All Exams >
Class 10 >
Online MCQ Tests for Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Heredity and Evolution for Class 10 Exam
The initial function of feathers is to provide:- a)Beauty
- b)Strength
- c)Flight
- d)Shape
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The initial function of feathers is to provide:
a)
Beauty
b)
Strength
c)
Flight
d)
Shape
|
|
Rohan Kapoor answered |
The primary function of the flight feathers is to aid in the generation of both thrust and lift, thereby enabling flight. The flight feathers of some birds have evolved to perform additional functions, generally associated with territorial displays, courtship rituals or feeding methods.
What will happen if change occurs in the reproductive tissues of an organism?- a)It will have no effect
- b)The changes will be restricted to that generation only
- c)The changes will be inherited
- d)The organism will not be able to survive
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What will happen if change occurs in the reproductive tissues of an organism?
a)
It will have no effect
b)
The changes will be restricted to that generation only
c)
The changes will be inherited
d)
The organism will not be able to survive
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The changes occurring in the reproductive tissues of an organism are inherited from one generation to another.
In humans, the sex of children is determined by- a)Chromosomes present in non-reproductive cells
- b)Environmental conditions
- c)The chromosome inherited from mother
- d)The chromosome inherited from father
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In humans, the sex of children is determined by
a)
Chromosomes present in non-reproductive cells
b)
Environmental conditions
c)
The chromosome inherited from mother
d)
The chromosome inherited from father
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The sex of the child is determined in human beings by the chromosomes like female have two X chromosomes XX and male have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome XY. So in this way, sex is determined
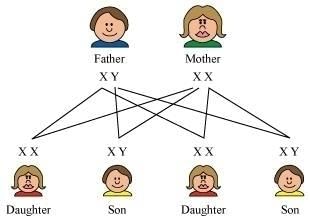

By studying the ratio of different isotopes of same element in a material we can know the age of- a)Living animals
- b)Fossil
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)Living plants
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
By studying the ratio of different isotopes of same element in a material we can know the age of
a)
Living animals
b)
Fossil
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
Living plants
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
There are two ways by which we can determine the age of fossils-
(1) If we dig into the earth and start finding fossils, it is reasonable to suppose that the fossils we find closer to the surface are more recent than the fossils we find in deeper layers.
(2) By detecting the ratios of different isotopes of the same element in the fossil material.This method is known as carbon dating.
Carbon dating is a method to estimate the age of carbon containing materials like trees. Carbon (C) has three naturally occurring isotopes. Both C-12 and C-13 are stable, but C-14 decay to nitrogen-14 with a half-life of approximately 5,730 years. Animals and plants naturally incorporate both the C-12 and C-14 during their lifetimes. When a creature dies, it ceases to consume more radiocarbon while the C-14 already in its body continues to decay back into nitrogen. With the help of C-12 to C-14 ratio, we can estimate the age of dead plants/ animals.
A basket of vegetables contains carrot, potato, radish and tomato. Which of them represent the correct homologous structures?- a)Carrot and potato
- b)Carrot and tomato
- c)Radish and carrot
- d)Radish and potato
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A basket of vegetables contains carrot, potato, radish and tomato. Which of them represent the correct homologous structures?
a)
Carrot and potato
b)
Carrot and tomato
c)
Radish and carrot
d)
Radish and potato

|
Sonika Attitdejaatni answered |
Homologous structures are those that are related by common ancestry. The common ancestry is reflected in a common structural plan. These structures might be adapted to suit different functional roles. Of the given options, potato is a storage stem, tomato is a fruit (in fact, it is a berry), radish and carrots are roots. Since both radish and carrots are roots, they have similar structural plans and are homologous.
So, the correct option is C
The traits which are expressed in first filial (F1) generation are known as which traits.- a)inherited
- b)dominant
- c)recessive
- d)acquired
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The traits which are expressed in first filial (F1) generation are known as which traits.
a)
inherited
b)
dominant
c)
recessive
d)
acquired
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Blending Theory of Inheritance - offspring of two parents "blend" the traits of both parents
Particulate Theory of Inheritance - traits are inherited as "particles", offspring receive a "particle" from each parent.
Analysis:
- The F1 generation always displayed one trait (he later called this the dominant trait)
- The F1 generation must have within it the trait from the original parents - the white trait
- The F2 generation displayed the hidden trait, 1/4 of the F2 generation had it (he later called this hidden trait the recessive trait)
- Each individual has two "factors" that determine what external appearance the offspring will have. (We now call these factors genes or alleles)
Different kinds of wild cabbage are evolved as a result of:- a)Artificial selection
- b)Decomposition
- c)Reproduction
- d)Natural selection
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Different kinds of wild cabbage are evolved as a result of:
a)
Artificial selection
b)
Decomposition
c)
Reproduction
d)
Natural selection
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
Artificial selection is a process in which man selects a particular desired traits for breeding, in order to generate new plants/ animals with improved characters. For e.g. Early farmers cultivated wild cabbage orBrassica oleracea. This wild cabbage developed into many varieties such as cabbage, broccoli, kohlrabi, cauliflower, kale, and brussels. These varieties were artificially selected because of their characteristic traits.
The normal number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained when the germ cells:- a)take all maternal and paternal chromosomes
- b)divide by the process of mitosis
- c)divide by mitosis and take all maternal and paternal chromosome
- d)take one chromosome from each pair
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The normal number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained when the germ cells:
a)
take all maternal and paternal chromosomes
b)
divide by the process of mitosis
c)
divide by mitosis and take all maternal and paternal chromosome
d)
take one chromosome from each pair
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
The number of chromosomes in each generation are maintained due to meiosis. The meiosis is a kind of reductive division. When gametes are formed by meiosis, the number of chromosomes are halved. Hence each gamete will have only one pair of chromosome.
Later the haploid gamete will fuse with the complementary haploid gamete and form Diploid Zygote(2n). Hence the number of chromosomes are maintained.
For more details you can view my old answers regarding S-phase, certain stages of meiosis etc. If still you have doubts, you can ask anytime or you can refer Molecular cell biology by Bruce Alberts.
Genetic drift is- a)Change of gene frequency in same generation
- b)Change of gene frequency in the same organism
- c)Appearance of recessive genes
- d)Change of gene frequency from one generation to another
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Genetic drift is
a)
Change of gene frequency in same generation
b)
Change of gene frequency in the same organism
c)
Appearance of recessive genes
d)
Change of gene frequency from one generation to another
|
|
Official. Nik answered |
Genetic Drift Means Change In the frequency of gene from Generation to generation.. So D is Correct
The reason why pea plants were suitable than dogs for Mendel's experiments :-- a)Dogs have many genetic traits
- b)Pea plants can be self fertilized
- c)There are no pedigree records of dogs
- d)The pea plants favour cross-fertilization
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reason why pea plants were suitable than dogs for Mendel's experiments :-
a)
Dogs have many genetic traits
b)
Pea plants can be self fertilized
c)
There are no pedigree records of dogs
d)
The pea plants favour cross-fertilization
|
|
Kuldeep Raj answered |

Which of the following is not a characteristic of Genetic drift?- a)Occurs due to chance factor
- b)Causes change in the gene frequency.
- c)Confer no survival advantage
- d)Occurs in large sized population
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of Genetic drift?
a)
Occurs due to chance factor
b)
Causes change in the gene frequency.
c)
Confer no survival advantage
d)
Occurs in large sized population
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Genetic drift (also known as allelic drift or the Sewall Wright effect) is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms. ... A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form.
A zygote which has an X-chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a- a)Boy
- b)Girl
- c) X-chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
- d)Either boy or girl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A zygote which has an X-chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a
a)
Boy
b)
Girl
c)
X-chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
d)
Either boy or girl

|
Sushant Sen answered |
Explanation: Humans follow XX- XY mechanism of sex determination.
The study of fossils is helpful to know:- a)Biodiversity in an ecosystem
- b)Hierarchical relationships
- c)Environment of earth
- d)Evolutionary relationships
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The study of fossils is helpful to know:
a)
Biodiversity in an ecosystem
b)
Hierarchical relationships
c)
Environment of earth
d)
Evolutionary relationships
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
We only know about extinct groups like dinosaurs, ammonites and trilobites through fossils. Some animals and plant are only known to us as fossils. By studying the fossil record we can tell how long life has existed on Earth, and how different plants and animals are related to each other.
Theoretically taking about a common ancestor and making small groups of species on this basis, we keep going- a)Forward
- b)Backward
- c)Both forward and backward
- d)In any direction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Theoretically taking about a common ancestor and making small groups of species on this basis, we keep going
a)
Forward
b)
Backward
c)
Both forward and backward
d)
In any direction
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
It is so because we are only in the influence of our culture and heritage and making small groups make us remote and self centered so ultimately not aware of the activities outside of group of species and this overall makes us backward.
Which is not a tool of tracing evolutionary relationships?- a)Excavating
- b)Time- dating
- c)Historical details
- d)Determining DNA sequences
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not a tool of tracing evolutionary relationships?
a)
Excavating
b)
Time- dating
c)
Historical details
d)
Determining DNA sequences
|
|
Nisha Choudhury answered |
(i)By studying their structural design - homologous or anologous .It can give evidences of common ancestor. Forelimbs of humans and wings of birds look different externally. However, their skeletal structure is similar. Thus, their origin is similar, but functions are different. While wings help a bird in flight, the forearm helps human beings in various activities. These structures are called homologous organs.
(ii)By the study of fossils.A million years later, some dinosaurs died at the same place with their bodies getting buried on top of the sedimentary rock. As a result, the mud, containing the dinosaurs, also turned into rock.Now, if that area is excavated deeper, dinosaur and invertebrate fossils can also be found.
(iii)Comparing the DNA of different organisms. All species have the same genetic code. So we can trace some evolutionary relationship among the species.
A pea plant shows the genetic makeup TtRr. How will the plant appear externally?- a)Tall with wrinkled seeds
- b)Dwarf with round seeds
- c)Dwarf with wrinkled seeds
- d)Tall with round seeds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A pea plant shows the genetic makeup TtRr. How will the plant appear externally?
a)
Tall with wrinkled seeds
b)
Dwarf with round seeds
c)
Dwarf with wrinkled seeds
d)
Tall with round seeds

|
The Eliminator answered |
Correct answer is:- (d) tall with round seeds
explanation:- since T and R are dominant traits and t and r are ressassive traits. So tall and round are dominant that's why they hide the identity of dwarf and wrinkled so that the seeds looks tall and round.
explanation:- since T and R are dominant traits and t and r are ressassive traits. So tall and round are dominant that's why they hide the identity of dwarf and wrinkled so that the seeds looks tall and round.
A trait in an organism is influenced by- a) Paternal DNA only
- b) Maternal DNA only
- c)Both maternal and paternal DNA
- d)Neither by paternal nor by maternal DNA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A trait in an organism is influenced by
a)
Paternal DNA only
b)
Maternal DNA only
c)
Both maternal and paternal DNA
d)
Neither by paternal nor by maternal DNA

|
Anisha Mukherjee answered |
Explanation: An organism develops from zygote which in turn is product of fusion of male and female gamete.
Which feature has to be selected in wild cabbage if the vegetable kale has to be artificially bred from it?- a)Slightly larger leaves
- b)Swollen parts of flowers
- c)Very short distance between leaves
- d)Sterile flowers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which feature has to be selected in wild cabbage if the vegetable kale has to be artificially bred from it?
a)
Slightly larger leaves
b)
Swollen parts of flowers
c)
Very short distance between leaves
d)
Sterile flowers
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Selecting and breeding wild cabbage plants with slightly larger leaves gave rise to the leafy vegetable called kale.
Selecting for arrested flower development in wild cabbage led to the development of which plant ?- a)Kohlrabi
- b)Cauliflower
- c)Kale
- d)Broccoli
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Selecting for arrested flower development in wild cabbage led to the development of which plant ?
a)
Kohlrabi
b)
Cauliflower
c)
Kale
d)
Broccoli
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Some farmers wanted to select for arrested flower development, and have bred broccoli.
Body parts of different animals having a common origin but different functions are called:- a)Heterologus
- b)Paralogous
- c)Homologus
- d)Analogous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Body parts of different animals having a common origin but different functions are called:
a)
Heterologus
b)
Paralogous
c)
Homologus
d)
Analogous
|
|
Anjana Khatri answered |
Homologous Structures
Homologous structures, on the other hand, are characteristics which are shared by related species because they have been inherited in some way from a common ancestor. For example, the bones on the front fins of a whale are homologous to the bones in a human arm and both are homologous to the bones in a chimpanzee arm. The bones in all of these different body parts on different animals are basically the same bones, but their sizes are different and they serve slightly different functions in the animals where they are found.
Which of the following act as an information source for making proteins in a cell?- a)DNA
- b)Lipids
- c)RNA
- d)Carbohydrates
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following act as an information source for making proteins in a cell?
a)
DNA
b)
Lipids
c)
RNA
d)
Carbohydrates
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The DNA in the nucleus of a cell is the information source for making proteins. If the information is changed, different proteins will be made. The basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy. Cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA. This creates two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell and they need to get separated from each other. DNA copying is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus, and then the DNA copies separate, each with its own cellular apparatus.
Archaeopteryx is a missing link between:- a)Reptiles and Birds
- b)Amphibians and Reptiles
- c)Aves and Mammals
- d)Fishes and Amphibians
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Archaeopteryx is a missing link between:
a)
Reptiles and Birds
b)
Amphibians and Reptiles
c)
Aves and Mammals
d)
Fishes and Amphibians

|
Bhargavi Basak answered |
Archaeopteryx was first described as the 'missing link' between reptiles and birds in 1861 - and is now regarded as the link between dinosaurs and birds. Only 12 specimens have ever been found and all are from the late Jurassic of Bavaria, now Germany, dating back approximately 150 million years.
If a heterozygous tall palnt is crossed with a homozygous dwarf palnt, the proportion of dwarf progeny will:-- a)50%
- b)75%
- c)100%
- d)25%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a heterozygous tall palnt is crossed with a homozygous dwarf palnt, the proportion of dwarf progeny will:-
a)
50%
b)
75%
c)
100%
d)
25%
|
|
Rohan pandey answered |
A) 50%
Explanation:
A heterozygous tall plant has the genotype Tt (T for the tall allele and t for the dwarf allele). A homozygous dwarf plant has the genotype tt. When these two plants are crossed, the possible genotypes of the progeny can be determined using a Punnett square.
Tt (heterozygous tall plant)
T | t
---------
t | Tt | tt
t | Tt | tt
As we can see, there are 4 possible outcomes: 2 Tt (tall) and 2 tt (dwarf). So, the proportion of dwarf progeny (tt) is 2 out of the 4 possibilities, which is equal to 50%.
Explanation:
A heterozygous tall plant has the genotype Tt (T for the tall allele and t for the dwarf allele). A homozygous dwarf plant has the genotype tt. When these two plants are crossed, the possible genotypes of the progeny can be determined using a Punnett square.
Tt (heterozygous tall plant)
T | t
---------
t | Tt | tt
t | Tt | tt
As we can see, there are 4 possible outcomes: 2 Tt (tall) and 2 tt (dwarf). So, the proportion of dwarf progeny (tt) is 2 out of the 4 possibilities, which is equal to 50%.
Which is not correct regarding the relation of human beings with chimpanzees?- a)Both had a common ancestor long time ago
- b)Human beings evolved from chimpanzees
- c)Chimpanzees are very closely related to humans in DNA structure
- d)Both evolved due to generation of diversity and its selection by nature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not correct regarding the relation of human beings with chimpanzees?
a)
Both had a common ancestor long time ago
b)
Human beings evolved from chimpanzees
c)
Chimpanzees are very closely related to humans in DNA structure
d)
Both evolved due to generation of diversity and its selection by nature
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
The chimpanzee and another ape, the bonobo, are humans' closest living relatives. These three species look alike in many ways, both in body and behavior.
Human and chimpanzee DNA is so similar because the two species are so closely related. Humans, chimpanzees and bonobos descended from a single ancestor species that lived six or seven million years ago. As humans and chimps gradually evolved from a common ancestor, their DNA, passed from generation to generation, changed too. In fact, many of these DNA changes led to differences between human and chimpanzee appearance and behavior.
Which is not correct regarding the relation of human beings with chimpanzees?- a)Both had a common ancestor long time ago
- b)Human beings evolved from chimpanzees
- c)Chimpanzees are very closely related to humans in DNA structure
- d)Both evolved due to generation of diversity and its selection by nature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not correct regarding the relation of human beings with chimpanzees?
a)
Both had a common ancestor long time ago
b)
Human beings evolved from chimpanzees
c)
Chimpanzees are very closely related to humans in DNA structure
d)
Both evolved due to generation of diversity and its selection by nature
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
For most DNA sequences, humans and chimpanzees appear to be most closely related, but some point to a human-gorilla or chimpanzee-gorilla clade. The human genome has been sequenced, as well as the chimpanzee genome. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, while chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans have 24.
Exchange of genetic material takes place in- a)Vegetative reproduction
- b)Asexual reproduction
- c)Sexual reproduction
- d)Budding
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Exchange of genetic material takes place in
a)
Vegetative reproduction
b)
Asexual reproduction
c)
Sexual reproduction
d)
Budding

|
Om Menon answered |
Understanding Genetic Material Exchange
Genetic material exchange is a fundamental process in biological reproduction, particularly significant in the context of sexual reproduction.
What is Sexual Reproduction?
- Sexual reproduction involves the combination of genetic material from two parent organisms.
- It typically requires the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) through a process called meiosis.
Mechanism of Genetic Exchange
- During fertilization, a sperm cell merges with an egg cell, resulting in a zygote.
- This zygote contains a unique combination of genes from both parents, contributing to genetic diversity.
Key Benefits of Genetic Exchange
- Genetic Variation: Sexual reproduction promotes genetic diversity, which is crucial for the adaptation and survival of species in changing environments.
- Evolution: The variation introduced through genetic exchange is a driving force in the process of evolution, enabling populations to adapt over generations.
Contrast with Other Reproductive Methods
- Asexual Reproduction:
- Involves a single organism producing offspring identical to itself.
- No exchange of genetic material occurs, leading to clones.
- Vegetative Reproduction:
- A form of asexual reproduction where new plants grow from parts of the parent plant.
- Again, no genetic exchange takes place.
- Budding:
- A type of asexual reproduction where a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud.
- This method also results in genetically identical offspring.
Conclusion
In summary, sexual reproduction is the only method among the options listed that involves the exchange of genetic material, resulting in genetic diversity and evolutionary potential.
Genetic material exchange is a fundamental process in biological reproduction, particularly significant in the context of sexual reproduction.
What is Sexual Reproduction?
- Sexual reproduction involves the combination of genetic material from two parent organisms.
- It typically requires the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) through a process called meiosis.
Mechanism of Genetic Exchange
- During fertilization, a sperm cell merges with an egg cell, resulting in a zygote.
- This zygote contains a unique combination of genes from both parents, contributing to genetic diversity.
Key Benefits of Genetic Exchange
- Genetic Variation: Sexual reproduction promotes genetic diversity, which is crucial for the adaptation and survival of species in changing environments.
- Evolution: The variation introduced through genetic exchange is a driving force in the process of evolution, enabling populations to adapt over generations.
Contrast with Other Reproductive Methods
- Asexual Reproduction:
- Involves a single organism producing offspring identical to itself.
- No exchange of genetic material occurs, leading to clones.
- Vegetative Reproduction:
- A form of asexual reproduction where new plants grow from parts of the parent plant.
- Again, no genetic exchange takes place.
- Budding:
- A type of asexual reproduction where a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud.
- This method also results in genetically identical offspring.
Conclusion
In summary, sexual reproduction is the only method among the options listed that involves the exchange of genetic material, resulting in genetic diversity and evolutionary potential.
Genotype means :-- a)Genetic composition of the individual
- b)Genetic composition of the germ cell
- c)Genetic composition of plastids
- d)Genetic compositon of an organ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Genotype means :-
a)
Genetic composition of the individual
b)
Genetic composition of the germ cell
c)
Genetic composition of plastids
d)
Genetic compositon of an organ

|
Janhavi Chakraborty answered |
The genotype of an organism is the chemical composition of its DNA, which gives rise to the phenotype, or observable traits of an organism. A genotype consists of all the nucleic acids present in a DNA molecule that code for a particular trait
What would be the possible genotypic ratio of the F2 generation in a monohybrid cross?- a)1:1.
- b)2:2:1.
- c)1:2:1.
- d)3:1.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
1:1.
b)
2:2:1.
c)
1:2:1.
d)
3:1.

|
Nk Classes answered |
The genotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a monohybrid cross is 1:2:1, corresponding to homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive individuals, respectively.
Which type of reproduction leads to more variations in offspring?- a)Asexual reproduction
- b)Sexual reproduction
- c)Both asexual and sexual reproduction
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of reproduction leads to more variations in offspring?
a)
Asexual reproduction
b)
Sexual reproduction
c)
Both asexual and sexual reproduction
d)
None of the above

|
Kds Coaching answered |
Sexual Reproduction:
- Involves the combination of genetic material from two parents.
- Each parent contributes half of the genetic material, resulting in offspring with a unique mix of genes.
- This genetic recombination increases variation and diversity among offspring.
Asexual Reproduction:
- Involves a single parent and produces genetically identical offspring, known as clones.
- Does not lead to genetic variation apart from occasional mutations.
- More genetic variation occurs through sexual reproduction, making it the correct answer.
What is heredity?- a)The transfer of characteristics from offspring to parents.
- b)The transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring.
- c)The transfer of characteristics between siblings.
- d)The transfer of characteristics within a generation.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is heredity?
a)
The transfer of characteristics from offspring to parents.
b)
The transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring.
c)
The transfer of characteristics between siblings.
d)
The transfer of characteristics within a generation.
|
|
Jatin Chaudhary answered |
The Concept of Heredity
Heredity refers to the biological process through which traits and characteristics are passed down from parents to their offspring. This fundamental concept is crucial in understanding genetics and how living organisms inherit various features.
Key Points about Heredity:
- Transfer of Genetic Information:
- Heredity involves the transmission of genes, which are units of heredity located on chromosomes.
- These genes carry information that determines physical traits, such as eye color, height, and susceptibility to certain diseases.
- Role of DNA:
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the molecule that contains the genetic blueprint for an organism.
- During reproduction, DNA from both parents combines, resulting in a unique genetic makeup for the offspring.
- Mendelian Inheritance:
- The principles of heredity were first systematically studied by Gregor Mendel in the 19th century.
- Mendel’s laws describe how traits are inherited through dominant and recessive alleles.
- Variability and Evolution:
- While heredity ensures that offspring resemble their parents, it also introduces variations due to mutations and recombination.
- This genetic diversity is essential for evolution and adaptation to changing environments.
Conclusion
Understanding heredity is crucial for fields such as medicine, agriculture, and evolutionary biology. It provides insights into how traits are inherited and can influence health and behavior in future generations. In summary, option 'B' accurately represents heredity as the transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring, highlighting its fundamental role in biology.
Heredity refers to the biological process through which traits and characteristics are passed down from parents to their offspring. This fundamental concept is crucial in understanding genetics and how living organisms inherit various features.
Key Points about Heredity:
- Transfer of Genetic Information:
- Heredity involves the transmission of genes, which are units of heredity located on chromosomes.
- These genes carry information that determines physical traits, such as eye color, height, and susceptibility to certain diseases.
- Role of DNA:
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the molecule that contains the genetic blueprint for an organism.
- During reproduction, DNA from both parents combines, resulting in a unique genetic makeup for the offspring.
- Mendelian Inheritance:
- The principles of heredity were first systematically studied by Gregor Mendel in the 19th century.
- Mendel’s laws describe how traits are inherited through dominant and recessive alleles.
- Variability and Evolution:
- While heredity ensures that offspring resemble their parents, it also introduces variations due to mutations and recombination.
- This genetic diversity is essential for evolution and adaptation to changing environments.
Conclusion
Understanding heredity is crucial for fields such as medicine, agriculture, and evolutionary biology. It provides insights into how traits are inherited and can influence health and behavior in future generations. In summary, option 'B' accurately represents heredity as the transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring, highlighting its fundamental role in biology.
What is the genotypic ratio in Mendel's F2 generation for a single trait?- a)3:1
- b)1:2:1
- c)9:3:3:1
- d)2:2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the genotypic ratio in Mendel's F2 generation for a single trait?
a)
3:1
b)
1:2:1
c)
9:3:3:1
d)
2:2
|
|
Pratibha dubey answered |
Understanding Mendel's F2 Generation
Mendel's experiments with pea plants laid the foundation for genetics, especially in understanding inheritance patterns.
Single Trait Inheritance
When studying a single trait, Mendel observed the inheritance of dominant and recessive alleles. In his experiments, he crossed homozygous parents:
- P Generation: One parent with two dominant alleles (AA) and another with two recessive alleles (aa).
- F1 Generation: All offspring (Aa) displayed the dominant trait.
F2 Generation Results
When F1 plants were self-fertilized, the F2 generation emerged, revealing a classic 3:1 phenotypic ratio of dominant to recessive traits:
- Phenotypic Ratio: 3 dominant (AA or Aa) : 1 recessive (aa)
However, when considering the genotypes:
- Genotypic Ratio: This includes:
- 1 homozygous dominant (AA)
- 2 heterozygous (Aa)
- 1 homozygous recessive (aa)
Thus, the genotypic ratio for the F2 generation is:
- 1 AA : 2 Aa : 1 aa
Correct Answer: 1:2:1
This corresponds to option 'B'. The 1:2:1 ratio illustrates the distribution of genotypes resulting from the segregation of alleles during meiosis.
Conclusion
Mendel's work exemplifies the foundational principles of genetic inheritance, with the F2 generation showcasing the predictable ratios of genotypes and phenotypes, crucial for understanding heredity.
Mendel's experiments with pea plants laid the foundation for genetics, especially in understanding inheritance patterns.
Single Trait Inheritance
When studying a single trait, Mendel observed the inheritance of dominant and recessive alleles. In his experiments, he crossed homozygous parents:
- P Generation: One parent with two dominant alleles (AA) and another with two recessive alleles (aa).
- F1 Generation: All offspring (Aa) displayed the dominant trait.
F2 Generation Results
When F1 plants were self-fertilized, the F2 generation emerged, revealing a classic 3:1 phenotypic ratio of dominant to recessive traits:
- Phenotypic Ratio: 3 dominant (AA or Aa) : 1 recessive (aa)
However, when considering the genotypes:
- Genotypic Ratio: This includes:
- 1 homozygous dominant (AA)
- 2 heterozygous (Aa)
- 1 homozygous recessive (aa)
Thus, the genotypic ratio for the F2 generation is:
- 1 AA : 2 Aa : 1 aa
Correct Answer: 1:2:1
This corresponds to option 'B'. The 1:2:1 ratio illustrates the distribution of genotypes resulting from the segregation of alleles during meiosis.
Conclusion
Mendel's work exemplifies the foundational principles of genetic inheritance, with the F2 generation showcasing the predictable ratios of genotypes and phenotypes, crucial for understanding heredity.
What determines the traits of an organism?- a)Genes passed down from the parents
- b)Environment and upbringing
- c)Random chance
- d)Changes in DNA during an organism's life
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What determines the traits of an organism?
a)
Genes passed down from the parents
b)
Environment and upbringing
c)
Random chance
d)
Changes in DNA during an organism's life

|
Nk Classes answered |
Genes passed down from the parents:
- Genes are parts of DNA that contain instructions for how an organism develops and functions.
- They encode proteins that determine traits, affecting the organism's structure and processes.
- Traits like eye colour, blood type, and some inherited diseases are influenced by genetic information.
- Inheritance follows Mendelian genetics, where traits are passed from parents to offspring through alleles.
The wings of a bat are basically
- a) Feathery skin folds of fingers
- b) Skin folds stretched between elongated fingers
- c) Modified limbs
- d) Feathery covering all along the arm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The wings of a bat are basically
a)
Feathery skin folds of fingersb)
Skin folds stretched between elongated fingersc)
Modified limbsd)
Feathery covering all along the arm|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
In bat, skin folds are stretched between the elongated fingers and serve the purpose of wings.
Which of the following is true about sex chromosomes in humans?- a)Both males and females have two X chromosomes.
- b)Males have two Y chromosomes.
- c)Females have two X chromosomes (XX) and males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
- d)Sex chromosomes do not affect the sex determination.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true about sex chromosomes in humans?
a)
Both males and females have two X chromosomes.
b)
Males have two Y chromosomes.
c)
Females have two X chromosomes (XX) and males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
d)
Sex chromosomes do not affect the sex determination.

|
Sahana Basu answered |
Understanding Human Sex Chromosomes
In humans, the determination of biological sex is primarily influenced by the composition of sex chromosomes. Let's break down the key aspects:
Sex Chromosome Composition
- Females (XX): Women have two X chromosomes, which are denoted as XX. This configuration is essential for typical female development and functions in reproduction.
- Males (XY): Men possess one X and one Y chromosome, represented as XY. The presence of the Y chromosome triggers male biological development and characteristics.
Significance of the Y Chromosome
- The Y chromosome carries genes that are critical for male sex determination and sperm production. One of the key genes on the Y chromosome is the SRY gene, which initiates the pathway for male sex differentiation.
Why Other Options are Incorrect
- Option A (Both males and females have two X chromosomes): This statement is false because only females have two X chromosomes. Males have one X and one Y.
- Option B (Males have two Y chromosomes): This is incorrect. Males have one Y chromosome, not two. Having two Y chromosomes is not viable in humans.
- Option D (Sex chromosomes do not affect sex determination): This statement is misleading. Sex chromosomes are crucial for determining biological sex in humans.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C': Females have two X chromosomes (XX), and males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). This chromosomal structure is fundamental to our understanding of human biology and reproduction.
In humans, the determination of biological sex is primarily influenced by the composition of sex chromosomes. Let's break down the key aspects:
Sex Chromosome Composition
- Females (XX): Women have two X chromosomes, which are denoted as XX. This configuration is essential for typical female development and functions in reproduction.
- Males (XY): Men possess one X and one Y chromosome, represented as XY. The presence of the Y chromosome triggers male biological development and characteristics.
Significance of the Y Chromosome
- The Y chromosome carries genes that are critical for male sex determination and sperm production. One of the key genes on the Y chromosome is the SRY gene, which initiates the pathway for male sex differentiation.
Why Other Options are Incorrect
- Option A (Both males and females have two X chromosomes): This statement is false because only females have two X chromosomes. Males have one X and one Y.
- Option B (Males have two Y chromosomes): This is incorrect. Males have one Y chromosome, not two. Having two Y chromosomes is not viable in humans.
- Option D (Sex chromosomes do not affect sex determination): This statement is misleading. Sex chromosomes are crucial for determining biological sex in humans.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C': Females have two X chromosomes (XX), and males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). This chromosomal structure is fundamental to our understanding of human biology and reproduction.
Name the organs which have different basic structure but have a similar appearance and perform similar functions?- a)Analogous organs
- b)Homologous organs
- c)Both A and B
- d)Neither A nor B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the organs which have different basic structure but have a similar appearance and perform similar functions?
a)
Analogous organs
b)
Homologous organs
c)
Both A and B
d)
Neither A nor B
|
|
Kritika Sharma answered |
Analogous organs have different basic structure but have similar appearance and perform similar functions. Example wings of an insect and a bird have different structures but similar functions.
What is the phenotypic ratio of a dihybrid cross in Mendel’s experiments?- a)3:1.
- b)9:3:3:1.
- c)1:2:1.
- d)2:1.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3:1.
b)
9:3:3:1.
c)
1:2:1.
d)
2:1.

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
In a dihybrid cross, Mendel observed a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1, showing the independent inheritance of two traits (e.g., seed shape and color).
What is the purpose of DNA copying during reproduction?- a)To prevent mutations.
- b)To create variations for survival.
- c)To ensure exact copies of the parent.
- d)To increase the size of chromosomes.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To prevent mutations.
b)
To create variations for survival.
c)
To ensure exact copies of the parent.
d)
To increase the size of chromosomes.

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
DNA copying during reproduction creates variations, which can provide different individuals with advantages for survival. These variations are essential for the adaptability and evolution of species.
By identifying hierarchies of characteristics between species, we are able to trace:- a)Hereditary relationships
- b)Genetic drift
- c)Evolutionary relationships
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
By identifying hierarchies of characteristics between species, we are able to trace:
a)
Hereditary relationships
b)
Genetic drift
c)
Evolutionary relationships
d)
All of the above
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
Evolutionary relationships help us to trace who we are more close to and who is our common ancestor. A group of organisms is similar enough to be thought of together by certain characteristics.Thus, the homologous and analogous characteristics help to trace an evolutionary relationship between different species.
How do variations occur during reproduction?- a)By environmental influences
- b)By genetic recombination and mutations
- c)By genetic inheritance alone
- d)By changes in physical characteristics
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How do variations occur during reproduction?
a)
By environmental influences
b)
By genetic recombination and mutations
c)
By genetic inheritance alone
d)
By changes in physical characteristics

|
Kds Coaching answered |
Variations during reproduction primarily occur through:
- Genetic Recombination: During sexual reproduction, chromosomes from both parents exchange genetic material, creating unique combinations in offspring.
- Mutations: Random changes in the DNA sequence can lead to new traits, introducing variations across generations.
These processes ensure diversity within a species, aiding in adaptation and survival. Genetic inheritance alone does not account for new variations, making option B the correct answer.
What is the phenotypic ratio in Mendel’s F2 generation for a single trait?- a)1:1
- b)3:1
- c)9:3:3:1
- d)1:2:1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the phenotypic ratio in Mendel’s F2 generation for a single trait?
a)
1:1
b)
3:1
c)
9:3:3:1
d)
1:2:1

|
Nk Classes answered |
- Gregor Mendel, known as the father of genetics, studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants.
- He observed that when crossing two heterozygous parents (F1 generation) for a single trait, the F2 generation showed a 3:1 phenotypic ratio.
- This means 3 offspring displayed the dominant trait, while 1 displayed the recessive.
- This ratio results from the combination of alleles: 1 homozygous dominant (AA), 2 heterozygous (Aa), and 1 homozygous recessive (aa).
Mendel chose pea plants because they :-- a)were cheap
- b)were easily available
- c)have great economic importance
- d)were having contrasting characters
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mendel chose pea plants because they :-
a)
were cheap
b)
were easily available
c)
have great economic importance
d)
were having contrasting characters
|
|
Abhi answered |
Mendel performed cross-breeding experiments on garden pea (Pisum sativum).
Although he studied the inheritance of seven different pairs of contrasting characters in this plant, he considered only one pair at a time.
He crossed two pea plants having contrasting characters (e.g., tall and dwarf pea plants) by artificial pollination and obtained the hybrids.
The resulting hybrid plants were then crossed with each other. He obtained the data from these crosses and analyzed the results carefully.
Although he studied the inheritance of seven different pairs of contrasting characters in this plant, he considered only one pair at a time.
He crossed two pea plants having contrasting characters (e.g., tall and dwarf pea plants) by artificial pollination and obtained the hybrids.
The resulting hybrid plants were then crossed with each other. He obtained the data from these crosses and analyzed the results carefully.
Tick the correct sentence.- a)Age of fossil is not related to the depth where it is found
- b)Fossil found near earth surface is more recent
- c)Fossil found at deeper layers is more recent
- d)Fossil found in the rocks is more recent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Tick the correct sentence.
a)
Age of fossil is not related to the depth where it is found
b)
Fossil found near earth surface is more recent
c)
Fossil found at deeper layers is more recent
d)
Fossil found in the rocks is more recent

|
Abhishek Datta answered |
Explanation:
Introduction:
The question is asking which sentence is correct regarding the relationship between the age of a fossil and the depth at which it is found. We need to determine which statement accurately describes this relationship.
Analysis:
Let's analyze each option to determine which one is correct:
- Option a: "Age of fossil is not related to the depth where it is found." This statement is incorrect. The age of a fossil is often related to the depth at which it is found because fossils found in deeper layers are generally older than those found near the surface.
- Option b: "Fossil found near earth surface is more recent." This statement is correct. Fossils found near the Earth's surface are usually more recent because they have been deposited more recently and have not been subjected to the same geological processes as fossils found in deeper layers.
- Option c: "Fossil found at deeper layers is more recent." This statement is incorrect. Fossils found in deeper layers are generally older, not more recent. This is because the layers of sedimentary rock that contain fossils are formed over time, with older layers being deposited first and newer layers being deposited on top.
- Option d: "Fossil found in the rocks is more recent." This statement is incorrect. All fossils are found in rocks, so this statement does not provide any information about the relationship between the age of a fossil and the depth at which it is found.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, we can conclude that option b is the correct sentence. Fossils found near the Earth's surface are generally more recent because they have been deposited more recently and have not undergone the same geological processes as fossils found in deeper layers.
Introduction:
The question is asking which sentence is correct regarding the relationship between the age of a fossil and the depth at which it is found. We need to determine which statement accurately describes this relationship.
Analysis:
Let's analyze each option to determine which one is correct:
- Option a: "Age of fossil is not related to the depth where it is found." This statement is incorrect. The age of a fossil is often related to the depth at which it is found because fossils found in deeper layers are generally older than those found near the surface.
- Option b: "Fossil found near earth surface is more recent." This statement is correct. Fossils found near the Earth's surface are usually more recent because they have been deposited more recently and have not been subjected to the same geological processes as fossils found in deeper layers.
- Option c: "Fossil found at deeper layers is more recent." This statement is incorrect. Fossils found in deeper layers are generally older, not more recent. This is because the layers of sedimentary rock that contain fossils are formed over time, with older layers being deposited first and newer layers being deposited on top.
- Option d: "Fossil found in the rocks is more recent." This statement is incorrect. All fossils are found in rocks, so this statement does not provide any information about the relationship between the age of a fossil and the depth at which it is found.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, we can conclude that option b is the correct sentence. Fossils found near the Earth's surface are generally more recent because they have been deposited more recently and have not undergone the same geological processes as fossils found in deeper layers.
Grain colour in wheat is determined by three pairs of polygene. Following the cross AABBCC (dark colour) x aabbcc (light colour), in F2-generation what proportion of the progeny is likely to resemble either parent- a)One fourth
- b)Less than 5 percent
- c)One third
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Grain colour in wheat is determined by three pairs of polygene. Following the cross AABBCC (dark colour) x aabbcc (light colour), in F2-generation what proportion of the progeny is likely to resemble either parent
a)
One fourth
b)
Less than 5 percent
c)
One third
d)
None of these
|
|
Learnever Education answered |
Polygene results in quantitative inheritance which is characterized by occurrence of intermediate forms between the parental type. In case of crossing between AABBCC (dark colour) and aabbcc (light colour), in F2 generation seven phenotypes will obtain with ratio of 1 : 6 : 15 : 20 : 15 : 6 : 1. The total number of progeny is 64, out of which only two will be likely resemble with either parents. Hence, their proportion in F2 generation would be 3.12 ie, less than 5%.
What is the main mechanism of sex determination in humans?- a)The temperature of fertilized eggs
- b)The environment of the offspring
- c)The chromosomes inherited from parents
- d)The dominance of X or Y chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the main mechanism of sex determination in humans?
a)
The temperature of fertilized eggs
b)
The environment of the offspring
c)
The chromosomes inherited from parents
d)
The dominance of X or Y chromosomes

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
- Chromosomes from Parents: Human sex determination is based on the chromosomes inherited from parents. Each parent contributes one sex chromosome.
- Chromosome Pairs: Females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
- Role of Y Chromosome: The presence of a Y chromosome determines male development because it carries the SRY gene, which triggers male characteristics.
- Genetic Basis: The combination of these chromosomes at fertilization determines the sex of the offspring.
Identify the incorrect statement:- a)Initially, feathers probably evolved to provide insulation in cold weather.
- b)Gradually over a period of time, feathers became useful for flight.
- c)All dinosaurs possessing feathers adapted them to flight.
- d)Birds evolved later than dinosaurs and used feathers to fly.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the incorrect statement:
a)
Initially, feathers probably evolved to provide insulation in cold weather.
b)
Gradually over a period of time, feathers became useful for flight.
c)
All dinosaurs possessing feathers adapted them to flight.
d)
Birds evolved later than dinosaurs and used feathers to fly.

|
Prasad Chavan answered |
The use of feathers by birds for flying means that birds have evolved from reptiles. Dinosaurs had feathers but could not fly using them. Birds, later adapted the feathers for flight. Since, dinosaurs were reptiles, this means that birds have evolved from them.
The term used to express details of appearance or behaviour is:- a)Relation
- b)Classification
- c)Life-cycle
- d)Characteristic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The term used to express details of appearance or behaviour is:
a)
Relation
b)
Classification
c)
Life-cycle
d)
Characteristic

|
Sreemoyee Patel answered |
Characteristic defines the details of a particular function or about behavior or about the appearance of a living being.
Among the following which is the most fundamental characteristic of all living organisms?- a)Cell is the basic unit of life
- b)Presence of a body skeleton
- c)Their cells can do photosynthesis
- d)Presence of nucleus in their cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following which is the most fundamental characteristic of all living organisms?
a)
Cell is the basic unit of life
b)
Presence of a body skeleton
c)
Their cells can do photosynthesis
d)
Presence of nucleus in their cells

|
Janhavi Chakraborty answered |
The unified cell theory states that: all living things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing cells.
Considering tallness and dwarfness, tallness is more wide spread among pea plants because :-- a)Tallness is dominant over dwarfness
- b)Tallness is determined by one gene having many effects
- c)Tallness is determined by many genes having multiple effects
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Considering tallness and dwarfness, tallness is more wide spread among pea plants because :-
a)
Tallness is dominant over dwarfness
b)
Tallness is determined by one gene having many effects
c)
Tallness is determined by many genes having multiple effects
d)
None of these

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Explanation:
- Most likely explanation for tallness being more widespread among pea plants is that tallness is dominant over dwarfness.
- This means that even if a pea plant inherits the dwarf allele from one parent, it can still exhibit the tall phenotype if it inherits the tall allele from the other parent.
What is the phenotypic ratio observed in the F2 generation after self-fertilization in the given diagram?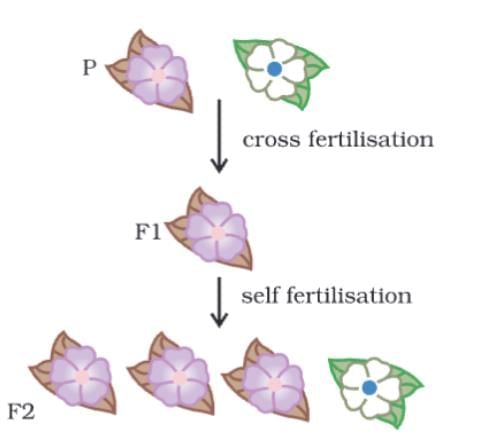
- a)1:1
- b)2:1
- c)3:1
- d)4:1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the phenotypic ratio observed in the F2 generation after self-fertilization in the given diagram?

a)
1:1
b)
2:1
c)
3:1
d)
4:1

|
Kds Coaching answered |
F2 Generation (Second Filial Generation):
The result shows a phenotypic ratio of 3:1:
3 purple-flowered plants (dominant phenotype)
1 white-flowered plant (recessive phenotype)
This 3:1 ratio is the classic Mendelian phenotypic ratio for a monohybrid cross.
What is the role of chromosomes during sexual reproduction?- a)To transfer dominant traits only.
- b)To ensure that each germ cell has two sets of genes.
- c)To randomly combine gene sets from parents.
- d)To maintain the stability of DNA in the species.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To transfer dominant traits only.
b)
To ensure that each germ cell has two sets of genes.
c)
To randomly combine gene sets from parents.
d)
To maintain the stability of DNA in the species.
|
|
Pratibha chauhan answered |
Role of Chromosomes in Sexual Reproduction
Chromosomes play a crucial role in sexual reproduction, ensuring genetic diversity while maintaining the stability of DNA within species. Here’s how they contribute:
1. Genetic Material Organization
- Chromosomes are structures that organize and package DNA, making it possible for genetic information to be efficiently replicated and distributed during cell division.
- Each species has a specific number of chromosomes that carry genes, which are the units of heredity.
2. Halving Chromosome Numbers in Germ Cells
- During sexual reproduction, germ cells (sperm and egg) undergo meiosis, a special type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half.
- This reduction is essential so that when fertilization occurs, the resulting organism has the correct diploid number of chromosomes.
3. Genetic Variation
- Chromosomes facilitate genetic variation through processes like crossing over and independent assortment during meiosis.
- This variation is vital for evolution and adaptation, allowing populations to respond to environmental changes.
4. Stability of DNA
- The maintenance of chromosome structure is crucial for the stability of DNA across generations.
- Proper chromosome alignment and segregation during cell division prevent mutations and ensure that genetic material is accurately copied and passed on.
Conclusion
In summary, while chromosomes indeed play a role in combining genetic material and ensuring stability, the correct answer to the role of chromosomes during sexual reproduction is more aligned with maintaining stability in DNA rather than solely transferring dominant traits or merely combining genes. Hence, option 'D' is the most fitting choice in this context.
Chromosomes play a crucial role in sexual reproduction, ensuring genetic diversity while maintaining the stability of DNA within species. Here’s how they contribute:
1. Genetic Material Organization
- Chromosomes are structures that organize and package DNA, making it possible for genetic information to be efficiently replicated and distributed during cell division.
- Each species has a specific number of chromosomes that carry genes, which are the units of heredity.
2. Halving Chromosome Numbers in Germ Cells
- During sexual reproduction, germ cells (sperm and egg) undergo meiosis, a special type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half.
- This reduction is essential so that when fertilization occurs, the resulting organism has the correct diploid number of chromosomes.
3. Genetic Variation
- Chromosomes facilitate genetic variation through processes like crossing over and independent assortment during meiosis.
- This variation is vital for evolution and adaptation, allowing populations to respond to environmental changes.
4. Stability of DNA
- The maintenance of chromosome structure is crucial for the stability of DNA across generations.
- Proper chromosome alignment and segregation during cell division prevent mutations and ensure that genetic material is accurately copied and passed on.
Conclusion
In summary, while chromosomes indeed play a role in combining genetic material and ensuring stability, the correct answer to the role of chromosomes during sexual reproduction is more aligned with maintaining stability in DNA rather than solely transferring dominant traits or merely combining genes. Hence, option 'D' is the most fitting choice in this context.
Chapter doubts & questions for Heredity and Evolution - Online MCQ Tests for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Heredity and Evolution - Online MCQ Tests for Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Related Class 10 Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









