All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Body Fluids and Circulation for NEET Exam
Which of the following engulfs pathogens rapidly?- a)Basophils
- b)Acidophils
- c)Monocytes
- d)Neutrophils
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following engulfs pathogens rapidly?
a)
Basophils
b)
Acidophils
c)
Monocytes
d)
Neutrophils
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Neutrophils are the type of WBCs which can engulf the pathogen rapidly. Neutrophils are more in number i.e. upto 60% of Total Leukocyte Count. They immediately engulf bacteria and viruses to destroy them by phagocytosis.
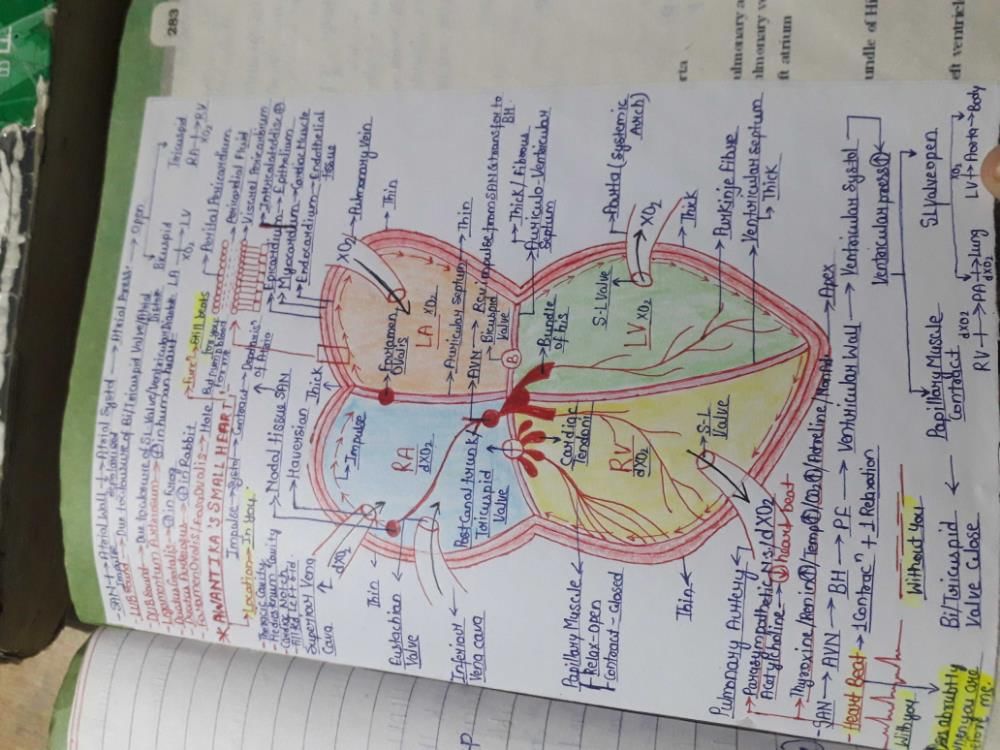
How many contraction nodes are found in heart of Human :-- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Many
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many contraction nodes are found in heart of Human :-
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Many
d)
None
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Two contraction nodes...SAN and AVN..option B
Which of the following is a non-granulocyte?- a)Neutrophils
- b)Monocytes
- c)Basophils
- d)Eosinophils
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a non-granulocyte?
a)
Neutrophils
b)
Monocytes
c)
Basophils
d)
Eosinophils
|
|
Anjana Chakraborty answered |
Non-Granulocytes in Blood
Blood cells are divided into two groups: granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes have granules in their cytoplasm and include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Agranulocytes, on the other hand, lack granules and include lymphocytes and monocytes.
Non-Granulocyte
A non-granulocyte is simply an agranulocyte or a leukocyte that lacks granules in its cytoplasm. Monocytes are non-granulocytes and belong to the agranulocyte group of leukocytes.
Monocytes
Monocytes are the largest leukocytes in the blood, accounting for 2-8% of all leukocytes. They have a large kidney-shaped nucleus and are characterized by their ability to differentiate into macrophages, which are cells that engulf and digest foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body.
Functions of Monocytes
Monocytes have several functions in the body, including:
1. Phagocytosis: Monocytes, when differentiated into macrophages, are capable of phagocytosis, which is the process of engulfing and digesting foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body.
2. Antigen presentation: Monocytes play a crucial role in the immune response by presenting antigens to T cells, which are responsible for activating the immune response.
3. Cytokine production: Monocytes produce cytokines, which are signaling molecules that regulate the immune response.
Conclusion
In conclusion, monocytes are non-granulocytes and belong to the agranulocyte group of leukocytes. They are characterized by their ability to differentiate into macrophages, which are cells that engulf and digest foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body. Monocytes also play a crucial role in the immune response by presenting antigens to T cells and producing cytokines.
Blood cells are divided into two groups: granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes have granules in their cytoplasm and include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Agranulocytes, on the other hand, lack granules and include lymphocytes and monocytes.
Non-Granulocyte
A non-granulocyte is simply an agranulocyte or a leukocyte that lacks granules in its cytoplasm. Monocytes are non-granulocytes and belong to the agranulocyte group of leukocytes.
Monocytes
Monocytes are the largest leukocytes in the blood, accounting for 2-8% of all leukocytes. They have a large kidney-shaped nucleus and are characterized by their ability to differentiate into macrophages, which are cells that engulf and digest foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body.
Functions of Monocytes
Monocytes have several functions in the body, including:
1. Phagocytosis: Monocytes, when differentiated into macrophages, are capable of phagocytosis, which is the process of engulfing and digesting foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body.
2. Antigen presentation: Monocytes play a crucial role in the immune response by presenting antigens to T cells, which are responsible for activating the immune response.
3. Cytokine production: Monocytes produce cytokines, which are signaling molecules that regulate the immune response.
Conclusion
In conclusion, monocytes are non-granulocytes and belong to the agranulocyte group of leukocytes. They are characterized by their ability to differentiate into macrophages, which are cells that engulf and digest foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body. Monocytes also play a crucial role in the immune response by presenting antigens to T cells and producing cytokines.
The valve situated between the left atrium and the left ventricle is called
(1) Bicuspid valve
(2) Tricuspid valve
(3) Mitral valve
(4) Eustachian tube- a)2 and 4 are correct.
- b)1 and 2 are correct.
- c)1 and 3 are correct.
- d)1, 2 and 3 are correct.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The valve situated between the left atrium and the left ventricle is called
(1) Bicuspid valve
(2) Tricuspid valve
(3) Mitral valve
(4) Eustachian tube
(1) Bicuspid valve
(2) Tricuspid valve
(3) Mitral valve
(4) Eustachian tube
a)
2 and 4 are correct.
b)
1 and 2 are correct.
c)
1 and 3 are correct.
d)
1, 2 and 3 are correct.
|
|
Bhaskar Ala answered |
The valve situated between left atria and the left ventricle is BICUSPID VALVE also known as MITRAL VALVE.. closure of this valve produce first heart sound "LUB"..
Can you explain the answer of this question below: Find out the wrong match:
- A:
Eosinophils – Allergic response
- B:
Basophils – Secrete histamine and serotonin
- C:
Monocytes – Secrete heparin
- D:
Neutrophils – Phagocytic and eat foreign organisms
The answer is c.
Find out the wrong match:
Eosinophils – Allergic response
Basophils – Secrete histamine and serotonin
Monocytes – Secrete heparin
Neutrophils – Phagocytic and eat foreign organisms
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Monocytes and macrophages synthesize and secrete thrombospondin.
Mark the odd one:- a)Neutrophil
- b)Erythrocyte
- c)Monocyte
- d)Lymphocyte
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mark the odd one:
a)
Neutrophil
b)
Erythrocyte
c)
Monocyte
d)
Lymphocyte
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Erythrocytes bcs its stands for rbc's whereas others are different types of wbc's
Blood circulation take following course in heart of man :-- a)Left auricle - left ventricle - body - right auricle -right ventricle
- b)Right auricle - left ventricle
- c)Left auricle - left ventricle - lungs-right auricle -right ventricle
- d)None of them
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood circulation take following course in heart of man :-
a)
Left auricle - left ventricle - body - right auricle -right ventricle
b)
Right auricle - left ventricle
c)
Left auricle - left ventricle - lungs-right auricle -right ventricle
d)
None of them
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The blood pumped by the right ventricle enters the pulmonary artery, whereas the left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta. The deoxygenated blood pumped into the pulmonary artery is passed onto the lungs from where the oxygenated blood is carried by the pulmonary veins into the left atrium. This pathway constitutes the pulmonary circulation. The oxygenated blood entering the aorta is carried by a network of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries to the tissues from where the deoxygenated blood is collected by a system of venules, veins and vena cava and emptied into the right atrium. This is the systemic circulation. The systemic circulation provides nutrients, O2 and other essential substances to the tissues and takes CO2 and other harmful substances away for elimination.
So, the correct answer is option A.
So, the correct answer is option A.
The blood during diastole :-- a)Leaves the heart
- b)Enters the heart
- c)Enters lungs
- d)Leaves the ventricles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The blood during diastole :-
a)
Leaves the heart
b)
Enters the heart
c)
Enters lungs
d)
Leaves the ventricles
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Diastole This should really be called “ventricular diastole”, but don't worry about this for GCSE. During diastole the thick muscular walls of the ventricles relax. Again, this happens to both sides of the heart. The pressure of the blood in the ventricles falls low enough for the bicuspid valve to open.
Read the following :
i. Blood vessels include arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from heart to body parts and veins bring back blood from body parts to heart.
ii. The blood vessel which carry blood from heart to lungs is pulmonary artery and it carries oxygenated blood.- a)Statement ii) is correct and i) is wrong.
- b)both are correct
- c)Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
- d)both are wrong
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following :
i. Blood vessels include arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from heart to body parts and veins bring back blood from body parts to heart.
ii. The blood vessel which carry blood from heart to lungs is pulmonary artery and it carries oxygenated blood.
i. Blood vessels include arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from heart to body parts and veins bring back blood from body parts to heart.
ii. The blood vessel which carry blood from heart to lungs is pulmonary artery and it carries oxygenated blood.
a)
Statement ii) is correct and i) is wrong.
b)
both are correct
c)
Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
d)
both are wrong
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- The arteries carry blood from the heart to all over body parts. Hence, statement (i) is correct.
- The vessels which carry blood from the heart to the lungs is the pulmonary artery but it carries deoxygenated blood. Hence, statement (ii) is correct.
The specialised patch of modified heart muscles from where contraction initiates, is/are :- a)Pacesetter of heart
- b)both SAN and AVN together
- c)Pacemaker of heart
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The specialised patch of modified heart muscles from where contraction initiates, is/are :
a)
Pacesetter of heart
b)
both SAN and AVN together
c)
Pacemaker of heart
d)
none of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- The nodal musculature has the ability to generate action potentials without any external stimuli.
- The number of action potentials that could be generated in a minute varies at different parts of the nodal system.
- The SAN can generate the maximum number of action potentials and is responsible for initiating and maintaining the rhythmic contractile activity of the heart.
- Therefore, it is called the pacemaker.
Which one of the following is correct?- a)Plasma = Blood − Lymphocytes
- b)Neuron = Cyton + Dendron + Axon + Synapse
- c)Lymph = Plasma + WBCs + RBCs
- d)Blood = Plasma + RBCs + WBCs + Platelets
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is correct?
a)
Plasma = Blood − Lymphocytes
b)
Neuron = Cyton + Dendron + Axon + Synapse
c)
Lymph = Plasma + WBCs + RBCs
d)
Blood = Plasma + RBCs + WBCs + Platelets
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
It has four main components: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Blood has many different functions, including: transporting oxygen and nutrients to the lungs and tissues. forming blood clots to prevent excess blood loss.
In human beings, the duration of the cardiac cycle is- a)8.0 second
- b)0.5 second
- c)0.8 second
- d)0.08 second
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In human beings, the duration of the cardiac cycle is
a)
8.0 second
b)
0.5 second
c)
0.8 second
d)
0.08 second
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Cardiac cycle a complex process which involves a sequence of activities and that too within 0.8 sec. The cardiac cycle consists of a systole and a diastole. The cardiac cycle begins with a joint diastole (relaxation of all four chambers of the heart).
Which of the following is not a granulocyte? [1997] - a)Lymphocyte
- b)Eosinophil
- c)Basophil
- d)Neutrophil
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a granulocyte? [1997]
a)
Lymphocyte
b)
Eosinophil
c)
Basophil
d)
Neutrophil

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
White blood cells are of two types : (i) Granulocytes (with granular cytoplasm) - neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils. (ii) Agranulocytes (with clear cytoplasm) - Lymphocytes and monocytes
The maximum surface area of the circulatory system is seen in- a)Heart
- b)Capillaries
- c)Arterioles
- d)Veins
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum surface area of the circulatory system is seen in
a)
Heart
b)
Capillaries
c)
Arterioles
d)
Veins
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
An adult human has been estimated to have some 60,000 miles (96,560 km) of capillaries with a total surface area of some 8001000 m2. The total volume of this system is roughly 5 liters, the same as the total volume of blood.
The SA node is located in- a)Upper lateral wall of the left atrium
- b)Lower lateral wall of the right atrium
- c)Lower lateral wall of the left atrium
- d)Upper lateral wall of the right atrium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The SA node is located in
a)
Upper lateral wall of the left atrium
b)
Lower lateral wall of the right atrium
c)
Lower lateral wall of the left atrium
d)
Upper lateral wall of the right atrium
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
SA node (sino-atrial node) is located in right upper corner of right atrium .of heart..option D is the answer
Antigens are present- a)Inside the cytoplasm
- b)Inside the nucleus
- c)On the nuclear membrane
- d)On the cell surface
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Antigens are present
a)
Inside the cytoplasm
b)
Inside the nucleus
c)
On the nuclear membrane
d)
On the cell surface

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
Cell markers, also known as cell surface antigens, serve as monograms to help identify and classify cells. The majority of them are molecules or antigens within cell's plasma membrane. Unique to different cell types, there exist specific combinations of markers or antigens.
Blood enters the heart because muscles of the- a)Ventricles contract
- b)Ventricles relax
- c)Atria contract
- d)Atria relax
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood enters the heart because muscles of the
a)
Ventricles contract
b)
Ventricles relax
c)
Atria contract
d)
Atria relax
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Atrial diastole is characterized by the relaxation of the atrial muscles. During this stage, the blood enters into the atria, as the volume of the blood in the atria increases the pressure within it decreases.
So, the correct answer is option D.
So, the correct answer is option D.
In the systemic circulation, blood vessel that carries blood from the intestine to liver is named :- a)Hepatic portal arch
- b)none of these
- c)Hepatic portal artery
- d)Hepatic portal vein
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the systemic circulation, blood vessel that carries blood from the intestine to liver is named :
a)
Hepatic portal arch
b)
none of these
c)
Hepatic portal artery
d)
Hepatic portal vein
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Lienal vein is an old term for splenic vein. The portal vein or hepatic portal vein is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents.
There is no DNA in: [2009]- a)mature RBCs
- b)a mature spermatozoan
- c)hair root
- d)an enucleated ovum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
There is no DNA in: [2009]
a)
mature RBCs
b)
a mature spermatozoan
c)
hair root
d)
an enucleated ovum

|
Krish Chakraborty answered |
The chromatin material inside the nucleus is composed of DNA, some proteins and RNA. In fact it is DNA?protein complex basically. Thus, in an enucleated ovum, DNA will be absent. The mature RBCs, mature spermatozoan and root hair are nucleated, thus, contain DNA.
The life span of human W.B.C. is approximately [1997]- a)less than 10 days
- b)between 20 to 30 days
- c)between 2 to 3 months
- d)more than 4 months
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The life span of human W.B.C. is approximately [1997]
a)
less than 10 days
b)
between 20 to 30 days
c)
between 2 to 3 months
d)
more than 4 months
|
|
Vishal Kumar answered |
The life span of WBC ranges from 6 - 20 days, depending on the type, after which they are destroyed in the lymphatic system. When immature WBCs are first released from the bone marrow into the blood, they are called bands or stabs.
Arteries are best defined as the vessels which : [2011]- a)supply oxygenated blood to the different organs
- b)break up into capillaries which reunite to form a vein
- c)break up into capillaries which reunite to form one visceral organ
- d)carry blood from one visceral organ to another visceral organ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arteries are best defined as the vessels which : [2011]
a)
supply oxygenated blood to the different organs
b)
break up into capillaries which reunite to form a vein
c)
break up into capillaries which reunite to form one visceral organ
d)
carry blood from one visceral organ to another visceral organ
|
|
Bindu Bhavani answered |
Arteries supply blood to tissue by breaking into capillaries and deoxy blood from tissue is collected to form vein
Rh incompatibility develops when :- a)foetus is Rh-ve and father is Rh+ve
- b)foetus is Rh+ve and mother is Rh-ve
- c)foetus is Rh-ve and mother is Rh+ve
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rh incompatibility develops when :
a)
foetus is Rh-ve and father is Rh+ve
b)
foetus is Rh+ve and mother is Rh-ve
c)
foetus is Rh-ve and mother is Rh+ve
d)
None of these

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
A special case of Rh incompatibility (mismatching) has been observed between the Rh-veblood of a pregnant mother with Rh+ve blood of the foetus.
Which of the following statements doesn’t hold true for blood clotting cascade?
i. Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin.
ii. Prothrombinis converted into thrombin in the presence of vitamin K and Na+ions.
iii. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin in the presence of Ca++ions
iv. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.- a)only statement i) and iv) are wrong
- b)only statement ii) and iii) are wrong
- c)all statements are wrong
- d)only statement iv) is wrong
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements doesn’t hold true for blood clotting cascade?
i. Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin.
ii. Prothrombinis converted into thrombin in the presence of vitamin K and Na+ions.
iii. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin in the presence of Ca++ions
iv. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.
i. Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin.
ii. Prothrombinis converted into thrombin in the presence of vitamin K and Na+ions.
iii. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin in the presence of Ca++ions
iv. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.
a)
only statement i) and iv) are wrong
b)
only statement ii) and iii) are wrong
c)
all statements are wrong
d)
only statement iv) is wrong

|
Krish Patel answered |
Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin. Fibrinogen present in blood plasma is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.
The course of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart is called- a)Systemic circulation
- b)Double circulation
- c)Pulmonary circulation
- d)Single circulation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The course of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart is called
a)
Systemic circulation
b)
Double circulation
c)
Pulmonary circulation
d)
Single circulation

|
Vipe Saga answered |
The blood circulation from heart to lungs and back to heart is pulmonary circulation and the circulation between heart to tissue and back to heart is systematic circulation and both are included in double circulation.
What would be the cardiac output of a person having 72 heart beats per minute and a stroke volume of 50 ml?- a)360 ml
- b)7200 ml
- c)5000 ml
- d)3600 ml
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What would be the cardiac output of a person having 72 heart beats per minute and a stroke volume of 50 ml?
a)
360 ml
b)
7200 ml
c)
5000 ml
d)
3600 ml
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
(d) Cardiac Output (i) The volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per minute is called the cardiac output. It is 500 mL or 5 liters in a healthy individual. It is determined by multiplying the heart rate with the volume of blood ejected by each ventricle during each beat, which is called as stroke volume. Cardiac output = Heart rate x Stroke volume = 72 beats/min x 0.08 litre/beat = 5.5 litre/min (iii) Cardiac index is the minute volume per sq. m. of body surface area. Its normal value is 3.3 lit/min/sq.m.
Heart of Man is :-- a)Myogenic
- b)Neurogenic
- c)Cardiogenic
- d)Digenic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Heart of Man is :-
a)
Myogenic
b)
Neurogenic
c)
Cardiogenic
d)
Digenic
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |
The muscles of the human heart are stimulated to contract by nerve impulses generated by the Sino Atrial(SA) node. It is a cluster of cells which are part of the heart muscle.
•Hence the human heart is myogenic.
•Hence the human heart is myogenic.
Compared to blood our lymph has: [2009]- a)plasma without proteins
- b)more WBCs and no RBCs
- c)more RBCs and less WBCs
- d)no plasma
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Compared to blood our lymph has: [2009]
a)
plasma without proteins
b)
more WBCs and no RBCs
c)
more RBCs and less WBCs
d)
no plasma

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Lymph is a mobile connective tissue comprising lymph plasma and lymph corpuscles. Its composition is just like blood plasma except that it lacks RBCs and large plasma proteins.
Which one of the following vertebrate organs receives the oxygenated blood only ? [1996]- a)Gill
- b)Lung
- c)Liver
- d)Spleen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following vertebrate organs receives the oxygenated blood only ? [1996]
a)
Gill
b)
Lung
c)
Liver
d)
Spleen

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
Spleen and brain are the organs which receive only oxygenated blood. In gills and lungs blood picks up oxygen.
Each cardiac cycle takes 0.8 seconds to occur. Calculate how many cardiac cycles occur in 4 minutes ?- a)250
- b)75
- c)400
- d)300
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Each cardiac cycle takes 0.8 seconds to occur. Calculate how many cardiac cycles occur in 4 minutes ?
a)
250
b)
75
c)
400
d)
300

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
4 min = 240 sec. Therefore, 240/0.8 = 300 cardiac cycles.
Rate of heart beat is under the control of :-- a)Autonomic nervous system
- b)Vagus nerve
- c)Glossopharyngeal nerve
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of heart beat is under the control of :-
a)
Autonomic nervous system
b)
Vagus nerve
c)
Glossopharyngeal nerve
d)
None

|
M. Vishnu answered |
Heart rate is controlled by the two branches of the autonomic(involuntary) nervous system. Thesympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) releases the hormones (catecholamines - epinephrine and norepinephrine) to accelerate the heart rate.
Bundle of His is a network of [2003]- a)nerve fibres found throughout the heart
- b)muscle fibres distributed throughout the heart walls
- c)muscle fibres found only in the ventricle wall
- d)nerve fibres distributed in ventricles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bundle of His is a network of [2003]
a)
nerve fibres found throughout the heart
b)
muscle fibres distributed throughout the heart walls
c)
muscle fibres found only in the ventricle wall
d)
nerve fibres distributed in ventricles
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Bundle of His is a network of specialised conducting muscle fibres (Purkinje fibres) which transmit the impulse from AV node to all parts of both the ventricles.
In humans, blood passes from the post caval to the diastolic right atrium of heart due to. [2008]
- a)pushing open of the venous valves
- b)pressure difference between the caval and atrium
- c)stimulation of the sino auricular node
- d)suction pull
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In humans, blood passes from the post caval to the diastolic right atrium of heart due to. [2008]
a)
pushing open of the venous valves
b)
pressure difference between the caval and atrium
c)
stimulation of the sino auricular node
d)
suction pull

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
In human, blood passes from the post caval to the diastolic right atrium of heart due to suction pull.
Coronary heart disease is due to- a)Insufficient blood supply to the heart muscles
- b)Weakening of the heart valves
- c)Inflammation of pericardium
- d)Streptococci bacteria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Coronary heart disease is due to
a)
Insufficient blood supply to the heart muscles
b)
Weakening of the heart valves
c)
Inflammation of pericardium
d)
Streptococci bacteria
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a disease in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries. These arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle. When plaque builds up in the arteries, the condition is called atherosclerosis. The buildup of plaque occurs over many years.
Which one of the following has an open circulatory system ? [2006]
- a)Periplaneta
- b)Hirudinaria
- c)Octopus
- d)Pheretima
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following has an open circulatory system ? [2006]
a)
Periplaneta
b)
Hirudinaria
c)
Octopus
d)
Pheretima

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
Periplaneta (P. americana, the Indian Cockroach) is an insect & insects do not have closed blood circulation. Their blood (called haemolymph) even does not serve for respiration. They do not possess blood vessels in this circulatory system and hence it is an open system. Hirudinaria is a pure exception for having a closed circulatory system, even though it belongs to the phylum Annelida, which generally has an open circulatory system.
Bulk of carbon dioxide (CO2) released from body tissues into the blood is present as [2011M]- a)bicarbonate in blood plasma and RBCs
- b)free CO2 in blood plasma
- c)70% carbamino- haemoglobin and 30% as bicarbonate
- d)carbamino-haemoglobin in RBCs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bulk of carbon dioxide (CO2) released from body tissues into the blood is present as [2011M]
a)
bicarbonate in blood plasma and RBCs
b)
free CO2 in blood plasma
c)
70% carbamino- haemoglobin and 30% as bicarbonate
d)
carbamino-haemoglobin in RBCs

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
At the tissue site where partial pressure of CO2, is high due to catabolism, CO2, diffuses into blood (RBCs and plasma) and forms HCO2 and IT. At the alveolar site where pCO2, is low, the reaction proceeds in the opposite direction leading to the formation of CO2, and CO2. Thus, CO2, trapped as bicarbonate at the tissue level and transported to the alveoli is released out as CO2
Which of the following statments is true for lymph? [2002]- a)WBC and serum
- b)all components of blood except RBCs and some proteins
- c)RBCs, WBCs and plasma
- d)RBCs proteins and platelets
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statments is true for lymph? [2002]
a)
WBC and serum
b)
all components of blood except RBCs and some proteins
c)
RBCs, WBCs and plasma
d)
RBCs proteins and platelets

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
Lymph is colourless vascular connective tissue derived from tissue fluid. RBCs and platelets are absent. Only leucocytes and floating amoeboid lymphocytes are present.
Manoj has AB blood group, so he will have the following antibodies in his blood plasma :- a)a antibody
- b)both a and b antibodies
- c)b antibody
- d)No antibodies are present
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Manoj has AB blood group, so he will have the following antibodies in his blood plasma :
a)
a antibody
b)
both a and b antibodies
c)
b antibody
d)
No antibodies are present

|
Kunal Rane answered |
AB blood group does not have any antibodies in plasma.
Another term for heart attack is- a)Coronary thrombosis
- b)Myocardial infarction
- c)Cardiac arrest
- d)Ischaemia
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Another term for heart attack is
a)
Coronary thrombosis
b)
Myocardial infarction
c)
Cardiac arrest
d)
Ischaemia
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Other terms used for a heart attack include myocardial infarction, cardiac infarction, and coronary thrombosis. An infarction is when the blood supply to an area is cut off, and the tissue in that area dies.
The cardiac pacemaker in a patient fails to function normally. The doctors find that an artificial pacemaker is to be grafted in him. It is likely that it will be grafted at the site of- a)Atrioventricular bundle [2004]
- b)Purkinje system
- c)Sinuatrial node
- d)Atrioventricular node
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cardiac pacemaker in a patient fails to function normally. The doctors find that an artificial pacemaker is to be grafted in him. It is likely that it will be grafted at the site of
a)
Atrioventricular bundle [2004]
b)
Purkinje system
c)
Sinuatrial node
d)
Atrioventricular node
|
|
User Right answered |
Sinoatrial node is known as pacemaker of the heart. It helps in the generation and conduction of heart beat. It is located in the walls of the right atria just below the opening of superior venacva. The sympathetic nerves release the neurotransmitters and activates the SA node and generates electric impulse which is conducted as heart beat through out the heart.
When the cardiac pacemaker in a patient fails to function normally a artificial pacemaker is implanted at the site of SA node. It is a medical device which uses electrical impulse, generated by electrodes to contract the heart muscles, and regulate the heart beat.
When the cardiac pacemaker in a patient fails to function normally a artificial pacemaker is implanted at the site of SA node. It is a medical device which uses electrical impulse, generated by electrodes to contract the heart muscles, and regulate the heart beat.
You are required to draw blood from a patient and to keep it in a test tube for analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma. You are also provided with the following four types of test tubes. Which of them will you not use for the purpose? [2004]- a)Test tube containing calcium bicarbonate
- b)Chilled test tube
- c)Test tube containing heparin
- d)Test tube containing sodium oxalate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
You are required to draw blood from a patient and to keep it in a test tube for analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma. You are also provided with the following four types of test tubes. Which of them will you not use for the purpose? [2004]
a)
Test tube containing calcium bicarbonate
b)
Chilled test tube
c)
Test tube containing heparin
d)
Test tube containing sodium oxalate

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
Presence of calcium will remove heparin - blood anti-coagulant and will promote blood clotting. Sodium oxalate and heparin containing test tubes will not allow the blood to clot.
If due to some injury the chordae tendinae of the tricuspid valve of the human heart is partially non - functional, what will be the immediate effect? [2010]- a)The flow of blood into the aorta will be slowed down
- b)The ‘pacemaker’ will stop working
- c)The blood will tend to flow back into the left atrium
- d)The flow of blood into the pulmonary artery will be reduced
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If due to some injury the chordae tendinae of the tricuspid valve of the human heart is partially non - functional, what will be the immediate effect? [2010]
a)
The flow of blood into the aorta will be slowed down
b)
The ‘pacemaker’ will stop working
c)
The blood will tend to flow back into the left atrium
d)
The flow of blood into the pulmonary artery will be reduced

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
Tricuspid valve is the valve in the heart between the right atrium and right ventricle. The valve opens to allow blood to flow from atrium into the ventricle. Thus if tricuspid valve is partially nonfunctional, then the flow of blood into the pulmonary artery will be reduced
Which one of the following statements is incorrect ? [2006]
- a)In insects, circulating body fluids serve to distribute oxygen to tissues
- b)The residual air in lungs slightly decreases the efficiency of respiration in mammals
- c)The principle of countercurrent flow facilitates efficient respiration in gills of fishes
- d)The presence of non-respiratory air sacs, increases the efficiency of respiration in birds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is incorrect ? [2006]
a)
In insects, circulating body fluids serve to distribute oxygen to tissues
b)
The residual air in lungs slightly decreases the efficiency of respiration in mammals
c)
The principle of countercurrent flow facilitates efficient respiration in gills of fishes
d)
The presence of non-respiratory air sacs, increases the efficiency of respiration in birds
|
|
Ujwal Basu answered |
The residual air is the air that remains in the lungs after the most forceful expiration. The residual air remains in the lungs. Hence, it has no effect on respiration efficiency in mammals. The presence of non-respiratory air sacs increases the efficiency of respiration in birds. These air sacs increase the metabolic rate in birds. In insects, circulating body fluids serve to distribute oxygen to tissues. Countercurrent oxygen flow is the flow of blood through the gills in the opposite direction as the water flowing over the gills. This facilitates efficient respiration in gills of fishes.
Thus, the correct answer is 'The residual air in the lungs slightly decreases the efficiency of respiration in mammals.'
In a standard ECG which one of the following alphabets is the correct representation of the respective activity of the human heart?- a)S - start of systole [2009]
- b)T - end of diastole
- c)P - depolarisation of the atria
- d)R - repolarisation of ventricles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a standard ECG which one of the following alphabets is the correct representation of the respective activity of the human heart?
a)
S - start of systole [2009]
b)
T - end of diastole
c)
P - depolarisation of the atria
d)
R - repolarisation of ventricles

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
In a standard ECG, the P-wave is a small upward wave that indicates the depolarisation of the atria. This is caused by the activation of SA node.
Blood pressure is expressed as the ratio of systolic over diastolic pressure. The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is called pulse pressure. What will be its value for a normal healthy adult?- a)40 mm Hg
- b)30 mm Hg
- c)70 mm Hg
- d)50 mm Hg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood pressure is expressed as the ratio of systolic over diastolic pressure. The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is called pulse pressure. What will be its value for a normal healthy adult?
a)
40 mm Hg
b)
30 mm Hg
c)
70 mm Hg
d)
50 mm Hg

|
Tejas Chavan answered |
Blood pressure is represented as the ratio of systolic over diastolic pressure. The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is called pulse pressure. The value of normal healthy pulse pressure is 40 mm Hg.
Blood plasma proteins :
i. decrease in their level causes excessive absorption of water from tissues into blood.
ii. they maintain osmotic pressure.
- a)both are correct.
- b)both are wrong
- c)Statement i) is wrong and ii) is correct.
- d)Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood plasma proteins :
i. decrease in their level causes excessive absorption of water from tissues into blood.
ii. they maintain osmotic pressure.
i. decrease in their level causes excessive absorption of water from tissues into blood.
ii. they maintain osmotic pressure.
a)
both are correct.
b)
both are wrong
c)
Statement i) is wrong and ii) is correct.
d)
Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
Let's analyze the statements about blood plasma proteins:
Statement i: "Decrease in their level causes excessive absorption of water from tissues into blood."
- This statement is incorrect. A decrease in the level of blood plasma proteins would actually result in a decrease in osmotic pressure, leading to less water being drawn from tissues into the blood. Instead, it would cause water to accumulate in the tissues, leading to edema.
Statement ii: "They maintain osmotic pressure."
- This statement is correct. Blood plasma proteins, especially albumin, play a crucial role in maintaining the osmotic pressure of the blood.
Therefore, the correct option is:
3. Statement i) is wrong and ii) is correct.
Contraction of the ventricle in the heart begins by the command from [1999]- a)Chordae tendinae
- b)S.A. node
- c)Purkinje fibres
- d)A. V. node
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Contraction of the ventricle in the heart begins by the command from [1999]
a)
Chordae tendinae
b)
S.A. node
c)
Purkinje fibres
d)
A. V. node

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
SA is the site of generation of the rhythmic cardiac impulse. AV node is a compact mass of myogenic fibres which receives impulse from SA node and transmits it to ventricles. Purkinje fibres are in contact with the contractile muscles of the ventricular walls. Chordae tendinae are the muscles which keep the AV valves in position.
With respect to the ABO group, there are four major blood types because this blood group is determined by [1998]- a)three alleles, all of which are recessive
- b)three alleles, of which, two are recessive and the third is dominant
- c)three alleles, of which two are codominant and the third is recessive
- d)three alleles , all of which are codominant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
With respect to the ABO group, there are four major blood types because this blood group is determined by [1998]
a)
three alleles, all of which are recessive
b)
three alleles, of which, two are recessive and the third is dominant
c)
three alleles, of which two are codominant and the third is recessive
d)
three alleles , all of which are codominant

|
Kajal Bose answered |
Blood group is determined by three alleles - IA, IB, and Io. Alleles IA and IB are codominant. Blood group A is determined by IA IA or IA Io. Blood group B is IB IB or IB Io. Blood group O is Io Io. Blood group AB is IA IB.
In ECG, the depolarisation of atria is indicated by- a)S-wave
- b)R-wave
- c)P-wave
- d)Q-wave
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In ECG, the depolarisation of atria is indicated by
a)
S-wave
b)
R-wave
c)
P-wave
d)
Q-wave

|
Savita Soni answered |
By P wave
11 ncert page no 286
11 ncert page no 286
Chapter doubts & questions for Body Fluids and Circulation - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Body Fluids and Circulation - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily