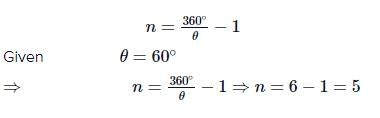All Exams >
Grade 8 >
Science for Grade 8 >
All Questions
All questions of Color of Light for Grade 8 Exam
What is the phenomenon of light bouncing back into the same medium called?- a)Reflection
- b)Refraction
- c)Dispersion
- d)Splitting
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the phenomenon of light bouncing back into the same medium called?
a)
Reflection
b)
Refraction
c)
Dispersion
d)
Splitting

|
Anoushka Das answered |
The phenomenon of light in which, light is reflected or bounced back into the same medium is called reflection.
If the angle of incidence is 80o, what will be the angle of reflection?- a) 80o
- b) 100o
- c) 160o
- d) 20o
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the angle of incidence is 80o, what will be the angle of reflection?
a)
80o
b)
100o
c)
160o
d)
20o

|
Pallabi Choudhury answered |
The angle of incidence = the angle of reflection. So, the angle of reflection is 80o.
X is a surface that cannot produce clear images. What is X?- a)Rough surface
- b)Ideal surface
- c)Smooth surface
- d)Smooth but curved surface
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
X is a surface that cannot produce clear images. What is X?
a)
Rough surface
b)
Ideal surface
c)
Smooth surface
d)
Smooth but curved surface

|
Prerna Chavan answered |
When light is incident on a rough surface, irregular reflection takes place, hence the image formed is not clear.
With what is glass coated in order to convert it into a mirror?
- a)Silver
- b)Copper
- c)Aluminium
- d)Platinum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
With what is glass coated in order to convert it into a mirror?
a)
Silver
b)
Copper
c)
Aluminium
d)
Platinum

|
Ashwin Jain answered |
Glasses are coated with silver to be used as mirrors to increase their reflection property.
In a periscope, how are the reflecting mirrors arranged?- a)Perpendicular to each other
- b)At an angle of 45o
- c)At an angle of 90o
- d)At an angle of 60o
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a periscope, how are the reflecting mirrors arranged?
a)
Perpendicular to each other
b)
At an angle of 45o
c)
At an angle of 90o
d)
At an angle of 60o
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Correct Answer :-B
Explanation:- A periscope is an optical instrument used to view object which is not in direct sight of human eye. It works by using the Laws of Reflection and are widely used in submarines to navigate under water.
It works by using two mirrors placed at angle of 45 degree with each other. When light falls on one mirror, it bounces to the other mirror and then reaches the human eye.
A simple periscope only uses mirrors but complex periscope uses prisms instead of mirror. These periscopes are used in the field of medicine particularly in cystoscopy and endoscopy.
What makes objects visible?- a)The absorption of light by objects
- b)The reflected light from the object
- c)The total internal reflection taking place in an object
- d)The refracted light from the object
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What makes objects visible?
a)
The absorption of light by objects
b)
The reflected light from the object
c)
The total internal reflection taking place in an object
d)
The refracted light from the object
|
|
Sanjana Banerjee answered |
Introduction:
The visibility of objects is primarily due to the reflected light from the objects. When light falls on an object, it interacts with the surface of the object in various ways, resulting in the perception of visibility. Let's explore this in more detail.
Explanation:
Visible light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that consists of a spectrum of different wavelengths. When light falls on an object, it interacts with the atoms and molecules present on the surface of the object. This interaction can lead to three possible outcomes: absorption, reflection, and refraction.
Absorption:
When light is absorbed by an object, it means that the object absorbs certain wavelengths of light and converts them into other forms of energy, such as heat. The absorbed light is not reflected or transmitted, making the object appear dark or invisible. Therefore, absorption of light does not contribute to the visibility of objects.
Refraction:
Refraction occurs when light passes through a transparent object and changes its direction. It happens due to the change in speed of light as it travels from one medium to another. While refraction can affect the path of light, it does not directly contribute to the visibility of objects.
Reflection:
Reflection is the key process that makes objects visible. When light falls on an object, some of it is reflected back into the surrounding environment. The reflected light carries information about the object's color and appearance, allowing our eyes to detect and perceive the object. The reflected light reaches our eyes, and the brain processes this information to create the sensation of visibility.
During reflection, the angle of incidence (the angle at which light strikes the object) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle at which light is reflected). This phenomenon follows the law of reflection and allows us to see objects from different angles and perspectives.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the visibility of objects is primarily due to the reflected light from the objects. When light falls on an object, some of it is reflected back, carrying information about the object's appearance. This reflected light is what allows us to see and perceive objects in our surroundings.
The visibility of objects is primarily due to the reflected light from the objects. When light falls on an object, it interacts with the surface of the object in various ways, resulting in the perception of visibility. Let's explore this in more detail.
Explanation:
Visible light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that consists of a spectrum of different wavelengths. When light falls on an object, it interacts with the atoms and molecules present on the surface of the object. This interaction can lead to three possible outcomes: absorption, reflection, and refraction.
Absorption:
When light is absorbed by an object, it means that the object absorbs certain wavelengths of light and converts them into other forms of energy, such as heat. The absorbed light is not reflected or transmitted, making the object appear dark or invisible. Therefore, absorption of light does not contribute to the visibility of objects.
Refraction:
Refraction occurs when light passes through a transparent object and changes its direction. It happens due to the change in speed of light as it travels from one medium to another. While refraction can affect the path of light, it does not directly contribute to the visibility of objects.
Reflection:
Reflection is the key process that makes objects visible. When light falls on an object, some of it is reflected back into the surrounding environment. The reflected light carries information about the object's color and appearance, allowing our eyes to detect and perceive the object. The reflected light reaches our eyes, and the brain processes this information to create the sensation of visibility.
During reflection, the angle of incidence (the angle at which light strikes the object) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle at which light is reflected). This phenomenon follows the law of reflection and allows us to see objects from different angles and perspectives.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the visibility of objects is primarily due to the reflected light from the objects. When light falls on an object, some of it is reflected back, carrying information about the object's appearance. This reflected light is what allows us to see and perceive objects in our surroundings.
The characteristics of an eye disease are given below.
(i) Eye sight becomes foggy
(ii) Eye lens becomes cloudy
(iii) There is a loss of visionIn which of the following are the above characteristics observed?- a)Myopia
- b)Presbyopia
- c)Hypermetropia
- d)Cataract
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The characteristics of an eye disease are given below.
(i) Eye sight becomes foggy
(ii) Eye lens becomes cloudy
(iii) There is a loss of vision
(i) Eye sight becomes foggy
(ii) Eye lens becomes cloudy
(iii) There is a loss of vision
In which of the following are the above characteristics observed?
a)
Myopia
b)
Presbyopia
c)
Hypermetropia
d)
Cataract
|
|
Shubham Sharma answered |
Cataract occurs in old age due to the given characteristics and can be cured by introducing a new artificial lens.
Which of the following is the requirement of nocturnal animals like owl an bat?- a)Large cornea
- b)Large pupil
- c)Retina with large number of rods
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the requirement of nocturnal animals like owl an bat?
a)
Large cornea
b)
Large pupil
c)
Retina with large number of rods
d)
All of the above
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
The nocturnal animals need more light to see at night. The large cornea and pupil allow more light to enter into their eyes. They also have retina with large number of rods.
If the angle of incidence is 50o, then calculate the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray.- a)50o
- b)100o
- c)130o
- d)80o
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the angle of incidence is 50o, then calculate the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray.
a)
50o
b)
100o
c)
130o
d)
80o
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
In reflection of light, ∠i = 50oand ∠i = ∠r = the angle between incident ray and reflected ray = 50° + 50° = 100°
A uniform magnetic field B exists in the region between x = 0 and x = 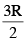 (region 2 in the figure) pointing normally into the plane of the paper. A particle with charge +Q and momentum p directed along x-axis enters region 2 from region 1 at point P1(y = –R). Which of the following options(s) is/are correct ?
(region 2 in the figure) pointing normally into the plane of the paper. A particle with charge +Q and momentum p directed along x-axis enters region 2 from region 1 at point P1(y = –R). Which of the following options(s) is/are correct ?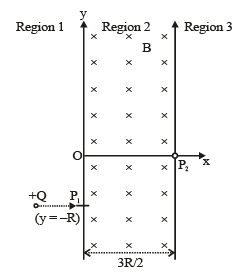
- a)For B =
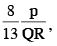 the particle will enter region 3 through the point P2 on x-axis
the particle will enter region 3 through the point P2 on x-axis - b)For B >
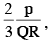 the particle will re-enter region 1
the particle will re-enter region 1 - c)For a fixed B, particle of same charge Q and same velocity v, the distance between the point P1 and the point of re-entry into region 1 is inversely proportional to the mass of the particle.
- d)When the particle re-enters region 1 through the longest possible path in region 2, the magnitude of the chage in its linear momentum between point P1 and the farthest point from y-axis is
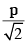
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
A uniform magnetic field B exists in the region between x = 0 and x = 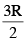 (region 2 in the figure) pointing normally into the plane of the paper. A particle with charge +Q and momentum p directed along x-axis enters region 2 from region 1 at point P1(y = –R). Which of the following options(s) is/are correct ?
(region 2 in the figure) pointing normally into the plane of the paper. A particle with charge +Q and momentum p directed along x-axis enters region 2 from region 1 at point P1(y = –R). Which of the following options(s) is/are correct ?
a)
For B =
b)
For B >
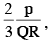 the particle will re-enter region 1
the particle will re-enter region 1
c)
For a fixed B, particle of same charge Q and same velocity v, the distance between the point P1 and the point of re-entry into region 1 is inversely proportional to the mass of the particle.
d)
When the particle re-enters region 1 through the longest possible path in region 2, the magnitude of the chage in its linear momentum between point P1 and the farthest point from y-axis is 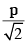
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
(A, B) For the charge +Q to return region 1, the radius of the circular path taken by charge should by 3R/2.
mv² ÷ (3R/2) = QvB
Therefore,
2p / 3R = Q
So,
B = 2p / 3QR
i.e., B should be equal or greater than 2p/2QR
'A' is the correct option.
When B = 8p / 13QR
mv² / r = Qv (8p / 13QR)
Therefore, v = 13R / 8
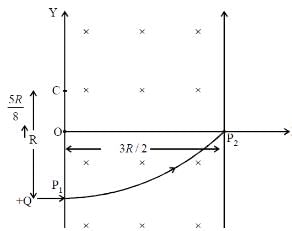
Also CP2² = CO² + OP2²
= [(5R/8)² + (3R/2)²]²
CP2 = 13R / 8
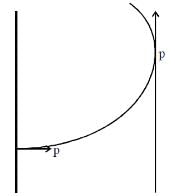
Thus the particle will enter region 3 through the point P1 on X-axis 'B' is the correct option.
Change in momentum =√2p
Thus, 'C' is incorrect.
Further, mv² / r = qvB
Therefore, r = mv / qB
'D' is incorrect.
mv² ÷ (3R/2) = QvB
Therefore,
2p / 3R = Q
So,
B = 2p / 3QR
i.e., B should be equal or greater than 2p/2QR
'A' is the correct option.
When B = 8p / 13QR
mv² / r = Qv (8p / 13QR)
Therefore, v = 13R / 8

Also CP2² = CO² + OP2²
= [(5R/8)² + (3R/2)²]²
CP2 = 13R / 8

Thus the particle will enter region 3 through the point P1 on X-axis 'B' is the correct option.
Change in momentum =√2p
Thus, 'C' is incorrect.
Further, mv² / r = qvB
Therefore, r = mv / qB
'D' is incorrect.
What is the perpendicular drawn at any point on a mirror called?- a)Incident ray
- b)Reflected ray
- c)Normal
- d)Image
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the perpendicular drawn at any point on a mirror called?
a)
Incident ray
b)
Reflected ray
c)
Normal
d)
Image

|
Priti Kaur answered |
In a plane mirror when incident ray comes and reflect to make reflected ray in the middle of the rays a perpendicular is drawn called Normal.
Which of the following statements is true?- a)The angle of incidence is twice the angle of reflection.
- b)The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
- c)Some virtual images can be caught on the screen.
- d)A convex mirror forms a real image.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true?
a)
The angle of incidence is twice the angle of reflection.
b)
The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
c)
Some virtual images can be caught on the screen.
d)
A convex mirror forms a real image.

|
Abhiram Das answered |
When a light ray is reflected from the reflecting surface, the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence = The angle of reflection.
How many images are obtained when plane mirrors are arranged parallel to each other?- a)A single image
- b)Two images
- c)Infinite number of images
- d)Zero image
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many images are obtained when plane mirrors are arranged parallel to each other?
a)
A single image
b)
Two images
c)
Infinite number of images
d)
Zero image
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
When two mirrors are kept parallel to each other, an infinite number of images can be seen.
What is the nature of image formed on the retina of human eye of an object?- a)Virtual and erect
- b)Virtual and inverted
- c)Real and erect
- d)Real and inverted
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the nature of image formed on the retina of human eye of an object?
a)
Virtual and erect
b)
Virtual and inverted
c)
Real and erect
d)
Real and inverted
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
The human eye serves as a convex lens. It forms real, inverted and diminished image of an object.
Identify the value of persistence of vision.- a)1/1 0th of a second
- b)1/12th of a second
- c)1/16th of a second
- d)1/20th of a second
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the value of persistence of vision.
a)
1/1 0th of a second
b)
1/12th of a second
c)
1/16th of a second
d)
1/20th of a second
|
|
Rutuja Kumar answered |
Understanding Persistence of Vision
Persistence of vision is a phenomenon that allows us to perceive motion in a series of still images. It plays a crucial role in how we experience animation and video.
Definition
- Persistence of vision refers to the optical illusion where the human eye retains an image for a fraction of a second after the source has changed.
- This ability helps create the illusion of motion when images are displayed in quick succession.
Duration of Persistence of Vision
- The commonly accepted duration for persistence of vision is approximately 1/16th of a second.
- This means that if a series of images are shown within this timeframe, they can be perceived as continuous movement rather than a series of still frames.
Importance in Media
- This concept is foundational in animation and film, where frames are played rapidly (typically 24 frames per second in cinema).
- By using persistence of vision, filmmakers can create smooth visual narratives that engage viewers.
Correct Answer Explanation
- Among the options given, the correct answer is c) 1/16th of a second.
- This time frame is crucial for ensuring that our brains process the images as fluid motion, rather than as individual frames.
Conclusion
- Understanding persistence of vision enriches our appreciation for visual media and its underlying mechanics.
- It explains why animations and movies feel seamless, drawing viewers into the story being told.
Persistence of vision is a phenomenon that allows us to perceive motion in a series of still images. It plays a crucial role in how we experience animation and video.
Definition
- Persistence of vision refers to the optical illusion where the human eye retains an image for a fraction of a second after the source has changed.
- This ability helps create the illusion of motion when images are displayed in quick succession.
Duration of Persistence of Vision
- The commonly accepted duration for persistence of vision is approximately 1/16th of a second.
- This means that if a series of images are shown within this timeframe, they can be perceived as continuous movement rather than a series of still frames.
Importance in Media
- This concept is foundational in animation and film, where frames are played rapidly (typically 24 frames per second in cinema).
- By using persistence of vision, filmmakers can create smooth visual narratives that engage viewers.
Correct Answer Explanation
- Among the options given, the correct answer is c) 1/16th of a second.
- This time frame is crucial for ensuring that our brains process the images as fluid motion, rather than as individual frames.
Conclusion
- Understanding persistence of vision enriches our appreciation for visual media and its underlying mechanics.
- It explains why animations and movies feel seamless, drawing viewers into the story being told.
What happens in lateral inversion?- a)The right side of the object will be on the right side of the image.
- b)The left side of the object will be on the left side of the image.
- c)The top of the object will be the bottom of the object.
- d)The right side of the object will be on the left side of the image.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens in lateral inversion?
a)
The right side of the object will be on the right side of the image.
b)
The left side of the object will be on the left side of the image.
c)
The top of the object will be the bottom of the object.
d)
The right side of the object will be on the left side of the image.
|
|
Simran Bose answered |
Lateral inversion:
Lateral inversion is a phenomenon that occurs when an image is reflected in a mirror. It leads to a reversal of the left and right sides of the object in the image. The correct answer, option 'D', states that the right side of the object will be on the left side of the image. Let's understand this concept in more detail.
Explanation:
When an object is placed in front of a mirror, the image formed is a reflection of that object. However, there is a change in the orientation of the image due to lateral inversion. This means that the image appears as a mirror image of the actual object, with the left and right sides interchanged.
Example:
To understand this concept, let's take the example of the letter 'A'. If we place a letter 'A' in front of a mirror, the image formed will be an 'A' as well, but the orientation will be laterally inverted. This means that the right side of the letter 'A' will appear on the left side of the image, and vice versa.
Visual representation:
To make it visually appealing, we can represent this concept as follows:
Object: A
Image: A
However, due to lateral inversion:
Object: A
Image: A
Here, the object and image appear the same, but the orientation is changed. The right side of the object 'A' is now on the left side of the image.
Conclusion:
In lateral inversion, the right side of the object will be on the left side of the image. This occurs when an object is reflected in a mirror, leading to a reversal of left and right sides in the image. It is important to understand this concept as it helps in understanding how mirrors reflect images and the effects of lateral inversion.
Lateral inversion is a phenomenon that occurs when an image is reflected in a mirror. It leads to a reversal of the left and right sides of the object in the image. The correct answer, option 'D', states that the right side of the object will be on the left side of the image. Let's understand this concept in more detail.
Explanation:
When an object is placed in front of a mirror, the image formed is a reflection of that object. However, there is a change in the orientation of the image due to lateral inversion. This means that the image appears as a mirror image of the actual object, with the left and right sides interchanged.
Example:
To understand this concept, let's take the example of the letter 'A'. If we place a letter 'A' in front of a mirror, the image formed will be an 'A' as well, but the orientation will be laterally inverted. This means that the right side of the letter 'A' will appear on the left side of the image, and vice versa.
Visual representation:
To make it visually appealing, we can represent this concept as follows:
Object: A
Image: A
However, due to lateral inversion:
Object: A
Image: A
Here, the object and image appear the same, but the orientation is changed. The right side of the object 'A' is now on the left side of the image.
Conclusion:
In lateral inversion, the right side of the object will be on the left side of the image. This occurs when an object is reflected in a mirror, leading to a reversal of left and right sides in the image. It is important to understand this concept as it helps in understanding how mirrors reflect images and the effects of lateral inversion.
Periscope is used to- a)view objects placed at a higher level from a position at lower level.
- b)magnify extremely small objects into bigger images
- c)observe the distant images such as planets and stars
- d)analyse the spectrum formed by the sunlight
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Periscope is used to
a)
view objects placed at a higher level from a position at lower level.
b)
magnify extremely small objects into bigger images
c)
observe the distant images such as planets and stars
d)
analyse the spectrum formed by the sunlight

|
Rohan Pradhan Pradhan answered |
C)observe the distant images such as planet and stars.
The image which can only be seen by the eye but cannot be taken on screen is called- a)inverted image
- b)lateral image
- c)virtual image
- d)illusionary image
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The image which can only be seen by the eye but cannot be taken on screen is called
a)
inverted image
b)
lateral image
c)
virtual image
d)
illusionary image

|
Prabhu Govindaswamy answered |
A virtual image cannot be captured on a screen that's why the answer is 'C'
Diffused reflection occurs if a ray of light is reflected by a- a)concave mirror
- b)convex mirror
- c)plane mirror
- d)rough surface
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Diffused reflection occurs if a ray of light is reflected by a
a)
concave mirror
b)
convex mirror
c)
plane mirror
d)
rough surface
|
|
Meghana Banerjee answered |
**Diffused Reflection**
Diffused reflection is a type of reflection that occurs when a ray of light strikes a rough or irregular surface and reflects in many different directions. It is also known as scattered reflection. Unlike regular reflection, where the light rays bounce off a smooth surface at the same angle, diffused reflection causes the light rays to scatter in various directions.
**Explanation**
Diffused reflection occurs on a rough surface because the irregularities on the surface cause the light rays to bounce off in different directions. These irregularities can be in the form of bumps, scratches, or any other roughness on the surface. When a ray of light strikes the surface, it interacts with these irregularities and gets scattered in many different directions.
**Comparison with Other Options**
a) Concave Mirror: A concave mirror is a curved mirror with a reflective surface that curves inward. It is commonly used in reflecting telescopes and makeup mirrors. When a ray of light strikes a concave mirror, it follows the law of reflection and bounces off at an angle equal to the angle of incidence. This is not diffused reflection but rather regular reflection.
b) Convex Mirror: A convex mirror is a curved mirror with a reflective surface that curves outward. It is commonly used in rear-view mirrors and security mirrors. Similar to a concave mirror, when a ray of light strikes a convex mirror, it follows the law of reflection and bounces off at an angle equal to the angle of incidence. Again, this is not diffused reflection but regular reflection.
c) Plane Mirror: A plane mirror is a flat mirror with a reflective surface. It is commonly used in bathrooms, dressing rooms, and for decorative purposes. When a ray of light strikes a plane mirror, it follows the law of reflection and bounces off at an angle equal to the angle of incidence. Just like concave and convex mirrors, this is regular reflection and not diffused reflection.
d) Rough Surface: A rough surface, as mentioned earlier, contains irregularities that cause light to scatter in different directions. When a ray of light strikes a rough surface, it interacts with these irregularities and gets reflected in multiple directions. This is diffused reflection.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - rough surface.
Diffused reflection is a type of reflection that occurs when a ray of light strikes a rough or irregular surface and reflects in many different directions. It is also known as scattered reflection. Unlike regular reflection, where the light rays bounce off a smooth surface at the same angle, diffused reflection causes the light rays to scatter in various directions.
**Explanation**
Diffused reflection occurs on a rough surface because the irregularities on the surface cause the light rays to bounce off in different directions. These irregularities can be in the form of bumps, scratches, or any other roughness on the surface. When a ray of light strikes the surface, it interacts with these irregularities and gets scattered in many different directions.
**Comparison with Other Options**
a) Concave Mirror: A concave mirror is a curved mirror with a reflective surface that curves inward. It is commonly used in reflecting telescopes and makeup mirrors. When a ray of light strikes a concave mirror, it follows the law of reflection and bounces off at an angle equal to the angle of incidence. This is not diffused reflection but rather regular reflection.
b) Convex Mirror: A convex mirror is a curved mirror with a reflective surface that curves outward. It is commonly used in rear-view mirrors and security mirrors. Similar to a concave mirror, when a ray of light strikes a convex mirror, it follows the law of reflection and bounces off at an angle equal to the angle of incidence. Again, this is not diffused reflection but regular reflection.
c) Plane Mirror: A plane mirror is a flat mirror with a reflective surface. It is commonly used in bathrooms, dressing rooms, and for decorative purposes. When a ray of light strikes a plane mirror, it follows the law of reflection and bounces off at an angle equal to the angle of incidence. Just like concave and convex mirrors, this is regular reflection and not diffused reflection.
d) Rough Surface: A rough surface, as mentioned earlier, contains irregularities that cause light to scatter in different directions. When a ray of light strikes a rough surface, it interacts with these irregularities and gets reflected in multiple directions. This is diffused reflection.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - rough surface.
In our houses, which of the following is used for looking at ourselves?- a)Convex mirror
- b)Concave mirror
- c)Convex lens
- d)Plane mirror
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In our houses, which of the following is used for looking at ourselves?
a)
Convex mirror
b)
Concave mirror
c)
Convex lens
d)
Plane mirror

|
Anoushka Das answered |
We use plane mirrors to see ourselves, because the image formed by a plane mirror is virtual, erect and of the same size.
If medium A is optically denser than medium B, then the speed of light is- a)the same in both mediums.
- b)higher in medium A than in medium B.
- c)higher in medium B than in medium A.
- d)higher in medium A or B depending on thickness of the two mediums.
Correct answer is option `A`. Can you explain this answer?
If medium A is optically denser than medium B, then the speed of light is
a)
the same in both mediums.
b)
higher in medium A than in medium B.
c)
higher in medium B than in medium A.
d)
higher in medium A or B depending on thickness of the two mediums.
|
|
Sahana Reddy answered |
If medium A is optically denser than medium B
,
then the speed of light is the same in both
mediums.
A series of fast moving still pictures can create an illusion of movement because- a)eye is quicker than the brain
- b)the optical cortex can see through the rapidly moving images.
- c)the eye can focus on very rapidly changing pictures.
- d)eye can separate two images only when the interval of separation between them is one tenth of second.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A series of fast moving still pictures can create an illusion of movement because
a)
eye is quicker than the brain
b)
the optical cortex can see through the rapidly moving images.
c)
the eye can focus on very rapidly changing pictures.
d)
eye can separate two images only when the interval of separation between them is one tenth of second.
|
|
Aman Mukherjee answered |
This happens due to a phenomenon called persistence of vision.
Which of the following is used by doctors?- a)Convex mirror
- b)Convex lens
- c)Plane mirror
- d)Concave mirror
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is used by doctors?
a)
Convex mirror
b)
Convex lens
c)
Plane mirror
d)
Concave mirror

|
EduRev Class 8 answered |
A concave mirror is used by E.N.T. doctors to get a magnified image of internal organs like ear, nose and throat.
Man observes that the distance between the mirror and his image is 4m. If he moves 1m towards the mirror, the distance between him and his image will be- a)6m
- b)7m
- c)8m
- d)9m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Man observes that the distance between the mirror and his image is 4m. If he moves 1m towards the mirror, the distance between him and his image will be
a)
6m
b)
7m
c)
8m
d)
9m
|
|
Kritika Chopra answered |
Given:
The distance between the mirror and the man's image = 4m
The man moves 1m towards the mirror
To find:
The new distance between the man and his image
Solution:
When an object is placed in front of a mirror, the image is formed at a distance equal to the distance between the object and the mirror. This distance is called the object distance.
In this case, the object distance is given as 4m.
Now, when the man moves towards the mirror by 1m, the new object distance becomes 4m - 1m = 3m.
Since the image distance is equal to the object distance, the new distance between the man and his image is also 3m.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) 6m.
Summary:
When the man moves 1m towards the mirror, the distance between him and his image reduces by 1m. So, if the initial distance between the mirror and the man's image is 4m, the new distance will be 4m - 1m = 3m. Hence, the correct answer is option A) 6m.
The distance between the mirror and the man's image = 4m
The man moves 1m towards the mirror
To find:
The new distance between the man and his image
Solution:
When an object is placed in front of a mirror, the image is formed at a distance equal to the distance between the object and the mirror. This distance is called the object distance.
In this case, the object distance is given as 4m.
Now, when the man moves towards the mirror by 1m, the new object distance becomes 4m - 1m = 3m.
Since the image distance is equal to the object distance, the new distance between the man and his image is also 3m.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) 6m.
Summary:
When the man moves 1m towards the mirror, the distance between him and his image reduces by 1m. So, if the initial distance between the mirror and the man's image is 4m, the new distance will be 4m - 1m = 3m. Hence, the correct answer is option A) 6m.
At a particular time of a day, the ratio of height of an object and the length of it’s shadow is ‘x’. Using this calculate the height of a tree if the length of the shadow of tree is L.- a)x + L
- b)x × L
- c)L – x
- d)x/L
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
At a particular time of a day, the ratio of height of an object and the length of it’s shadow is ‘x’. Using this calculate the height of a tree if the length of the shadow of tree is L.
a)
x + L
b)
x × L
c)
L – x
d)
x/L
|
|
Arshiya Pillai answered |
During the same time the ratio of the height and length of any object will be equal to that of any other including ‘x’.
Step 1- Let the height of the tree be ‘h’. The length of the tree is given as ‘L’
∴ the ratio of its height and length would be h/L
Step 2- This ratio will be the same as ‘x’
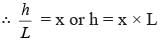
Step 1- Let the height of the tree be ‘h’. The length of the tree is given as ‘L’
∴ the ratio of its height and length would be h/L
Step 2- This ratio will be the same as ‘x’
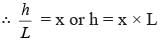
Look at the given figure. 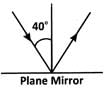 Find the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray.
Find the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray.- a)60o
- b)90o
- c)80o
- d)40o
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Look at the given figure.

Find the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray.
a)
60o
b)
90o
c)
80o
d)
40o

|
Anoushka Das answered |
∠i = 40o(given) ∠i = ∠r = 40o
The angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray =∠i +∠r = 40o+40o = 80o
The angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray =∠i +∠r = 40o+40o = 80o
Image formed by plane mirror is always- a)inverted and real
- b)real and erect
- c)virtual and of same size
- d)virtual and enlarged
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Image formed by plane mirror is always
a)
inverted and real
b)
real and erect
c)
virtual and of same size
d)
virtual and enlarged

|
Anirudh Maheshwari answered |
Image formed by a plane mirror can never be real and enlarged, So Option (c) is the correct option
The diagram shows the path of a light ray X, directed at a plane mirror.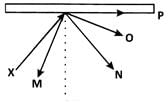 Which of the following is the correct reflected ray?
Which of the following is the correct reflected ray?- a)M
- b)N
- c)O
- d)P
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The diagram shows the path of a light ray X, directed at a plane mirror.

Which of the following is the correct reflected ray?
a)
M
b)
N
c)
O
d)
P

|
Rounak Sen answered |
We know that for a reflected ray, the angle that the incident ray makes with the line perpendicular to the surface is equal to the angle made by the reflected ray with this perpendicular line. N is the correct reflected ray of X.
Two plane mirrors kept at 600 from each other will form how many images of an object kept between them?- a)3
- b)5
- c)7
- d)11
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two plane mirrors kept at 600 from each other will form how many images of an object kept between them?
a)
3
b)
5
c)
7
d)
11
|
|
Janhavi Dasgupta answered |
**Answer:**
When two plane mirrors are kept parallel to each other, they form multiple images of an object placed between them. The number of images formed depends on the angle between the mirrors and the position of the object.
Given, distance between the mirrors = 600 cm
To find the number of images formed, we can use the formula:
Number of images = (360°/angle between the mirrors) - 1
where angle between the mirrors = 360°/n where n is an integer representing the number of images formed.
Now, let's calculate the angle between the mirrors:
angle between mirrors = 360°/n = 360°/2 = 180°
Therefore, the angle between the mirrors is 180°.
Substituting this value in the formula, we get:
Number of images = (360°/180°) - 1 = 2 - 1 = 1
Thus, we can conclude that when two plane mirrors are kept 600 cm apart, only one image of an object placed between them is formed.
However, if the object is placed at a certain distance from the mirrors, multiple images can be formed due to the reflection of light rays. The number of images formed in such cases can be calculated using the same formula mentioned above.
For example, if the object is placed at a distance of 200 cm from one of the mirrors, three images will be formed. If it is placed at a distance of 150 cm from one of the mirrors, five images will be formed.
In the given options, option B (5) is the correct answer if the object is placed at a distance of 200 cm from one of the mirrors. If the object is placed at a different distance, the number of images formed will be different.
When two plane mirrors are kept parallel to each other, they form multiple images of an object placed between them. The number of images formed depends on the angle between the mirrors and the position of the object.
Given, distance between the mirrors = 600 cm
To find the number of images formed, we can use the formula:
Number of images = (360°/angle between the mirrors) - 1
where angle between the mirrors = 360°/n where n is an integer representing the number of images formed.
Now, let's calculate the angle between the mirrors:
angle between mirrors = 360°/n = 360°/2 = 180°
Therefore, the angle between the mirrors is 180°.
Substituting this value in the formula, we get:
Number of images = (360°/180°) - 1 = 2 - 1 = 1
Thus, we can conclude that when two plane mirrors are kept 600 cm apart, only one image of an object placed between them is formed.
However, if the object is placed at a certain distance from the mirrors, multiple images can be formed due to the reflection of light rays. The number of images formed in such cases can be calculated using the same formula mentioned above.
For example, if the object is placed at a distance of 200 cm from one of the mirrors, three images will be formed. If it is placed at a distance of 150 cm from one of the mirrors, five images will be formed.
In the given options, option B (5) is the correct answer if the object is placed at a distance of 200 cm from one of the mirrors. If the object is placed at a different distance, the number of images formed will be different.
If you stand in front of a plane mirror and scratch your right cheek, your image- a)scratches its right cheek
- b)scratches its left cheek
- c)scratches both cheeks
- d)does not scratch at all
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If you stand in front of a plane mirror and scratch your right cheek, your image
a)
scratches its right cheek
b)
scratches its left cheek
c)
scratches both cheeks
d)
does not scratch at all
|
|
Jay Joshi answered |
Understanding Mirror Images
When you look into a plane mirror, the image you see is a reflection of yourself. This reflection has certain properties that can be confusing, especially when it comes to lateral inversion.
Lateral Inversion Explained
- When you move your right hand or scratch your right cheek, the image in the mirror shows the opposite side.
- This phenomenon is known as lateral inversion, where left and right are swapped.
Applying Lateral Inversion to the Scenario
- If you scratch your right cheek, the image in the mirror will appear to scratch the opposite side, which is your left cheek.
- This is because the mirror reverses the image, making your right side appear as the left side in the reflection.
Conclusion
- Thus, if you are standing in front of a plane mirror and you scratch your right cheek, your image will indeed scratch its left cheek.
- This is why the correct answer is option 'B', demonstrating the concept of lateral inversion in mirrors effectively.
When you look into a plane mirror, the image you see is a reflection of yourself. This reflection has certain properties that can be confusing, especially when it comes to lateral inversion.
Lateral Inversion Explained
- When you move your right hand or scratch your right cheek, the image in the mirror shows the opposite side.
- This phenomenon is known as lateral inversion, where left and right are swapped.
Applying Lateral Inversion to the Scenario
- If you scratch your right cheek, the image in the mirror will appear to scratch the opposite side, which is your left cheek.
- This is because the mirror reverses the image, making your right side appear as the left side in the reflection.
Conclusion
- Thus, if you are standing in front of a plane mirror and you scratch your right cheek, your image will indeed scratch its left cheek.
- This is why the correct answer is option 'B', demonstrating the concept of lateral inversion in mirrors effectively.
Chapter doubts & questions for Color of Light - Science for Grade 8 2025 is part of Grade 8 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 8 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 8 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Color of Light - Science for Grade 8 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 8 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 8 Exam by signing up for free.
Science for Grade 8
76 videos|170 docs|65 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup