All Exams >
ACT >
Science for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Carbohydrates and Glycobiology for ACT Exam
Glucose + Tollen’s reagent → Silver mirror. The process shows:- a)The presence of -CHO group
- b)The presence of alkaline group
- c)The presence of acidic group
- d)The presence of keto group
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose + Tollen’s reagent → Silver mirror. The process shows:
a)
The presence of -CHO group
b)
The presence of alkaline group
c)
The presence of acidic group
d)
The presence of keto group

|
Divyanshi Yadav answered |
Yes bcz only aldehyde group gives silver mirror test.
Glucose and fructose are:- a)Position isomers
- b)Functional isomers
- c)Chain isomers
- d)Optical isomers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose and fructose are:
a)
Position isomers
b)
Functional isomers
c)
Chain isomers
d)
Optical isomers
|
|
Tanvi Bose answered |
Glucose and fructose are functional isomers of each other Because they have same molecular formula that is C6H12O6 But different functional group in their chemical formula. Glucose has aldehyde group while fructose has ketone as functional group.
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called:- a)Hydration
- b)Inversion
- c)Esterification
- d)Saponification
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called:
a)
Hydration
b)
Inversion
c)
Esterification
d)
Saponification

|
Sahana Savalagi answered |
Hydrolysis of sucrose is inversion because the angle of specific rotation of the plane polarized light changes from positive to negative value due to the presence of optical isomers of mixture of glucose and fructose sugar...
Glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to form:- a)Monoacetate
- b)Diacetate
- c)Pentaacetate
- d) Hexaacetate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to form:
a)
Monoacetate
b)
Diacetate
c)
Pentaacetate
d)
Hexaacetate
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
It forms glucose pentaacetate. The acetic anhydride esterifies with all the alcohol groups on the glucose ring.
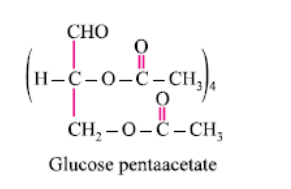

On hydrolysis maltose gives:- a)One molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose
- b)Two molecules of fructose
- c)One molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose
- d)Two molecules of glucose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
On hydrolysis maltose gives:
a)
One molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose
b)
Two molecules of fructose
c)
One molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose
d)
Two molecules of glucose
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
On hydrolysis, maltose gives glucose with the help of maltase enzyme which works as a catalysis of the hydrolysis of the glycoside bond.
Maltase is a disaccharide which will reduce sugar giving two molecules of glucose on hydrolysis.
It will give alpha-D-glucose and alpha-D-glucose.
Which of the following carbohydrate is an example of an oligosaccharide?- a)Cellulose
- b)Lactose
- c)Mannose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrate is an example of an oligosaccharide?
a)
Cellulose
b)
Lactose
c)
Mannose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Lactose intolerance is the inability to break down a type of natural sugar called lactose. Lactose is commonly found in dairy products, such as milk and yogurt. A person becomes lactose intolerant when his or her small intestine stops making enough of the enzyme lactase to digest and break down the lactose.
What is the relation between the following pairs of monosaccharides?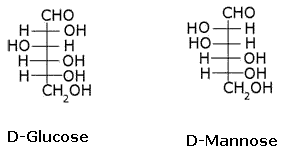
- a)Epimers
- b)Enatiomers
- c)Structural isomers
- d)Anomers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the relation between the following pairs of monosaccharides?
a)
Epimers
b)
Enatiomers
c)
Structural isomers
d)
Anomers

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The pairs of optical isomers which differ in configuration around any other C atom other than C1 atom are called epimers. D-glucose and D-mannose are C2 epimers.
The oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule when two monosaccharides are joined together through oxygen atom is called:- a)Carboxylic linkage
- b)Carbonyl linkage
- c)Peptide linkage
- d)Glycosidic linkage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule when two monosaccharides are joined together through oxygen atom is called:
a)
Carboxylic linkage
b)
Carbonyl linkage
c)
Peptide linkage
d)
Glycosidic linkage

|
Aleena Mathew answered |
All sacchrides /carbohydrates form glycosidic bond by eliminating water molecule
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because:- a)The -CHO group of glucose is not involved in glycosidic bond formation.
- b)Two monosaccharide units are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose.
- c)On hydrolysis, sucrose gives dextrorotatory and laevorotatory and the mixture is laevorotatory.
- d)Sucrose is dextrorotatory.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because:
a)
The -CHO group of glucose is not involved in glycosidic bond formation.
b)
Two monosaccharide units are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose.
c)
On hydrolysis, sucrose gives dextrorotatory and laevorotatory and the mixture is laevorotatory.
d)
Sucrose is dextrorotatory.
|
|
Gowri Menon answered |
Glucose and C2 of fructose, which does not have a free aldehyde or ketone group to undergo oxidation and reduction reactions.
c)Sucrose does not react with Benedict's reagent, which is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars.
d)Sucrose cannot be hydrolyzed by acid or enzyme into its constituent monosaccharides.
c)Sucrose does not react with Benedict's reagent, which is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars.
d)Sucrose cannot be hydrolyzed by acid or enzyme into its constituent monosaccharides.
The Molisch test is a chemical test that determines the presence of:- a)All carbohydrates
- b)Sucrose
- c)Fructose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Molisch test is a chemical test that determines the presence of:
a)
All carbohydrates
b)
Sucrose
c)
Fructose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The Molisch test uses concentrated sulphuric acid as the dehydrating acid. This acid dehydrates all carbohydrates, so the test is used to distinguish between carbohydrates and non-carbohydrates.
Which among the following is a non-reducing sugar?- a)Sucrose
- b)Maltose
- c)Lactose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is a non-reducing sugar?
a)
Sucrose
b)
Maltose
c)
Lactose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Non-reducing sugars do not have an OH group attached to the anomeric carbon so they cannot reduce other compounds. All monosaccharides such as glucose are reducing sugars. A disaccharide can be a reducing sugar or a non-reducing sugar. Maltose and lactose are reducing sugars, while sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
What does the following reaction of glucose with HI elucidates about the structure of glucose?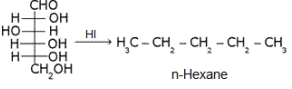
- a)Shows the presence of -CHO group
- b)Shows the presence of C=O group
- c)Shows the presence of six carbons linked linearly
- d)Shows the presence of ring structure of glucose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the following reaction of glucose with HI elucidates about the structure of glucose?
a)
Shows the presence of -CHO group
b)
Shows the presence of C=O group
c)
Shows the presence of six carbons linked linearly
d)
Shows the presence of ring structure of glucose
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
It shows that glucose exists as n-hexane...i.e. it has straight linear chain...
Which of the following carbohydrates is called an invert sugar?- a)Sucrose
- b)Fructose
- c)Glucose
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrates is called an invert sugar?
a)
Sucrose
b)
Fructose
c)
Glucose
d)
Cellulose

|
Sanjeevini Angadi answered |
It is called invert sugar because the angle of the specific rotation of the plain polarized light changes from a positive to a negative value due to the presence of the optical isomers of the mixture of glucose and fructosesugars.
What does the following reaction shows about the structure of glucose?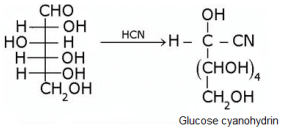
- a)It shows the presence of carbonyl group in glucose.
- b)It shows the presence of primary alcoholic group in glucose.
- c)It shows the presence of ring structure in glucose.
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the following reaction shows about the structure of glucose?
a)
It shows the presence of carbonyl group in glucose.
b)
It shows the presence of primary alcoholic group in glucose.
c)
It shows the presence of ring structure in glucose.
d)
none
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Glucose gets oxidized to cyanohydrin in reaction with HCN . This indicates that the carbonyl group is present as an aldehydic group.
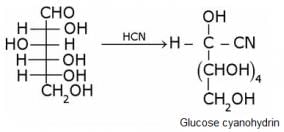
Glucose gets oxidized to cyanohydrin in reaction with HCN . This indicates that the carbonyl group is present as an aldehydic group.

The following is a reaction of glucose with Fehling’s reagent. What will happen in the reaction?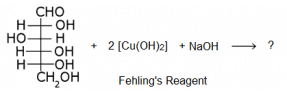
- a)Glucose will not react with Fehling’s reagent.
- b)Grey precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
- c)Red precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
- d)Saccharic acid will be formed when glucose will react with Fehling’s reagent.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The following is a reaction of glucose with Fehling’s reagent. What will happen in the reaction?
a)
Glucose will not react with Fehling’s reagent.
b)
Grey precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
c)
Red precipitate will be formed on warming glucose with Fehling’s reagent.
d)
Saccharic acid will be formed when glucose will react with Fehling’s reagent.

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Because it is the chemical property of aliphatic aldehyde to give red precipitate with fehling solution.
RCHO + 2 CuO -----------> Cu2O. + RCOOH
Fehling reagents is aq. alkaline CuSO4 solution along with Rochelle salt Na-K tartrate.
And glucose molecule consists of aldehydic group at first position and hence it is also a aldehyde and thus give this characteristic test.
RCHO + 2 CuO -----------> Cu2O. + RCOOH
Fehling reagents is aq. alkaline CuSO4 solution along with Rochelle salt Na-K tartrate.
And glucose molecule consists of aldehydic group at first position and hence it is also a aldehyde and thus give this characteristic test.
In polysaccharides, the linkage connecting monosaccharide is called:- a)peptide linkage
- b)glycogen linkage
- c)nucleosidic linkage
- d)glycosidic linkage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In polysaccharides, the linkage connecting monosaccharide is called:
a)
peptide linkage
b)
glycogen linkage
c)
nucleosidic linkage
d)
glycosidic linkage
|
|
Devanshi Mehta answered |
Introduction:
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of repeating units of monosaccharides. These monosaccharides are linked together by a specific type of bond known as the glycosidic linkage. The glycosidic linkage is a covalent bond formed between the anomeric carbon of one monosaccharide and a hydroxyl group on another monosaccharide. It is the key structural feature that gives polysaccharides their unique properties and functions.
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'D', the glycosidic linkage. Let's understand why this is the correct answer and explore the other options:
1. Peptide linkage:
- Peptide linkages are covalent bonds that connect amino acids to form proteins.
- Polysaccharides are not formed by peptide linkages, so this option is incorrect.
2. Glycogen linkage:
- Glycogen is a storage polysaccharide found in animals, including humans.
- While glycogen is composed of glucose monomers, the linkage connecting these monomers is the glycosidic linkage, not the glycogen linkage.
- Therefore, this option is incorrect.
3. Nucleosidic linkage:
- Nucleosidic linkages are covalent bonds that connect nucleotides to form nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA.
- Polysaccharides are not formed by nucleosidic linkages, so this option is incorrect.
The Glycosidic Linkage:
The glycosidic linkage is a specific type of covalent bond formed between the anomeric carbon of one monosaccharide and a hydroxyl group on another monosaccharide. It is formed through a condensation reaction, where a molecule of water is eliminated.
- The anomeric carbon is the carbon atom that is involved in forming the ring structure of a monosaccharide.
- The hydroxyl group can be located on a different monosaccharide or on the same monosaccharide, resulting in different types of glycosidic linkages.
Properties and Functions:
The glycosidic linkage plays a crucial role in determining the properties and functions of polysaccharides:
- The type of glycosidic linkage determines the structure and shape of the polysaccharide molecule.
- It affects the solubility, digestibility, and stability of the polysaccharide.
- Different types of glycosidic linkages result in different polysaccharides with distinct functions, such as energy storage (e.g., starch, glycogen) or structural support (e.g., cellulose, chitin).
Conclusion:
In polysaccharides, the linkage connecting monosaccharides is called the glycosidic linkage. This covalent bond is formed between the anomeric carbon of one monosaccharide and a hydroxyl group on another monosaccharide. The glycosidic linkage determines the structure, properties, and functions of polysaccharides.
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of repeating units of monosaccharides. These monosaccharides are linked together by a specific type of bond known as the glycosidic linkage. The glycosidic linkage is a covalent bond formed between the anomeric carbon of one monosaccharide and a hydroxyl group on another monosaccharide. It is the key structural feature that gives polysaccharides their unique properties and functions.
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'D', the glycosidic linkage. Let's understand why this is the correct answer and explore the other options:
1. Peptide linkage:
- Peptide linkages are covalent bonds that connect amino acids to form proteins.
- Polysaccharides are not formed by peptide linkages, so this option is incorrect.
2. Glycogen linkage:
- Glycogen is a storage polysaccharide found in animals, including humans.
- While glycogen is composed of glucose monomers, the linkage connecting these monomers is the glycosidic linkage, not the glycogen linkage.
- Therefore, this option is incorrect.
3. Nucleosidic linkage:
- Nucleosidic linkages are covalent bonds that connect nucleotides to form nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA.
- Polysaccharides are not formed by nucleosidic linkages, so this option is incorrect.
The Glycosidic Linkage:
The glycosidic linkage is a specific type of covalent bond formed between the anomeric carbon of one monosaccharide and a hydroxyl group on another monosaccharide. It is formed through a condensation reaction, where a molecule of water is eliminated.
- The anomeric carbon is the carbon atom that is involved in forming the ring structure of a monosaccharide.
- The hydroxyl group can be located on a different monosaccharide or on the same monosaccharide, resulting in different types of glycosidic linkages.
Properties and Functions:
The glycosidic linkage plays a crucial role in determining the properties and functions of polysaccharides:
- The type of glycosidic linkage determines the structure and shape of the polysaccharide molecule.
- It affects the solubility, digestibility, and stability of the polysaccharide.
- Different types of glycosidic linkages result in different polysaccharides with distinct functions, such as energy storage (e.g., starch, glycogen) or structural support (e.g., cellulose, chitin).
Conclusion:
In polysaccharides, the linkage connecting monosaccharides is called the glycosidic linkage. This covalent bond is formed between the anomeric carbon of one monosaccharide and a hydroxyl group on another monosaccharide. The glycosidic linkage determines the structure, properties, and functions of polysaccharides.
Which of the following carbohydrates is called milk sugar?- a)Glucose
- b)Galactose
- c)Lactose
- d)Maltose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrates is called milk sugar?
a)
Glucose
b)
Galactose
c)
Lactose
d)
Maltose

|
Nidhi Yadav answered |
Lactose is the carbohydrate that is commonly known as milk sugar. It is a disaccharide composed of two sugar molecules, galactose and glucose, linked together by a β-glycosidic bond. Lactose is found in the milk of mammals, including humans, and is an important source of energy for infants.
Here is a detailed explanation of why lactose is called milk sugar:
Lactose in Milk:
- Lactose is primarily found in the milk of mammals. It is the main carbohydrate present in milk, accounting for about 4-5% of its composition.
- It provides energy for the growing infant and is essential for their development.
- As mammals produce milk to nourish their young, lactose is present in varying amounts in the milk of different species, including humans.
Structure of Lactose:
- Lactose is a disaccharide, which means it is composed of two sugar molecules linked together.
- It consists of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose.
- The glucose and galactose molecules are joined by a β-glycosidic bond, which is a specific type of chemical bond between the two sugars.
Digestion of Lactose:
- Lactose is digested by the enzyme lactase, which is produced in the small intestine.
- Lactase breaks down lactose into its individual sugar components, glucose and galactose.
- These simple sugars can then be absorbed into the bloodstream and used as a source of energy by the body.
Intolerance to Lactose:
- Some individuals have a reduced ability to produce lactase, resulting in lactose intolerance.
- Lactose intolerance is characterized by symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming milk or dairy products.
- This occurs because undigested lactose reaches the large intestine, where it is fermented by bacteria, leading to the production of gas and other byproducts.
In conclusion, lactose is called milk sugar because it is the main carbohydrate found in milk. It consists of glucose and galactose linked together by a β-glycosidic bond. Lactose provides energy for infants and is digested by the enzyme lactase. Lactose intolerance can occur when there is a reduced ability to produce lactase, leading to digestive symptoms after consuming milk or dairy products.
Here is a detailed explanation of why lactose is called milk sugar:
Lactose in Milk:
- Lactose is primarily found in the milk of mammals. It is the main carbohydrate present in milk, accounting for about 4-5% of its composition.
- It provides energy for the growing infant and is essential for their development.
- As mammals produce milk to nourish their young, lactose is present in varying amounts in the milk of different species, including humans.
Structure of Lactose:
- Lactose is a disaccharide, which means it is composed of two sugar molecules linked together.
- It consists of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose.
- The glucose and galactose molecules are joined by a β-glycosidic bond, which is a specific type of chemical bond between the two sugars.
Digestion of Lactose:
- Lactose is digested by the enzyme lactase, which is produced in the small intestine.
- Lactase breaks down lactose into its individual sugar components, glucose and galactose.
- These simple sugars can then be absorbed into the bloodstream and used as a source of energy by the body.
Intolerance to Lactose:
- Some individuals have a reduced ability to produce lactase, resulting in lactose intolerance.
- Lactose intolerance is characterized by symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming milk or dairy products.
- This occurs because undigested lactose reaches the large intestine, where it is fermented by bacteria, leading to the production of gas and other byproducts.
In conclusion, lactose is called milk sugar because it is the main carbohydrate found in milk. It consists of glucose and galactose linked together by a β-glycosidic bond. Lactose provides energy for infants and is digested by the enzyme lactase. Lactose intolerance can occur when there is a reduced ability to produce lactase, leading to digestive symptoms after consuming milk or dairy products.
The commonest disaccharide have the molecular formula:- a)C10H20O10
- b)C12H22O11
- c)C10H18O9
- d)C11H22O11
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The commonest disaccharide have the molecular formula:
a)
C10H20O10
b)
C12H22O11
c)
C10H18O9
d)
C11H22O11

|
Sanjeev Kumar answered |
Because it is in the ratio of 1:2:1
Identify the following compound: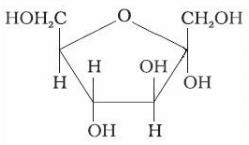
- a)β – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
- b)α – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
- c)α – D – (+) – Glucopyranose
- d)β – D – (+) – Glucopyranose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the following compound:
a)
β – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
b)
α – D – (-) – Fructofuranose
c)
α – D – (+) – Glucopyranose
d)
β – D – (+) – Glucopyranose

|
Mohit Kumar answered |
Here first of all we see that this compound has anomeric carbon at C2 thus it is a fructose.
Now since first hydroxyl is at the bottom, yeah starting from right always as usual this is similar to the fish configuration hence alpha
you see its a logic (or say rtafication) that alpha appears as a fish(α) and lives in sea ie bottom, while beta appears as bird(β) lives on top, try to draw symbols of alpha and beta to see alpha appears fish and so. Hope this helps.
Chapter doubts & questions for Carbohydrates and Glycobiology - Science for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Carbohydrates and Glycobiology - Science for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Science for ACT
486 videos|517 docs|337 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










