All Exams >
NEET >
Daily Test for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of August for NEET Exam
A wire of diameter 7 mm and length 1 m is stretched within the elastic limit by the 77 kN pull. If the elongation of the wire for this force is noted as 2 mm, then find Young's modulus of elasticity for the material of the wire.- a)106 Pa
- b)7 x 106 Pa
- c)105 Pa
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A wire of diameter 7 mm and length 1 m is stretched within the elastic limit by the 77 kN pull. If the elongation of the wire for this force is noted as 2 mm, then find Young's modulus of elasticity for the material of the wire.
a)
106 Pa
b)
7 x 106 Pa
c)
105 Pa
d)
None of these

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The Young's modulus of elasticity for the material of the wire is 106 Pa.
Which will make basic buffer?- a)50 mL of 0.1 M NaOH + 25 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH
- b)100 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH + 100 mL of 0.1 M NaOH
- c)100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 200 mL of 0.1 M NH4OH
- d)100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 100 mL of 0.1 M NaOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which will make basic buffer?
a)
50 mL of 0.1 M NaOH + 25 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH
b)
100 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH + 100 mL of 0.1 M NaOH
c)
100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 200 mL of 0.1 M NH4OH
d)
100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 100 mL of 0.1 M NaOH
|
|
Aditya Yadav answered |
Explanation:
Basic Buffer:
- A basic buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid are added.
- It is typically composed of a weak base and its conjugate acid.
Analysis of Options:
a) 50 mL of 0.1 M NaOH + 25 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH:
- NaOH is a strong base and CH3COOH is a weak acid, so this combination will not form a basic buffer.
b) 100 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH + 100 mL of 0.1 M NaOH:
- This combination will form a basic buffer as it contains a weak acid (CH3COOH) and its conjugate base (CH3COO-).
c) 100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 200 mL of 0.1 M NH4OH:
- HCl is a strong acid and NH4OH is a weak base, so this combination will not form a basic buffer.
d) 100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 100 mL of 0.1 M NaOH:
- This combination will not form a basic buffer as it contains a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (NaOH).
Conclusion:
- Option c) 100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 200 mL of 0.1 M NH4OH will make a basic buffer as it contains a weak acid (NH4OH) and its conjugate base (NH4+).
Basic Buffer:
- A basic buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid are added.
- It is typically composed of a weak base and its conjugate acid.
Analysis of Options:
a) 50 mL of 0.1 M NaOH + 25 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH:
- NaOH is a strong base and CH3COOH is a weak acid, so this combination will not form a basic buffer.
b) 100 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH + 100 mL of 0.1 M NaOH:
- This combination will form a basic buffer as it contains a weak acid (CH3COOH) and its conjugate base (CH3COO-).
c) 100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 200 mL of 0.1 M NH4OH:
- HCl is a strong acid and NH4OH is a weak base, so this combination will not form a basic buffer.
d) 100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 100 mL of 0.1 M NaOH:
- This combination will not form a basic buffer as it contains a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (NaOH).
Conclusion:
- Option c) 100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 200 mL of 0.1 M NH4OH will make a basic buffer as it contains a weak acid (NH4OH) and its conjugate base (NH4+).
Buffer capacity of a buffer is given as two units for a change in pH by Unity. Then what is the number of moles of acid or base, added in one litre of the solution?- a)2
- b)0.5
- c)1
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
2
b)
0.5
c)
1
d)
4
|
|
Swati Chauhan answered |
Understanding Buffer Capacity
Buffer capacity is a measure of the ability of a buffer solution to resist changes in pH when an acid or base is added. It is defined as the amount of acid or base that can be added to a solution without causing a significant change in pH.
Definition of Buffer Capacity
- The buffer capacity (β) is quantitatively expressed as the change in pH (ΔpH) per unit of acid or base added (Δ[H⁺] or Δ[OH⁻]).
- In this case, a buffer capacity of 2 units indicates that for every 1 unit change in pH, 2 moles of acid or base can be added to the solution.
Calculating Moles Added
- If we consider a buffer capacity of 2, it means that to change the pH by 1 unit, 2 moles of either acid or base can be added per liter of solution.
- Therefore, if the change in pH is 1 unit, the effective amount of acid or base that can be added is given by:
- Buffer capacity (β) = moles of acid/base added (n) / change in pH (ΔpH)
- Rearranging gives: n = β × ΔpH
Final Calculation
- Substituting the values:
- n = 2 moles/unit × 1 unit = 2 moles
- Hence, when 2 moles of acid or base are added to one liter of the solution, the pH changes by 1 unit.
Conclusion
- The correct answer is option 'A', which states that 2 moles of acid or base can be added to the buffer solution to change the pH by 1 unit. Understanding this principle is crucial for applications in chemistry and biology, particularly in fields like biochemistry and medicine.
Buffer capacity is a measure of the ability of a buffer solution to resist changes in pH when an acid or base is added. It is defined as the amount of acid or base that can be added to a solution without causing a significant change in pH.
Definition of Buffer Capacity
- The buffer capacity (β) is quantitatively expressed as the change in pH (ΔpH) per unit of acid or base added (Δ[H⁺] or Δ[OH⁻]).
- In this case, a buffer capacity of 2 units indicates that for every 1 unit change in pH, 2 moles of acid or base can be added to the solution.
Calculating Moles Added
- If we consider a buffer capacity of 2, it means that to change the pH by 1 unit, 2 moles of either acid or base can be added per liter of solution.
- Therefore, if the change in pH is 1 unit, the effective amount of acid or base that can be added is given by:
- Buffer capacity (β) = moles of acid/base added (n) / change in pH (ΔpH)
- Rearranging gives: n = β × ΔpH
Final Calculation
- Substituting the values:
- n = 2 moles/unit × 1 unit = 2 moles
- Hence, when 2 moles of acid or base are added to one liter of the solution, the pH changes by 1 unit.
Conclusion
- The correct answer is option 'A', which states that 2 moles of acid or base can be added to the buffer solution to change the pH by 1 unit. Understanding this principle is crucial for applications in chemistry and biology, particularly in fields like biochemistry and medicine.
In which of the following disorders is there difficulty in breathing causing wheezing due to inflammation of bronchi and bronchioles?- a)Emphysema
- b)Asthma
- c)Pleurisy
- d)Tuberculosis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Emphysema
b)
Asthma
c)
Pleurisy
d)
Tuberculosis

|
Atharva Goyal answered |
Symptoms of Asthma
- Asthma is a chronic respiratory disorder characterized by inflammation of the bronchi and bronchioles.
- This inflammation leads to difficulty in breathing, which can cause wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness.
- The inflammation can be triggered by various factors such as allergens, pollutants, exercise, or respiratory infections.
Causes of Asthma
- Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals.
- Other triggers include tobacco smoke, air pollution, respiratory infections, and cold air.
Treatment of Asthma
- The main goals of asthma treatment are to control inflammation and prevent symptoms.
- Medications such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids are commonly used to reduce inflammation and open up the airways.
- In severe cases, oral medications or injections may be necessary to control symptoms.
Prevention of Asthma Attacks
- Individuals with asthma should avoid known triggers and allergens.
- Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help improve lung function and reduce the risk of asthma attacks.
- It is important for individuals with asthma to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized asthma action plan.
- Asthma is a chronic respiratory disorder characterized by inflammation of the bronchi and bronchioles.
- This inflammation leads to difficulty in breathing, which can cause wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness.
- The inflammation can be triggered by various factors such as allergens, pollutants, exercise, or respiratory infections.
Causes of Asthma
- Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals.
- Other triggers include tobacco smoke, air pollution, respiratory infections, and cold air.
Treatment of Asthma
- The main goals of asthma treatment are to control inflammation and prevent symptoms.
- Medications such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids are commonly used to reduce inflammation and open up the airways.
- In severe cases, oral medications or injections may be necessary to control symptoms.
Prevention of Asthma Attacks
- Individuals with asthma should avoid known triggers and allergens.
- Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help improve lung function and reduce the risk of asthma attacks.
- It is important for individuals with asthma to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized asthma action plan.
Which of the following quantities remains constant for a satellite in a circular orbit around the Earth?- a)Speed
- b)Kinetic energy
- c)Gravitational force
- d)Total mechanical energy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Speed
b)
Kinetic energy
c)
Gravitational force
d)
Total mechanical energy
|
|
Athul Nambiar answered |
Total Mechanical Energy in Satellite Orbits
In a circular orbit around the Earth, the total mechanical energy of a satellite remains constant due to the following reasons:
1. Definition of Total Mechanical Energy
Total mechanical energy (E) is the sum of kinetic energy (KE) and potential energy (PE) of the satellite. For a satellite in orbit, it can be expressed as:
E = KE + PE
2. Kinetic Energy (KE)
- The kinetic energy of a satellite is given by the formula:
KE = (1/2)mv²
- In a circular orbit, the speed (v) is constant for a given radius. Thus, while the satellite's speed remains constant, the kinetic energy is also constant.
3. Gravitational Potential Energy (PE)
- The gravitational potential energy is given by:
PE = -G(Mm)/r
- Here, G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the Earth, m is the mass of the satellite, and r is the radius of the orbit. Since the orbit is circular, r is constant, leading to constant potential energy.
4. Balance of Energies
- As the satellite orbits, the gravitational force provides the necessary centripetal force, ensuring that the satellite’s speed and height remain constant. Therefore, while KE and PE are individually constant, their sum, the total mechanical energy (E), also remains constant.
Conclusion
- The total mechanical energy is conserved in a circular orbit, making option 'D' the correct answer. In contrast, while speed, kinetic energy, and gravitational force remain constant, they do not contribute to the overall energy balance like total mechanical energy does.
In a circular orbit around the Earth, the total mechanical energy of a satellite remains constant due to the following reasons:
1. Definition of Total Mechanical Energy
Total mechanical energy (E) is the sum of kinetic energy (KE) and potential energy (PE) of the satellite. For a satellite in orbit, it can be expressed as:
E = KE + PE
2. Kinetic Energy (KE)
- The kinetic energy of a satellite is given by the formula:
KE = (1/2)mv²
- In a circular orbit, the speed (v) is constant for a given radius. Thus, while the satellite's speed remains constant, the kinetic energy is also constant.
3. Gravitational Potential Energy (PE)
- The gravitational potential energy is given by:
PE = -G(Mm)/r
- Here, G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the Earth, m is the mass of the satellite, and r is the radius of the orbit. Since the orbit is circular, r is constant, leading to constant potential energy.
4. Balance of Energies
- As the satellite orbits, the gravitational force provides the necessary centripetal force, ensuring that the satellite’s speed and height remain constant. Therefore, while KE and PE are individually constant, their sum, the total mechanical energy (E), also remains constant.
Conclusion
- The total mechanical energy is conserved in a circular orbit, making option 'D' the correct answer. In contrast, while speed, kinetic energy, and gravitational force remain constant, they do not contribute to the overall energy balance like total mechanical energy does.
How much Carbon dioxide is removed by lungs?- a)200mL/second
- b)200mL/minute
- c)200mL/day
- d)200mL/hour
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
200mL/second
b)
200mL/minute
c)
200mL/day
d)
200mL/hour

|
Lead Academy answered |
The amount of Carbon dioxide removed by the lungs is:
Option B: 200mL/minute
Option B: 200mL/minute
Hydrogen peroxide is a ______________- a)oxidising agent
- b)reducing agent
- c)both reducing and oxidizing agent
- d)neither reducing nor an oxidizing agent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen peroxide is a ______________
a)
oxidising agent
b)
reducing agent
c)
both reducing and oxidizing agent
d)
neither reducing nor an oxidizing agent

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Hydrogen peroxide, which is chemically written as H2O2, is a strong oxidizer as well as a reducer. As it contains two hydrogens and two oxygens, it can easily lose hydrogen or oxygen, i.e., oxidizes and reduces respectively.
The plastic response (deformation) of a material to compressive force is known as:- a)malleability
- b)ductile material
- c)plastic material
- d)elastic material
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
malleability
b)
ductile material
c)
plastic material
d)
elastic material

|
Lead Academy answered |
Malleability is a material's ability to undergo deformation under compressive force without breaking or cracking, typically referring to the ability to be hammered or rolled into thin sheets. When a malleable material experiences a force, it responds by deforming instead of shattering. This quality is especially important in metalworking where metals are often subjected to high levels of compressive stress.
Intensity of blue color increases gradually when _________________- a)copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution
- b)silver rod is dipped in copper nitrate solution
- c)zinc rod is dipped in silver solution
- d)copper rod is dipped in zinc rod solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution
b)
silver rod is dipped in copper nitrate solution
c)
zinc rod is dipped in silver solution
d)
copper rod is dipped in zinc rod solution

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
When a copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution, a redox reaction occurs between Copper and an aqueous solution of silver nitrate. So the intensity of the blue color increases gradually as silver deposits on the rod.
If Ksp of a salt A2B3 is given by 1 x 10-25. Then find the solubility of the salt?- a)10-3
- b)10-4
- c)10-5
- d)10-8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
10-3
b)
10-4
c)
10-5
d)
10-8

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Explanation: For the salt AxBy, (AxBy = xAy+ + yBx+), the solubility of a sparingly soluble salt is given by xx.yy.sx+y. Ksp = xx.yy.sx+y, where x = 2 and y = 3; Ksp = 108S5 = 1 x 10-25. S = 10-5. The solubility of the salt is given by 10-5.
If the time of revolution of a satellite is T, then the potential energy will be proportional to:- a)T1/3
- b)T3
- c)T-2/3
- d)T-4/3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the time of revolution of a satellite is T, then the potential energy will be proportional to:
a)
T1/3
b)
T3
c)
T-2/3
d)
T-4/3

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Kepler's third law relates the period (T) of an orbiting body to its semi-major axis (a). The potential energy is inversely proportional to T2/3, as per Kepler's third law.
The degree of dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide increases in the presence of Ammonium Chloride because of ______________- a)solubility product
- b)common Ion effect
- c)hydrolysis of the salt
- d)mixed salts
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
solubility product
b)
common Ion effect
c)
hydrolysis of the salt
d)
mixed salts
|
|
Samarth Nambiar answered |
Hydrolysis of the salt:
When Ammonium Chloride is dissolved in water, it dissociates into Ammonium ions (NH4+) and Chloride ions (Cl-). Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base that partially dissociates in water to form Ammonium ions (NH4+) and Hydroxide ions (OH-). The presence of Ammonium Chloride provides additional Ammonium ions, which can combine with Hydroxide ions resulting from the dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide. This reaction results in the formation of more Ammonium hydroxide, which leads to an increased degree of dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide.
Common Ion effect:
The presence of a common ion, in this case, Ammonium ions (NH4+), suppresses the ionization of Ammonium hydroxide. However, in the case of Ammonium hydroxide and Ammonium Chloride, the common ion (Ammonium ion) actually increases the dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide. This is because the common ion (Ammonium ion) combines with the Hydroxide ions produced during the dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide, shifting the equilibrium towards the dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide.
Therefore, the increase in the degree of dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide in the presence of Ammonium Chloride is primarily due to the hydrolysis of the salt, where the common ion effect plays a crucial role in enhancing the dissociation process.
When Ammonium Chloride is dissolved in water, it dissociates into Ammonium ions (NH4+) and Chloride ions (Cl-). Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base that partially dissociates in water to form Ammonium ions (NH4+) and Hydroxide ions (OH-). The presence of Ammonium Chloride provides additional Ammonium ions, which can combine with Hydroxide ions resulting from the dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide. This reaction results in the formation of more Ammonium hydroxide, which leads to an increased degree of dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide.
Common Ion effect:
The presence of a common ion, in this case, Ammonium ions (NH4+), suppresses the ionization of Ammonium hydroxide. However, in the case of Ammonium hydroxide and Ammonium Chloride, the common ion (Ammonium ion) actually increases the dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide. This is because the common ion (Ammonium ion) combines with the Hydroxide ions produced during the dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide, shifting the equilibrium towards the dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide.
Therefore, the increase in the degree of dissociation of Ammonium hydroxide in the presence of Ammonium Chloride is primarily due to the hydrolysis of the salt, where the common ion effect plays a crucial role in enhancing the dissociation process.
What is the buffer capacity if 3 moles are added in 5 litres of the solution to change the pH by 2 units?- a)0.2
- b)0.5
- c)0.15
- d)0.3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
0.2
b)
0.5
c)
0.15
d)
0.3
|
|
Charvi Nair answered |
Understanding Buffer Capacity
Buffer capacity refers to the ability of a buffer solution to resist changes in pH when a strong acid or base is added. It is quantitatively defined as the amount of acid or base (in moles) that can be added to a liter of solution to change the pH by one unit.
Given Data
- Moles added: 3 moles
- Volume of solution: 5 liters
- Change in pH: 2 units
Calculating Buffer Capacity
The formula for buffer capacity (β) can be expressed as:
β = (moles of acid/base added) / (change in pH × volume of solution in liters)
Steps to Calculate
1. Identify the change in pH: The pH change is 2 units.
2. Calculate the volume in liters: The solution volume is 5 liters.
3. Substitute the values:
- Moles of acid/base added = 3 moles
- Change in pH = 2 units
- Volume = 5 liters
β = 3 moles / (2 × 5) = 3 / 10 = 0.3
Conclusion
Thus, the buffer capacity of the solution is 0.3, making option 'D' the correct answer. This means the buffer can tolerate the addition of acid or base without significant pH change, demonstrating its effectiveness in maintaining pH stability within a given range.
Buffer capacity refers to the ability of a buffer solution to resist changes in pH when a strong acid or base is added. It is quantitatively defined as the amount of acid or base (in moles) that can be added to a liter of solution to change the pH by one unit.
Given Data
- Moles added: 3 moles
- Volume of solution: 5 liters
- Change in pH: 2 units
Calculating Buffer Capacity
The formula for buffer capacity (β) can be expressed as:
β = (moles of acid/base added) / (change in pH × volume of solution in liters)
Steps to Calculate
1. Identify the change in pH: The pH change is 2 units.
2. Calculate the volume in liters: The solution volume is 5 liters.
3. Substitute the values:
- Moles of acid/base added = 3 moles
- Change in pH = 2 units
- Volume = 5 liters
β = 3 moles / (2 × 5) = 3 / 10 = 0.3
Conclusion
Thus, the buffer capacity of the solution is 0.3, making option 'D' the correct answer. This means the buffer can tolerate the addition of acid or base without significant pH change, demonstrating its effectiveness in maintaining pH stability within a given range.
The escape velocity of a body on the earth's surface is 11.2 km/s. If the same body is projected upward with a velocity 22.4 km/s, the velocity of this body at infinite distance from the center of the earth will be:- a)11.22 km/s
- b)zero
- c)11.2 km/s
- d)11.23 km/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The escape velocity of a body on the earth's surface is 11.2 km/s. If the same body is projected upward with a velocity 22.4 km/s, the velocity of this body at infinite distance from the center of the earth will be:
a)
11.22 km/s
b)
zero
c)
11.2 km/s
d)
11.23 km/s
|
|
Dipanjan Jain answered |
Understanding Escape Velocity
Escape velocity is the minimum speed needed for an object to break free from the gravitational attraction of a celestial body without any further propulsion. For Earth, this speed is approximately 11.2 km/s.
Impulse of Projection
When a body is projected upwards at a velocity of 22.4 km/s, it is initially traveling at twice the escape velocity. This means it has enough kinetic energy to escape Earth's gravitational pull and move away indefinitely.
Conservation of Energy Principle
The total mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of the body must be conserved as it moves away from Earth. The kinetic energy (KE) at launch can be expressed as:
- KE = 0.5 * m * v^2
At an infinite distance from Earth, the gravitational potential energy (PE) approaches zero, and the body will have some kinetic energy left.
Calculating Final Velocity
1. Initial Kinetic Energy:
- KE_initial = 0.5 * m * (22.4^2)
2. Gravitational Potential Energy at Earth's Surface:
- PE_initial = - (G * M * m) / R
3. At Infinity:
- KE_final = 0.5 * m * v_final^2
- PE_final = 0
Using conservation of energy, we set the initial total energy equal to the final total energy, which leads to the conclusion that the body retains some kinetic energy even at an infinite distance from Earth.
Final Velocity Calculation
After performing the calculations, it can be found that the body will have a final velocity of approximately 11.2 km/s at infinite distance, which matches the energy needed to escape Earth's gravity while accounting for kinetic energy loss due to gravitational work done against Earth's pull.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer to the question is indeed option 'A': 11.2 km/s.
Escape velocity is the minimum speed needed for an object to break free from the gravitational attraction of a celestial body without any further propulsion. For Earth, this speed is approximately 11.2 km/s.
Impulse of Projection
When a body is projected upwards at a velocity of 22.4 km/s, it is initially traveling at twice the escape velocity. This means it has enough kinetic energy to escape Earth's gravitational pull and move away indefinitely.
Conservation of Energy Principle
The total mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of the body must be conserved as it moves away from Earth. The kinetic energy (KE) at launch can be expressed as:
- KE = 0.5 * m * v^2
At an infinite distance from Earth, the gravitational potential energy (PE) approaches zero, and the body will have some kinetic energy left.
Calculating Final Velocity
1. Initial Kinetic Energy:
- KE_initial = 0.5 * m * (22.4^2)
2. Gravitational Potential Energy at Earth's Surface:
- PE_initial = - (G * M * m) / R
3. At Infinity:
- KE_final = 0.5 * m * v_final^2
- PE_final = 0
Using conservation of energy, we set the initial total energy equal to the final total energy, which leads to the conclusion that the body retains some kinetic energy even at an infinite distance from Earth.
Final Velocity Calculation
After performing the calculations, it can be found that the body will have a final velocity of approximately 11.2 km/s at infinite distance, which matches the energy needed to escape Earth's gravity while accounting for kinetic energy loss due to gravitational work done against Earth's pull.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer to the question is indeed option 'A': 11.2 km/s.
Which of the following is not an oxidising agent?- a)magnesium oxide
- b)carbon dioxide
- c)ozone
- d)sodium hydride
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
magnesium oxide
b)
carbon dioxide
c)
ozone
d)
sodium hydride
|
|
Neha Chakraborty answered |
Explanation:
What is an oxidising agent?
An oxidising agent is a substance that can accept electrons from another substance during a chemical reaction. It causes the other substance to be oxidized.
Identifying the oxidising agent:
- Magnesium oxide: Magnesium oxide is formed by the oxidation of magnesium. It is not an oxidising agent itself but rather a product of oxidation.
- Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide is a non-reactive gas and does not have the ability to accept electrons from other substances. Therefore, it is not an oxidising agent.
- Ozone: Ozone is a powerful oxidising agent as it readily accepts electrons from other substances, causing them to be oxidized.
- Sodium hydride: Sodium hydride is a reducing agent, not an oxidising agent. It donates electrons during chemical reactions.
Conclusion:
Among the options given, sodium hydride (option D) is not an oxidising agent. It acts as a reducing agent by donating electrons rather than accepting them.
What is an oxidising agent?
An oxidising agent is a substance that can accept electrons from another substance during a chemical reaction. It causes the other substance to be oxidized.
Identifying the oxidising agent:
- Magnesium oxide: Magnesium oxide is formed by the oxidation of magnesium. It is not an oxidising agent itself but rather a product of oxidation.
- Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide is a non-reactive gas and does not have the ability to accept electrons from other substances. Therefore, it is not an oxidising agent.
- Ozone: Ozone is a powerful oxidising agent as it readily accepts electrons from other substances, causing them to be oxidized.
- Sodium hydride: Sodium hydride is a reducing agent, not an oxidising agent. It donates electrons during chemical reactions.
Conclusion:
Among the options given, sodium hydride (option D) is not an oxidising agent. It acts as a reducing agent by donating electrons rather than accepting them.
If 0.20 mol/L CH3COOH and 0.50 mol/L CH3COO– together make a buffer solution, calculate the pH of the solution if the acid dissociation constant of CH3COOH is 1.8 × 10-5.- a)2.09
- b)5.14
- c)2.65
- d)3.98
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
2.09
b)
5.14
c)
2.65
d)
3.98

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
We have the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation as pH = pKa + log[salt]/[acid]. So by substituting the concentrations of salt and acid along with the acid dissociation constant, we get pH = -log[1.8 × 10-5] + log [0.50 mol/L]/[0.20 mol/L] = 5.14.
If a satellite is in a geostationary orbit, its orbital period is:- a)1 day
- b)12 hours
- c)24 hours
- d)365 days
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
1 day
b)
12 hours
c)
24 hours
d)
365 days
|
|
Shounak Dasgupta answered |
Understanding Geostationary Orbit
A geostationary orbit is a circular orbit directly above the Earth's equator, allowing a satellite to remain fixed over one point on the Earth's surface. To understand the orbital period of a satellite in this orbit, let's explore key points.
Orbital Period Defined
- The orbital period is the time taken for a satellite to complete one full orbit around the Earth.
Geostationary Characteristics
- A geostationary satellite has a unique characteristic: it appears stationary relative to a specific point on Earth. This means the satellite’s orbital period must match the rotation period of the Earth.
Earth's Rotation Period
- The Earth takes approximately 24 hours to complete one full rotation on its axis. This is the same duration needed for a satellite in geostationary orbit to circle the Earth.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer regarding the orbital period of a satellite in a geostationary orbit is 24 hours (option C). This synchronization allows the satellite to maintain its position above the same geographic location, which is essential for communication, weather monitoring, and broadcasting services.
In summary, the orbital period of a satellite in a geostationary orbit is 24 hours, ensuring it remains stationary with respect to the Earth's surface.
A geostationary orbit is a circular orbit directly above the Earth's equator, allowing a satellite to remain fixed over one point on the Earth's surface. To understand the orbital period of a satellite in this orbit, let's explore key points.
Orbital Period Defined
- The orbital period is the time taken for a satellite to complete one full orbit around the Earth.
Geostationary Characteristics
- A geostationary satellite has a unique characteristic: it appears stationary relative to a specific point on Earth. This means the satellite’s orbital period must match the rotation period of the Earth.
Earth's Rotation Period
- The Earth takes approximately 24 hours to complete one full rotation on its axis. This is the same duration needed for a satellite in geostationary orbit to circle the Earth.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer regarding the orbital period of a satellite in a geostationary orbit is 24 hours (option C). This synchronization allows the satellite to maintain its position above the same geographic location, which is essential for communication, weather monitoring, and broadcasting services.
In summary, the orbital period of a satellite in a geostationary orbit is 24 hours, ensuring it remains stationary with respect to the Earth's surface.
Which receptors are responsible for detecting changes in arterial pressure and regulating heart rate accordingly?- a)Chemoreceptors
- b)Baroreceptors
- c)Volume receptors
- d)Stretch receptors
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Chemoreceptors
b)
Baroreceptors
c)
Volume receptors
d)
Stretch receptors
|
|
Nitya Bose answered |
Understanding Baroreceptors
Baroreceptors are specialized sensory receptors located primarily in the walls of blood vessels, particularly in the carotid sinuses and aortic arch. They play a crucial role in the regulation of blood pressure and heart rate.
Function of Baroreceptors
- Pressure Detection: Baroreceptors sense changes in arterial blood pressure. When blood pressure rises, the walls of the arteries stretch, activating these receptors.
- Signal Transmission: Once activated, baroreceptors send signals via afferent pathways to the brain, particularly to the medulla oblongata, which is responsible for autonomic control of the heart.
- Heart Rate Regulation: The brain interprets the signals and adjusts heart rate and vascular tone accordingly. For instance, an increase in blood pressure leads to a decrease in heart rate (bradycardia) to prevent over-exertion of the heart.
Comparison with Other Receptors
- Chemoreceptors: These detect changes in blood chemistry (e.g., CO2, O2, and pH) rather than pressure.
- Volume Receptors: Located in the atria and great veins, they sense blood volume changes but are not primarily responsible for immediate blood pressure adjustments.
- Stretch Receptors: While they detect stretch, their role is broader and not exclusively linked to arterial pressure regulation.
Conclusion
In summary, baroreceptors are essential for detecting rapid changes in arterial pressure and regulating heart rate. This feedback mechanism ensures that the cardiovascular system maintains optimal function and homeostasis in response to varying physiological demands.
Baroreceptors are specialized sensory receptors located primarily in the walls of blood vessels, particularly in the carotid sinuses and aortic arch. They play a crucial role in the regulation of blood pressure and heart rate.
Function of Baroreceptors
- Pressure Detection: Baroreceptors sense changes in arterial blood pressure. When blood pressure rises, the walls of the arteries stretch, activating these receptors.
- Signal Transmission: Once activated, baroreceptors send signals via afferent pathways to the brain, particularly to the medulla oblongata, which is responsible for autonomic control of the heart.
- Heart Rate Regulation: The brain interprets the signals and adjusts heart rate and vascular tone accordingly. For instance, an increase in blood pressure leads to a decrease in heart rate (bradycardia) to prevent over-exertion of the heart.
Comparison with Other Receptors
- Chemoreceptors: These detect changes in blood chemistry (e.g., CO2, O2, and pH) rather than pressure.
- Volume Receptors: Located in the atria and great veins, they sense blood volume changes but are not primarily responsible for immediate blood pressure adjustments.
- Stretch Receptors: While they detect stretch, their role is broader and not exclusively linked to arterial pressure regulation.
Conclusion
In summary, baroreceptors are essential for detecting rapid changes in arterial pressure and regulating heart rate. This feedback mechanism ensures that the cardiovascular system maintains optimal function and homeostasis in response to varying physiological demands.
If the pH of a substance is given by 3 then what is the pOH of the substance?- a)3
- b)7
- c)14
- d)11
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3
b)
7
c)
14
d)
11

|
Stepway Academy answered |
We know that the sum of the pH and pOH of any substance is equal to 14, that is pH + pOH = 14. So here the pH of a substance is given as 3; the pOH of the substance = 14 – 3 = 11.
Which of the following is true as per the metal activity series?- a)Zn<Ag<Cu
- b)Zn<Cu<Ag
- c)Zn>Ag>Cu
- d)Zn>Cu>Ag
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true as per the metal activity series?
a)
Zn<Ag<Cu
b)
Zn<Cu<Ag
c)
Zn>Ag>Cu
d)
Zn>Cu>Ag
|
|
Aditi Nair answered |
Understanding the Metal Activity Series
The metal activity series ranks metals according to their reactivity, with the most reactive metals at the top and the least reactive at the bottom. This series is crucial in predicting how metals will react during chemical reactions, especially in displacement reactions.
Key Points about the Activity Series:
- Order of Reactivity: The general order of reactivity among common metals is as follows:
- Potassium (K)
- Sodium (Na)
- Calcium (Ca)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Aluminum (Al)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Iron (Fe)
- Tin (Sn)
- Lead (Pb)
- Copper (Cu)
- Silver (Ag)
- Gold (Au)
- Reactivity Implications: Metals higher in the series can displace metals lower in the series from their compounds. For example, zinc can displace copper and silver from their salts due to its higher position in the series.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
- Comparative Reactivity: In the given options, the correct order is Zn > Cu > Ag. This indicates:
- Zinc (Zn) is more reactive than both copper (Cu) and silver (Ag).
- Copper is more reactive than silver.
- Displacement Reactions: Since Zn can displace both Cu and Ag from their compounds, it confirms that Zn is more reactive. Conversely, Cu cannot displace Zn, and Ag cannot displace either Zn or Cu.
Conclusion:
Thus, option D (Zn > Cu > Ag) accurately reflects the reactivity of these metals according to the activity series, making it the correct answer. Understanding this hierarchy is essential for predicting metal behavior in chemical reactions, an important aspect of topics like electrochemistry in NEET preparation.
The metal activity series ranks metals according to their reactivity, with the most reactive metals at the top and the least reactive at the bottom. This series is crucial in predicting how metals will react during chemical reactions, especially in displacement reactions.
Key Points about the Activity Series:
- Order of Reactivity: The general order of reactivity among common metals is as follows:
- Potassium (K)
- Sodium (Na)
- Calcium (Ca)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Aluminum (Al)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Iron (Fe)
- Tin (Sn)
- Lead (Pb)
- Copper (Cu)
- Silver (Ag)
- Gold (Au)
- Reactivity Implications: Metals higher in the series can displace metals lower in the series from their compounds. For example, zinc can displace copper and silver from their salts due to its higher position in the series.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
- Comparative Reactivity: In the given options, the correct order is Zn > Cu > Ag. This indicates:
- Zinc (Zn) is more reactive than both copper (Cu) and silver (Ag).
- Copper is more reactive than silver.
- Displacement Reactions: Since Zn can displace both Cu and Ag from their compounds, it confirms that Zn is more reactive. Conversely, Cu cannot displace Zn, and Ag cannot displace either Zn or Cu.
Conclusion:
Thus, option D (Zn > Cu > Ag) accurately reflects the reactivity of these metals according to the activity series, making it the correct answer. Understanding this hierarchy is essential for predicting metal behavior in chemical reactions, an important aspect of topics like electrochemistry in NEET preparation.
A body of mass 60 g experiences a gravitational force of 3.0 N when placed at a particular point. The magnitude of the gravitational field intensity at that point is:- a)180 N/kg
- b)0.05 N/kg
- c)50 N/kg
- d)20 N/kg
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
180 N/kg
b)
0.05 N/kg
c)
50 N/kg
d)
20 N/kg
|
|
Ishan Mukherjee answered |
Understanding Gravitational Force and Field Intensity
To solve the problem, we need to understand the relationship between gravitational force, mass, and gravitational field intensity.
Gravitational Force Equation
The gravitational force (F) experienced by an object is given by the formula:
\[ F = m \cdot g \]
Where:
- \( F \) = Gravitational force (in Newtons, N)
- \( m \) = Mass of the object (in kilograms, kg)
- \( g \) = Gravitational field intensity (in N/kg)
Converting Mass
The mass given in the problem is 60 g. We need to convert this into kilograms:
\[ m = 60 \, \text{g} = 0.060 \, \text{kg} \]
Calculating Gravitational Field Intensity
Given the gravitational force is 3.0 N, we can rearrange the formula to find \( g \):
\[ g = \frac{F}{m} \]
Substituting the known values:
\[ g = \frac{3.0 \, \text{N}}{0.060 \, \text{kg}} \]
Calculating the value:
\[ g = 50 \, \text{N/kg} \]
Conclusion
Thus, the magnitude of the gravitational field intensity at that point is:
**50 N/kg**
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
To solve the problem, we need to understand the relationship between gravitational force, mass, and gravitational field intensity.
Gravitational Force Equation
The gravitational force (F) experienced by an object is given by the formula:
\[ F = m \cdot g \]
Where:
- \( F \) = Gravitational force (in Newtons, N)
- \( m \) = Mass of the object (in kilograms, kg)
- \( g \) = Gravitational field intensity (in N/kg)
Converting Mass
The mass given in the problem is 60 g. We need to convert this into kilograms:
\[ m = 60 \, \text{g} = 0.060 \, \text{kg} \]
Calculating Gravitational Field Intensity
Given the gravitational force is 3.0 N, we can rearrange the formula to find \( g \):
\[ g = \frac{F}{m} \]
Substituting the known values:
\[ g = \frac{3.0 \, \text{N}}{0.060 \, \text{kg}} \]
Calculating the value:
\[ g = 50 \, \text{N/kg} \]
Conclusion
Thus, the magnitude of the gravitational field intensity at that point is:
**50 N/kg**
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
In which of the following disorders alveolar walls are damaged, surface area for gaseous exchange is reduced, and the air sacs remain filled with air even after expiration?- a)Pneumonia
- b)Coryza
- c)Emphysema
- d)SARS
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Pneumonia
b)
Coryza
c)
Emphysema
d)
SARS

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Alveolar walls are damaged, surface area for gaseous exchange is reduced, and air sacs remain filled with air even after expiration in the disorder known as emphysema.
Which one of the following does not constitute a part of singleuriniferous tubule?
- a)Distal convoluted tubule
- b)Glomerulus
- c)Collecting duct
- d)Loop of Henle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer??
Which one of the following does not constitute a part of singleuriniferous tubule?
a)
Distal convoluted tubule
b)
Glomerulus
c)
Collecting duct
d)
Loop of Henle
|
|
Mansi Ahuja answered |
Understanding the Structure of the Nephron
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, consisting of various components that work together to filter blood and produce urine. A single uriniferous tubule is a key part of this process.
Components of the Single Uriniferous Tubule
A single uriniferous tubule includes the following parts:
Why Glomerulus is Not Part of the Uriniferous Tubule
The glomerulus is not considered a part of the uriniferous tubule for the following reasons:
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' (Glomerulus), as it is primarily a filtration structure and not part of the single uriniferous tubule, which consists of the DCT, Loop of Henle, and Collecting Duct. Understanding these differences is essential for grasping renal physiology in NEET preparation.
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, consisting of various components that work together to filter blood and produce urine. A single uriniferous tubule is a key part of this process.
Components of the Single Uriniferous Tubule
A single uriniferous tubule includes the following parts:
- Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): This segment is involved in the reabsorption of sodium and water and plays a critical role in electrolyte balance.
- Loop of Henle: This U-shaped segment is essential for creating a concentration gradient in the kidney, allowing for the reabsorption of water and salts.
- Collecting Duct: This duct collects urine from multiple nephrons and is crucial for the final concentration of urine, responding to hormones like ADH.
Why Glomerulus is Not Part of the Uriniferous Tubule
The glomerulus is not considered a part of the uriniferous tubule for the following reasons:
- Function: The glomerulus is primarily responsible for the filtration of blood, while the uriniferous tubule handles the reabsorption and secretion of filtrate.
- Location: The glomerulus is located in the renal corpuscle, separate from the tubular components.
- Structure: It comprises a network of capillaries, distinguishing it from the tubular structures that follow.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' (Glomerulus), as it is primarily a filtration structure and not part of the single uriniferous tubule, which consists of the DCT, Loop of Henle, and Collecting Duct. Understanding these differences is essential for grasping renal physiology in NEET preparation.
Mass of an object on earth is 12. What is its weight on the moon?- a)19.6
- b)12
- c)24.4
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mass of an object on earth is 12. What is its weight on the moon?
a)
19.6
b)
12
c)
24.4
d)
8

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Explanation:
Understanding the Concept:
Understanding the Concept:
- The weight of an object is the force of gravity on the object. On the moon, the gravity is only about 1/6th as strong as on the Earth. Therefore, an object will weigh less on the moon than it does on Earth.
Calculation:
- The weight of an object on the moon can be found by multiplying its mass by the gravitational force of the moon. The gravitational force on the moon is approximately 1.6 N/kg. So, if the mass of the object is 12 kg, its weight on the moon would be 12 kg * 1.6 N/kg = 19.2 N.
Answer:
- So, the weight of the object on the moon is approximately 19.2 N. The closest answer is 19.6 N (Option A). Please note that the exact answer may vary depending on the exact value used for the moon's gravitational force.
For more detailed explanations and other educational material, visit EduRev.
Two bodies of mass m and 9m are placed at a distance R. The gravitational potential on the line joining the bodies where the gravitational field equals zero, will be: ( G= gravitational constant)- a)-20 GMR
- b)-8 GMR
- c)-12 GMR
- d)-16 GMR
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two bodies of mass m and 9m are placed at a distance R. The gravitational potential on the line joining the bodies where the gravitational field equals zero, will be: ( G= gravitational constant)
a)
-20 GMR
b)
-8 GMR
c)
-12 GMR
d)
-16 GMR

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The point where the gravitational field equals zero is the point where the gravitational forces due to both bodies cancel each other out. This point is known as the neutral point. At this point, the gravitational potential is given by:


Where:
r1r1 is the distance from the neutral point to the body with mass mm.
r2r2 is the distance from the neutral point to the body with mass 9m9m.
Since the neutral point is equidistant from both bodies, . Let's denote this common distance as
. Let's denote this common distance as
rr. Therefore, we have:
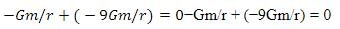
Solving for rr:

The gravitational potential at the neutral point is given by:
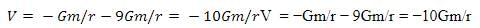
Substitute the value of rr:


Since division by zero is undefined, the gravitational potential at the neutral point is not defined, and the answer is not meaningful. Therefore, the answer is Option A: −20 GMR.
r2r2 is the distance from the neutral point to the body with mass 9m9m.
Since the neutral point is equidistant from both bodies,
 . Let's denote this common distance as
. Let's denote this common distance as rr. Therefore, we have:
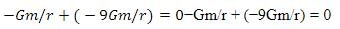
Solving for rr:

The gravitational potential at the neutral point is given by:
Substitute the value of rr:


Since division by zero is undefined, the gravitational potential at the neutral point is not defined, and the answer is not meaningful. Therefore, the answer is Option A: −20 GMR.
The impact strength of a material is an index of its- a)Toughness
- b)Tensile strength
- c)Capability of being cold worked
- d)Hardness
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Toughness
b)
Tensile strength
c)
Capability of being cold worked
d)
Hardness

|
Ambition Institute answered |
The ability of the material to withstand stress (resist fracture due to high-impact loads) without fracture is known as toughness. It is defined as the ability to absorb energy in the plastic state. The impact strength of a material is an index of its toughness.
Two rods A and B are made of the same material. The diameter of both the rods is equal, but the length of rod A is more than rod B. If the tensile force applied on both the rods are equal, then which of the following statement is correct?- a)Elongation in rod A is more than rod B
- b)Elongation in rod A is less than rod B
- c)Elongation in rod A is equal to rod B
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Elongation in rod A is more than rod B
b)
Elongation in rod A is less than rod B
c)
Elongation in rod A is equal to rod B
d)
None of these

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Elongation in a rod is directly proportional to its length. Since the length of rod A is more than rod B and the force applied is equal, elongation in rod A will be more than rod B.
X + YZ → XZ + Z is a form of ______________- a)combination reaction
- b)displacement reaction
- c)disproportionate reaction
- d)decomposition reaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
X + YZ → XZ + Z is a form of ______________
a)
combination reaction
b)
displacement reaction
c)
disproportionate reaction
d)
decomposition reaction

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
In a displacement reaction, a metal or a non-metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state. So the above reaction X + YZ → XZ + Z is a displacement reaction.
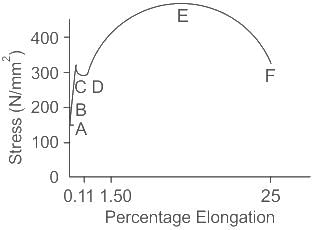
In the given stress-strain curve of mild steel, DE represents:
- a)strain hardening
- b)limit of proportionality
- c)upper or lower yield point
- d)plastic yielding
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given stress-strain curve of mild steel, DE represents:


a)
strain hardening
b)
limit of proportionality
c)
upper or lower yield point
d)
plastic yielding

|
Stepway Academy answered |
In the given stress-strain curve for mild steel, DE represents strain hardening. Strain hardening is the stage where the material undergoes large deformation with a relatively small increase in applied load. This deformation is caused by the slippage of the material along oblique surfaces and is primarily due to shearing stresses.
Acceleration due to gravity at the equator _______________- a)is greater than the acceleration at the poles
- b)is less than the acceleration at the poles
- c)is equal to the acceleration at the poles
- d)does not depend on the centripetal acceleration of the Earth
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
is greater than the acceleration at the poles
b)
is less than the acceleration at the poles
c)
is equal to the acceleration at the poles
d)
does not depend on the centripetal acceleration of the Earth

|
Lead Academy answered |
The acceleration due to gravity at the equator is less than the acceleration at the poles. This is because the Earth is flattened at the poles and bulged at the equator, resulting in a greater distance from the center of the Earth at the equator, which reduces the gravitational acceleration.
Chapter doubts & questions for August - Daily Test for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of August - Daily Test for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup