All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Hydrocarbons for NEET Exam
The most stable free radical among the following Is- a)
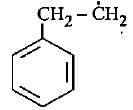
- b)

- c)
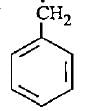
- d)
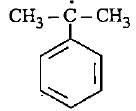
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most stable free radical among the following Is
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Muskan Sharma answered |
In option D there is 6 alpha - H is present where as in option A only 2 alpha - H, option B 3 alpha - H and option C no alpha - H is present. This is because of hyperconjugation, more alpha - H more stability therefore option D is more stable.
How many different isomeric alkynes on catalytic hydrogenation gives the same 3-ethyl hexane?- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many different isomeric alkynes on catalytic hydrogenation gives the same 3-ethyl hexane?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
6
|
|
Divya Menon answered |
Isomeric Alkynes and Catalytic Hydrogenation
Concept: Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. Alkynes are hydrocarbons having at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms. Catalytic hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated organic compound in the presence of a catalyst. Catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes involves the addition of two hydrogen atoms across the triple bond, resulting in an alkane.
Explanation:
The given compound is 3-ethylhexane. The molecular formula of 3-ethylhexane is C8H18. The possible isomeric alkynes of C8H18 are:
1. Octyne-1
2. Octyne-2
3. Octyne-3
4. Octyne-4
5. Octyne-5
6. Octyne-6
Catalytic hydrogenation of octyne-1 and octyne-5 would result in the formation of the same product, i.e., 3-ethylhexane. Similarly, catalytic hydrogenation of octyne-2 and octyne-4 would also result in the formation of 3-ethylhexane. However, catalytic hydrogenation of octyne-3 and octyne-6 would result in the formation of different products.
Therefore, the total number of different isomeric alkynes that on catalytic hydrogenation gives the same 3-ethylhexane is 4.
Answer: The correct option is (C) 4.
Concept: Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. Alkynes are hydrocarbons having at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms. Catalytic hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated organic compound in the presence of a catalyst. Catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes involves the addition of two hydrogen atoms across the triple bond, resulting in an alkane.
Explanation:
The given compound is 3-ethylhexane. The molecular formula of 3-ethylhexane is C8H18. The possible isomeric alkynes of C8H18 are:
1. Octyne-1
2. Octyne-2
3. Octyne-3
4. Octyne-4
5. Octyne-5
6. Octyne-6
Catalytic hydrogenation of octyne-1 and octyne-5 would result in the formation of the same product, i.e., 3-ethylhexane. Similarly, catalytic hydrogenation of octyne-2 and octyne-4 would also result in the formation of 3-ethylhexane. However, catalytic hydrogenation of octyne-3 and octyne-6 would result in the formation of different products.
Therefore, the total number of different isomeric alkynes that on catalytic hydrogenation gives the same 3-ethylhexane is 4.
Answer: The correct option is (C) 4.
Which of the following statements correctly describes the general reactivity of alkynes?- a)Alkynes are more reactive than alkenes
- b)Alkynes reacts as an electrophile
- c)Unlike alkenes, alkynes do not undergo electrophilic addition reaction
- d)An alkene is electron rich molecule, therefore react as a nucleophile
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the general reactivity of alkynes?
a)
Alkynes are more reactive than alkenes
b)
Alkynes reacts as an electrophile
c)
Unlike alkenes, alkynes do not undergo electrophilic addition reaction
d)
An alkene is electron rich molecule, therefore react as a nucleophile
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
The correct answer is option D
The clouds of electrons surrounding the sigma bond makes an alkyne an electron-rich molecule. They are therefore nucleophiles that react with electrophiles. Thus alkynes, like alkenes, undergo electrophilic addition reactions because of their weak pi bonds. When a proton adds to an alkyne, a vinylic cation is formed.
The clouds of electrons surrounding the sigma bond makes an alkyne an electron-rich molecule. They are therefore nucleophiles that react with electrophiles. Thus alkynes, like alkenes, undergo electrophilic addition reactions because of their weak pi bonds. When a proton adds to an alkyne, a vinylic cation is formed.
What is the major bromination product in the following reaction? 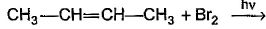
- a)
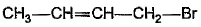
- b)
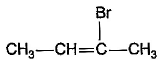
- c)
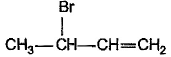
- d)
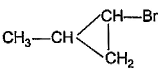
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the major bromination product in the following reaction?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The correct answer is option c
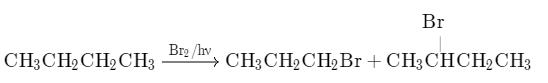
Thus, a racemic mixture is obtained. A racemic mixture is one that has an equal amount of left and right handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule.
Thus, a racemic mixture is obtained. A racemic mixture is one that has an equal amount of left and right handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule.
If 3-methyl-2-pentanol is heated with concentrated H2SO4 , in principle how many different alkenes result?
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
If 3-methyl-2-pentanol is heated with concentrated H2SO4 , in principle how many different alkenes result?
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
- methyl 1 pentene
- 3 methyl 2 butene
- 2 ethyl 1 butene
Hence 3 is the correct answer.
In which of the following reactions, reactants and products are correctly matched ?- a)
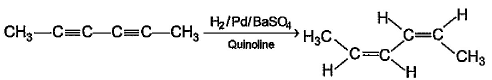
- b)
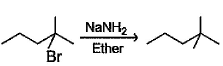
- c)
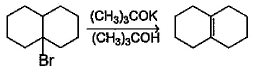
- d)
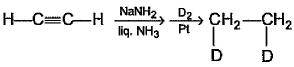
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following reactions, reactants and products are correctly matched ?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The correct answer is option A,B
With H2/Pd−BaSO4, cis hydrogenation will take place at both triple bonds.
With NaNH2, Sytzeff's elimination product will be the major one
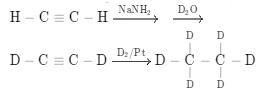
(A) Cis addition of hydrogen
(B) Carbanion is more stable at secondary carbon so Saytzeff's elimination product will form.
(C) Carbanion should form at secondary carbon but given product is formed from tertiary unstable carbanion carbon so this is not possible.
(D) Complete reduction of alkyne to alkane in Pt reduction
With H2/Pd−BaSO4, cis hydrogenation will take place at both triple bonds.
With NaNH2, Sytzeff's elimination product will be the major one

(A) Cis addition of hydrogen
(B) Carbanion is more stable at secondary carbon so Saytzeff's elimination product will form.
(C) Carbanion should form at secondary carbon but given product is formed from tertiary unstable carbanion carbon so this is not possible.
(D) Complete reduction of alkyne to alkane in Pt reduction
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group
- a)Isocyanide
- b)Isocyano
- c)Carboxyl
- d)Carbonyl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group
a)
Isocyanide
b)
Isocyano
c)
Carboxyl
d)
Carbonyl
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Isocyanide is a compound and it is not a functional group.
What is true about the compound calicene?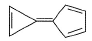
- a)It is highly soluble in water
- b)It exists mainly as dipolar ion with +ve charge in the three membered ring while -ve charge in five membered ring
- c)It exists mainly as dipolar ion with -ve charge in the three membered ring and +ve charge in five membered ring
- d)In solution it shows very high electrical conductivity
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true about the compound calicene?
a)
It is highly soluble in water
b)
It exists mainly as dipolar ion with +ve charge in the three membered ring while -ve charge in five membered ring
c)
It exists mainly as dipolar ion with -ve charge in the three membered ring and +ve charge in five membered ring
d)
In solution it shows very high electrical conductivity
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
- In calicene, the electrons move towared the five-membered ring because both rings are aromatic in the resonance contributor that has a negative charge on a carbon of the five-membered ring and a positive charge on a carbon of the three-membered ring
- It is highly soluble in water and in solution it shows very high electrical conductivity
So, Option C is not correct and other Options are Correct.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 18) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
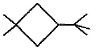
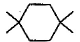
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (cj and (d).PassageA hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.Q. Which of the following satisfy the criteria of X ?- a)
- b)
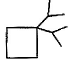
- c)
- d)
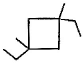
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 18) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (cj and (d).
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (cj and (d).
Passage
A hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.
Q. Which of the following satisfy the criteria of X ?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
In option c, there are only two different position which can be chlorinated,
So, option c is correct.
So, option c is correct.
Propene on ozonolysis forms:- a)Acetaldehyde
- b)Formaldehyde
- c)Both acetaldehyde and formaldehyde
- d)Acetone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Propene on ozonolysis forms:
a)
Acetaldehyde
b)
Formaldehyde
c)
Both acetaldehyde and formaldehyde
d)
Acetone
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
When propene on ozonolysis it yields a new structure called ozonide
and there cleavage takes place and it yields two products namely
1.acetaldehyde
2.formaldehyde
and there cleavage takes place and it yields two products namely
1.acetaldehyde
2.formaldehyde
When vicinal dibromide is heated with KOH in ethanol (~ 200°C), double dehydrohalogenation takes place giving alkyne. Which of the following fails to give alkyne according to this procedure?- a)
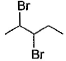
- b)
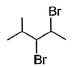
- c)
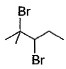
- d)
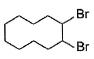
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When vicinal dibromide is heated with KOH in ethanol (~ 200°C), double dehydrohalogenation takes place giving alkyne. Which of the following fails to give alkyne according to this procedure?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The correct answer is option C
CH³)²BrC*–CHBr–CH²–CH³
C* has no H attached to it hence the next Bromine cannot perform dehydrohalogenation using this Carbon. Therefore, triple bond formation is not possible in this compound.
CH³)²BrC*–CHBr–CH²–CH³
C* has no H attached to it hence the next Bromine cannot perform dehydrohalogenation using this Carbon. Therefore, triple bond formation is not possible in this compound.
How many different heptenes result by partial hydrogenation of all possible, unbranched heptynes?
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
How many different heptenes result by partial hydrogenation of all possible, unbranched heptynes?
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The correct answer is 5.
C=C-C-C-C-C-C , no geometrical isomerism so 1
C-C=C-C-C-C-C 2 , geometrical cis trans
C-C-C=C-C-C-C , cis trans again so 2
∴ 2+2+1=5
C=C-C-C-C-C-C , no geometrical isomerism so 1
C-C=C-C-C-C-C 2 , geometrical cis trans
C-C-C=C-C-C-C , cis trans again so 2
∴ 2+2+1=5
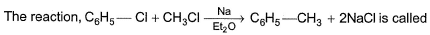
- a)Fittig reaction
- b)Wurtz’s-Fittig reaction
- c)Ullmann reaction
- d)Wurtz’s reaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Fittig reaction
b)
Wurtz’s-Fittig reaction
c)
Ullmann reaction
d)
Wurtz’s reaction
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is option B
Wurtz - Fittig reaction:
Aryl halide and alkyl halide couple in presence of sodium metal / dry ether to form alkyl benzene.
For example, bromobenzene reacts with methyl bromide in presence of sodium. dry ether to form toluene.
C6H6 - Br + CH3 - Br + 2Na(dry ether)------> C6H5 - CH3 + 2NaBr
Wurtz - Fittig reaction:
Aryl halide and alkyl halide couple in presence of sodium metal / dry ether to form alkyl benzene.
For example, bromobenzene reacts with methyl bromide in presence of sodium. dry ether to form toluene.
C6H6 - Br + CH3 - Br + 2Na(dry ether)------> C6H5 - CH3 + 2NaBr
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of polarity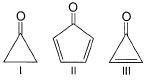
- a)I < II < III
- b)III < II < I
- c)II < I < III
- d)III < I < II
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of polarity
a)
I < II < III
b)
III < II < I
c)
II < I < III
d)
III < I < II
|
|
Om Desai answered |
In case 1, the bond is broken in oxygen’s favor and it will attain its octet. Also, carbon becomes sp2 hybridized, so there is a chance of polarity.
In case 2, if the bond is broken in favor of oxygen, then the ring will become anti-aromatic which is highly unstable and the bond won’t be broken in that way. If the bond is broken in favor of carbon in the ring, then although the ring becomes aromatic but oxygen will bear +ve charge which is very unstable. So, there is no chance to break the bond.
In case 3, if the double bond is broken in favor of oxygen, then oxygen will acquire a negative charge and the ring will become aromatic. So, it is a highly favorable case of double bond breaking.
Therefore, the order of polarity: - III>I>II
In case 2, if the bond is broken in favor of oxygen, then the ring will become anti-aromatic which is highly unstable and the bond won’t be broken in that way. If the bond is broken in favor of carbon in the ring, then although the ring becomes aromatic but oxygen will bear +ve charge which is very unstable. So, there is no chance to break the bond.
In case 3, if the double bond is broken in favor of oxygen, then oxygen will acquire a negative charge and the ring will become aromatic. So, it is a highly favorable case of double bond breaking.
Therefore, the order of polarity: - III>I>II
What is the minimum number of carbon atoms of an alkane must have to form an isomer?- a)4
- b)3
- c)2
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the minimum number of carbon atoms of an alkane must have to form an isomer?
a)
4
b)
3
c)
2
d)
1
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
An alkane with minimum four carbon atoms can show isomerism.
Out of the following compounds , which will be have a zero dipole moment.- a)1,1 - dichloroethylene
- b)cis-1,2-dichlorethylene
- c)trans-1,2-dichlorethylene
- d)none of these.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of the following compounds , which will be have a zero dipole moment.
a)
1,1 - dichloroethylene
b)
cis-1,2-dichlorethylene
c)
trans-1,2-dichlorethylene
d)
none of these.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In case of trans-1,2-dichloroethylene
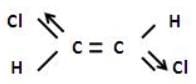
The net dipole moment is zero but in case of cis -1,2 -dicholorethylene.
There is some resultant dipole moment.
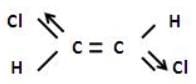
The net dipole moment is zero but in case of cis -1,2 -dicholorethylene.
There is some resultant dipole moment.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. How many different alkenes are formed when 2 -chlorobutane is treated with ethanolic solution of KOH?
- a)1
- b)3
- c)2
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. How many different alkenes are formed when 2 -chlorobutane is treated with ethanolic solution of KOH?
a)
1
b)
3
c)
2
d)
4
|
|
Arya Dasgupta answered |
The reaction of 2-chlorobutane with ethanolic solution of KOH is an example of an elimination reaction known as dehydrohalogenation. In this reaction, a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom are removed from adjacent carbon atoms to form a double bond.
The possible alkenes that can be formed are:
1. Butene
2. But-2-ene
3. But-1-ene
4. Isobutene
The number of different alkenes formed depends on the position of the double bond. In the case of 2-chlorobutane, the chlorine atom is attached to the second carbon atom, so the double bond can form between the first and second carbon atoms or between the second and third carbon atoms.
Hence, the correct answer is option (b) 2.
The possible alkenes that can be formed are:
1. Butene
2. But-2-ene
3. But-1-ene
4. Isobutene
The number of different alkenes formed depends on the position of the double bond. In the case of 2-chlorobutane, the chlorine atom is attached to the second carbon atom, so the double bond can form between the first and second carbon atoms or between the second and third carbon atoms.
Hence, the correct answer is option (b) 2.
Direction (Q, Nos. 13 - 16) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.Q.Statement I : 2-butyne on reduction with Pd/CaCO3 gives c/s-2-butene.
Statement II : Hydrogenation proceed through adsorption mechanism.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q, Nos. 13 - 16) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : 2-butyne on reduction with Pd/CaCO3 gives c/s-2-butene.
Statement II : Hydrogenation proceed through adsorption mechanism.
Statement II : Hydrogenation proceed through adsorption mechanism.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
A Lindlar catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst that consists of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate or barium sulphate which is then poisoned with various forms of lead or sulphur. It is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to cis alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes) When the triple bond is (2-butyne) hydrogenated over the Lindlar’s catalyst i.e.Pd/CaCO3
it gives predominantly cis alkene(2-butene).
it gives predominantly cis alkene(2-butene).
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 -15) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. In the following free radical bromination reaction, the im portant product(s) is/are
- a)
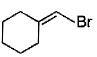
- b)
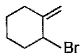
- c)
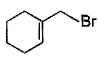
- d)
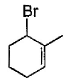
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 -15) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. In the following free radical bromination reaction, the im portant product(s) is/are
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
This is the case of allylic substitution. The radical will delocalise itself to two locations. And so, we will get two different positions for radical substitution.

There is also a possibility at C6, but it is not in our option.

There is also a possibility at C6, but it is not in our option.
Ethylene reacts with HBr to give:- a)Acetylene
- b)Ethyl alcohol
- c)Acetaldehyde
- d)Ethyl bromide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethylene reacts with HBr to give:
a)
Acetylene
b)
Ethyl alcohol
c)
Acetaldehyde
d)
Ethyl bromide
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Ethylene reacts with HBr to form Ethyl bromide. The reaction propagates as follow:-
H2C=CH2 + HBr → H2C+-CH3 →H2BrC-CH3
Since π cloud is electron rich, so HBr dissociates into H+ and Br-. H+ attacks on alkene to give a carbocation and then Br- attacks to get ethyl bromide.
H2C=CH2 + HBr → H2C+-CH3 →H2BrC-CH3
Since π cloud is electron rich, so HBr dissociates into H+ and Br-. H+ attacks on alkene to give a carbocation and then Br- attacks to get ethyl bromide.
Ethene and ethyne can be distinguished by:- a)Bromine water
- b)KMnO4 solution
- c)Ammoniacal Cuprous chloride solution
- d)Any of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethene and ethyne can be distinguished by:
a)
Bromine water
b)
KMnO4 solution
c)
Ammoniacal Cuprous chloride solution
d)
Any of the above
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The two hydrocarbons can be easily distinguished by simple chemical tests, as ethyne molecule is supposed to have acidic hydrogen.
1. When ethyne is bubbled through ammoniacal silver nitrate solution , a yellow-white precipitate of silver acetylide would be formed.
C2H2 + 2AgNO3 = Ag2C2 + 2HNO3
2. Similarly, ethyne forms a red precipitate of copper acetylide (Cu2C2) when it is passed through ammoniacal cuprous chloride solution.
Ethene does not react with AgNO3 or Cu2Cl2 solution.
Direction (Q. Nos. 17 - 20) This section contains 4 questions. When worked o u t wili result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. If 3-bromo-4-methyl hexane is treated with ethanolic KOH solution, how many different alkenes would be formed?
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17 - 20) This section contains 4 questions. When worked o u t wili result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. If 3-bromo-4-methyl hexane is treated with ethanolic KOH solution, how many different alkenes would be formed?
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
2 is the right answer.
Alcoholic KOH causes dehydrohalogenation reaction i.e. elimination reaction.
The increasing order of electron donating inductive effect of alkyl groups is- a)- H < - CH3 < - C2H5 < - C3H7
- b)- H > - CH3 > - C2H5 > - C3H7
- c)- H < - C2H5 < - CH3 < - C3H7
- d)-H>-C2H5>-CH3>-C3H7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The increasing order of electron donating inductive effect of alkyl groups is
a)
- H < - CH3 < - C2H5 < - C3H7
b)
- H > - CH3 > - C2H5 > - C3H7
c)
- H < - C2H5 < - CH3 < - C3H7
d)
-H>-C2H5>-CH3>-C3H7
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The order of +I effect of alkyl group is given as
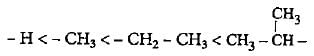
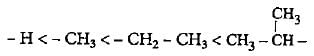
Which of the following reactions can bring about chlorination of cyclohexane?- a)
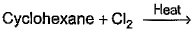
- b)
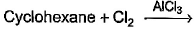
- c)
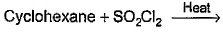
- d)
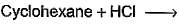
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions can bring about chlorination of cyclohexane?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
For SO2Cl2: The reactivity patterns of SO2Cl2 and SOCl2 are quite different. SOCl2 is a good electrophile, and can be thought of as a source of Cl− ions. These ions can go on to react in their typical nucleophilic fashion. SO2Cl2 however is often a Cl2 source, as it readily decomposes giving off sulfur dioxide. Usually, much easier/safer to use this than measuring out (and getting into solution) chlorine gas. The chlorination of simple alkanes by Cl2 gas (or something that makes it in solution) happens by a radical mechanism i.e. Cl⋅ not Cl
For Cl2 and heat/light:
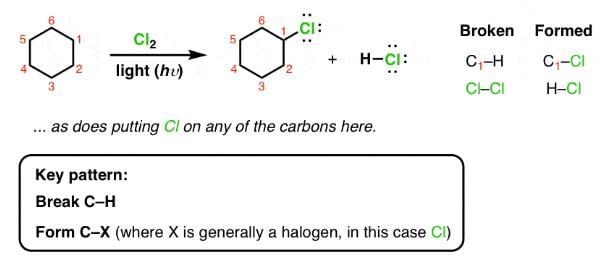
For Cl2 and heat/light:

For Cl with AlCl3: It is used for chlorination of compounds like benzene
For HCl: It is used for halogenations of a double bond.
For HCl: It is used for halogenations of a double bond.
Cis isomer have:- a)High boiling point than trans isomer
- b)Lower boiling point than trans isomer
- c)Same boiling point
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cis isomer have:
a)
High boiling point than trans isomer
b)
Lower boiling point than trans isomer
c)
Same boiling point
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The cis isomer in this case has a boiling point of 60.3 degC, while the trans isomer has a boiling point of 47.5 degC. In the cis isomer the two polar C-Cl bond dipole moments combine to give an overall molecular dipole, so that there are intermolecular dipole–dipole forces (or Keesom forces), which add to the London.
Which among these is not a structural isomer of the compound C4H8?- a)But-1-ene
- b)But-2-ene
- c)But-3-ene
- d)2-methylpropene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among these is not a structural isomer of the compound C4H8?
a)
But-1-ene
b)
But-2-ene
c)
But-3-ene
d)
2-methylpropene

|
Saqib Shabir answered |
The answer is c. But-3-ene. But-3-ene is not a structural isomer of C4H8 because it is the same molecule as But-1-ene, just numbered differently. The structural isomers of C4H8 are But-1-ene, But-2-ene, and 2-methylpropene. But-1-ene and But-2-ene are position isomers, differing in the position of the double bond. 2-methylpropene is a branched isomer. But-3-ene is not a distinct isomer because the numbering of the carbon chain starts from the end closest to the double bond, making it identical to But-1-ene.
How many monobromo derivatives exists for anthracene?
- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many monobromo derivatives exists for anthracene?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
5
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
There are 3 monobromo derivatives exists for anthracene:
1-Chloroanthracene
2-Chloroanthracene
and 9-Chloroanthracene
1-Chloroanthracene
2-Chloroanthracene
and 9-Chloroanthracene
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. How many distinct alkynes exist for C6H10 which gives effervescence on heating with Na?- a)5
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. How many distinct alkynes exist for C6H10 which gives effervescence on heating with Na?
a)
5
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Upasana Bose answered |
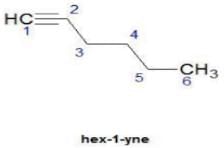
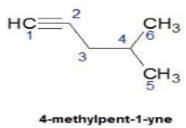
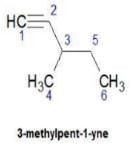
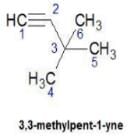
Hence D
The correct statement(s) regarding 1,2-butadiene(l) and 1,3-butadiene, (II) is/are- a)I has perpendicular pi planes while II has parallel pi planes
- b)Both gives the same product on adding 1.0 equivalent at HBr of -80° C
- c)I gives 2, 2-dibromobutane while II gives 2, 3-dibromobutane, when reacted with excess of HBr at very low temperature
- d)Both have same length of C = C double bonds
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement(s) regarding 1,2-butadiene(l) and 1,3-butadiene, (II) is/are
a)
I has perpendicular pi planes while II has parallel pi planes
b)
Both gives the same product on adding 1.0 equivalent at HBr of -80° C
c)
I gives 2, 2-dibromobutane while II gives 2, 3-dibromobutane, when reacted with excess of HBr at very low temperature
d)
Both have same length of C = C double bonds
|
|
Vivek answered |
Adjacent hybrid orbitals are perpendicular to each other irrespective of the type of the hybridization. In 1,2-butadiene, adjacent 2× bonds are perpendicular to each other while in 1,3-butadiene, 2× bond and
1× bond are adjacent to each other and the compound is a straight chain, so, the single bone and a double bond are perpendicular to each other and this is true for both the pairs of single and double bonds. Thus , both the pi orbitals in 1,3-butadiene are parallel to each other.
I hope it helps. If u still have any doubt, u can discuss with me.
1× bond are adjacent to each other and the compound is a straight chain, so, the single bone and a double bond are perpendicular to each other and this is true for both the pairs of single and double bonds. Thus , both the pi orbitals in 1,3-butadiene are parallel to each other.
I hope it helps. If u still have any doubt, u can discuss with me.
Arrange the halogens F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 in order of their increasing reactivity with alkanes.- a)I2 < Br2 < Cl2 < F2
- b)Br2 < Cl2 < F2 < I2
- c)F2 < Cl2 < Br2 < I2
- d)Br2 < I2 < Cl2 < F2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the halogens F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 in order of their increasing reactivity with alkanes.
a)
I2 < Br2 < Cl2 < F2
b)
Br2 < Cl2 < F2 < I2
c)
F2 < Cl2 < Br2 < I2
d)
Br2 < I2 < Cl2 < F2
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Since reactivity decreases down the group as the electronegativity of the halogen decreases down the group. Thus, rate of reaction of alkanes with halogens is
I2 < Br2 < Cl2 <F2
Since reactivity decreases down the group as the electronegativity of the halogen decreases down the group. Thus, rate of reaction of alkanes with halogens is
I2 < Br2 < Cl2 <F2
Consider the following reaction sequence. The correct statement(s) regarding diois formed in the final step is/are
The correct statement(s) regarding diois formed in the final step is/are - a)Three different diois are formed
- b)One pair of diastereomers is formed
- c)Two enantiomers are formed
- d)Product is optically inactive
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction sequence.
The correct statement(s) regarding diois formed in the final step is/are
a)
Three different diois are formed
b)
One pair of diastereomers is formed
c)
Two enantiomers are formed
d)
Product is optically inactive
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answers are Options A and C.

Consider the following bromides :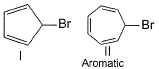
- a)Both decomposes to form
- b)Both decomposes to forms Br+
- c)I decomposes to give
 and II gives Br+
and II gives Br+ - d)I decomposes to give Br+ while II gives
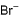
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following bromides :
a)
Both decomposes to form 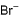
b)
Both decomposes to forms Br+
c)
I decomposes to give 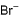 and II gives Br+
and II gives Br+
d)
I decomposes to give Br+ while II gives 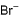
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
In the compound I, Br will dispatch as Br+ so that a -ve charge appears on carbon which will give us 6π electrons. So ring will become aromatic.(4n+2 π electron is needed for aromaticity)
In compound II, Br will dispatch as Br-. So that carbon has +ve charge and all the double bond will circulate in the ring. This will maintain 4n+2 π electron and the molecule will remain as aromatic.
In compound II, Br will dispatch as Br-. So that carbon has +ve charge and all the double bond will circulate in the ring. This will maintain 4n+2 π electron and the molecule will remain as aromatic.
Which of the following is not a possible termination step in the free radical chlorination of methane?- a)
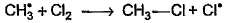
- b)

- c)
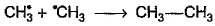
- d)
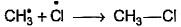
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a possible termination step in the free radical chlorination of methane?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Lohit Matani answered |
Termination is the last step. So there shouldn't be any free radical atom remaining. In first option there is Cl• remaining it can't be termination step.The steps in free radical halogenation are as
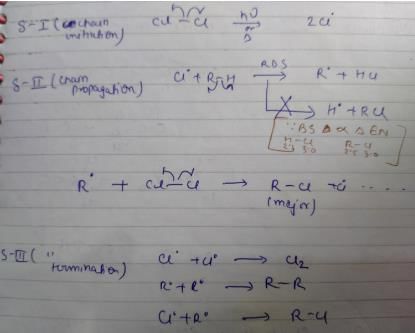
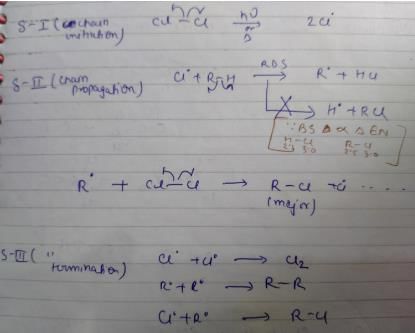
Direction (Q. Nos, 19 - 22) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. How many different isomers of alkenes {including stereoisomers) exist that all upon catalytic hydrogenation adds one mole of H2 to give the same 2, 2, 3,5-tetramethyl hexane?
Correct answer is '7'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos, 19 - 22) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. How many different isomers of alkenes {including stereoisomers) exist that all upon catalytic hydrogenation adds one mole of H2 to give the same 2, 2, 3,5-tetramethyl hexane?

|
Ashish Mishra answered |
7 is correct.
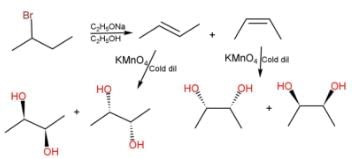
If 4-methyl cyclopentene is treated with OsO4 followed by work-up with NaHSO3/H2O, how many different diols would result?
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
If 4-methyl cyclopentene is treated with OsO4 followed by work-up with NaHSO3/H2O, how many different diols would result?
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Since, OsO4 + NaHSO4/H2O syn hydroxylation, so two products can be obtained.
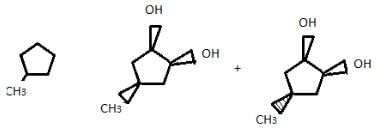

Addition of halogens to alkenes is an example of:- a)Nucleophilic addition reaction
- b)Electrophilic addition reaction
- c)Electrophilic substitution reaction
- d)Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Addition of halogens to alkenes is an example of:
a)
Nucleophilic addition reaction
b)
Electrophilic addition reaction
c)
Electrophilic substitution reaction
d)
Nucleophilic substitution reaction

|
Avantika Chakraborty answered |
Halogens can act as electrophiles to attack a double bond in alkene. Double bond represents a region of electron density and therefore functions as a nucleophile.
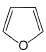
Select the species which is not aromatic.- a)
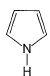
- b)
- c)
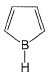
- d)
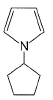
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the species which is not aromatic.
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
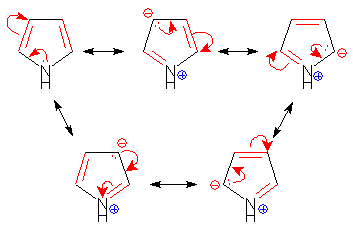
Here, we can see that Nitrogen gave its lone pair to make the system aromatic. The same case happens with option b and d. But with option c, Boron is not having any lone pair to donate. So option c is correct answer
A hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.Q. How many different alkenes on hydrogenation, can gives X ?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.
Q. How many different alkenes on hydrogenation, can gives X ?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
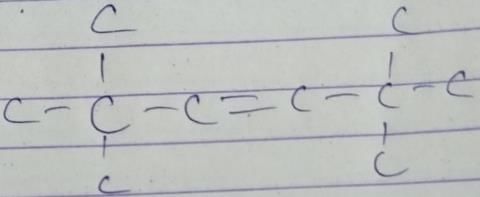
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. When light is shined on a mixture of chlorine and ethane, chloroethane is formed besides dichloroethane, trichloroethane and several other products. What reaction condition can optimise the yield of chloroethane?- a)Higher reaction temperature
- b)High concentration of chlorine gas
- c)Excess of ethane reactan
- d)Low reaction temperature
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. When light is shined on a mixture of chlorine and ethane, chloroethane is formed besides dichloroethane, trichloroethane and several other products. What reaction condition can optimise the yield of chloroethane?
a)
Higher reaction temperature
b)
High concentration of chlorine gas
c)
Excess of ethane reactan
d)
Low reaction temperature
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
When chlorine and Ethane are taken with chlorine in excess only then we have more than one product like chloroethane, dichloroethane, trichloroethane etc. To avoid this we should take Ethane in excess because when we will take it then in excess then we will have only single time chlorination and we will get monochloroethane.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Consider the following transformations.
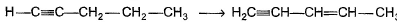
Q. Which reaction sequence will bent bring about the above transformation?
- A:
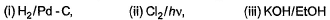
- B:
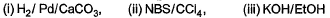
- C:
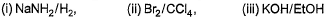
- D:
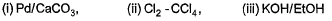
The answer is b.
Consider the following transformations.
Q. Which reaction sequence will bent bring about the above transformation?
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
we get H-CH=C-CH2-CH2-CH3
H-CH=C-CH2-CH2-CH3 + NBS/CCl4 → H-CH=C-CHCl-CH2-CH3 (NBS adds Br to carbon at next alternate to double bond)
H-CH=C-CHCl-CH2-CH3 + KOH/EtOH → H2C=C-CH=CH-CH3
(by E2 elimination)
The halogen which is most reactive in the halogenation of alkanes under sunlight is:- a)Iodine
- b)Chlorine
- c)Fluorine
- d)Bromine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The halogen which is most reactive in the halogenation of alkanes under sunlight is:
a)
Iodine
b)
Chlorine
c)
Fluorine
d)
Bromine
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The halogen which is most reactive in the halogenation of alkanes under sunlight is Chlorine.
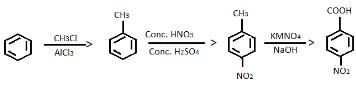
Provide the appropriate sequence of reagents that can bring about the following transformation.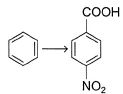
- a)CH3CI/AICI3 then conc.HNO3/conc.H2SO4 then KMnO4/NaOH
- b)cone. HNO3 /conc.H2SO4 then CH3CI/AICI3 then KMnO4/NaOH
- c)CH3CI/AICI3 then KMnO4/NaOH then conc.HNO3/conc.H2SO4
- d)conc.H2SO4 /conc.HNO3 then CH3COCI/AICI3 then KMnO4/NaOH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Provide the appropriate sequence of reagents that can bring about the following transformation.
a)
CH3CI/AICI3 then conc.HNO3/conc.H2SO4 then KMnO4/NaOH
b)
cone. HNO3 /conc.H2SO4 then CH3CI/AICI3 then KMnO4/NaOH
c)
CH3CI/AICI3 then KMnO4/NaOH then conc.HNO3/conc.H2SO4
d)
conc.H2SO4 /conc.HNO3 then CH3COCI/AICI3 then KMnO4/NaOH
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option A.

Which of the following is a false statement?- a)Free radicals, carbonium ions or carbanions are reaction intermediates
- b)Reaction between methane and chlorine in presence of sunlight proceeds via free radical
- c)The electronegative atom in the carbon chain produces +I effect
- d)Homolytlc fission of C - C bonds gives free radicals
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a false statement?
a)
Free radicals, carbonium ions or carbanions are reaction intermediates
b)
Reaction between methane and chlorine in presence of sunlight proceeds via free radical
c)
The electronegative atom in the carbon chain produces +I effect
d)
Homolytlc fission of C - C bonds gives free radicals
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The electronegative atom in the carbon chain produces -I effect.
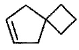
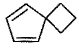
What is the major dehydration product in the following reaction ?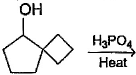
- a)

- b)
- c)
- d)
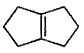
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the major dehydration product in the following reaction ?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
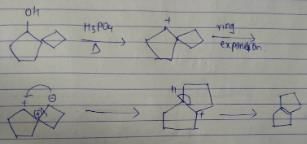
Note that H2SO4, H3PO4 and KHSO4 are dehydrating agents with rearrangement possible. While P2O5, P4O10, ThO2, POCl3 and Al2O3 are dehydrating agents without any possibility of rearrangement.
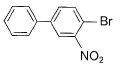
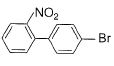
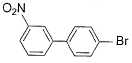
What is major product of the reaction below?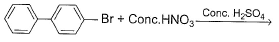
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is major product of the reaction below?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The correct answer is option D


During free radical bromination of isobutane, an alkene is produced as by product via disproportionation of the intermediate alkyl free radical. What is this alkene?- a)1-butene
- b)2-butene
- c)2-methyl propene
- d)Both ‘b’ and ‘c’
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During free radical bromination of isobutane, an alkene is produced as by product via disproportionation of the intermediate alkyl free radical. What is this alkene?
a)
1-butene
b)
2-butene
c)
2-methyl propene
d)
Both ‘b’ and ‘c’

|
Aquib Anwer answered |
3
Which of the following statem ents regarding free radical halogenation o f alkane is not true?- a)Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in the propagation step is exothermic in both chlorination and bromination
- b)Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in propagation step is exothermic in chlorination but endothermic in bromination
- c)A single halogen radical may bring about halogenation of thousands of alkane molecules
- d)Continuous source of energy is required to continue the free radical halogenation reaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statem ents regarding free radical halogenation o f alkane is not true?
a)
Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in the propagation step is exothermic in both chlorination and bromination
b)
Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in propagation step is exothermic in chlorination but endothermic in bromination
c)
A single halogen radical may bring about halogenation of thousands of alkane molecules
d)
Continuous source of energy is required to continue the free radical halogenation reaction
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in the propagation step is exothermic in chlorination but endothermic in bromination. Hence, the option (A) is an incorrect statement.
The alkene which on ozonolysis gives only acetone is:- a)(CH3)2C = CH2
- b)CH3CH = CHCH3
- c)CH3CH = C(CH3)2
- d)(CH3)2C = C(CH3)2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The alkene which on ozonolysis gives only acetone is:
a)
(CH3)2C = CH2
b)
CH3CH = CHCH3
c)
CH3CH = C(CH3)2
d)
(CH3)2C = C(CH3)2

|
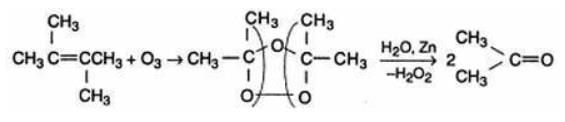
Pioneer Academy answered |
The reductive ozaonalysis of 2,3 -Dimethyl-2-butene yields acetone.The reaction is as follows: 2,3 -Dimethyl-2-butene acetone
What is the correct order of increasing acidic strength of the following?
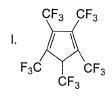
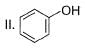
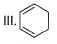
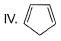
- a)Ill < I < IV < II
- b)Ill < IV < II < I
- c) Ill < II < IV < I
- d)III<IV<I<II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct order of increasing acidic strength of the following?




a)
Ill < I < IV < II
b)
Ill < IV < II < I
c)
Ill < II < IV < I
d)
III<IV<I<II
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Compound I is having the highest acidic strength due to the -I effect of five CF3 substituents.
Compound II is having less acidic strength than I but more than the rest due to the extremely stable conjugate anion formed after deprrotonation.
So, Option B is correct.
When two or more different substituents are attached with a benzene ring the number 1 position in the ring is given to a high priority group. Which one of the following groups has highest - priority?- a)?NH2
- b)?CHO
- c)?COOH
- d)?CN
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When two or more different substituents are attached with a benzene ring the number 1 position in the ring is given to a high priority group. Which one of the following groups has highest - priority?
a)
?NH2
b)
?CHO
c)
?COOH
d)
?CN
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Option C is correct, because in Nomenclature of Organic Compounds. Priority is given to that functional group that is on the top of the Priority Order of Functional Groups. Among the given Functional Groups COOH is having the highest priority so, the number 1 position in the ring is given to it.
Chapter doubts & questions for Hydrocarbons - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Hydrocarbons - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









