All Exams >
ACT >
Science for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Biomolecules for ACT Exam
Cellulose is made up of- a)Fructose
- b)Glucose
- c)Sucrose
- d)Ribose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cellulose is made up of
a)
Fructose
b)
Glucose
c)
Sucrose
d)
Ribose
|
|
Ayush Chauhan answered |
Cellulose is a third polymer made from beta glucose molecules and the polymer molecules are straight cellulose serves a very different purpose in nature to starch and glycogen it make up the cell walls in plant cell.
A homopolymer has only one type of building block called a monomer repeated ‘n’ number of times. A heteropolymer has more than one type of monomer. Proteins are heteropolymers made of amino acids. While a nucleic acid like DNA or RNA is made of only 4 types of nucleotide monomers, proteins are made of- a)20 types of monomers
- b)3 types of monomers
- c)40 types of monomers
- d)Only one type of monomer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A homopolymer has only one type of building block called a monomer repeated ‘n’ number of times. A heteropolymer has more than one type of monomer. Proteins are heteropolymers made of amino acids. While a nucleic acid like DNA or RNA is made of only 4 types of nucleotide monomers, proteins are made of
a)
20 types of monomers
b)
3 types of monomers
c)
40 types of monomers
d)
Only one type of monomer

|
Syed Hussain answered |
In living systems, like our own bodies, these larger molecules include carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins. The monomers of these organic groups are: Carbohydrates - monosaccharides. Lipids - glycerol and fatty acids
The number of amino acids found in proteins are- a)20
- b)21
- c)18
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of amino acids found in proteins are
a)
20
b)
21
c)
18
d)
16
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation. ... Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids, 20 in the standard genetic code and an additional 2 that can be incorporated by special translation mechanisms.
The bacterial cell wall is formed of- a)Cellulose
- b)Hemicellulose
- c)Peptidoglycan
- d)Glycogen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The bacterial cell wall is formed of
a)
Cellulose
b)
Hemicellulose
c)
Peptidoglycan
d)
Glycogen
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Bacterial cell walls are made of peptidoglycan (also called murein), which is made from polysaccharide chains cross-linked by unusual peptides containing D-amino acids. Bacterial cell walls are different from the cell walls of plants and fungi which are made of cellulose and chitin, respectively.
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is- a)Protein
- b)Lipid
- c)Steroids
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is
a)
Protein
b)
Lipid
c)
Steroids
d)
Cellulose
|
|
Raghavendra Datta answered |
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is cellulose.
What is Cellulose?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that is found in the cell walls of plants. It is composed of repeating units of glucose molecules that are linked together to form long chains. These chains are then arranged in a way that gives cellulose its characteristic strength and rigidity.
Why is Cellulose Abundant on Earth?
Cellulose is abundant on earth for several reasons:
1. It is found in the cell walls of plants - Plants are the most abundant form of life on earth, and cellulose is a major component of their cell walls. This means that there is a huge amount of cellulose present on earth.
2. It is resistant to degradation - Unlike other organic molecules, cellulose is highly resistant to degradation by enzymes and other biological processes. This means that it can persist in the environment for a long time, contributing to its abundance.
3. It is a major component of biomass - Cellulose is a major component of the biomass of plants. When plants die and decompose, the cellulose in their cell walls is broken down into smaller molecules that can be used by other organisms. This means that there is a constant supply of cellulose being produced and broken down on earth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule present on earth due to its presence in the cell walls of plants, its resistance to degradation, and its role as a major component of biomass.
What is Cellulose?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that is found in the cell walls of plants. It is composed of repeating units of glucose molecules that are linked together to form long chains. These chains are then arranged in a way that gives cellulose its characteristic strength and rigidity.
Why is Cellulose Abundant on Earth?
Cellulose is abundant on earth for several reasons:
1. It is found in the cell walls of plants - Plants are the most abundant form of life on earth, and cellulose is a major component of their cell walls. This means that there is a huge amount of cellulose present on earth.
2. It is resistant to degradation - Unlike other organic molecules, cellulose is highly resistant to degradation by enzymes and other biological processes. This means that it can persist in the environment for a long time, contributing to its abundance.
3. It is a major component of biomass - Cellulose is a major component of the biomass of plants. When plants die and decompose, the cellulose in their cell walls is broken down into smaller molecules that can be used by other organisms. This means that there is a constant supply of cellulose being produced and broken down on earth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule present on earth due to its presence in the cell walls of plants, its resistance to degradation, and its role as a major component of biomass.
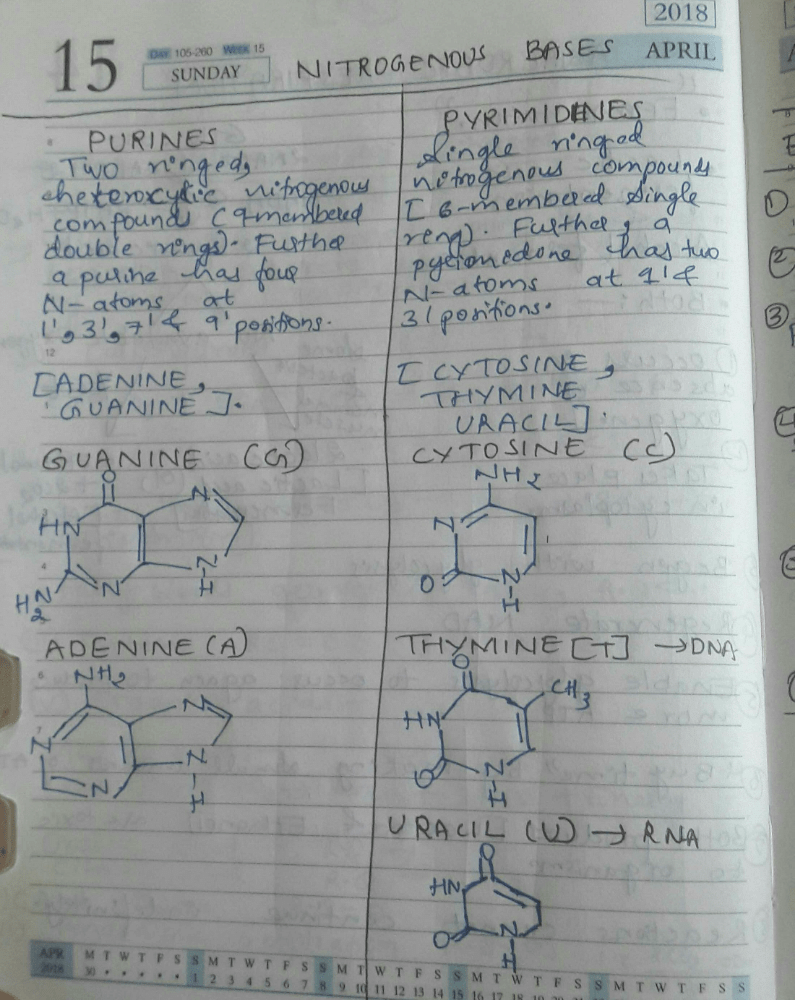
Double hydrogen bond occurs in DNA between- a)Adenine and guanine
- b)Thymine and cytosine
- c)Adenine and thymine
- d)Uracil and thymine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Double hydrogen bond occurs in DNA between
a)
Adenine and guanine
b)
Thymine and cytosine
c)
Adenine and thymine
d)
Uracil and thymine
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The complementary base pairs of guanine with cytosine and adenine with thymine connect to one another using hydrogen bonds. In addition to holding the DNA strands together, the hydrogen bonding between the complementary bases also sequester the bases in the interior of the double helix. Since, the option of Guanine and Cytosine is not provided. Hence, the correct option is Option C.
An ester bond is present between- a)Amino acids
- b)Nucleoside
- c)Nucleotide
- d)Monosaccharides
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An ester bond is present between
a)
Amino acids
b)
Nucleoside
c)
Nucleotide
d)
Monosaccharides

|
Syed Hussain answered |
Phosphodiester bond definition. A bondbetween a two sugar groups and a phosphate group; such bonds form the sugar-phosphate-sugar backbone of DNA and RNA. A diester bond (between phosphoric acid and two sugar molecules) linking two nucleotides together to form the nucleotide polymers DNA and RNA.
A segment of DNA has 120 adenine and 120 cytosine bases. The total number of nucleotides present in the segment is- a)480
- b)240
- c)60
- d)120
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A segment of DNA has 120 adenine and 120 cytosine bases. The total number of nucleotides present in the segment is
a)
480
b)
240
c)
60
d)
120
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
According to Chargaff’s rule, the amount of adenine is always equal to that of thymine and the amount of guanine is always equal to that of cytosine.
A = T(120), G = C(120)
The total number of nucleotides would be 120 × 4 = 480.
The plant cell wall are made up of- a)Cellulose
- b)Starch
- c)Glycogen Bacteria
- d)Inulin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The plant cell wall are made up of
a)
Cellulose
b)
Starch
c)
Glycogen Bacteria
d)
Inulin

|
Srishti Sen answered |
Plant cell walls are made of cellulose. Paper made from plant pulp is cellulose.
The oils have- a)High melting point
- b)Low melting point
- c)Optimum melting point
- d)No melting point
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The oils have
a)
High melting point
b)
Low melting point
c)
Optimum melting point
d)
No melting point
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Oils have lower melting point (e.g., gingely oil) and hence remain as oil in winters.
Proteins perform many physiological functions. For example, some function as enzymes. Which one of the following represents an additional function which some proteins discharge?- a)Antibiotics
- b)Pigments making colours of flowers
- c)Hormones
- d)Pigments conferring colour to skin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Proteins perform many physiological functions. For example, some function as enzymes. Which one of the following represents an additional function which some proteins discharge?
a)
Antibiotics
b)
Pigments making colours of flowers
c)
Hormones
d)
Pigments conferring colour to skin
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Proteins perform many physiological functions. For example, some proteins function as enzymes. Hormones represents an additional function that some proteins discharge (like insulin).
Enormous diversity of protein molecules is due to- a)R groups of amino acids
- b)Sequence of amino acids
- c)Peptide bonds
- d)Amino groups of amino acids
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Enormous diversity of protein molecules is due to
a)
R groups of amino acids
b)
Sequence of amino acids
c)
Peptide bonds
d)
Amino groups of amino acids
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The third is tertiary; this is the folding of the secondary structures into the final 3D structure of a protein. Amino acids have properties that guide this; some interact easily with water (hydrophilic) and these orient themselves on the outside of a protein, while others don't interact well with water (hydrophobic) and will try to get themselves on the inside of the folded structure where they will be protected. Hydrophobicity/philicity is the major driving force in protein folding but other bonds will also be formed between amino acids like S-S linkages, other ionic bonds and HYDROGEN BONDS (tons of these are made). These smaller interactions generally stabilize the protein and keep it folded in the most ideal conformation possible.
DNA nucleotides are attached by
- a)Hydrogen bond
- b)Covalent bond
- c)Van der Waals bond
- d)Electrovalent bond
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA nucleotides are attached by
a)
Hydrogen bond
b)
Covalent bond
c)
Van der Waals bond
d)
Electrovalent bond
|
|
Gopikas S answered |
Explanation: DNA nucleotides are attached by the Hydrogen bond. A nucleotide is the basic unit of polynucleotide chain of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (Ribonucleic acid).
The nitrogenous bases are found in the strand's inward direction. The nitrogenous bases of the two antiparallel strands form hydrogen bonds, resulting in the formation of two helical strands.
The nitrogenous bases used in DNA (double-stranded helical structure) are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
Adenine is joined to thymine with two hydrogen bonds, whereas guanine is joined to cytosine by three hydrogen bonds.
Thus, DNA nucleotides are attached by Hydrogen bond.
The nucleotide chemical components are- a)Heterocyclic compounds, sugar and phosphate
- b)Sugar and Phosphate
- c)Heterocyclic compounds and sugar
- d)Phosphate and heterocyclic compounds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The nucleotide chemical components are
a)
Heterocyclic compounds, sugar and phosphate
b)
Sugar and Phosphate
c)
Heterocyclic compounds and sugar
d)
Phosphate and heterocyclic compounds

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
The nucleotide has three chemically distinct components. One is a heterocyclic compound, the second is a monosaccharide and the third a phosphoric acid or phosphate.
Which one is not a denaturing factor for protein?- a)High energy radiation
- b)High pressure
- c)Drastic change in pH
- d)High temperature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not a denaturing factor for protein?
a)
High energy radiation
b)
High pressure
c)
Drastic change in pH
d)
High temperature

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
Protein molecules get denatured due to high temperature, very high or low pH and high energy radiation but there is no effect due to high pressure.
The energy currency of cell is—- a)GDP
- b)ATP
- c)ADP
- d)NAD
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The energy currency of cell is—
a)
GDP
b)
ATP
c)
ADP
d)
NAD
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
When the ATP converts to ADP, the ATP is said to be spent. he molecule is used like a battery within cells and allows the consumption of one of its phosphorous molecules.The energy currency used by all cells from bacteria to man is adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Which is the most abundant chemical for the living organisms?- a)Lipids
- b)Proteins
- c)Ions
- d)Water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the most abundant chemical for the living organisms?
a)
Lipids
b)
Proteins
c)
Ions
d)
Water

|
Anand Jain answered |
Water is the most abundant chemical for the living organisms.
Which of the following is not a conjugated protein?- a)Peptone
- b)Glycoprotein
- c)Chromoprotein
- d)Lipoprotein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a conjugated protein?
a)
Peptone
b)
Glycoprotein
c)
Chromoprotein
d)
Lipoprotein
|
|
Suyash Jain answered |
A conjugated protein is a protein that functions in interaction with other (non-polypeptide) chemical groups attached by covalent bonding or weak interactions.
. __________ is a globular protein of 6 kDa consisting of 51 amino acids arranged in 2 polypeptide chains held together by a disulphide bridge- a)Fibrinogen
- b)Keratin
- c)Insulin
- d)Glucagon
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
. __________ is a globular protein of 6 kDa consisting of 51 amino acids arranged in 2 polypeptide chains held together by a disulphide bridge
a)
Fibrinogen
b)
Keratin
c)
Insulin
d)
Glucagon
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Human insulin is a peptide hormone composed of 51 ammo acids and has a molecular weight of 5805 Da.(∼6 Kda). In this molecule, there are two polypeptide chains (A and B) held together by disulphide bridge.
Which one of the following is fibrous protein?- a)Collagen
- b)Ribozymes
- c)Haemoglobin
- d)Hemicellulose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is fibrous protein?
a)
Collagen
b)
Ribozymes
c)
Haemoglobin
d)
Hemicellulose

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
Collagen is a fibrous protein. It is the main structural protein in the extracellular space in thevarious connective tissues. It is the most abundant protein in mammals.
One turn of the DNA double helix spans a distance of- a)3.4 nm
- b)4.26 nm
- c)4.56 nm
- d)2.46 nm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One turn of the DNA double helix spans a distance of
a)
3.4 nm
b)
4.26 nm
c)
4.56 nm
d)
2.46 nm
|
|
Suresh Kumar answered |
Refer biomolecules chapter in Ncert .Its mentioned in that chapter...
A peptide bond is formed by the process of- a)Amination
- b)Rehydration
- c)Deamination
- d)Dehydration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A peptide bond is formed by the process of
a)
Amination
b)
Rehydration
c)
Deamination
d)
Dehydration
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (H2O). This is a dehydration synthesis reaction (also known as a condensation reaction), and usually occurs between amino acids.
In a DNA molecule, two strands are held by- a)Nitrogen bonds
- b)Phosphate bonds
- c)Carbon bonds
- d)Hydrogen bonds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a DNA molecule, two strands are held by
a)
Nitrogen bonds
b)
Phosphate bonds
c)
Carbon bonds
d)
Hydrogen bonds
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
By hydrogen bonds between the two bases. Basically, the bases are ‘polar’, meaning they have slight differences in electrical charge at certain points. This allows them to attract one another like a balloon sticking to your hair.
Hydrogen bonds are weaker than the covalent bonds that hold the rest of the molecule together, making them easier to break and re-form.
DNA differs from RNA in having- a)Thymine but no uracil
- b)Uracil but no thymine
- c)Thymine but no cytosine
- d)Cytosine but no guanine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA differs from RNA in having
a)
Thymine but no uracil
b)
Uracil but no thymine
c)
Thymine but no cytosine
d)
Cytosine but no guanine
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Uracil is energetically less expensive to produce than thymine, which may account for its use in RNA. In DNA, however, uracil is readily produced by chemical degradation of cytosine, so having thymine as the normal base makes detection and repair of such incipient mutations more efficient.
A polysaccharide present as storehouse of energy of plant tissues- a)Chitin
- b)Starch
- c)Hemi cellulose
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A polysaccharide present as storehouse of energy of plant tissues
a)
Chitin
b)
Starch
c)
Hemi cellulose
d)
Cellulose
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Polysaccharide
A polysaccharide is a large molecule made of many smaller monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars, like glucose. Special enzymes bind these small monomers together creating large sugar polymers, or polysaccharides. A polysaccharide is also called a glycan. A polysaccharide can be a homopolysaccharide, in which all the monosaccharides are the same, or a heteropolysaccharide in which the monosaccharides vary. Depending on which monosaccharides are connected, and which carbons in the monosaccharides connects, polysaccharides take on a variety of forms. A molecule with a straight chain of monosaccharides is called a linear polysaccharide, while a chain that has arms and turns is known as a branched polysaccharide.
The part of enzyme bound to the protein part by a covalent bond is called- a)Holoenzyme
- b)Cofactor
- c)Prosthetic group
- d)Apoenzyme
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The part of enzyme bound to the protein part by a covalent bond is called
a)
Holoenzyme
b)
Cofactor
c)
Prosthetic group
d)
Apoenzyme

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
A prosthetic group is a tightly covalently bound, specific non-polypeptide unit required for the biological function of some proteins. The prosthetic group may be organic (such as a vitamin, sugar, or lipid) or inorganic (such as a metal ion), but is not composed of amino acids.
In yeast, during fermentation the glycolysis pathway leads to- a)Production of glucose
- b)Production of oxygen
- c)Production of pyruvic acid
- d)Production of ethanol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In yeast, during fermentation the glycolysis pathway leads to
a)
Production of glucose
b)
Production of oxygen
c)
Production of pyruvic acid
d)
Production of ethanol

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
In yeast, during fermentation, the same pathway leads to the production of ethanol(alcohol).
Which of the following carries the hereditary information from parents to progeny?- a)Nucleotides
- b)Nucleoside
- c)Nucleic acids
- d)Proteins
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carries the hereditary information from parents to progeny?
a)
Nucleotides
b)
Nucleoside
c)
Nucleic acids
d)
Proteins
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Nucleic acid is the chemical name for the molecules RNA and DNA. The name comes from the fact that these molecules are acids – that is, they are good at donating protons and accepting electron pairs in chemical reactions – and the fact that they were first discovered in the nuclei of our cells.
Assertion (A): Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing substrate binding. Reason (R): Competitive inhibition can be overcome by increasing the concentration of the substrate.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing substrate binding.
Reason (R): Competitive inhibition can be overcome by increasing the concentration of the substrate.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- The Assertion is correct because competitive inhibitors indeed bind to the active site of an enzyme, which prevents the substrate from binding.
- The Reason is also correct as increasing the substrate concentration can outcompete the inhibitor for the active site, thereby restoring enzyme activity.
- Additionally, the Reason effectively explains the Assertion as it describes how competitive inhibition can be mitigated, confirming that both statements are true and that the Reason is the correct explanation for the Assertion.
Proteins are made up of- a)Monomers
- b)Amino acids
- c)Homopolymers
- d)Nucleosides
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Proteins are made up of
a)
Monomers
b)
Amino acids
c)
Homopolymers
d)
Nucleosides
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Proteins are heteropolymers usually made of amino acids. While a nucleic acid like DNA or RNA is made of of only 4 types of nucleotide monomers, proteins are made of 20 types of monomers. Ans: (d) Proteins perform many physiological functions. ... Ans: (a) Glycogen is a homopolymer made of glucose units.
Read the following passage to answer the following questions:The enzyme molecule operates by chemically binding with the substrate molecule, to form an enzyme-substrate complex. The enzyme's tertiary structure consists of a unique pocket or site on which the substrate molecules can become attached and interact subsequently. This brings about an interaction between the specific active sites in the enzyme molecule and the reactive sites in the substrate molecule. The enzyme now breaks down the substrate into- products. The products initially remain attached to the enzyme for a short while forming an enzyme product complex. The products get released from the enzyme molecule subsequently. The enzyme is now ready to receive another substrate molecule again. Thus, the same enzyme can be used again and again.Direction : In the following questions the Assertions (A) and Reasons (R) have been put forward. Read both the statements and choose the correct option from the following:Assertion : Enzyme and substrate respectively have active and reactive sites on their surface.Reason : Active and reactive sites push the enzyme and substrate molecules away from each other.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)A is false but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following passage to answer the following questions:
The enzyme molecule operates by chemically binding with the substrate molecule, to form an enzyme-substrate complex. The enzyme's tertiary structure consists of a unique pocket or site on which the substrate molecules can become attached and interact subsequently. This brings about an interaction between the specific active sites in the enzyme molecule and the reactive sites in the substrate molecule. The enzyme now breaks down the substrate into- products. The products initially remain attached to the enzyme for a short while forming an enzyme product complex. The products get released from the enzyme molecule subsequently. The enzyme is now ready to receive another substrate molecule again. Thus, the same enzyme can be used again and again.
Direction : In the following questions the Assertions (A) and Reasons (R) have been put forward. Read both the statements and choose the correct option from the following:
Assertion : Enzyme and substrate respectively have active and reactive sites on their surface.
Reason : Active and reactive sites push the enzyme and substrate molecules away from each other.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
A is false but R is true.

|
Abhishek Mishraclasses answered |
Active and reactive sites of enzyme and substrate do not push away each either but make them to unite to form the ES complex.
Which of the following is not obtained on hydrolysis of nucleic acid?- a)Purine
- b)Phosphoric acid
- c)Pyrimidine
- d)Pentose sugar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not obtained on hydrolysis of nucleic acid?
a)
Purine
b)
Phosphoric acid
c)
Pyrimidine
d)
Pentose sugar

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
Hydrolysis of nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) produces pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) purine and pyrimidine. Phosphoric acid is not released on hydrolysis of DNA or RNA.
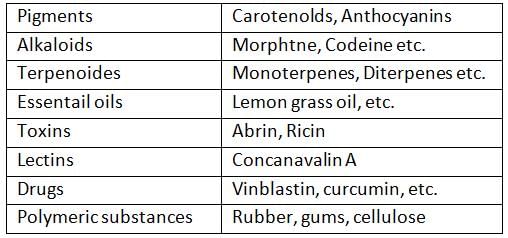
Assertion (A): Secondary metabolites like rubber and essential oils do not play known roles in the normal physiological processes of the organisms that produce them.
Reason (R): Secondary metabolites are often involved in defense mechanisms or ecological functions rather than primary metabolic processes.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Secondary metabolites like rubber and essential oils do not play known roles in the normal physiological processes of the organisms that produce them.
Reason (R): Secondary metabolites are often involved in defense mechanisms or ecological functions rather than primary metabolic processes.
Reason (R): Secondary metabolites are often involved in defense mechanisms or ecological functions rather than primary metabolic processes.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Assertion A is true as secondary metabolites such as rubber and essential oils generally do not have identifiable roles in the normal physiological functions of the organisms that produce them. Reason R correctly explains this by stating that these metabolites are involved in ecological functions such as defense, rather than in primary metabolic processes. Therefore, Option A is correct as R is the correct explanation of A.
How many subunits are there in human adult haemoglobin?- a)4
- b)5
- c)3
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many subunits are there in human adult haemoglobin?
a)
4
b)
5
c)
3
d)
2

|
Rajat Roy answered |
Proteins human haemoglobin consists of 4 subunits. Two of these are identical toeach other. Hence, two subunits of αα type and two subunits of ββ type together constitute the human haemoglobin (Hb).
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.Assertion: Both amino group and acidic group act as substituents on the same carbon called α-amino acids.Reason: Amino acids are inorganic compounds containing an amino group.- a)Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Assertion is true but the reason is false.
- c)Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- d)Assertion is false but the reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion: Both amino group and acidic group act as substituents on the same carbon called α-amino acids.
Reason: Amino acids are inorganic compounds containing an amino group.
a)
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Assertion is true but the reason is false.
c)
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
d)
Assertion is false but the reason is true.

|
Lead Academy answered |
Amino acids are organic compounds containing an amino group and an acidic group as substituents on the same carbon, i.e. the α-carbon. Hence, they are called α-amino acids.
Secondary structure of protein refers to- a)Folding patterns of polypeptide chain
- b)Sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain
- c)Bonds between alternate polypeptide chains
- d)Bonding between NH+3 and COO– of two peptides
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Secondary structure of protein refers to
a)
Folding patterns of polypeptide chain
b)
Sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain
c)
Bonds between alternate polypeptide chains
d)
Bonding between NH+3 and COO– of two peptides

|
Top Rankers answered |
The secondary structure of a protein refers to regular folding patterns of continuous portions of the polypeptide chain. It is primarily determined by hydrogen bonding interactions between the amino acid residues of the chain. The two most common types of secondary structure are alpha helices and beta sheets.
Which of the following statements regarding the catalytic cycle of enzyme action is/are correct?i. The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting perfectly into it.ii. The enzyme changes shape to fit more tightly around the substrate after binding occurs.iii. The enzyme-product complex is formed when the active site breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate.iv. The enzyme remains permanently altered after releasing the products of the reaction.- a)ii and iii
- b)i and ii
- c)iii and iv
- d)i, ii, and iii
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding the catalytic cycle of enzyme action is/are correct?
i. The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting perfectly into it.
ii. The enzyme changes shape to fit more tightly around the substrate after binding occurs.
iii. The enzyme-product complex is formed when the active site breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate.
iv. The enzyme remains permanently altered after releasing the products of the reaction.
a)
ii and iii
b)
i and ii
c)
iii and iv
d)
i, ii, and iii
|
|
Ashish Dasgupta answered |
Understanding the Catalytic Cycle of Enzyme Action
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate biochemical reactions. The statements provided pertain to the catalytic cycle of enzyme action, and the correct answer is option 'D' (i, ii, and iii). Let’s analyze each statement:
i. Substrate Binding
- The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting perfectly into it.
- This statement is partially true; however, it is more accurate to say that the substrate does not always fit perfectly. The "induced fit" model suggests that the enzyme undergoes a conformational change to accommodate the substrate.
ii. Enzyme Conformational Change
- The enzyme changes shape to fit more tightly around the substrate after binding occurs.
- This is true and describes the induced fit model, wherein the binding of the substrate induces a change in the enzyme's shape, enhancing the interaction between enzyme and substrate.
iii. Formation of Enzyme-Product Complex
- The enzyme-product complex is formed when the active site breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate.
- This statement is correct. The enzyme catalyzes the reaction, lowering the activation energy and facilitating the breaking and formation of bonds, leading to the production of products.
iv. Permanent Alteration of the Enzyme
- The enzyme remains permanently altered after releasing the products of the reaction.
- This statement is incorrect. Enzymes typically return to their original state after the reaction, allowing them to participate in subsequent reactions.
Conclusion
The correct statements are ii and iii, affirming that the answer is option 'D' (i, ii, and iii are considered correct in context). Understanding these concepts is essential for grasping enzyme functionality in biochemical processes.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate biochemical reactions. The statements provided pertain to the catalytic cycle of enzyme action, and the correct answer is option 'D' (i, ii, and iii). Let’s analyze each statement:
i. Substrate Binding
- The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting perfectly into it.
- This statement is partially true; however, it is more accurate to say that the substrate does not always fit perfectly. The "induced fit" model suggests that the enzyme undergoes a conformational change to accommodate the substrate.
ii. Enzyme Conformational Change
- The enzyme changes shape to fit more tightly around the substrate after binding occurs.
- This is true and describes the induced fit model, wherein the binding of the substrate induces a change in the enzyme's shape, enhancing the interaction between enzyme and substrate.
iii. Formation of Enzyme-Product Complex
- The enzyme-product complex is formed when the active site breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate.
- This statement is correct. The enzyme catalyzes the reaction, lowering the activation energy and facilitating the breaking and formation of bonds, leading to the production of products.
iv. Permanent Alteration of the Enzyme
- The enzyme remains permanently altered after releasing the products of the reaction.
- This statement is incorrect. Enzymes typically return to their original state after the reaction, allowing them to participate in subsequent reactions.
Conclusion
The correct statements are ii and iii, affirming that the answer is option 'D' (i, ii, and iii are considered correct in context). Understanding these concepts is essential for grasping enzyme functionality in biochemical processes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?i. Lipids are generally water soluble and include simple fatty acids.ii. Fatty acids can be either saturated (without double bonds) or unsaturated (with one or more double bonds).iii. Glycerol is a simple sugar that can be esterified with fatty acids to form triglycerides.iv. Phospholipids are found in cell membranes and contain phosphorus.- a)ii and iv
- b)i and iii
- c)i, ii, and iv
- d)ii and iii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Lipids are generally water soluble and include simple fatty acids.
ii. Fatty acids can be either saturated (without double bonds) or unsaturated (with one or more double bonds).
iii. Glycerol is a simple sugar that can be esterified with fatty acids to form triglycerides.
iv. Phospholipids are found in cell membranes and contain phosphorus.
a)
ii and iv
b)
i and iii
c)
i, ii, and iv
d)
ii and iii

|
Top Rankers answered |
To determine the correct statements:
- Statement i is incorrect because lipids are generally water insoluble, not soluble.
- Statement ii is correct as it accurately describes the types of fatty acids.
- Statement iii is incorrect because glycerol is not a simple sugar; it is a trihydroxy alcohol (trihydroxy propane) that combines with fatty acids to form triglycerides.
- Statement iv is correct as phospholipids are indeed found in cell membranes and contain phosphorus.
Thus, the correct statements are ii and iv, making Option A the right choice.
Read the following passage to answer the following questions:
Proteins are polypeptide chains made up of amino acids. There are 20 types of amino acids joined together by peptide bond between amino and carboxylic group. There are two kinds of amino acids, Essential amino acids and Non-essential amino acids. The Primary structure of protein is the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The first amino acid of sequence is called N-terminal amino acids and last amino acid of peptide chain is called C-terminal amino acids. The secondary structure proteins forms helix. There are three types of secondary structure: a helix, P pleated and collagen helix. In tertiary structure long protein chain is folded upon itself like a hollow woollen ball to give three-dimensional view of protein. In quaternary structure, each polypeptide develops its own tertiary structure and function as subunit of protein.
Direction: In the following questions the Assertions (A) and Reasons (R) have been put forward. Read both the statements and choose the correct option from the following:
Assertion : Amino acids are monomers of nucleic acid.
Reason : Protein amino acids have an unlimited variety.
- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following passage to answer the following questions:
Proteins are polypeptide chains made up of amino acids. There are 20 types of amino acids joined together by peptide bond between amino and carboxylic group. There are two kinds of amino acids, Essential amino acids and Non-essential amino acids. The Primary structure of protein is the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The first amino acid of sequence is called N-terminal amino acids and last amino acid of peptide chain is called C-terminal amino acids. The secondary structure proteins forms helix. There are three types of secondary structure: a helix, P pleated and collagen helix. In tertiary structure long protein chain is folded upon itself like a hollow woollen ball to give three-dimensional view of protein. In quaternary structure, each polypeptide develops its own tertiary structure and function as subunit of protein.
Direction: In the following questions the Assertions (A) and Reasons (R) have been put forward. Read both the statements and choose the correct option from the following:
Assertion : Amino acids are monomers of nucleic acid.
Reason : Protein amino acids have an unlimited variety.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Amino acids are monomers of protein and are not of nucleic acid. Proteins are built from a set of only 20 amino acid.
Nitrogen is an important component of- a)Polyphosphates
- b)Carbohydrates
- c)Lipids
- d)Proteins
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitrogen is an important component of
a)
Polyphosphates
b)
Carbohydrates
c)
Lipids
d)
Proteins
|
|
Neha Menon answered |
**Nitrogen and Proteins**
**Explanation:**
Nitrogen is an essential element for the growth and development of living organisms. It is a vital component of many biomolecules, including proteins. Proteins are large, complex molecules that play crucial roles in the structure, function, and regulation of cells and tissues.
**1. Nitrogen in Amino Acids:**
Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids. Nitrogen is a key component of these amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid contains an amino group (-NH2) that includes a nitrogen atom. The amino group is responsible for the nitrogen content in proteins.
**2. Role of Nitrogen in Protein Structure:**
Nitrogen atoms within amino acids play a crucial role in forming the peptide bonds that link individual amino acids together. These peptide bonds create a polypeptide chain, which folds and twists to form the unique three-dimensional structure of a protein. This structure is essential for the protein's function.
**3. Protein Functions:**
Proteins have diverse functions in living organisms. Some of the important functions of proteins include:
- Enzymes: Proteins act as enzymes, which are catalysts that facilitate biochemical reactions in cells.
- Structural Support: Proteins provide structural support to cells and tissues. For example, collagen is a protein that forms the structural framework of connective tissues like skin, tendons, and bones.
- Transport: Certain proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. For instance, hemoglobin is a protein responsible for carrying oxygen in red blood cells.
- Signaling: Proteins can act as signaling molecules, transmitting signals within and between cells. Examples include hormones and neurotransmitters.
- Immunity: Antibodies, a type of protein, play a crucial role in the immune system by recognizing and neutralizing foreign substances in the body.
**Conclusion:**
Nitrogen is an important component of proteins. Proteins are essential for various biological processes, including cell structure, enzyme function, transport, signaling, and immunity. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Proteins.
**Explanation:**
Nitrogen is an essential element for the growth and development of living organisms. It is a vital component of many biomolecules, including proteins. Proteins are large, complex molecules that play crucial roles in the structure, function, and regulation of cells and tissues.
**1. Nitrogen in Amino Acids:**
Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids. Nitrogen is a key component of these amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid contains an amino group (-NH2) that includes a nitrogen atom. The amino group is responsible for the nitrogen content in proteins.
**2. Role of Nitrogen in Protein Structure:**
Nitrogen atoms within amino acids play a crucial role in forming the peptide bonds that link individual amino acids together. These peptide bonds create a polypeptide chain, which folds and twists to form the unique three-dimensional structure of a protein. This structure is essential for the protein's function.
**3. Protein Functions:**
Proteins have diverse functions in living organisms. Some of the important functions of proteins include:
- Enzymes: Proteins act as enzymes, which are catalysts that facilitate biochemical reactions in cells.
- Structural Support: Proteins provide structural support to cells and tissues. For example, collagen is a protein that forms the structural framework of connective tissues like skin, tendons, and bones.
- Transport: Certain proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. For instance, hemoglobin is a protein responsible for carrying oxygen in red blood cells.
- Signaling: Proteins can act as signaling molecules, transmitting signals within and between cells. Examples include hormones and neurotransmitters.
- Immunity: Antibodies, a type of protein, play a crucial role in the immune system by recognizing and neutralizing foreign substances in the body.
**Conclusion:**
Nitrogen is an important component of proteins. Proteins are essential for various biological processes, including cell structure, enzyme function, transport, signaling, and immunity. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Proteins.
Which type of lipid is glycerol classified as?- a)Fatty acid
- b)Triglyceride
- c)Simple lipid
- d)Phospholipid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Fatty acid
b)
Triglyceride
c)
Simple lipid
d)
Phospholipid

|
Top Rankers answered |
Glycerol is classified as a simple lipid and is a component of many complex lipids like triglycerides.
Read the following passage to answer the following questions:The enzyme molecule operates by chemically binding with the substrate molecule, to form an enzyme-substrate complex. The enzyme's tertiary structure consists of a unique pocket or site on which the substrate molecules can become attached and interact subsequently. This brings about an interaction between the specific active sites in the enzyme molecule and the reactive sites in the substrate molecule. The enzyme now breaks down the substrate into- products. The products initially remain attached to the enzyme for a short while forming an enzyme product complex. The products get released from the enzyme molecule subsequently. The enzyme is now ready to receive another substrate molecule again. Thus, the same enzyme can be used again and again.Q. Khosland's model of enzyme action implies that:- a)Enzyme and substrate unit at the active site like lock and key fits a lock.
- b)Inducible change is brought about at the active site of enzyme by substrate.
- c)Active site of enzyme brings about the conformational change in the substrate.
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following passage to answer the following questions:
The enzyme molecule operates by chemically binding with the substrate molecule, to form an enzyme-substrate complex. The enzyme's tertiary structure consists of a unique pocket or site on which the substrate molecules can become attached and interact subsequently. This brings about an interaction between the specific active sites in the enzyme molecule and the reactive sites in the substrate molecule. The enzyme now breaks down the substrate into- products. The products initially remain attached to the enzyme for a short while forming an enzyme product complex. The products get released from the enzyme molecule subsequently. The enzyme is now ready to receive another substrate molecule again. Thus, the same enzyme can be used again and again.
Q. Khosland's model of enzyme action implies that:
a)
Enzyme and substrate unit at the active site like lock and key fits a lock.
b)
Inducible change is brought about at the active site of enzyme by substrate.
c)
Active site of enzyme brings about the conformational change in the substrate.
d)
None of the above
|
|
Raghavendra Roy answered |
Explanation:
Khosland's Model of Enzyme Action:
- Khosland's model of enzyme action implies that an inducible change is brought about at the active site of the enzyme by the substrate.
Key Points:
- In this model, the enzyme and substrate do not simply fit together like a lock and key, as in the lock-and-key model. Instead, the substrate induces a change in the active site of the enzyme.
- This change in the active site allows the enzyme to interact more effectively with the substrate, leading to the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex.
- The active site of the enzyme plays a crucial role in bringing about conformational changes in the substrate, facilitating the breakdown of the substrate into products.
- Once the products are formed, they initially remain attached to the enzyme, forming an enzyme-product complex.
- The products are then released from the enzyme molecule, allowing the enzyme to receive another substrate molecule and repeat the process.
Conclusion:
- Khosland's model highlights the dynamic interaction between enzymes and substrates, emphasizing the role of inducible changes at the active site of the enzyme in facilitating enzymatic reactions.
Khosland's Model of Enzyme Action:
- Khosland's model of enzyme action implies that an inducible change is brought about at the active site of the enzyme by the substrate.
Key Points:
- In this model, the enzyme and substrate do not simply fit together like a lock and key, as in the lock-and-key model. Instead, the substrate induces a change in the active site of the enzyme.
- This change in the active site allows the enzyme to interact more effectively with the substrate, leading to the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex.
- The active site of the enzyme plays a crucial role in bringing about conformational changes in the substrate, facilitating the breakdown of the substrate into products.
- Once the products are formed, they initially remain attached to the enzyme, forming an enzyme-product complex.
- The products are then released from the enzyme molecule, allowing the enzyme to receive another substrate molecule and repeat the process.
Conclusion:
- Khosland's model highlights the dynamic interaction between enzymes and substrates, emphasizing the role of inducible changes at the active site of the enzyme in facilitating enzymatic reactions.
Go through the following statements— A. Primary metabolites are biochemicals formed as intermediates and products of normal vital metabolic pathways of organisms
B. Plant tissues produce only secondary metabolites
C. Secondary metabolites have restricted distribution in the plant kingdoms only.
D. Secondary metabolites are derivatives of primary metabolites.
E. Many plants, fungi, and microbes synthesize secondary metabolites.
F. No secondary metabolite has ecological importance.
G. We understand the role of all secondary metabolites in the host organisms.
H. Many secondary metabolites are of economic importance to us.
Which of the above statements are wrong?- a)A, B, C are wrong
- b)D, E, F are wrong
- c)A, D, E are wrong
- d)B, C, F, G are wrong
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
B. Plant tissues produce only secondary metabolites
C. Secondary metabolites have restricted distribution in the plant kingdoms only.
D. Secondary metabolites are derivatives of primary metabolites.
E. Many plants, fungi, and microbes synthesize secondary metabolites.
F. No secondary metabolite has ecological importance.
G. We understand the role of all secondary metabolites in the host organisms.
H. Many secondary metabolites are of economic importance to us.
Which of the above statements are wrong?
a)
A, B, C are wrong
b)
D, E, F are wrong
c)
A, D, E are wrong
d)
B, C, F, G are wrong
|
|
Vandana Sharma answered |
Understanding the Statements on Metabolites
The statements provided relate to primary and secondary metabolites in plants and other organisms. Here’s a breakdown of the incorrect statements among options B, C, F, and G.
Analysis of Incorrect Statements
- B: Plant tissues produce only secondary metabolites
This statement is incorrect because plant tissues produce both primary and secondary metabolites. Primary metabolites are essential for growth and development, while secondary metabolites serve various ecological functions.
- C: Secondary metabolites have restricted distribution in the plant kingdoms only
This is misleading. Secondary metabolites are found in a wide variety of organisms, including plants, fungi, and bacteria. Therefore, their distribution is not restricted to just the plant kingdom.
- F: No secondary metabolite has ecological importance
This statement is false. Many secondary metabolites play crucial ecological roles, such as defense against herbivores, attracting pollinators, and inhibiting competing plant species.
- G: We understand the role of all secondary metabolites in the host organisms
This statement is also incorrect. While some secondary metabolites have well-documented roles, many remain poorly understood, and research is ongoing to uncover their functions.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option D, as statements B, C, F, and G are indeed wrong. Understanding these aspects of primary and secondary metabolites is crucial for fields like ecology, pharmacology, and agriculture.
The statements provided relate to primary and secondary metabolites in plants and other organisms. Here’s a breakdown of the incorrect statements among options B, C, F, and G.
Analysis of Incorrect Statements
- B: Plant tissues produce only secondary metabolites
This statement is incorrect because plant tissues produce both primary and secondary metabolites. Primary metabolites are essential for growth and development, while secondary metabolites serve various ecological functions.
- C: Secondary metabolites have restricted distribution in the plant kingdoms only
This is misleading. Secondary metabolites are found in a wide variety of organisms, including plants, fungi, and bacteria. Therefore, their distribution is not restricted to just the plant kingdom.
- F: No secondary metabolite has ecological importance
This statement is false. Many secondary metabolites play crucial ecological roles, such as defense against herbivores, attracting pollinators, and inhibiting competing plant species.
- G: We understand the role of all secondary metabolites in the host organisms
This statement is also incorrect. While some secondary metabolites have well-documented roles, many remain poorly understood, and research is ongoing to uncover their functions.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option D, as statements B, C, F, and G are indeed wrong. Understanding these aspects of primary and secondary metabolites is crucial for fields like ecology, pharmacology, and agriculture.
Select the incorrect statement regarding metabolites.- a)Primary metabolites are directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction.
- b)Secondary metabolites include antibiotics and pigments that are crucial for human welfare.
- c)All secondary metabolites have been conclusively identified in their roles in host organisms.
- d)Secondary metabolites can have ecological roles such as in plant defense mechanisms.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Primary metabolites are directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction.
b)
Secondary metabolites include antibiotics and pigments that are crucial for human welfare.
c)
All secondary metabolites have been conclusively identified in their roles in host organisms.
d)
Secondary metabolites can have ecological roles such as in plant defense mechanisms.

|
Top Rankers answered |
The incorrect statement is Option C. While many secondary metabolites have been identified as beneficial to humans and have ecological roles, the specific roles or functions of all secondary metabolites in their host organisms are not fully understood. Thus, it is incorrect to state that all secondary metabolites' roles have been conclusively identified.
A nucleoside consists of _____- a)sugar, phosphate
- b)base, phosphate
- c)base, sugar
- d)base, sugar, phosphate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A nucleoside consists of _____
a)
sugar, phosphate
b)
base, phosphate
c)
base, sugar
d)
base, sugar, phosphate

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- N nucleoside consists of a nitrogenous base such as adenine, guanine, cytosine or thymine linked to a deoxyribose sugar.
- When a phosphate group is attached, it is known as a nucleotide.
What are nucleotides that include adenine and a sugar molecule called?- a)Adenine bases
- b)Adenylic acids
- c)Adenosine
- d)Adenosine phosphates
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Adenine bases
b)
Adenylic acids
c)
Adenosine
d)
Adenosine phosphates
|
|
Arya Nambiar answered |
Understanding Nucleotides
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They consist of three components: a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and one or more phosphate groups.
Components of Nucleotides
- Nitrogenous Base: This can be adenine, guanine, cytosine, or thymine/uracil.
- Sugar: In nucleotides, the sugar is either ribose (in RNA) or deoxyribose (in DNA).
- Phosphate Group: This group can be present in varying numbers, leading to different forms of nucleotides.
Adenosine Explained
- What is Adenosine?: Adenosine is specifically a nucleotide that includes the nitrogenous base adenine linked to a ribose sugar molecule.
- Structure: It comprises:
- Adenine: The nitrogenous base.
- Ribose: A sugar molecule that forms the backbone of the nucleotide.
Why Option C is Correct
- Adenosine vs. Other Options:
- Adenine Bases: Refers only to the nitrogenous base and not the sugar component.
- Adenylic Acids: These typically refer to nucleotides that have a phosphate group attached.
- Adenosine Phosphates: This term implies the presence of phosphate groups, which is not the case for adenosine alone.
Thus, the correct answer is C) Adenosine, as it accurately describes a nucleotide containing adenine and a sugar molecule without additional modifications like phosphates.
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They consist of three components: a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and one or more phosphate groups.
Components of Nucleotides
- Nitrogenous Base: This can be adenine, guanine, cytosine, or thymine/uracil.
- Sugar: In nucleotides, the sugar is either ribose (in RNA) or deoxyribose (in DNA).
- Phosphate Group: This group can be present in varying numbers, leading to different forms of nucleotides.
Adenosine Explained
- What is Adenosine?: Adenosine is specifically a nucleotide that includes the nitrogenous base adenine linked to a ribose sugar molecule.
- Structure: It comprises:
- Adenine: The nitrogenous base.
- Ribose: A sugar molecule that forms the backbone of the nucleotide.
Why Option C is Correct
- Adenosine vs. Other Options:
- Adenine Bases: Refers only to the nitrogenous base and not the sugar component.
- Adenylic Acids: These typically refer to nucleotides that have a phosphate group attached.
- Adenosine Phosphates: This term implies the presence of phosphate groups, which is not the case for adenosine alone.
Thus, the correct answer is C) Adenosine, as it accurately describes a nucleotide containing adenine and a sugar molecule without additional modifications like phosphates.
Identify the correct pairing between nitrogen bases in DNA.- a)T+C/G+A
- b)A+G/C+T
- c)A+C/T+G
- d)G+C/A+T
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct pairing between nitrogen bases in DNA.
a)
T+C/G+A
b)
A+G/C+T
c)
A+C/T+G
d)
G+C/A+T

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
There are two hydrogen bonds between A and T pairing. There are three hydrogen bonds between G andC pairing. Each strand appears like a helical staircase.
The spatial arrangement produced by the twisting and folding of peptide chains in proteins is called:- a)Secondary structure
- b)Primary structure
- c)Tertiary structure
- d)Quaternary structure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The spatial arrangement produced by the twisting and folding of peptide chains in proteins is called:
a)
Secondary structure
b)
Primary structure
c)
Tertiary structure
d)
Quaternary structure
|
|
Tanvi Dasgupta answered |
Secondary Structure
The spatial arrangement produced by the twisting and folding of peptide chains in proteins is referred to as the secondary structure. This level of protein structure is primarily characterized by the formation of regular, repeated patterns such as alpha helices and beta strands.
Alpha Helices and Beta Strands
In the secondary structure, alpha helices are right-handed coiled structures where the peptide chain is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the amino acid residues. On the other hand, beta strands are extended structures where the peptide chain forms a zig-zag pattern, and adjacent strands can be held together by hydrogen bonds to form beta sheets.
Importance of Secondary Structure
The secondary structure plays a crucial role in determining the overall shape and function of proteins. It helps in defining the local conformation and stability of the protein molecule. The interactions between amino acid residues within the secondary structure contribute to the overall stability of the protein.
Difference from Tertiary and Quaternary Structure
While the secondary structure refers to the local folding patterns of the peptide chain, the tertiary structure involves the overall three-dimensional arrangement of the protein molecule. Tertiary structure is formed by interactions between secondary structural elements and other regions of the protein. Quaternary structure, on the other hand, refers to the arrangement of multiple protein subunits in a complex.
In conclusion, the secondary structure of proteins is essential for understanding their function and stability. It provides insights into the folding patterns of the peptide chain and contributes to the overall organization of the protein molecule.
The spatial arrangement produced by the twisting and folding of peptide chains in proteins is referred to as the secondary structure. This level of protein structure is primarily characterized by the formation of regular, repeated patterns such as alpha helices and beta strands.
Alpha Helices and Beta Strands
In the secondary structure, alpha helices are right-handed coiled structures where the peptide chain is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the amino acid residues. On the other hand, beta strands are extended structures where the peptide chain forms a zig-zag pattern, and adjacent strands can be held together by hydrogen bonds to form beta sheets.
Importance of Secondary Structure
The secondary structure plays a crucial role in determining the overall shape and function of proteins. It helps in defining the local conformation and stability of the protein molecule. The interactions between amino acid residues within the secondary structure contribute to the overall stability of the protein.
Difference from Tertiary and Quaternary Structure
While the secondary structure refers to the local folding patterns of the peptide chain, the tertiary structure involves the overall three-dimensional arrangement of the protein molecule. Tertiary structure is formed by interactions between secondary structural elements and other regions of the protein. Quaternary structure, on the other hand, refers to the arrangement of multiple protein subunits in a complex.
In conclusion, the secondary structure of proteins is essential for understanding their function and stability. It provides insights into the folding patterns of the peptide chain and contributes to the overall organization of the protein molecule.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biomolecules - Science for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biomolecules - Science for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Science for ACT
504 videos|539 docs|348 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup