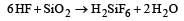All Exams >
NEET >
Inorganic Chemistry for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of The p - Block Elements for NEET Exam
An example of a double salt is [1989]- a)Bleaching powder
- b)K4[Fe(CN)6]
- c)Hypo
- d)Potash Alum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of a double salt is [1989]
a)
Bleaching powder
b)
K4[Fe(CN)6]
c)
Hypo
d)
Potash Alum

|
Surbhi Das answered |
Potash Alum, K2SO4. Al2(SO4). 24H2O is a double salt.
Which of the following statements is true?a)The atomic radius of Ga is less than B.
b)The atomic radius of Ga is more than Al.c)The atomic radius of Ga is less than Al.d)The atomic radius of Ga is equal to AlCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
b)The atomic radius of Ga is more than Al.
c)The atomic radius of Ga is less than Al.
d)The atomic radius of Ga is equal to Al
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The atomic radius of the Ga is less than Al because of poor screening effect. The atomic radius of Ga is slightly lesser than of Al because in going from Al to Ga, the electrons have already occupied 3d sub shell in Ga
Which of the following elements exist as liquid in summer among group 13 elements?
- a) Tl
- b) Al
- c) B
- d) Ga
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following elements exist as liquid in summer among group 13 elements?
a)
Tlb)
Alc)
Bd)
Ga|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Galium can occur in liquid state if the room is above 29.76C which is its melting point. So,option d is correct
In trivalent state, for example, the trichlorides, being covalent are hydrolysed in water form- a)pentagonal structure
- b)planar structure
- c)trigonal structure
- d)tetrahedral structure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In trivalent state, for example, the trichlorides, being covalent are hydrolysed in water form
a)
pentagonal structure
b)
planar structure
c)
trigonal structure
d)
tetrahedral structure
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
trihalides hydrolysis to form tetrahedral structure
The maximum oxidation state shown by a p-block element is equal to the:- a)Total number of valence electrons (i.e., the sum of the s and p-electrons)
- b)Total number of s electrons
- c)Total number of p electrons
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum oxidation state shown by a p-block element is equal to the:
a)
Total number of valence electrons (i.e., the sum of the s and p-electrons)
b)
Total number of s electrons
c)
Total number of p electrons
d)
None of these
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
- The oxidation state of an element is related to the number of electrons that an atom loses, gains, or appears to use when joining with another atom in compounds.
- It also determines the ability of an atom to oxidize (to lose electrons) or to reduce (to gain electrons) other atoms or species.
- They should release the total valence electrons to attain stability, so the maximum possible oxidation state is the number of valence electrons.
The exhibition of highest co-ordination number depends on the availability of vacant orbitals in the central atom. Which of the following elements is not likely to act as central atom in MF3-6?- a)B
- b)Al
- c)Ga
- d)In
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The exhibition of highest co-ordination number depends on the availability of vacant orbitals in the central atom. Which of the following elements is not likely to act as central atom in MF3-6?
a)
B
b)
Al
c)
Ga
d)
In
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
The element M in the complex ion MF6^3- has a coordination number of six. Since B has only s- and p-orbitals and no d – orbitals, therefore, at the maximum it can show a coordination number of 4. Thus, B cannot form complex of the type MF6^3-, i.e., option (a) is correct.
The substance used as a smoke screen in warfare is[1989]- a)SiCl4
- b)PH3
- c)PCl5
- d)Acetylene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The substance used as a smoke screen in warfare is[1989]
a)
SiCl4
b)
PH3
c)
PCl5
d)
Acetylene

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
SiCl4 gets hydrolysed in moist air and gives white fumes which are used as a smoke screen in warfare.
The order of ionization enthalpy for B, Al and Ga is:- a)B>Al<Ga
- b)B
- c)B>Al>Ga
- d)Ga
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The order of ionization enthalpy for B, Al and Ga is:
a)
B>Al<Ga
b)
B
c)
B>Al>Ga
d)
Ga

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
(A) B>Al<Ga
The trend in ionization enthalpy is because there is decrease in Ionisation enthalpy from B to Al due to increase in size and from Al to Ga. Ga has more ionisation energy than Al due to uneffective screening effect.
Nitrogen dioxide is dissolved in water to produce- a)HNO3 and HNO2
- b)Only HNO3
- c)Only HNO2
- d)HNO2 and N2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitrogen dioxide is dissolved in water to produce
a)
HNO3 and HNO2
b)
Only HNO3
c)
Only HNO2
d)
HNO2 and N2

|
Uday Chakraborty answered |
NO2 + H2O → HNO3 + HNO2
Mixed
anhydride
Mixed
anhydride
Which of the following group 13 elements oxide is acidic in nature?- a)Al2O3
- b)B2O3
- c)Tl2O3
- d)Ga2O3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following group 13 elements oxide is acidic in nature?
a)
Al2O3
b)
B2O3
c)
Tl2O3
d)
Ga2O3
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
The acidic character of oxides of group 13 decreases down the group, because non-metallic character of elements decreases down the group and metallic character increases.
And we know that oxides of metals are basic in nature and oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature. So acidic character of oxides of group 13 decreases down the group.
For example boron (1st element of group 13) is non-metal, so its oxide is acidic.
Aluminum (2nd element of group 13) shows characteristics of both metal and non-metal, so its oxide shows amphoteric nature.
As we go down the group, indium and thalium (4th and 5th element of group 13) show metallic properties, so their oxides are basic.
One of the following p-block elements has unusually low melting point- a)Indium
- b)boron
- c)gallium
- d)aluminium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following p-block elements has unusually low melting point
a)
Indium
b)
boron
c)
gallium
d)
aluminium
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Argon
Argon is most abundant in composition of air percent by volume. It is in 0.934% in composition of air and is one of the major gas in the Earth's atmosphere.
XeF2 is isostructural with- a)SbCl3
- b)BaCl2
- c)TeF2
- d)ICl2–
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
XeF2 is isostructural with
a)
SbCl3
b)
BaCl2
c)
TeF2
d)
ICl2–
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option D
XeF2 is isostructural with ICl2−.
Both contain the same number of lone pairs and bond pairs on the central atom.
There are 3 lone pairs and 2 bond pairs.
This results in linear geometry.
Both contain the same number of lone pairs and bond pairs on the central atom.
There are 3 lone pairs and 2 bond pairs.
This results in linear geometry.
Inert pair effect of p-block elements is due to the- a)the most unstable valence number of p-block elements
- b)the most stable valence number of p-block elements
- c)the group oxidation state of p-block elements
- d)the oxidation state two unit less than the group oxidation state
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Inert pair effect of p-block elements is due to the
a)
the most unstable valence number of p-block elements
b)
the most stable valence number of p-block elements
c)
the group oxidation state of p-block elements
d)
the oxidation state two unit less than the group oxidation state

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Due to the presence of inner lying d and f electrons oxidation state which is 2 unit less than the group oxidation state become popular.
The elements of group 14 are slightly more electronegative than group 13 elements because of- a)small size
- b)their being liquids
- c)high melting point
- d)high boiling point
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The elements of group 14 are slightly more electronegative than group 13 elements because of
a)
small size
b)
their being liquids
c)
high melting point
d)
high boiling point

|
Pankaj Sengupta answered |
As we move along the period electronegativity increases due to increase in nuclear charge.
As we move from B to Al in the p-block elements the sum of the first three ionisation enthalpies- a)slightly decreases
- b)remains the same
- c)considerably decreases
- d)increases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
As we move from B to Al in the p-block elements the sum of the first three ionisation enthalpies
a)
slightly decreases
b)
remains the same
c)
considerably decreases
d)
increases
|
|
Om Desai answered |
On moving from B to Al size increases so sum of ionization energies also decreases.
Which of these is not a monomer for a high molecular mass silicone polymer? [NEET 2013]- a)Me2SiCl2
- b)Me3SiCl
- c)PhSiCl3
- d)MeSiCl3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is not a monomer for a high molecular mass silicone polymer? [NEET 2013]
a)
Me2SiCl2
b)
Me3SiCl
c)
PhSiCl3
d)
MeSiCl3

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
Since Me3SiCl contains only one Cl, therefore it can’t form high molecular mass silicon polymer. It can form only dimer.
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from- a)Zero to – 1 and zero to +3
- b)Zero to + 1 and zero to –3
- c)Zero to + 1 and zero to –5
- d)Zero to – 1 and zero to +5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from
a)
Zero to – 1 and zero to +3
b)
Zero to + 1 and zero to –3
c)
Zero to + 1 and zero to –5
d)
Zero to – 1 and zero to +5
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The correct answer is option D
The reaction of chlorine gas with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution is
3Cl2 + 6NaOH⟶NaClO3+ 5NaCl+3H2O
Oxidation number of Cl is 0 in Cl2, −1 in NaCl and +5 in NaClO3
So the oxidation number of chlorine changes from Zero to -1 and Zero to +5.
The reaction of chlorine gas with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution is
3Cl2 + 6NaOH⟶NaClO3+ 5NaCl+3H2O
Oxidation number of Cl is 0 in Cl2, −1 in NaCl and +5 in NaClO3
So the oxidation number of chlorine changes from Zero to -1 and Zero to +5.
Glass is a [1991]- a)Liquid
- b)Solid
- c)Supercooled liquid
- d)Transparent organic polymer
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glass is a [1991]
a)
Liquid
b)
Solid
c)
Supercooled liquid
d)
Transparent organic polymer

|
Yash Saha answered |
Glass is a super cooled liquid.
Which is incorrectly matched ?- a)CsBr3
 Cs+ + Br3_
Cs+ + Br3_ - b)I4O9
 I3+ + (IO3_)3
I3+ + (IO3_)3 - c)AgBrO3
 Ag+ + BrO3_
Ag+ + BrO3_ - d)I2O4
 IO2_ + IO2+
IO2_ + IO2+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is incorrectly matched ?
a)
CsBr3  Cs+ + Br3_
Cs+ + Br3_
b)
I4O9  I3+ + (IO3_)3
I3+ + (IO3_)3
c)
AgBrO3  Ag+ + BrO3_
Ag+ + BrO3_
d)
I2O4  IO2_ + IO2+
IO2_ + IO2+
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
It is strictly covalent does not shows cationic & anionic form.
The tendency of BF3, BCl3 and BBr3 to behave as Lewis acid decreases in the sequence:- a)BF3> BCl3> BBr3
- b)BCl3> BF3> BBr3
- c)BBr3> BF3> BCl3
- d)BBR3> BCl3> BF3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The tendency of BF3, BCl3 and BBr3 to behave as Lewis acid decreases in the sequence:
a)
BF3> BCl3> BBr3
b)
BCl3> BF3> BBr3
c)
BBr3> BF3> BCl3
d)
BBR3> BCl3> BF3
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
because in BF3 there is backbonding which decreases its acidity. And as we for from BF3 to BBr3 tendency of back bonding decreases so acidity increases,.
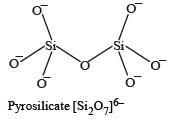
The basic structural unit of silicates is : [NEET 2013]- a)SiO44-
- b)SiO32-
- c)SiO24-
- d)SiO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The basic structural unit of silicates is : [NEET 2013]
a)
SiO44-
b)
SiO32-
c)
SiO24-
d)
SiO

|
Anand Jain answered |
SiO44– is basic structural unit of silicates.
Which of the following statements regarding ozone is not correct?
- a)Ozone is used as a germicide and disinfectant for the purification of air.
- b)The ozone molecule is angular in shape
- c)The oxygen-oxygen bond length in ozone is identical with that of molecular oxygen
- d)The ozone is response hybrid of two structures
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding ozone is not correct?
a)
Ozone is used as a germicide and disinfectant for the purification of air.
b)
The ozone molecule is angular in shape
c)
The oxygen-oxygen bond length in ozone is identical with that of molecular oxygen
d)
The ozone is response hybrid of two structures

|
Aryan Sen answered |
bond order of O-O bond in ozone is less than that in oxygen.
The element having the noble gas plus 14 f- electrons plus 10 d-electron cores- a)Aluminium
- b)Boron
- c)thallium
- d)Gallium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The element having the noble gas plus 14 f- electrons plus 10 d-electron cores
a)
Aluminium
b)
Boron
c)
thallium
d)
Gallium
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Tl have bole gas + 14 f +10 d electrons.
When oxalic acid reacts with conc. H2SO4, two gases produced are of neutral and acidic in nature respectively. Potassium hydroxide absorbs one of the two gases. The product formed during this absorption and the gas which gets absorbed are respectively- a)K2CO3 and CO2
- b)KHCO3 and CO2
- c)K2CO3 and CO
- d)KHCO3 and CO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When oxalic acid reacts with conc. H2SO4, two gases produced are of neutral and acidic in nature respectively. Potassium hydroxide absorbs one of the two gases. The product formed during this absorption and the gas which gets absorbed are respectively
a)
K2CO3 and CO2
b)
KHCO3 and CO2
c)
K2CO3 and CO
d)
KHCO3 and CO
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Which of the following structure is similar to graphite? [NEET 2013]- a)B
- b)B4C
- c)B2H6
- d)BN
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following structure is similar to graphite? [NEET 2013]
a)
B
b)
B4C
c)
B2H6
d)
BN

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
Boron nitride (BN) is known as inorganic graphite. The most stable form is hexagonal one. It has layered structure similar to graphite.

In which of the following compounds, nitrogen exhibits highest oxidation state?
- a)N3H
- b)NH2OH
- c)N2H4
- d)NH3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following compounds, nitrogen exhibits highest oxidation state?
a)
N3H
b)
NH2OH
c)
N2H4
d)
NH3
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
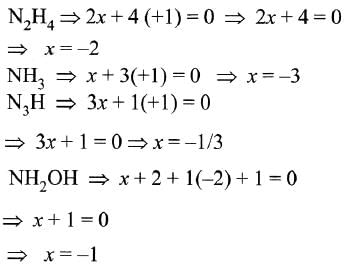
so clearly N3H has the highest oxidation state
Three reactions involving 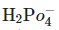 are given below
are given below
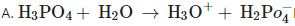 B.
B. 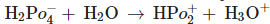 C.
C. 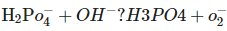 In which of the above does
In which of the above does 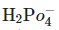 act as an acid?
act as an acid?
- a)C. only
- b)B. only
- c)A. only
- d)A. and B.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Three reactions involving 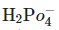 are given below
are given below
B. 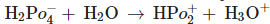
C. 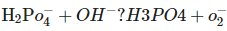
In which of the above does 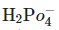 act as an acid?
act as an acid?
a)
C. only
b)
B. only
c)
A. only
d)
A. and B.

|
Jaideep Sengupta answered |
in B only 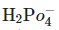 is losing its proton therefore act as acid.
is losing its proton therefore act as acid.
Which one of the following statements about the zeolites is false ? [2004]
- a)They are used as cation exchangers
- b)They have open structure which enables them to take up small molecules
- c)none of the SiO44- units are replaced by AlO45- and AlO69- ions in zeolites
- d)Zeolites are aluminosilicates having three dimensional network
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements about the zeolites is false ? [2004]
a)
They are used as cation exchangers
b)
They have open structure which enables them to take up small molecules
c)
none of the SiO44- units are replaced by AlO45- and AlO69- ions in zeolites
d)
Zeolites are aluminosilicates having three dimensional network

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Zeolite are microporous crystalline solid with well defined structure. They contain silicon, aluminium and oxygen in their framework and cations, water & other molecules within their pores. The general formula of zeolite is Mx/y[(AlO2)x(SiO2)y]. mH2O.
Among the following which is the strongest oxidizing agent?- a)Cl2
- b)Br2
- c)I2
- d)F2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following which is the strongest oxidizing agent?
a)
Cl2
b)
Br2
c)
I2
d)
F2

|
Atharva Pillai answered |
F2 is very strong oxidizing agent.
The non-metal oxides are:- a)acidic or neutral
- b)basic or neutral
- c)basic or acidic
- d)basic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The non-metal oxides are:
a)
acidic or neutral
b)
basic or neutral
c)
basic or acidic
d)
basic
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
nonmetallic oxides are either neutral or acidic. Example CO is neutral while CO2 is acidic.
The compounds formed by highly reactive non-metals with highly reactive metals are generally- a)slightly different in their ionisation enthalpies
- b)ionic
- c)slightly different in their electronegativities
- d)covalent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The compounds formed by highly reactive non-metals with highly reactive metals are generally
a)
slightly different in their ionisation enthalpies
b)
ionic
c)
slightly different in their electronegativities
d)
covalent

|
Sahana Ahuja answered |
Explanation:
When highly reactive non-metals react with highly reactive metals, the compounds formed are generally ionic in nature. This means that they are made up of positively charged metal ions and negatively charged non-metal ions.
1. Formation of Ionic Compounds:
When a highly reactive non-metal reacts with a highly reactive metal, the non-metal tends to gain electrons and become negatively charged, while the metal tends to lose electrons and become positively charged. This transfer of electrons results in the formation of ions, and these oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces, forming an ionic compound.
2. High Reactivity of Non-Metals and Metals:
Highly reactive non-metals have a strong tendency to gain electrons because their outermost energy level is almost empty, and they can achieve a stable electron configuration by gaining electrons. On the other hand, highly reactive metals have a strong tendency to lose electrons because their outermost energy level is almost full, and they can achieve a stable electron configuration by losing electrons.
3. Ionic Bonding:
The high reactivity of non-metals and metals makes it easier for them to undergo electron transfer, resulting in the formation of ions. The attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms an ionic bond. The ionization energy of metals is generally lower than that of non-metals, which facilitates the loss of electrons by metals. The electronegativity of non-metals is generally higher than that of metals, which promotes the gain of electrons by non-metals. These factors contribute to the formation of ionic compounds.
4. Covalent Bonding:
Covalent bonding occurs when non-metals react with non-metals, where they share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. In the case of highly reactive non-metals and highly reactive metals, the difference in reactivity and electron configuration leads to the formation of ionic compounds rather than covalent compounds. The high electronegativity difference and the strong tendency for electron transfer make the formation of covalent bonds less favorable in these combinations.
Therefore, the compounds formed by highly reactive non-metals with highly reactive metals are generally ionic in nature.
When highly reactive non-metals react with highly reactive metals, the compounds formed are generally ionic in nature. This means that they are made up of positively charged metal ions and negatively charged non-metal ions.
1. Formation of Ionic Compounds:
When a highly reactive non-metal reacts with a highly reactive metal, the non-metal tends to gain electrons and become negatively charged, while the metal tends to lose electrons and become positively charged. This transfer of electrons results in the formation of ions, and these oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces, forming an ionic compound.
2. High Reactivity of Non-Metals and Metals:
Highly reactive non-metals have a strong tendency to gain electrons because their outermost energy level is almost empty, and they can achieve a stable electron configuration by gaining electrons. On the other hand, highly reactive metals have a strong tendency to lose electrons because their outermost energy level is almost full, and they can achieve a stable electron configuration by losing electrons.
3. Ionic Bonding:
The high reactivity of non-metals and metals makes it easier for them to undergo electron transfer, resulting in the formation of ions. The attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms an ionic bond. The ionization energy of metals is generally lower than that of non-metals, which facilitates the loss of electrons by metals. The electronegativity of non-metals is generally higher than that of metals, which promotes the gain of electrons by non-metals. These factors contribute to the formation of ionic compounds.
4. Covalent Bonding:
Covalent bonding occurs when non-metals react with non-metals, where they share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. In the case of highly reactive non-metals and highly reactive metals, the difference in reactivity and electron configuration leads to the formation of ionic compounds rather than covalent compounds. The high electronegativity difference and the strong tendency for electron transfer make the formation of covalent bonds less favorable in these combinations.
Therefore, the compounds formed by highly reactive non-metals with highly reactive metals are generally ionic in nature.
Aluminium is extracted from alumina (Al2O3) by electrolysis of a molten mixture of : [2012]- a)Al2O3 + HF + NaAlF4
- b)Al2O3 + CaF2 + NaAlF4
- c)Al2O3 + Na3AlF6 + CaF2
- d)Al2O3 + KF + Na3AlF6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Aluminium is extracted from alumina (Al2O3) by electrolysis of a molten mixture of : [2012]
a)
Al2O3 + HF + NaAlF4
b)
Al2O3 + CaF2 + NaAlF4
c)
Al2O3 + Na3AlF6 + CaF2
d)
Al2O3 + KF + Na3AlF6

|
Sinjini Datta answered |
Extraction of Aluminium from Alumina (Al2O3)
Aluminium is an important metal that is widely used in various industries due to its low density, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance. It is extracted from its ore, alumina (Al2O3), through a process called electrolysis. The correct combination of molten mixture for the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis is given in option 'C', which consists of Al2O3, Na3AlF6, and CaF2.
Electrolysis of Alumina (Al2O3)
The extraction of aluminium from alumina involves the process of electrolysis. In this process, a molten mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 is used as an electrolyte. The following steps explain the extraction process in detail:
1. Formation of Cryolite (Na3AlF6):
- Cryolite is a mineral that is added to the mixture to lower the melting point of alumina and improve its conductivity.
- Na3AlF6 is formed by the reaction between alumina and sodium fluoride (NaF).
- 2 Al2O3 + 6 NaF → 2 Na3AlF6 + 3 O2
2. Electrolysis of Alumina (Al2O3):
- The mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 is heated to a high temperature to form a molten electrolyte.
- The mixture is then placed in an electrolytic cell, which consists of a carbon anode and a carbon cathode.
- The carbon anode is connected to the positive terminal of a power supply, while the carbon cathode is connected to the negative terminal.
- The molten mixture acts as the electrolyte, and alumina is dissolved in it.
- When an electric current is passed through the electrolyte, the following reactions occur:
- At the anode (oxidation): 2 O2- → O2 + 4 e-
- At the cathode (reduction): 4 Al3+ + 12 e- → 4 Al
- The oxygen ions (O2-) are attracted to the anode and combine to form oxygen gas (O2), which is released.
- The aluminium ions (Al3+) are attracted to the cathode and gain electrons to form aluminium metal (Al), which is deposited on the cathode.
Advantages of the Molten Mixture
The molten mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 has several advantages for the extraction of aluminium:
- Lower Melting Point: The addition of cryolite (Na3AlF6) lowers the melting point of alumina, reducing the amount of energy required for the process.
- Improved Conductivity: The presence of the molten mixture enhances the conductivity of the electrolyte, allowing for efficient electrolysis.
- Electrolyte Stability: The molten mixture remains stable at high temperatures, ensuring the continuous flow of current and the extraction of aluminium.
Conclusion
The correct combination of the molten mixture for the extraction of aluminium from alumina (Al2O3) is option 'C', which consists of Al2O3, Na3AlF6, and CaF
Aluminium is an important metal that is widely used in various industries due to its low density, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance. It is extracted from its ore, alumina (Al2O3), through a process called electrolysis. The correct combination of molten mixture for the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis is given in option 'C', which consists of Al2O3, Na3AlF6, and CaF2.
Electrolysis of Alumina (Al2O3)
The extraction of aluminium from alumina involves the process of electrolysis. In this process, a molten mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 is used as an electrolyte. The following steps explain the extraction process in detail:
1. Formation of Cryolite (Na3AlF6):
- Cryolite is a mineral that is added to the mixture to lower the melting point of alumina and improve its conductivity.
- Na3AlF6 is formed by the reaction between alumina and sodium fluoride (NaF).
- 2 Al2O3 + 6 NaF → 2 Na3AlF6 + 3 O2
2. Electrolysis of Alumina (Al2O3):
- The mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 is heated to a high temperature to form a molten electrolyte.
- The mixture is then placed in an electrolytic cell, which consists of a carbon anode and a carbon cathode.
- The carbon anode is connected to the positive terminal of a power supply, while the carbon cathode is connected to the negative terminal.
- The molten mixture acts as the electrolyte, and alumina is dissolved in it.
- When an electric current is passed through the electrolyte, the following reactions occur:
- At the anode (oxidation): 2 O2- → O2 + 4 e-
- At the cathode (reduction): 4 Al3+ + 12 e- → 4 Al
- The oxygen ions (O2-) are attracted to the anode and combine to form oxygen gas (O2), which is released.
- The aluminium ions (Al3+) are attracted to the cathode and gain electrons to form aluminium metal (Al), which is deposited on the cathode.
Advantages of the Molten Mixture
The molten mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 has several advantages for the extraction of aluminium:
- Lower Melting Point: The addition of cryolite (Na3AlF6) lowers the melting point of alumina, reducing the amount of energy required for the process.
- Improved Conductivity: The presence of the molten mixture enhances the conductivity of the electrolyte, allowing for efficient electrolysis.
- Electrolyte Stability: The molten mixture remains stable at high temperatures, ensuring the continuous flow of current and the extraction of aluminium.
Conclusion
The correct combination of the molten mixture for the extraction of aluminium from alumina (Al2O3) is option 'C', which consists of Al2O3, Na3AlF6, and CaF
Fluorine differs from rest of the halogens in some of its properties. This is due to
- a)its smaller size and high electronegativity
- b)lack of d-orbitals
- c)low bond dissociation energy
- d)Both A and B
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Fluorine differs from rest of the halogens in some of its properties. This is due to
a)
its smaller size and high electronegativity
b)
lack of d-orbitals
c)
low bond dissociation energy
d)
Both A and B

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Fluorine differs from rest of the elements of its family due to (i) its small size (ii) highest electronegativity, (iii) low bond dissociation energy and (iv) absence of d-orbitals in the valence shell.
Of the following compounds the most acidic is- a)Bi2O3
- b)P2O5
- c)Sb2O3
- d)As2O3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the following compounds the most acidic is
a)
Bi2O3
b)
P2O5
c)
Sb2O3
d)
As2O3
|
|
Muskaan Kumar answered |
Introduction:
In this question, we are asked to identify the most acidic compound among the given options. Acidity is a property of compounds that can donate a proton (H+ ion). The stronger the acid, the more easily it donates a proton. To determine the acidity of a compound, we need to consider the strength of the corresponding acid it forms when dissolved in water.
Explanation:
Among the given options, the most acidic compound is P2O5 (option B). Let's understand why.
1. Oxidation state:
The acidity of an oxide compound mainly depends on the oxidation state of the central atom. In this case, the central atom is phosphorus (P).
- In P2O5, the oxidation state of phosphorus is +5.
- In Bi2O3, the oxidation state of bismuth is +3.
- In Sb2O3, the oxidation state of antimony is +3.
- In As2O3, the oxidation state of arsenic is +3.
2. Acidic behavior of oxides:
In general, oxides with higher oxidation states tend to be more acidic. This is because higher oxidation states lead to greater electronegativity, resulting in stronger acidic behavior.
3. Acid formation:
When oxides dissolve in water, they form corresponding acids. The acidity of an oxide is determined by the strength of the acid it forms.
- P2O5 forms phosphoric acid (H3PO4), which is a strong acid.
- Bi2O3 forms bismuthic acid (HBiO3), which is a weak acid.
- Sb2O3 forms antimonious acid (HSbO2), which is a weak acid.
- As2O3 forms arsenious acid (H3AsO3), which is also a weak acid.
4. Conclusion:
Based on the above analysis, we can conclude that P2O5 (option B) is the most acidic compound among the given options. It has the highest oxidation state of +5 and forms phosphoric acid, which is a strong acid.
In this question, we are asked to identify the most acidic compound among the given options. Acidity is a property of compounds that can donate a proton (H+ ion). The stronger the acid, the more easily it donates a proton. To determine the acidity of a compound, we need to consider the strength of the corresponding acid it forms when dissolved in water.
Explanation:
Among the given options, the most acidic compound is P2O5 (option B). Let's understand why.
1. Oxidation state:
The acidity of an oxide compound mainly depends on the oxidation state of the central atom. In this case, the central atom is phosphorus (P).
- In P2O5, the oxidation state of phosphorus is +5.
- In Bi2O3, the oxidation state of bismuth is +3.
- In Sb2O3, the oxidation state of antimony is +3.
- In As2O3, the oxidation state of arsenic is +3.
2. Acidic behavior of oxides:
In general, oxides with higher oxidation states tend to be more acidic. This is because higher oxidation states lead to greater electronegativity, resulting in stronger acidic behavior.
3. Acid formation:
When oxides dissolve in water, they form corresponding acids. The acidity of an oxide is determined by the strength of the acid it forms.
- P2O5 forms phosphoric acid (H3PO4), which is a strong acid.
- Bi2O3 forms bismuthic acid (HBiO3), which is a weak acid.
- Sb2O3 forms antimonious acid (HSbO2), which is a weak acid.
- As2O3 forms arsenious acid (H3AsO3), which is also a weak acid.
4. Conclusion:
Based on the above analysis, we can conclude that P2O5 (option B) is the most acidic compound among the given options. It has the highest oxidation state of +5 and forms phosphoric acid, which is a strong acid.
Which of the following elements is extracted commercially by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its compound ? [1993]- a)Cl
- b)Br
- c)Al
- d)Na
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following elements is extracted commercially by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its compound ? [1993]
a)
Cl
b)
Br
c)
Al
d)
Na

|
Arindam Unni answered |
Electrolysis is a process that involves the decomposition of a compound through the use of an electric current. It is commonly used to extract metals from their compounds. In this case, we are looking for an element that is commercially extracted by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its compound.
The correct answer is option C, chlorine (Cl).
Explanation:
Electrolysis of an Aqueous Solution:
When an aqueous solution is electrolyzed, the compound in the solution is broken down into its constituent elements. The positive ions (cations) migrate towards the negative electrode (cathode), where reduction occurs, while the negative ions (anions) migrate towards the positive electrode (anode), where oxidation occurs.
Chlorine Extraction:
Chlorine is commercially extracted by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its compound, typically sodium chloride (NaCl), which is commonly known as table salt. During the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution, chlorine gas is released at the anode, while hydrogen gas is released at the cathode.
At the anode:
At the anode, chloride ions (Cl-) are oxidized to chlorine gas (Cl2). The half-reaction at the anode is:
2Cl- -> Cl2 + 2e-
At the cathode:
At the cathode, water molecules are reduced to hydrogen gas (H2) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The half-reaction at the cathode is:
2H2O + 2e- -> H2 + 2OH-
Overall Reaction:
The overall reaction during the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution can be represented as:
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) -> Cl2(g) + H2(g) + 2NaOH(aq)
Importance of Chlorine:
Chlorine is an important element in various industries. It is used for the production of PVC (polyvinyl chloride), which is widely used in the manufacturing of pipes, cables, and other plastic products. Chlorine is also used in the production of bleach, disinfectants, and various organic compounds.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, chlorine is commercially extracted by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its compound, such as sodium chloride. The process involves the oxidation of chloride ions at the anode, resulting in the release of chlorine gas, while hydrogen gas is released at the cathode. Chlorine is an important element used in different industries for various purposes.
The correct answer is option C, chlorine (Cl).
Explanation:
Electrolysis of an Aqueous Solution:
When an aqueous solution is electrolyzed, the compound in the solution is broken down into its constituent elements. The positive ions (cations) migrate towards the negative electrode (cathode), where reduction occurs, while the negative ions (anions) migrate towards the positive electrode (anode), where oxidation occurs.
Chlorine Extraction:
Chlorine is commercially extracted by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its compound, typically sodium chloride (NaCl), which is commonly known as table salt. During the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution, chlorine gas is released at the anode, while hydrogen gas is released at the cathode.
At the anode:
At the anode, chloride ions (Cl-) are oxidized to chlorine gas (Cl2). The half-reaction at the anode is:
2Cl- -> Cl2 + 2e-
At the cathode:
At the cathode, water molecules are reduced to hydrogen gas (H2) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The half-reaction at the cathode is:
2H2O + 2e- -> H2 + 2OH-
Overall Reaction:
The overall reaction during the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution can be represented as:
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) -> Cl2(g) + H2(g) + 2NaOH(aq)
Importance of Chlorine:
Chlorine is an important element in various industries. It is used for the production of PVC (polyvinyl chloride), which is widely used in the manufacturing of pipes, cables, and other plastic products. Chlorine is also used in the production of bleach, disinfectants, and various organic compounds.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, chlorine is commercially extracted by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its compound, such as sodium chloride. The process involves the oxidation of chloride ions at the anode, resulting in the release of chlorine gas, while hydrogen gas is released at the cathode. Chlorine is an important element used in different industries for various purposes.
Aqueous solution of Na2S2O3 on reaction with Cl2Cl2 gives- a)NaHSO4
- b)NaCl
- c)Na2S4O6
- d)NaOH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Aqueous solution of Na2S2O3 on reaction with Cl2Cl2 gives
a)
NaHSO4
b)
NaCl
c)
Na2S4O6
d)
NaOH

|
Anand Khanna answered |
Aqueous Na2S2O3 on reaction with Cl2Cl2 produces NaHSO4
Which of the following types of forces bind together the carbon atoms in diamond ? [1992]- a)Ionic
- b)Covalent
- c)Dipolar
- d)vander Waals.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following types of forces bind together the carbon atoms in diamond ? [1992]
a)
Ionic
b)
Covalent
c)
Dipolar
d)
vander Waals.

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
In diamond each carbon atom is sp 3 hybridized and thus forms covalent bonds with four other carbon atoms lying at the corners of a regular tetrahedron.
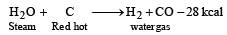
Water gas is produced by [1992]- a)Passing steam through a red hot coke bed
- b)Saturating hydrogen with moisture
- c)Mixing oxygen and hydrogen in the ratio of 1 : 2
- d)Heating a mixture of CO2 and CH4 in petroleum refineries.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Water gas is produced by [1992]
a)
Passing steam through a red hot coke bed
b)
Saturating hydrogen with moisture
c)
Mixing oxygen and hydrogen in the ratio of 1 : 2
d)
Heating a mixture of CO2 and CH4 in petroleum refineries.

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Water gas is made by blowing steam through the layer of incandescent coal.
A gas at low temperature does not react with the most of compounds. It is almost inert and is used to create intent atmosphere in bulbs. The combustion of this gas is exceptionally an endothermic reaction Based on the given information, we can conclude that the gas is.- a)Oxygen
- b)Nitrogen
- c)Carbon mono-oxide
- d)Hydrogen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A gas at low temperature does not react with the most of compounds. It is almost inert and is used to create intent atmosphere in bulbs. The combustion of this gas is exceptionally an endothermic reaction Based on the given information, we can conclude that the gas is.
a)
Oxygen
b)
Nitrogen
c)
Carbon mono-oxide
d)
Hydrogen

|
Aravind Nambiar answered |
N2 is higly stable due
A tetra atomic molecule (A) on reaction with nitrogen (I) oxide, produces two substances (B) and (C) ,(B) is a dehyderating agent in its monometric form while substance (C) is a diatomic gas which shows almost intert behavior. The substances (A) and (B) and (C) respectively will be- a)P4, P4O10, N2
- b)P4, N2O5, N2
- c)P4, P2O3, Ar
- d)P4, P2O3, H2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A tetra atomic molecule (A) on reaction with nitrogen (I) oxide, produces two substances (B) and (C) ,(B) is a dehyderating agent in its monometric form while substance (C) is a diatomic gas which shows almost intert behavior. The substances (A) and (B) and (C) respectively will be
a)
P4, P4O10, N2
b)
P4, N2O5, N2
c)
P4, P2O3, Ar
d)
P4, P2O3, H2
|
|
Puja Pillai answered |
Tetra atomic molecule (A) reacts with nitrogen (I) oxide to produce two substances (B) and (C). Substance (B) is a dehydrating agent in its monomeric form, while substance (C) is a diatomic gas that exhibits almost inert behavior. The substances (A), (B), and (C) can be determined as follows:
1. Substance A:
Since substance A is a tetra atomic molecule, it consists of four atoms. The molecular formula of substance A is P4 (phosphorus tetramer). Phosphorus exists as a tetra atomic molecule in its elemental form.
2. Substance B:
Substance B is a dehydrating agent in its monomeric form. This means that it removes water molecules. The dehydrating agent formed by the reaction of substance A with nitrogen (I) oxide is P4O10 (phosphorus pentoxide). Phosphorus pentoxide is a white, crystalline solid that readily absorbs moisture from the air and reacts with water to form phosphoric acid.
3. Substance C:
Substance C is a diatomic gas that exhibits almost inert behavior. Nitrogen (I) oxide is a diatomic gas with the formula N2O. It is commonly known as nitrous oxide or laughing gas. Nitrous oxide is a colorless, sweet-smelling gas that is used in anesthesia and as a propellant in aerosol cans.
Therefore, the substances (A), (B), and (C) produced in the reaction are:
- Substance A: P4 (phosphorus tetramer)
- Substance B: P4O10 (phosphorus pentoxide)
- Substance C: N2O (nitrous oxide)
1. Substance A:
Since substance A is a tetra atomic molecule, it consists of four atoms. The molecular formula of substance A is P4 (phosphorus tetramer). Phosphorus exists as a tetra atomic molecule in its elemental form.
2. Substance B:
Substance B is a dehydrating agent in its monomeric form. This means that it removes water molecules. The dehydrating agent formed by the reaction of substance A with nitrogen (I) oxide is P4O10 (phosphorus pentoxide). Phosphorus pentoxide is a white, crystalline solid that readily absorbs moisture from the air and reacts with water to form phosphoric acid.
3. Substance C:
Substance C is a diatomic gas that exhibits almost inert behavior. Nitrogen (I) oxide is a diatomic gas with the formula N2O. It is commonly known as nitrous oxide or laughing gas. Nitrous oxide is a colorless, sweet-smelling gas that is used in anesthesia and as a propellant in aerosol cans.
Therefore, the substances (A), (B), and (C) produced in the reaction are:
- Substance A: P4 (phosphorus tetramer)
- Substance B: P4O10 (phosphorus pentoxide)
- Substance C: N2O (nitrous oxide)
Chapter doubts & questions for The p - Block Elements - Inorganic Chemistry for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The p - Block Elements - Inorganic Chemistry for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup