All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of D and F - Block Elements for NEET Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which one of the following is a diamagnetic ion?- A:CO2+
- B:Cu2+
- C:Mn2+
- D:Sc3+
The answer is d.
Which one of the following is a diamagnetic ion?
A:
CO2+
B:
Cu2+
C:
Mn2+
D:
Sc3+

|
Learners Habitat answered |
Co+2 = [Ar] 3d7
Cu2+ = [Ar] 3d9
Mn+2 = [Ar] 3d5
Sc+3 = [Ar]
We can see that only Sc+3 has no unpaired electron, so it is a diamagnetic ion.
Cu2+ = [Ar] 3d9
Mn+2 = [Ar] 3d5
Sc+3 = [Ar]
We can see that only Sc+3 has no unpaired electron, so it is a diamagnetic ion.
Which one of the following exists in the oxidation state other than +3?- a)B
- b)Al
- c)Ce
- d)Ga
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following exists in the oxidation state other than +3?
a)
B
b)
Al
c)
Ce
d)
Ga
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The correct answer is option C
Ce exist in the oxidation state other than +3 .
(a) B - Boron has +1 and +3 oxidation state.
(b) Al - Aluminium has +1,+2 and +3 oxidation state.
(c) Ce - Cerium has +3 and +4 oxidation state.
(d) Ga - Gallium has +1 and +3 oxidation state.
Cerium (Ce) have [Xe] 4f²6s² electronic configuration.
Which form of silver is colourless?- a)Ag2+
- b)Ag
- c)Ag3+
- d)Ag+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which form of silver is colourless?
a)
Ag2+
b)
Ag
c)
Ag3+
d)
Ag+
|
|
Om Desai answered |
ilver in the form of Ag+ is colourless. For transition metal ions to exhibit color, their metal ions must have incompletely filled (n-1)d orbitals.
Ag+ =4d10,5s0
Ag+ has completely filled d orbitals hence is colourless.
Which ion will show more paramagnetic behaviour ?- a)Cu+
- b)Fe2+
- c)Ag+
- d)Fe3+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which ion will show more paramagnetic behaviour ?
a)
Cu+
b)
Fe2+
c)
Ag+
d)
Fe3+
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Since the configuration of Fe3+ ion is (argon ) 3d5,which contains maximum number of unpaired electrons, hence more will be paramagnetic behavior.
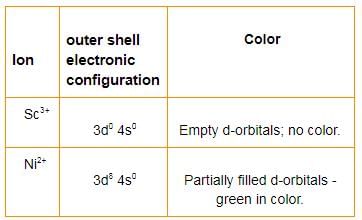
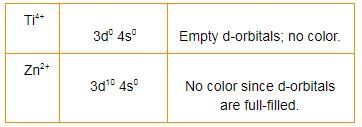
Which among the following is colourless?- a)Sc2+
- b)Zn2+
- c)Ti3+
- d)V3+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is colourless?
a)
Sc2+
b)
Zn2+
c)
Ti3+
d)
V3+
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Zn2+ has completely filled d-orbitals and there are no vacant d-orbitals for the transition of electrons, hence it is colourless.
A member of the lanthanoid series which is well known to exhibit +4 oxidation state is:- a)Lutetium
- b)Thulium
- c)Cerium
- d)Europium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A member of the lanthanoid series which is well known to exhibit +4 oxidation state is:
a)
Lutetium
b)
Thulium
c)
Cerium
d)
Europium
|
|
Mumtaj Ali answered |
Ce( 58) in +4 oxidation state show noble gas configuration so it is well known to exhibit +4 ox state.
The first ionization energy of the d-block elements are?- a)Lesser than p-block elements
- b)Between s and p-block elements
- c)Lesser than s-block elements
- d)Higher than p-block elements
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The first ionization energy of the d-block elements are?
a)
Lesser than p-block elements
b)
Between s and p-block elements
c)
Lesser than s-block elements
d)
Higher than p-block elements
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The first ionization energy of the d-block elements are between s and p-block elements. Thus they are more electropositive than p-block elements and less electropositive than s-block elements.
Statement TypeDirection (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.Q. Statement I : The highest oxidation state of osmium is +8.Statement II : Osmium is a 5-d block element.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement Type
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : The highest oxidation state of osmium is +8.
Statement II : Osmium is a 5-d block element.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Vikas Saini answered |
B hona chayie
Which of the following group of elements are not regarded as transition elements?- a)Sc,Y,La
- b)Cu, Ag, Au
- c)Zn, Cd, Hg
- d)Cr ,Mo,W
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following group of elements are not regarded as transition elements?
a)
Sc,Y,La
b)
Cu, Ag, Au
c)
Zn, Cd, Hg
d)
Cr ,Mo,W
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Zn, Cd & Hg because the d-orbital of these elements are completely filled. So, they don't show the characteristics of transition elements (i.e. the d-orbital of transition elements is incomplete.
In which of the following oxidation states La achieve the noble gas configuration?- a)+7
- b)+3
- c)+5
- d)+2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following oxidation states La achieve the noble gas configuration?
a)
+7
b)
+3
c)
+5
d)
+2
|
|
Shail Chawla answered |
La stands for Lanthanum, which is a member of the lanthanide series of elements in the periodic table. It has an atomic number of 57 and an electronic configuration of [Xe]5d1 6s2.
Achieving Noble Gas Configuration
To achieve a noble gas configuration, an element must have its outermost shell filled with electrons. The noble gases are stable because they have a filled outermost shell. Lanthanum can achieve this configuration by losing three electrons from its outermost shell.
Oxidation States
The oxidation state of an element is the charge that it carries when it forms a compound or ion. Lanthanum can form compounds in various oxidation states, including +2, +3, and +4.
In order to determine in which oxidation state La achieves noble gas configuration, we need to look at its electron configuration and determine how many electrons it needs to lose to achieve a filled outermost shell.
La3+ (Oxidation State of +3)
When Lanthanum loses three electrons, it forms a +3 ion (La3+). In this oxidation state, La has a noble gas configuration of [Xe]. Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Other Oxidation States
Lanthanum can also form compounds in other oxidation states, but they do not achieve a noble gas configuration. For example, in the +2 oxidation state, La has an electron configuration of [Xe]5d1, which is not a filled outermost shell.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lanthanum achieves noble gas configuration in the +3 oxidation state by losing three electrons and forming a La3+ ion.
Achieving Noble Gas Configuration
To achieve a noble gas configuration, an element must have its outermost shell filled with electrons. The noble gases are stable because they have a filled outermost shell. Lanthanum can achieve this configuration by losing three electrons from its outermost shell.
Oxidation States
The oxidation state of an element is the charge that it carries when it forms a compound or ion. Lanthanum can form compounds in various oxidation states, including +2, +3, and +4.
In order to determine in which oxidation state La achieves noble gas configuration, we need to look at its electron configuration and determine how many electrons it needs to lose to achieve a filled outermost shell.
La3+ (Oxidation State of +3)
When Lanthanum loses three electrons, it forms a +3 ion (La3+). In this oxidation state, La has a noble gas configuration of [Xe]. Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Other Oxidation States
Lanthanum can also form compounds in other oxidation states, but they do not achieve a noble gas configuration. For example, in the +2 oxidation state, La has an electron configuration of [Xe]5d1, which is not a filled outermost shell.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lanthanum achieves noble gas configuration in the +3 oxidation state by losing three electrons and forming a La3+ ion.
The inner transition elements are the elements in which the added electrons go to:- a)(n-1)d-orbitals
- b)(n-1)d-orbitals and (n-1)f-orbitals
- c)(n-1)d-orbitals and ns orbitals
- d)(n-2)f-orbitals
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The inner transition elements are the elements in which the added electrons go to:
a)
(n-1)d-orbitals
b)
(n-1)d-orbitals and (n-1)f-orbitals
c)
(n-1)d-orbitals and ns orbitals
d)
(n-2)f-orbitals
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Lanthanides and actinides are called inner transition elements because they are a group of elements that are shown as the bottom two rows of the periodic table. ... Lanthanides and actinides belong to the f-block elements, which means that they have filled up their f-orbitals with electrons.
Photographic films and plates have an essential ingredient of [1989]- a)Silver nitrate
- b)Silver bromide
- c)Sodium chloride
- d)Oleic acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Photographic films and plates have an essential ingredient of [1989]
a)
Silver nitrate
b)
Silver bromide
c)
Sodium chloride
d)
Oleic acid

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
AgBr is highly photosensitive and is used in photographic films and plates.
The electronic configuration of Eu 3+ ion is:- a)[Xe] 4f4
- b)[Xe] 4f7
- c)[Xe] 4f2
- d)[Xe] 4f6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The electronic configuration of Eu 3+ ion is:
a)
[Xe] 4f4
b)
[Xe] 4f7
c)
[Xe] 4f2
d)
[Xe] 4f6

|
Aditi Azade answered |
Atomic number of Eu is 63...so electronic configuration of Eu is, Eu=[xe] 4f^9 Hence,Eu^+3=[xe]4f^6
Number of electrons with l = 2 and s = 1/2 in zinc atom are
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of electrons with l = 2 and s = 1/2 in zinc atom are
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
l = 2 means d-subshell. Zinc has 10 electrons ind-subshell in which 5 electrons are + 1/2 spin and 5 electrons are - 1/2.
One Integer Value Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. The number of elements that do not have completely filled d subshell among the elements Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd and Hg are
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
The number of elements that do not have completely filled d subshell among the elements Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd and Hg are
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Ni has 3d84s2 and Pt has 5d96s1.
A red solid is insoluble in water. However, it becomes soluble if some KI is added to water. Heating the red solid in a test tube results in liberation of some violet coloured fumes and droplets of a metal appear on the cooler parts of the test tube. The red solid is - a)(NH4)2Cr2O7
- b)HgI2
- c)HgO
- d)Pb3O4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A red solid is insoluble in water. However, it becomes soluble if some KI is added to water. Heating the red solid in a test tube results in liberation of some violet coloured fumes and droplets of a metal appear on the cooler parts of the test tube. The red solid is
a)
(NH4)2Cr2O7
b)
HgI2
c)
HgO
d)
Pb3O4

|
Infinity Academy answered |

What is the most common oxidation state for actinoids?- a)+3
- b)+7
- c)+2
- d)+5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the most common oxidation state for actinoids?
a)
+3
b)
+7
c)
+2
d)
+5

|
Mamali . answered |
Unlike lanthanides which show the +3, oxidation States,actinides show a variety of Oxidation State from +3to+6.However+3&+4 are the principal Oxidation State.The+3 Oxidation state is the most stable in AC and all the other elements of the series.Thats it.
The elements which lie between s and p block elements in the long form periodic table are called as:- a)Actinides
- b)d-block elements
- c)Lanthanides
- d)Electropositive elements
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The elements which lie between s and p block elements in the long form periodic table are called as:
a)
Actinides
b)
d-block elements
c)
Lanthanides
d)
Electropositive elements
|
|
Harsh Desai answered |
D-block elements
The long form periodic table consists of four blocks: s, p, d, and f. The s and p blocks are located on the left and right sides of the periodic table, respectively. The d-block elements are located in the middle of the periodic table, between the s and p blocks. These elements are also known as transition elements.
Explanation:
The d-block elements are characterized by the presence of partially filled d-orbitals in their valence shells. These elements are often referred to as transition elements because they exhibit a transition between the highly reactive s-block elements and the relatively inert p-block elements. The d-block elements are known for their unique chemical and physical properties, such as their ability to form complex ions and their high melting and boiling points.
Examples of d-block elements include titanium, iron, copper, and zinc. These elements are widely used in industry and technology due to their unique properties, such as their strength, durability, and conductivity.
In summary, the elements which lie between s and p block elements in the long form periodic table are called d-block elements or transition elements. These elements exhibit unique chemical and physical properties and are widely used in industry and technology.
The long form periodic table consists of four blocks: s, p, d, and f. The s and p blocks are located on the left and right sides of the periodic table, respectively. The d-block elements are located in the middle of the periodic table, between the s and p blocks. These elements are also known as transition elements.
Explanation:
The d-block elements are characterized by the presence of partially filled d-orbitals in their valence shells. These elements are often referred to as transition elements because they exhibit a transition between the highly reactive s-block elements and the relatively inert p-block elements. The d-block elements are known for their unique chemical and physical properties, such as their ability to form complex ions and their high melting and boiling points.
Examples of d-block elements include titanium, iron, copper, and zinc. These elements are widely used in industry and technology due to their unique properties, such as their strength, durability, and conductivity.
In summary, the elements which lie between s and p block elements in the long form periodic table are called d-block elements or transition elements. These elements exhibit unique chemical and physical properties and are widely used in industry and technology.
The second series of transition element starts with:- a)Scandium
- b)Rhodium
- c)Ytterium
- d)Actinium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The second series of transition element starts with:
a)
Scandium
b)
Rhodium
c)
Ytterium
d)
Actinium

|
Technical Om answered |
Why not Rhodium(Rh) since its also comes in 2nd series also given in N.C.E.R.T.
Melting point of d block elements across a period:- a)Increases from left to right
- b)Deceases from left to right
- c)Increases to a maximum at d5 and then decreases with increase of atomic number.
- d)Does not change on moving from left to right.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Melting point of d block elements across a period:
a)
Increases from left to right
b)
Deceases from left to right
c)
Increases to a maximum at d5 and then decreases with increase of atomic number.
d)
Does not change on moving from left to right.
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The melting and boiling points first increase, reaches maximum and then steadily decrease across any transition series. ... The low melting points of Zn, Cd, and Hg are due to the absence of unpaired d-electrons in their atoms and thus low metallic bonding.
Which one is of the following is the lightest transition element?- a)Ti
- b)Sc
- c)Fe
- d)Hg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is of the following is the lightest transition element?
a)
Ti
b)
Sc
c)
Fe
d)
Hg
|
|
T.ttttt answered |
Scandium (Sc) is the lightest transition element. It is the first element in the 3d transition series. Among the transition elements, Sc has the lowest density.
The transition elements have a general electronic configuration [1991]- a)ns2, np6, nd1-10
- b)(n - 1) d1-10 , ns0 - 2 , np0 - 6
- c)(n - 1) d1-10 , ns1- 2
- d)n d1 -10 , ns-2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The transition elements have a general electronic configuration [1991]
a)
ns2, np6, nd1-10
b)
(n - 1) d1-10 , ns0 - 2 , np0 - 6
c)
(n - 1) d1-10 , ns1- 2
d)
n d1 -10 , ns-2

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
General electronic configuration of transition elements is (n - 1)d1 -10ns1- 2
Which of the following group contain mostly radioactive elements ?- a)Lanthanoids
- b)3 d transition series
- c)4 d transition series
- d)Actinoids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following group contain mostly radioactive elements ?
a)
Lanthanoids
b)
3 d transition series
c)
4 d transition series
d)
Actinoids

|
Parth Sharma answered |
The actinoids are said to be most radioactive metals because in this group all the metals have very oxidation number and are very rare metals found on earth and it has all the elements radioactive in its group and it has most radioactive metal uranium in it's group.
Mischmetal is an alloy of:
- a)Lanthanoid metal and Iron
- b)Actinoid metal and Iron
- c)Manganese, nickel and iron
- d)Zinc ,cobalt and iron
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mischmetal is an alloy of:
a)
Lanthanoid metal and Iron
b)
Actinoid metal and Iron
c)
Manganese, nickel and iron
d)
Zinc ,cobalt and iron
|
|
Snehal Iyer answered |
Explanation:
Mischmetal is an alloy of Lanthanoid Metal and Iron. It is a rare earth alloy, which is primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys.
Composition:
Mischmetal typically contains 50-55% cerium, 20-25% lanthanum, and small amounts of other rare earth metals such as neodymium, praseodymium, and gadolinium. The remaining portion of the alloy is typically iron.
Properties:
Mischmetal has a number of unique properties that make it an attractive alloy for use in a variety of applications. These properties include:
- High heat resistance
- High strength and durability
- Corrosion resistance
- Good machinability
Applications:
Mischmetal is primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys. It is also used in the production of magnesium alloys, which are used in a variety of applications, including aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods.
Some other applications of Mischmetal are:
- In the production of lighter flints
- As a pyrophoric material for the ignition of torches and lighters
- In the production of certain types of electrodes for welding and cutting
- In the production of certain types of batteries
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Mischmetal is an alloy of lanthanoid metal and iron, primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys. It has a number of unique properties that make it an attractive alloy for use in a variety of applications.
Mischmetal is an alloy of Lanthanoid Metal and Iron. It is a rare earth alloy, which is primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys.
Composition:
Mischmetal typically contains 50-55% cerium, 20-25% lanthanum, and small amounts of other rare earth metals such as neodymium, praseodymium, and gadolinium. The remaining portion of the alloy is typically iron.
Properties:
Mischmetal has a number of unique properties that make it an attractive alloy for use in a variety of applications. These properties include:
- High heat resistance
- High strength and durability
- Corrosion resistance
- Good machinability
Applications:
Mischmetal is primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys. It is also used in the production of magnesium alloys, which are used in a variety of applications, including aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods.
Some other applications of Mischmetal are:
- In the production of lighter flints
- As a pyrophoric material for the ignition of torches and lighters
- In the production of certain types of electrodes for welding and cutting
- In the production of certain types of batteries
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Mischmetal is an alloy of lanthanoid metal and iron, primarily used in the production of alloy steels, stainless steels, and other high-performance alloys. It has a number of unique properties that make it an attractive alloy for use in a variety of applications.
Transition metals with highest melting point is- a)Cr
- b)W
- c)Hg
- d)Sc
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Transition metals with highest melting point is
a)
Cr
b)
W
c)
Hg
d)
Sc

|
Pragati Choudhury answered |
W belongs to 5d series and also it have lot of unpaired electrons thus it forms strong metallic bonding.
During the process of electrolytic refining of copper, some metals present as impurity settle as ‘anode mud’ These are- a)Sn and Ag
- b)Pb and Zn
- c)Ag and Au
- d)Fe and Ni
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During the process of electrolytic refining of copper, some metals present as impurity settle as ‘anode mud’ These are
a)
Sn and Ag
b)
Pb and Zn
c)
Ag and Au
d)
Fe and Ni
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option C
In Electrolytic refining, the impure metal is made to act as an anode. A strip of the same metal in pure form is used as a cathode.
They are put in a suitable electrolytic bath containing a soluble salt of the same metal.
The more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
Copper is refined using an electrolytic method.
Impurities from the blister copper deposit as anode mud which contains antimony, selenium, tellurium, silver, gold, and platinum; recovery of these elements may meet the cost of refining.
In Electrolytic refining, the impure metal is made to act as an anode. A strip of the same metal in pure form is used as a cathode.
They are put in a suitable electrolytic bath containing a soluble salt of the same metal.
The more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
Copper is refined using an electrolytic method.
Impurities from the blister copper deposit as anode mud which contains antimony, selenium, tellurium, silver, gold, and platinum; recovery of these elements may meet the cost of refining.
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Atomic number of second transition series lies from- a)38 to 47
- b)39 to 48
- c)40 to 49
- d)41 to 50
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Atomic number of second transition series lies from
a)
38 to 47
b)
39 to 48
c)
40 to 49
d)
41 to 50

|
Khushi Mittal answered |
Transition series means d-block elements which have 10 elements in one series.... according to the question 2nd d block elements includes elements from atomic number 39 (i.e.yttrium) to atomic number 48(i.e. cadmium)
Ag+ ion is isoelectronic with- a)Zn2+
- b)Cd2+
- c)Pd2+
- d)Cu2+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ag+ ion is isoelectronic with
a)
Zn2+
b)
Cd2+
c)
Pd2+
d)
Cu2+

|
Malavika Shah answered |
Ag+ is isoelectronic with Cd2+
Which one of the following is a diamagnetic ion?- a)CO2+
- b)Cu2+
- c)Mn2+
- d)Sc3+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a diamagnetic ion?
a)
CO2+
b)
Cu2+
c)
Mn2+
d)
Sc3+
|
|
Ameya Pillai answered |
Co2+ (Z = 27) : [Ar]183d7 (3 unpaired electrons)
Cu2+ (Z = 29) : [Ar]183d9 (1 unpaired electrons)
Mn2+ (Z = 25): [Ar]183d5 (5 unpaired electrons)
Sc3+ (Z = 21): [Ar]183d0 (No unpaired electron)
Sc3+ with no unpaired electron will be diamagnetic
Cu2+ (Z = 29) : [Ar]183d9 (1 unpaired electrons)
Mn2+ (Z = 25): [Ar]183d5 (5 unpaired electrons)
Sc3+ (Z = 21): [Ar]183d0 (No unpaired electron)
Sc3+ with no unpaired electron will be diamagnetic
Which of the following shows maximum number of oxidation states? [2002]- a)Cr
- b)Fe
- c)Mn
- d)V
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following shows maximum number of oxidation states? [2002]
a)
Cr
b)
Fe
c)
Mn
d)
V

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
Mn : [Ar] 3d5 4s2
Shows +2, +3, +4, +5, +6 & +7 oxidation states
Shows +2, +3, +4, +5, +6 & +7 oxidation states
In which of the following oxidation state Cerium achieves the noble gas configuration?- a)+5
- b)+2
- c)+7
- d)+4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following oxidation state Cerium achieves the noble gas configuration?
a)
+5
b)
+2
c)
+7
d)
+4

|
Mamali . answered |
The reason for this behaviour is a result of the stability of half filled, empty or fulfilled F orbitals that these elements achieve in these Oxidation State.Thats it.
For the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe and Co), the stability of +2 oxidation state will be there in which of the following order?- a)Mn > Fe > Cr > Co [2011]
- b)Fe > Mn > Co > Cr
- c)Co > Mn > Fe > Cr
- d)Cr > Mn > Co > Fe
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe and Co), the stability of +2 oxidation state will be there in which of the following order?
a)
Mn > Fe > Cr > Co [2011]
b)
Fe > Mn > Co > Cr
c)
Co > Mn > Fe > Cr
d)
Cr > Mn > Co > Fe
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
More the number of unpaired electrons more will be the stability.
Hence, the correct order is, Mn >Fe >Cr>Co.
The addition of excess of aqueous HNO3 to a solution containing [Cu(NH3)4]2+ produces [1999]- a)Cu+
- b)[Cu(H2O)4]2+
- c)Cu(OH)2
- d)Cu(NO3)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The addition of excess of aqueous HNO3 to a solution containing [Cu(NH3)4]2+ produces [1999]
a)
Cu+
b)
[Cu(H2O)4]2+
c)
Cu(OH)2
d)
Cu(NO3)2

|
Prisha Singh answered |
[Cu (NH3)4]2+ on addition of excess of aqneous HNO3 gives [Cu (H2O)4]2+
Which has lowest and highest first ionisation enthalpy in 3d series?- a)Sc and Zn
- b)Zn and Sc
- c)Cu and Zn
- d)Cr and Zn
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which has lowest and highest first ionisation enthalpy in 3d series?
a)
Sc and Zn
b)
Zn and Sc
c)
Cu and Zn
d)
Cr and Zn

|
Beyond the Horizon answered |
Losing one electron gives Sc noble gas configuration (Ar). While Zn has d10 s2 configuration so it won't give its electron easily. So, it has high ionization enthalpy.
Number of elements that generally do not show variable valencies Cu, Zn Au, Cd, Sc, La, Pt, Co.
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of elements that generally do not show variable valencies Cu, Zn Au, Cd, Sc, La, Pt, Co.
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Zn, Cd, Sc and La do not show variable valencies.
A blue colouration is not obtained when [1989]- a)Ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate
- b)Coppersulp hate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6]
- c)Ferric chloride reacts with sod. ferrocyanide
- d)Anhydrous CuSO4 is dissolved in water
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A blue colouration is not obtained when [1989]
a)
Ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate
b)
Coppersulp hate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6]
c)
Ferric chloride reacts with sod. ferrocyanide
d)
Anhydrous CuSO4 is dissolved in water

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
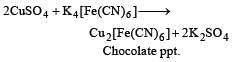
Among the lanthanides the one obtained by synthetic method is [1994]- a)Lu
- b)Pm
- c)Pr
- d)Gd
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the lanthanides the one obtained by synthetic method is [1994]
a)
Lu
b)
Pm
c)
Pr
d)
Gd

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
Pm is obtained by synthetic method.
The catalytic activity of transition metals and their compounds is ascribed mainly to :[2012 M]- a)their magnetic behaviour
- b)their unfilled d-orbitals
- c)their ability to adopt variable oxidation state
- d)their chemical reactivity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The catalytic activity of transition metals and their compounds is ascribed mainly to :[2012 M]
a)
their magnetic behaviour
b)
their unfilled d-orbitals
c)
their ability to adopt variable oxidation state
d)
their chemical reactivity

|
Maheshwar Saini answered |
The transition metals and their compounds are used as catalysts. Because of the variable oxidation states, due to this, they easily absorb and re-emit wide range of energy to provide the necessary activation energy.
Stainless steel contains iron and [1995]- a)Cr + Ni
- b)Cr + Zn
- c)Zn + Pb
- d)Fe +Cr + Ni
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Stainless steel contains iron and [1995]
a)
Cr + Ni
b)
Cr + Zn
c)
Zn + Pb
d)
Fe +Cr + Ni

|
Sonal Kulkarni answered |
Stainless steel contains 73% Fe, 18% Cr and 8% Ni.
Mohr’s salt is a- a)Acidic salt
- b)Double salt
- c)Basic Acidic salt
- d)Normal salt
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mohr’s salt is a
a)
Acidic salt
b)
Double salt
c)
Basic Acidic salt
d)
Normal salt

|
Amar Pillai answered |
Mohr salt is an example of double salt. Mohr Salt is
FeSO4 . (NH4)2 SO4.6H2O
The pair of ions that have same electronic configuration- a)Fe2+ and Mn2+
- b)Fe2+ and Co3+
- c)Fe3+ and Co3+
- d)V2+ and Cr3+
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The pair of ions that have same electronic configuration
a)
Fe2+ and Mn2+
b)
Fe2+ and Co3+
c)
Fe3+ and Co3+
d)
V2+ and Cr3+

|
Saikat Dey answered |
You simply count the electron number, though , co is present just after fe, so from this logic you count the electron number is same in fe2+ and co3+,(just think) simultaneously v2+, cr3+ electron number is same, in mathematical, fe 2+ electron number is 26-2=24,, and co 3+,electron number is 27-3=24,so simultaneously v2+, and cr 3+ has same number of electron,
Which of the following statement is true?- a)Actinoid contraction is smaller than lanthanoid contraction.
- b)There is no actinoid contraction observed.
- c)Actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoid contraction.
- d)Actinoid contraction is equally same as lanthanoid contraction.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is true?
a)
Actinoid contraction is smaller than lanthanoid contraction.
b)
There is no actinoid contraction observed.
c)
Actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoid contraction.
d)
Actinoid contraction is equally same as lanthanoid contraction.
|
|
Anshika Menon answered |
Actinoid Contraction and Lanthanoid Contraction
Actinoid contraction and lanthanoid contraction are terms used to describe the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the actinide and lanthanide series, respectively.
Actinoid Contraction
- Actinoid contraction refers to the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the actinide series.
- It is caused by the imperfect shielding of the 5f electrons by the 6s and 6p electrons.
- The 5f electrons are located closer to the nucleus and experience a greater effective nuclear charge, which leads to a smaller atomic and ionic radius.
- Actinoid contraction is observed in the actinide series from thorium (Z=90) to lawrencium (Z=103).
Lanthanoid Contraction
- Lanthanoid contraction refers to the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series.
- It is caused by the imperfect shielding of the 4f electrons by the 5s, 5p, and 6s electrons.
- The 4f electrons are located closer to the nucleus and experience a greater effective nuclear charge, which leads to a smaller atomic and ionic radius.
- Lanthanoid contraction is observed in the lanthanide series from cerium (Z=58) to lutetium (Z=71).
Comparison of Actinoid Contraction and Lanthanoid Contraction
- Actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoid contraction.
- The 5f electrons in the actinide series experience a greater effective nuclear charge than the 4f electrons in the lanthanide series, which leads to a greater decrease in atomic and ionic radii.
- Actinoid contraction is also observed over a smaller range of elements than lanthanoid contraction.
Actinoid contraction and lanthanoid contraction are terms used to describe the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the actinide and lanthanide series, respectively.
Actinoid Contraction
- Actinoid contraction refers to the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the actinide series.
- It is caused by the imperfect shielding of the 5f electrons by the 6s and 6p electrons.
- The 5f electrons are located closer to the nucleus and experience a greater effective nuclear charge, which leads to a smaller atomic and ionic radius.
- Actinoid contraction is observed in the actinide series from thorium (Z=90) to lawrencium (Z=103).
Lanthanoid Contraction
- Lanthanoid contraction refers to the decrease in atomic and ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series.
- It is caused by the imperfect shielding of the 4f electrons by the 5s, 5p, and 6s electrons.
- The 4f electrons are located closer to the nucleus and experience a greater effective nuclear charge, which leads to a smaller atomic and ionic radius.
- Lanthanoid contraction is observed in the lanthanide series from cerium (Z=58) to lutetium (Z=71).
Comparison of Actinoid Contraction and Lanthanoid Contraction
- Actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoid contraction.
- The 5f electrons in the actinide series experience a greater effective nuclear charge than the 4f electrons in the lanthanide series, which leads to a greater decrease in atomic and ionic radii.
- Actinoid contraction is also observed over a smaller range of elements than lanthanoid contraction.
An element has configuration 4d55s2. The element belongs to- a)3rd group and 4th period
- b)5th group and 5th period
- c)7th group and 5th period
- d)7th group and 7th period
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An element has configuration 4d55s2. The element belongs to
a)
3rd group and 4th period
b)
5th group and 5th period
c)
7th group and 5th period
d)
7th group and 7th period
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Ford-block elements, group number is equal to the number of electrons in (n - 1)d subshell + number of electrons in valence shell (nth shell).
Chapter doubts & questions for D and F - Block Elements - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of D and F - Block Elements - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily