flows from cold surface to hot surface, unaided.
2. heat flows from hot surface to cold surface, unaided.
3. heat can flow from cold surface to hot surface with the aid of external work.
Which of the above statement is /are correct ?
a)
2 only
b)
1 and 3
c)
2 and 3
d)
3 only

|
Engineers Club answered |
Heat flows from hot to cold. ... It is important to emphasize that this statement of the 2nd law applies to the spontaneous flow of heat from hot to cold. It is possible, of course, to make a cool object in a warm place cooler - this is what a refrigerator does - but this involves the input of some external energy.
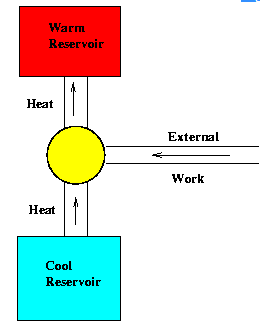

Moist air at a pressure of 100 kPa is compressed to 500 kPa and then cooled to 35°C in an aftercooler. The air at the entry to the aftercooler is unsaturated and becomes just saturated at the exit of the aftercooler. The saturation pressure of water at 35°C is 5.628 kPa. The partial pressure of water vapour (in kPa) in the moist air entering the compressor is closest to- a)0.57
- b)1.13
- c)2.26
- d)4.52
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Moist air at a pressure of 100 kPa is compressed to 500 kPa and then cooled to 35°C in an aftercooler. The air at the entry to the aftercooler is unsaturated and becomes just saturated at the exit of the aftercooler. The saturation pressure of water at 35°C is 5.628 kPa. The partial pressure of water vapour (in kPa) in the moist air entering the compressor is closest to
a)
0.57
b)
1.13
c)
2.26
d)
4.52
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Assuming that compression is isentropicin air compressors, the process can be described on the T - s diagram. The process in the intercooler is constant pressure
p2 = p3
But p2 = 5p1
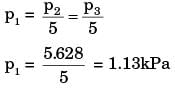
p2 = p3
But p2 = 5p1

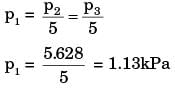
For flow of fluid over a heated plate , the following fluid properties are known: viscosity = 0.001 Pa.s; specific heat at constant pressure = 1 kJ/kgK; thermal conductivity = 1 W/mK.
The hydrodynamic boundary layer thickness at a specified location on the plate is 1 mm. The thermal boundary layer thickness at the same location is[2008] - a)0.001 mm
- b)0.01 mm
- c)1 mm
- d)1000 mm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For flow of fluid over a heated plate , the following fluid properties are known: viscosity = 0.001 Pa.s; specific heat at constant pressure = 1 kJ/kgK; thermal conductivity = 1 W/mK.
The hydrodynamic boundary layer thickness at a specified location on the plate is 1 mm. The thermal boundary layer thickness at the same location is
The hydrodynamic boundary layer thickness at a specified location on the plate is 1 mm. The thermal boundary layer thickness at the same location is
[2008]
a)
0.001 mm
b)
0.01 mm
c)
1 mm
d)
1000 mm
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Given:
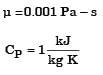
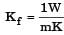 (Fluid thermal conductivity)
(Fluid thermal conductivity)
Hydrodynamic boundary layer thickness, δ = 1 mm
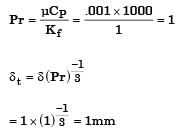
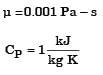
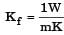 (Fluid thermal conductivity)
(Fluid thermal conductivity)Hydrodynamic boundary layer thickness, δ = 1 mm
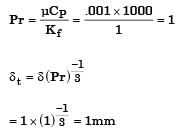
Two infinite parallel plates are placed at a certain distance apart. An infinite radiation shield is inserted between the plates without touching any of them to reduce heat exchange between the plates. Assume that the emissivities of plates and radiation shield are equal. The ratio of the net heat exchange between the plates with and without the shield is[2014]- a)1/2
- b)1/3
- c)1/4
- d)1/8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two infinite parallel plates are placed at a certain distance apart. An infinite radiation shield is inserted between the plates without touching any of them to reduce heat exchange between the plates. Assume that the emissivities of plates and radiation shield are equal. The ratio of the net heat exchange between the plates with and without the shield is
[2014]
a)
1/2
b)
1/3
c)
1/4
d)
1/8

|
Pioneer Academy answered |

here, n = 1
∴
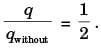
Degree of freedom of super structure is- a)less than zero
- b)zero
- c)less than one
- d)greater than one
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Degree of freedom of super structure is
a)
less than zero
b)
zero
c)
less than one
d)
greater than one
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
A superstructure has negative degree of freedom..0
The number of degree of freedom of a planar linkage with 8 links and 9 simple revolute joint is- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of degree of freedom of a planar linkage with 8 links and 9 simple revolute joint is
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Given l= 8, j= 9
We know that, Degree of freedom,
n =3(l − 1)−2j = 3(8 − 1)−2 x 9 = 3.
Round the clock cooling of an apartment having a load of 300 MJ/day requires and air conditioning plant of capacity about[1993]- a)1 ton
- b)5 tons
- c)10 tons
- d)100 tons
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Round the clock cooling of an apartment having a load of 300 MJ/day requires and air conditioning plant of capacity about
[1993]
a)
1 ton
b)
5 tons
c)
10 tons
d)
100 tons

|
Naroj Boda answered |
Capacity= Q . 300 MJ/day
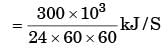
= 3.47 kW
1 ton = 3.5 kW
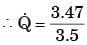
= 0.99 ton
= 1 ton
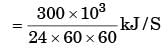
= 3.47 kW
1 ton = 3.5 kW
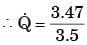
= 0.99 ton
= 1 ton
A small copper ball of 5 mm diameter at 500 K is dropped into an oil bath whose temperature is 300 K. The thermal conductivity of copper is 400 W/mK, its density 9000 kg/m3 and its specific heat 385 J/kgK. If the heat transfer coefficient is 250 W/m2K and lumped analysis is assumed to be valid, the rate of fall of the temperature of the ball at the beginning of cooling will be, in K/s,[2005]- a)8.7
- b)13.9
- c)17.3
- d)27.7
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A small copper ball of 5 mm diameter at 500 K is dropped into an oil bath whose temperature is 300 K. The thermal conductivity of copper is 400 W/mK, its density 9000 kg/m3 and its specific heat 385 J/kgK. If the heat transfer coefficient is 250 W/m2K and lumped analysis is assumed to be valid, the rate of fall of the temperature of the ball at the beginning of cooling will be, in K/s,
[2005]
a)
8.7
b)
13.9
c)
17.3
d)
27.7
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Given data
K = 400 W/mK; Ti = 500 K; ρ = 9000 Kg/m3.
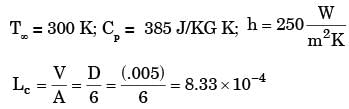
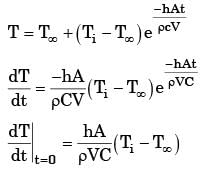
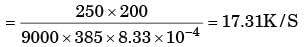
K = 400 W/mK; Ti = 500 K; ρ = 9000 Kg/m3.
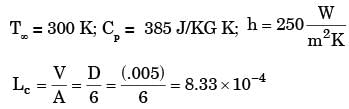
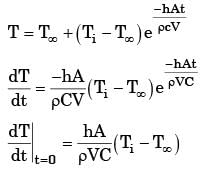
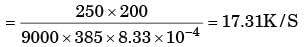
If five forces are acting on the single particle and having an angle of 72˚ between each and are collinear, then:- a)The net force acting on the body is zero and it is stable
- b)The net force acting on the body is horizontal
- c)The net force acting on the body is vertical
- d)The net force acting on the body is at an angle of 45
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If five forces are acting on the single particle and having an angle of 72˚ between each and are collinear, then:
a)
The net force acting on the body is zero and it is stable
b)
The net force acting on the body is horizontal
c)
The net force acting on the body is vertical
d)
The net force acting on the body is at an angle of 45
|
|
Disha Nambiar answered |
The net force acting on the body is zero. This means that the forces cancel out. This means that the body is in equilibrium and doesn’t need any of the external force to make itself in the equilibrium.
For a heat exchanger, ΔTmax is the maximum temperature difference and ΔTmin is the minimum temperature difference between the two fluids. LMTD is the log mean temperature difference. Cmin and Cmax are the minimum and the maximum heat capacity rates. The maximum possible heat transfer (Qmax) between the two fluids is[2014]- a)CminLMTD
- b)CminΔTmax
- c)CmaxΔTmax
- d)CmaxΔTmin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For a heat exchanger, ΔTmax is the maximum temperature difference and ΔTmin is the minimum temperature difference between the two fluids. LMTD is the log mean temperature difference. Cmin and Cmax are the minimum and the maximum heat capacity rates. The maximum possible heat transfer (Qmax) between the two fluids is
[2014]
a)
CminLMTD
b)
CminΔTmax
c)
CmaxΔTmax
d)
CmaxΔTmin
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
The temperature difference is not for a given fluid but across the fluids and maximum heat transfer occurs for Cmin and the temperature difference is equal to 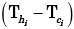 .
.
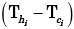 .
.If the resultant of two equal forces has the same magnitude as either of the forces, then the angle between the two forces is- a)30º
- b)60º
- c)90º
- d)120º
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the resultant of two equal forces has the same magnitude as either of the forces, then the angle between the two forces is
a)
30º
b)
60º
c)
90º
d)
120º

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
Law of Cosine- R^2=P^2+Q^2-2PQ Cosθ
So θ = 60degree
When Forces are Nose to tail, θ = 60degree
When Forces are Tail to Tail, θ = 180degree-60degree = 120degree
A 4-bar mechanism with all revolute pairs has link lengths lf = 20 mm, lin = 40 mm, lco = 50 mm and lout = 60 mm. The suffixes 'f, in', 'co' and 'out' denote the fixed link, the input link, the coupler and output link respectively. Which one of the following statements is true about the input and output links?[2014]- a)Both links can execute full circular motion
- b)Both links cannot execute full circular motion
- c)Only the output link cannot execute full circular motion
- d)Only the input link cannot execute full circular motion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A 4-bar mechanism with all revolute pairs has link lengths lf = 20 mm, lin = 40 mm, lco = 50 mm and lout = 60 mm. The suffixes 'f, in', 'co' and 'out' denote the fixed link, the input link, the coupler and output link respectively. Which one of the following statements is true about the input and output links?
[2014]
a)
Both links can execute full circular motion
b)
Both links cannot execute full circular motion
c)
Only the output link cannot execute full circular motion
d)
Only the input link cannot execute full circular motion
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
S + L < P + Q
20 + 60 < 40 + 50
⇒ 80 < 90
If smaller link is fixed both input and Output link execute full circular motion.
20 + 60 < 40 + 50
⇒ 80 < 90
If smaller link is fixed both input and Output link execute full circular motion.
As the temperature increases, the thermal conductivity of a gas[2014]- a)increases
- b)decreases
- c)remains constant
- d)increases up to a certain temperature and then decreases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
As the temperature increases, the thermal conductivity of a gas
[2014]
a)
increases
b)
decreases
c)
remains constant
d)
increases up to a certain temperature and then decreases
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
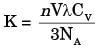
Where K is thermal conductivity
V is mean particle speed
λ is mean free path
CV is molar head capacity
NA is Avogadro's number
n is particles per unit volume
Gases transfer heat by direct collisions between molecules. As the temperature increases, the thermal conductivity increases due to increase in speed, movement and collisions in the molecules.
From the above expression, by increasing mean particle speed, the thermal conductivity increases.
A spherical steel ball of 12 mm diameter is initially at 1000 K. It is slowly cooled in a surrounding of 300 K. The heat transfer coefficient between the steel ball and the surroundings is 5 W/m2K. The thermal conductivity of steel is 20 W/mK. The ternperature difference between the centre and the surface of the steel ball is[2011]- a)large because conduction resistance is far higher than the convective resistance.
- b)large because conduction resistance is far less than the convective resistance.
- c)small because conduction resistance is far higher than the convective resistance.
- d)small because conduction resistance is far less than the convective resistance.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A spherical steel ball of 12 mm diameter is initially at 1000 K. It is slowly cooled in a surrounding of 300 K. The heat transfer coefficient between the steel ball and the surroundings is 5 W/m2K. The thermal conductivity of steel is 20 W/mK. The ternperature difference between the centre and the surface of the steel ball is
[2011]
a)
large because conduction resistance is far higher than the convective resistance.
b)
large because conduction resistance is far less than the convective resistance.
c)
small because conduction resistance is far higher than the convective resistance.
d)
small because conduction resistance is far less than the convective resistance.

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
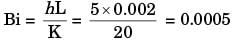
For the given condition, Biot number tends to zero, i.e. conduction resistance is far less than convection resistance. Therefore temperature between centre and surface is very small.
Biot number signifies[1991]- a)The ratio of heat conducted to heat convected
- b)The ratio of heat convected to heat conducted
- c)The ratio of external convective resistance to internal conductive resistance
- d)The ratio of internal conductive resistance to external convective resistance
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Biot number signifies
[1991]
a)
The ratio of heat conducted to heat convected
b)
The ratio of heat convected to heat conducted
c)
The ratio of external convective resistance to internal conductive resistance
d)
The ratio of internal conductive resistance to external convective resistance

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Biot number 

A thin cylinder with both ends closed is subjected to internal pressure p. The longitudinal stress atthe surface has been calculated as so. maximum shear stress at the surface will be equal to- a)2s0
- b)1.5s0
- c)s0
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A thin cylinder with both ends closed is subjected to internal pressure p. The longitudinal stress atthe surface has been calculated as so. maximum shear stress at the surface will be equal to
a)
2s0
b)
1.5s0
c)
s0
d)
None of these
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
Since, S0 is the longitudinal stress in a thin cylinder then 2S0 will be the hoop stress
Maximum (absolute) shear stress
=1/2(maximum principal stress)
=1/2(hoop stress)
=1/2(2S0)
=S0
The angle of inclination of a vehicle when moving along a circular path __________ upon its mass.- a)depends
- b)does not depend
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of inclination of a vehicle when moving along a circular path __________ upon its mass.
a)
depends
b)
does not depend
|
|
Ayush Chawla answered |
Angle of Inclination of a Vehicle on a Circular Path
The angle of inclination of a vehicle on a circular path is defined as the angle between the horizontal plane and the line passing through the center of gravity of the vehicle and the point of contact of the tire with the ground.
The angle of inclination is affected by various factors such as the speed of the vehicle, the radius of the circular path, the coefficient of friction between the tire and the ground, and the width of the tire.
Effect of Mass on Angle of Inclination
The mass of the vehicle does not affect the angle of inclination when moving along a circular path. This is because the gravitational force acting on the vehicle is perpendicular to the plane of the circular path, and hence does not affect the angle of inclination.
The angle of inclination is primarily determined by the lateral forces acting on the vehicle due to the centripetal acceleration. These lateral forces are a function of the speed of the vehicle, the radius of the circular path, and the coefficient of friction between the tire and the ground.
In fact, a heavier vehicle may actually have a smaller angle of inclination than a lighter vehicle when moving along the same circular path, since the heavier vehicle would have a greater tendency to resist lateral forces due to its greater inertia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mass of a vehicle does not affect the angle of inclination when moving along a circular path. The angle of inclination is primarily determined by the lateral forces acting on the vehicle due to the centripetal acceleration, which are a function of the speed of the vehicle, the radius of the circular path, and the coefficient of friction between the tire and the ground.
The angle of inclination of a vehicle on a circular path is defined as the angle between the horizontal plane and the line passing through the center of gravity of the vehicle and the point of contact of the tire with the ground.
The angle of inclination is affected by various factors such as the speed of the vehicle, the radius of the circular path, the coefficient of friction between the tire and the ground, and the width of the tire.
Effect of Mass on Angle of Inclination
The mass of the vehicle does not affect the angle of inclination when moving along a circular path. This is because the gravitational force acting on the vehicle is perpendicular to the plane of the circular path, and hence does not affect the angle of inclination.
The angle of inclination is primarily determined by the lateral forces acting on the vehicle due to the centripetal acceleration. These lateral forces are a function of the speed of the vehicle, the radius of the circular path, and the coefficient of friction between the tire and the ground.
In fact, a heavier vehicle may actually have a smaller angle of inclination than a lighter vehicle when moving along the same circular path, since the heavier vehicle would have a greater tendency to resist lateral forces due to its greater inertia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mass of a vehicle does not affect the angle of inclination when moving along a circular path. The angle of inclination is primarily determined by the lateral forces acting on the vehicle due to the centripetal acceleration, which are a function of the speed of the vehicle, the radius of the circular path, and the coefficient of friction between the tire and the ground.
The change in moment in shear stress diagrams is equal to _________- a)Rotational moment
- b)Bending moment
- c)Total weight
- d)Area under shear diagram
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The change in moment in shear stress diagrams is equal to _________
a)
Rotational moment
b)
Bending moment
c)
Total weight
d)
Area under shear diagram
|
|
Manoj Pillai answered |
After the application of the force equation of equilibrium to the segment of the beam, we have the above result. This is done on the very small part of the beam. That is the minimal section of the beam is to be considered and then the application of the equilibrium equations are done so as to calculate the final result.
Dew point temperature is the temperature at which condensation begins when the air is cooled at constant- a)volume
- b)entropy
- c)pressure
- d)enthalpy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dew point temperature is the temperature at which condensation begins when the air is cooled at constant
a)
volume
b)
entropy
c)
pressure
d)
enthalpy

|
Naroj Boda answered |
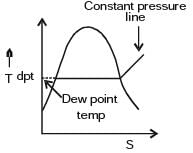
Air is cooled at constant pressure to make unsaturated air to saturated one.
A moist air sample has dry bulb temperature of 30°C and specific humidity of 11.5 g water vapour per kg dry air. Assume molecular weight of air as 28.93. If the saturation vapour pressure of water at 30°C is 4.24 kPa and the total pressure is 90 kPa, then the relative humidity (in %) of air sample is- a)50.5
- b)38.5
- c)56.5
- d)68.5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A moist air sample has dry bulb temperature of 30°C and specific humidity of 11.5 g water vapour per kg dry air. Assume molecular weight of air as 28.93. If the saturation vapour pressure of water at 30°C is 4.24 kPa and the total pressure is 90 kPa, then the relative humidity (in %) of air sample is
a)
50.5
b)
38.5
c)
56.5
d)
68.5
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Given : DBT = 30°C, w = 11.5 g/kg
∴ Relative humidity
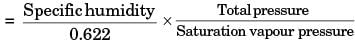
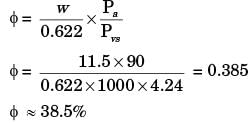
∴ Relative humidity
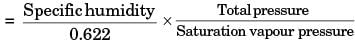
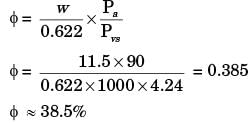
Atmospheric air at a flow rate of 3 kg/s (on dry basis) enters a cooling and dehumidifying coil with an enthalpy of 85 kJ/kg of dry air and a humidity ratio of 19 grams/kg of dry air. The air leaves the coil with an enthalpy of 43 kJ/kg of dry air and a humidity ratio of 8 grams/kg of dry air. If the condensate water leaves the coil with an enthalpy of 67 kJ/kg, the required cooling capacity of the coil in kW is- a)75.0
- b)123.8
- c)128.2
- d)159.0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Atmospheric air at a flow rate of 3 kg/s (on dry basis) enters a cooling and dehumidifying coil with an enthalpy of 85 kJ/kg of dry air and a humidity ratio of 19 grams/kg of dry air. The air leaves the coil with an enthalpy of 43 kJ/kg of dry air and a humidity ratio of 8 grams/kg of dry air. If the condensate water leaves the coil with an enthalpy of 67 kJ/kg, the required cooling capacity of the coil in kW is
a)
75.0
b)
123.8
c)
128.2
d)
159.0
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Mass flow rate of condensate,
mw = ma (w1 - w2 ) = 3 x (.019 - .008) = .033 kg/s
By applying energy balance equation we get
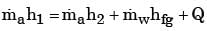
3×85 = 3×43 + 0.033×67 + Q
Q = 123.8 kW
mw = ma (w1 - w2 ) = 3 x (.019 - .008) = .033 kg/s
By applying energy balance equation we get
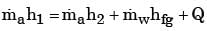
3×85 = 3×43 + 0.033×67 + Q
Q = 123.8 kW
In a condenser of a power plant, the steam condenses at a temperature of 60°C. The cooling water enters at 30°C and leaves at 45°C. The Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) of the condenser is[2011]- a)16.2°C
- b)21.6°C
- c)30°C
- d)37.5*C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
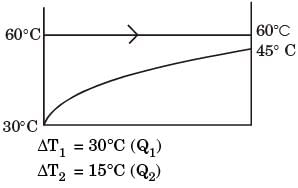
In a condenser of a power plant, the steam condenses at a temperature of 60°C. The cooling water enters at 30°C and leaves at 45°C. The Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) of the condenser is
[2011]
a)
16.2°C
b)
21.6°C
c)
30°C
d)
37.5*C

|
Naroj Boda answered |
Flow configuration in condenser as shown below.
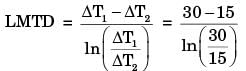
= 21.6° C

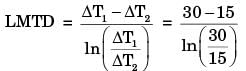
= 21.6° C
A pipe of 25 mm outer diameter carries steam. The heat transfer coefficient between the cylinder and surroundings is 5 W/m2K. It is proposed to reduce the heat loss from the pipe by adding insulation having a thermal conductivity of 0.05 W/mK. Which one of the following statements is TRUE?[2011]- a)The outer radius of the pipe is equal to the critical radius.
- b)The outer radius of the pipe is less than the critical radius.
- c)Adding the insulation will reduce the heat loss.
- d)Adding the insulation will increase the heat loss.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A pipe of 25 mm outer diameter carries steam. The heat transfer coefficient between the cylinder and surroundings is 5 W/m2K. It is proposed to reduce the heat loss from the pipe by adding insulation having a thermal conductivity of 0.05 W/mK. Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
[2011]
a)
The outer radius of the pipe is equal to the critical radius.
b)
The outer radius of the pipe is less than the critical radius.
c)
Adding the insulation will reduce the heat loss.
d)
Adding the insulation will increase the heat loss.
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Critical radius of insulation = (k/h)
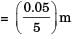 = 10mm
= 10mm
(router) > rcritical
Thus, adding insulation shall decrease H.T. Rate.
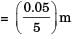 = 10mm
= 10mm(router) > rcritical
Thus, adding insulation shall decrease H.T. Rate.
A smooth cylinder lying on its convex surface remains in __________ equilibrium.- a)stable
- b)unstable
- c)neutral
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A smooth cylinder lying on its convex surface remains in __________ equilibrium.
a)
stable
b)
unstable
c)
neutral

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
Actually for justify stability we consider all possible way of cylinder and we see here it is kept on floor by means of convex surface so if we apply small disturbance then it will roll on the floor but if we kept it vertically on base then it will be stable so it is unstable.
The pressure, dry bulb temperature and relative humidity of air in a room are 1 bar, 30°C and 70%, respectively. If the saturated steam pressure at 30°C is 4.25 kPa, the specific humidity of the room air in kg of water vapour/kg dry air is- a)0.0083
- b)0.0101
- c)0.0191
- d)0.0232
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure, dry bulb temperature and relative humidity of air in a room are 1 bar, 30°C and 70%, respectively. If the saturated steam pressure at 30°C is 4.25 kPa, the specific humidity of the room air in kg of water vapour/kg dry air is
a)
0.0083
b)
0.0101
c)
0.0191
d)
0.0232

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
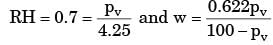
The slope of the shear diagram is equal to__________- a)Rotational moment
- b)Bending moment
- c)Total weight
- d)Distributed load intensity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The slope of the shear diagram is equal to__________
a)
Rotational moment
b)
Bending moment
c)
Total weight
d)
Distributed load intensity
|
|
Suyash Patel answered |
After the application of the force equation of equilibrium to the segment of the beam, we have the above result. This is done on the very small part of the beam. That is the minimal section of the beam is to be considered and then the application of the equilibrium equations are done so as to calculate the final result.
Lumped heat transfer analysis of a solid object suddenly exposed to a fluid medium at a different temp is valid when[2001]- a)Biot number < 0.1
- b)Biot number > 0.1
- c)Fourier number < 0.1
- d)Fourier number > 0.1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lumped heat transfer analysis of a solid object suddenly exposed to a fluid medium at a different temp is valid when
[2001]
a)
Biot number < 0.1
b)
Biot number > 0.1
c)
Fourier number < 0.1
d)
Fourier number > 0.1

|
Sahana Choudhary answered |
Is less than 0.1
b)Biot number is greater than 0.1
c)Fourier number is less than 0.1
d)Fourier number is greater than 0.1
The correct answer is b) Biot number is greater than 0.1.
The Biot number is a dimensionless number that represents the ratio of convective heat transfer to conductive heat transfer. It is defined as the product of the characteristic length (L) of the solid object and the convective heat transfer coefficient (h), divided by the thermal conductivity of the solid (k).
Bi = hL/k
In the lumped heat transfer analysis, it is assumed that the Biot number is greater than 0.1, meaning that the convective heat transfer is dominant compared to the conductive heat transfer. This assumption is valid when the solid object is relatively small or when the fluid medium has a high convective heat transfer coefficient.
Therefore, the lumped heat transfer analysis of a solid object suddenly exposed to a fluid medium at a different temperature is valid when the Biot number is greater than 0.1.
b)Biot number is greater than 0.1
c)Fourier number is less than 0.1
d)Fourier number is greater than 0.1
The correct answer is b) Biot number is greater than 0.1.
The Biot number is a dimensionless number that represents the ratio of convective heat transfer to conductive heat transfer. It is defined as the product of the characteristic length (L) of the solid object and the convective heat transfer coefficient (h), divided by the thermal conductivity of the solid (k).
Bi = hL/k
In the lumped heat transfer analysis, it is assumed that the Biot number is greater than 0.1, meaning that the convective heat transfer is dominant compared to the conductive heat transfer. This assumption is valid when the solid object is relatively small or when the fluid medium has a high convective heat transfer coefficient.
Therefore, the lumped heat transfer analysis of a solid object suddenly exposed to a fluid medium at a different temperature is valid when the Biot number is greater than 0.1.
If a car is moving forward, what is the direction of the moment of the moment caused by the rotation of the tires?- a)It is heading inwards, i.e. the direction is towards inside of the car
- b)It is heading outwards, i.e. the direction is towards outside of the car
- c)It is heading forward, i.e. the direction is towards the forward direction of the motion of the car
- d)It is heading backward, i.e. the direction is towards back side of the motion of the car
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a car is moving forward, what is the direction of the moment of the moment caused by the rotation of the tires?
a)
It is heading inwards, i.e. the direction is towards inside of the car
b)
It is heading outwards, i.e. the direction is towards outside of the car
c)
It is heading forward, i.e. the direction is towards the forward direction of the motion of the car
d)
It is heading backward, i.e. the direction is towards back side of the motion of the car

|
Navya Sarkar answered |
When you curl your wrist in the direction in which the tires are moving then you will find that the thumb is pointing outwards. That is outwards the body of the car. This phenomena is also observed in rainy seasons. When cars travel on the roads, the water is thrown outside from the tires, due to moment.
An instantaneous configuration of a four-bar mechanism, whose plane is horizontal, is shown in the figure below. At this instant, the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link O2A are ω = 8 rad/s and α = 0, respectively, and the driving torque (τ) is zero. The link O2A is balanced so that its centre of mass falls at O2.
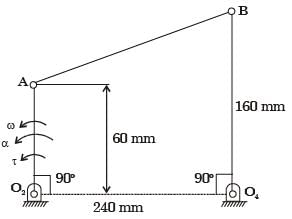 Which kind of 4-bar mechanism is O2ABO4?[2005]
Which kind of 4-bar mechanism is O2ABO4?[2005]- a)Double crank mechanism
- b)Crank-rocker mechanism
- c)Double rocker mechanism
- d)Parallelogram mechanism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An instantaneous configuration of a four-bar mechanism, whose plane is horizontal, is shown in the figure below. At this instant, the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link O2A are ω = 8 rad/s and α = 0, respectively, and the driving torque (τ) is zero. The link O2A is balanced so that its centre of mass falls at O2.


Which kind of 4-bar mechanism is O2ABO4?
[2005]
a)
Double crank mechanism
b)
Crank-rocker mechanism
c)
Double rocker mechanism
d)
Parallelogram mechanism
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
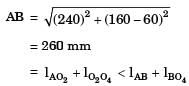
and O2O4 is fixed link. It will act as a crank-rocker mechanism
The coefficient of restitution for elastic bodies is one.- a)Correct
- b)Incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The coefficient of restitution for elastic bodies is one.
a)
Correct
b)
Incorrect

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
Coefficient of restitution for elastic bodies is 0 - 1.
Coefficient of restitution for perfect elastic bodies is 1.
An instantaneous configuration of a four-bar mechanism, whose plane is horizontal, is shown in the figure below. At this instant, the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link O2A are ω = 8 rad/s and α = 0, respectively, and the driving torque (τ) is zero. The link O2A is balanced so that its centre of mass falls at O2.
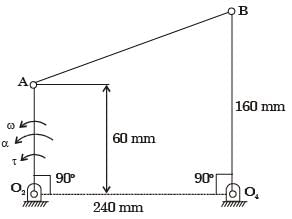 At the instant considered, what is the magnitude of the angular velocity of O4B?[2005]
At the instant considered, what is the magnitude of the angular velocity of O4B?[2005]- a)1 rad/s
- b)3 rad/s
- c)8 rad/s
- d)64/3 rad/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An instantaneous configuration of a four-bar mechanism, whose plane is horizontal, is shown in the figure below. At this instant, the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link O2A are ω = 8 rad/s and α = 0, respectively, and the driving torque (τ) is zero. The link O2A is balanced so that its centre of mass falls at O2.


At the instant considered, what is the magnitude of the angular velocity of O4B?
[2005]
a)
1 rad/s
b)
3 rad/s
c)
8 rad/s
d)
64/3 rad/s

|
Gate Funda answered |
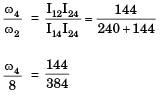
∴
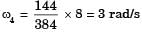
For air at a given temperature, as the relative humidity is increased isothermally,- a)the wet bulb temperature and specific enthalpy increase
- b)the wet bulb temperature and specific enthalpy decrease
- c)the wet bulb temperature increases and specific enthalpy decreases
- d)the wet bulb temperature decreases and specific enthalpy increases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For air at a given temperature, as the relative humidity is increased isothermally,
a)
the wet bulb temperature and specific enthalpy increase
b)
the wet bulb temperature and specific enthalpy decrease
c)
the wet bulb temperature increases and specific enthalpy decreases
d)
the wet bulb temperature decreases and specific enthalpy increases

|
Anshu Kumar answered |
Answer:
To understand why the correct answer is option 'A', let's break down the relationship between relative humidity, wet bulb temperature, and specific enthalpy.
Relative Humidity:
Relative humidity is a measure of the amount of moisture in the air compared to the maximum amount it can hold at a given temperature. It is expressed as a percentage. As the relative humidity increases, the air becomes more saturated with moisture.
Wet Bulb Temperature:
The wet bulb temperature is the temperature recorded by a thermometer that has its bulb covered with a wet cloth and exposed to moving air. It is a measure of the cooling effect due to evaporation. When the air is dry, the wet bulb temperature is lower than the dry bulb temperature. As the air becomes more saturated with moisture, the wet bulb temperature approaches the dry bulb temperature.
Specific Enthalpy:
Specific enthalpy is a measure of the total energy contained in a unit mass of air. It takes into account the internal energy of the air, as well as the energy associated with its pressure and volume. It is usually expressed in units of energy per unit mass (e.g., kJ/kg).
Relationship between Relative Humidity, Wet Bulb Temperature, and Specific Enthalpy:
1. As the relative humidity increases, the air becomes more saturated with moisture. This means that the air is already holding a significant amount of moisture.
2. When the air is holding more moisture, the cooling effect due to evaporation (wet bulb temperature) becomes less pronounced because there is less room for additional evaporation.
3. Therefore, as the relative humidity increases, the wet bulb temperature increases because less cooling is taking place.
4. The specific enthalpy of the air is directly related to its temperature. As the wet bulb temperature increases, so does the specific enthalpy.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, we can conclude that as the relative humidity is increased isothermally, both the wet bulb temperature and specific enthalpy of the air increase. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.
To understand why the correct answer is option 'A', let's break down the relationship between relative humidity, wet bulb temperature, and specific enthalpy.
Relative Humidity:
Relative humidity is a measure of the amount of moisture in the air compared to the maximum amount it can hold at a given temperature. It is expressed as a percentage. As the relative humidity increases, the air becomes more saturated with moisture.
Wet Bulb Temperature:
The wet bulb temperature is the temperature recorded by a thermometer that has its bulb covered with a wet cloth and exposed to moving air. It is a measure of the cooling effect due to evaporation. When the air is dry, the wet bulb temperature is lower than the dry bulb temperature. As the air becomes more saturated with moisture, the wet bulb temperature approaches the dry bulb temperature.
Specific Enthalpy:
Specific enthalpy is a measure of the total energy contained in a unit mass of air. It takes into account the internal energy of the air, as well as the energy associated with its pressure and volume. It is usually expressed in units of energy per unit mass (e.g., kJ/kg).
Relationship between Relative Humidity, Wet Bulb Temperature, and Specific Enthalpy:
1. As the relative humidity increases, the air becomes more saturated with moisture. This means that the air is already holding a significant amount of moisture.
2. When the air is holding more moisture, the cooling effect due to evaporation (wet bulb temperature) becomes less pronounced because there is less room for additional evaporation.
3. Therefore, as the relative humidity increases, the wet bulb temperature increases because less cooling is taking place.
4. The specific enthalpy of the air is directly related to its temperature. As the wet bulb temperature increases, so does the specific enthalpy.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, we can conclude that as the relative humidity is increased isothermally, both the wet bulb temperature and specific enthalpy of the air increase. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.
The number of degrees of freedom of a planar linkage with 8 links and 9 simple revolute joints is[2019]- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of degrees of freedom of a planar linkage with 8 links and 9 simple revolute joints is
[2019]
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Number of degree of freedom,
n =3(l – 1) – 2j – h
= (3 × 7) – (2 × 9) – 0 = 3
n =3(l – 1) – 2j – h
= (3 × 7) – (2 × 9) – 0 = 3
The state of plane stress at a point in a loaded member is given by:sx = + 800 MPasy = + 200 MPatxy = ± 400 MPaThe maximum principal stress and maximum shear stress are given by:- a)smax = 800 MPa and tmax = 400 MPa
- b)smax = 800 MPa and tmax = 500 MPa
- c)smax = 1000 MPa and tmax = 500 MPa
- d)smax = 1000 MPa and tmax = 400 MPa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The state of plane stress at a point in a loaded member is given by:
sx = + 800 MPa
sy = + 200 MPa
txy = ± 400 MPa
The maximum principal stress and maximum shear stress are given by:
a)
smax = 800 MPa and tmax = 400 MPa
b)
smax = 800 MPa and tmax = 500 MPa
c)
smax = 1000 MPa and tmax = 500 MPa
d)
smax = 1000 MPa and tmax = 400 MPa
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Water (Prandtl number = 6) flows over a flat plate which is heated over the entire length. Which one of the following relationship between the hydrodynamic boundary layer thickness (δ) and thermal boundary layer thickness (δt) is true[2001]- a)δt = δ
- b)δt < δ
- c)δt > δ
- d)Can not be predicted
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water (Prandtl number = 6) flows over a flat plate which is heated over the entire length. Which one of the following relationship between the hydrodynamic boundary layer thickness (δ) and thermal boundary layer thickness (δt) is true
[2001]
a)
δt = δ
b)
δt < δ
c)
δt > δ
d)
Can not be predicted
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
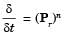
Here, Pr = 6 > 1
or
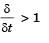
∴ δ > δt
In a counter flow heat exchanger, for the hot fluid the heat capacity = 2 kJ/kgK, mass flow rate = 5 kg/s, inlet temperature = 150°C, outlet temperature = 100°C. For the cold fluid, heat capacity = 4 kJ/kg K, mass flow rate = 10 kg/s, inlet temperature = 20°C. Neglecting heat transfer to the surroundings, the outlet temperature of the cold fluid in °C is[1994]- a)7.5
- b)32.5
- c)45.5
- d)70.0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a counter flow heat exchanger, for the hot fluid the heat capacity = 2 kJ/kgK, mass flow rate = 5 kg/s, inlet temperature = 150°C, outlet temperature = 100°C. For the cold fluid, heat capacity = 4 kJ/kg K, mass flow rate = 10 kg/s, inlet temperature = 20°C. Neglecting heat transfer to the surroundings, the outlet temperature of the cold fluid in °C is
[1994]
a)
7.5
b)
32.5
c)
45.5
d)
70.0
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Heat lost by fluid = Heat gained by cold fluid
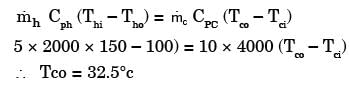
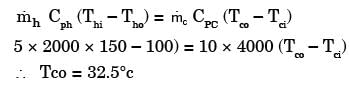
Chapter doubts & questions for Tests - Additional Study Material for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Tests - Additional Study Material for Mechanical Engineering in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Additional Study Material for Mechanical Engineering
1 videos|30 docs|57 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup