All Exams >
UPSC >
Lucent For GK >
All Questions
All questions of System of Human Body for UPSC CSE Exam
Which of the following is NOT a function of lymphocytes?- a)Producing antibodies
- b)Engulfing bacteria and foreign particles
- c)Recognizing and destroying cancer cells
- d)Transporting nutrients to the cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a function of lymphocytes?
a)
Producing antibodies
b)
Engulfing bacteria and foreign particles
c)
Recognizing and destroying cancer cells
d)
Transporting nutrients to the cells

|
Knowledge Center answered |
Lymphocytes are responsible for producing antibodies, which are proteins that help recognize and neutralize specific pathogens or foreign substances in the body. Other functions of lymphocytes include engulfing bacteria and foreign particles, as well as recognizing and destroying cancer cells.
Where do the majority of the digestive processes occur?- a)Small intestine
- b)Large intestine
- c)Stomach
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where do the majority of the digestive processes occur?
a)
Small intestine
b)
Large intestine
c)
Stomach
d)
None of the above
|
|
Ipsita Mishra answered |
Overview of Digestive Processes
The human digestive system is a complex network responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. While various organs play critical roles, the majority of digestion occurs in the small intestine.
Role of the Small Intestine
- The small intestine, comprising three sections—duodenum, jejunum, and ileum—is where most digestive processes take place.
- It is approximately 20 feet long, providing ample surface area for nutrient absorption.
Digestive Enzymes and Bile
- In the duodenum, digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver mix with chyme (partially digested food).
- These substances break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller molecules, making them easier to absorb.
Absorption of Nutrients
- The jejunum and ileum have tiny, finger-like projections called villi and microvilli that increase the surface area, allowing for maximum nutrient absorption.
- Essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and fatty acids are absorbed into the bloodstream here.
Limited Digestion in Other Organs
- While the stomach initiates digestion through acid and enzymes, its primary role is to break down food into a semi-liquid form called chyme.
- The large intestine mainly absorbs water and electrolytes and is involved in the formation of stool, rather than active digestion.
Conclusion
The small intestine’s structure and function make it the primary site for digestive processes. Its role in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
The human digestive system is a complex network responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. While various organs play critical roles, the majority of digestion occurs in the small intestine.
Role of the Small Intestine
- The small intestine, comprising three sections—duodenum, jejunum, and ileum—is where most digestive processes take place.
- It is approximately 20 feet long, providing ample surface area for nutrient absorption.
Digestive Enzymes and Bile
- In the duodenum, digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver mix with chyme (partially digested food).
- These substances break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller molecules, making them easier to absorb.
Absorption of Nutrients
- The jejunum and ileum have tiny, finger-like projections called villi and microvilli that increase the surface area, allowing for maximum nutrient absorption.
- Essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and fatty acids are absorbed into the bloodstream here.
Limited Digestion in Other Organs
- While the stomach initiates digestion through acid and enzymes, its primary role is to break down food into a semi-liquid form called chyme.
- The large intestine mainly absorbs water and electrolytes and is involved in the formation of stool, rather than active digestion.
Conclusion
The small intestine’s structure and function make it the primary site for digestive processes. Its role in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Which of the following is made and stored in the liver cells?- a)Galactose
- b)Lactose
- c)Glycogen
- d)Arabinose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is made and stored in the liver cells?
a)
Galactose
b)
Lactose
c)
Glycogen
d)
Arabinose

|
Bank Exams India answered |
- The polysaccharide is produced and then stored as glycogen in the liver. Glycogen is transformed into glucose when the body needs energy, and then glucose is released into the blood to reach the target cell.
- A multibranched polymer of glucose is called glycogen.
- In both humans and animals, glucose is stored as glycogen.
- Mostly in the liver and muscles, glycogen is created and stored.
- The process of glycogenesis transforms any glucose that is not immediately consumed into glycogen for storage in the liver and muscles.
What is the primary function of the lymphatic system?- a)Transport oxygen to the cells
- b)Pump blood throughout the body
- c)Regulate body temperature
- d)Maintain fluid balance and fight infections
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary function of the lymphatic system?
a)
Transport oxygen to the cells
b)
Pump blood throughout the body
c)
Regulate body temperature
d)
Maintain fluid balance and fight infections

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The primary function of the lymphatic system is to maintain fluid balance in the body by returning excess tissue fluid, called lymph, back into the bloodstream. It also plays a crucial role in the immune system by filtering and fighting infections.
What is the function of saliva in digestion?- a)Starch
- b)Fiber
- c)Proteins
- d)Fats
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the function of saliva in digestion?
a)
Starch
b)
Fiber
c)
Proteins
d)
Fats

|
Kalyan Verma answered |
Function of Saliva in Digestion
Saliva plays a crucial role in the digestive process, particularly in the breakdown of starches.
Composition of Saliva
- Saliva is composed mainly of water, electrolytes, mucus, and enzymes.
- The most significant enzyme present in saliva is **amylase** (specifically salivary amylase or ptyalin).
Role of Salivary Amylase
- **Starch Breakdown**: Salivary amylase initiates the process of starch digestion by breaking down complex carbohydrates (starches) into simpler sugars like maltose and dextrin.
- **Chemical Reaction**: When food is chewed and mixed with saliva, amylase begins to hydrolyze starch molecules, making them more accessible for further digestion in the stomach and small intestine.
Facilitation of Taste and Swallowing
- **Taste Enhancement**: Saliva helps dissolve food particles, allowing taste buds on the tongue to detect flavors more effectively.
- **Lubrication**: It moistens food, facilitating easier swallowing and preventing irritation in the esophagus.
Overall Importance
- Saliva not only aids in the mechanical breakdown of food but also begins the chemical digestion of starches.
- This enzymatic action is vital for the efficient absorption of nutrients later in the digestive tract.
In summary, while saliva has multiple functions, its primary role in digestion revolves around the enzymatic breakdown of starches, making option 'A' the correct answer.
Saliva plays a crucial role in the digestive process, particularly in the breakdown of starches.
Composition of Saliva
- Saliva is composed mainly of water, electrolytes, mucus, and enzymes.
- The most significant enzyme present in saliva is **amylase** (specifically salivary amylase or ptyalin).
Role of Salivary Amylase
- **Starch Breakdown**: Salivary amylase initiates the process of starch digestion by breaking down complex carbohydrates (starches) into simpler sugars like maltose and dextrin.
- **Chemical Reaction**: When food is chewed and mixed with saliva, amylase begins to hydrolyze starch molecules, making them more accessible for further digestion in the stomach and small intestine.
Facilitation of Taste and Swallowing
- **Taste Enhancement**: Saliva helps dissolve food particles, allowing taste buds on the tongue to detect flavors more effectively.
- **Lubrication**: It moistens food, facilitating easier swallowing and preventing irritation in the esophagus.
Overall Importance
- Saliva not only aids in the mechanical breakdown of food but also begins the chemical digestion of starches.
- This enzymatic action is vital for the efficient absorption of nutrients later in the digestive tract.
In summary, while saliva has multiple functions, its primary role in digestion revolves around the enzymatic breakdown of starches, making option 'A' the correct answer.
Which of the following Enzyme in the human body starts the digestion of proteins?- a)Trypsin
- b)Lactose
- c)Pepsin
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following Enzyme in the human body starts the digestion of proteins?
a)
Trypsin
b)
Lactose
c)
Pepsin
d)
None of these

|
Knowledge Center answered |
- The enzyme pepsin digests proteins.
- Protein is the basic molecule in the human body.
- The proenzyme pepsinogen that is in contact with hydrochloric acid gets transformed into the active enzyme pepsin.
- Pepsin transformed proteins into peptones.
How many phalanges are present in each hand of an adult human?
- a)5
- b)14
- c)11
- d)20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many phalanges are present in each hand of an adult human?
a)
5
b)
14
c)
11
d)
20

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Each hand of an adult human has 10 phalanges: 3 in each finger (proximal, middle, and distal) and 2 in the thumb (proximal and distal).
Which of the following organs is affected by the illness cirrhosis?- a)Kidney
- b)Liver
- c)Pancreas
- d)Small intestine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organs is affected by the illness cirrhosis?
a)
Kidney
b)
Liver
c)
Pancreas
d)
Small intestine

|
Debanshi Sarkar answered |
Understanding Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a progressive liver disease characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, leading to a decline in liver function. It is a serious condition that can result from various factors, primarily chronic alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Key Effects on the Liver
- **Scar Tissue Formation**: Cirrhosis causes the liver to become scarred, which impairs its ability to function effectively.
- **Impaired Liver Functions**: The liver plays a critical role in detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile for digestion, and synthesizing proteins necessary for blood clotting. Cirrhosis disrupts these functions.
- **Complications**: Patients with cirrhosis may experience complications such as portal hypertension, liver failure, and an increased risk of liver cancer.
Common Causes of Cirrhosis
- **Chronic Alcohol Abuse**: Long-term excessive drinking can lead to alcoholic liver disease and ultimately cirrhosis.
- **Chronic Viral Hepatitis**: Hepatitis B and C can cause long-term inflammation and damage to the liver, leading to cirrhosis.
- **Fatty Liver Disease**: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasingly recognized as a cause of cirrhosis, often associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Conclusion
In summary, cirrhosis primarily affects the liver, leading to severe health complications and requiring ongoing medical management. Early detection and addressing the underlying causes are crucial for preventing further liver damage.
Cirrhosis is a progressive liver disease characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, leading to a decline in liver function. It is a serious condition that can result from various factors, primarily chronic alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Key Effects on the Liver
- **Scar Tissue Formation**: Cirrhosis causes the liver to become scarred, which impairs its ability to function effectively.
- **Impaired Liver Functions**: The liver plays a critical role in detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile for digestion, and synthesizing proteins necessary for blood clotting. Cirrhosis disrupts these functions.
- **Complications**: Patients with cirrhosis may experience complications such as portal hypertension, liver failure, and an increased risk of liver cancer.
Common Causes of Cirrhosis
- **Chronic Alcohol Abuse**: Long-term excessive drinking can lead to alcoholic liver disease and ultimately cirrhosis.
- **Chronic Viral Hepatitis**: Hepatitis B and C can cause long-term inflammation and damage to the liver, leading to cirrhosis.
- **Fatty Liver Disease**: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasingly recognized as a cause of cirrhosis, often associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Conclusion
In summary, cirrhosis primarily affects the liver, leading to severe health complications and requiring ongoing medical management. Early detection and addressing the underlying causes are crucial for preventing further liver damage.
Nervous System consists of- a)Brain
- b)Spinal Cord
- c)Nerves
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nervous System consists of
a)
Brain
b)
Spinal Cord
c)
Nerves
d)
All the above

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. These components work together to process and transmit information throughout the body, allowing for the coordination of various bodily functions and responses.
The brain is the central control center of the nervous system. It receives, interprets, and processes sensory information, initiates voluntary movements, and regulates numerous physiological processes.
The spinal cord is a long, cylindrical bundle of nerves that extends from the brain down the vertebral column. It serves as a communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body. The spinal cord relays signals between the brain and peripheral nerves, and it also carries out reflex actions independently of the brain.
Nerves are bundles of specialized cells called neurons that transmit electrical signals throughout the body. They connect the central nervous system to various organs, muscles, and sensory receptors, allowing for the transmission of sensory information to the brain and the initiation of motor responses.
Together, the brain, spinal cord, and nerves form the complex network of the nervous system, enabling the body to interact with its environment and regulate its internal functions.
Which of the following muscles is primarily responsible for breathing during normal respiration?- a)Diaphragm
- b)Quadriceps
- c)Biceps
- d)Hamstrings
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following muscles is primarily responsible for breathing during normal respiration?
a)
Diaphragm
b)
Quadriceps
c)
Biceps
d)
Hamstrings

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
The diaphragm is the primary muscle responsible for breathing during normal respiration. It contracts and relaxes to create changes in lung volume.
Which of the following is not a human salivary gland?- a)Parotid
- b)Submaxillary
- c)Sublingual
- d)Infra-orbital
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a human salivary gland?
a)
Parotid
b)
Submaxillary
c)
Sublingual
d)
Infra-orbital

|
Knowledge Center answered |
- The parotid gland, submaxillary gland, sublingual gland, and infra-orbital gland are the four pairs of salivary glands found in rabbits.
- Humans do not have an infraorbital gland.
Which of the following is a harmful effect of smoking on the respiratory system?- a)Increased lung capacity
- b)Improved oxygenation of blood
- c)Chronic bronchitis
- d)Enhanced sense of smell
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a harmful effect of smoking on the respiratory system?
a)
Increased lung capacity
b)
Improved oxygenation of blood
c)
Chronic bronchitis
d)
Enhanced sense of smell

|
Knowledge Center answered |
Smoking can lead to chronic bronchitis, a condition characterized by persistent inflammation of the bronchial tubes, excessive mucus production, and coughing.
In which of the following excess blood is stored and released when there is deficiency?- a)Adrenal gland
- b)Pancreas
- c)Spleen
- d)Thyroid gland
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following excess blood is stored and released when there is deficiency?
a)
Adrenal gland
b)
Pancreas
c)
Spleen
d)
Thyroid gland

|
Knowledge Center answered |
- In the body, the spleen serves a variety of supportive functions.
- As a component of the immune system, it filters blood.
- The spleen stores platelets and white blood cells in addition to recycling old red blood cells.
- Additionally, certain types of germs that cause meningitis and pneumonia are combated by the spleen.
- Your spleen has the capacity to store up to a cup of reserve blood when the arteries are opened up.
- In response, your spleen may discharge that reserve blood into your body.
Which is the longest segment of the digestive system in the human body?- a)Pancreatic duct
- b)Small intestine
- c)Large intestine
- d)Esophagus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the longest segment of the digestive system in the human body?
a)
Pancreatic duct
b)
Small intestine
c)
Large intestine
d)
Esophagus

|
Knowledge Center answered |
- The small intestine is the longest component of the digestive system.
- The length of the small intestine is 7 meters (22 feet).
- The small intestine’s primary activities are to absorb nutrients and finish food digestion.
Which of the following has a closed-type circulatory system?- a)Cockroach
- b)Fish
- c)Mollusca
- d)Scorpion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has a closed-type circulatory system?
a)
Cockroach
b)
Fish
c)
Mollusca
d)
Scorpion

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
Phylum Arthropoda and Mollusca are related and include an open circulatory system. Fish belong to the phylum Chordata which consists of a close circulatory system. Cockroaches and scorpions are part of the class Insecta phylum Arthropoda.
Which of the following are NOT a component of the circulatory system?- a)Capillaries
- b)Villi
- c)Veins
- d)Arteries
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are NOT a component of the circulatory system?
a)
Capillaries
b)
Villi
c)
Veins
d)
Arteries

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
Very tiny blood vessels are referred to as capillaries. The body’s capillaries spread out like a mesh. Blood is carried to every area of the body by way of these capillaries. The blood channels that convey blood away from the heart are known as arteries. Except for the pulmonary and avascular arteries, all arteries contain blood that is rich in oxygen. A “vein” is a tube that transfers blood from the body to the heart and back again. Villi is a component of the gut that aids in the absorption of nutrients from food.
A double membrane sac known as the _______ protects the human heart.- a)Plura
- b)Kura
- c)Epicardium
- d)Pericardium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A double membrane sac known as the _______ protects the human heart.
a)
Plura
b)
Kura
c)
Epicardium
d)
Pericardium

|
Knowledge Center answered |
The pericardium is the heart’s outermost layer of protection. It is a membrane that surrounds the heart and is made up of an inner double layer of serous membrane and an outside fibrous layer. In most animals, the heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood by the circulatory system to the blood arteries. The liver aids in the breakdown of fat molecules. For maintaining a healthy balance of fluids, the kidney aids in the removal of waste and poisons from the body. Bones protect our important organs and assist in structural bodily support.
Which of the following statements about lymph is correct?- a)Lymph is composed of only white blood cells
- b)Lymph is a clear fluid that does not contain any cells
- c)Lymph carries oxygen to the body's cells
- d)Lymph transports fats, proteins, and other substances throughout the body
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about lymph is correct?
a)
Lymph is composed of only white blood cells
b)
Lymph is a clear fluid that does not contain any cells
c)
Lymph carries oxygen to the body's cells
d)
Lymph transports fats, proteins, and other substances throughout the body

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Lymph is a clear fluid that contains white blood cells, proteins, fats, and other substances. It is responsible for transporting these substances throughout the body and plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, immune responses, and the absorption of fats from the small intestine.
All of the following are hormones of the anterior pituitary except:- a)Human growth hormone (GH)
- b)Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- c)Parathyroid hormone(PTH)
- d)Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
All of the following are hormones of the anterior pituitary except:
a)
Human growth hormone (GH)
b)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
c)
Parathyroid hormone(PTH)
d)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is not a hormone of the anterior pituitary. It is a hormone produced by the parathyroid glands, which are separate from the pituitary gland. PTH plays a crucial role in regulating calcium and phosphate levels in the blood and bones. The other options, human growth hormone (GH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), are all hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.
Which of the following is responsible for producing sound in the respiratory system?- a)Larynx
- b)Pharynx
- c)Trachea
- d)Bronchi
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is responsible for producing sound in the respiratory system?
a)
Larynx
b)
Pharynx
c)
Trachea
d)
Bronchi

|
Knowledge Center answered |
The larynx, also known as the voice box, is responsible for producing sound and housing the vocal cords.
The respiratory center, which controls breathing, is located in the:- a)Brainstem
- b)Cerebellum
- c)Cerebrum
- d)Hypothalamus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The respiratory center, which controls breathing, is located in the:
a)
Brainstem
b)
Cerebellum
c)
Cerebrum
d)
Hypothalamus

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
The respiratory center, which controls breathing, is located in the brainstem.
he medical condition characterized by the inflammation of the air passages and excessive mucus production is called:- a)Pneumonia
- b)Asthma
- c)Tuberculosis
- d)Bronchitis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
he medical condition characterized by the inflammation of the air passages and excessive mucus production is called:
a)
Pneumonia
b)
Asthma
c)
Tuberculosis
d)
Bronchitis

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Bronchitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to excessive mucus production and difficulty breathing.
Which of the following statement is correct about Cerebellum?- a)It regulates the muscular movement for locomotion
- b)It is a part of brain
- c)Both A and B
- d)(C2H2O)n COOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is correct about Cerebellum?
a)
It regulates the muscular movement for locomotion
b)
It is a part of brain
c)
Both A and B
d)
(C2H2O)n COOH

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
The correct statement about the cerebellum is that it regulates muscular movement for locomotion and it is a part of the brain.
In the pancreas, which are the cells that secrete insulin, decrease the blood levels of glucose.- a)delta
- b)alpha
- c)beta
- d)theta
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the pancreas, which are the cells that secrete insulin, decrease the blood levels of glucose.
a)
delta
b)
alpha
c)
beta
d)
theta

|
Knowledge Center answered |
In the pancreas, the cells that secrete insulin and decrease blood glucose levels are called beta cells. Insulin is a hormone produced and released by these beta cells in response to high blood glucose levels. When you eat food, especially carbohydrates, the blood glucose levels rise, and insulin is released to help transport glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it can be used for energy or stored for future use. This process helps regulate blood sugar levels and prevents them from becoming too high. Alpha (option B), delta (option A), and gamma (option D) cells have different functions in the pancreas and are not involved in insulin secretion.
Which of the following is NOT an endocrine gland?- a)Hypothalamus
- b)Pituitary
- c)Parathyroid
- d)Pancreas
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT an endocrine gland?
a)
Hypothalamus
b)
Pituitary
c)
Parathyroid
d)
Pancreas

|
Knowledge Center answered |
The hypothalamus is NOT an endocrine gland. While it plays a crucial role in the endocrine system by producing and releasing neurohormones that control the pituitary gland's activities, it is a region in the brain and not a gland itself. The pituitary gland (option B), parathyroid glands (option C), and pancreas (option D) are all endocrine glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate various physiological processes in the body.
The Rennin enzyme is secreted in which of the following areas of the Alimentary Canal?- a)Stomach
- b)Mouth
- c)Pancreas
- d)Duodenum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Rennin enzyme is secreted in which of the following areas of the Alimentary Canal?
a)
Stomach
b)
Mouth
c)
Pancreas
d)
Duodenum

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
- Rennin is a proteolytic enzyme present in the gastric juice in the stomach of infants which aids in the digestion of Casein (milk protein).
- Rennin is produced by the main cells and is also referred to as chymosin.
- Its help in digestion is to curdle or coagulate milk in the stomach, which is crucial for young animals.
- Rennin secretions are at their highest in the first few days after birth, then they start to fall, and then pepsin takes their place.
- Rennin is released as an inactive proenzyme that is known as prochymosin and becomes active when it comes into contact with an acidic media.
Which of the following statements is true about the epiglottis?- a)It covers the trachea during swallowing to prevent food from entering the airway.
- b)It is responsible for gas exchange in the lungs.
- c)It produces sound during speech.
- d)It is located in the nasal cavity.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true about the epiglottis?
a)
It covers the trachea during swallowing to prevent food from entering the airway.
b)
It is responsible for gas exchange in the lungs.
c)
It produces sound during speech.
d)
It is located in the nasal cavity.

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The epiglottis is a flap-like structure that covers the trachea during swallowing to ensure that food does not enter the airway and cause choking.
Which of the following portion of the stomach opens into the small intestine?- a)Cardiac portion
- b)Fundic portion
- c)Pyloric portion
- d)Body portion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following portion of the stomach opens into the small intestine?
a)
Cardiac portion
b)
Fundic portion
c)
Pyloric portion
d)
Body portion

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
The stomach is a muscular J- shaped thickly walled bag-like structure that is one function that stores the food for several hours by a sphincter called the gastro-esophageal sphincter.
It is divided into four portions that are Fundus, Cardiac, Body, and Pyloric regions.
The pylorus is a narrow cone-shaped constriction placed at the end of the stomach and the starting of the small intestine.
It consists of two sections antrum which combines the parts of the stomach and the pyloric canal and also joins the stomach and small intestine.
The pyloric region opens into the small intestine through the Pyloric sphincter.
It is divided into four portions that are Fundus, Cardiac, Body, and Pyloric regions.
The pylorus is a narrow cone-shaped constriction placed at the end of the stomach and the starting of the small intestine.
It consists of two sections antrum which combines the parts of the stomach and the pyloric canal and also joins the stomach and small intestine.
The pyloric region opens into the small intestine through the Pyloric sphincter.
Name the hormone, which is released by the posterior pituitary.- a)Oxytocin
- b)TSH
- c)ICSH
- d)Prolactin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the hormone, which is released by the posterior pituitary.
a)
Oxytocin
b)
TSH
c)
ICSH
d)
Prolactin

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Oxytocin is the hormone that is released by the posterior pituitary gland. The posterior pituitary stores and releases two main hormones: oxytocin and vasopressin (also known as antidiuretic hormone, ADH). Oxytocin is responsible for various functions, including uterine contractions during childbirth and milk ejection during breastfeeding. It also plays a role in social bonding and affectionate behaviors. TSH (option B), ICSH (option C), and prolactin (option D) are hormones released by the anterior pituitary gland, which is a separate part of the pituitary gland with different functions.
Which of the following is NOT a part of the axial skeleton?- a)Skull
- b)Spine
- c)Ribs
- d)Clavicle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the axial skeleton?
a)
Skull
b)
Spine
c)
Ribs
d)
Clavicle

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The clavicle, also known as the collarbone, is not a part of the axial skeleton. It is included in the appendicular skeleton.
What is the primary difference between lymph and blood?- a)Lymph contains only white blood cells
- b)Lymph lacks red blood cells and platelets
- c)Lymph is pumped by the heart, while blood is not
- d)Lymph is responsible for transporting hormones, while blood is not
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary difference between lymph and blood?
a)
Lymph contains only white blood cells
b)
Lymph lacks red blood cells and platelets
c)
Lymph is pumped by the heart, while blood is not
d)
Lymph is responsible for transporting hormones, while blood is not

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The primary difference between lymph and blood is that lymph lacks red blood cells and platelets. Lymph mainly consists of a clear fluid called plasma, white blood cells (including lymphocytes), proteins, fats, and other substances.
Loop of Henle is concerned with- a)Reproduction
- b)Digestion
- c)Excretion
- d)Respiration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Loop of Henle is concerned with
a)
Reproduction
b)
Digestion
c)
Excretion
d)
Respiration

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
- Loop of Henle is part of Nephron.
- It is a functional and structural unit of the kidney which plays major role in Excretion.
- Loop of Henle, long U-shaped portion of the tubule that conducts urine within each nephron of the kidney of reptiles, birds, and mammals.
- The principal function of the Loop of Henle is in the recovery of water and sodium chloride from urine.
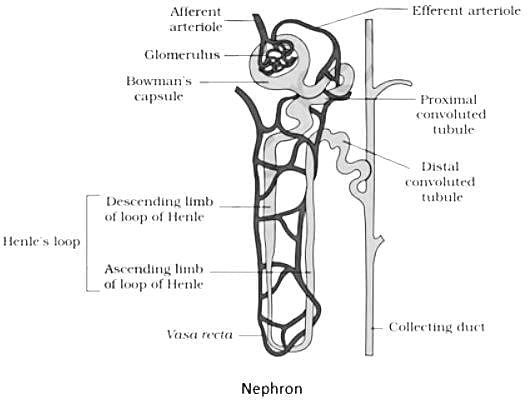
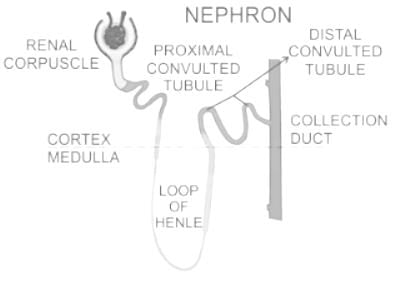
The excretory unit in human is- a)Urethra
- b)Nephron
- c)Nephridia
- d)Neurons
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The excretory unit in human is
a)
Urethra
b)
Nephron
c)
Nephridia
d)
Neurons

|
Knowledge Center answered |
The excretory unit in humans is Nephron.
The nephron:
The nephron:
- The nephron in human beings is part of the system for excretion. It is the functional unit of the mammalian kidney.
- These nephrons perform the function of filtration of blood and deposition of urine in the collecting duct.
- This urine is later excreted out from the body through the urethral opening.
- A Nephron has three main parts:
- Proximal Nephron.
- Loop of Henle.
- Distal Nephron
What are lymph nodes responsible for?- a)Producing red blood cells
- b)Filtering foreign substances from the lymph
- c)Absorbing nutrients from the intestines
- d)Pumping lymph throughout the body
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What are lymph nodes responsible for?
a)
Producing red blood cells
b)
Filtering foreign substances from the lymph
c)
Absorbing nutrients from the intestines
d)
Pumping lymph throughout the body

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
Lymph nodes are responsible for filtering foreign substances, such as pathogens and toxins, from the lymph fluid. They contain specialized immune cells that help identify and destroy these harmful substances.
Which part of the body can be called a kind of “blood bank”:- a)Heart
- b)Liver
- c)Spleen
- d)Lungs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the body can be called a kind of “blood bank”:
a)
Heart
b)
Liver
c)
Spleen
d)
Lungs

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Spleen is referred to as a blood bank because it is cleaned the blood filtering and storing blood cells for an emergency situation like Hemorrhagic Shock Spleen is another name for the “graveyard of blood” as it purifies the blood by removing microbes and worn-out RBCs. The spleen is placed beneath the ribcage and much above the stomach (upper left of the abdomen) under the diaphragm.
Who operates the first heart transplant procedure?- a)William Harvey
- b)Watson
- c)Christian Bernard
- d)Khorana
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who operates the first heart transplant procedure?
a)
William Harvey
b)
Watson
c)
Christian Bernard
d)
Khorana

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Christiaan Neethling Barnard, a South African cardiac surgeon who is regarded as the founder of heart transplantation, carried out the first successful human-to-human heart transplant on December 3, 1967. The world’s media reported on the patient’s improvement virtually hourly. Although Mr. Louis Washansky, the patient, passed away after just 18 days, Barnard quickly performed a second transplant, and this patient went on to live an active life for almost 19 months.
Which hydrolytic enzymes react in a low pH environment?- a)Peroxidases
- b)Hydrolases
- c)Amylases
- d)Proteases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which hydrolytic enzymes react in a low pH environment?
a)
Peroxidases
b)
Hydrolases
c)
Amylases
d)
Proteases

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
Hydrolytic enzymes disassembled protein, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fat molecules into their most basic components.
Mostly all digestive enzymes are hydrolytic enzymes.
Due to the release of HCl, the pH of the stomach is low. Protease, a protein-digesting enzyme, operates in low pH environments, such as the stomach.
Amylase is a starch (carbohydrate) digesting enzyme that’s why carbohydrate digestion does not take place in the stomach.
The dehydrogenation (oxidation) of numerous compounds in the presence of hydrogen peroxide is catalyzed by peroxidase, an iron-containing enzyme that is primarily found in plants but is also present in leucocytes and milk.
Mostly all digestive enzymes are hydrolytic enzymes.
Due to the release of HCl, the pH of the stomach is low. Protease, a protein-digesting enzyme, operates in low pH environments, such as the stomach.
Amylase is a starch (carbohydrate) digesting enzyme that’s why carbohydrate digestion does not take place in the stomach.
The dehydrogenation (oxidation) of numerous compounds in the presence of hydrogen peroxide is catalyzed by peroxidase, an iron-containing enzyme that is primarily found in plants but is also present in leucocytes and milk.
The condition "osteoarthritis" primarily affects which part of a joint?- a)Synovium
- b)Articular cartilage
- c)Bursae
- d)Meniscus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The condition "osteoarthritis" primarily affects which part of a joint?
a)
Synovium
b)
Articular cartilage
c)
Bursae
d)
Meniscus

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Osteoarthritis primarily affects the articular cartilage, causing its degeneration and leading to joint pain and stiffness.
Name the hormone which is synthesized from histidine amino acid?- a)Dopamine
- b)Norepinephrine
- c)Epinephrine
- d)Histamine
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the hormone which is synthesized from histidine amino acid?
a)
Dopamine
b)
Norepinephrine
c)
Epinephrine
d)
Histamine

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
Histamine is a hormone that is synthesized from the amino acid histidine. It plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including regulating the immune response, stomach acid secretion, and neurotransmission. Histamine is released by certain cells in the body, such as mast cells, and is involved in allergic reactions and inflammation. It also acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain, contributing to various functions related to sleep, appetite, and cognition.
The patella is an example of which type of bone?- a)Long bone
- b)Flat bone
- c)Short bone
- d)Sesamoid bone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The patella is an example of which type of bone?
a)
Long bone
b)
Flat bone
c)
Short bone
d)
Sesamoid bone

|
Knowledge Center answered |
The patella, commonly known as the kneecap, is a sesamoid bone. Sesamoid bones develop within tendons, increasing their mechanical effect.
The long bones of the body are responsible for:- a)Providing support and structure
- b)Assisting in digestion
- c)Producing hormones
- d)Aiding in nerve transmission
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The long bones of the body are responsible for:
a)
Providing support and structure
b)
Assisting in digestion
c)
Producing hormones
d)
Aiding in nerve transmission

|
Glance Learning Institute answered |
Long bones in the body, such as the femur and humerus, provide support and structure to the body and help with movement.
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by:- a)Excessive bone growth
- b)Weak and brittle bones
- c)Inflammation of the joints
- d)Dislocation of bones
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by:
a)
Excessive bone growth
b)
Weak and brittle bones
c)
Inflammation of the joints
d)
Dislocation of bones

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Osteoporosis is a condition in which bones become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures.
What is the primary function of red bone marrow?- a)Lipid storage
- b)Muscle attachment
- c)Blood cell formation
- d)Calcium regulation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary function of red bone marrow?
a)
Lipid storage
b)
Muscle attachment
c)
Blood cell formation
d)
Calcium regulation

|
Knowledge Center answered |
Red bone marrow is responsible for the production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
The flap-like structure that covers the trachea during swallowing is called:- a)Epiglottis
- b)Larynx
- c)Pharynx
- d)Bronchus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The flap-like structure that covers the trachea during swallowing is called:
a)
Epiglottis
b)
Larynx
c)
Pharynx
d)
Bronchus

|
Bank Exams India answered |
The epiglottis is a flap-like structure that covers the trachea during swallowing to prevent food from entering the airway.
What is the function of the spleen in the lymphatic system?- a)Production of lymphocytes
- b)Filtration of blood and removal of old red blood cells
- c)Absorption of nutrients from the intestines
- d)Pumping lymph throughout the body
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the function of the spleen in the lymphatic system?
a)
Production of lymphocytes
b)
Filtration of blood and removal of old red blood cells
c)
Absorption of nutrients from the intestines
d)
Pumping lymph throughout the body

|
Knowledge Center answered |
The spleen filters blood and removes old or damaged red blood cells from circulation. It also plays a role in immune responses by producing lymphocytes and antibodies, as well as storing platelets.
The secretions from which of these glands differs between males and females?- a)Adrenal
- b)Parathyroid
- c)Pancreas
- d)Gonadal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The secretions from which of these glands differs between males and females?
a)
Adrenal
b)
Parathyroid
c)
Pancreas
d)
Gonadal

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The secretions from the gonadal glands (testes in males and ovaries in females) differ between males and females. These glands produce hormones such as testosterone in males and estrogen and progesterone in females, which play crucial roles in the development and functioning of the male and female reproductive systems, leading to the development of secondary sexual characteristics and regulating reproductive processes.
Where are produced red blood cells?- a)Heart
- b)Lymph Nodes
- c)Liver
- d)Bone Marrow
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Where are produced red blood cells?
a)
Heart
b)
Lymph Nodes
c)
Liver
d)
Bone Marrow

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
- Bone Marrow is the soft tissue found inside the Medullary cavities of a bone
- It is primarily placed in the hip and thigh bones.
- Bone marrow generates immature cells called Stem cells that can develop into various types of cells later on.
- Bone marrow produces two different types of stem cells: mesenchymal and hematopoietic
- Mesenchymal cells develop into fat cartilage and bones
- whereas Hematopoietic cells develop and turn into Blood cells (RBC, WBC, and Platelets)
The respiratory system works closely with which other body system to provide oxygen and remove carbon dioxide?- a)Digestive system
- b)Nervous system
- c)Circulatory system
- d)Muscular system
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The respiratory system works closely with which other body system to provide oxygen and remove carbon dioxide?
a)
Digestive system
b)
Nervous system
c)
Circulatory system
d)
Muscular system

|
Bank Exams India answered |
The respiratory system works closely with the circulatory system to provide oxygen to body tissues and remove carbon dioxide produced during cellular respiration.
The fontanelles in a baby's skull serve what purpose?- a)Allow for brain growth during infancy
- b)Aid in chewing food
- c)Regulate body temperature
- d)Facilitate vision development
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The fontanelles in a baby's skull serve what purpose?
a)
Allow for brain growth during infancy
b)
Aid in chewing food
c)
Regulate body temperature
d)
Facilitate vision development

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Fontanelles are soft spots in a baby's skull that allow for brain growth during infancy and make the skull more flexible during birth.
Chapter doubts & questions for System of Human Body - Lucent For GK 2025 is part of UPSC CSE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UPSC CSE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UPSC CSE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of System of Human Body - Lucent For GK in English & Hindi are available as part of UPSC CSE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC CSE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










