All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Evolution for NEET Exam
An inter-breeding population of finches became separated geographically, forming two isolated groups. Each group then became subject to different selective pressures. One group was then introduced into the habitat of the other. Which one of the following would determine whether they now formed two distinct species?- a)They had been separated for more than three million years
- b)They failed to produce fertile F1 hybrids
- c)They showed marked differences in the shape of their beaks
- d)Their plumage had become markedly different
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An inter-breeding population of finches became separated geographically, forming two isolated groups. Each group then became subject to different selective pressures. One group was then introduced into the habitat of the other. Which one of the following would determine whether they now formed two distinct species?
a)
They had been separated for more than three million years
b)
They failed to produce fertile F1 hybrids
c)
They showed marked differences in the shape of their beaks
d)
Their plumage had become markedly different
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Once inter-breeding population of finches, now have failed to produce fertile F1 hybrids, this means they have now formed two distinct species.
What is correct arrangement of periods of palaeozoic era in ascending order in geological time scale?- a)Cambrian → Devonian → Ordovician → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
- b)Cambrian → Ordovician → Silurian → Devonian → Carboniferous → Permian
- c)Cambrian → Ordovician Devonian → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
- d)Silurian → Devonian → Cambrian → Ordovician Permian → Carboniferous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is correct arrangement of periods of palaeozoic era in ascending order in geological time scale?
a)
Cambrian → Devonian → Ordovician → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
b)
Cambrian → Ordovician → Silurian → Devonian → Carboniferous → Permian
c)
Cambrian → Ordovician Devonian → Silurian → Carboniferous → Permian
d)
Silurian → Devonian → Cambrian → Ordovician Permian → Carboniferous
|
|
Dhruv Jain answered |
B) Ordovician
c) Silurian
d) Devonian
e) Carboniferous
f) Permian
c) Silurian
d) Devonian
e) Carboniferous
f) Permian
Which of the following evidences does not favour the Lamarckian concept of inheritance of acquired characters?- a)Lack of pigment in cave-dwelling animals
- b)Melanisation in peppered moth
- c)Absence of limbs in snakes
- d)Presence of webbed toes in aquatic birds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following evidences does not favour the Lamarckian concept of inheritance of acquired characters?
a)
Lack of pigment in cave-dwelling animals
b)
Melanisation in peppered moth
c)
Absence of limbs in snakes
d)
Presence of webbed toes in aquatic birds
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
According to Lamarckism (proposed by Lamarck), whatever characters an individual acquires in its life time due to internal vital force, effect of environment, new needs, use and disuse of organs, they are inherited to next generations. This process continues and after several generations, the variations are accumulated upto such an extent that they give rise to new species. Melanisation in peppered moth favours Darwin's theory of natural selection.
In the developmental history of mammalian heart, it is observed that it passes through a two chambered fish like heart, three chambered frog like heart and finally four chambered stage
To which hypothesis can this above cited statement be approximated?- a)Lamarck's principle
- b)Mendelian principle
- c)Biogenetic law
- d)Hardy Weinberg law
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the developmental history of mammalian heart, it is observed that it passes through a two chambered fish like heart, three chambered frog like heart and finally four chambered stage
To which hypothesis can this above cited statement be approximated?
To which hypothesis can this above cited statement be approximated?
a)
Lamarck's principle
b)
Mendelian principle
c)
Biogenetic law
d)
Hardy Weinberg law
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Biogenetic law or Recapitulation theory was given by Ernst Haeckel in 1866. It states that 'ontogeny repeats phylogeny'. Ontogeny is the life history of an organism while phylogeny is the evolutionary history of the race of that organism. This means that an organism repeats its ancestral history during its development.
Read the following statements carefully and select the correct ones
(i) Alfred Wallace, a naturalist who worked in Malay Archipelago had also come to similar conclusions as Darwin around the same time
(ii) August Weismann by careful experimentation demonstrated that life comes only from pre-existing life.
(iii) The organs which have the same fundamental structure but are different in functions are called homologous organs
(iv) Rate of appearance' of new. form is inversely proportional to life span of organism- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and select the correct ones
(i) Alfred Wallace, a naturalist who worked in Malay Archipelago had also come to similar conclusions as Darwin around the same time
(ii) August Weismann by careful experimentation demonstrated that life comes only from pre-existing life.
(iii) The organs which have the same fundamental structure but are different in functions are called homologous organs
(iv) Rate of appearance' of new. form is inversely proportional to life span of organism
(i) Alfred Wallace, a naturalist who worked in Malay Archipelago had also come to similar conclusions as Darwin around the same time
(ii) August Weismann by careful experimentation demonstrated that life comes only from pre-existing life.
(iii) The organs which have the same fundamental structure but are different in functions are called homologous organs
(iv) Rate of appearance' of new. form is inversely proportional to life span of organism
a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Louis Pasteur by careful experimentation demonstrated that life comes only from pre-existing life. Rate of appearance of new forms is directly proportional to life span of organism. Microbes that divide fast evolve fast. For same process to occur in fish or fowl will take million of years.
Which one of the following phenomena supports Darwin's concept of natural selection in organic evolution?- a)Development of transgenic animals
- b)Production of 'Dolly', the sheep by cloning
- c)Prevalence of pesticide resistant insects
- d)Development of organs from 'stem cells' for organ transplantation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following phenomena supports Darwin's concept of natural selection in organic evolution?
a)
Development of transgenic animals
b)
Production of 'Dolly', the sheep by cloning
c)
Prevalence of pesticide resistant insects
d)
Development of organs from 'stem cells' for organ transplantation
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Prevalence of pesticide resistant insects supports natural selection theory, e.g., DDT was thought to be an effective insecticide against household pests (like mosquitoes, houseflies, body lice, etc.) in 1945. But, within 2 to 3 years of its introduction, new DDT resistant mosquitoes appeared in the population. These mutant strains, soon became well established in the population by natural selection and thus replaced the original DDT - sensitive mosquitoes.
Darwinism explains all the following except- a)off spring with better traits that over come competition are best suited for the environment
- b)variations may or may not be inherited from parents to offspring through genes
- c)within each species, there are variations
- d)organisms tend to produce more number of offspring than can survive
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Darwinism explains all the following except
a)
off spring with better traits that over come competition are best suited for the environment
b)
variations may or may not be inherited from parents to offspring through genes
c)
within each species, there are variations
d)
organisms tend to produce more number of offspring than can survive
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The main drawback of Darwinism is lack of knowledge of heredity. Darwin's theory could not explain the inheritance of variations from parents to off springs through genes.
Which one of the following describes correctly the homologous structures?- a)Organs with anatomical similarities, but performing different functions
- b)Organs with anatomical dissimilarities, but performing same function
- c)Organs that have no function now, but had important function in ancestors
- d)Organs appearing only in embryonic stage and disappearing later in the adult
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following describes correctly the homologous structures?
a)
Organs with anatomical similarities, but performing different functions
b)
Organs with anatomical dissimilarities, but performing same function
c)
Organs that have no function now, but had important function in ancestors
d)
Organs appearing only in embryonic stage and disappearing later in the adult
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Homologous organs have a common origin and are built on the same basic pattern but perform different functions and are modified accordingly.
Jurassic period belongs to the ______ era.- a)Cenozoic
- b)Mesozoic
- c)Palaeozoic
- d)Proterozoic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Jurassic period belongs to the ______ era.
a)
Cenozoic
b)
Mesozoic
c)
Palaeozoic
d)
Proterozoic
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The Jurassic Period was the second section of the Mesozoic Era. It happened from 199.6 to 145.5 million years back, after the Triassic Period and going before the Cretaceous Period.
Refer the given statements and select the correct one
(i) Fossils are remains of hard parts of life forms in Rocks
(ii) A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers indicates the geological period in which they live.
(iii) Radio isotopen are often used to determine the age of the fossils
(iv) Study of fossils is called paleontology- a)(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(i), (iii) and (iv)
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer the given statements and select the correct one
(i) Fossils are remains of hard parts of life forms in Rocks
(ii) A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers indicates the geological period in which they live.
(iii) Radio isotopen are often used to determine the age of the fossils
(iv) Study of fossils is called paleontology
(i) Fossils are remains of hard parts of life forms in Rocks
(ii) A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers indicates the geological period in which they live.
(iii) Radio isotopen are often used to determine the age of the fossils
(iv) Study of fossils is called paleontology
a)
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(i), (iii) and (iv)
d)
None of these
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The fossils can be defined as remains of impressions of the hard parts of the past life-forms in the strata of the earth. Fossils provide one of the most acceptable evidences in support of evolution, because we can study the evolutionary past of individuals in the form of their fossils. The study of fossils is known as paleontology. The evidence of evolution based on the knowledge of fossils is called paleontological evidence. Living organisms living in various ages and entombed in various starta of rocks provide concrete clues to the variety of life that existed in the past.
Age of the fossils can be determined by three methods: (i) Radioactive clock method (II) Radioactive carbon method and (iii) Potassium Organ method.
Age of the fossils can be determined by three methods: (i) Radioactive clock method (II) Radioactive carbon method and (iii) Potassium Organ method.
Given below are four statements (i) - (iv) regarding geological time scale. Read them carefully.
(i) Palaeozoic era is the era of ancient life
(ii) Ordovician period is the age of vertebrates
(iii) Carboniferous period is the age of reptiles
(iv) Proterozoic era is the era of early life
Which of the above two statements are incorrect?- a)(i) and (iv)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are four statements (i) - (iv) regarding geological time scale. Read them carefully.
(i) Palaeozoic era is the era of ancient life
(ii) Ordovician period is the age of vertebrates
(iii) Carboniferous period is the age of reptiles
(iv) Proterozoic era is the era of early life
Which of the above two statements are incorrect?
(i) Palaeozoic era is the era of ancient life
(ii) Ordovician period is the age of vertebrates
(iii) Carboniferous period is the age of reptiles
(iv) Proterozoic era is the era of early life
Which of the above two statements are incorrect?
a)
(i) and (iv)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iii)
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Ordovician period existed about 500 million years ago and is the age of invertebrates. Carboniferous period that existed 350 million years ago is the age of amphibians.
Which of the following factors contribute to changes in gene and allele frequencies, leading to speciation?
Gene migration or gene flow
Genetic drift
Mutation
Genetic recombination
Natural selection- a)1, 2, 3, and 5 are correct
- b)1, 3, and 4 are correct
- c)2, 4, and 5 are correct
- d)1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 are correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Gene migration or gene flow
Genetic drift
Mutation
Genetic recombination
Natural selection
a)
1, 2, 3, and 5 are correct
b)
1, 3, and 4 are correct
c)
2, 4, and 5 are correct
d)
1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 are correct

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Gene migration or gene flow (1) involves the movement of genes between populations, affecting gene frequencies.
Genetic drift (2) refers to random changes in gene frequencies due to chance events, especially in small populations.
Mutation (3) introduces new genetic variations that can alter gene frequencies.
Genetic recombination (4) during gametogenesis creates new combinations of alleles, influencing genetic diversity.
Natural selection (5) acts on heritable traits, enhancing reproductive success and influencing the frequency of advantageous alleles in future generations.
All these factors contribute to changes in allele frequencies and can lead to speciation over time.
Genetic drift (2) refers to random changes in gene frequencies due to chance events, especially in small populations.
Mutation (3) introduces new genetic variations that can alter gene frequencies.
Genetic recombination (4) during gametogenesis creates new combinations of alleles, influencing genetic diversity.
Natural selection (5) acts on heritable traits, enhancing reproductive success and influencing the frequency of advantageous alleles in future generations.
All these factors contribute to changes in allele frequencies and can lead to speciation over time.
Which of the following is true?- a)Wings of birds and insects are homologous organs.
- b)Human hands and wings of birds are analogous organs.
- c)Human hands and wings of bats are analogous organs.
- d)Flipper of seal and wings of birds are homologous organs.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true?
a)
Wings of birds and insects are homologous organs.
b)
Human hands and wings of birds are analogous organs.
c)
Human hands and wings of bats are analogous organs.
d)
Flipper of seal and wings of birds are homologous organs.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Flipper of seal and wing of birds are modified forelimbs, thus, have same fundamental structure but have different functions. Flippers are meant for swimming and wings are meant for flying. Therefore, these organs are homologous oroans.
Industrial melanism is an example of -- a)Mutation
- b)Natural selection
- c)Neo Darwinism
- d)Neo Lamarckism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Industrial melanism is an example of -
a)
Mutation
b)
Natural selection
c)
Neo Darwinism
d)
Neo Lamarckism

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Natural selection is the most widely accepted theory concerning the principal causal mechanism of evolutionary change profounded by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace. It results from the differential reproduction (some members of a population produce abundant offspring, some only a few and still others none), one phenotype as compared with other phenotypes in the same population. This determines the relative share of different genotypes which individuals possess and propagate in a population. Industrial melanism supports evolution by natural selection. It is an adaptation where the moths living in the industrial areas developed melanin pigments to match their bodies to the tree trunks.
Read the given statements (i) - (iv) regarding evolution and select the incorrect ones
(i) The oceanic water rich in mixture of organic compounds was termed by J.B.S. Haldane (1920) as 'hot dilute soap of organic substances'.
(ii) The term coacervate was given by Syndey Fox.
(iii) First cellular form of life appeared approximately 2000 mya on earth.
(iv) The first geological time scale was developed by Georges Cuvier.
- a)(ii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements (i) - (iv) regarding evolution and select the incorrect ones
(i) The oceanic water rich in mixture of organic compounds was termed by J.B.S. Haldane (1920) as 'hot dilute soap of organic substances'.
(ii) The term coacervate was given by Syndey Fox.
(iii) First cellular form of life appeared approximately 2000 mya on earth.
(iv) The first geological time scale was developed by Georges Cuvier.
(i) The oceanic water rich in mixture of organic compounds was termed by J.B.S. Haldane (1920) as 'hot dilute soap of organic substances'.
(ii) The term coacervate was given by Syndey Fox.
(iii) First cellular form of life appeared approximately 2000 mya on earth.
(iv) The first geological time scale was developed by Georges Cuvier.
a)
(ii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Correct answer is A.
What was the result of S.L. Miller's 1953 experiment?- a)Proved the theory of panspermia
- b)Formation of amino acids under simulated early Earth conditions
- c)Discovery of DNA
- d)Disproved the Big Bang theory
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Proved the theory of panspermia
b)
Formation of amino acids under simulated early Earth conditions
c)
Discovery of DNA
d)
Disproved the Big Bang theory

|
Stepway Academy answered |
In 1953, S.L. Miller conducted an experiment where he created conditions similar to early Earth with a mixture of gases and electrical discharges. This resulted in the formation of amino acids, supporting the idea of chemical evolution as a precursor to the origin of life.
Topic in NCERT: Origin of life
Line in NCERT: "he created electric discharge in a closed flask containing ch4, h2, nh3 and water vapour at 800°c. he observed formation of amino acids."
The following are some major events in the early history of life
P. First heterotrophic prokaryotes
Q. First genes
R. First eukaryotes
S. First autotrophic prokaryotes
T. First animals
Which option below places these events in the correct order?
- a)PQSRT
- b)QSPTR
- c)QPSRT
- d)QSPRT
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The following are some major events in the early history of life
P. First heterotrophic prokaryotes
Q. First genes
R. First eukaryotes
S. First autotrophic prokaryotes
T. First animals
Which option below places these events in the correct order?
P. First heterotrophic prokaryotes
Q. First genes
R. First eukaryotes
S. First autotrophic prokaryotes
T. First animals
Which option below places these events in the correct order?
a)
PQSRT
b)
QSPTR
c)
QPSRT
d)
QSPRT
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Organisms have evolved from simpler forms to complex form. Hence the order of the events are genes first, then heterotrophic prokaryotes, then autotrophic prokaryotes, then eukaryotes and then animals.
Which of the following are the two key concepts of Darwinian theory of evolution?- a)Genetic drift and mutation
- b)Adaptive radiation and homology
- c)Mutation and natural selection
- d)Branching descent and natural selection
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are the two key concepts of Darwinian theory of evolution?
a)
Genetic drift and mutation
b)
Adaptive radiation and homology
c)
Mutation and natural selection
d)
Branching descent and natural selection
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
According to Darwin's theory of evolution, nature selects the fittest. Fitness is based on characteristics which are inherited. Therefore, there must be a genetic basis for getting selected and to evolve. Some organisms are better adapted to survive in an otherwise hostile environment. Adaptative ability is inherited. Fitness is the end result of the ability to adapt and get selected by nature. Therefore, branching descent (inheritance) and natural selection are the two key concepts of Darwin's theory of evolution.
Industrial melanism as oberved in peppered moth proves that - a)The melanic form of the moth has no selective advantage over lighter form in industrial area
- b)The lighter-form the moth has no selective advantage either in polluted industrial area or non-polluted area
- c)Melanism is a pollution-generated feature
- d)The true black melanic froms escaped unoticed so they managed to survive resulting in more population of black moths.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Industrial melanism as oberved in peppered moth proves that
a)
The melanic form of the moth has no selective advantage over lighter form in industrial area
b)
The lighter-form the moth has no selective advantage either in polluted industrial area or non-polluted area
c)
Melanism is a pollution-generated feature
d)
The true black melanic froms escaped unoticed so they managed to survive resulting in more population of black moths.
|
|
Sonal Chakraborty answered |
Explanation:
Industrial Melanism in Peppered Moths:
- Industrial melanism in peppered moths refers to the phenomenon where the population of moths shifted from predominantly light-colored to predominantly dark-colored in industrial areas during the Industrial Revolution.
Survival Advantage of Melanic Forms:
- The true black melanic forms of the peppered moths were able to blend into the polluted environment better than the lighter forms. This provided them with a survival advantage as they were able to avoid predators more effectively.
- As a result, the black melanic moths were able to survive and reproduce more successfully in the industrial areas, leading to an increase in the population of black moths.
Selective Advantage of Melanic Forms:
- The increase in the population of black moths in industrial areas demonstrates that the melanic form had a selective advantage over the lighter form in polluted environments.
- This selective advantage is a result of natural selection, where individuals with traits that provide them with a better chance of survival and reproduction in their environment are more likely to pass on their genes to the next generation.
Conclusion:
- Therefore, the industrial melanism observed in peppered moths supports the idea that the true black melanic forms had a survival advantage in polluted industrial areas, leading to an increase in their population over time.
Similarities in organisms with different genotypes indicate:- a) Microevolution
- b) Macroevolution
- c) Convergent evolution
- d) Divergent evolution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Similarities in organisms with different genotypes indicate:
a)
Microevolution
b)
Macroevolution
c)
Convergent evolution
d)
Divergent evolution

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Hence, analogous structures are a result of convergent evolution - different structures evolving for the same function and hence having similarity
Which one of the following sequences was proposed by Darwin and Wallace for organic evolution?- a)Overproduction, variations, constancy of population size, natural selection
- b)Variations, constancy of population size, over production, natural selection
- c)Overproduction, constancy of population size, variations, natural selection
- d)Variations, natural selection, overproduction, constancy of population size
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following sequences was proposed by Darwin and Wallace for organic evolution?
a)
Overproduction, variations, constancy of population size, natural selection
b)
Variations, constancy of population size, over production, natural selection
c)
Overproduction, constancy of population size, variations, natural selection
d)
Variations, natural selection, overproduction, constancy of population size
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Though living organisms tend to multiply geometrically, the number of individuals of a species tend to remain constant over a long period of time. Out of heterogeneous population (due to the variation) best adapted individuals are selected by nature.
Single step large mutation leading to speciation is also called- a)founder effect
- b)saltation
- c)branching descent
- d)natural selection
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Single step large mutation leading to speciation is also called
a)
founder effect
b)
saltation
c)
branching descent
d)
natural selection
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Hugo de Vries believed that mutation causes evolution and not the minor heritable variations which were mentioned by Darwin. According to Darwin, evolution was gradual while de Vries believed mutations appear suddenly and hence called it saltation (single step large mutation)
Read the following statements and choose the correct option.
(i) Increase in melanised moths after industrialisation in Great Britain is a proof for Natural Selection
(ii) When more individuals of a population acquire a mean character value, it is called disruption
(iii) Changes in allelic frequency in a population will lead to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
(iv) Genetic drift changes the existing gene or allelic frequency in future generations- a)(ii) alone is correct
- b)(iv) alone is correct
- c)both (i) and (iv) are eorrect
- d)both (i) and (iii) are correct
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and choose the correct option.
(i) Increase in melanised moths after industrialisation in Great Britain is a proof for Natural Selection
(ii) When more individuals of a population acquire a mean character value, it is called disruption
(iii) Changes in allelic frequency in a population will lead to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
(iv) Genetic drift changes the existing gene or allelic frequency in future generations
(i) Increase in melanised moths after industrialisation in Great Britain is a proof for Natural Selection
(ii) When more individuals of a population acquire a mean character value, it is called disruption
(iii) Changes in allelic frequency in a population will lead to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
(iv) Genetic drift changes the existing gene or allelic frequency in future generations
a)
(ii) alone is correct
b)
(iv) alone is correct
c)
both (i) and (iv) are eorrect
d)
both (i) and (iii) are correct
|
|
Niharika Banerjee answered |
Melanised moths and natural selection:
The statement (i) is correct. The increase in melanised moths after industrialisation in Great Britain is indeed a proof for natural selection. Before industrialisation, the majority of moths in Britain were light-colored (non-melanised) because they blended well with the lichen-covered trees. However, with the onset of industrial pollution, the lichens died out, and the trees became darkened with soot. This led to an increase in the number of melanised (dark-colored) moths as they were better camouflaged against the new background. This change in the moth population over time is an example of natural selection, where individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Mean character value and disruption:
The statement (ii) is incorrect. The term "disruption" refers to a type of natural selection where individuals with extreme or divergent traits have higher fitness than those with intermediate traits. This can lead to the splitting of a population into two distinct groups or the formation of multiple phenotypic clusters. It does not involve the acquisition of a mean character value by more individuals.
Allelic frequency and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium:
The statement (iii) is incorrect. Changes in allelic frequency in a population do not necessarily lead to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium describes a theoretical population in which the allelic frequencies remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary forces like mutation, migration, selection, and genetic drift. Any change in allelic frequency indicates that the population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Genetic drift and gene frequency:
The statement (iv) is correct. Genetic drift refers to the random fluctuations in gene frequencies within a population due to chance events, particularly in small populations. These chance events can lead to the loss or fixation of certain alleles over time, resulting in changes in the existing gene or allelic frequencies in future generations. Genetic drift is one of the mechanisms of evolution and can have significant effects on the genetic diversity of populations.
Therefore, the correct option is (c) both (i) and (iv) are correct.
The statement (i) is correct. The increase in melanised moths after industrialisation in Great Britain is indeed a proof for natural selection. Before industrialisation, the majority of moths in Britain were light-colored (non-melanised) because they blended well with the lichen-covered trees. However, with the onset of industrial pollution, the lichens died out, and the trees became darkened with soot. This led to an increase in the number of melanised (dark-colored) moths as they were better camouflaged against the new background. This change in the moth population over time is an example of natural selection, where individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Mean character value and disruption:
The statement (ii) is incorrect. The term "disruption" refers to a type of natural selection where individuals with extreme or divergent traits have higher fitness than those with intermediate traits. This can lead to the splitting of a population into two distinct groups or the formation of multiple phenotypic clusters. It does not involve the acquisition of a mean character value by more individuals.
Allelic frequency and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium:
The statement (iii) is incorrect. Changes in allelic frequency in a population do not necessarily lead to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium describes a theoretical population in which the allelic frequencies remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary forces like mutation, migration, selection, and genetic drift. Any change in allelic frequency indicates that the population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Genetic drift and gene frequency:
The statement (iv) is correct. Genetic drift refers to the random fluctuations in gene frequencies within a population due to chance events, particularly in small populations. These chance events can lead to the loss or fixation of certain alleles over time, resulting in changes in the existing gene or allelic frequencies in future generations. Genetic drift is one of the mechanisms of evolution and can have significant effects on the genetic diversity of populations.
Therefore, the correct option is (c) both (i) and (iv) are correct.
Who proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing nonliving organic molecules?- a)SL Miller
- b)Oparin and Haldane
- c)Charles Darwin
- d)Alfred Wallace
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing nonliving organic molecules?
a)
SL Miller
b)
Oparin and Haldane
c)
Charles Darwin
d)
Alfred Wallace
|
|
Jaspreet answered |
This theory was given by A. L.Oparin and J.B.S. haldane !!!
The extinct human ancestor, who ate only fruits and hunted with stone weapons was- a)Ramapithecus
- b)Australopithecus
- c)Dryopithecus
- d)Homo erectus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The extinct human ancestor, who ate only fruits and hunted with stone weapons was
a)
Ramapithecus
b)
Australopithecus
c)
Dryopithecus
d)
Homo erectus
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Australopithecus probably lived in East African grasslands about 2 million years ago. They hunted with stone weapons but essentially ate fruit. They were about 1.5m high and their brain capacity was about 500c.c. They had bipedal locomotion and erect posture.
A population will not exist in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium if- a)there are no mutations
- b)individuals mate selectively
- c)the population is large
- d)there is no migration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A population will not exist in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium if
a)
there are no mutations
b)
individuals mate selectively
c)
the population is large
d)
there is no migration

|
Lead Academy answered |
The theory of Hardy- Weinberg equilibrium states that in the absence of disturbance on the level of genetic structure, a population’s existance will not continue. Thus mating should be in a random way.
In evolution, the studies can be made at molecular level. For example, the proteins present in the blood of man and ape are similar. The base sequence in nucleic acids and amino acids sequence in proteins of related organism is alike. These are the examples which are specifically referred to in- a)convergent evolution
- b)molecular analogy
- c)molecular homology
- d)homoplastic appearance
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In evolution, the studies can be made at molecular level. For example, the proteins present in the blood of man and ape are similar. The base sequence in nucleic acids and amino acids sequence in proteins of related organism is alike. These are the examples which are specifically referred to in
a)
convergent evolution
b)
molecular analogy
c)
molecular homology
d)
homoplastic appearance
|
|
Siddharth Iyer answered |
The Concept of Molecular Homology
Molecular homology refers to the similarities in molecular structures, such as nucleic acids and proteins, that indicate a common evolutionary ancestor. This concept is fundamental in understanding evolutionary relationships among species.
Understanding Molecular Homology
- Shared Genetic Material:
- Organisms that share a common ancestor will often have similar DNA sequences. For example, humans and apes exhibit significant similarities in their DNA, which can be traced back to a shared evolutionary lineage.
- Protein Similarities:
- The amino acid sequences of proteins in related organisms also show remarkable similarities. This is evident in blood proteins, where humans and apes have closely related structures, reflecting their evolutionary connection.
Importance of Molecular Homology
- Evolutionary Relationships:
- Molecular homology provides evidence for the evolutionary relationships between species. The closer the genetic similarity, the more likely the organisms are related through common ancestry.
- Phylogenetic Analysis:
- Scientists utilize molecular homology in constructing phylogenetic trees, which visually represent the evolutionary pathways and connections among different species.
Distinction from Other Concepts
- Convergent Evolution:
- Unlike molecular homology, convergent evolution refers to unrelated species developing similar traits due to similar environmental pressures, not shared ancestry.
- Molecular Analogy and Homoplastic Appearance:
- These terms often refer to similar features arising independently in different species, rather than from a common ancestor, distinguishing them from molecular homology.
In summary, molecular homology plays a crucial role in the study of evolution, providing insights into the genetic and protein similarities that highlight the connections among various organisms.
Molecular homology refers to the similarities in molecular structures, such as nucleic acids and proteins, that indicate a common evolutionary ancestor. This concept is fundamental in understanding evolutionary relationships among species.
Understanding Molecular Homology
- Shared Genetic Material:
- Organisms that share a common ancestor will often have similar DNA sequences. For example, humans and apes exhibit significant similarities in their DNA, which can be traced back to a shared evolutionary lineage.
- Protein Similarities:
- The amino acid sequences of proteins in related organisms also show remarkable similarities. This is evident in blood proteins, where humans and apes have closely related structures, reflecting their evolutionary connection.
Importance of Molecular Homology
- Evolutionary Relationships:
- Molecular homology provides evidence for the evolutionary relationships between species. The closer the genetic similarity, the more likely the organisms are related through common ancestry.
- Phylogenetic Analysis:
- Scientists utilize molecular homology in constructing phylogenetic trees, which visually represent the evolutionary pathways and connections among different species.
Distinction from Other Concepts
- Convergent Evolution:
- Unlike molecular homology, convergent evolution refers to unrelated species developing similar traits due to similar environmental pressures, not shared ancestry.
- Molecular Analogy and Homoplastic Appearance:
- These terms often refer to similar features arising independently in different species, rather than from a common ancestor, distinguishing them from molecular homology.
In summary, molecular homology plays a crucial role in the study of evolution, providing insights into the genetic and protein similarities that highlight the connections among various organisms.
Which of the following statements about Darwin's theory of evolution is/are correct?
1. Evolution by natural selection started when cellular life forms with differences in metabolic capability originated on Earth.
2. The rate of appearance of new species is faster in organisms with longer life spans.
3. Fitness is determined by inherited characteristics and is the result of the ability to adapt and get selected by nature.
4. Lamarck believed that evolution occurred through the use and disuse of organs, such as the elongation of giraffes' necks.- a)1, 2, and 3 are correct
- b)1, 3, and 4 are correct
- c)2 and 4 are correct
- d)1, 3, and 4 are correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about Darwin's theory of evolution is/are correct?
1. Evolution by natural selection started when cellular life forms with differences in metabolic capability originated on Earth.
2. The rate of appearance of new species is faster in organisms with longer life spans.
3. Fitness is determined by inherited characteristics and is the result of the ability to adapt and get selected by nature.
4. Lamarck believed that evolution occurred through the use and disuse of organs, such as the elongation of giraffes' necks.
1. Evolution by natural selection started when cellular life forms with differences in metabolic capability originated on Earth.
2. The rate of appearance of new species is faster in organisms with longer life spans.
3. Fitness is determined by inherited characteristics and is the result of the ability to adapt and get selected by nature.
4. Lamarck believed that evolution occurred through the use and disuse of organs, such as the elongation of giraffes' necks.
a)
1, 2, and 3 are correct
b)
1, 3, and 4 are correct
c)
2 and 4 are correct
d)
1, 3, and 4 are correct

|
Bs Academy answered |
Statement 1 is correct: Evolution by natural selection began with differences in metabolic capabilities of early cellular life.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The rate of appearance of new species is slower in organisms with longer life spans, not faster.
Statement 3 is correct: Fitness is based on inherited characteristics that allow an organism to adapt and be selected by nature.
Statement 4 is correct: Lamarck believed evolution occurred through the use and disuse of organs, such as giraffes elongating their necks.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The rate of appearance of new species is slower in organisms with longer life spans, not faster.
Statement 3 is correct: Fitness is based on inherited characteristics that allow an organism to adapt and be selected by nature.
Statement 4 is correct: Lamarck believed evolution occurred through the use and disuse of organs, such as giraffes elongating their necks.
The factors involved in the formation of new species are- a)isolation and competition
- b)gene flow and competition
- c)competition and mutation
- d)isolation and variation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The factors involved in the formation of new species are
a)
isolation and competition
b)
gene flow and competition
c)
competition and mutation
d)
isolation and variation
|
|
Swara Dey answered |
Isolation and variation are the factors involved in the formation of new species. Isolation refers to the separation of populations, while variation refers to the genetic differences that arise within populations. Both of these factors play a crucial role in driving the formation of new species.
Isolation:
- Isolation can occur in several ways, such as geographical barriers (e.g., mountains, rivers, oceans) or reproductive barriers (e.g., differences in mating behaviors, reproductive anatomy).
- When populations become isolated from one another, they are no longer able to freely exchange genetic material through gene flow.
- Without gene flow, populations can evolve independently and accumulate genetic differences over time.
- These genetic differences can eventually become significant enough that individuals from different populations are unable to produce viable offspring, leading to the formation of new species.
Variation:
- Variation refers to the genetic differences that exist within a population.
- This genetic diversity arises due to mutations, which are random changes in the DNA sequence.
- Mutations can introduce new genetic variations into a population, which can then be acted upon by natural selection.
- Natural selection favors individuals with traits that are advantageous in their specific environment, allowing them to survive and reproduce at higher rates.
- Over time, these advantageous traits become more common in the population, while less advantageous or detrimental traits are eliminated.
- This process, known as adaptive evolution, can lead to the formation of new species as populations diverge genetically and phenotypically.
The combination of isolation and variation is essential for speciation to occur:
- Isolation prevents gene flow between populations, allowing them to evolve independently.
- Variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, driving adaptive evolution.
- As populations become more genetically and phenotypically distinct due to isolation and variation, they can eventually reach a point where they are reproductively isolated and can no longer interbreed.
- At this stage, they are considered separate species.
In summary, isolation and variation are two key factors involved in the formation of new species. Isolation prevents gene flow between populations, while variation provides the genetic diversity necessary for adaptive evolution. Together, these factors contribute to the divergence and eventual reproductive isolation of populations, leading to the formation of new species.
Isolation:
- Isolation can occur in several ways, such as geographical barriers (e.g., mountains, rivers, oceans) or reproductive barriers (e.g., differences in mating behaviors, reproductive anatomy).
- When populations become isolated from one another, they are no longer able to freely exchange genetic material through gene flow.
- Without gene flow, populations can evolve independently and accumulate genetic differences over time.
- These genetic differences can eventually become significant enough that individuals from different populations are unable to produce viable offspring, leading to the formation of new species.
Variation:
- Variation refers to the genetic differences that exist within a population.
- This genetic diversity arises due to mutations, which are random changes in the DNA sequence.
- Mutations can introduce new genetic variations into a population, which can then be acted upon by natural selection.
- Natural selection favors individuals with traits that are advantageous in their specific environment, allowing them to survive and reproduce at higher rates.
- Over time, these advantageous traits become more common in the population, while less advantageous or detrimental traits are eliminated.
- This process, known as adaptive evolution, can lead to the formation of new species as populations diverge genetically and phenotypically.
The combination of isolation and variation is essential for speciation to occur:
- Isolation prevents gene flow between populations, allowing them to evolve independently.
- Variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, driving adaptive evolution.
- As populations become more genetically and phenotypically distinct due to isolation and variation, they can eventually reach a point where they are reproductively isolated and can no longer interbreed.
- At this stage, they are considered separate species.
In summary, isolation and variation are two key factors involved in the formation of new species. Isolation prevents gene flow between populations, while variation provides the genetic diversity necessary for adaptive evolution. Together, these factors contribute to the divergence and eventual reproductive isolation of populations, leading to the formation of new species.
Which one of the following statements is correct?- a)Australopithecus is the real ancestor of modern man.
- b)Neanderthal man is the direct ancestor of Homo sapiens.
- c)Homo erectus is the ancestor of man.
- d)Cro-magnon man's fossil has been found in Ethiopia.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is correct?
a)
Australopithecus is the real ancestor of modern man.
b)
Neanderthal man is the direct ancestor of Homo sapiens.
c)
Homo erectus is the ancestor of man.
d)
Cro-magnon man's fossil has been found in Ethiopia.
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Homo erectus that appeared about 1.7 million years ago in middle pleistocence is the ancestor of fan.
The primate which existed 15 mya was __________.- a)Homo habilis
- b)Australophithecus
- c)Ramapithecus
- d)Homo erectus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The primate which existed 15 mya was __________.
a)
Homo habilis
b)
Australophithecus
c)
Ramapithecus
d)
Homo erectus
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Ramapithecus appeared about 15 million years ago in Pliocene epoch. Fossil of Ramapithecus was discovered by Edward Lewis (1932) from rocks of Shivalik Hills of India.
Which of the following statements about early human-like primates is accurate?- a)Ramapithecus was more ape-like, while Dryopithecus was more man-like.
- b)Australopithecines lived in East African grasslands and ate mainly meat.
- c)Homo habilis had a brain capacity between 650-800cc and likely did not eat meat.
- d)Homo erectus had a brain capacity of around 650-800cc.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Ramapithecus was more ape-like, while Dryopithecus was more man-like.
b)
Australopithecines lived in East African grasslands and ate mainly meat.
c)
Homo habilis had a brain capacity between 650-800cc and likely did not eat meat.
d)
Homo erectus had a brain capacity of around 650-800cc.

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Ramapithecus was more man-like, while Dryopithecus was more ape-like. Australopithecines lived in East African grasslands, but they mainly ate fruit and not meat. Homo habilis had a brain capacity between 650-800cc and likely did not consume meat, making Option C correct. Homo erectus, the next evolutionary stage, had a larger brain capacity of around 900cc.
What does the Big Bang theory suggest about the universe's origin?- a)It originated from the condensation of gases
- b)It began with a singular huge explosion
- c)It was always in a steady state
- d)It formed through gradual accumulation of matter
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It originated from the condensation of gases
b)
It began with a singular huge explosion
c)
It was always in a steady state
d)
It formed through gradual accumulation of matter

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The Big Bang theory suggests that the universe originated from a singular, immense explosion, leading to its ongoing expansion and cooling, eventually forming stars, galaxies, and other celestial bodies.
Topic in NCERT: Origin of universe
Line in NCERT: "the big bang theory attempts to explain to us the origin of universe. it talks of a singular huge explosion unimaginable in physical terms."
According to Oparin and Haldane, what preceded the formation of life?- a)Formation of water from oxygen and hydrogen
- b)Disappearance of the dinosaurs
- c)Chemical evolution from inorganic constituents
- d)Development of multicellular organisms
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Formation of water from oxygen and hydrogen
b)
Disappearance of the dinosaurs
c)
Chemical evolution from inorganic constituents
d)
Development of multicellular organisms

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Oparin of Russia and Haldane of England proposed that the formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution, which involved the formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents under Earth's early conditions.
Topic in NCERT: Origin of life
Line in NCERT: "oparin of russia and haldane of england proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules (e.g. rna, protein, etc.) and that formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution, i.e., formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents."
The cranial capacity was largest among the- a)Peking man
- b)Java ape man
- c)African man
- d)Neanderthal man
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cranial capacity was largest among the
a)
Peking man
b)
Java ape man
c)
African man
d)
Neanderthal man
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The cranial capacity of Neanderthal man was 1400c.c., Peking man had 850−1100c.c., Java ape man had 800−1000c.c. and African man had 500c.c.
Consider the following three statements and select the correct option stating which one is true (T) and which one is false (F).
(i) The skull of baby chimpanzee is more like adult human skull than adult chimpanzee skull.
(ii) The first mammals were like shrews.
(iii) The work of Thomas Malthus on populations influenced Lamarck.
- a)(i) - T, (ii) - F, (iii) - T
- b)(i) - F, (ii) - T, (iii) - T
- c)(i) - T, (ii) - T, (iii) - F
- d)(i) - F, (ii) - T, (iii) - F
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following three statements and select the correct option stating which one is true (T) and which one is false (F).
(i) The skull of baby chimpanzee is more like adult human skull than adult chimpanzee skull.
(ii) The first mammals were like shrews.
(iii) The work of Thomas Malthus on populations influenced Lamarck.
(i) The skull of baby chimpanzee is more like adult human skull than adult chimpanzee skull.
(ii) The first mammals were like shrews.
(iii) The work of Thomas Malthus on populations influenced Lamarck.
a)
(i) - T, (ii) - F, (iii) - T
b)
(i) - F, (ii) - T, (iii) - T
c)
(i) - T, (ii) - T, (iii) - F
d)
(i) - F, (ii) - T, (iii) - F
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
(i) The skull of a baby chimpanzee is more like an adult human skull than an adult chimpanzee skull. This is true. The skulls of baby chimpanzees and humans are very similar in shape and size. As they grow, the skulls of chimpanzees begin to differentiate and become more distinct.
(ii) The first mammals were like shrews. This is also true. The earliest known mammals were small, shrew-like creatures that lived during the Mesozoic Era, around 200 million years ago.
(iii) The work of Thomas Malthus on populations influenced Lamarck. This is false. It was Charles Darwin, not Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, who was influenced by Thomas Malthus's work on population growth. Malthus's ideas on population growth and scarcity of resources influenced Darwin's theory of natural selection. Lamarck, on the other hand, proposed a different theory of evolution based on the inheritance of acquired characteristics.
Correct answer is C.
(ii) The first mammals were like shrews. This is also true. The earliest known mammals were small, shrew-like creatures that lived during the Mesozoic Era, around 200 million years ago.
(iii) The work of Thomas Malthus on populations influenced Lamarck. This is false. It was Charles Darwin, not Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, who was influenced by Thomas Malthus's work on population growth. Malthus's ideas on population growth and scarcity of resources influenced Darwin's theory of natural selection. Lamarck, on the other hand, proposed a different theory of evolution based on the inheritance of acquired characteristics.
Correct answer is C.
Each of us is part of the ongoing evolution of the species. Which of the following occurrences would have the greatest impact on the future biological evolution of the human population?- a)A mutation occurs in one of your sperm or egg cells
- b)You do exercise every day so that you stay physically fit and healthy
- c)You move to Kerala, the state of highest medical facilities and literacy
- d)You encourage your children to develop their intellectual abilities
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Each of us is part of the ongoing evolution of the species. Which of the following occurrences would have the greatest impact on the future biological evolution of the human population?
a)
A mutation occurs in one of your sperm or egg cells
b)
You do exercise every day so that you stay physically fit and healthy
c)
You move to Kerala, the state of highest medical facilities and literacy
d)
You encourage your children to develop their intellectual abilities
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
A mutation in sperms or egg cells means mutation in offspring. This will have greatest impact on the future biological evolution of the human population.
What was the primary goal of S.L. Miller's experiment conducted in 1953?- a) To understand volcanic activity
- b) To create life in a laboratory
- c) To study meteorite composition
- d) To investigate chemical evolution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What was the primary goal of S.L. Miller's experiment conducted in 1953?
a)
To understand volcanic activity
b)
To create life in a laboratory
c)
To study meteorite composition
d)
To investigate chemical evolution

|
EduRev NEET answered |
S.L. Miller's experiment aimed to explore the origins of organic compounds and their role in chemical evolution.
The most apparent change during the evolutionary history of Homo sapiens is traced by- a)Loss of body hair
- b)Walking upright
- c)Shortening of the jaws
- d)Remarkable increase in the brain size
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most apparent change during the evolutionary history of Homo sapiens is traced by
a)
Loss of body hair
b)
Walking upright
c)
Shortening of the jaws
d)
Remarkable increase in the brain size
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The brain capacity gradually increased from early human ancestors. Homo habilis has 650−800c.c., brain capacity which increased around 900c.c., in Homo erectus The Neanderthal man had 1400c.c., brain capacity which evolved to around 1450c.c., in Homo sapiens sapiens.
Forelimbs of cat, lizard used in walking, forelimbs of whale used in swimming and forelimbs of bats used in flying are an example of:- a)Analogous organs
- b)Homologous organs
- c)Convergent evolution
- d)Adaptive radiation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Forelimbs of cat, lizard used in walking, forelimbs of whale used in swimming and forelimbs of bats used in flying are an example of:
a)
Analogous organs
b)
Homologous organs
c)
Convergent evolution
d)
Adaptive radiation

|
Lead Academy answered |
Organs which have a common fundamental anatomical plan and similar embryonic origin whatever varied functions they may perform are regarded as homologous organs. For examples the flippers of a whale, a bats wing, fore-limb of a horse, a bird’s wing and forelimbs of human are structurally as well as functionally different.
The diversity in the type of beaks of finches adapted to different feeding habits on the Galapagos Islands, as observed by Darwin, provides evidence for- a)intraspecific competition
- b)interspecific competition
- c)origin of species by natural selection
- d)origin of species by mutation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The diversity in the type of beaks of finches adapted to different feeding habits on the Galapagos Islands, as observed by Darwin, provides evidence for
a)
intraspecific competition
b)
interspecific competition
c)
origin of species by natural selection
d)
origin of species by mutation
|
|
Shubham Khanna answered |
Introduction to Darwin's Observations
Charles Darwin's study of finches on the Galapagos Islands was pivotal in shaping his theory of evolution. The diverse beak shapes among finches illustrate a key concept in natural selection.
Diversity in Beak Types
- Finches on the islands developed various beak shapes and sizes.
- Each beak type is adapted to specific food sources, such as seeds, insects, or nectar.
Natural Selection Explained
- The differences in beak morphology are a result of natural selection.
- Finches with beak shapes suited to their environment were more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Over generations, these advantageous traits became more common in the population.
Evidence for Speciation
- As finches adapted to unique feeding habits on different islands, they began to diverge genetically.
- This process led to the emergence of new species, illustrating how natural selection drives speciation.
- The varying beak types serve as clear evidence of adaptive radiation, where one ancestral species evolves into multiple forms.
Conclusion
- Darwin’s observations of finch beaks provide compelling evidence for the origin of species by natural selection.
- The adaptability and evolution of these finches highlight the fundamental principles of evolutionary biology.
In summary, the diversity of finch beaks is a classic example of how natural selection can lead to the emergence of new species, supporting Darwin's theory of evolution.
Charles Darwin's study of finches on the Galapagos Islands was pivotal in shaping his theory of evolution. The diverse beak shapes among finches illustrate a key concept in natural selection.
Diversity in Beak Types
- Finches on the islands developed various beak shapes and sizes.
- Each beak type is adapted to specific food sources, such as seeds, insects, or nectar.
Natural Selection Explained
- The differences in beak morphology are a result of natural selection.
- Finches with beak shapes suited to their environment were more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Over generations, these advantageous traits became more common in the population.
Evidence for Speciation
- As finches adapted to unique feeding habits on different islands, they began to diverge genetically.
- This process led to the emergence of new species, illustrating how natural selection drives speciation.
- The varying beak types serve as clear evidence of adaptive radiation, where one ancestral species evolves into multiple forms.
Conclusion
- Darwin’s observations of finch beaks provide compelling evidence for the origin of species by natural selection.
- The adaptability and evolution of these finches highlight the fundamental principles of evolutionary biology.
In summary, the diversity of finch beaks is a classic example of how natural selection can lead to the emergence of new species, supporting Darwin's theory of evolution.
Which of the following statements is correct regarding evolution of mankind?- a)Homo erectus is preceded by Homo habilis
- b)Neanderthal man and Cro-Magnon man were living at the same time
- c)Australopithecus was living in Australia
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct regarding evolution of mankind?
a)
Homo erectus is preceded by Homo habilis
b)
Neanderthal man and Cro-Magnon man were living at the same time
c)
Australopithecus was living in Australia
d)
None of these
|
|
Isha Roy answered |
Understanding Human Evolution
Human evolution is a complex process that involves various species of hominins over millions of years. Let's break down the statements to clarify why option 'A' is correct.
Statement A: Homo erectus is preceded by Homo habilis
- Homo habilis, known as the "handy man," is one of the earliest members of the genus Homo, dating back around 2.4 to 1.4 million years ago.
- Homo erectus, which translates to "upright man," emerged later, around 1.9 million years ago and continued to exist until about 110,000 years ago.
- This evolutionary sequence highlights that Homo habilis indeed precedes Homo erectus in the timeline of human evolution.
Statement B: Neanderthal man and Cro-Magnon man were living at the same time
- While Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons (early modern humans) coexisted for a period in Europe, Neanderthals became extinct around 40,000 years ago, while Cro-Magnons emerged around the same time.
- However, the interaction and timeline are complex, and while they were contemporaneous, the statement lacks nuance and is somewhat misleading.
Statement C: Australopithecus was living in Australia
- Australopithecus, an early hominin, primarily lived in Africa, not Australia.
- This statement is factually incorrect and misrepresents the geographical range of early human ancestors.
Conclusion: Why Option A is Correct
- The clear evolutionary progression from Homo habilis to Homo erectus is well-supported by fossil evidence.
- Understanding these timelines is crucial in the study of human evolution, making option 'A' the correct answer regarding the sequence of species in the evolution of mankind.
Human evolution is a complex process that involves various species of hominins over millions of years. Let's break down the statements to clarify why option 'A' is correct.
Statement A: Homo erectus is preceded by Homo habilis
- Homo habilis, known as the "handy man," is one of the earliest members of the genus Homo, dating back around 2.4 to 1.4 million years ago.
- Homo erectus, which translates to "upright man," emerged later, around 1.9 million years ago and continued to exist until about 110,000 years ago.
- This evolutionary sequence highlights that Homo habilis indeed precedes Homo erectus in the timeline of human evolution.
Statement B: Neanderthal man and Cro-Magnon man were living at the same time
- While Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons (early modern humans) coexisted for a period in Europe, Neanderthals became extinct around 40,000 years ago, while Cro-Magnons emerged around the same time.
- However, the interaction and timeline are complex, and while they were contemporaneous, the statement lacks nuance and is somewhat misleading.
Statement C: Australopithecus was living in Australia
- Australopithecus, an early hominin, primarily lived in Africa, not Australia.
- This statement is factually incorrect and misrepresents the geographical range of early human ancestors.
Conclusion: Why Option A is Correct
- The clear evolutionary progression from Homo habilis to Homo erectus is well-supported by fossil evidence.
- Understanding these timelines is crucial in the study of human evolution, making option 'A' the correct answer regarding the sequence of species in the evolution of mankind.
The first life originated- a)on land
- b)in air
- c)in water
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The first life originated
a)
on land
b)
in air
c)
in water
d)
all of these
|
|
Jaspreet answered |
It's a Ncert line life originated first in water 😊✌️
Theory of spontaneous generation was rejected because:- a)It explained origin of first life from non-living or inanimate matter and lacked experimental evidence.
- b)It was based on the biogenesis concept.
- c)It did not explain about the origin of first life on earth.
- d)It proposed origin of life from outer space.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Theory of spontaneous generation was rejected because:
a)
It explained origin of first life from non-living or inanimate matter and lacked experimental evidence.
b)
It was based on the biogenesis concept.
c)
It did not explain about the origin of first life on earth.
d)
It proposed origin of life from outer space.
|
|
Advait Joshi answered |
Theory of Spontaneous Generation Rejection Explanation
Theory of Spontaneous Generation:
- The theory of spontaneous generation proposed that life could arise from non-living or inanimate matter through a process of spontaneous generation.
Reasons for Rejection:
- Lack of Experimental Evidence:
- One of the main reasons why the theory of spontaneous generation was rejected was due to the lack of experimental evidence to support it.
- Scientists found no concrete proof that life could spontaneously arise from non-living matter.
- Biogenesis Concept:
- The concept of biogenesis, which states that living organisms can only arise from pre-existing living organisms, gained more support as it was backed by experimental evidence.
- This contradicted the idea of spontaneous generation.
- Origin of First Life on Earth:
- The theory of spontaneous generation did not provide a satisfactory explanation for the origin of the first life on Earth.
- It failed to address the specific mechanisms by which life could arise from non-living matter.
- Origin of Life from Outer Space:
- Some proponents of the theory of spontaneous generation suggested that life could have originated from outer space.
- However, this idea lacked substantial evidence and was not widely accepted by the scientific community.
In conclusion, the theory of spontaneous generation was rejected primarily because it lacked experimental evidence to support its claims and failed to provide a comprehensive explanation for the origin of life on Earth. The concept of biogenesis, which has experimental backing, gained more acceptance in the scientific community.
Theory of Spontaneous Generation:
- The theory of spontaneous generation proposed that life could arise from non-living or inanimate matter through a process of spontaneous generation.
Reasons for Rejection:
- Lack of Experimental Evidence:
- One of the main reasons why the theory of spontaneous generation was rejected was due to the lack of experimental evidence to support it.
- Scientists found no concrete proof that life could spontaneously arise from non-living matter.
- Biogenesis Concept:
- The concept of biogenesis, which states that living organisms can only arise from pre-existing living organisms, gained more support as it was backed by experimental evidence.
- This contradicted the idea of spontaneous generation.
- Origin of First Life on Earth:
- The theory of spontaneous generation did not provide a satisfactory explanation for the origin of the first life on Earth.
- It failed to address the specific mechanisms by which life could arise from non-living matter.
- Origin of Life from Outer Space:
- Some proponents of the theory of spontaneous generation suggested that life could have originated from outer space.
- However, this idea lacked substantial evidence and was not widely accepted by the scientific community.
In conclusion, the theory of spontaneous generation was rejected primarily because it lacked experimental evidence to support its claims and failed to provide a comprehensive explanation for the origin of life on Earth. The concept of biogenesis, which has experimental backing, gained more acceptance in the scientific community.
At a particular locus, frequency of allele A is 0.6 and that of allele a is 0.4. What would be the frequency of heterozygotes in a random mating population at equilibrium?- a)0.36
- b)0.16
- c)0.24
- d)0.48
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
At a particular locus, frequency of allele A is 0.6 and that of allele a is 0.4. What would be the frequency of heterozygotes in a random mating population at equilibrium?
a)
0.36
b)
0.16
c)
0.24
d)
0.48
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
In a stable population, for a gene with two alleles, 'A' (dominant) and 'a' (recessive), if the frequency of 'A' is p and the frequency of 'a' is q, then the frequencies of the three possible genotypes (AA, Aa and aa) can be expressed by the Hardy-Weinberg equation:
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
where p2 = Frequency of AA (homozygous dominant) individuals
q2 = Frequency of aa (homozygous recessive) individuals
2pq = Frequency of Aa (heterozygous) individuals
so, p = 0.6 and q = 0.4 (given)
∴ 2pq (frequency of heterozygote)
= 2 × 0.6 × 0.4
= 0.48
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
where p2 = Frequency of AA (homozygous dominant) individuals
q2 = Frequency of aa (homozygous recessive) individuals
2pq = Frequency of Aa (heterozygous) individuals
so, p = 0.6 and q = 0.4 (given)
∴ 2pq (frequency of heterozygote)
= 2 × 0.6 × 0.4
= 0.48
Consider the following three statements and select the correct option stating which one is true (T) and which one is false (F)
(i) Oparin of Russia and Haldane of England proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules (e.g., RNA, protein, etc.) and that formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution
(ii) Based on observations made during a sea voyage around the world, Charles Darwin concluded that existing living forms share similarities to varying degrees only among themselves
(iii) Evolution by natural selection must have started when cellular forms of life with different metabolic capability originated on Earth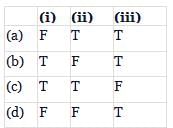
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following three statements and select the correct option stating which one is true (T) and which one is false (F)
(i) Oparin of Russia and Haldane of England proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules (e.g., RNA, protein, etc.) and that formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution
(ii) Based on observations made during a sea voyage around the world, Charles Darwin concluded that existing living forms share similarities to varying degrees only among themselves
(iii) Evolution by natural selection must have started when cellular forms of life with different metabolic capability originated on Earth
(i) Oparin of Russia and Haldane of England proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules (e.g., RNA, protein, etc.) and that formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution
(ii) Based on observations made during a sea voyage around the world, Charles Darwin concluded that existing living forms share similarities to varying degrees only among themselves
(iii) Evolution by natural selection must have started when cellular forms of life with different metabolic capability originated on Earth

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Based on observations made during a sea voyage around the world, Charles Darwin concluded that existing living forms share similarities to varying degrees not only among themselves but also with life forms that existed millions of years ago.
What did Oparin and Haldane propose about the origin of the first forms of life?- a) They came from pre-existing non-living organic molecules.
- b) They originated from extraterrestrial sources.
- c) They evolved directly from inorganic materials.
- d) They were created through divine intervention.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What did Oparin and Haldane propose about the origin of the first forms of life?
a)
They came from pre-existing non-living organic molecules.
b)
They originated from extraterrestrial sources.
c)
They evolved directly from inorganic materials.
d)
They were created through divine intervention.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Oparin and Haldane proposed that the first forms of life originated from pre-existing non-living organic molecules that formed under the conditions present on early Earth.
The character that proves that frogs have evolved from fishes is- a)Their ability to swim in water
- b)Tadpole larva in frogs
- c)Similarity in the shape of the head
- d)Their feeding on aquatic plants
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The character that proves that frogs have evolved from fishes is
a)
Their ability to swim in water
b)
Tadpole larva in frogs
c)
Similarity in the shape of the head
d)
Their feeding on aquatic plants
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The tadpole larva of frog bears gills, which proves that frogs have evolved from gilled ancestors.
Fill up the blanks in the following paragraph by selecting the correct option
When migration of a section of population to another place and population occurs, (i) change in the original as well as in the new population. New genes/alleles are added to the (ii) population and these are lost from the (iii) population. There would be a (iv) if this gene migration, happens multiple times. If the same change occurs by chance, it is called (v). Sometimes the change in allele frequency is so different in the new sample of population that they become a different species. The original drifted population becomes founders and the effect is called (vi).
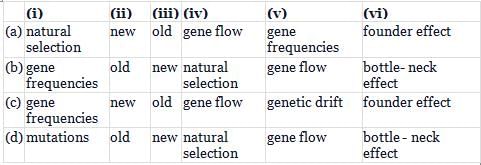
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fill up the blanks in the following paragraph by selecting the correct option
When migration of a section of population to another place and population occurs, (i) change in the original as well as in the new population. New genes/alleles are added to the (ii) population and these are lost from the (iii) population. There would be a (iv) if this gene migration, happens multiple times. If the same change occurs by chance, it is called (v). Sometimes the change in allele frequency is so different in the new sample of population that they become a different species. The original drifted population becomes founders and the effect is called (vi).

When migration of a section of population to another place and population occurs, (i) change in the original as well as in the new population. New genes/alleles are added to the (ii) population and these are lost from the (iii) population. There would be a (iv) if this gene migration, happens multiple times. If the same change occurs by chance, it is called (v). Sometimes the change in allele frequency is so different in the new sample of population that they become a different species. The original drifted population becomes founders and the effect is called (vi).

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When migration of a section of population to another place and population occurs, gene frequencies change in the original as well as in the new population. New genes/alleles are added to the new population and these are lost from the old population. There would be a gene flow if this gene migration, happens multiple times. If the same change occurs by chance, it is called genetic drift. Sometimes the change in allele frequency is so different in the new sample of population that they become a different species. The original drifted population becomes founders and the effect is called founder effect.
The wings of a bird and the wings of an insect are :- a)homologous structures and represent divergent evolution
- b)phylogenetic structures and represent divergent evolution
- c)homologous structures and represent convergent evolution
- d)analogous structures and represent convergent evolution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The wings of a bird and the wings of an insect are :
a)
homologous structures and represent divergent evolution
b)
phylogenetic structures and represent divergent evolution
c)
homologous structures and represent convergent evolution
d)
analogous structures and represent convergent evolution

|
Lead Academy answered |
Analogous organs are the organs which have similar function but are different in their structural details and origin. The analogous structures are the result of convergent evolution. The wings of an insect are analogous to wings of a bird because the basic structure of the wings of the insects is different from the wings of bird. However, their function is similar.
Chapter doubts & questions for Evolution - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Evolution - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









