All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of p-Block Elements for NEET Exam
The correct statements among the given are
- a)Antimony belongs to 15th group and 5th period
- b)electron gain enthalpy of P > N > S > O
- c)Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus is -3 and +6
- d)Fluoroapatite, formula is Ca6(PO4)6 CaF2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statements among the given are
a)
Antimony belongs to 15th group and 5th period
b)
electron gain enthalpy of P > N > S > O
c)
Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus is -3 and +6
d)
Fluoroapatite, formula is Ca6(PO4)6 CaF2

|
Divey Sethi answered |
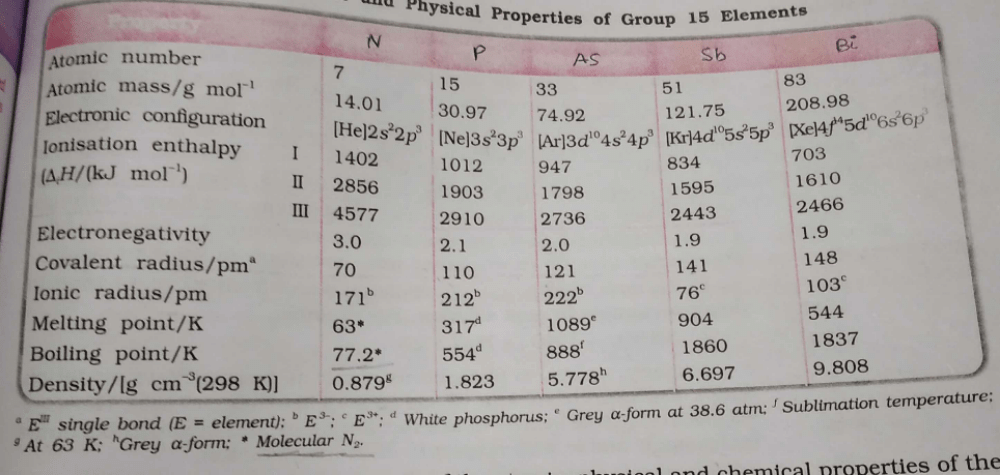
Option A: Group 5A (or VA) of the periodic table are the pnictogens: the nonmetals nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P), the metalloids arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb), and the metal bismuth (Bi).
Option B: The electron gain enthalpy of P< N< S< O.
Option C: Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus are -3 and +5 respectively.
Option D: Fluorapatite is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca5(PO4)3F .
Option B: The electron gain enthalpy of P< N< S< O.
Option C: Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus are -3 and +5 respectively.
Option D: Fluorapatite is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca5(PO4)3F .
Hence, option A is correct.
HClO is known as- a)chloric acid
- b)Chlorine
- c)bacteria killer
- d)water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
HClO is known as
a)
chloric acid
b)
Chlorine
c)
bacteria killer
d)
water
|
|
Nada Sharin answered |
Hypohalous acid is also known as CHLORIC (I) ACID
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Subhankar Choudhary answered |
Molecular Orbital Theory and Antibonding Orbitals in Nitrogen
Molecular orbital theory (MOT) is a theoretical model that describes the behavior of electrons in molecules based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It is used to explain and predict the properties of molecules, including their electronic and magnetic properties, bond lengths, bond angles, and so on.
In MOT, the electrons in a molecule are treated as waves that are described by molecular orbitals (MOs), which are mathematical functions that represent the probability of finding an electron at a given point in space. These MOs are formed by combining the atomic orbitals of the atoms in the molecule.
Antibonding orbitals are MOs that have a higher energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed. When electrons occupy these orbitals, they weaken the bond between the atoms in the molecule, making it more likely to break apart.
Nitrogen has five valence electrons, which are represented by the atomic orbitals s and p. In the molecule N2, these atomic orbitals combine to form five MOs: two bonding MOs, two antibonding MOs, and one nonbonding MO.
The two bonding MOs are lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they help to hold the two nitrogen atoms together. The nonbonding MO is filled with two electrons, which are shared equally between the two nitrogen atoms and do not contribute to the bond strength.
The two antibonding MOs are higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they weaken the bond between the two nitrogen atoms. When all five valence electrons are placed into the MOs, there are four electrons in the antibonding MOs and one electron in the nonbonding MO.
Therefore, according to molecular orbital theory, there are four electrons present in the antibonding orbitals of nitrogen.
Molecular orbital theory (MOT) is a theoretical model that describes the behavior of electrons in molecules based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It is used to explain and predict the properties of molecules, including their electronic and magnetic properties, bond lengths, bond angles, and so on.
In MOT, the electrons in a molecule are treated as waves that are described by molecular orbitals (MOs), which are mathematical functions that represent the probability of finding an electron at a given point in space. These MOs are formed by combining the atomic orbitals of the atoms in the molecule.
Antibonding orbitals are MOs that have a higher energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed. When electrons occupy these orbitals, they weaken the bond between the atoms in the molecule, making it more likely to break apart.
Nitrogen has five valence electrons, which are represented by the atomic orbitals s and p. In the molecule N2, these atomic orbitals combine to form five MOs: two bonding MOs, two antibonding MOs, and one nonbonding MO.
The two bonding MOs are lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they help to hold the two nitrogen atoms together. The nonbonding MO is filled with two electrons, which are shared equally between the two nitrogen atoms and do not contribute to the bond strength.
The two antibonding MOs are higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they weaken the bond between the two nitrogen atoms. When all five valence electrons are placed into the MOs, there are four electrons in the antibonding MOs and one electron in the nonbonding MO.
Therefore, according to molecular orbital theory, there are four electrons present in the antibonding orbitals of nitrogen.
Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products?- a) Cu
- b)S
- c)C
- d)zn
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products?
a)
Cu
b)
S
c)
C
d)
zn
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
C element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?- a)Oxidation state of sulphur in its compounds vary from -2 to +8
- b)Tetrahalides of 16th group have see-saw shap
- c)S2CI2 has linear geometr
- d)SCI4 on hydrolysis yields sulphurous acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a)
Oxidation state of sulphur in its compounds vary from -2 to +8
b)
Tetrahalides of 16th group have see-saw shap
c)
S2CI2 has linear geometr
d)
SCI4 on hydrolysis yields sulphurous acid
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
Disulphur dichlor
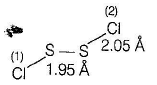
The angle between the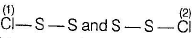 planes is 90°.
planes is 90°.
The structure is referred to as gauche.
The angle between the
The structure is referred to as gauche.
- a)
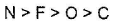
- b)
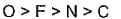
- c)
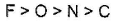
- d)
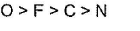
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The second ionization energy refers to the energy required to remove the electron from the corresponding monovalent cation of the respective atom.
It is expected to increase from left to right in the periodic table with the decrease in atomic size.
Since the Oxygen atom gets a stable electronic configuration, 2s22p3 after removing one electron, the O+ shows greater ionization energy than F+ as well as N+.
Thus, correct order will be: O > F > N > C
In the third period of the periodic table the element having smallest size is - a)Na
- b)CI
- c)Ar
- d)Si
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the third period of the periodic table the element having smallest size is
a)
Na
b)
CI
c)
Ar
d)
Si
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon.
In a period from left to right atomic size decreases due to Increase in nuclear charge.
but the noble gases are bigger than the halogens as they have octet and sort of repulsion occurs in the shells.
so the smallest element in a period is the halogen.so chlorine Cl is the smallest.
Maximum number of compounds are known in case of :- a)Krypton
- b)Helium
- c)Argon
- d)Xenon
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum number of compounds are known in case of :
a)
Krypton
b)
Helium
c)
Argon
d)
Xenon

|
Aaditya Ghoshal answered |
Only xenon is well known to form chemical compounds, because xenon is large in size and having higer atomic mass.Due to having larger atomic radius the force of attraction between the outer electron and the protons in the nucleus is weaker.
Which is incorrectly matched ?- a)CsBr3
 Cs+ + Br3–
Cs+ + Br3– - b)I4O9
 I3+ + (IO3–)3
I3+ + (IO3–)3 - c)AgBrO3
 Ag+ + BrO3–
Ag+ + BrO3– - d)I2O4
 IO2– + IO2+
IO2– + IO2+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is incorrectly matched ?
a)
CsBr3  Cs+ + Br3–
Cs+ + Br3–
b)
I4O9  I3+ + (IO3–)3
I3+ + (IO3–)3
c)
AgBrO3 Ag+ + BrO3–
Ag+ + BrO3–
d)
I2O4  IO2– + IO2+
IO2– + IO2+

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
It is strictly covalent does not shows cationic & anionic form.
Which of the outer electronic configuration represent argon?- a)ns2np4
- b)ns2
- c)ns2np2
- d)ns2np6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the outer electronic configuration represent argon?
a)
ns2np4
b)
ns2
c)
ns2np2
d)
ns2np6

|
Aadhar Academy answered |
The correct answer is option D
Outer electronic configuration represents argon ns2,np6.
Atomic no. of argon is 18. Its electronic configuration will be
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6.
As the outermost shell is full (3s23p6) it is called noble gas.
Outer electronic configuration represents argon ns2,np6.
Atomic no. of argon is 18. Its electronic configuration will be
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6.
As the outermost shell is full (3s23p6) it is called noble gas.
Partial hydrolysis of XeF6 yields:- a)Xenon trioxide
- b)Xenon tetrafluoride
- c)Xenon dioxydifluoride
- d)Xenon oxyfluoride
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Partial hydrolysis of XeF6 yields:
a)
Xenon trioxide
b)
Xenon tetrafluoride
c)
Xenon dioxydifluoride
d)
Xenon oxyfluoride
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Partial hydrolysis of XeF6 yields xenon oxyfluoride.
XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
Which of the following gaseous molecule is monoatomic?- a)Oxygen
- b)Helium
- c)Nitrogen
- d)Chlorine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following gaseous molecule is monoatomic?
a)
Oxygen
b)
Helium
c)
Nitrogen
d)
Chlorine
|
|
Swara Sharma answered |
Explanation:
Monoatomic molecules are the molecules that consist of only one atom of an element. They are rare because most elements tend to bond with other atoms to form molecules. However, some elements are stable in their monoatomic form.
The given options are:
a) Oxygen (O2) - Oxygen molecule is diatomic, which means it consists of two atoms of oxygen.
b) Helium (He) - Helium is a rare example of a monoatomic molecule. It exists as a single atom and does not bond with other atoms.
c) Nitrogen (N2) - Nitrogen molecule is diatomic, which means it consists of two atoms of nitrogen.
d) Chlorine (Cl2) - Chlorine molecule is diatomic, which means it consists of two atoms of chlorine.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B', Helium, which is a monoatomic molecule.
Monoatomic molecules are the molecules that consist of only one atom of an element. They are rare because most elements tend to bond with other atoms to form molecules. However, some elements are stable in their monoatomic form.
The given options are:
a) Oxygen (O2) - Oxygen molecule is diatomic, which means it consists of two atoms of oxygen.
b) Helium (He) - Helium is a rare example of a monoatomic molecule. It exists as a single atom and does not bond with other atoms.
c) Nitrogen (N2) - Nitrogen molecule is diatomic, which means it consists of two atoms of nitrogen.
d) Chlorine (Cl2) - Chlorine molecule is diatomic, which means it consists of two atoms of chlorine.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B', Helium, which is a monoatomic molecule.
A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3– ion. It is due to the formation of- a)[Fe(H2O)5 (NO)]2+
- b) FeSO4.NO2
- c)[Fe(H2O)4(NO)2]2+
- d)FeSO4.HNO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3– ion. It is due to the formation of
a)
[Fe(H2O)5 (NO)]2+
b)
FeSO4.NO2
c)
[Fe(H2O)4(NO)2]2+
d)
FeSO4.HNO3

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
When freshly prepared solution of FeSO4 is added in a solution containing NO3– ion, it leads to formation of a brown coloured complex. This is known as brown ring test of nitrate.
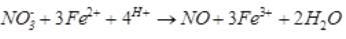
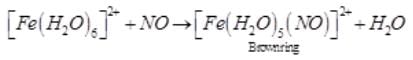
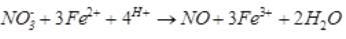
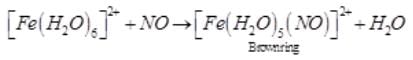

- a)
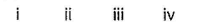

- b)
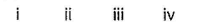

- c)
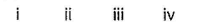
- d)
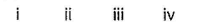
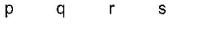
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
(i) Nitrogen is a non-metal.
(ii) Phosphorus is a non-metal.
(iii) Arsenic is a metalloid and shows Sublimation.
(iv) Bismuth is metal and shows the Inert pair effect.
(ii) Phosphorus is a non-metal.
(iii) Arsenic is a metalloid and shows Sublimation.
(iv) Bismuth is metal and shows the Inert pair effect.
Hence, option A is correct.
The valency of inert gas is:- a)Zero
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The valency of inert gas is:
a)
Zero
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Valency of an element is defined as its tendency to accept valence electrons.
Since noble gas has completely filled valence (outer) shells, they have the least reactivity.
Hence noble gases are already stable in its elemental form. So its valency is zero.
Since noble gas has completely filled valence (outer) shells, they have the least reactivity.
Hence noble gases are already stable in its elemental form. So its valency is zero.
Find the sum of bond pairs and non-bonding electron pairs in ICI molecule.
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the sum of bond pairs and non-bonding electron pairs in ICI molecule.

|
Tarun Chakraborty answered |
3 lone pairs and 1 bond pair.
In XeF2, state the total number of electron pairs in its Lewis dot structure.
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
In XeF2, state the total number of electron pairs in its Lewis dot structure.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Electron dot structure of XeF2 is
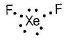

Among the following compounds, the number of compounds which have oxidation states of S is +4 ?PbS, SO2, SF6, Na2S2O3, H2SO3
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following compounds, the number of compounds which have oxidation states of S is +4 ?
PbS, SO2, SF6, Na2S2O3, H2SO3
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
SO2...x+2(-2)=0.x=4..H2SO3.2(1)+x+3(-2)=0.2+x-6=0.-4+x=0.x=4...
- a)
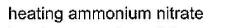
- b)

- c)

- d)
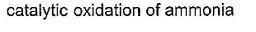
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gauri Datta answered |
Oxidation of ammonia with CuO produces nitrogen gas and water vapor. This reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + 3CuO → 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
The gaseous chemical produced in this reaction is nitrogen gas (N2), which is also obtained by reacting excess ammonia with chlorine. This reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Explanation:
- Ammonium nitrate: Heating ammonium nitrate results in the decomposition of ammonium nitrate into nitrogen gas, water vapor, and oxygen gas. The reaction is represented as:
NH4NO3 → N2 + 2H2O + O2
- Potassium dichromate: Heating potassium dichromate results in the production of oxygen gas and potassium chromate. The reaction is represented as:
4K2Cr2O7 → 4K2CrO4 + 3O2
- Catalytic oxidation of ammonia: Catalytic oxidation of ammonia involves the use of a catalyst (such as platinum or palladium) to oxidize ammonia to nitrogen gas and water vapor. The reaction is represented as:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
4NO2 + O2 → 2N2O5
N2O5 → N2 + 2.5O2
- Reacting excess ammonia with chlorine: This reaction involves the reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine gas to produce nitrogen gas and hydrochloric acid. The reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Therefore, option B, reacting excess ammonia with chlorine, is the correct answer.
2NH3 + 3CuO → 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
The gaseous chemical produced in this reaction is nitrogen gas (N2), which is also obtained by reacting excess ammonia with chlorine. This reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Explanation:
- Ammonium nitrate: Heating ammonium nitrate results in the decomposition of ammonium nitrate into nitrogen gas, water vapor, and oxygen gas. The reaction is represented as:
NH4NO3 → N2 + 2H2O + O2
- Potassium dichromate: Heating potassium dichromate results in the production of oxygen gas and potassium chromate. The reaction is represented as:
4K2Cr2O7 → 4K2CrO4 + 3O2
- Catalytic oxidation of ammonia: Catalytic oxidation of ammonia involves the use of a catalyst (such as platinum or palladium) to oxidize ammonia to nitrogen gas and water vapor. The reaction is represented as:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
4NO2 + O2 → 2N2O5
N2O5 → N2 + 2.5O2
- Reacting excess ammonia with chlorine: This reaction involves the reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine gas to produce nitrogen gas and hydrochloric acid. The reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Therefore, option B, reacting excess ammonia with chlorine, is the correct answer.
The element having highest ionisation potential is:- a)Oxygen
- b)Helium
- c)Nitrogen
- d)Hydrogen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The element having highest ionisation potential is:
a)
Oxygen
b)
Helium
c)
Nitrogen
d)
Hydrogen
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Thereby, the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the atom decreases. Ionization potential, thus, decreases down a group. The element with highest ionization potential in the periodic table is Helium (2372.1 kj/mol), while the element with the lowest ionization potential is Caesium (375.7 kj/mol).
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
|
|
Nandita Ahuja answered |
Fluorine atom have 2+7 electrons so an F2 molecule contain 18 electrons.
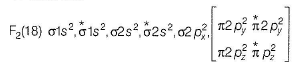
Hence, 8 electrons occupy the antibonding orbitals.
Hence, 8 electrons occupy the antibonding orbitals.
The correct statements among the following are
- a)Bond lengths in O2 ,
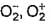 are 121 , 134, 149 pm
are 121 , 134, 149 pm
- b)Ozone is stronger oxidising agent than dioxygen
- c)O2 acts as reducing agent when it reacts with powerful oxidising agents like PtF6
- d)Ozone is much more stable than oxygen
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statements among the following are
a)
Bond lengths in O2 , 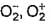 are 121 , 134, 149 pm
are 121 , 134, 149 pm
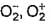 are 121 , 134, 149 pm
are 121 , 134, 149 pmb)
Ozone is stronger oxidising agent than dioxygen
c)
O2 acts as reducing agent when it reacts with powerful oxidising agents like PtF6
d)
Ozone is much more stable than oxygen

|
Srishti Kaur answered |
The correct option is Option A, B and C.
Bond length is inversely proportional to bond order. O2+ has the highest bond order among these three, so it should have the shortest bond length.
Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent as compared to oxygen. This is due to the unstable nature of ozone and the nascent oxygen that is released during the reaction.
O2 when gas makes others like H2 gas to lose electrons, therefore, O2 gas is an oxidizing agent and H2 when gas loses electrons in redox reaction, therefore H2 gas is a reducing agent.
Oxygen is more stable than ozone. On heating, ozone readily dissociates and forms oxygen and free radicals of oxygen known as nascent oxygen which take part in reaction, thus ozone is more reactive than oxygen
The chemical species having sp2-hybridisation for the central atom is- a)SOCI2
- b)
- c)SCI2
- d)SO3
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The chemical species having sp2-hybridisation for the central atom is
a)
SOCI2
b)
c)
SCI2
d)
SO3

|
C.k Singh answered |
Only option D has sp2 hybridisation for the central atom.Rest is sp3 hybridisation.
Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron(s) ?- a)N2
- b)O2
- c)NO+
- d)CN-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron(s) ?
a)
N2
b)
O2
c)
NO+
d)
CN-
|
|
Priya Chavan answered |
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
- a)

- b)
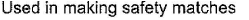
- c)
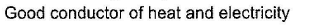
- d)
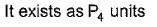
Correct answer is 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Rahul Desai answered |
(a.c) Being goad conductor of neat and elecnicky, black phosphorus is a most stabte allotrope of phosphorus
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?- a)SRP values of halogens F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
- b)Bond dissociation enthalpy of Br2 > F2 > Cl2 > I2
- c)Boiling points of I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
- d)Reducing power of I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
a)
SRP values of halogens F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
b)
Bond dissociation enthalpy of Br2 > F2 > Cl2 > I2
c)
Boiling points of I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
d)
Reducing power of I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
The correct order of bond dissociation enthalpy is
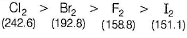
Noble gases are inert and do not form compounds like other elements because of their:- a)Low ionization energy
- b)High electron affinities
- c)Close shell electronic configuration
- d)High density
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Noble gases are inert and do not form compounds like other elements because of their:
a)
Low ionization energy
b)
High electron affinities
c)
Close shell electronic configuration
d)
High density

|
Aravind Kapoor answered |
Helium has two electrons in its outer shell and the rest have eight electrons. Because of their full outer shells, they are very inert and stable. This means they don't tend to react with other elements to form compounds. They are gases under standard conditions.
Direction: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Ozone is an unstable, dark blue diamagnetic gas. It absorbs the UV radiation strongly, thus protecting the people on earth from the harmful UV-radiation from the sun. The use of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) in aerosol and refrigerator and their subsequent escape into the atmosphere, is blamed for making holes in the ozone layer over the Antarctica. Ozone acts as a strong oxidising agent in acidic and alkaline medium. For this property, ozone is used as a germicide and disinfectant for sterilizing water. It is also used in laboratory for the ozonolysis of organic compounds and in industry for the manufacture of potassium permanganate, artificial silk, etc.
Q. Ozone gives carbonyl compounds with- a)alkyl chloride
- b)alkanes
- c)alkenes followed by decomposition with Zn/ H2O
- d)alcohols followed by decomposition with Zn/H2O
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Ozone is an unstable, dark blue diamagnetic gas. It absorbs the UV radiation strongly, thus protecting the people on earth from the harmful UV-radiation from the sun. The use of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) in aerosol and refrigerator and their subsequent escape into the atmosphere, is blamed for making holes in the ozone layer over the Antarctica. Ozone acts as a strong oxidising agent in acidic and alkaline medium. For this property, ozone is used as a germicide and disinfectant for sterilizing water. It is also used in laboratory for the ozonolysis of organic compounds and in industry for the manufacture of potassium permanganate, artificial silk, etc.
Q. Ozone gives carbonyl compounds with
Ozone is an unstable, dark blue diamagnetic gas. It absorbs the UV radiation strongly, thus protecting the people on earth from the harmful UV-radiation from the sun. The use of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) in aerosol and refrigerator and their subsequent escape into the atmosphere, is blamed for making holes in the ozone layer over the Antarctica. Ozone acts as a strong oxidising agent in acidic and alkaline medium. For this property, ozone is used as a germicide and disinfectant for sterilizing water. It is also used in laboratory for the ozonolysis of organic compounds and in industry for the manufacture of potassium permanganate, artificial silk, etc.
Q. Ozone gives carbonyl compounds with
a)
alkyl chloride
b)
alkanes
c)
alkenes followed by decomposition with Zn/ H2O
d)
alcohols followed by decomposition with Zn/H2O
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |


Which of the following is thermally the most stable?- a)H2Te
- b)H2S
- c)H2O
- d)H2Se
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is thermally the most stable?
a)
H2Te
b)
H2S
c)
H2O
d)
H2Se

|
Ujwal Patel answered |
Stability of hydrides decreases down the group so most stable is H2O
Direction (Q. Nos. 8-12) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Which of the following can act as dehydrating agent ?- a)P4O10
- b)POCI3
- c)Cone.H2SO4
- d)P4O6
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 8-12) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which of the following can act as dehydrating agent ?
a)
P4O10
b)
POCI3
c)
Cone.H2SO4
d)
P4O6

|
Keshav Bhatheja answered |
Conc h2so4 is a very good dehydrating agent as extract h2o from reaction very easily...by breaking into hso4- and h+ and the rest of two i dont know i think we have to learn them
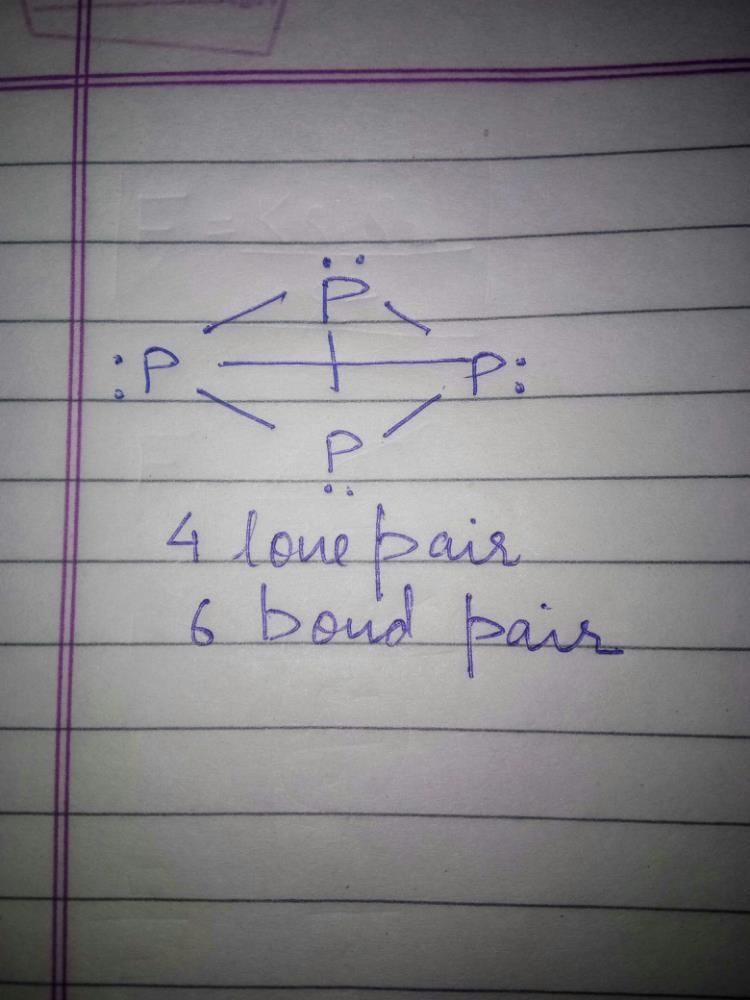
The number of P – O bonds and lone pairs of electron present in P4O6 molecule respectively - a)12 and 4
- b)8 and 8
- c)12 and 16
- d)12 and 12
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of P – O bonds and lone pairs of electron present in P4O6 molecule respectively
a)
12 and 4
b)
8 and 8
c)
12 and 16
d)
12 and 12

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Number of P – O bonds = 12
Number of pair of electron = 16
Number of pair of electron = 16
Geometry of xenon oxyfluoride (XeOF4) is- a)Octahedral
- b)Tetrahedral
- c)Linear
- d)Square pyramidal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Geometry of xenon oxyfluoride (XeOF4) is
a)
Octahedral
b)
Tetrahedral
c)
Linear
d)
Square pyramidal

|
Naina Menon answered |
Answer:
Square pyramidal.
Explanation:
In order to be able to determine the molecular geometry of xenon oxytetrafluoride,
XeOF4, you need to start by drawing its Lewis structure.
To find the number of valence electron you get in one molecule of xenon oxytetrafluoride, add the number of valence electrons of each individual atom that makes up the molecule.
So, xenon oxytetrafluoride will have a total of
42 valence electrons 8 valence electrons are coming from the xenon atom 6 valence electrons are coming from the oxygen atom 7 valence electrons from each of the four fluorine atoms.
Now, xenon will be the central atom. It will bond with the oxygen atom via a double bond. This will ensure that oxygen has a complete octet.
The xenon atom will bond with the four fluorine atoms via four single bonds, which will ensure that each of the four fluorine atoms gets a complete octet. Afterwards the xenon atom will make double bond with oxygen atom to fulfill its octet. The remaining two electrons will remain as a lone pair.
Which of the following is/are correct among the following?i. XeF2 = sp3d, linear
ii. XeF4 = sp3, square planar
iii. XeO4 = sp3, tetrahedral
iv. XeF6 = sp3d2, octahedral- a)ii and ii
- b)i and iii
- c)i, ii and iii
- d)Only iii
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are correct among the following?
i. XeF2 = sp3d, linear
ii. XeF4 = sp3, square planar
iii. XeO4 = sp3, tetrahedral
iv. XeF6 = sp3d2, octahedral
ii. XeF4 = sp3, square planar
iii. XeO4 = sp3, tetrahedral
iv. XeF6 = sp3d2, octahedral
a)
ii and ii
b)
i and iii
c)
i, ii and iii
d)
Only iii

|
Amar Jain answered |
Hybridisation of the compounds are
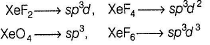
Which one of the following has a linear shape?- a)XeF4
- b)XeF2
- c)XeO3
- d)XeOF4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following has a linear shape?
a)
XeF4
b)
XeF2
c)
XeO3
d)
XeOF4
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Xe has an electronic configuration of 5s25p6
In XeF2, there are two bonding pairs and three lone pairs of electrons. So acc. to VSEPR theory, the structure would be trigonal bipyramidal to avoid electron pair repulsions.(sp3d)
In XeF4, the structure would be square planar. There are four pairs of bonding electrons and two lone pairs in the molecule. The hybridisation would be sp3d2
XeOF4 has an octahedral geometry due to sp3d2 hybridization. One trans position is occupied by a lone pair giving pyramid shape to the molecule.
Thus XeF2 has sp3d hybridization.
In XeF2, there are two bonding pairs and three lone pairs of electrons. So acc. to VSEPR theory, the structure would be trigonal bipyramidal to avoid electron pair repulsions.(sp3d)
In XeF4, the structure would be square planar. There are four pairs of bonding electrons and two lone pairs in the molecule. The hybridisation would be sp3d2
XeOF4 has an octahedral geometry due to sp3d2 hybridization. One trans position is occupied by a lone pair giving pyramid shape to the molecule.
Thus XeF2 has sp3d hybridization.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1- 10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Regarding the properties of hydrogen halides, which is wrong order?- a)Melting point order HI> HF > HBr > HCI
- b)Boiling point order HF > HI > HBr > HC
- c)Acidic nature HI > HBr > HCI > HF
- d)Percentage of ionic character HF > HI > HBr > HCI
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1- 10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Regarding the properties of hydrogen halides, which is wrong order?
a)
Melting point order HI> HF > HBr > HCI
b)
Boiling point order HF > HI > HBr > HC
c)
Acidic nature HI > HBr > HCI > HF
d)
Percentage of ionic character HF > HI > HBr > HCI
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct order of % of ionic character is
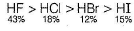
The number of covalent bonds present in H2SO5.
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of covalent bonds present in H2SO5.
|
|
Sounak Mukherjee answered |
H2SO5 (peroxomonosulphuric acid)
It has nine covalent bonds.
It has nine covalent bonds.
Which of the following is wrong statement?- a)Dissolution of H2SO4 in H2O is exothermic
- b)H2SO4 is volatile liquid
- c)In SO2 and SO3, hybridisation of S is same agent
- d) H2SO4 is drying and dehydrating agent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is wrong statement?
a)
Dissolution of H2SO4 in H2O is exothermic
b)
H2SO4 is volatile liquid
c)
In SO2 and SO3, hybridisation of S is same agent
d)
H2SO4 is drying and dehydrating agent

|
Bhavana Banerjee answered |
The chemical reaction of H2SO4 as a result of its low volatility, strong acidic character, stiong affinity for water and ability to act as an oxidising agent.
When chlorine reacts with hot, cone. NaOH, the products formed are- a)NaCI
- b)NaOCI
- c)NaCIO3
- d)HCI
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
When chlorine reacts with hot, cone. NaOH, the products formed are
a)
NaCI
b)
NaOCI
c)
NaCIO3
d)
HCI

|
Anupama Nair answered |
When Cl2 reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH, then....6NaOH+3Cl2→5NaCl +NaClO3+3H2O...When Cl2 reacts with cold and dilute NaOH then ...2NaOH+Cl2→NaCl+NaOCl+H2O
Which pair is isostructural?- a)
- b)CO2 and OCS
- c)SO2 and CS2
- d)
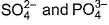
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which pair is isostructural?
a)
b)
CO2 and OCS
c)
SO2 and CS2
d)

|
C.k Singh answered |
In option B co2 and OCS has Sp2 hybridisation for the central atom.in option D Sp3 hybridisation for the central atom.
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below

- a)

- b)

- c)
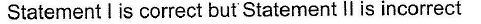
- d)
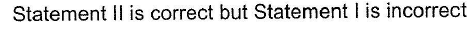
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below

This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
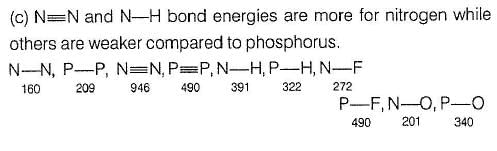
Pranjal Pillai answered |
P — P single bond in P4 molecule is much weaker
(213 kJ mol-1) than N ≡ N triple bond (941.4 kJ mol-1) in N2.
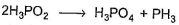 in this equivalent weight of the acid in the reactant side is obtained by dividing molecular weight with
in this equivalent weight of the acid in the reactant side is obtained by dividing molecular weight with
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Abc Bcd answered |
Because there are two molecules of acid in balanced equation.
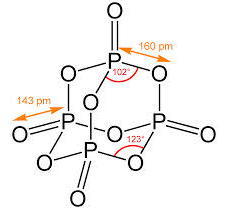
In a molecule of phosphorus (V) oxide, there are- a)4P-P, 10 P –O and 4P = O bonds
- b)12P–O, and 4P = O bonds
- c)2P–O and 4P = P bonds
- d)6P–P, 12P–O and 4P = P bonds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a molecule of phosphorus (V) oxide, there are
a)
4P-P, 10 P –O and 4P = O bonds
b)
12P–O, and 4P = O bonds
c)
2P–O and 4P = P bonds
d)
6P–P, 12P–O and 4P = P bonds

|
Gauri Khanna answered |
As can be seen from the image, it contains 12 P-O bonds and 4P=O bonds.

Chapter doubts & questions for p-Block Elements - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of p-Block Elements - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup