All Exams >
NEET >
NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions >
All Questions
All questions of Photosynthesis in Higher Plants for NEET Exam
In comparison to C3 cycle, the number of extra ATP molecules required in C4 cycle is- a)12
- b)18
- c)36
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In comparison to C3 cycle, the number of extra ATP molecules required in C4 cycle is
a)
12
b)
18
c)
36
d)
6

|
Stepway Academy answered |
It takes 12 more ATPs than C3 cycle to replenish this PEP because additional 2 ATPs are needed for every CO2 molecule fixed.
Which of the following products of the light reaction are subsequently used during the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis?- a)Electrons and photons
- b)Water and carbon
- c)ATP and NADPH
- d)Carbon dioxide and RuBP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following products of the light reaction are subsequently used during the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis?
a)
Electrons and photons
b)
Water and carbon
c)
ATP and NADPH
d)
Carbon dioxide and RuBP
|
|
Anoushka Dasgupta answered |
ATP and NADPH:
The products of the light reaction - ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) - are subsequently used during the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis, also known as the Calvin cycle.
ATP:
- ATP is a molecule that stores and transfers energy within cells.
- During the light reaction, ATP is produced through the process of photophosphorylation, where light energy is used to add a phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), forming ATP.
- In the Calvin cycle, ATP is utilized to drive the various chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide into glucose, a process known as carbon fixation.
NADPH:
- NADPH is a coenzyme that acts as a reducing agent in many anabolic reactions, including photosynthesis.
- In the light reaction, NADPH is produced by transferring electrons from water molecules to NADP+, forming NADPH.
- During the Calvin cycle, NADPH plays a crucial role in providing reducing power for the synthesis of carbohydrates from carbon dioxide.
Overall:
- ATP and NADPH, generated during the light reaction, are essential for powering the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide is converted into carbohydrates with the help of these energy-rich molecules.
- Without the ATP and NADPH generated in the light reaction, the Calvin cycle would not be able to proceed efficiently, highlighting the interconnected nature of the two phases of photosynthesis.
The products of the light reaction - ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) - are subsequently used during the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis, also known as the Calvin cycle.
ATP:
- ATP is a molecule that stores and transfers energy within cells.
- During the light reaction, ATP is produced through the process of photophosphorylation, where light energy is used to add a phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), forming ATP.
- In the Calvin cycle, ATP is utilized to drive the various chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide into glucose, a process known as carbon fixation.
NADPH:
- NADPH is a coenzyme that acts as a reducing agent in many anabolic reactions, including photosynthesis.
- In the light reaction, NADPH is produced by transferring electrons from water molecules to NADP+, forming NADPH.
- During the Calvin cycle, NADPH plays a crucial role in providing reducing power for the synthesis of carbohydrates from carbon dioxide.
Overall:
- ATP and NADPH, generated during the light reaction, are essential for powering the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide is converted into carbohydrates with the help of these energy-rich molecules.
- Without the ATP and NADPH generated in the light reaction, the Calvin cycle would not be able to proceed efficiently, highlighting the interconnected nature of the two phases of photosynthesis.
Read the following statement and select the correct ones.
(i) PS I is involved in non-cyclic photophosphorylation only.
(ii) PS II is involved in both cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
(iii) Stroma lamellae membranes possess PS I only, whereas grana lamellae membranes possess both PS I and PS II. - a)(i) only
- b)(ii) only
- c)(iii) only
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statement and select the correct ones.
(i) PS I is involved in non-cyclic photophosphorylation only.
(ii) PS II is involved in both cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
(iii) Stroma lamellae membranes possess PS I only, whereas grana lamellae membranes possess both PS I and PS II.
(i) PS I is involved in non-cyclic photophosphorylation only.
(ii) PS II is involved in both cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
(iii) Stroma lamellae membranes possess PS I only, whereas grana lamellae membranes possess both PS I and PS II.
a)
(i) only
b)
(ii) only
c)
(iii) only
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
PSI is involved in both cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation PS II is involved only in non-cyclic photophosphorylation PS II is present in the aprressed (inner) part of grana thylakoids, PS I is located in the non-appressed (outer) part of grana thylakoids as well as stroma thylakoids
Select the incorrect statement as far as kranz anatomy is concerned.- a)Undifferentiated mesophyll occurs in concentric layers around vascular bundles
- b)Centrifugal chloroplasts are present in bundle sheath cells
- c)Large sized bundle sheath cells are arranged in a wreath-like manner in one to several layers
- d)Chloroplasts of bundle sheath cells possess well- developed grana lamellae
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statement as far as kranz anatomy is concerned.
a)
Undifferentiated mesophyll occurs in concentric layers around vascular bundles
b)
Centrifugal chloroplasts are present in bundle sheath cells
c)
Large sized bundle sheath cells are arranged in a wreath-like manner in one to several layers
d)
Chloroplasts of bundle sheath cells possess well- developed grana lamellae
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Kranz anatomy is a characteristic of C4 plants. In kranz anatomy, the mesophyll is undifferentiated and its cells occur in concentric layers around vascular bundles. Vascular which are surrounded by large-sized bundle sheath cells which are arranged in a wreath like a manner in one to several layers. The chloroplasts of mesophyll cells are smaller, they have well-developed grana and a peripheral reticulum but no starch. Mesophyll cells possess enzyme PEP case for initial fixation of CO2. The chloroplasts of the bundle sheath cells are agranal. They possess a peripheral reticulum and starch grains. Bundle sheath cells possess enzyme RuBisCO.
Photochemical phase does not include - a)Light absorption
- b)Water splitting and O2 release
- c)ATP and NADPH formation
- d)CO2 fixation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Photochemical phase does not include
a)
Light absorption
b)
Water splitting and O2 release
c)
ATP and NADPH formation
d)
CO2 fixation
|
|
Anoushka Kaur answered |
Introduction:
The photochemical phase, also known as the light-dependent reactions or the light reactions, is the first stage of photosynthesis. It takes place in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts and involves the absorption of light energy, the splitting of water molecules, the release of oxygen, and the formation of ATP and NADPH. However, it does not include the process of carbon dioxide fixation.
Explanation:
The photochemical phase can be divided into two main processes: the non-cyclic photophosphorylation and the cyclic photophosphorylation.
1. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation:
- The process begins with the absorption of light energy by pigments, such as chlorophyll, in the thylakoid membrane.
- This light energy is transferred to the reaction center, where it excites an electron.
- The excited electron is then passed through a series of electron carriers, creating an electron transport chain.
- As the electron moves down the electron transport chain, it releases energy, which is used to pump protons (H+) across the thylakoid membrane, creating a proton gradient.
- The protons then flow back through ATP synthase, an enzyme embedded in the membrane, which uses the energy from the proton flow to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. This process is called photophosphorylation.
- Simultaneously, water molecules are split by an enzyme called water-splitting complex, releasing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions.
- The hydrogen ions are transported across the thylakoid membrane and are later used in the formation of NADPH.
2. Cyclic photophosphorylation:
- In certain conditions, such as when there is a shortage of NADP+ or a high concentration of NADPH, an alternative pathway called cyclic photophosphorylation occurs.
- In this process, the excited electron from the reaction center is returned to the same pigment molecule, rather than being passed to NADP+.
- The electron is then recycled through the electron transport chain, generating ATP through photophosphorylation without the production of NADPH or oxygen.
Role of the photochemical phase:
- The photochemical phase is essential for capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
- ATP is the primary energy currency of cells, while NADPH is a reducing agent used in the subsequent dark reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle or the light-independent reactions) to fix carbon dioxide and produce glucose.
- The oxygen released during the photochemical phase is a byproduct and is important for aerobic respiration in organisms that consume oxygen.
Conclusion:
In summary, the photochemical phase of photosynthesis includes processes such as light absorption, water splitting, oxygen release, ATP formation through photophosphorylation, and NADPH formation. However, it does not include the process of carbon dioxide fixation, which occurs in the subsequent dark reactions.
The photochemical phase, also known as the light-dependent reactions or the light reactions, is the first stage of photosynthesis. It takes place in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts and involves the absorption of light energy, the splitting of water molecules, the release of oxygen, and the formation of ATP and NADPH. However, it does not include the process of carbon dioxide fixation.
Explanation:
The photochemical phase can be divided into two main processes: the non-cyclic photophosphorylation and the cyclic photophosphorylation.
1. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation:
- The process begins with the absorption of light energy by pigments, such as chlorophyll, in the thylakoid membrane.
- This light energy is transferred to the reaction center, where it excites an electron.
- The excited electron is then passed through a series of electron carriers, creating an electron transport chain.
- As the electron moves down the electron transport chain, it releases energy, which is used to pump protons (H+) across the thylakoid membrane, creating a proton gradient.
- The protons then flow back through ATP synthase, an enzyme embedded in the membrane, which uses the energy from the proton flow to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. This process is called photophosphorylation.
- Simultaneously, water molecules are split by an enzyme called water-splitting complex, releasing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions.
- The hydrogen ions are transported across the thylakoid membrane and are later used in the formation of NADPH.
2. Cyclic photophosphorylation:
- In certain conditions, such as when there is a shortage of NADP+ or a high concentration of NADPH, an alternative pathway called cyclic photophosphorylation occurs.
- In this process, the excited electron from the reaction center is returned to the same pigment molecule, rather than being passed to NADP+.
- The electron is then recycled through the electron transport chain, generating ATP through photophosphorylation without the production of NADPH or oxygen.
Role of the photochemical phase:
- The photochemical phase is essential for capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
- ATP is the primary energy currency of cells, while NADPH is a reducing agent used in the subsequent dark reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle or the light-independent reactions) to fix carbon dioxide and produce glucose.
- The oxygen released during the photochemical phase is a byproduct and is important for aerobic respiration in organisms that consume oxygen.
Conclusion:
In summary, the photochemical phase of photosynthesis includes processes such as light absorption, water splitting, oxygen release, ATP formation through photophosphorylation, and NADPH formation. However, it does not include the process of carbon dioxide fixation, which occurs in the subsequent dark reactions.
Which of the following statements are true about photosynthesis?A. In this process, solar energy is converted into chemical energy.
B. In photosynthesis, CO2 and H2O are used.
C. In photosynthesis, CO2 is released and O2 is consumed.
D. In photosynthesis, O2 is released and carbon monoxide is consumed.- a)A and B
- b)B and C
- c)C and D
- d)A and D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are true about photosynthesis?
A. In this process, solar energy is converted into chemical energy.
B. In photosynthesis, CO2 and H2O are used.
C. In photosynthesis, CO2 is released and O2 is consumed.
D. In photosynthesis, O2 is released and carbon monoxide is consumed.
B. In photosynthesis, CO2 and H2O are used.
C. In photosynthesis, CO2 is released and O2 is consumed.
D. In photosynthesis, O2 is released and carbon monoxide is consumed.
a)
A and B
b)
B and C
c)
C and D
d)
A and D

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Both statements (A) and (B) are correct about photosynthesis reaction.
A. In this process, solar energy is converted into chemical energy.
B. In photosynthesis, CO2 and H2O are used to give glucose and oxygen in the presence of sunlight with the help of green pigment chlorophyll.
A. In this process, solar energy is converted into chemical energy.
B. In photosynthesis, CO2 and H2O are used to give glucose and oxygen in the presence of sunlight with the help of green pigment chlorophyll.
Optimum temperature conditions for photosynthesis in C3 and C4 plants are respectively- a)10∘C−25∘C and 30∘C−45∘C
- b)30∘C−45∘C and 10∘C−25∘C
- c)0∘C−10∘C and 10∘C−30∘C
- d)25∘C−30∘C and 40∘C−50∘C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Optimum temperature conditions for photosynthesis in C3 and C4 plants are respectively
a)
10∘C−25∘C and 30∘C−45∘C
b)
30∘C−45∘C and 10∘C−25∘C
c)
0∘C−10∘C and 10∘C−30∘C
d)
25∘C−30∘C and 40∘C−50∘C
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The Optimum temperature Is 10∘C−25∘C for C3, plants and 30°C-45°C for C4 plants.
Who, after conducting experiments on purple and green sulfur bacteria, inferred that O2 evolved during photosynthesis comes from H2O not from CO2?- a)Sachs
- b)Engelmann
- c)van Niel
- d)Blackmann
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who, after conducting experiments on purple and green sulfur bacteria, inferred that O2 evolved during photosynthesis comes from H2O not from CO2?
a)
Sachs
b)
Engelmann
c)
van Niel
d)
Blackmann
|
|
Niti Das answered |
Introduction
The discovery regarding the source of oxygen produced during photosynthesis was significantly advanced by the experiments conducted by van Niel on purple and green sulfur bacteria.
Van Niel's Hypothesis
- Van Niel proposed the revolutionary idea that the oxygen released during photosynthesis originates from water (H2O) rather than carbon dioxide (CO2).
- His experiments with purple and green sulfur bacteria demonstrated that these organisms could utilize hydrogen sulfide (H2S) instead of water, producing sulfur instead of oxygen. This indicated that the splitting of water molecules was the source of O2 in photosynthesis.
Experimental Evidence
- Van Niel's work involved tracing the fate of oxygen isotopes in photosynthetic organisms, which reinforced the idea that water is the source of the released oxygen gas.
- By utilizing different isotopes of oxygen, he could confirm that the O2 released came from water molecules, changing the understanding of photosynthesis fundamentally.
Impact on Photosynthesis Understanding
- Prior to van Niel, the prevailing theory suggested that oxygen came from carbon dioxide. His findings shifted this paradigm, leading to the modern understanding of photosynthesis in plants.
- This discovery laid the groundwork for later research, including the elucidation of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Conclusion
Van Niel's experiments were critical in establishing the origin of oxygen in photosynthesis, marking a pivotal moment in biological and ecological research. His insights remain integral to our understanding of how photosynthetic organisms function.
The discovery regarding the source of oxygen produced during photosynthesis was significantly advanced by the experiments conducted by van Niel on purple and green sulfur bacteria.
Van Niel's Hypothesis
- Van Niel proposed the revolutionary idea that the oxygen released during photosynthesis originates from water (H2O) rather than carbon dioxide (CO2).
- His experiments with purple and green sulfur bacteria demonstrated that these organisms could utilize hydrogen sulfide (H2S) instead of water, producing sulfur instead of oxygen. This indicated that the splitting of water molecules was the source of O2 in photosynthesis.
Experimental Evidence
- Van Niel's work involved tracing the fate of oxygen isotopes in photosynthetic organisms, which reinforced the idea that water is the source of the released oxygen gas.
- By utilizing different isotopes of oxygen, he could confirm that the O2 released came from water molecules, changing the understanding of photosynthesis fundamentally.
Impact on Photosynthesis Understanding
- Prior to van Niel, the prevailing theory suggested that oxygen came from carbon dioxide. His findings shifted this paradigm, leading to the modern understanding of photosynthesis in plants.
- This discovery laid the groundwork for later research, including the elucidation of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Conclusion
Van Niel's experiments were critical in establishing the origin of oxygen in photosynthesis, marking a pivotal moment in biological and ecological research. His insights remain integral to our understanding of how photosynthetic organisms function.
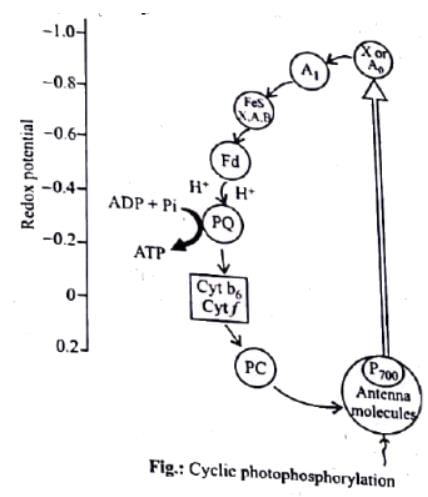
In cyclic photophosphorylation, the electron released by reaction centre (P700) is ultimately accepted by- a)Ferredoxin
- b)NADP+
- c)Reaction centre (P700)
- d)Plastocyanin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In cyclic photophosphorylation, the electron released by reaction centre (P700) is ultimately accepted by
a)
Ferredoxin
b)
NADP+
c)
Reaction centre (P700)
d)
Plastocyanin
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In cyclic photophosphorylation, an electron expelled by the excited photocentre (P700) is returned to it after passing through a series of electron carriers. Its photocentre P700 extrudes an electron with a gain of 23kcal/mole of energy after absorbing a photon of light (hv). After losing the electron the photocentre becomes oxidised. The expelled electron passes through a series of carriers including X or A0 (a special P700 chlorophyll molecule), A1, (a quinone), FeS complexes (FeSx,FeSA,FeSB), ferredoxin (Fd), plastoquinone (PQ), cytochrome b−f complex and plastocyanin (PC) before returning to photocentre. While over the cytochrome complex, the electron energises passage of protons to create a proton gradient for synthesis of ATP form ADP and inorganic phosphate.
The enzyme RuBisCO has _________.- a)more affinity for CO2, than for O2
- b)more affinity for O2, than for CO2
- c)equal affinity for both
- d)more affinity for sugars, than for CO2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme RuBisCO has _________.
a)
more affinity for CO2, than for O2
b)
more affinity for O2, than for CO2
c)
equal affinity for both
d)
more affinity for sugars, than for CO2
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The active site of RuBisCO for carboxylation and oxygenation is the same. The enzyme has more affinity for CO2 as compared to oxygen. Active oxygenation occurs only when CO2:O2 ratio favours it. At hight temperature, concentration of dissolved CO2 in equilibrium with air decreases more than concentration of O2, which favours oxygenation, High temperature occurs in tropical areas. Therefore, tropical plants are the major sufferers. At high temperature, RuBisCo functions as oxygenase and instead of fixing CO, oxidizes RuBP to produce a 3-C phosphoglyceric acid and a 2-C phosphoglycolate. This is the first reaction of photorespiration or C2 cycle.
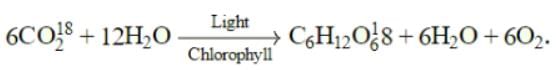
Which one of the following equations suggests that O2 released during photosynthesis comes from water?- a)6CO218+12H2O→6O218+C6H12O6+6H2O18
- b)6CO2+12H2O18→6O2+C6H12O6+6H2O18
- c)6CO218+12H2O→6O218+C6H12O6+6H2O
- d)6CO2+12H2O18→6O218+C6H12O6+6H2O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following equations suggests that O2 released during photosynthesis comes from water?
a)
6CO218+12H2O→6O218+C6H12O6+6H2O18
b)
6CO2+12H2O18→6O2+C6H12O6+6H2O18
c)
6CO218+12H2O→6O218+C6H12O6+6H2O
d)
6CO2+12H2O18→6O218+C6H12O6+6H2O
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Ruben and Kamen (1941), while working on chlorella (unicellular green alga ) found that oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from water.
(i) When normal H2O radioactive CO2(i.e.CO218) were used, normal O2 is evolved.
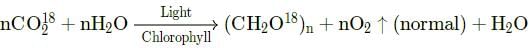
(ii) When normal CO2 radioactive H2O(i.e.H2O18) were used, radioactive O2 (i.e.O218) is evolved.
nCO2+nH2O18→(CH2O)n+O218↑ (radioactive oxygen)+H2O
So the correct option is 'D'.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Crassulacean acid metabolism occurs in succulent plants which grow in xeric conditions.
Statement 2 : Stomata are generally sunken in succulent plants.
- a)Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct.
- b)Both statements are correct
- c)Statement 1 s correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statement are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Crassulacean acid metabolism occurs in succulent plants which grow in xeric conditions.
Statement 2 : Stomata are generally sunken in succulent plants.
Statement 1 : Crassulacean acid metabolism occurs in succulent plants which grow in xeric conditions.
Statement 2 : Stomata are generally sunken in succulent plants.
a)
Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct.
b)
Both statements are correct
c)
Statement 1 s correct but statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statement are incorrect.
|
|
Krithika Kumar answered |
Statement 1: Crassulacean acid metabolism occurs in succulent plants which grow in xeric conditions.
Statement 2: Stomata are generally sunken in succulent plants.
Explanation:
Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM):
- Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) is a specialized type of photosynthesis that has evolved in succulent plants as an adaptation to xeric (dry) conditions.
- In xeric conditions, water availability is limited, and plants need to conserve water to survive.
- CAM plants, such as cacti and agave, have developed a unique mechanism to minimize water loss while still carrying out photosynthesis.
Stomata in Succulent Plants:
- Stomata are tiny openings found on the surface of leaves and stems that enable the exchange of gases (such as carbon dioxide and oxygen) between the plant and the environment.
- In succulent plants, which are adapted to xeric conditions, the stomata are generally sunken.
- The sunken stomata are located in pits or depressions on the leaf surface, which helps to reduce water loss through evaporation.
- The sunken stomata create a small microclimate that traps moist air and reduces transpiration, thus minimizing water loss.
Explanation of the Statements:
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
- Statement 1 correctly states that Crassulacean acid metabolism occurs in succulent plants that grow in xeric conditions.
- Statement 2 correctly states that stomata are generally sunken in succulent plants.
- However, statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1. The sunken stomata in succulent plants are an adaptation to reduce water loss, but they are not directly related to the occurrence of Crassulacean acid metabolism.
Conclusion:
- The correct option is option B: Both statements 1 and 2 are correct, but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- Crassulacean acid metabolism is an adaptation in succulent plants to xeric conditions, while sunken stomata are an adaptation to reduce water loss in succulent plants.
Statement 2: Stomata are generally sunken in succulent plants.
Explanation:
Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM):
- Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) is a specialized type of photosynthesis that has evolved in succulent plants as an adaptation to xeric (dry) conditions.
- In xeric conditions, water availability is limited, and plants need to conserve water to survive.
- CAM plants, such as cacti and agave, have developed a unique mechanism to minimize water loss while still carrying out photosynthesis.
Stomata in Succulent Plants:
- Stomata are tiny openings found on the surface of leaves and stems that enable the exchange of gases (such as carbon dioxide and oxygen) between the plant and the environment.
- In succulent plants, which are adapted to xeric conditions, the stomata are generally sunken.
- The sunken stomata are located in pits or depressions on the leaf surface, which helps to reduce water loss through evaporation.
- The sunken stomata create a small microclimate that traps moist air and reduces transpiration, thus minimizing water loss.
Explanation of the Statements:
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
- Statement 1 correctly states that Crassulacean acid metabolism occurs in succulent plants that grow in xeric conditions.
- Statement 2 correctly states that stomata are generally sunken in succulent plants.
- However, statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1. The sunken stomata in succulent plants are an adaptation to reduce water loss, but they are not directly related to the occurrence of Crassulacean acid metabolism.
Conclusion:
- The correct option is option B: Both statements 1 and 2 are correct, but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- Crassulacean acid metabolism is an adaptation in succulent plants to xeric conditions, while sunken stomata are an adaptation to reduce water loss in succulent plants.
The biochemical objective of PS I is to - a)Oxidise NADPH
- b)Hydrolyse ATP
- c)Phosphorylate ADP
- d)Reduce NADP+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The biochemical objective of PS I is to
a)
Oxidise NADPH
b)
Hydrolyse ATP
c)
Phosphorylate ADP
d)
Reduce NADP+
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
During Z- scheme, the electron extrucded by PS I passes through special chlorophyll X, Fe-S, ferredoxin, to finally reach NADP+,NADP+ is ultimately reduced by combining with H+ (released during photolysis) with the help of NADP+ reductase enzyme.
Which of the below statements is/are not correct regarding chlorophyll a molecule?(i) Molecule formula of chl a is C55H72O5N4Mg
(ii) It is the primary photosynthetic pigment.
(iii) In the pure state, it is red in colour and thus it absorbs more blue wavelength of light than the red wavelength.
(iv) It is a soluble in water as well as petroleum ether.- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(ii) only
- d)(iv) only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the below statements is/are not correct regarding chlorophyll a molecule?
(i) Molecule formula of chl a is C55H72O5N4Mg
(ii) It is the primary photosynthetic pigment.
(iii) In the pure state, it is red in colour and thus it absorbs more blue wavelength of light than the red wavelength.
(iv) It is a soluble in water as well as petroleum ether.
(ii) It is the primary photosynthetic pigment.
(iii) In the pure state, it is red in colour and thus it absorbs more blue wavelength of light than the red wavelength.
(iv) It is a soluble in water as well as petroleum ether.
a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(ii) only
d)
(iv) only
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Chlorophyll a is the primary photosynthetic pigment, which is bluish green in the pure state. It has an empirical formula C55H72O5N4 Mgand molecular weight of 893. It absorbs more red wavelength of light than violet blue . It is soluble in a number of organic solvents such as petroleum ether.
Which organelle out of these does not participate in photorespiration?- a)Peroxisomes
- b)Mitochondria
- c)Chloroplasts
- d)Golgi bodies
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which organelle out of these does not participate in photorespiration?
a)
Peroxisomes
b)
Mitochondria
c)
Chloroplasts
d)
Golgi bodies
|
|
Kajal Pillai answered |
Chloroplasts
- Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells.
- During photosynthesis, chloroplasts use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen.
- Photorespiration is a process that occurs in plant cells when there is a lack of carbon dioxide, leading to the oxygenation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) by the enzyme RuBisCO.
- This process leads to the formation of toxic by-products and can be detrimental to the plant.
- Peroxisomes and mitochondria play a role in photorespiration by helping to break down the toxic by-products and recycle carbon compounds.
- Peroxisomes contain enzymes that convert glycolate, a by-product of photorespiration, into glyoxylate, which can be used in the glyoxylate cycle to produce glucose.
- Mitochondria are involved in the conversion of glyoxylate into glycine, which can then be used in the synthesis of other important molecules.
- Golgi bodies, on the other hand, are responsible for processing and packaging proteins and lipids for secretion or for use within the cell. They do not directly participate in the photorespiration process.
________ is the process of synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi in the presence of light.- a)Phosphorylation
- b)Photophosphorylation
- c)Photosystem
- d)Oxidative phosphorylation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
________ is the process of synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi in the presence of light.
a)
Phosphorylation
b)
Photophosphorylation
c)
Photosystem
d)
Oxidative phosphorylation
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The process by which ATP is sysnthesised by cells in mitochondria and chloroplasta is named as phosphorylation. Photophosphorylation is the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) in the presence of light, inside chloroplast. Photosphosphorylation is of two main types-Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Read the given statement and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Carboxylation is the most crucial step of Calvin where CO2 is utilised for the carboxylation of RuBP.
Statement 2: This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme RuBisCO which results in the formation of two molcules of 3-PGA.
- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statement and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Carboxylation is the most crucial step of Calvin where CO2 is utilised for the carboxylation of RuBP.
Statement 2: This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme RuBisCO which results in the formation of two molcules of 3-PGA.
Statement 1: Carboxylation is the most crucial step of Calvin where CO2 is utilised for the carboxylation of RuBP.
Statement 2: This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme RuBisCO which results in the formation of two molcules of 3-PGA.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Carboxylation is the most crucial step of Calvin cycle where CO2 is utilized for the carboxylation of RuBP through the use of ATP and NADPH generated by the light reactions. The reaction is catalysed by enzyme RuBisCO CO2 combines with RuBP (ribulose-1, 5-biphosphate) to produce a transient intermediate compound called 2-carboxy 3-keto 1,5-biphosphoribotol. The intermediat splits up immediately in the presence of water to form two molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric acid or PGA, which is the first stable product of photosynthesis
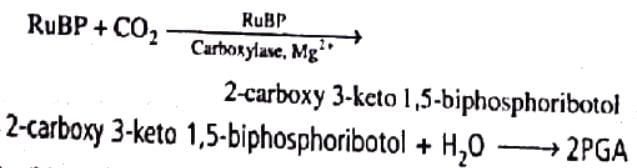
Select the incorrect pair- a)2-carbon compound - Aspartic acid
- b)3-cabon compound - PGA
- c)4- cabon compound - malic acid
- d)5-carbon compound - RuBP
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect pair
a)
2-carbon compound - Aspartic acid
b)
3-cabon compound - PGA
c)
4- cabon compound - malic acid
d)
5-carbon compound - RuBP
|
|
Prasenjit Khanna answered |
Incorrect Pair: 2-Carbon Compound - Aspartic Acid
Explanation:
- Aspartic Acid is a 4-Carbon compound and belongs to the category of amino acids.
- Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and contain both an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to the same carbon atom.
- Aspartic acid is one of the 20 amino acids that are found in proteins and is commonly abbreviated as Asp or D.
- Some other examples of 2-carbon compounds include acetic acid, ethylene, and carbon dioxide.
Therefore, the incorrect pair is option A) 2-carbon compound - Aspartic acid.
Explanation:
- Aspartic Acid is a 4-Carbon compound and belongs to the category of amino acids.
- Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and contain both an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to the same carbon atom.
- Aspartic acid is one of the 20 amino acids that are found in proteins and is commonly abbreviated as Asp or D.
- Some other examples of 2-carbon compounds include acetic acid, ethylene, and carbon dioxide.
Therefore, the incorrect pair is option A) 2-carbon compound - Aspartic acid.
In purple sulphur bacterial photosynthesis, ________.- a)Water provides the electrons
- b)Hydrogen sulphide provides the electrons
- c)Organic substance is an electron donor
- d)Oxygen is not released
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In purple sulphur bacterial photosynthesis, ________.
a)
Water provides the electrons
b)
Hydrogen sulphide provides the electrons
c)
Organic substance is an electron donor
d)
Oxygen is not released

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- Chromatiaceae is a family of purple sulphur bacteria, e.g. Chromatium.
- These are short, Gram-negative rods, ~1 µm in diameter and 3-4 µm long.
- They are able to use sulphur and sulphide as the sole photosynthetic electron donor and sulphur can be oxidised to sulphate.
- These bacteria use an inorganic sulphur compound, such as hydrogen sulphide, as an electron donor.
During non-cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are continuously lost from the reaction centre of PSII. Which source is used to replace these electrons?- a)Sunlight
- b)O2
- c)H2O
- d)CO2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During non-cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are continuously lost from the reaction centre of PSII. Which source is used to replace these electrons?
a)
Sunlight
b)
O2
c)
H2O
d)
CO2
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Non-cydic photophosphorylation is the normal process of photophosphorylation in which the electron expelled by the excited photocentre does not return to it. Non- cydic photophosphorylation is carried out in collaboration of both photosystems I and II. Electron released during photolysis of H2O is picked up by photocentre of PSII called P680. The same is extruded out when the photocentre absorbs light energy (hv). Electrons released during the photolysis of water are immediately accepted by oxidised reaction centre of PSII (i.e., P680) through an unknown substance Z.
The synthesis of complex organic substances from simple inorganic raw materials in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll is called ..........., which is a ............ process.- a)Photosynthesis, anabolic
- b)Photosynthesis, catabolic
- c)Respiration, anabolic
- d)Respiration, catabolic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The synthesis of complex organic substances from simple inorganic raw materials in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll is called ..........., which is a ............ process.
a)
Photosynthesis, anabolic
b)
Photosynthesis, catabolic
c)
Respiration, anabolic
d)
Respiration, catabolic
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Photosynthesis is an enzyme regulated anabolic process which involves the synthesis of organic compounds, inside the chlorophyll containing cells, from CO2 and H2O with the help of sunlight as a source of energy. Oxygen evolved during photosynthesis comes from water. The equation for photosynthesis can be summarised as follows.
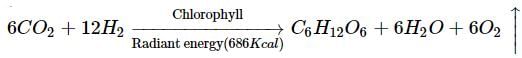
Which reaction in the Calvin cycle is catalysed by the enzyme RuBP carboxylase which results in the formation of two molecules of 3-PGA?- a)Carboxylation
- b)Reduction
- c)Regeneration
- d)PEP carboxylase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which reaction in the Calvin cycle is catalysed by the enzyme RuBP carboxylase which results in the formation of two molecules of 3-PGA?
a)
Carboxylation
b)
Reduction
c)
Regeneration
d)
PEP carboxylase
|
|
Shilpa Basak answered |
Carboxylation is the correct answer.
Calvin cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions, is a series of biochemical reactions that take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts in plants. It is responsible for converting carbon dioxide (CO2) into glucose, a process known as carbon fixation.
The Calvin cycle consists of several steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme. One of the key enzymes involved in the Calvin cycle is RuBP carboxylase, also known as Rubisco (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase). This enzyme catalyzes the carboxylation reaction, which is the first step in the Calvin cycle.
Explanation of the carboxylation reaction:
1. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP), a five-carbon molecule, combines with carbon dioxide (CO2) in the presence of RuBP carboxylase.
2. The enzyme catalyzes the addition of a CO2 molecule to RuBP, resulting in the formation of an unstable six-carbon intermediate compound.
3. This intermediate compound immediately breaks down into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA), a three-carbon compound.
The overall reaction can be represented as follows:
RuBP + CO2 → 2 × 3-PGA
Significance of the carboxylation reaction:
1. The carboxylation reaction is essential for carbon fixation, as it incorporates carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into an organic molecule.
2. The resulting 3-PGA molecules are then used in subsequent reactions of the Calvin cycle to produce glucose and other carbohydrate molecules.
3. The regeneration of RuBP, which is necessary for the continuation of the Calvin cycle, is also dependent on the carboxylation reaction.
In summary, the carboxylation reaction catalyzed by RuBP carboxylase is a crucial step in the Calvin cycle. It allows for the fixation of carbon dioxide and the subsequent production of glucose and other carbohydrates, providing energy and organic compounds for the plant.
Calvin cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions, is a series of biochemical reactions that take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts in plants. It is responsible for converting carbon dioxide (CO2) into glucose, a process known as carbon fixation.
The Calvin cycle consists of several steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme. One of the key enzymes involved in the Calvin cycle is RuBP carboxylase, also known as Rubisco (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase). This enzyme catalyzes the carboxylation reaction, which is the first step in the Calvin cycle.
Explanation of the carboxylation reaction:
1. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP), a five-carbon molecule, combines with carbon dioxide (CO2) in the presence of RuBP carboxylase.
2. The enzyme catalyzes the addition of a CO2 molecule to RuBP, resulting in the formation of an unstable six-carbon intermediate compound.
3. This intermediate compound immediately breaks down into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA), a three-carbon compound.
The overall reaction can be represented as follows:
RuBP + CO2 → 2 × 3-PGA
Significance of the carboxylation reaction:
1. The carboxylation reaction is essential for carbon fixation, as it incorporates carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into an organic molecule.
2. The resulting 3-PGA molecules are then used in subsequent reactions of the Calvin cycle to produce glucose and other carbohydrate molecules.
3. The regeneration of RuBP, which is necessary for the continuation of the Calvin cycle, is also dependent on the carboxylation reaction.
In summary, the carboxylation reaction catalyzed by RuBP carboxylase is a crucial step in the Calvin cycle. It allows for the fixation of carbon dioxide and the subsequent production of glucose and other carbohydrates, providing energy and organic compounds for the plant.
Assume a thylakoid which is somehow punctured so that the interior of the thylakoid is no longer separated from the stroma. This damage will have the most direct effect on which of the following processes?- a)Splitting of water
- b)Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
- c)Flow of electrons from photosystem II to photosystem I
- d)Synthesis of ATP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume a thylakoid which is somehow punctured so that the interior of the thylakoid is no longer separated from the stroma. This damage will have the most direct effect on which of the following processes?
a)
Splitting of water
b)
Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
c)
Flow of electrons from photosystem II to photosystem I
d)
Synthesis of ATP
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
If thylakoid is punctured, then the interior of the thylakoid is no longer separated from the stroma and this leads to stoppage of ATP synthesis.
Chlorophyll in a leaf is required for- a)trapping light energy
- b)emitting green energy
- c)breaking down water into hydrogen and oxygen
- d)storing starch in the leaves
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Chlorophyll in a leaf is required for
a)
trapping light energy
b)
emitting green energy
c)
breaking down water into hydrogen and oxygen
d)
storing starch in the leaves
|
|
Kirti Kulkarni answered |
Role of Chlorophyll in Photosynthesis
Chlorophyll is a vital pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant leaves, playing a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis.
Trapping Light Energy
- Chlorophyll primarily absorbs light energy from the sun, which is essential for photosynthesis.
- It absorbs mainly blue and red wavelengths of light while reflecting green, which is why leaves appear green.
- The absorbed light energy is converted into chemical energy, which is used to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
Importance of Light Energy
- The energy captured by chlorophyll initiates a series of reactions, known as the light-dependent reactions.
- This energy is then used to create ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are crucial for the subsequent light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
Why Other Options are Incorrect
- Emitting Green Energy: Chlorophyll does not emit energy; it reflects green light, which is why leaves look green.
- Breaking Down Water: While chlorophyll plays a role in the process where water molecules are split to release oxygen, it does not directly break down water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Storing Starch: Chlorophyll is not involved in the storage of starch; rather, glucose produced during photosynthesis can be converted into starch for storage.
In conclusion, chlorophyll's primary function is to trap light energy, making option 'A' the correct answer. Understanding this role is essential for grasping the fundamentals of photosynthesis and plant biology.
Chlorophyll is a vital pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant leaves, playing a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis.
Trapping Light Energy
- Chlorophyll primarily absorbs light energy from the sun, which is essential for photosynthesis.
- It absorbs mainly blue and red wavelengths of light while reflecting green, which is why leaves appear green.
- The absorbed light energy is converted into chemical energy, which is used to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
Importance of Light Energy
- The energy captured by chlorophyll initiates a series of reactions, known as the light-dependent reactions.
- This energy is then used to create ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are crucial for the subsequent light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
Why Other Options are Incorrect
- Emitting Green Energy: Chlorophyll does not emit energy; it reflects green light, which is why leaves look green.
- Breaking Down Water: While chlorophyll plays a role in the process where water molecules are split to release oxygen, it does not directly break down water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Storing Starch: Chlorophyll is not involved in the storage of starch; rather, glucose produced during photosynthesis can be converted into starch for storage.
In conclusion, chlorophyll's primary function is to trap light energy, making option 'A' the correct answer. Understanding this role is essential for grasping the fundamentals of photosynthesis and plant biology.
Which of the following is produced during the light phase of photosynthesis?- a)ATP
- b)NADPH2
- c)Both ATP and NADPH2
- d)Carbohydrates
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is produced during the light phase of photosynthesis?
a)
ATP
b)
NADPH2
c)
Both ATP and NADPH2
d)
Carbohydrates
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Photochemical phase, also called light or Hill reaction, occurs inside the thylakoids, especially those of grana region. Photochemical step is dependent upon light .The function of this phase is to produce assimilatory power consisting of reduced coenzyme NADPH and energy rich ATP molecules.
Which one is involved in Z-scheme of photosynthesis?- a)PS I
- b)PS II
- c)e−carriers
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is involved in Z-scheme of photosynthesis?
a)
PS I
b)
PS II
c)
e−carriers
d)
All of the above
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In non cyclic photophosphorylation, the whole scheme of transfer of electrons, starting from the PSII, uphill to the acceptor, down the electron transport chain to PSI, excitation of electrons, transfer to another acceptor, and finally down hill to NADP+ causing it to be reduced to NADPH + H+ is called as the Z scheme, due to its characteristic shape. This shape is formed when all the carriers are placed in a sequence on the redox potential scale.
One scientist cultured Cladophora in a suspension of Azotobacter and illuminated the culture by splitting light through a prism. He observed that bacteria accumulated mainly in the region of:- a)Violet and green light
- b)Indigo and green light
- c)Orange and yellow light
- d)Blue and red light
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One scientist cultured Cladophora in a suspension of Azotobacter and illuminated the culture by splitting light through a prism. He observed that bacteria accumulated mainly in the region of:
a)
Violet and green light
b)
Indigo and green light
c)
Orange and yellow light
d)
Blue and red light
|
|
Ananya Dasgupta answered |
Understanding the Experiment
The scientist's experiment involved culturing Cladophora (a type of green algae) in a suspension of Azotobacter (a nitrogen-fixing bacterium) while illuminating the culture with light split by a prism. The goal was to observe bacterial accumulation in relation to different wavelengths of light.
Light Spectrum and Photosynthesis
- Photosynthetic Activity: Cladophora, like other photosynthetic organisms, utilizes light energy for photosynthesis, converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- Wavelengths of Light: Different colors of light (wavelengths) can influence the rate of photosynthesis and, consequently, the growth and distribution of associated bacteria like Azotobacter.
Why Blue and Red Light?
- Blue Light:
- Has a short wavelength and high energy.
- It is crucial for chlorophyll absorption, promoting efficient photosynthesis.
- Red Light:
- Has a longer wavelength, which is also effectively absorbed by chlorophyll.
- This light enhances the photosynthetic process, leading to increased organic matter production, which bacteria can utilize.
Conclusion: Bacterial Accumulation
- The study found that bacteria accumulated mainly in the blue and red light regions because:
- Both wavelengths are optimal for photosynthesis in Cladophora.
- Enhanced photosynthetic activity leads to more organic substrates available for Azotobacter, promoting its growth.
Thus, the correct answer, option 'D', reflects the importance of blue and red light in driving photosynthesis and supporting the growth of associated bacteria in the culture.
The scientist's experiment involved culturing Cladophora (a type of green algae) in a suspension of Azotobacter (a nitrogen-fixing bacterium) while illuminating the culture with light split by a prism. The goal was to observe bacterial accumulation in relation to different wavelengths of light.
Light Spectrum and Photosynthesis
- Photosynthetic Activity: Cladophora, like other photosynthetic organisms, utilizes light energy for photosynthesis, converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- Wavelengths of Light: Different colors of light (wavelengths) can influence the rate of photosynthesis and, consequently, the growth and distribution of associated bacteria like Azotobacter.
Why Blue and Red Light?
- Blue Light:
- Has a short wavelength and high energy.
- It is crucial for chlorophyll absorption, promoting efficient photosynthesis.
- Red Light:
- Has a longer wavelength, which is also effectively absorbed by chlorophyll.
- This light enhances the photosynthetic process, leading to increased organic matter production, which bacteria can utilize.
Conclusion: Bacterial Accumulation
- The study found that bacteria accumulated mainly in the blue and red light regions because:
- Both wavelengths are optimal for photosynthesis in Cladophora.
- Enhanced photosynthetic activity leads to more organic substrates available for Azotobacter, promoting its growth.
Thus, the correct answer, option 'D', reflects the importance of blue and red light in driving photosynthesis and supporting the growth of associated bacteria in the culture.
Tropical plants have a ______ temperature optimum than the plants adapted to temperate climates.- a)Lower
- b)Equal
- c)Higher
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Tropical plants have a ______ temperature optimum than the plants adapted to temperate climates.
a)
Lower
b)
Equal
c)
Higher
d)
None of these
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The C4 plants respond to higher temperatures and show higher rate of photosynthesis while C3 plants have a much lower temperature optimum. The temperature optimum for photosynthesis of different plants depends on the habitat that they are adapted to. Tropical plants have a higher temperature optimum than the plants adapted to temperate climates as tropical areas have higher temperature as compared to temperate areas.
Which of the following statement about dark reaction is correct?- a)They occur in darkness
- b)They are not light dependent
- c)They are dependent upon the products synthesized during light reaction
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement about dark reaction is correct?
a)
They occur in darkness
b)
They are not light dependent
c)
They are dependent upon the products synthesized during light reaction
d)
All of the above
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Bisoynthetic phase (Dark or Blackman's reaction) catalyses the assimilation of CO2 to cabohydrates. These reactions occurs in stroma or matrix of chloroplasts and all the enzyme required for the processes are present in the stroma/matrix of choroplasts. These reactions do not require light, instead assimilatory power (ATP and NADPH) produced during photochemical (light) phase is used in fixation and reduction of CO2 However, this should not be construed to mean that they occur in darkness or that they are not light dependent.
During fixation of one molecule of CO2 by C3 plants, number of ATP and NADPH2 required are - a)3ATP and 2 NADPH2
- b)5ATP and 2 NADPH2
- c)12ATP and 12 NADPH2
- d)2ATP and 3 NADPH2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During fixation of one molecule of CO2 by C3 plants, number of ATP and NADPH2 required are
a)
3ATP and 2 NADPH2
b)
5ATP and 2 NADPH2
c)
12ATP and 12 NADPH2
d)
2ATP and 3 NADPH2
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
For every CO2 molecule entering the Calvin cycle, 3 molecules of ATP and 2 molecules of NADPH are required. To make one molecule of glucose, 6 turns of the cycles are required (6 × 3ATP = 18ATP and 6 × 2NADPH = 12NADPH)
In
6 CO2
18ATP
6 CO2
18ATP
Out
1 glucose
18ADP
1 glucose
18ADP
12NADPH 12NADP, So, the correct answer is ' 3ATP and 2NADPH2'
निम्न में से कौन सी स्थितियां ओस के निर्माण के लिए आवश्यक हैं?
1. बादल वाला आकाश
2. तेज हवाएं
3. उच्च सापेक्ष आर्द्रता
नीचे दिए गए कोड का उपयोग करके सही उत्तर चुनें।- a)1, 2 और 3
- b)केवल 1 और 2
- c)केवल 3
- d)2 और 3 ही
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
निम्न में से कौन सी स्थितियां ओस के निर्माण के लिए आवश्यक हैं?
1. बादल वाला आकाश
2. तेज हवाएं
3. उच्च सापेक्ष आर्द्रता
नीचे दिए गए कोड का उपयोग करके सही उत्तर चुनें।
1. बादल वाला आकाश
2. तेज हवाएं
3. उच्च सापेक्ष आर्द्रता
नीचे दिए गए कोड का उपयोग करके सही उत्तर चुनें।
a)
1, 2 और 3
b)
केवल 1 और 2
c)
केवल 3
d)
2 और 3 ही
|
|
Rahul Choudhury answered |
• ओस नमी है जो संक्षेपण के परिणामस्वरूप बनती है। संक्षेपण एक ऐसी प्रक्रिया है जो एक सामग्री से गुजरती है क्योंकि यह एक गैस से एक तरल में बदलती है। ओस पानी के वाष्प से तरल में बदलने का परिणाम है।
• तापमान में गिरावट के कारण ओस बनता है और वस्तुएं ठंडी हो जाती हैं। यदि वस्तु पर्याप्त ठंडी हो जाती है, तो वस्तु के चारों ओर की हवा भी ठंडी हो जाएगी। ठंडी हवा की तुलना में ठंडी हवा वाष्प को कम पकड़ पाती है। यह ठंडा करने वाली वस्तुओं के चारों ओर हवा में जल वाष्प को संघनित करने के लिए मजबूर करता है। जब संक्षेपण होता है, तो पानी की छोटी बूंदें-ओस बन जाती हैं।
• जिस तापमान पर ओस के रूप को ओस बिंदु कहा जाता है। स्थान, मौसम और दिन के समय के आधार पर ओस बिंदु व्यापक रूप से भिन्न होता है।
• इसके गठन के लिए आदर्श स्थिति स्पष्ट आकाश, शांत हवा, उच्च सापेक्ष आर्द्रता और ठंड और लंबी रातें हैं। ओस के गठन के लिए, यह आवश्यक है कि ओस बिंदु हिमांक से ऊपर हो।
• उदाहरण के लिए, तेज हवाएं, वायु की विभिन्न परतों को मिलाती हैं, जिसमें विभिन्न मात्रा में जलवाष्प होती है। इससे वायुमंडल की ओस बनने की क्षमता कम हो जाती है।
• तापमान में गिरावट के कारण ओस बनता है और वस्तुएं ठंडी हो जाती हैं। यदि वस्तु पर्याप्त ठंडी हो जाती है, तो वस्तु के चारों ओर की हवा भी ठंडी हो जाएगी। ठंडी हवा की तुलना में ठंडी हवा वाष्प को कम पकड़ पाती है। यह ठंडा करने वाली वस्तुओं के चारों ओर हवा में जल वाष्प को संघनित करने के लिए मजबूर करता है। जब संक्षेपण होता है, तो पानी की छोटी बूंदें-ओस बन जाती हैं।
• जिस तापमान पर ओस के रूप को ओस बिंदु कहा जाता है। स्थान, मौसम और दिन के समय के आधार पर ओस बिंदु व्यापक रूप से भिन्न होता है।
• इसके गठन के लिए आदर्श स्थिति स्पष्ट आकाश, शांत हवा, उच्च सापेक्ष आर्द्रता और ठंड और लंबी रातें हैं। ओस के गठन के लिए, यह आवश्यक है कि ओस बिंदु हिमांक से ऊपर हो।
• उदाहरण के लिए, तेज हवाएं, वायु की विभिन्न परतों को मिलाती हैं, जिसमें विभिन्न मात्रा में जलवाष्प होती है। इससे वायुमंडल की ओस बनने की क्षमता कम हो जाती है।
Visible part of electromagnetic spectrum consists of radiations having a wavelength in the range of- a)400−800nm
- b)300−2600nm
- c)390−760nm
- d)650−760nm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Visible part of electromagnetic spectrum consists of radiations having a wavelength in the range of
a)
400−800nm
b)
300−2600nm
c)
390−760nm
d)
650−760nm
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Light is the visible part of electomagnetic radiations. Visible light consists of radiations having a wavelength between 390-760 nm (or 399-430nm), blue of indigo (430-470nm), blue green or blue (470-500nm), green (500-580nm), yellow (580-600nm), orange (600-650nm), orange red (650-600nm) and red (660-760nm).
Kranz anatomy is not exhibited by which of the following plants?- a)Maize
- b)Sorghum
- c)Sugarcane
- d)Sunflower
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Kranz anatomy is not exhibited by which of the following plants?
a)
Maize
b)
Sorghum
c)
Sugarcane
d)
Sunflower
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Kranz anatomy is shown by C4 plants such as Sorghum, sugarcane, maize, Cyperus rotundus, etc.
The law of limiting factors' was given by _______ in the year _______.- a)Blackman, 1905
- b)Blackman, 1804
- c)Engelmann, 1909
- d)Warburg, 1920
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The law of limiting factors' was given by _______ in the year _______.
a)
Blackman, 1905
b)
Blackman, 1804
c)
Engelmann, 1909
d)
Warburg, 1920
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Blackman's (1905) law of limiting factors states that a chemical process is affected by more than one factor, then its rate will be determined by the factor which is nearest to its minimal value: it is the factor which directly affects the process its quantity is changed.
Which one of the following is essential for the photolysis of water?- a)Manganese
- b)Zinc
- c)Copper
- d)Boron
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is essential for the photolysis of water?
a)
Manganese
b)
Zinc
c)
Copper
d)
Boron
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The phenomenon of breaking up of water into hydrogen and oxygen in the illuminated chloroplasts is called photolysis or photocatalytic splitting of water. It can be depicted as: 4H2O ⇌ 4H+ + 4OH−
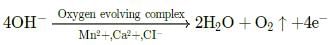
Given graph represents the absorption spectra of three photosynthetic pigments, chl a chl b and β-carotene. 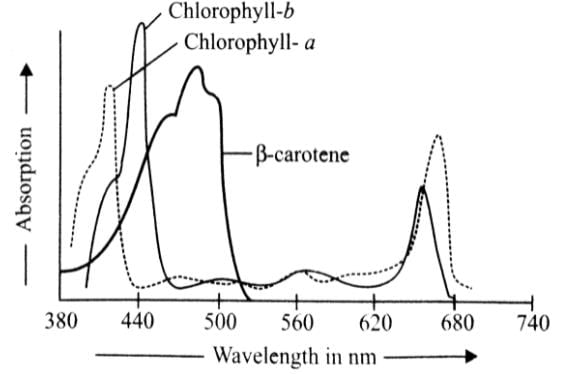
Select the correct statement regarding this.- a)The curve showing the amount of absorption of different wavelengths of light by a photosynthetic pigment is called the absorption spectrum
- b)Chl a and chl b absorb maximum light in the blue and red wavelengths of light
- c)Rate of photosynthesis is maximum in blue and red wavelengths of light
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given graph represents the absorption spectra of three photosynthetic pigments, chl a chl b and β-carotene.

Select the correct statement regarding this.
a)
The curve showing the amount of absorption of different wavelengths of light by a photosynthetic pigment is called the absorption spectrum
b)
Chl a and chl b absorb maximum light in the blue and red wavelengths of light
c)
Rate of photosynthesis is maximum in blue and red wavelengths of light
d)
All of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The graphical curve showing the amount of energy of different wavelengths of light absorbed by a pgment is called absorption spectrum,. It is studies with the help of spectrophotometer. The absorption spectra of chorophylls a and b show that they absorb maximum light in the blue-violet and red wavelengths. The pgments are often known after the wvelength which is absorbed to the maximum e.g., chl a673 Chl a683(P680), Chl a703(P700).
When the temperature is increased from minimum to optimum, rate of photosynthesis doubles for every _______ rise in temperature.- a)1oC
- b)10oC
- c)20oC
- d)30oC
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the temperature is increased from minimum to optimum, rate of photosynthesis doubles for every _______ rise in temperature.
a)
1oC
b)
10oC
c)
20oC
d)
30oC
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The rate of photosynthesis usually increases with an increase in temperature up to 40oC. Above this temperature, the rate of photosynthesis starts decreasing due to the inactivation of enzymes. The minimum temperature at which most plants start photosynthesis is 0o−5oC but it can be as low as - 20oC for lichens and - 35oC for some gymnosperms.The maximum temperature at which photosynthesis can occur is 55oC in some desert plants and 75o for hot spring algae. When the temperature is increased from minimum to optimum, the rate of photosynthesis doubles for every 10oC rise in temperature.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Photorespiration interferes with the successful functioning of Calvin cycle.
Statement 2: Photorespiration oxidises ribulose-1,5 biphosphate which is an acceptor of CO2 in Calvin cycle.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Photorespiration interferes with the successful functioning of Calvin cycle.
Statement 2: Photorespiration oxidises ribulose-1,5 biphosphate which is an acceptor of CO2 in Calvin cycle.
Statement 1: Photorespiration interferes with the successful functioning of Calvin cycle.
Statement 2: Photorespiration oxidises ribulose-1,5 biphosphate which is an acceptor of CO2 in Calvin cycle.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Photorespiration (Photosynthetic carbon oxidative or PCO cycle) is the light dependent process of oxygenation of ribulose-1,5-biphosphate (RuBP) and release of CO2 by the photosynthetic organs of a plant. Under normal conditions, in Calvin cycle, carboxylation of RuBP takes place whereas during photorespiration instead of carboxylation, oxygenation of RuBP takes place. This is due to abnormal behaviour of enzyme RuBisCO, which at high temperature (more than 35∘C), functions as oxygenase (instead of carboxylase). Instead of fixing CO2, it performs oxygenation of RuBP to produce a 3-carbon phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) and a 2-carbon phosphoglycolate. It is the first reaction of photorespiration and can be represented as:
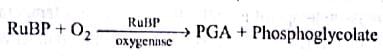
In this way, photorespiration interferes with the successful functioning of Calvin cycle by causing oxygenation of RuBP instead of carboxylation.
Accessory photosynthetic pigments in most green plants are - a)Chlorophyll a
- b)Chlorophyll b
- c)Carotenoids and xanthophylls
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Accessory photosynthetic pigments in most green plants are
a)
Chlorophyll a
b)
Chlorophyll b
c)
Carotenoids and xanthophylls
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Chlorophyll a is found in almost all photosynthetic plants except bacteria. It is called primary photosynthetic pigment because it performs primary reactions of photosynthesis which involve conversion of light energy into chemical energy. Other photosynthetic pigments like chlorophyll b, xanthophylls and carotenes are called accessory pigments. They absorb light energy of different wavelengths, broaden the spectrum of light absorption and hand over the energy to chlorophyll a through electron spin resonance and also protect chlorophyll a from photo-oxidation.
Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding the Calvin cycle of C3 plants?- a)First stable product of Calvin cycle in C3 plants is 3-phosphoglyceric acid.
- b)Sunflower is an example of C3 plants.
- c)Calvin cycle occurs in bundle sheath calls of C3 plants.
- d)Enzyme PEP case is absent in C3 plants.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding the Calvin cycle of C3 plants?
a)
First stable product of Calvin cycle in C3 plants is 3-phosphoglyceric acid.
b)
Sunflower is an example of C3 plants.
c)
Calvin cycle occurs in bundle sheath calls of C3 plants.
d)
Enzyme PEP case is absent in C3 plants.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
In C3 plants, bundle sheath cells usually do not contain chloroplasts and the whole C3 cycle operates in mesophyll cells of leaves. in C4 plants showing Hatch-Slack cycle however, intial fixation of CO2 occurs in mesophyll cells followed by final fixation in bundle sheath cells.
Identify the parts marked as A, B and C in the given figure showing ATP synthesis through chemiosmosis.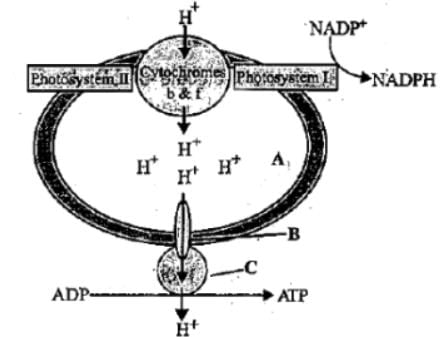
- a)A-Thylakoid lumen; B-F0; C-F1
- b)A-Thylakoid lumen; B- F1; C-F0
- c)A-Chloroplast lumen; B-F0; C-F1
- d)A-Chloroplast lumen; B-F1; C-F0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the parts marked as A, B and C in the given figure showing ATP synthesis through chemiosmosis.

a)
A-Thylakoid lumen; B-F0; C-F1
b)
A-Thylakoid lumen; B- F1; C-F0
c)
A-Chloroplast lumen; B-F0; C-F1
d)
A-Chloroplast lumen; B-F1; C-F0
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a semipermeable membrane, down their electrochemical gradient.
A represents the thylakoid lumen, b-Fo & c-F1.
A represents the thylakoid lumen, b-Fo & c-F1.
The reaction center for PS- I ______ and reaction center of PS- II is ______.- a)P680,P700
- b)P700,P680
- c)P800,P600
- d)P700,P900
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction center for PS- I ______ and reaction center of PS- II is ______.
a)
P680,P700
b)
P700,P680
c)
P800,P600
d)
P700,P900
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The reaction centre of photosystem I (PS I) is referred to as P700 where "P" stands for "Pigment" and "700" stands for the wavelenght of light that this particular chlorophyll molecule absorbs most strongly. The reaction centre of photosystem II (PS II) is referred to as P680 for comparable reason.
Refer to the given reaction.
2H2O → 4H+ + O2 + 4e−
Where does this reaction take place in the chloroplasts of plants?- a)Outer surface of thylakoid membrane
- b)Inner surface of thylakoid membrane
- c)In the matrix (stroma)
- d)Intermembrane space
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer to the given reaction.
2H2O → 4H+ + O2 + 4e−
Where does this reaction take place in the chloroplasts of plants?
2H2O → 4H+ + O2 + 4e−
Where does this reaction take place in the chloroplasts of plants?
a)
Outer surface of thylakoid membrane
b)
Inner surface of thylakoid membrane
c)
In the matrix (stroma)
d)
Intermembrane space
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The splitting of water is associated with the PSII, water is split into H+,[O] and electrons. The needed to replace those removed from photosystem I are provided by photosystem II.
2H2O → 4H+ + O2 + 4e−
Water splitting complex is associated with the PSII, which itself physically located on the inner side of the membrane of are thylakoid.
2H2O → 4H+ + O2 + 4e−
Water splitting complex is associated with the PSII, which itself physically located on the inner side of the membrane of are thylakoid.
RuBisCO is- a)RuBisCO carboxylase
- b)RuBisCO oxygenase
- c)RuBisCO carboxylase-oxygenase
- d)RuBisCO carboxy dismutase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
RuBisCO is
a)
RuBisCO carboxylase
b)
RuBisCO oxygenase
c)
RuBisCO carboxylase-oxygenase
d)
RuBisCO carboxy dismutase
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The enzyme RuBisCO carries out photosynthetic carboxylation of RuBP The enzyme was previously called as carboxydismutase. RuBisCO is the most abundant protein of the biological world. RuBisCO is located int the stroma on the outer surface of thylakoid membranes. As it is capable of carrying out both carboxylation and oxygenation and oxygenation reaction in C3 and C4 plants respectively, thus it is correctly named as RuBP carboxylase-oxygenase.
In an experiment in which photosynthesis is performed during the day you provide a plant with radioactive carbon dioxide (14CO2) as a metabolic tracer. The 14C is incorporated first into oxaloacetic acid. The plant is best characterised as a- a)C4 plant
- b)C3 plant
- c)CAM plant
- d)Insectivorous plant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In an experiment in which photosynthesis is performed during the day you provide a plant with radioactive carbon dioxide (14CO2) as a metabolic tracer. The 14C is incorporated first into oxaloacetic acid. The plant is best characterised as a
a)
C4 plant
b)
C3 plant
c)
CAM plant
d)
Insectivorous plant
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
In C4 plants, the first stable photosynthetic product is a 4-carbon compound, i.e., oxaloacetic acid (OAA), which is formed by initial fixation of CO2 by the carboxylation of phosphoenol pyruvate in the mesophyll cells. So, when radioactive 14CO2 is introduced into the reaction, it is first incorporated into the OAA.

In a CAM plant, although the first product formed is OAA, but here the initial CO2 fixation occurs at night.
Given figure represents C4 pathway. Select the suitable option for A, B and C. 
- a)A-Decarboxylaton; B-Reduction; C-Regeneration
- b)A-Fixation; B-Transamination; C-Regeneration
- c)A-Carboxylation; B-Decarboxylation; C-Reduction
- d)A-Fixation; B-Decarboxylation; C-Regeneration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given figure represents C4 pathway. Select the suitable option for A, B and C.

a)
A-Decarboxylaton; B-Reduction; C-Regeneration
b)
A-Fixation; B-Transamination; C-Regeneration
c)
A-Carboxylation; B-Decarboxylation; C-Reduction
d)
A-Fixation; B-Decarboxylation; C-Regeneration
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
A - Fixation
B - Decarboxylation
C - Regeneration
So, the correct answer (D).
B - Decarboxylation
C - Regeneration
So, the correct answer (D).
Refer to the given diagrammatic of an electron micrograph of a section of chloroplast.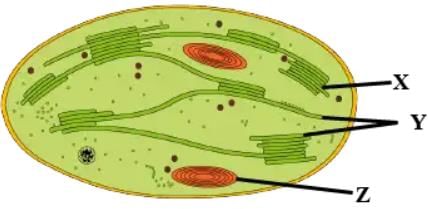 Select the option which correctly depicts the function of parts X, Y and Z.
Select the option which correctly depicts the function of parts X, Y and Z.- a)X-Dark reaction ; Y-Light reaction ; Z-Cytoplasmic inheritance
- b)X-Light reaction ; Y-Carbohydrate synthesis ; Z-Carbohydrate storage
- c)X-Light reaction ; Y-Carbohydrate storage ;Z-Carbohydrate synthesis
- d)X-Carbohydrate synthesis; Y- Carbohydrate storage ; Z- Cytoplasmic inheritance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer to the given diagrammatic of an electron micrograph of a section of chloroplast.

Select the option which correctly depicts the function of parts X, Y and Z.
a)
X-Dark reaction ; Y-Light reaction ; Z-Cytoplasmic inheritance
b)
X-Light reaction ; Y-Carbohydrate synthesis ; Z-Carbohydrate storage
c)
X-Light reaction ; Y-Carbohydrate storage ;Z-Carbohydrate synthesis
d)
X-Carbohydrate synthesis; Y- Carbohydrate storage ; Z- Cytoplasmic inheritance
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Light reaction (or photochemical phase) of photosynthesis mainly occur on the grana thylakoids. Dark reaction (or biosynthetic phase) which involve the synthesis of carbohydrates by CO2 fixation occur in the stroma (or matrix) of chloroplasts. The chloroplast matrix of higher plants stores starches temporarily in the form of starch granules.
The most abundant plant protein on the earth is- a)aleurone protein
- b)RuBisCo
- c)nucleoprotein
- d)albumin protein
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant plant protein on the earth is
a)
aleurone protein
b)
RuBisCo
c)
nucleoprotein
d)
albumin protein

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The most abundant plant protein in the world is RuBisCo, which is an enzyme that catalyses the first step in carbon fixation. RuBisCo is found in plants, algae, cyanobacteria and certain other bacteria. It takes part in photosynthesis and converts inorganic CO2 into organic forms containing C-C bonds and H atoms.
During photochemical reactions of photosynthesis,- a)assimilation of CO2 takes place
- b)liberation of O2 and formation of NADPH2 take place
- c)formation of ATP and NADPH2 takes place
- d)liberation of O2 and formation of ATP and NADPH2 takes place
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During photochemical reactions of photosynthesis,
a)
assimilation of CO2 takes place
b)
liberation of O2 and formation of NADPH2 take place
c)
formation of ATP and NADPH2 takes place
d)
liberation of O2 and formation of ATP and NADPH2 takes place

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Light reactions or the 'photochemical' phase include light absorption, water splitting, and oxygen release. The splitting of water is associated with the PS II - water is split into H+, [O] and electrons. This creates oxygen, one of the net products of photosynthesis and the formation of high-energy chemical intermediates, ATP and NADPH2. The light reactions capture energy from sunlight, which they change to chemical energy that is stored in molecules of NADPH2 and ATP.
Chapter doubts & questions for Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily