All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Locomotion and Movement for NEET Exam
Pick out the correct match.- a)Pelvis = 3 bones
- b)Sternum = 14 bones
- c)Ribs = 20 bones
- d)Face = 5 bones
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick out the correct match.
a)
Pelvis = 3 bones
b)
Sternum = 14 bones
c)
Ribs = 20 bones
d)
Face = 5 bones
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The pelvic girdle, as above, is made up of three fused bones: the ischium, the ilium, and the pubis. The pubis forms the anterior part of the pelvic girdle. It is a flattened, irregular-shaped bone that articulates with the pubic symphysis, a cartilaginous joint.
A sesamoid bone is- a)Palatine
- b)Patella
- c)Pterygoid
- d)Presphenoid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A sesamoid bone is
a)
Palatine
b)
Patella
c)
Pterygoid
d)
Presphenoid
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Patella is the small bone in knee joint between femur and tibia. It is a sesamoid bone developed in the tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle.
Contractile unit of muscle fibres :-- a)H line
- b)Sarcomere
- c)H zone
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Contractile unit of muscle fibres :-
a)
H line
b)
Sarcomere
c)
H zone
d)
None

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
A sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of muscle fiber.
Each sarcomere is composed of two main protein filaments, actin and myosin, which are the active structures responsible for muscular contraction.
Which of the following facial bones is unpaired?- a)Nasal
- b)Vomer
- c)Palatine
- d)Lacrimal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following facial bones is unpaired?
a)
Nasal
b)
Vomer
c)
Palatine
d)
Lacrimal
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The unpaired bones of the human skull are: frontal, occipital, ethmoid, sphenoid, mandible and vomer. The frontal bone is self explanatory in name.
Which of the following statements about the mechanism of muscle contraction are correct?A. Acetylcholine is released when the neural signal reaches the motor end plate.B. Muscle contraction is initiated by a signal sent by CNS via a sensory neuron.C. During muscle contraction, the isotropic band gets elongated.D. Repeated activation of the muscle can lead to accumulation of lactic acid.- a)B and C are correct.
- b)A and D are correct.
- c)A, Band C are correct.
- d)A and C are correct.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the mechanism of muscle contraction are correct?
A. Acetylcholine is released when the neural signal reaches the motor end plate.
B. Muscle contraction is initiated by a signal sent by CNS via a sensory neuron.
C. During muscle contraction, the isotropic band gets elongated.
D. Repeated activation of the muscle can lead to accumulation of lactic acid.
a)
B and C are correct.
b)
A and D are correct.
c)
A, Band C are correct.
d)
A and C are correct.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Following are the correct statements about the mechanism of muscle contraction:
(i) Acetylcholine is released when the neural signal reaches the motor end plate.
(ii) Repeated activation of the muscles can lead to lactic acid accumulation.
So, the correct answer is (B).
(i) Acetylcholine is released when the neural signal reaches the motor end plate.
(ii) Repeated activation of the muscles can lead to lactic acid accumulation.
So, the correct answer is (B).
Cardiac muscles Fibres :-- a)Involuntary
- b)Non-fatigue
- c)Striated like
- d)All
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cardiac muscles Fibres :-
a)
Involuntary
b)
Non-fatigue
c)
Striated like
d)
All

|
Anand Jain answered |
Cardiac muscle is found only in the walls of the heart. When cardiac muscle contracts, the heart beats and pumps blood. Cardiac muscle contains a great many mitochondria, which produce ATP for energy. This helps the heart resist fatigue. Contractions of cardiac muscle are involuntary, like those of smooth muscle. Cardiac muscle, like skeletal muscle, is arranged in bundles, so it appears striated, or striped.
Hence, the answer is (D)
ATP-ase activity found in :-- a)Myosin filament
- b)Actin filament
- c)Both
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
ATP-ase activity found in :-
a)
Myosin filament
b)
Actin filament
c)
Both
d)
None
|
|
Wahid Khan answered |
In all myosins, the head domain is a specialized ATPase that is able to couple the hydrolysis of ATP with motion. A critical feature of the myosin ATPase activity is that it is actin-activated. In the absence of actin, solutions of myosin slowly convertATP into ADP and phosphate.
The contractile unit of muscle is a part of myofibril between- a)A band and I band
- b)Z line and Z line
- c)Z line and A band
- d)Z line and I band
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The contractile unit of muscle is a part of myofibril between
a)
A band and I band
b)
Z line and Z line
c)
Z line and A band
d)
Z line and I band
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
The region between two Z lines is called a sarcomere; sarcomeres can be considered the primary structural and functional unit of muscle tissue. Ultrastructure of a group of myofibrils, showing the sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules, which constitute the two membrane systems within a muscle fibre.
Which one of the following pairs of chemical substances is correctly categorized? [2012M]- a)Calcitonin and thymosin - Thyroid hormones
- b)Pepsin and prolactin - Two digestive enzymes secreted in stomach
- c)Troponin and myosin - Complex proteins in striated muscles
- d)Secretin and rhodopsin - Polypeptide hormones
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of chemical substances is correctly categorized? [2012M]
a)
Calcitonin and thymosin - Thyroid hormones
b)
Pepsin and prolactin - Two digestive enzymes secreted in stomach
c)
Troponin and myosin - Complex proteins in striated muscles
d)
Secretin and rhodopsin - Polypeptide hormones

|
Shounak Nair answered |
Troponin is a protein which is found on actin filament and myosin protein is found in myosin filament. Both actin and myosin are complex proteins in striated muscles.
Thymosin is a hormone secreted by the thymus that stimulates development of T cells. Prolactin is a hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates breast development and milk production in women. Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is not a hormone. It is a biological pigment in photoreceptor cells of the retina that is responsible for the first events in the perception of light
Thymosin is a hormone secreted by the thymus that stimulates development of T cells. Prolactin is a hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates breast development and milk production in women. Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is not a hormone. It is a biological pigment in photoreceptor cells of the retina that is responsible for the first events in the perception of light
ATPase enzyme needed for muscle contraction is located in- a)Myosin
- b)Actin
- c)Troponin
- d)Actinin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
ATPase enzyme needed for muscle contraction is located in
a)
Myosin
b)
Actin
c)
Troponin
d)
Actinin
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
During muscle contraction, hydrolysis of ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate occurs. The energy released during the process raises the meromyosin head to a high-energy state. The enzyme myosin ATPase catalyses the reaction in the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+.


During contraction of muscles :-- a)Actin Filament slide over actin
- b)Myosin filament slide over actin
- c)Actin filament slide over myosin
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During contraction of muscles :-
a)
Actin Filament slide over actin
b)
Myosin filament slide over actin
c)
Actin filament slide over myosin
d)
none
|
|
Prem Darade answered |
Mechanism of muscle contraction is best explained by the sliding filament theory, which states that contraction of a muscle fibre takes place by the sliding of the thin filaments over the thick filaments. The actin filament slide over myosin filament thus reduces the length of the sarcomere and contracts the muscle fibre.
So, the correct answer is option C.
So, the correct answer is option C.
The H-zone in the skeletal muscle fibre is due to : [NEET 2013]- a)The central gap between myosin filaments in the A-band.
- b)The central gap between actin filaments extending through myosin filaments in the A-band
- c)Extension of myosin filaments in the central portion of the A-band.
- d)The absence of myofibrils in the central portion of A-band.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The H-zone in the skeletal muscle fibre is due to : [NEET 2013]
a)
The central gap between myosin filaments in the A-band.
b)
The central gap between actin filaments extending through myosin filaments in the A-band
c)
Extension of myosin filaments in the central portion of the A-band.
d)
The absence of myofibrils in the central portion of A-band.

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
Central part of thick filament, not overlapped by thin filaments is called the ‘H’ zone. ‘H’ zone is also called Hensen’s Line.
Which ion is essential for muscle contraction? [1994]- a)Na
- b)K
- c)Ca
- d)Cl
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which ion is essential for muscle contraction? [1994]
a)
Na
b)
K
c)
Ca
d)
Cl

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
Movement of Ca2+ out in sarcoplasmic reticulum controls the making and breaking of actin and myosin complex actomyosin due to which muscle contraction and relaxation takes place. Albert Szent Gyorgyi worked out biochemical events of muscle contraction.
During vigorous exercise :
i. lactic acid accumulates in muscle cells to meet its energy needs immediately.
ii. lactic acid is formed by anaerobic respiration hence oxygen consumption by muscles is reduced.
iii. This reduction in oxygen consumption is called oxygen debt of muscle.
Which of the following statement is Correct ?
- a)only statement ii) and iii) are correct.
- b)only statement i) and ii) are correct.
- c)only statement i) is correct.
- d)all statements are correct.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During vigorous exercise :
i. lactic acid accumulates in muscle cells to meet its energy needs immediately.
ii. lactic acid is formed by anaerobic respiration hence oxygen consumption by muscles is reduced.
iii. This reduction in oxygen consumption is called oxygen debt of muscle.
Which of the following statement is Correct ?
i. lactic acid accumulates in muscle cells to meet its energy needs immediately.
ii. lactic acid is formed by anaerobic respiration hence oxygen consumption by muscles is reduced.
iii. This reduction in oxygen consumption is called oxygen debt of muscle.
Which of the following statement is Correct ?
a)
only statement ii) and iii) are correct.
b)
only statement i) and ii) are correct.
c)
only statement i) is correct.
d)
all statements are correct.

|
Prisha Singh answered |
During vigorous exercise, lactic acid accumulates in muscles cells to meet the energy requirement of muscle cell. Lactic acid is formed due to insufficient availability of oxygen.
Select the correct statement with respect to locomotion in humans : [NEET 2013]- a)Accumulation of uric acid cr ystals in joints causes their inflammation
- b)The vertebral column has 10 thoracic vertebrae.
- c)The joint between adjacent vertebrae is a fibrous joint
- d)The decreased level of progesterone causes osteoporosis in old people
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement with respect to locomotion in humans : [NEET 2013]
a)
Accumulation of uric acid cr ystals in joints causes their inflammation
b)
The vertebral column has 10 thoracic vertebrae.
c)
The joint between adjacent vertebrae is a fibrous joint
d)
The decreased level of progesterone causes osteoporosis in old people

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
Vertebral column has 12th or acicvertebrate. The joints between adjacent vertebrae is cartilaginous joint which permits limited movements. Progesterone is secreted by corpus luteum which supports in pregnancy in females
Skeletal muscle bundles [fascicles] are held together by a common connective tissue layer called:- a)Perimysium
- b)Endomysium
- c)Fascia
- d)Aponeurosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Skeletal muscle bundles [fascicles] are held together by a common connective tissue layer called:
a)
Perimysium
b)
Endomysium
c)
Fascia
d)
Aponeurosis
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibers known as tendons. A skeletal muscle refers to multiple bundles (fascicles) of cells joined together called muscle fibers. The fibers and muscles are surrounded by connective tissue layers called fasciae.
Each pectoral girdle :
i. has 2 pairs of bones, a pair of clavicle and a pair of scapula.
ii. scapula contains expanded process and glenoid cavity, the latter is for articulation of the head of humerus.
- a)Both are correct
- b)Statement i) is wrong and ii) is correct.
- c)both are wrong
- d)Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Each pectoral girdle :
i. has 2 pairs of bones, a pair of clavicle and a pair of scapula.
ii. scapula contains expanded process and glenoid cavity, the latter is for articulation of the head of humerus.
i. has 2 pairs of bones, a pair of clavicle and a pair of scapula.
ii. scapula contains expanded process and glenoid cavity, the latter is for articulation of the head of humerus.
a)
Both are correct
b)
Statement i) is wrong and ii) is correct.
c)
both are wrong
d)
Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong.

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
Statement 1: Each pectoral girdle has two pairs of bones: a pair of clavicles and a pair of scapulae. The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, is a skeletal structure that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton.
Statement 2: The head of the humerus bone articulates with the glenoid cavity of the pectoral girdle.
Hence both are correct.
Statement 2: The head of the humerus bone articulates with the glenoid cavity of the pectoral girdle.
Hence both are correct.
Elbow joint is an example of: [2009]- a)hinge joint
- b)gliding joint
- c)ball and socket joint
- d)pivot joint
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Elbow joint is an example of: [2009]
a)
hinge joint
b)
gliding joint
c)
ball and socket joint
d)
pivot joint

|
Subham Chavan answered |
Elbow joint is an example of hinge joint. The elbow is a hinge joint; it can open and close like a door. Hinge joint is a form of diarthrosis (freely movable joint) that allows angular movement in one plane only, increasing or decreasing the angle between the bones e.g. elbow joint, knee joint etc.
Which of these disorders is caused due to low concentrations of calcium ions?- a)Muscular dystrophy
- b)Gout
- c)Tetany
- d)Osteoporosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these disorders is caused due to low concentrations of calcium ions?
a)
Muscular dystrophy
b)
Gout
c)
Tetany
d)
Osteoporosis
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Muscular dystrophy, gout, tetany and osteoporosis are disorders of the muscular system and the skeletal system. Out of these, tetany is caused due to low concentrations of calcium ions.
Which one of the following is anatomically correct for the human body?- a)Cranial nerves: 10 pairs
- b)Floating ribs: 2 pairs
- c)Collar bones: 3 pairs
- d)Salivary glands: 1 pair
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is anatomically correct for the human body?
a)
Cranial nerves: 10 pairs
b)
Floating ribs: 2 pairs
c)
Collar bones: 3 pairs
d)
Salivary glands: 1 pair

|
Smrity answered |
Ya correct option is B in the rib cage of human body the floating ribs only 2 pairs .
Select the correct statement with respect to disorders of muscles in humans [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Rapid contractions of skeletal muscles causes muscle dystrophy
- b)Failure of neuromuscular transmission in myasthenia gravis can prevent normal swallowing
- c)Accumulation of urea and creatine in the joints cause their inflammation
- d)An over dose of vitamin D causes osteoporosis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement with respect to disorders of muscles in humans [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Rapid contractions of skeletal muscles causes muscle dystrophy
b)
Failure of neuromuscular transmission in myasthenia gravis can prevent normal swallowing
c)
Accumulation of urea and creatine in the joints cause their inflammation
d)
An over dose of vitamin D causes osteoporosis

|
Shounak Nair answered |
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune muscular disease. It causes
breakdown of neuromuscular junction due to which the brain loses control over muscles. The symptoms may include drooping eyelids, difficulty in swallowing muscle fatigue, difficult breathing and inability to control facial expressions.
breakdown of neuromuscular junction due to which the brain loses control over muscles. The symptoms may include drooping eyelids, difficulty in swallowing muscle fatigue, difficult breathing and inability to control facial expressions.
Axial skeleton consists of- a)22 bones
- b)65 bones
- c)80 bones
- d)70 bones
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Axial skeleton consists of
a)
22 bones
b)
65 bones
c)
80 bones
d)
70 bones

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
The axial skeleton comprises 80 bones distributed along the main axis of the body.
Which statement is correct for muscle contraction? [2001]- a)Length of H-line decreases
- b)Length of A-band remains constant
- c)Length of I-band increases
- d)Length of two Z-lines increase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is correct for muscle contraction? [2001]
a)
Length of H-line decreases
b)
Length of A-band remains constant
c)
Length of I-band increases
d)
Length of two Z-lines increase

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
When Ca+ ions combine with troponin contraction of muscles initiates. During Contraction the Z lines come closer together and the sarcomere becomes shorter. The length of A band remains constant. I bands shortens and H-band narrows.
Read the statements carefully and comment on them.
A. A bands of muscle fibre are dark and contain myosin.
B. I bands of muscle fibre are light and contain actin.
C. During muscle contraction, the A bands contract.
D. The part between two Z lines is called sarcomere.
E. The central part of the thin filament not overlapped by the thick filament is the H zone.
- a)A, C and E are correct, while B and D are incorrect.
- b)A, B and D are correct, while C and E are incorrect.
- c)A, B and C are correct, while D and E are incorrect.
- d)A and B are correct, while C, D and E are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the statements carefully and comment on them.
A. A bands of muscle fibre are dark and contain myosin.
B. I bands of muscle fibre are light and contain actin.
C. During muscle contraction, the A bands contract.
D. The part between two Z lines is called sarcomere.
E. The central part of the thin filament not overlapped by the thick filament is the H zone.
a)
A, C and E are correct, while B and D are incorrect.
b)
A, B and D are correct, while C and E are incorrect.
c)
A, B and C are correct, while D and E are incorrect.
d)
A and B are correct, while C, D and E are incorrect.

|
Arohi Shinde answered |
Statement E is correct
Read the following statements carefully and select the correct ones.
(i) Cardiac fibres are branched with one or more nuclei.
(ii) Smooth muscles are unbranched and cylindrical.
(iii) Skeletal muscles can be branched or unbranched.
(iv) Smooth muscles are non-striated.- a)only (iv)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(iii) and (iv)
- d)only (iii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and select the correct ones.
(i) Cardiac fibres are branched with one or more nuclei.
(ii) Smooth muscles are unbranched and cylindrical.
(iii) Skeletal muscles can be branched or unbranched.
(iv) Smooth muscles are non-striated.
(i) Cardiac fibres are branched with one or more nuclei.
(ii) Smooth muscles are unbranched and cylindrical.
(iii) Skeletal muscles can be branched or unbranched.
(iv) Smooth muscles are non-striated.
a)
only (iv)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(iii) and (iv)
d)
only (iii)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Smooth muscles are non-striated, unbranched and spindle shaped. Skeletal muscles are unbranched. Cardiac muscles fibres are uni-nucleated.
Read the following statements about muscle contraction in humans :
i. chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
ii. a neurotransmitter acetylcholine at motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
iii. in a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
iv. a contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
- a)only iv) is correct.
- b)only i), iii) and iv) are correct.
- c)only i) and iv) are correct.
- d)only ii), iii) and iv) are correct.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements about muscle contraction in humans :
i. chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
ii. a neurotransmitter acetylcholine at motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
iii. in a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
iv. a contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
i. chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
ii. a neurotransmitter acetylcholine at motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
iii. in a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
iv. a contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
a)
only iv) is correct.
b)
only i), iii) and iv) are correct.
c)
only i) and iv) are correct.
d)
only ii), iii) and iv) are correct.
|
|
Akash Khanna answered |
Explanation:
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the conversion of chemical energy into mechanical energy. Let's analyze each statement to understand why option 'B' is the correct answer.
i. Chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction, and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
During muscle contraction, chemical energy stored in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is converted into mechanical energy. ATP is the primary energy source for muscle contraction. The release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine initiates the process of muscle contraction by transmitting the electrical signal from the nervous system to the muscle fibers.
ii. A neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
This statement is incorrect. Acetylcholine released at the motor end plate does not directly convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. It acts as a chemical messenger that binds to receptors on the muscle fibers, triggering a series of events that lead to muscle contraction. The electrical energy from the nerve impulse is converted into a chemical signal (acetylcholine) which then initiates the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, leading to muscle contraction.
iii. In a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
This statement is incorrect. During muscle contraction, the volume of the muscle decreases. As the muscle fibers generate force, they pull on the tendons, causing the muscle to shorten. This shortening leads to a decrease in muscle volume.
iv. A contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
This statement is correct. When a muscle contracts, it becomes shorter and thicker. The individual muscle fibers slide past each other, causing the overlapping actin and myosin filaments to shorten. This sliding filament mechanism is responsible for muscle contraction. As the muscle fibers shorten, the muscle as a whole becomes thicker.
Based on the explanations above, we can conclude that only statements i), iii), and iv) are correct. Hence, the correct answer is option 'B' - only i), iii), and iv) are correct.
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the conversion of chemical energy into mechanical energy. Let's analyze each statement to understand why option 'B' is the correct answer.
i. Chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction, and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
During muscle contraction, chemical energy stored in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is converted into mechanical energy. ATP is the primary energy source for muscle contraction. The release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine initiates the process of muscle contraction by transmitting the electrical signal from the nervous system to the muscle fibers.
ii. A neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
This statement is incorrect. Acetylcholine released at the motor end plate does not directly convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. It acts as a chemical messenger that binds to receptors on the muscle fibers, triggering a series of events that lead to muscle contraction. The electrical energy from the nerve impulse is converted into a chemical signal (acetylcholine) which then initiates the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, leading to muscle contraction.
iii. In a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
This statement is incorrect. During muscle contraction, the volume of the muscle decreases. As the muscle fibers generate force, they pull on the tendons, causing the muscle to shorten. This shortening leads to a decrease in muscle volume.
iv. A contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
This statement is correct. When a muscle contracts, it becomes shorter and thicker. The individual muscle fibers slide past each other, causing the overlapping actin and myosin filaments to shorten. This sliding filament mechanism is responsible for muscle contraction. As the muscle fibers shorten, the muscle as a whole becomes thicker.
Based on the explanations above, we can conclude that only statements i), iii), and iv) are correct. Hence, the correct answer is option 'B' - only i), iii), and iv) are correct.
Which of the following is not a function of vertebral column?- a)Protects spinal cord and supports the head
- b)Serves as the point of attachment for ribs and musculature of the back
- c)Supports tarsals and metacarpals
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a function of vertebral column?
a)
Protects spinal cord and supports the head
b)
Serves as the point of attachment for ribs and musculature of the back
c)
Supports tarsals and metacarpals
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Tarsals and metacarpals are the bones of the limb, therefore, they are the part of appendicular skeleton and not the axial skeleton which consists of vertebral column.
निम्नलिखित में से कौन भारत का पहला स्वदेशी रूप से डिजाइन और विकसित लड़ाकू विमान है?- a)तेजस
- b)गुस्सा
- c)हंसा
- d)सरस
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन भारत का पहला स्वदेशी रूप से डिजाइन और विकसित लड़ाकू विमान है?
a)
तेजस
b)
गुस्सा
c)
हंसा
d)
सरस
|
|
Meera Kapoor answered |
भारत के 72 वें गणतंत्र दिवस के अवसर पर, आगंतुकों के लिए, लॉकडाउन अवधि के दौरान बहाल किए गए रेल लोकोमोटिव के अपने कलाकृतियों को नेहरू विज्ञान केंद्र, मुंबई ने फिर से समर्पित किया।
- भारत का पहला स्वदेशी रूप से डिजाइन और विकसित लड़ाकू विमान मारुत अब जनता के देखने के लिए उपलब्ध होगा।
- डीसी इलेक्ट्रिक लोको नं 20024 एन वी सी पी 2 को 1938 में ग्रेट इंडियन पेनिनसुलर रेलवे में कमीशन किया गया था और 40 साल तक कल्याण-पुणे सेक्शन पर पैसेंजर ट्रेनों को चलाने के लिए इस्तेमाल किया गया था।
- इसमें मुंबई से पुणे तक प्रतिष्ठित डेक्कन क्वीन के शासन का गौरव है।
- डीसी इलेक्ट्रिक लोको नं 20024 एन वी सी पी 2 भारतीय उप-महाद्वीप में इलेक्ट्रिक ट्रैक्शन की शुरूआत के बाद सेवा में शामिल किए गए पहले इलेक्ट्रिक इंजनों में से एक है
- मारुत को शुरू में सुपरसोनिक गति को पार करने के लिए विकसित किया गया था, लेकिन कभी भी मच 1 को छू नहीं सकता था, इसलिए अब यह रिकॉर्ड तेजस एलसीए के साथ है। कुल 147 मारुत का निर्माण किया गया, और भारतीय वायुसेना ने 1967 में पहली इकाई को शामिल किया। एचएफ -24 मारुत ने 1961 में अपनी पहली उड़ान का संचालन किया। जबकि मारुत ने 1971 के भारत-पाक युद्ध के दौरान लोंगेवाला सीमा पर 1980 के दशक में एक बड़ी भूमिका निभाई। अप्रचलित हो गया और 1990 तक चरणबद्ध हो गया।
The correctorganisation of skeletal muscle is :- a)muscle bundles →→ myofibrils →→ muscle cells →→ sarcomere
- b)fascicles →→ muscle fibres →→ myofilaments →→ sarcomere
- c)muscle bundles →→ muscle cells →→ muscle fibres →→ sarcomere
- d)fascia →→ muscle cells →→ myofibrils →→ sarcomere
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correctorganisation of skeletal muscle is :
a)
muscle bundles →→ myofibrils →→ muscle cells →→ sarcomere
b)
fascicles →→ muscle fibres →→ myofilaments →→ sarcomere
c)
muscle bundles →→ muscle cells →→ muscle fibres →→ sarcomere
d)
fascia →→ muscle cells →→ myofibrils →→ sarcomere

|
Pooja Saha answered |
Each organised skeletal muscle in our body is made of a number of muscle bundles or fascicles held together by a common collagenous connective tissue layer called fascia. Each muscle bundle contains a number of muscle fibres. A characteristic feature of the muscle fibre is the presence of a large number of parallelly arranged filaments in the sarcoplasm called myofilaments or myofibrils. The portion of the myofibril between two successive ‘Z’ lines is considered as the functional unit of contraction and is called a sarcomere.
The slow twitch muscle fibres which are rich in myoglobin and have abundant mitochondria are- a)white skeletal muscles
- b)cardiac muscles
- c)red skeletal muscles
- d)involuntary muscles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The slow twitch muscle fibres which are rich in myoglobin and have abundant mitochondria are
a)
white skeletal muscles
b)
cardiac muscles
c)
red skeletal muscles
d)
involuntary muscles
|
|
Akshat Joshi answered |
Red skeletal muscles, also known as slow twitch muscle fibers, are rich in myoglobin and have abundant mitochondria. These muscle fibers are responsible for endurance activities and are found in muscles that are used for sustained, repetitive movements.
Myoglobin is a protein that is responsible for storing and transporting oxygen within muscle cells. It has a high affinity for oxygen, allowing it to efficiently bind and release oxygen as needed during muscle contraction. Red skeletal muscles have a high concentration of myoglobin, which gives them their characteristic red color.
The abundance of mitochondria in red skeletal muscles is another key characteristic of these muscle fibers. Mitochondria are known as the "powerhouses" of the cell because they are responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The aerobic metabolism that takes place in mitochondria is essential for providing the sustained energy needed for endurance activities.
The high concentration of myoglobin and abundant mitochondria in red skeletal muscles allow them to generate energy efficiently and sustain muscle contractions for extended periods of time. This makes them well-suited for activities such as long-distance running, cycling, and swimming.
In contrast, white skeletal muscles, also known as fast twitch muscle fibers, have a lower concentration of myoglobin and fewer mitochondria. These muscle fibers are responsible for generating quick, powerful contractions but fatigue more quickly compared to red skeletal muscles. White skeletal muscles are typically used for activities that require short bursts of intense effort, such as weightlifting or sprinting.
Cardiac muscles, on the other hand, are a type of involuntary muscle found in the heart. They also have a high concentration of myoglobin and abundant mitochondria to support their continuous contraction and pumping action.
In summary, the slow twitch muscle fibers found in red skeletal muscles are rich in myoglobin and have abundant mitochondria. These muscle fibers are well-suited for endurance activities and provide sustained energy for prolonged periods of muscle contraction.
Myoglobin is a protein that is responsible for storing and transporting oxygen within muscle cells. It has a high affinity for oxygen, allowing it to efficiently bind and release oxygen as needed during muscle contraction. Red skeletal muscles have a high concentration of myoglobin, which gives them their characteristic red color.
The abundance of mitochondria in red skeletal muscles is another key characteristic of these muscle fibers. Mitochondria are known as the "powerhouses" of the cell because they are responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The aerobic metabolism that takes place in mitochondria is essential for providing the sustained energy needed for endurance activities.
The high concentration of myoglobin and abundant mitochondria in red skeletal muscles allow them to generate energy efficiently and sustain muscle contractions for extended periods of time. This makes them well-suited for activities such as long-distance running, cycling, and swimming.
In contrast, white skeletal muscles, also known as fast twitch muscle fibers, have a lower concentration of myoglobin and fewer mitochondria. These muscle fibers are responsible for generating quick, powerful contractions but fatigue more quickly compared to red skeletal muscles. White skeletal muscles are typically used for activities that require short bursts of intense effort, such as weightlifting or sprinting.
Cardiac muscles, on the other hand, are a type of involuntary muscle found in the heart. They also have a high concentration of myoglobin and abundant mitochondria to support their continuous contraction and pumping action.
In summary, the slow twitch muscle fibers found in red skeletal muscles are rich in myoglobin and have abundant mitochondria. These muscle fibers are well-suited for endurance activities and provide sustained energy for prolonged periods of muscle contraction.
Which of the following is/are not correctly matched pairs?
(i) Ball and socket joint — Between humerus and pectoral girdle
(ii) Pivot joint — Between carpal and metacarpal
(iii) Saddle joint — Between atlas and axis
(iv) Gliding joint — Between the carpals
(v) Fibrous joint — In flat skull bones
- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(i) and (iv)
- c)(v) only
- d)(ii) only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are not correctly matched pairs?
(i) Ball and socket joint — Between humerus and pectoral girdle
(ii) Pivot joint — Between carpal and metacarpal
(iii) Saddle joint — Between atlas and axis
(iv) Gliding joint — Between the carpals
(v) Fibrous joint — In flat skull bones
(i) Ball and socket joint — Between humerus and pectoral girdle
(ii) Pivot joint — Between carpal and metacarpal
(iii) Saddle joint — Between atlas and axis
(iv) Gliding joint — Between the carpals
(v) Fibrous joint — In flat skull bones
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(i) and (iv)
c)
(v) only
d)
(ii) only
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Pivot joint — between atlas and axis.
Saddle joint — between carpal and metacarpal.
Saddle joint — between carpal and metacarpal.
Which of the following bones form a link between axial and appendicular skeleton?- a)First rib
- b)Clavicle
- c)Scapula
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following bones form a link between axial and appendicular skeleton?
a)
First rib
b)
Clavicle
c)
Scapula
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Clavicle is a bone that forms part of the pectoral girdle (part of appendicular skeleton) linking the scapula to the sternum (part of axial skeleton).
The property which doesn’t belong to muscle fibres is :- a)conductivity
- b)Excitability
- c)Contractility
- d)elasticity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The property which doesn’t belong to muscle fibres is :
a)
conductivity
b)
Excitability
c)
Contractility
d)
elasticity

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Muscle fibres have properties of excitability, elasticity and contractility but conductivity is not present in muscles fibers. These fibres help in movement of different body parts.
Myasthenia gravis leads to fatigue and weakness. It is not :- a)neuromuscular disease
- b)causing paralysis of respiratory muscles
- c)autoimmune disorder
- d)affecting heart muscles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Myasthenia gravis leads to fatigue and weakness. It is not :
a)
neuromuscular disease
b)
causing paralysis of respiratory muscles
c)
autoimmune disorder
d)
affecting heart muscles

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
Myasthenia gravis is an auto immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle.
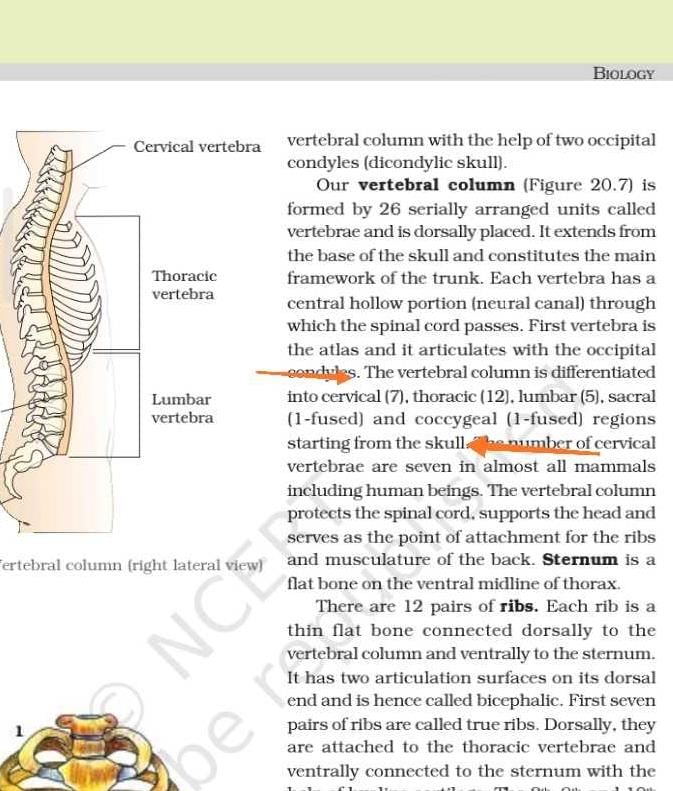
The following X-ray shows :
- a)a person with osteoporosis in his knee
- b)a person with gout in his knee
- c)a person with muscular dystrophy
- d)a person with bone cancer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following X-ray shows :
a)
a person with osteoporosis in his knee
b)
a person with gout in his knee
c)
a person with muscular dystrophy
d)
a person with bone cancer

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
The X-ray of knee shows gout in the knee. Gout is a kind of arthritis. It can cause an attack of sudden burning pain, stiffness and swelling in joint.
In human body, which one of the following is anatomically correct? [2007]- a)Collar bones - 3 pairs
- b)Salivary glands - 1 pairs
- c)Cranial nerves - 10 pairs
- d)Floating ribs - 2 pairs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In human body, which one of the following is anatomically correct? [2007]
a)
Collar bones - 3 pairs
b)
Salivary glands - 1 pairs
c)
Cranial nerves - 10 pairs
d)
Floating ribs - 2 pairs

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Floating ribs are 2- pairs (11th and 12th pair) which are not attached to sternum
Actin binding sites are located on- a)troponin
- b)tropomyosin
- c)meromyosin
- d)both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Actin binding sites are located on
a)
troponin
b)
tropomyosin
c)
meromyosin
d)
both (b) and (c)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Heavy meromyosin consists of two globular sub-frament (S-1) and one rod shaped fibre sub-fragment (S-2). Each S-1 segment contains an ATPase site and a binding site for actin.
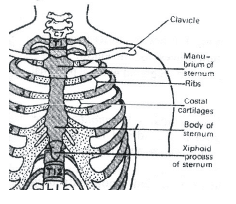
The figures given here represent three different conditions of sarcomeres. Identify these conditions and select the correct option.
- a)A - Contracting B - Relax C - Maximally contacted
- b)A - Relax B - Contracting C - Maximally contacted
- c)A - Maximally contacted B - Contracting C - Relax
- d)A - Relax B - Contracting C - Contacting
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The figures given here represent three different conditions of sarcomeres. Identify these conditions and select the correct option.


a)
A - Contracting B - Relax C - Maximally contacted
b)
A - Relax B - Contracting C - Maximally contacted
c)
A - Maximally contacted B - Contracting C - Relax
d)
A - Relax B - Contracting C - Contacting
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
In the given figure A, the length of the two sarcomeres is normal i.e., the muscle is in relaxed state. In figure B. the length of sarcomeres, shortens, H-zone narrows and size of l-band decreases i.e., the muscle is contracting. In figure C, the length of sarcomere further shortens and H-zone disappears and l-band further decreases i.e., the muscle is maximally contracted.
Assertion (A): Red fibres in muscles have a high content of myoglobin, which contributes to their reddish appearance.Reason (R): These fibres primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism for energy production.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Red fibres in muscles have a high content of myoglobin, which contributes to their reddish appearance.
Reason (R): These fibres primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism for energy production.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- The Assertion is true because red fibres do indeed have a high content of myoglobin, which gives them a reddish appearance.
- The Reason is false because red fibres primarily rely on aerobic metabolism due to their high myoglobin and mitochondrial content, not anaerobic metabolism.
- Since the Assertion is true and the Reason is false, Option B is correct as both statements are true, but the Reason does not correctly explain the Assertion.
Line in NCERT: Muscle contains a red coloured oxygen storing pigment called myoglobin. Myoglobin content is high in some of the muscles which gives a reddish appearance. Such muscles are called the Red fibres. These muscles also contain plenty of mitochondria which can utilise the large amount of oxygen stored in them for ATP production. These muscles, therefore, can also be called aerobic muscles
Line in NCERT: Muscle contains a red coloured oxygen storing pigment called myoglobin. Myoglobin content is high in some of the muscles which gives a reddish appearance. Such muscles are called the Red fibres. These muscles also contain plenty of mitochondria which can utilise the large amount of oxygen stored in them for ATP production. These muscles, therefore, can also be called aerobic muscles
Which of the statements given above is/are correct regarding the structure and function of actin filaments?i. Each actin filament is composed of two helically wound 'F' (filamentous) actins.ii. 'G' (Globular) actins are monomers that polymerize to form 'F' actins.iii. Tropomyosin runs parallel to the 'F' actins and does not interact with them.iv. Troponin is attached to tropomyosin at regular intervals and regulates the binding sites for myosin on the actin filaments.- a)i and ii
- b)ii and iv
- c)i, ii and iv
- d)i, ii and iii
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct regarding the structure and function of actin filaments?
i. Each actin filament is composed of two helically wound 'F' (filamentous) actins.
ii. 'G' (Globular) actins are monomers that polymerize to form 'F' actins.
iii. Tropomyosin runs parallel to the 'F' actins and does not interact with them.
iv. Troponin is attached to tropomyosin at regular intervals and regulates the binding sites for myosin on the actin filaments.
a)
i and ii
b)
ii and iv
c)
i, ii and iv
d)
i, ii and iii
|
|
Harsh Chauhan answered |
Understanding Actin Filaments
Actin filaments are crucial components of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells, playing vital roles in muscle contraction, cell shape, and motility. Let's analyze the statements regarding their structure and function.
Statement Analysis
- i. Each actin filament is composed of two helically wound F (filamentous) actins.
This statement is correct. Actin filaments, or F-actin, are formed by the polymerization of G-actin monomers into long, helical structures.
- ii. G (Globular) actins are monomers that polymerize to form F actins.
This statement is also correct. G-actin monomers assemble to create F-actin, highlighting the dynamic nature of actin filaments.
- iii. Tropomyosin runs parallel to the F actins and does not interact with them.
This statement is incorrect. Tropomyosin binds to F-actin and stabilizes it, playing a significant role in muscle contraction and regulation of myosin binding sites.
- iv. Troponin is attached to tropomyosin at regular intervals and regulates the binding sites for myosin on the actin filaments.
This statement is correct. Troponin interacts with tropomyosin and, in the presence of calcium ions, regulates the exposure of binding sites for myosin, which is essential for muscle contraction.
Conclusion
Given the analysis, the correct statements are ii and iv. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' (i, ii, and iv). Understanding these components is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms of muscle contraction and cellular movement.
Actin filaments are crucial components of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells, playing vital roles in muscle contraction, cell shape, and motility. Let's analyze the statements regarding their structure and function.
Statement Analysis
- i. Each actin filament is composed of two helically wound F (filamentous) actins.
This statement is correct. Actin filaments, or F-actin, are formed by the polymerization of G-actin monomers into long, helical structures.
- ii. G (Globular) actins are monomers that polymerize to form F actins.
This statement is also correct. G-actin monomers assemble to create F-actin, highlighting the dynamic nature of actin filaments.
- iii. Tropomyosin runs parallel to the F actins and does not interact with them.
This statement is incorrect. Tropomyosin binds to F-actin and stabilizes it, playing a significant role in muscle contraction and regulation of myosin binding sites.
- iv. Troponin is attached to tropomyosin at regular intervals and regulates the binding sites for myosin on the actin filaments.
This statement is correct. Troponin interacts with tropomyosin and, in the presence of calcium ions, regulates the exposure of binding sites for myosin, which is essential for muscle contraction.
Conclusion
Given the analysis, the correct statements are ii and iv. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' (i, ii, and iv). Understanding these components is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms of muscle contraction and cellular movement.
Which of the following statements about the molecular arrangement of actin and myosin in myofibrils is/are incorrect?
(i) Each actin (thin filament) is made of 2F (filamentous) actins.
(ii) F-actin is the polymer of G (globular) actin.
(iii) 2F-actins are twisted into a helix.
(iv) Two strands of tropomyosin (protein) lie in the grooves of F-actin.
(v) Troponin molecules (complex proteins) are distributed at regular intervals on the tropomyosin.
(vi) Troponin forms the head of the myosin molecule.
(vii) The myosin is a polymerised protein.- a)(i), (iii) and (vii)
- b)(ii), (iv) and (v)
- c)Only (vi)
- d)Only (iii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the molecular arrangement of actin and myosin in myofibrils is/are incorrect?
(i) Each actin (thin filament) is made of 2F (filamentous) actins.
(ii) F-actin is the polymer of G (globular) actin.
(iii) 2F-actins are twisted into a helix.
(iv) Two strands of tropomyosin (protein) lie in the grooves of F-actin.
(v) Troponin molecules (complex proteins) are distributed at regular intervals on the tropomyosin.
(vi) Troponin forms the head of the myosin molecule.
(vii) The myosin is a polymerised protein.
(i) Each actin (thin filament) is made of 2F (filamentous) actins.
(ii) F-actin is the polymer of G (globular) actin.
(iii) 2F-actins are twisted into a helix.
(iv) Two strands of tropomyosin (protein) lie in the grooves of F-actin.
(v) Troponin molecules (complex proteins) are distributed at regular intervals on the tropomyosin.
(vi) Troponin forms the head of the myosin molecule.
(vii) The myosin is a polymerised protein.
a)
(i), (iii) and (vii)
b)
(ii), (iv) and (v)
c)
Only (vi)
d)
Only (iii)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
A complex troponin protein of three globular peptides (Troponin T - Binding to tropomyosin as well as to the other two troponin components; Troponin I - inhibiting the F-actin - myosin interaction, also binding to other components of troponin; Troponin C - calcium binding polypeptide) is distributed at regular intervals on the tropomyosin. In the resting stage of muscle fibre, a sub - unit of troponin masks the active sites for myosin on the actin filaments.
Which of these is a genetic disorder?- a)Gout
- b)Myasthenia gravis
- c)Muscular dystrophy
- d)Tetany
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is a genetic disorder?
a)
Gout
b)
Myasthenia gravis
c)
Muscular dystrophy
d)
Tetany
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Muscular dystrophy is a genetic disorder of the muscular system. It leads to the progressive degeneration of skeletal muscles and loss of muscle mass. The life span of patients is often shortened.
Assertion (A): Myasthenia gravis is primarily characterized by the rapid degeneration of skeletal muscle fibers.
Reason (R): Myasthenia gravis affects the neuromuscular junction, leading to fatigue and weakness in skeletal muscles.- a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d) If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Myasthenia gravis is primarily characterized by the rapid degeneration of skeletal muscle fibers.
Reason (R): Myasthenia gravis affects the neuromuscular junction, leading to fatigue and weakness in skeletal muscles.
Reason (R): Myasthenia gravis affects the neuromuscular junction, leading to fatigue and weakness in skeletal muscles.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
- The Assertion (A) is false because myasthenia gravis does not primarily involve the degeneration of muscle fibers; rather, it is an autoimmune disorder affecting the communication at the neuromuscular junction.
- The Reason (R) is true as it correctly describes the mechanism of myasthenia gravis, which indeed leads to fatigue and weakness in skeletal muscles due to the disruption at the neuromuscular junction.
- Therefore, since the Assertion is false and the Reason is true, the correct answer is Option 4: If both Assertion and Reason are false.
The functional unit of contractile system in a striated muscle is- a)sarcomere
- b)Z-band
- c)cross bridges
- d)myofibril
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The functional unit of contractile system in a striated muscle is
a)
sarcomere
b)
Z-band
c)
cross bridges
d)
myofibril
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Sarcomere is the functional unit of myofibril. It contains two types of protein filaments called actin and myosin. These filaments slide upon each other to bring about the contraction of the muscles.
Which of these is disorder of the muscular system?- a)Crohn’s Disease
- b)Celiac Disease
- c)Myasthenia gravis
- d)Gastroenteritis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is disorder of the muscular system?
a)
Crohn’s Disease
b)
Celiac Disease
c)
Myasthenia gravis
d)
Gastroenteritis
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder of the muscular system which affects neuromuscular junctions. Crohn’s Disease, Celiac Disease and gastroenteritis are disorders of the digestive system.
Which of these disorders lead to rapid spasms?- a)Gout
- b)Myasthenia gravis
- c)Muscular dystrophy
- d)Tetany
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these disorders lead to rapid spasms?
a)
Gout
b)
Myasthenia gravis
c)
Muscular dystrophy
d)
Tetany
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Tetany is a disorder of the muscular system characterized by rapid spasms or wild contractions. It occurs due to low concentrations of calcium ions in body fluids. Calcium ions play an important role in muscle contraction.
Appendicular skeleton includes- a)girdles and their limbs
- b)vertebrae
- c)skull and vertebral column
- d)ribs and sternum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Appendicular skeleton includes
a)
girdles and their limbs
b)
vertebrae
c)
skull and vertebral column
d)
ribs and sternum
|
|
Gitanjali Dasgupta answered |
Appendicular skeleton includes
The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the limbs and their associated girdles. It is one of the two main divisions of the human skeleton, with the other being the axial skeleton. The appendicular skeleton provides support and enables movement of the limbs.
1. Girdles
The appendicular skeleton includes two girdles: the pectoral girdle and the pelvic girdle.
- Pectoral Girdle: The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, consists of the clavicle (collarbone) and the scapula (shoulder blade). It connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton, allowing for the movement of the arms and shoulders.
- Pelvic Girdle: The pelvic girdle, also known as the hip girdle, consists of two hip bones, also called coxal bones or innominate bones. The pelvic girdle connects the lower limbs to the axial skeleton and supports the weight of the body.
2. Limbs
The appendicular skeleton also includes the bones of the limbs, including the upper limbs (arms) and the lower limbs (legs).
- Upper Limbs: The upper limbs consist of the humerus (upper arm bone), radius and ulna (forearm bones), carpals (wrist bones), metacarpals (hand bones), and phalanges (finger bones). These bones provide support and allow for various movements of the arms, hands, and fingers.
- Lower Limbs: The lower limbs consist of the femur (thigh bone), tibia and fibula (leg bones), tarsals (ankle bones), metatarsals (foot bones), and phalanges (toe bones). These bones provide support and enable movements such as walking, running, and jumping.
3. Function
The appendicular skeleton plays a crucial role in maintaining posture, supporting the body's weight, and facilitating movement. The girdles connect the limbs to the axial skeleton and provide a stable base for the movement of the arms and legs. The bones of the limbs allow for various movements and actions, such as reaching, grasping, walking, running, and performing fine motor skills.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the appendicular skeleton includes the girdles and the bones of the limbs. It provides support, stability, and enables movement of the limbs, allowing for a wide range of activities and functions.
The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the limbs and their associated girdles. It is one of the two main divisions of the human skeleton, with the other being the axial skeleton. The appendicular skeleton provides support and enables movement of the limbs.
1. Girdles
The appendicular skeleton includes two girdles: the pectoral girdle and the pelvic girdle.
- Pectoral Girdle: The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, consists of the clavicle (collarbone) and the scapula (shoulder blade). It connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton, allowing for the movement of the arms and shoulders.
- Pelvic Girdle: The pelvic girdle, also known as the hip girdle, consists of two hip bones, also called coxal bones or innominate bones. The pelvic girdle connects the lower limbs to the axial skeleton and supports the weight of the body.
2. Limbs
The appendicular skeleton also includes the bones of the limbs, including the upper limbs (arms) and the lower limbs (legs).
- Upper Limbs: The upper limbs consist of the humerus (upper arm bone), radius and ulna (forearm bones), carpals (wrist bones), metacarpals (hand bones), and phalanges (finger bones). These bones provide support and allow for various movements of the arms, hands, and fingers.
- Lower Limbs: The lower limbs consist of the femur (thigh bone), tibia and fibula (leg bones), tarsals (ankle bones), metatarsals (foot bones), and phalanges (toe bones). These bones provide support and enable movements such as walking, running, and jumping.
3. Function
The appendicular skeleton plays a crucial role in maintaining posture, supporting the body's weight, and facilitating movement. The girdles connect the limbs to the axial skeleton and provide a stable base for the movement of the arms and legs. The bones of the limbs allow for various movements and actions, such as reaching, grasping, walking, running, and performing fine motor skills.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the appendicular skeleton includes the girdles and the bones of the limbs. It provides support, stability, and enables movement of the limbs, allowing for a wide range of activities and functions.
A cricket player is fast chasing a ball in the field. Which one of the following groups of bones are directly contributing in this movement?- a)Femur, malleus, tibia, metatarsals
- b)Pelvis, ulna, patella, tarsals
- c)Sternum, femur, tibia, fibula
- d)Tarsals, femur, metatarsals, tibia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cricket player is fast chasing a ball in the field. Which one of the following groups of bones are directly contributing in this movement?
a)
Femur, malleus, tibia, metatarsals
b)
Pelvis, ulna, patella, tarsals
c)
Sternum, femur, tibia, fibula
d)
Tarsals, femur, metatarsals, tibia
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Trasals, femur, metatarsals and tibia are bones of the legs which are involved in running during chasing the ball by a cricket player.
Smallest bone in human system is- a)stapes
- b)patella
- c)malleus
- d)incus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Smallest bone in human system is
a)
stapes
b)
patella
c)
malleus
d)
incus
|
|
Yash Shah answered |
Smallest Bone in Human System - Stapes
The smallest bone in the human body is called the stapes. It is located in the middle ear and is one of the three tiny bones known as the ossicles. The stapes is also commonly referred to as the stirrup bone due to its stirrup-like shape.
Function of Stapes
The primary function of the stapes is to transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. It plays a crucial role in the process of hearing by amplifying and transferring sound waves through the middle ear.
Size and Structure
Despite its small size, the stapes is a significant component of the auditory system. It measures approximately 3 millimeters in length and resembles a stirrup, with a head, neck, and two branches known as the crura.
Importance in Hearing
The stapes is vital for the process of hearing as it helps convert sound waves into mechanical vibrations that can be interpreted by the brain. Any damage or abnormalities in the stapes can lead to hearing loss or other auditory problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the stapes is the smallest bone in the human body and plays a crucial role in the auditory system. Its small size belies its importance in the process of hearing, making it an essential component of the middle ear.
The smallest bone in the human body is called the stapes. It is located in the middle ear and is one of the three tiny bones known as the ossicles. The stapes is also commonly referred to as the stirrup bone due to its stirrup-like shape.
Function of Stapes
The primary function of the stapes is to transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. It plays a crucial role in the process of hearing by amplifying and transferring sound waves through the middle ear.
Size and Structure
Despite its small size, the stapes is a significant component of the auditory system. It measures approximately 3 millimeters in length and resembles a stirrup, with a head, neck, and two branches known as the crura.
Importance in Hearing
The stapes is vital for the process of hearing as it helps convert sound waves into mechanical vibrations that can be interpreted by the brain. Any damage or abnormalities in the stapes can lead to hearing loss or other auditory problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the stapes is the smallest bone in the human body and plays a crucial role in the auditory system. Its small size belies its importance in the process of hearing, making it an essential component of the middle ear.
Chapter doubts & questions for Locomotion and Movement - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Locomotion and Movement - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily