All Exams >
BPSC (Bihar) >
History for State PSC Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Beginning of European Commerce for BPSC (Bihar) Exam
Who is the first President of the Council of Fort William?- a)Job Charnock
- b)Sir Charles Eyre
- c)Francis Day
- d)Gerald Aungier
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is the first President of the Council of Fort William?
a)
Job Charnock
b)
Sir Charles Eyre
c)
Francis Day
d)
Gerald Aungier
|
|
Pritam Chaudhary answered |
First President of the Council of Fort William
The first President of the Council of Fort William was Sir Charles Eyre. He served as the President from 1690 to 1692. The Council of Fort William was established in 1690 by the East India Company in Fort William, Bengal. It was the first administrative body of the British in India and was responsible for the governance of the British territories in Bengal.
Sir Charles Eyre
Sir Charles Eyre was a British administrator and soldier. He was appointed as the President of the Council of Fort William in 1690. He was also the Governor of Bombay from 1708 to 1710. Sir Charles Eyre was known for his administrative skills and he played an important role in the expansion of the British territories in India.
Establishment of the Council of Fort William
The Council of Fort William was established by the East India Company in 1690. The Council was responsible for the administration of the British territories in Bengal. The Council was headed by the President and it included other members such as the Governor of Fort William, the Chief Justice, and other senior officials.
Functions of the Council
The Council of Fort William had several functions, some of which are:
- Administration of justice
- Collection of revenue
- Maintenance of law and order
- Regulation of trade
- Management of the Company's affairs
Conclusion
In conclusion, Sir Charles Eyre was the first President of the Council of Fort William. The Council of Fort William was established in 1690 by the East India Company and was responsible for the governance of the British territories in Bengal. The Council had several functions such as administration of justice, collection of revenue, maintenance of law and order, regulation of trade, and management of the Company's affairs.
The first President of the Council of Fort William was Sir Charles Eyre. He served as the President from 1690 to 1692. The Council of Fort William was established in 1690 by the East India Company in Fort William, Bengal. It was the first administrative body of the British in India and was responsible for the governance of the British territories in Bengal.
Sir Charles Eyre
Sir Charles Eyre was a British administrator and soldier. He was appointed as the President of the Council of Fort William in 1690. He was also the Governor of Bombay from 1708 to 1710. Sir Charles Eyre was known for his administrative skills and he played an important role in the expansion of the British territories in India.
Establishment of the Council of Fort William
The Council of Fort William was established by the East India Company in 1690. The Council was responsible for the administration of the British territories in Bengal. The Council was headed by the President and it included other members such as the Governor of Fort William, the Chief Justice, and other senior officials.
Functions of the Council
The Council of Fort William had several functions, some of which are:
- Administration of justice
- Collection of revenue
- Maintenance of law and order
- Regulation of trade
- Management of the Company's affairs
Conclusion
In conclusion, Sir Charles Eyre was the first President of the Council of Fort William. The Council of Fort William was established in 1690 by the East India Company and was responsible for the governance of the British territories in Bengal. The Council had several functions such as administration of justice, collection of revenue, maintenance of law and order, regulation of trade, and management of the Company's affairs.
When and to whom did the Danes sell all their settlements in India?
- a) 1745-Portuguese
- b) 1776-French
- c) 1800-Dutch
- d) 1845-British
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When and to whom did the Danes sell all their settlements in India?
a)
1745-Portugueseb)
1776-Frenchc)
1800-Dutchd)
1845-British|
|
Anand Kulkarni answered |
**Answer:**
The Danes, who had established settlements in India, sold all their settlements to the British in 1845. This marked the end of Danish colonial presence in India.
**Danish Settlements in India:**
The Danes had established three settlements in India during the colonial era. These settlements were:
1. Tranquebar (Tharangambadi): Tranquebar was the first Danish settlement in India, established in 1620. It was located on the Coromandel Coast of present-day Tamil Nadu.
2. Serampore (Frederiksnagore): Serampore was established in 1755 and was located near Kolkata in present-day West Bengal. It was an important center for Danish trade and missionary activities.
3. Nicobar Islands: The Danes also briefly controlled the Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal. However, due to its remoteness and lack of economic viability, the Danish control over the Nicobar Islands was short-lived.
**Sale of Danish Settlements:**
Over time, the Danish settlements in India faced various challenges, including conflicts with other European powers, financial difficulties, and declining trade. As a result, the Danes decided to sell their settlements to the British.
The sale of Danish settlements took place in 1845, and it involved negotiations between the Danish and British authorities. The British East India Company, which had already established its dominance in India, saw the acquisition of the Danish settlements as an opportunity to further consolidate its control.
**Reasons for Sale:**
There were several reasons behind the Danish decision to sell their settlements in India:
1. Financial Difficulties: The Danish settlements had been facing financial difficulties for some time. The declining trade and increasing expenses made it difficult for the Danes to sustain their presence in India.
2. Decline in Trade: The Danish settlements had lost their significance as centers of trade. The competition from other European powers, including the British, Dutch, and French, had reduced their trade opportunities.
3. Strategic Considerations: The Danish settlements were vulnerable to attacks from other European powers. Selling the settlements to the British ensured their protection and security under British rule.
4. Lack of Support: The Danish government was not able to provide sufficient support to the settlements due to its own limitations and priorities. This further contributed to the decision to sell the settlements.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, the Danes sold all their settlements in India to the British in 1845. This was due to financial difficulties, declining trade, strategic considerations, and lack of support from the Danish government. The sale marked the end of Danish colonial presence in India and further strengthened British control in the region.
The Danes, who had established settlements in India, sold all their settlements to the British in 1845. This marked the end of Danish colonial presence in India.
**Danish Settlements in India:**
The Danes had established three settlements in India during the colonial era. These settlements were:
1. Tranquebar (Tharangambadi): Tranquebar was the first Danish settlement in India, established in 1620. It was located on the Coromandel Coast of present-day Tamil Nadu.
2. Serampore (Frederiksnagore): Serampore was established in 1755 and was located near Kolkata in present-day West Bengal. It was an important center for Danish trade and missionary activities.
3. Nicobar Islands: The Danes also briefly controlled the Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal. However, due to its remoteness and lack of economic viability, the Danish control over the Nicobar Islands was short-lived.
**Sale of Danish Settlements:**
Over time, the Danish settlements in India faced various challenges, including conflicts with other European powers, financial difficulties, and declining trade. As a result, the Danes decided to sell their settlements to the British.
The sale of Danish settlements took place in 1845, and it involved negotiations between the Danish and British authorities. The British East India Company, which had already established its dominance in India, saw the acquisition of the Danish settlements as an opportunity to further consolidate its control.
**Reasons for Sale:**
There were several reasons behind the Danish decision to sell their settlements in India:
1. Financial Difficulties: The Danish settlements had been facing financial difficulties for some time. The declining trade and increasing expenses made it difficult for the Danes to sustain their presence in India.
2. Decline in Trade: The Danish settlements had lost their significance as centers of trade. The competition from other European powers, including the British, Dutch, and French, had reduced their trade opportunities.
3. Strategic Considerations: The Danish settlements were vulnerable to attacks from other European powers. Selling the settlements to the British ensured their protection and security under British rule.
4. Lack of Support: The Danish government was not able to provide sufficient support to the settlements due to its own limitations and priorities. This further contributed to the decision to sell the settlements.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, the Danes sold all their settlements in India to the British in 1845. This was due to financial difficulties, declining trade, strategic considerations, and lack of support from the Danish government. The sale marked the end of Danish colonial presence in India and further strengthened British control in the region.
Most European powers reached India after crossing the- a)Red Sea
- b)Pacific Ocean
- c)Cape of Good Hope
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most European powers reached India after crossing the
a)
Red Sea
b)
Pacific Ocean
c)
Cape of Good Hope
d)
None of these
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The answer is (C) Cape of Good Hope, because the European came to India by land from Iraq, Saudi Arabia then Saudi Arabia and Iraq are wanted to European by this land to India then the Vasco The Gama came to India from Portugal by water way from Cape of Good Hope so all European come from this way to India.
Arrange the following chronologically:I. Fracois Martin
II. Lenoir
III. Dumas
IV. Dupleix
V. Count de Lally- a)I, II, IV, III, V
- b)II, III, IV, I, V
- c)I, II, III, IV, V
- d)I, II, III, V, IV
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following chronologically:
I. Fracois Martin
II. Lenoir
III. Dumas
IV. Dupleix
V. Count de Lally
II. Lenoir
III. Dumas
IV. Dupleix
V. Count de Lally
a)
I, II, IV, III, V
b)
II, III, IV, I, V
c)
I, II, III, IV, V
d)
I, II, III, V, IV
|
|
Poulomi Sengupta answered |
Chronological Order of Events:
Fracois Martin
Francois Martin was appointed as the Governor of Pondicherry in 1725.
Lenoir
Lenoir is not placed in the correct chronological order based on the information provided.
Dumas
Dumas was the Governor of Pondicherry in 1735.
Dupleix
Dupleix was the Governor of French establishments in India from 1742 to 1754.
Count de Lally
Count de Lally was appointed as the Governor of Pondicherry in 1758.
Therefore, the correct chronological order of events is:
I. Fracois Martin
II. Lenoir
III. Dumas
IV. Dupleix
V. Count de Lally
The correct option is:
c) I, II, III, IV, V
Initially, the Mughals tried to develop friendly relations with the English. Why?I. They could use the English to counter the Portuguese on the sea.
II. They could use the English to help them in opening trading posts in the Spice Islands.
III. Indian merchants would certainly benefit by competition among their foreign buyers.- a)I, II
- b)I, III
- c)III only
- d)I, II, III
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Initially, the Mughals tried to develop friendly relations with the English. Why?
I. They could use the English to counter the Portuguese on the sea.
II. They could use the English to help them in opening trading posts in the Spice Islands.
III. Indian merchants would certainly benefit by competition among their foreign buyers.
II. They could use the English to help them in opening trading posts in the Spice Islands.
III. Indian merchants would certainly benefit by competition among their foreign buyers.
a)
I, II
b)
I, III
c)
III only
d)
I, II, III

|
Upsc Toppers answered |
Initially, the Mughals tried to develop friendly relations with the English for several reasons:
- To counter the Portuguese on the sea (Statement I): The Portuguese had established a strong naval presence in the Indian Ocean and posed a challenge to Mughal power. By aligning with the English, the Mughals could weaken the Portuguese influence and control over sea routes and trade.
- Indian merchants benefiting from competition among foreign buyers (Statement III): The presence of multiple foreign trading companies, such as the Portuguese, Dutch, and English, created competition, which could potentially benefit Indian merchants by giving them more options and better prices for their goods.
Statement II is incorrect because the Mughals were not focused on using the English to help them open trading posts in the Spice Islands, as the Spice Islands were more of interest to European powers (Dutch and Portuguese), not the Mughals.
Thus, I and III are the correct reasons, making Option B the right answer.
Who gave Bombay to Charles II of England as a dowry gift for his marriage with Catherine of Braganza?
- a)The Spanish
- b)The Portugues
- c)The Dutch
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who gave Bombay to Charles II of England as a dowry gift for his marriage with Catherine of Braganza?
a)
The Spanish
b)
The Portugues
c)
The Dutch
d)
None of these

|
Master Training Institute answered |
Bombay (now Mumbai) was given to Charles II of England as part of the dowry for his marriage to Catherine of Braganza, a Portuguese princess, in 1661. The Portuguese handed over the islands of Bombay to the English crown as part of the marriage treaty. Charles II later leased Bombay to the English East India Company in 1668, which played a key role in the British expansion in India.
The English opened their first factory in south India in 1611 at- a)Cochin
- b)Masulipatam
- c)Pulicat
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The English opened their first factory in south India in 1611 at
a)
Cochin
b)
Masulipatam
c)
Pulicat
d)
None of these
|
|
Sanchita Singh answered |
The English opened their first factory in the South at Masulipatam in 1611. But they soon shifted the center of their activity to Madras the lease of which was granted to them by the local king in 1639. The English built a small fort around their factory called Fort St.
What were Calicoes?- a)Indigo exports from India
- b)Cotton exports from India
- c)Textile exports from India
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What were Calicoes?
a)
Indigo exports from India
b)
Cotton exports from India
c)
Textile exports from India
d)
None of these
|
|
Nitya Kulkarni answered |
Calico, all-cotton fabric woven in plain, or tabby, weave and printed with simple designs in one or more colours. Calico originated in Calicut, India, by the 11th century, if not earlier, and in the 17th and 18th centuries calicoes were an important commodity traded between India and Europe.
The Portuguese built their first fort on Indian soil in the territory of the Raja of- a)Calicut
- b)Cochin
- c)Daman
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Portuguese built their first fort on Indian soil in the territory of the Raja of
a)
Calicut
b)
Cochin
c)
Daman
d)
None of these

|
Lakshya Ias answered |
The Portuguese built their first fort on Indian soil in Cochin in 1503. This was after establishing friendly relations with the Raja of Cochin. The fort, known as Fort Manuel, was the first European fort in India and played a significant role in solidifying Portuguese influence on the Malabar Coast. Cochin became an important base for the Portuguese in their early years of trading and conquest in India.
The resistance from Arab traders was completely crushed by the Portuguese under - a)Albuquerque
- b)De Almedia
- c)General Pestado
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The resistance from Arab traders was completely crushed by the Portuguese under
a)
Albuquerque
b)
De Almedia
c)
General Pestado
d)
None of these
|
|
Anu Choudhary answered |
Correct Answer:A
Albuquerque left Lisbon with Tristão da Cunha in April 1506 to explore the east coast of Africa and build a fortress on the island of Socotra to block the mouth of the Red Sea and cut off Arab trade with India.
The Battle of Bedara in 1759 was fought between the English and an European power whose influence in India came to an end.Identify it.- a)The Portuguese
- b)The Danes
- c)The French
- d)The Dutch
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Battle of Bedara in 1759 was fought between the English and an European power whose influence in India came to an end.Identify it.
a)
The Portuguese
b)
The Danes
c)
The French
d)
The Dutch

|
Divey Sethi answered |
The Battle of Bedara (also known as the Battle of Chinsurah) was fought in 1759 between the English East India Company and the Dutch near Chinsurah (in modern-day West Bengal). The Dutch attempted to challenge the growing power of the English in India, but they were decisively defeated in this battle. This defeat marked the end of Dutch political and military influence in India, although they continued to engage in trade on a limited scale.
Like the Dutch the English had come to the east for the spice trade. But soon they were forced to concentrate on India. Why did his happen?- a)The powerful Dutch were well established in the spice Islands.
- b)The English were quick in realizing that a few offensives against European powers in India was enough for them to become commercial masters of the region.
- c)The Dutch were shifting the focus of their trade to the Red seaports.
- d)Both (a) and (c).
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Like the Dutch the English had come to the east for the spice trade. But soon they were forced to concentrate on India. Why did his happen?
a)
The powerful Dutch were well established in the spice Islands.
b)
The English were quick in realizing that a few offensives against European powers in India was enough for them to become commercial masters of the region.
c)
The Dutch were shifting the focus of their trade to the Red seaports.
d)
Both (a) and (c).
|
|
Srestha Kulkarni answered |
Reason for English concentration on India:
Powerful Dutch presence in the Spice Islands:
- The Dutch had a strong hold on the Spice Islands and were well established in the region.
- This made it difficult for the English to compete with them in the spice trade.
Therefore, the English were forced to shift their focus to India where they could establish themselves more successfully in the trade industry.
Powerful Dutch presence in the Spice Islands:
- The Dutch had a strong hold on the Spice Islands and were well established in the region.
- This made it difficult for the English to compete with them in the spice trade.
Therefore, the English were forced to shift their focus to India where they could establish themselves more successfully in the trade industry.
In 1658, who conquered Ceylon from the Portuguese?- a)The English
- b)The Danes
- c)The Dutch
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In 1658, who conquered Ceylon from the Portuguese?
a)
The English
b)
The Danes
c)
The Dutch
d)
None of these
|
|
Kavya Deshpande answered |
Conquest of Ceylon from the Portuguese
In 1658, the Dutch conquered Ceylon from the Portuguese in a significant military achievement in the region. This marked the end of Portuguese rule on the island and the beginning of Dutch colonial presence in Ceylon.
Reasons for the Dutch Conquest
- The Dutch East India Company, also known as the VOC, sought to expand its trade and control in the lucrative spice trade in the Indian Ocean region.
- The strategic location of Ceylon made it an attractive target for the Dutch who aimed to establish a stronghold in the region.
- The Portuguese were weakened due to internal conflicts and the Dutch saw an opportunity to challenge their dominance in the area.
Consequences of the Conquest
- The Dutch established control over key ports and territories in Ceylon, leading to the decline of Portuguese influence in the region.
- Dutch colonial rule in Ceylon lasted for over a century until they were eventually replaced by the British in the late 18th century.
- The Dutch legacy in Ceylon can still be seen in the architecture, culture, and language of the country.
Overall, the Dutch conquest of Ceylon from the Portuguese in 1658 was a significant event that shaped the colonial history of the island and the wider Indian Ocean region.
In 1658, the Dutch conquered Ceylon from the Portuguese in a significant military achievement in the region. This marked the end of Portuguese rule on the island and the beginning of Dutch colonial presence in Ceylon.
Reasons for the Dutch Conquest
- The Dutch East India Company, also known as the VOC, sought to expand its trade and control in the lucrative spice trade in the Indian Ocean region.
- The strategic location of Ceylon made it an attractive target for the Dutch who aimed to establish a stronghold in the region.
- The Portuguese were weakened due to internal conflicts and the Dutch saw an opportunity to challenge their dominance in the area.
Consequences of the Conquest
- The Dutch established control over key ports and territories in Ceylon, leading to the decline of Portuguese influence in the region.
- Dutch colonial rule in Ceylon lasted for over a century until they were eventually replaced by the British in the late 18th century.
- The Dutch legacy in Ceylon can still be seen in the architecture, culture, and language of the country.
Overall, the Dutch conquest of Ceylon from the Portuguese in 1658 was a significant event that shaped the colonial history of the island and the wider Indian Ocean region.
The centre of Portuguese power in India was- a)Goa
- b)Bijapur
- c)Calicut
- d)Cochin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The centre of Portuguese power in India was
a)
Goa
b)
Bijapur
c)
Calicut
d)
Cochin
|
|
Malavika Datta answered |
The correct option is A.
Alfonso de Albuquerque who replaced Almeida as the governor in 1509 AD, and captured Goa from the Sultan of Bijapur in 1510 AD is considered the real founder of the Portuguese power in India. Goa subsequently became the headquarters of the Portuguese settlements in India.
Alfonso de Albuquerque who replaced Almeida as the governor in 1509 AD, and captured Goa from the Sultan of Bijapur in 1510 AD is considered the real founder of the Portuguese power in India. Goa subsequently became the headquarters of the Portuguese settlements in India.
The Dutch had a stronger navy than the Portuguese. Nevertheless, the Dutch soon realized that it was difficult to trade profitably in pepper and spices in the east without the aid of- a)Cotton textiles from India
- b)The Portuguese controlled ports on the west coast of India
- c)The prevailing regional Indian power in the Deccan
- d)Both (a) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Dutch had a stronger navy than the Portuguese. Nevertheless, the Dutch soon realized that it was difficult to trade profitably in pepper and spices in the east without the aid of
a)
Cotton textiles from India
b)
The Portuguese controlled ports on the west coast of India
c)
The prevailing regional Indian power in the Deccan
d)
Both (a) and (c)

|
Lohit Matani answered |
Despite having a stronger navy than the Portuguese, the Dutch soon realized that to trade profitably in pepper and spices from the East, they needed the support of:
- Cotton textiles from India (d): Indian cotton textiles were highly valued in the Southeast Asian spice markets, and trading these textiles helped the Dutch acquire spices in exchange. Without access to Indian cotton, it was difficult to trade profitably in spices.
- The prevailing regional Indian power in the Deccan (c): The Dutch also needed the cooperation of regional powers, such as the rulers in the Deccan, to secure access to ports and trading routes, as well as to ensure safe passage for their goods.
Thus, both (d) and (c) were crucial for the Dutch to maintain profitable trade in the region.
Who was General Augier?- a)First President of the Council of Surat
- b)First Governor of Bombay and responsible for its rise into prominance
- c)First President of the Council of Madras
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who was General Augier?
a)
First President of the Council of Surat
b)
First Governor of Bombay and responsible for its rise into prominance
c)
First President of the Council of Madras
d)
None of the above
|
|
Academic Studio answered |
General Gerald Aungier (often spelled Augier) was appointed the first Governor of Bombay in 1669. He is credited with laying the foundation for Bombay (now Mumbai) to become an important trading center and one of the most significant cities under British control in India. Aungier's tenure is noted for administrative reforms and efforts to improve the infrastructure and defense of Bombay, which led to its growth in importance during the British colonial period.
What is the historical sequence of the establishment of the following French factories?I. Mahe
II. Surat
III. Masulipatnam
IV. Pondichery.- a)II, I, III, IV
- b)II, III, IV, I
- c)I, II, III, IV
- d)III, II, I, IV
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the historical sequence of the establishment of the following French factories?
I. Mahe
II. Surat
III. Masulipatnam
IV. Pondichery.
II. Surat
III. Masulipatnam
IV. Pondichery.
a)
II, I, III, IV
b)
II, III, IV, I
c)
I, II, III, IV
d)
III, II, I, IV
|
|
Deepika Dey answered |
The historical sequence of the establishment of the French factories is as follows:
II. Surat (1668): The French established their first factory in Surat in 1668. Surat was an important port city on the west coast of India and was a center of trade with Europe. The French established their factory here to tap into this trade and to compete with the Portuguese and the British who already had a presence in Surat.
III. Masulipatnam (1669): The French established their second factory at Masulipatnam in 1669. Masulipatnam was an important port city on the east coast of India and was a center of trade with Southeast Asia. The French established their factory here to tap into this trade and to compete with the Dutch who already had a presence in Masulipatnam.
IV. Pondicherry (1674): The French established their third factory at Pondicherry in 1674. Pondicherry was a small fishing village on the east coast of India, but it had a deep and safe harbor that could accommodate large ships. The French saw the potential of Pondicherry as a center of trade and established their factory here.
I. Mahe (1725): The French established their fourth and final factory at Mahe in 1725. Mahe was a small town on the west coast of India, and the French established their factory here to compete with the British who had a presence in nearby Tellicherry.
Therefore, the correct historical sequence of the establishment of the French factories is II, III, IV, I, or option B.
II. Surat (1668): The French established their first factory in Surat in 1668. Surat was an important port city on the west coast of India and was a center of trade with Europe. The French established their factory here to tap into this trade and to compete with the Portuguese and the British who already had a presence in Surat.
III. Masulipatnam (1669): The French established their second factory at Masulipatnam in 1669. Masulipatnam was an important port city on the east coast of India and was a center of trade with Southeast Asia. The French established their factory here to tap into this trade and to compete with the Dutch who already had a presence in Masulipatnam.
IV. Pondicherry (1674): The French established their third factory at Pondicherry in 1674. Pondicherry was a small fishing village on the east coast of India, but it had a deep and safe harbor that could accommodate large ships. The French saw the potential of Pondicherry as a center of trade and established their factory here.
I. Mahe (1725): The French established their fourth and final factory at Mahe in 1725. Mahe was a small town on the west coast of India, and the French established their factory here to compete with the British who had a presence in nearby Tellicherry.
Therefore, the correct historical sequence of the establishment of the French factories is II, III, IV, I, or option B.
Which is/are incorrect regarding the lease of Madras to the English by the local Raja in 1639?- a)The Raja authorised them to fortify Madras.
- b)The Raja did not authorise them to administer Madras.
- c)The Raja did not authorise them to coin money.
- d)The English built a small fort around their factory?
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is/are incorrect regarding the lease of Madras to the English by the local Raja in 1639?
a)
The Raja authorised them to fortify Madras.
b)
The Raja did not authorise them to administer Madras.
c)
The Raja did not authorise them to coin money.
d)
The English built a small fort around their factory?

|
Upsc Rank Holders answered |
In 1639, the English East India Company was granted a lease by the local Raja of Chandragiri (a vassal of the Vijayanagara Empire) to establish a trading post at Madraspatnam (now Chennai). The English were authorized to:
- Fortify Madras, which led to the construction of Fort St. George (related to statement A).
- Administer the town, meaning they could exercise some administrative control, so statement B is incorrect.
- They were not authorised to coin money (related to statement C, which is correct).
- The English did build a fort around their factory (related to statement D, which is correct).
Therefore, the only incorrect statement is B.
Between 1654 and 1667, which two powers fought in India?- a)The Dutch and the English
- b)The Dutch and the Portuguese
- c)The Portuguese and the English
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Between 1654 and 1667, which two powers fought in India?
a)
The Dutch and the English
b)
The Dutch and the Portuguese
c)
The Portuguese and the English
d)
None of these

|
K.L Institute answered |
Between 1654 and 1667, the Dutch and the English fought a series of conflicts in various parts of the world, including India, as part of the broader Anglo-Dutch Wars. These wars were primarily about control over trade routes and colonial dominance, especially in the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia. Both the Dutch East India Company (VOC) and the English East India Company were competing for control over valuable trading regions, particularly in India and the Spice Islands.
The rivalry between these two powers in India was part of their larger global struggle for supremacy in the spice trade and other lucrative markets.
Which of the following is correct?- a)By the farmans of Farrukh Siyar of 1717, the right of the East India Company to trade duty free in Bengal in lieu of Rs. 3000 was confirmed.
- b)By the farmans of Farrukhsiyar, the English were allowed to settle wherever they chose.
- c)By the farmans of Farrukhsiyar, the English were allowed to acquire additional territories around Calcutta.
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correct?
a)
By the farmans of Farrukh Siyar of 1717, the right of the East India Company to trade duty free in Bengal in lieu of Rs. 3000 was confirmed.
b)
By the farmans of Farrukhsiyar, the English were allowed to settle wherever they chose.
c)
By the farmans of Farrukhsiyar, the English were allowed to acquire additional territories around Calcutta.
d)
All of the above.
|
|
Swati Sharma answered |
Confirmation of the East India Company's Trade Rights:
- By the farmans of Farrukh Siyar of 1717, the right of the East India Company to trade duty-free in Bengal in lieu of Rs. 3000 was confirmed.
Permission for English Settlement:
- By the farmans of Farrukhsiyar, the English were allowed to settle wherever they chose.
Acquisition of Additional Territories:
- By the farmans of Farrukhsiyar, the English were allowed to acquire additional territories around Calcutta.
Summary:
- Therefore, all the statements provided in the options are correct as per historical records. Farrukhsiyar's farmans of 1717 played a significant role in granting important rights and permissions to the East India Company in Bengal, ultimately shaping the course of British colonial rule in India.
- By the farmans of Farrukh Siyar of 1717, the right of the East India Company to trade duty-free in Bengal in lieu of Rs. 3000 was confirmed.
Permission for English Settlement:
- By the farmans of Farrukhsiyar, the English were allowed to settle wherever they chose.
Acquisition of Additional Territories:
- By the farmans of Farrukhsiyar, the English were allowed to acquire additional territories around Calcutta.
Summary:
- Therefore, all the statements provided in the options are correct as per historical records. Farrukhsiyar's farmans of 1717 played a significant role in granting important rights and permissions to the East India Company in Bengal, ultimately shaping the course of British colonial rule in India.
In the sixteenth century bulk of the Portuguese trade was with- a)Vijaynagar
- b)Bijapur
- c)Malwa
- d)Cochin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the sixteenth century bulk of the Portuguese trade was with
a)
Vijaynagar
b)
Bijapur
c)
Malwa
d)
Cochin
|
|
Simran Mehta answered |
The correct option is A.
it was also decided that Vijayanagar will help the Portuguese to build ships and forts anywhere except Bhaktal.
it was also decided that Vijayanagar will help the Portuguese to build ships and forts anywhere except Bhaktal.
Fort St. David was chief centre of the Coromandal trade. It later developed into- a)Madras
- b)Pondicherry
- c)Masulimpatam
- d)Cochin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Fort St. David was chief centre of the Coromandal trade. It later developed into
a)
Madras
b)
Pondicherry
c)
Masulimpatam
d)
Cochin
|
|
Nidhi Yadav answered |
Introduction: Fort St. David played a significant role in the Coromandel trade and later developed into Madras. Let's explore the details of this transformation.
Fort St. David and the Coromandel Trade:
- Fort St. David was a British fort located in Tamil Nadu, India. It was established in 1680 near the town of Cuddalore.
- The fort was strategically located on the Coromandel Coast, making it a crucial center for trade between the British East India Company and the local merchants.
- The Coromandel Coast, also known as the Chennai Coast, was a region on the eastern coast of India that was rich in resources and attracted European traders.
- The Coromandel trade primarily involved the export of textiles, spices, indigo, and other goods from India to Europe, as well as the import of European products.
- Fort St. David served as a major trading post and a hub for the British East India Company's operations in the region.
Development into Madras:
- Over time, the British East India Company recognized the strategic importance of Fort St. David and decided to establish a more permanent settlement in the area.
- In 1639, a few kilometers north of Fort St. David, the British East India Company established a new fortified settlement called "Fort St. George."
- Fort St. George gradually grew in importance and became the headquarters of the British East India Company's operations in the Madras Presidency.
- The settlement around Fort St. George developed and expanded, attracting merchants, traders, and settlers from various parts of India and Europe.
- The British East India Company eventually named the settlement "Madras," derived from the Portuguese term "Madre de Deus" (Mother of God), referring to a church built by the Portuguese in the area.
- Madras became a prominent center of trade, administration, and culture in the region, and it played a crucial role in the British colonization of India.
Conclusion:
Fort St. David, initially established as a British fort on the Coromandel Coast, later developed into the significant settlement of Madras. This transformation was driven by the strategic importance of the area for the Coromandel trade and the subsequent growth and expansion of the British East India Company's operations. Madras went on to become a major center of trade and played a pivotal role in British colonial rule in India.
Fort St. David and the Coromandel Trade:
- Fort St. David was a British fort located in Tamil Nadu, India. It was established in 1680 near the town of Cuddalore.
- The fort was strategically located on the Coromandel Coast, making it a crucial center for trade between the British East India Company and the local merchants.
- The Coromandel Coast, also known as the Chennai Coast, was a region on the eastern coast of India that was rich in resources and attracted European traders.
- The Coromandel trade primarily involved the export of textiles, spices, indigo, and other goods from India to Europe, as well as the import of European products.
- Fort St. David served as a major trading post and a hub for the British East India Company's operations in the region.
Development into Madras:
- Over time, the British East India Company recognized the strategic importance of Fort St. David and decided to establish a more permanent settlement in the area.
- In 1639, a few kilometers north of Fort St. David, the British East India Company established a new fortified settlement called "Fort St. George."
- Fort St. George gradually grew in importance and became the headquarters of the British East India Company's operations in the Madras Presidency.
- The settlement around Fort St. George developed and expanded, attracting merchants, traders, and settlers from various parts of India and Europe.
- The British East India Company eventually named the settlement "Madras," derived from the Portuguese term "Madre de Deus" (Mother of God), referring to a church built by the Portuguese in the area.
- Madras became a prominent center of trade, administration, and culture in the region, and it played a crucial role in the British colonization of India.
Conclusion:
Fort St. David, initially established as a British fort on the Coromandel Coast, later developed into the significant settlement of Madras. This transformation was driven by the strategic importance of the area for the Coromandel trade and the subsequent growth and expansion of the British East India Company's operations. Madras went on to become a major center of trade and played a pivotal role in British colonial rule in India.
In 1686 a war broke out in Bengal between Aurangzeb and the English East India Company. What was its outcome?
- a)The Mughals suffered heavy losses.
- b)The East India Company suffered heavy losses.
- c)Hugli was ceded to the East India Company by Aurangzeb.
- d)Both (a) and (c).
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In 1686 a war broke out in Bengal between Aurangzeb and the English East India Company. What was its outcome?
a)
The Mughals suffered heavy losses.
b)
The East India Company suffered heavy losses.
c)
Hugli was ceded to the East India Company by Aurangzeb.
d)
Both (a) and (c).

|
Innovative Classes answered |
In 1686, the English East India Company attempted to assert its power in Bengal, leading to a conflict with the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. The war did not go well for the English, and they suffered heavy losses. Aurangzeb's forces were too strong for the English, and the Company was forced to surrender and negotiate. As a result, the English had to seek forgiveness from the emperor and relocate their base of operations from Hugli to Calcutta (now Kolkata), where they later established their stronghold.
Thus, the outcome of the war was unfavorable for the East India Company.
Who was appointed as the first Viceroy of the Portuguese possessions in India?- a)Vasco-de-Gama
- b)Albuquerque
- c)De Almeida
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who was appointed as the first Viceroy of the Portuguese possessions in India?
a)
Vasco-de-Gama
b)
Albuquerque
c)
De Almeida
d)
None of these
|
|
Ameya Malik answered |
The correct answer is c) De Almeida.
De Almeida, also known as Afonso de Albuquerque, was appointed as the first Viceroy of the Portuguese possessions in India. He played a crucial role in establishing and expanding the Portuguese presence in the Indian Ocean region during the early 16th century.
Afonso de Albuquerque's Early Career:
- Afonso de Albuquerque was born in Portugal in 1453. He joined the Portuguese navy at a young age and quickly rose through the ranks due to his military skills and strategic thinking.
- During his early career, Albuquerque participated in several expeditions to North Africa. He gained valuable experience in naval warfare and diplomacy.
The Arrival in India:
- In 1503, Afonso de Albuquerque arrived in India as the captain of a fleet of Portuguese ships. At that time, the Portuguese had already established a trading post in Calicut (now Kozhikode) on the Malabar Coast.
- Albuquerque was determined to expand Portuguese influence in the Indian Ocean and challenge the dominance of other maritime powers such as the Arabs and the Ottomans.
Appointment as Viceroy:
- In 1509, Albuquerque was appointed as the first Viceroy of Portuguese India by King Manuel I of Portugal. This appointment gave him significant authority and control over Portuguese possessions in the region.
- As Viceroy, Albuquerque was responsible for establishing a strong Portuguese presence in the Indian Ocean and safeguarding Portuguese trade routes.
Achievements and Policies:
- Albuquerque implemented a series of policies to strengthen Portuguese control in India. He built fortified settlements, established trade agreements, and formed alliances with local rulers.
- He captured strategic ports along the Indian coastline, including Goa, which became the capital of Portuguese India. Albuquerque also established a Portuguese presence in Sri Lanka and the Persian Gulf.
- Albuquerque adopted a policy of forceful conquest and established a strong Portuguese naval presence in the region. He successfully defeated several Arab fleets and secured Portuguese dominance.
Legacy:
- Afonso de Albuquerque's tenure as Viceroy laid the foundation for Portuguese dominance in the Indian Ocean and the establishment of a vast maritime empire.
- His policies and strategies shaped Portuguese colonial rule in India for centuries to come.
- Albuquerque's legacy is still evident in the historical landmarks and architectural structures that he built, including the Fort of St. Angelo in Kannur and the Portuguese-built churches in Goa.
In conclusion, Afonso de Albuquerque, also known as De Almeida, was appointed as the first Viceroy of the Portuguese possessions in India. He played a significant role in expanding Portuguese influence in the Indian Ocean region and establishing a strong Portuguese presence in India.
De Almeida, also known as Afonso de Albuquerque, was appointed as the first Viceroy of the Portuguese possessions in India. He played a crucial role in establishing and expanding the Portuguese presence in the Indian Ocean region during the early 16th century.
Afonso de Albuquerque's Early Career:
- Afonso de Albuquerque was born in Portugal in 1453. He joined the Portuguese navy at a young age and quickly rose through the ranks due to his military skills and strategic thinking.
- During his early career, Albuquerque participated in several expeditions to North Africa. He gained valuable experience in naval warfare and diplomacy.
The Arrival in India:
- In 1503, Afonso de Albuquerque arrived in India as the captain of a fleet of Portuguese ships. At that time, the Portuguese had already established a trading post in Calicut (now Kozhikode) on the Malabar Coast.
- Albuquerque was determined to expand Portuguese influence in the Indian Ocean and challenge the dominance of other maritime powers such as the Arabs and the Ottomans.
Appointment as Viceroy:
- In 1509, Albuquerque was appointed as the first Viceroy of Portuguese India by King Manuel I of Portugal. This appointment gave him significant authority and control over Portuguese possessions in the region.
- As Viceroy, Albuquerque was responsible for establishing a strong Portuguese presence in the Indian Ocean and safeguarding Portuguese trade routes.
Achievements and Policies:
- Albuquerque implemented a series of policies to strengthen Portuguese control in India. He built fortified settlements, established trade agreements, and formed alliances with local rulers.
- He captured strategic ports along the Indian coastline, including Goa, which became the capital of Portuguese India. Albuquerque also established a Portuguese presence in Sri Lanka and the Persian Gulf.
- Albuquerque adopted a policy of forceful conquest and established a strong Portuguese naval presence in the region. He successfully defeated several Arab fleets and secured Portuguese dominance.
Legacy:
- Afonso de Albuquerque's tenure as Viceroy laid the foundation for Portuguese dominance in the Indian Ocean and the establishment of a vast maritime empire.
- His policies and strategies shaped Portuguese colonial rule in India for centuries to come.
- Albuquerque's legacy is still evident in the historical landmarks and architectural structures that he built, including the Fort of St. Angelo in Kannur and the Portuguese-built churches in Goa.
In conclusion, Afonso de Albuquerque, also known as De Almeida, was appointed as the first Viceroy of the Portuguese possessions in India. He played a significant role in expanding Portuguese influence in the Indian Ocean region and establishing a strong Portuguese presence in India.
At which of the following places on the West coast the English had their factories?I.Ahmedabad
II. Bassein
III. Salsette
IV. Broach
V. Baroda- a)I, II,III,IV
- b)II, III, IV,V
- c)I, II, III, V
- d)II, III, IV, V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At which of the following places on the West coast the English had their factories?
I.Ahmedabad
II. Bassein
III. Salsette
IV. Broach
V. Baroda
II. Bassein
III. Salsette
IV. Broach
V. Baroda
a)
I, II,III,IV
b)
II, III, IV,V
c)
I, II, III, V
d)
II, III, IV, V
|
|
Ipsita Mishra answered |
English Factories on the West Coast
The English established several factories on the West coast of India primarily during the period of trade expansion in the 17th and 18th centuries. The correct answer to the locations where the English had their factories is option 'A', which includes Ahmedabad, Bassein, Salsette, and Broach.
Key Locations of English Factories
- Ahmedabad:
- A significant center for trade, particularly in textiles. The English East India Company had a presence here to facilitate textile exports.
- Bassein:
- Located near modern-day Vasai, Bassein was an important port where the English set up a factory to control trade routes and engage in maritime commerce.
- Salsette:
- This island was strategically important due to its proximity to Mumbai (then Bombay). The English established their presence here to manage trade activities.
- Broach:
- An essential port city for the English, Broach served as a hub for the export of textiles and spices. The establishment of a factory here helped strengthen trade links.
Incorrect Locations
- Baroda:
- Unlike the other locations listed, Baroda (modern-day Vadodara) did not have a significant English factory. The region was more influenced by local princely states than by direct English trade activities.
Conclusion
The English factories in Ahmedabad, Bassein, Salsette, and Broach played a vital role in establishing trade networks and expanding British influence in India during the colonial period. Understanding these locations is crucial for grasping the dynamics of colonial trade in India.
The English established several factories on the West coast of India primarily during the period of trade expansion in the 17th and 18th centuries. The correct answer to the locations where the English had their factories is option 'A', which includes Ahmedabad, Bassein, Salsette, and Broach.
Key Locations of English Factories
- Ahmedabad:
- A significant center for trade, particularly in textiles. The English East India Company had a presence here to facilitate textile exports.
- Bassein:
- Located near modern-day Vasai, Bassein was an important port where the English set up a factory to control trade routes and engage in maritime commerce.
- Salsette:
- This island was strategically important due to its proximity to Mumbai (then Bombay). The English established their presence here to manage trade activities.
- Broach:
- An essential port city for the English, Broach served as a hub for the export of textiles and spices. The establishment of a factory here helped strengthen trade links.
Incorrect Locations
- Baroda:
- Unlike the other locations listed, Baroda (modern-day Vadodara) did not have a significant English factory. The region was more influenced by local princely states than by direct English trade activities.
Conclusion
The English factories in Ahmedabad, Bassein, Salsette, and Broach played a vital role in establishing trade networks and expanding British influence in India during the colonial period. Understanding these locations is crucial for grasping the dynamics of colonial trade in India.
With the coming of the Portuguese the complexion of Indian trade changed in the sense that- a)India was opened to the New World.
- b)Bulkier goods could now be traded.
- c)The spice trade now shifted from Java and Sumatra to India.
- d)Both (a) and (b).
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
With the coming of the Portuguese the complexion of Indian trade changed in the sense that
a)
India was opened to the New World.
b)
Bulkier goods could now be traded.
c)
The spice trade now shifted from Java and Sumatra to India.
d)
Both (a) and (b).

|
T.S Academy answered |
With the arrival of the Portuguese in India, the complexion of Indian trade changed in several ways:
- India was opened to the New World (A): The Portuguese played a key role in establishing direct sea routes between Europe and India, and also indirectly opened up trade between India and the New World (the Americas), as European powers began global exploration and colonization.
- Bulkier goods could now be traded (B): The Portuguese introduced large, ocean-going ships that could carry bulkier goods like textiles, cotton, and other commodities in larger quantities compared to the smaller, traditional trading vessels previously used.
Thus, both statements (a) and (b) are correct, making Option D the right answer.
The linkage with European trade had negative factors. Which was not one of them?- a)There was a rapid rise in prices.
- b)Europe had little to supply to India in return for its goods.
- c)India was forced to export large quantities of gold and silver.
- d)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The linkage with European trade had negative factors. Which was not one of them?
a)
There was a rapid rise in prices.
b)
Europe had little to supply to India in return for its goods.
c)
India was forced to export large quantities of gold and silver.
d)
None of these.
|
|
Krish Dasgupta answered |
The correct option is C.
India was forced to export large quantities of gold and silver. This led to drainage of wealth of india.
India was forced to export large quantities of gold and silver. This led to drainage of wealth of india.
The East India Company opened its first factory in south at- a)Masulipatam
- b)Madras
- c)Pondicherry
- d)Calicut
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The East India Company opened its first factory in south at
a)
Masulipatam
b)
Madras
c)
Pondicherry
d)
Calicut

|
Lakshya Ias answered |
The East India Company opened its first factory in southern India at Masulipatam (in present-day Andhra Pradesh) in 1611. Masulipatam was an important port on the Coromandel Coast and played a crucial role in the Company's early trading activities in southern India. This factory helped the English establish a foothold in the region before they eventually moved to other areas like Madras (modern-day Chennai).
The Dutch and the English entered the East as friend against the common enemy, the Portuguese. However, their commercial rivalry led to the massacre of the Englishman by the Dutch at- a)Amboyna
- b)Malacca
- c)Surat
- d)Calicut
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Dutch and the English entered the East as friend against the common enemy, the Portuguese. However, their commercial rivalry led to the massacre of the Englishman by the Dutch at
a)
Amboyna
b)
Malacca
c)
Surat
d)
Calicut
|
|
Rounak Iyer answered |
Historical Context
In the late 16th and early 17th centuries, the Dutch and the English both sought to expand their trade networks in Asia, primarily targeting the lucrative spice trade which was dominated by the Portuguese. Initially, both nations formed a temporary alliance against this common enemy, the Portuguese Empire.
Commercial Rivalry
As both the Dutch East India Company (VOC) and the English East India Company (EIC) began to establish their footholds in Asia, their interests increasingly clashed. This rivalry intensified as each sought to secure exclusive trade routes and monopolize spices and other resources.
Massacre at Amboyna
The culmination of this rivalry became evident in 1623 with the infamous Amboyna massacre:
- The Dutch accused several English merchants and a number of Japanese traders of conspiring against them.
- Under pressure and torture, many were forced to confess to false charges.
- Ultimately, 20 Englishmen were executed in a brutal display of Dutch power, marking a significant turning point in Anglo-Dutch relations.
Significance of the Incident
The Amboyna massacre had far-reaching consequences:
- It solidified the animosity between the English and Dutch, leading to a series of conflicts over trade supremacy in Asia.
- This event is often considered a catalyst for the decline of amicable relations and a precursor to later wars between the two nations.
In summary, the massacre at Amboyna stands as a pivotal moment in the history of European colonial competition in Asia, illustrating how commercial rivalry can escalate into violent confrontations.
In the late 16th and early 17th centuries, the Dutch and the English both sought to expand their trade networks in Asia, primarily targeting the lucrative spice trade which was dominated by the Portuguese. Initially, both nations formed a temporary alliance against this common enemy, the Portuguese Empire.
Commercial Rivalry
As both the Dutch East India Company (VOC) and the English East India Company (EIC) began to establish their footholds in Asia, their interests increasingly clashed. This rivalry intensified as each sought to secure exclusive trade routes and monopolize spices and other resources.
Massacre at Amboyna
The culmination of this rivalry became evident in 1623 with the infamous Amboyna massacre:
- The Dutch accused several English merchants and a number of Japanese traders of conspiring against them.
- Under pressure and torture, many were forced to confess to false charges.
- Ultimately, 20 Englishmen were executed in a brutal display of Dutch power, marking a significant turning point in Anglo-Dutch relations.
Significance of the Incident
The Amboyna massacre had far-reaching consequences:
- It solidified the animosity between the English and Dutch, leading to a series of conflicts over trade supremacy in Asia.
- This event is often considered a catalyst for the decline of amicable relations and a precursor to later wars between the two nations.
In summary, the massacre at Amboyna stands as a pivotal moment in the history of European colonial competition in Asia, illustrating how commercial rivalry can escalate into violent confrontations.
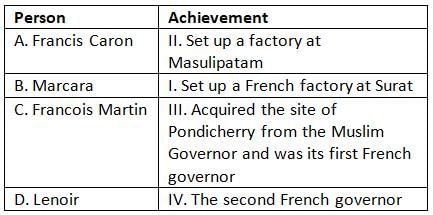
Match the following:
- a)(A-II) (B-III) (C-I) (D-IV)
- b)(A-I) (B-II) (C-III) (D-IV)
- c)(A-III) (B-IV) (C-II) (D-I)
- d)(A-III) (B-II) (C-IV) (D-I)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following:

a)
(A-II) (B-III) (C-I) (D-IV)
b)
(A-I) (B-II) (C-III) (D-IV)
c)
(A-III) (B-IV) (C-II) (D-I)
d)
(A-III) (B-II) (C-IV) (D-I)
|
|
Nani Chowdary answered |
Option B is correct.1) In 1668 francis Caron set up a french factory at surat. 2)In 1669 marcara was successful to set up a another french factory at masulipatnam.3)Francois Martin is the person who acquired site of pondicherry from Muslim government led by sher Khan in 1673.later in 1674 the french accepted pondicherry as their capital . Matin is first governor general of pondicherry.4)lenoir is the second french governor.
In 1691 the East India Company was granted exemption from the payment of custom duties in return for Rs. 3,000 a year in- a)Bihar
- b)Bengal
- c)Orissa
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In 1691 the East India Company was granted exemption from the payment of custom duties in return for Rs. 3,000 a year in
a)
Bihar
b)
Bengal
c)
Orissa
d)
None of these

|
Akanksha Ahuja answered |
Historical Context
In the late 17th century, the British East India Company was expanding its influence in India, particularly in the Bengal region.
Exemption from Duties
In 1691, the East India Company negotiated a significant deal with the Mughal Empire that exempted it from paying custom duties. This arrangement was crucial for the Company's trade operations and profitability.
Details of the Agreement
- The Company agreed to pay Rs. 3,000 annually to the Mughal Treasury.
- This payment allowed the Company to conduct trade without the burden of customs duties, which would have otherwise increased their operational costs.
Bengal's Importance
- Bengal was a rich province known for its lucrative trade in textiles, spices, and other commodities.
- The exemption facilitated the Company's ability to monopolize trade and establish a strong economic foothold in the region.
Impact on Trade
- The duty exemption significantly boosted the Company's profits.
- It also enabled the East India Company to outcompete local merchants and other European traders.
Conclusion
The agreement made in 1691 marked a pivotal moment in the East India Company's history, particularly in Bengal. It not only highlighted the Company's growing power but also set the stage for its eventual dominance in India. The exemption from customs duties was a strategic move that benefited the Company immensely, allowing for increased trade and expansion in one of India's most prosperous regions.
In the late 17th century, the British East India Company was expanding its influence in India, particularly in the Bengal region.
Exemption from Duties
In 1691, the East India Company negotiated a significant deal with the Mughal Empire that exempted it from paying custom duties. This arrangement was crucial for the Company's trade operations and profitability.
Details of the Agreement
- The Company agreed to pay Rs. 3,000 annually to the Mughal Treasury.
- This payment allowed the Company to conduct trade without the burden of customs duties, which would have otherwise increased their operational costs.
Bengal's Importance
- Bengal was a rich province known for its lucrative trade in textiles, spices, and other commodities.
- The exemption facilitated the Company's ability to monopolize trade and establish a strong economic foothold in the region.
Impact on Trade
- The duty exemption significantly boosted the Company's profits.
- It also enabled the East India Company to outcompete local merchants and other European traders.
Conclusion
The agreement made in 1691 marked a pivotal moment in the East India Company's history, particularly in Bengal. It not only highlighted the Company's growing power but also set the stage for its eventual dominance in India. The exemption from customs duties was a strategic move that benefited the Company immensely, allowing for increased trade and expansion in one of India's most prosperous regions.
By the middle of the 18th century, the population of three major cities had increased tremendously. Keeping this in mind, match the following.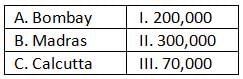
- a)[A-I], [B-II], [C-III]
- b)[A-II], [B-I], [C-III]
- c) [A-III], [B-I], [C-II]
- d)[A-III], [B-II], [C-I]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
By the middle of the 18th century, the population of three major cities had increased tremendously. Keeping this in mind, match the following.

a)
[A-I], [B-II], [C-III]
b)
[A-II], [B-I], [C-III]
c)
[A-III], [B-I], [C-II]
d)
[A-III], [B-II], [C-I]

|
Ias Masters answered |
By the middle of the 18th century, the population of three major cities—Bombay, Madras, and Calcutta—had grown significantly due to the increasing commercial and administrative activities of the European trading companies, especially the British East India Company.
- Bombay (A) – 70,000 (III): Bombay was still developing during this period, and its population was relatively smaller compared to the other major cities. The city had a population of around 70,000.
- Madras (B) – 200,000 (I): Madras, one of the first strongholds of the English, had grown significantly by the mid-18th century, reaching a population of 200,000. It was an important port and trading hub for the British in South India.
- Calcutta (C) – 300,000 (II): Calcutta had become the capital of British India in the eastern region and was the most populous of the three cities, with 300,000 people. Its significance as a center for trade, administration, and commerce contributed to its rapid growth.
Thus, the correct matching is: A-III, B-I, and C-II, which corresponds to Option C.
In 1612 the English East India Company opened its first factories in- a)Surat
- b)Bengal
- c)Assam
- d)Bihar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In 1612 the English East India Company opened its first factories in
a)
Surat
b)
Bengal
c)
Assam
d)
Bihar
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
Thomas Best was an English captain who had sunk four Portuguese ships. This impressed the Mughal Governor and therefore he gave them a treaty which was approved by emperor Jhangir who gave them trading rights.
The first English factory in India was established at Surat. However, after four centuries, these early footmarks of the British had been wiped out. There were no remains of a factory or a warehouse. According to historian HG Rawlinson, the factory in Surat was one of the best one. It was a two-storey building. The location was not far from the Surat fort. The fort was said to have been commissioned by Sultan Mahmud III. Surat was one of the most important ports for trading with the Mughals. This port was used by the textile manufacturers of Gujarat. However, the Portuguese were already trading with the Mughals and they were the master of the sea. It would take a lot of time for the British to take over. In 1612, the factory of the East India Company was established in Surat.
Note: In 1611, another factory was established by the East India Company in Masulipatam in Coromandel Coast.in 1626, it extended to the South in Armagaon and settled there because of the availability of cheap cloth. In the main production areas like Gujarat, Bengal and Coromandel, several weavers, washers were employed who worked on muslins, cotton and quilt.
Which of the following died in 1515 and was buried at Goa?- a)De Almeida
- b)Vasco-de-Gama
- c)Albuquerque
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following died in 1515 and was buried at Goa?
a)
De Almeida
b)
Vasco-de-Gama
c)
Albuquerque
d)
None of these

|
Master Training Institute answered |
Afonso de Albuquerque, the Portuguese viceroy and a key figure in establishing Portuguese dominance in India, died in 1515 and was buried in Goa. Albuquerque played a crucial role in expanding Portuguese control in the Indian Ocean, including the capture of Goa in 1510, which became the center of Portuguese India. His leadership and conquests were instrumental in establishing Portugal as a dominant maritime and colonial power in the region.
Chapter doubts & questions for Beginning of European Commerce - History for State PSC Exams 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Beginning of European Commerce - History for State PSC Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of BPSC (Bihar) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
History for State PSC Exams
125 videos|772 docs|270 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









