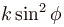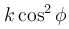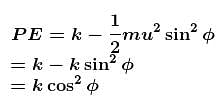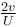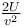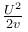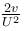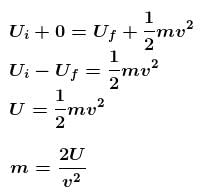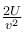All Exams >
ACT >
Physics for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Fundamental Concepts for ACT Exam
A block attached to a spring, pulled by a constant horizontal force, is kept on a smooth surface as shown in the figure. Initially, the spring is in the natural state. Then the maximum positive work that the applied force F can do is : [Given that spring does not break]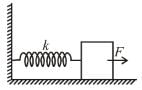
- a)
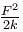
- b)
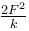
- c)∞
- d)
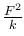
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A block attached to a spring, pulled by a constant horizontal force, is kept on a smooth surface as shown in the figure. Initially, the spring is in the natural state. Then the maximum positive work that the applied force F can do is :
[Given that spring does not break]

a)
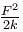
b)
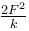
c)
∞
d)
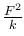
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Applying work-energy theorem on the block, we get
Fl − kt2/2 = 0
l = 2F/k
or work done = Fl = 2F2/k
Fl − kt2/2 = 0
l = 2F/k
or work done = Fl = 2F2/k
The spring block system lies on a smooth horizontal surface. The free end of the spring is being pulled towards right with constant speed v0 = 2m/s. At t = 0 sec, the spring of constant k = 100 N/cm in unstretched and the block has a speed 1m/s to left. The maximum extension of the spring is :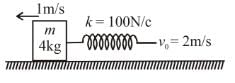
- a)8cm
- b)2cm
- c)4cm
- d)6cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The spring block system lies on a smooth horizontal surface. The free end of the spring is being pulled towards right with constant speed v0 = 2m/s. At t = 0 sec, the spring of constant k = 100 N/cm in unstretched and the block has a speed 1m/s to left. The maximum extension of the spring is :

a)
8cm
b)
2cm
c)
4cm
d)
6cm
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
In the frame (inertial w.r.t. earth) of free end of spring, the initial velocity of block is 3 m/s to left and the spring unstretched.
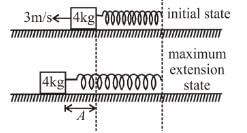
Applying conservation of energy between initial and maximum extension state.
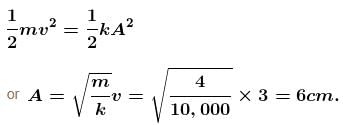
The correct answer is: 6cm
Work done by a force on an rigid object having no rotational motion will be zero, if :- a)the force is always perpendicular to acceleration of object
- b)the object is at rest relative to ground but the point of application of force moves on the object
- c)the force is always perpendicular to velocity of object
- d)the point of application of force is fixed relative to ground but the object moves
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done by a force on an rigid object having no rotational motion will be zero, if :
a)
the force is always perpendicular to acceleration of object
b)
the object is at rest relative to ground but the point of application of force moves on the object
c)
the force is always perpendicular to velocity of object
d)
the point of application of force is fixed relative to ground but the object moves
|
|
Vanshika Patel answered |
Work done by a force on a rigid object with no rotational motion:
When a force is applied to a rigid object, the work done by the force can be determined by considering the displacement of the point of application of the force. In the case of a rigid object with no rotational motion, the work done by the force can be zero under certain conditions.
a) The force is always perpendicular to the acceleration of the object:
If the force applied to the object is always perpendicular to the acceleration of the object, then the work done by the force will be zero. This is because the angle between the force and the displacement is 90 degrees, and the work done is given by the equation W = F * d * cos(theta), where theta is the angle between the force and the displacement. Since cos(90) = 0, the work done will be zero.
b) The object is at rest relative to the ground, but the point of application of the force moves on the object:
In this scenario, although the object is not moving, the point of application of the force is moving. As a result, the displacement of the point of application of the force is non-zero. If the force is applied at different points on the object and the displacement of the point of application is perpendicular to the force, then the work done by the force will be zero. This is because the angle between the force and the displacement is 90 degrees, and cos(90) = 0.
c) The force is always perpendicular to the velocity of the object:
If the force applied to the object is always perpendicular to the velocity of the object, then the work done by the force will be zero. Similar to the previous cases, the angle between the force and the displacement is 90 degrees, and cos(90) = 0.
d) The point of application of the force is fixed relative to the ground, but the object moves:
In this case, as the object moves, the displacement of the point of application of the force is non-zero. If the force is applied at a fixed point on the object and the displacement of the point of application is perpendicular to the force, then the work done by the force will be zero. Again, this is because the angle between the force and the displacement is 90 degrees, and cos(90) = 0.
Therefore, the correct options are B and C, as in both cases the work done by the force on the rigid object with no rotational motion will be zero.
When a force is applied to a rigid object, the work done by the force can be determined by considering the displacement of the point of application of the force. In the case of a rigid object with no rotational motion, the work done by the force can be zero under certain conditions.
a) The force is always perpendicular to the acceleration of the object:
If the force applied to the object is always perpendicular to the acceleration of the object, then the work done by the force will be zero. This is because the angle between the force and the displacement is 90 degrees, and the work done is given by the equation W = F * d * cos(theta), where theta is the angle between the force and the displacement. Since cos(90) = 0, the work done will be zero.
b) The object is at rest relative to the ground, but the point of application of the force moves on the object:
In this scenario, although the object is not moving, the point of application of the force is moving. As a result, the displacement of the point of application of the force is non-zero. If the force is applied at different points on the object and the displacement of the point of application is perpendicular to the force, then the work done by the force will be zero. This is because the angle between the force and the displacement is 90 degrees, and cos(90) = 0.
c) The force is always perpendicular to the velocity of the object:
If the force applied to the object is always perpendicular to the velocity of the object, then the work done by the force will be zero. Similar to the previous cases, the angle between the force and the displacement is 90 degrees, and cos(90) = 0.
d) The point of application of the force is fixed relative to the ground, but the object moves:
In this case, as the object moves, the displacement of the point of application of the force is non-zero. If the force is applied at a fixed point on the object and the displacement of the point of application is perpendicular to the force, then the work done by the force will be zero. Again, this is because the angle between the force and the displacement is 90 degrees, and cos(90) = 0.
Therefore, the correct options are B and C, as in both cases the work done by the force on the rigid object with no rotational motion will be zero.
In the figure the variation of components of acceleration of a particle of mass 1kg is shown w.r.t. time. The initial velocity of the particle is  The total work done by the resultant force on the particle in time interval from t = 0 to t = 4 second is :
The total work done by the resultant force on the particle in time interval from t = 0 to t = 4 second is :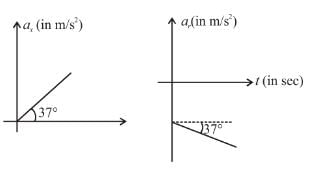
- a)22.5J
- b)10J
- c)0
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the figure the variation of components of acceleration of a particle of mass 1kg is shown w.r.t. time. The initial velocity of the particle is 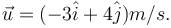 The total work done by the resultant force on the particle in time interval from t = 0 to t = 4 second is :
The total work done by the resultant force on the particle in time interval from t = 0 to t = 4 second is :
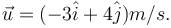 The total work done by the resultant force on the particle in time interval from t = 0 to t = 4 second is :
The total work done by the resultant force on the particle in time interval from t = 0 to t = 4 second is :
a)
22.5J
b)
10J
c)
0
d)
None of these
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Your answer is incorrect.
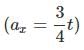 and
and 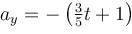
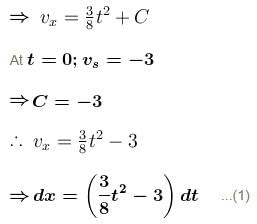
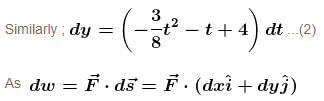
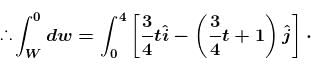
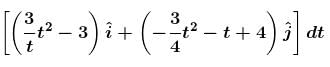
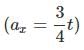 and
and 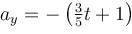
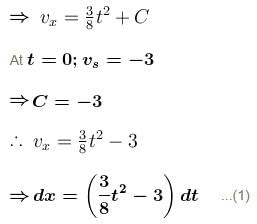
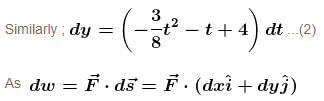
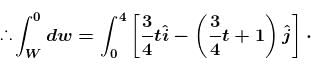
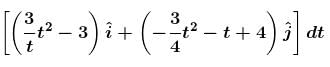
∴ W = 10 J
The correct answer is: 10J
The correct answer is: 10J
One end of an unstretched vertical spring is attached to the ceiling and an object attached to the other end is slowly lowered to its equilibrium position. If S be gain in spring energy and G be loss in gravitational potential energy in the process, then which of the following is false.- a)S = 2G
- b)S = G
- c)S = 3G
- d)G = 2S
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
One end of an unstretched vertical spring is attached to the ceiling and an object attached to the other end is slowly lowered to its equilibrium position. If S be gain in spring energy and G be loss in gravitational potential energy in the process, then which of the following is false.
a)
S = 2G
b)
S = G
c)
S = 3G
d)
G = 2S
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
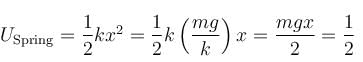 (loss in gravitationl potential energy)
(loss in gravitationl potential energy)⇒ G = 2S
The correct answers are: S = G, S = 2G, S = 3G
The potential energy (in Joules) of a particle of mass 1kg moving in a plane is given by V = 3x + 4y, the position coordinates of the point being x and y, measured in metres. If the particle is at rest at (6,4); then - a)it crosses the y-axis (x = 0) at y = –4
- b)its speed when it crosses the y-axis is 10m/s
- c)its acceleration is of magnitude 5m/s2
- d)it moves in a straight line passing through the origin (0,0)
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential energy (in Joules) of a particle of mass 1kg moving in a plane is given by V = 3x + 4y, the position coordinates of the point being x and y, measured in metres. If the particle is at rest at (6,4); then
a)
it crosses the y-axis (x = 0) at y = –4
b)
its speed when it crosses the y-axis is 10m/s
c)
its acceleration is of magnitude 5m/s2
d)
it moves in a straight line passing through the origin (0,0)
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
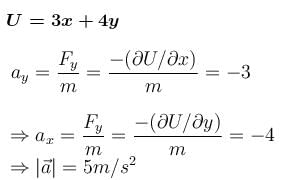
Let at time 't' particle crosses y-axis
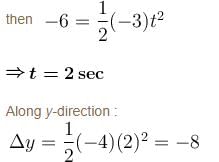
⇒ Particle crosses y-axis at y = –4
At (6, 4) U = 34 & KE = 0
At (0, 4); U = –16
⇒ KE = 50
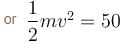
⇒ v = 10 m/s while crossing y-axis
The correct answers are: its acceleration is of magnitude 5m/s2, its speed when it crosses the y-axis is 10m/s, it crosses the y-axis (x = 0) at y = –4
A block of mass m is being pulled up the rough incline by the agent delivering constant power P. The coefficient of friction between the block and the incline is µ. The maximum speed of the block during the courses of ascent is :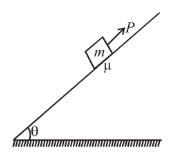
- a)
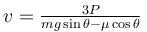
- b)
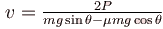
- c)
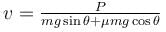
- d)
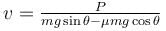
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass m is being pulled up the rough incline by the agent delivering constant power P. The coefficient of friction between the block and the incline is µ. The maximum speed of the block during the courses of ascent is :

a)
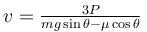
b)
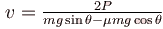
c)
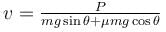
d)
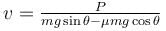
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Let at any time the speed of the block along the incline upwards be v.
Then from Newton’s second law
Then from Newton’s second law
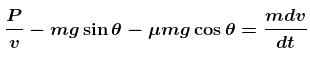
the speed is maximum when
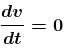
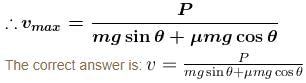
The potential energy (in SI units) of a particle of mass 2kg in a conservative fields U = 6x – 8y. If the initial velocity of the particle is 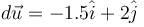 then the total distance traveled by the particle in first two seconds is :
then the total distance traveled by the particle in first two seconds is :- a)15m
- b)12m
- c)10m
- d)18m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential energy (in SI units) of a particle of mass 2kg in a conservative fields U = 6x – 8y. If the initial velocity of the particle is 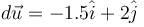 then the total distance traveled by the particle in first two seconds is :
then the total distance traveled by the particle in first two seconds is :
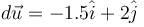 then the total distance traveled by the particle in first two seconds is :
then the total distance traveled by the particle in first two seconds is :a)
15m
b)
12m
c)
10m
d)
18m
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
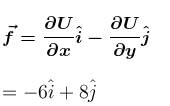
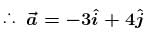 has same direction as that of
has same direction as that of 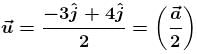
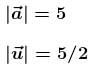
Since
 are in same direction, particle will move along a straight line
are in same direction, particle will move along a straight line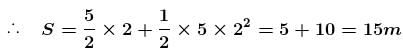
The correct answer is: 15m
The block of mass m initially at x = 0 is acted upon by a horizontal force at any position x is given as F = a – bx2, where a > μmg, as shown in the figure. The co-efficient of friction between the surfaces of contact is μ. The net work done on the blocks is zero. If the block travels a distance?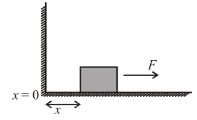
- a)
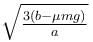
- b)
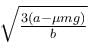
- c)
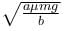
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The block of mass m initially at x = 0 is acted upon by a horizontal force at any position x is given as F = a – bx2, where a > μmg, as shown in the figure. The co-efficient of friction between the surfaces of contact is μ. The net work done on the blocks is zero. If the block travels a distance?

a)
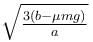
b)
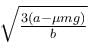
c)
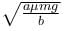
d)
None of these

|
Pie Academy answered |

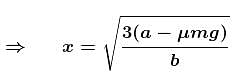
The correct answer is:
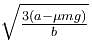
The potential energy of a particle of mass m free to move along x-axis is given by 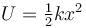 for x < 0 and U = 0 for x ≥ 0 (x denotes the x-coordinate of the particle and k is a positive constant). If the total mechanical energy of the particle is E, then its speed at
for x < 0 and U = 0 for x ≥ 0 (x denotes the x-coordinate of the particle and k is a positive constant). If the total mechanical energy of the particle is E, then its speed at 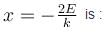
- a)
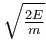
- b)0
- c)
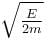
- d)
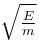
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential energy of a particle of mass m free to move along x-axis is given by 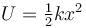 for x < 0 and U = 0 for x ≥ 0 (x denotes the x-coordinate of the particle and k is a positive constant). If the total mechanical energy of the particle is E, then its speed at
for x < 0 and U = 0 for x ≥ 0 (x denotes the x-coordinate of the particle and k is a positive constant). If the total mechanical energy of the particle is E, then its speed at 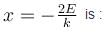
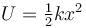 for x < 0 and U = 0 for x ≥ 0 (x denotes the x-coordinate of the particle and k is a positive constant). If the total mechanical energy of the particle is E, then its speed at
for x < 0 and U = 0 for x ≥ 0 (x denotes the x-coordinate of the particle and k is a positive constant). If the total mechanical energy of the particle is E, then its speed at 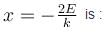
a)
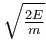
b)
0
c)
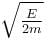
d)
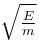

|
Pie Academy answered |
From conservation of energy
K.E. + P.E. = E
K.E. + P.E. = E


∴ The speed of particle at
 is zero.
is zero. Work done by static friction on an object :
- a)must be negative
- b)All of these
- c)may be positive
- d)must be zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done by static friction on an object :
a)
must be negative
b)
All of these
c)
may be positive
d)
must be zero
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
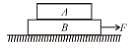
Consider the blocks shown in the figure to be moving together due to friction between them. The free body diagrams of both the blocks are shown below.
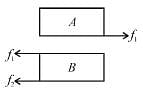
Work done by static friction on A is positive and on B is negative. However, the net work done by static friction is always zero.
A block of mass 2kg is hanging over a smooth and light pulley through a light string. The other end of the string is pulled by a constant force F = 40N. The kinetic energy of the particle increase 40J in a given interval of time. Then : (g = 10m/s2)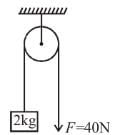
- a)tension in the string is 40N
- b)displacement of the block in the given interval of time is 2m
- c)work done by gravity is –20J
- d)work done by tension is 80J
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass 2kg is hanging over a smooth and light pulley through a light string. The other end of the string is pulled by a constant force F = 40N. The kinetic energy of the particle increase 40J in a given interval of time. Then : (g = 10m/s2)

a)
tension in the string is 40N
b)
displacement of the block in the given interval of time is 2m
c)
work done by gravity is –20J
d)
work done by tension is 80J
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Free body diagram of block is as shown in figure.
From work-energy theorem
From work-energy theorem
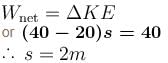
Work done by gravity is
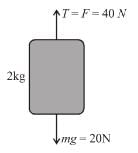
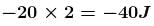
and work done by tension is
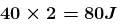
The correct answers are: tension in the string is 40N, displacement of the block in the given interval of time is 2m, work done by tension is 80J
An engine can pull 4 coaches at a maximum speed of 20m/s. Mass of the engine is twice the mass of every coach. Assuming resistive force to be proportional to the weight. (Power of engine remains constant) :- a)maximum speed of engine when it pulls 12 coaches is 6.5m/s
- b)maximum speed of engine when it pulls 6 coaches is 13m/s
- c)maximum speed of engine when it pulls 6 coaches is 15m/s
- d)maximum speed of engine when it pulls 12 coaches is 8.5m/s
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
An engine can pull 4 coaches at a maximum speed of 20m/s. Mass of the engine is twice the mass of every coach. Assuming resistive force to be proportional to the weight. (Power of engine remains constant) :
a)
maximum speed of engine when it pulls 12 coaches is 6.5m/s
b)
maximum speed of engine when it pulls 6 coaches is 13m/s
c)
maximum speed of engine when it pulls 6 coaches is 15m/s
d)
maximum speed of engine when it pulls 12 coaches is 8.5m/s

|
Rashi Choudhury answered |
When 4 coaches (m each) are attached with engine (2m)
according to questions P = K 6mgv ...(1)
(constant power), (K being proportionality constant)
Since resistive force is proportional to weight
Now if 12 coaches are attached
according to questions P = K 6mgv ...(1)
(constant power), (K being proportionality constant)
Since resistive force is proportional to weight
Now if 12 coaches are attached
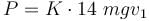 ...(2)
...(2)Since engine power is constant
So by equation (1) and (2)
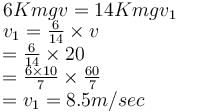
So by equation (1) and (2)
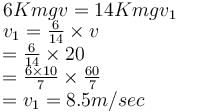
Similarly for 6 coaches
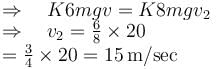
The correct answers are: maximum speed of engine when it pulls 12 coaches is 8.5m/s, maximum speed of engine when it pulls 6 coaches is 15m/s
A man places a chain (of mass m and length l) on a table slowly. Initially the lower end of the chain just touches the table. The man drops the chain. When half of the chain is in vertical position. The work done by the man in this process is :- a)
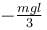
- b)
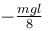
- c)
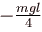
- d)
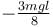
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A man places a chain (of mass m and length l) on a table slowly. Initially the lower end of the chain just touches the table. The man drops the chain. When half of the chain is in vertical position. The work done by the man in this process is :
a)
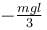
b)
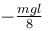
c)
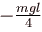
d)
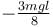
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The work done by man is negative of magnitude of decrease in potential energy of chain
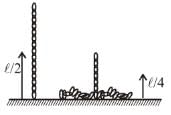
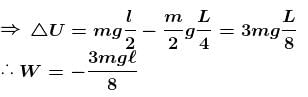
The correct answer is:
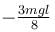
A self propelled vehicle of mass m whose engine delivers constant power P has an acceleration a = P/mv (assume that there is no friction). In order to increase its velocity from v1 to v2 the distance it has to travel will be :- a)
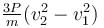
- b)
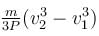
- c)
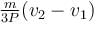
- d)
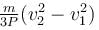
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A self propelled vehicle of mass m whose engine delivers constant power P has an acceleration a = P/mv (assume that there is no friction). In order to increase its velocity from v1 to v2 the distance it has to travel will be :
a)
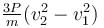
b)
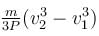
c)
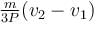
d)
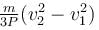

|
Bijoy Patel answered |
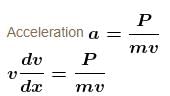
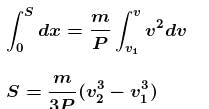
The correct answer is:
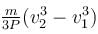
Block A is hanging from a vertical spring and is at rest. Block B strikes the block A with velocity v and sticks to it. Then the value of v for which the spring just attains natural length is :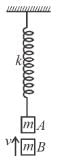
- a)
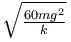
- b)
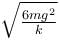
- c)
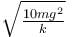
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Block A is hanging from a vertical spring and is at rest. Block B strikes the block A with velocity v and sticks to it. Then the value of v for which the spring just attains natural length is :

a)
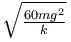
b)
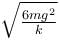
c)
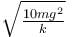
d)
None of these
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
The initial extension in spring is 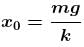
Just after collision of B with A the speed of combined mass is v/2.
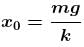
Just after collision of B with A the speed of combined mass is v/2.
For the spring to just attain natural length the combined mass must rise up by 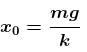 (see fig.) and comes to rest.
(see fig.) and comes to rest.
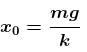 (see fig.) and comes to rest.
(see fig.) and comes to rest.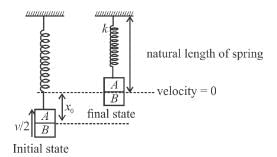
Applying conservation of energy between initial and final states.
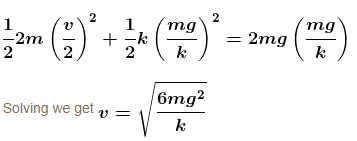
Alternate solution by SHM
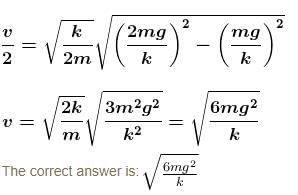
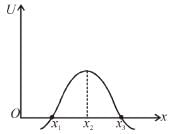
In the figure shown the potential energy U of a particle is plotted against its position x from origin. Then which of the following statement is incorrect.
- a)x3 is in stable equilibrium
- b)x2 is in unstable equilibrium
- c)x1 is in stable equilibrium
- d)x2 is in stable equilibrium
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the figure shown the potential energy U of a particle is plotted against its position x from origin. Then which of the following statement is incorrect.

a)
x3 is in stable equilibrium
b)
x2 is in unstable equilibrium
c)
x1 is in stable equilibrium
d)
x2 is in stable equilibrium

|
Pie Academy answered |
x = x1 and x = x3 are not equilibrium positions because du/dx ≠ 0 at these points. x = x2 is unstable, as U is maximum at this point.
A man places a chain (of mass m and length l) on a table slowly. Initially the lower end of the chain just touches the table. The man drops the chain. When half of the chain is in vertical position, the potential energy of chain is :- a)
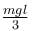
- b)
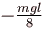
- c)
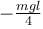
- d)
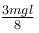
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A man places a chain (of mass m and length l) on a table slowly. Initially the lower end of the chain just touches the table. The man drops the chain. When half of the chain is in vertical position, the potential energy of chain is :
a)
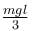
b)
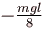
c)
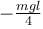
d)
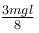
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The work done by man is negative of magnitude of decrease in potential energy of chain
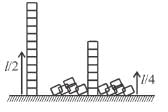
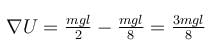
The correct answer is: 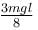
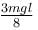
In the Figure, the ball A is released from rest when the spring is at its natural length. For the block B of mass M to leave contact with the ground of some stage, the minimum mass of A must be :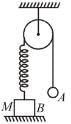
- a)2M
- b)M/4
- c)M/2
- d)M
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the Figure, the ball A is released from rest when the spring is at its natural length. For the block B of mass M to leave contact with the ground of some stage, the minimum mass of A must be :

a)
2M
b)
M/4
c)
M/2
d)
M
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Let m be minimum mass of ball
Let mass A moves downwards by x.
From conservation of energy
Let mass A moves downwards by x.
From conservation of energy
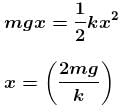
For mass M to leave contact with ground,
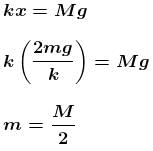
The correct answer is: M/2
Which of the following is/are conservative force(s)?- a)
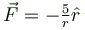
- b)
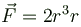
- c)
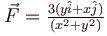
- d)
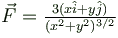
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are conservative force(s)?
a)
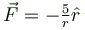
b)
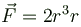
c)
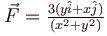
d)
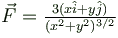

|
Pie Academy answered |

Clearly for forces  the integration do not require any information of the path taken.
the integration do not require any information of the path taken.
 the integration do not require any information of the path taken.
the integration do not require any information of the path taken.
Taking : x2 + y2 = t
2xdx + 2ydy = dt

which is solvable.
Hence  are conservative forces.
are conservative forces.
 are conservative forces.
are conservative forces.But 
requires some more information on path. Hence non-conservative.
The correct answers are: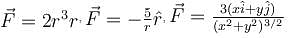

requires some more information on path. Hence non-conservative.
The correct answers are:
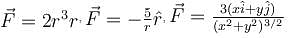
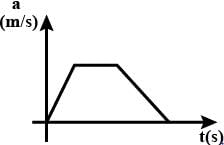
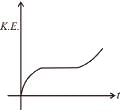
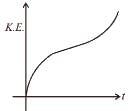
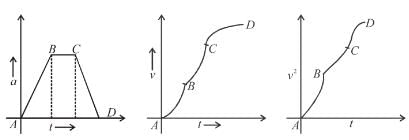
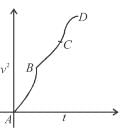
For a particle moving on a straight line the variation of acceleration with time is given by the graph as shown initially the particle was at rest. Then the corresponding kinetic energy of the particle versus time graph will be :
- a)
- b)
- c)
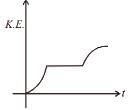
- d)
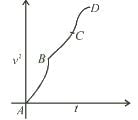
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For a particle moving on a straight line the variation of acceleration with time is given by the graph as shown initially the particle was at rest. Then the corresponding kinetic energy of the particle versus time graph will be :

a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The above graphs show v-t graph from a-t graph and then v2-t graph, which are self explanatory.
The correct answer is:

There are two massless springs A and B of spring constant KA and KB respectively and KA > KB. If WA and WB be denoted as work done on A and work done on B respectively, then :- a)If they are compressed by same distance, WA = WB
- b)If they are compressed to same distance, WA > WB
- c)If they are compressed by same force (upto equilibrium state) WA < WB
- d)If they are compressed by same force (upto equilibrium state) WA > WB
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are two massless springs A and B of spring constant KA and KB respectively and KA > KB. If WA and WB be denoted as work done on A and work done on B respectively, then :
a)
If they are compressed by same distance, WA = WB
b)
If they are compressed to same distance, WA > WB
c)
If they are compressed by same force (upto equilibrium state) WA < WB
d)
If they are compressed by same force (upto equilibrium state) WA > WB
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
If the springs are compressed to same amount :
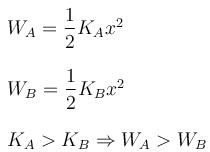
If the springs are compressed by same force.
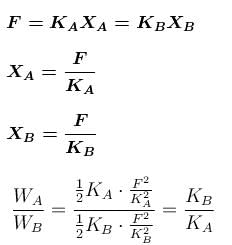
The correct answers are: If they are compressed to same distance, WA > WB, If they are compressed by same force (upto equilibrium state) WA < WB
A block of mass m is attached to two unstretched springs of spring constants k1 and k2 as shown in figure. The block is displaced towards right through a distance x and is released. Find the speed of the block as passes through the means position shown.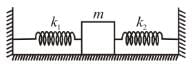
- a)
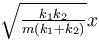
- b)
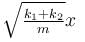
- c)
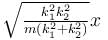
- d)
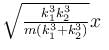
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass m is attached to two unstretched springs of spring constants k1 and k2 as shown in figure. The block is displaced towards right through a distance x and is released. Find the speed of the block as passes through the means position shown.

a)
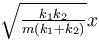
b)
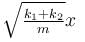
c)
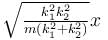
d)
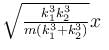

|
Pie Academy answered |
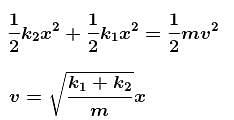
The correct answer is:

The blocks A and B shown in the figure have masses MA = 5kg and MB = 4 kg. The system is released from rest. The speed of B after A has traveled a distance 1 m along the incline is :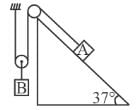
- a)
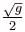
- b)
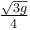
- c)
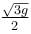
- d)
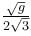
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The blocks A and B shown in the figure have masses MA = 5kg and MB = 4 kg. The system is released from rest. The speed of B after A has traveled a distance 1 m along the incline is :

a)
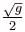
b)
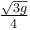
c)
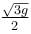
d)
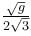
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
If A moves down the incline by 1 metre. B shall move up by 1/2 metre. If the speed of B is v then the speed of A will be 2v.
Gain in K.E. = loss in P.E.
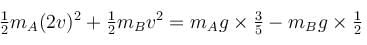
Solving, we get
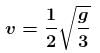
The correct answer is: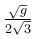
Gain in K.E. = loss in P.E.
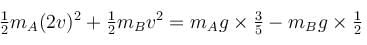
Solving, we get
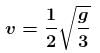
The correct answer is:
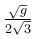
The potential energy for a force field 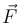 is given by U(x, y) = cos(x + y). The force is acting on a particle at position given by coordinates
is given by U(x, y) = cos(x + y). The force is acting on a particle at position given by coordinates 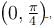 then which of the following statement is true.
then which of the following statement is true.- a)
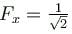
- b)
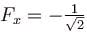
- c)
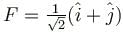
- d)
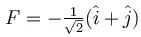
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential energy for a force field 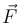 is given by U(x, y) = cos(x + y). The force is acting on a particle at position given by coordinates
is given by U(x, y) = cos(x + y). The force is acting on a particle at position given by coordinates 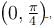 then which of the following statement is true.
then which of the following statement is true.
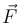 is given by U(x, y) = cos(x + y). The force is acting on a particle at position given by coordinates
is given by U(x, y) = cos(x + y). The force is acting on a particle at position given by coordinates 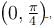 then which of the following statement is true.
then which of the following statement is true.a)
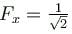
b)
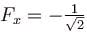
c)
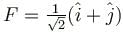
d)
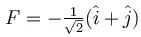
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
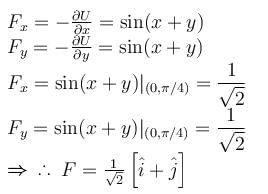
The correct answers are: 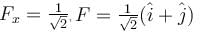
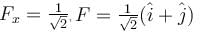
A collar B of mass 2kg is constrained to move along a horizontal smooth and fixed circular track of radius 5m. The spring lying in the plane of the circular track and having spring constant 200N/m is undeformed when the collar is at A. If the collar starts from rest at B the normal reaction exerted by the track on the collar when it passes through A is :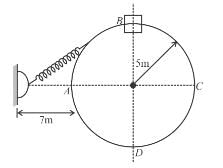
- a)720N
- b)2880N
- c)1440N
- d)360N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A collar B of mass 2kg is constrained to move along a horizontal smooth and fixed circular track of radius 5m. The spring lying in the plane of the circular track and having spring constant 200N/m is undeformed when the collar is at A. If the collar starts from rest at B the normal reaction exerted by the track on the collar when it passes through A is :

a)
720N
b)
2880N
c)
1440N
d)
360N
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Initial extension will be equal to 6 m.
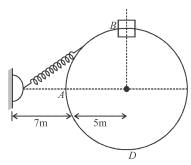
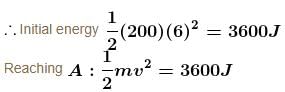
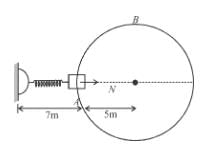
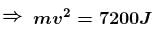
From F.B.D. at A :
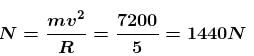
The correct answer is: 1440N
A ring of mass m can slide over a smooth vertical rod. The ring is connected to a spring of force constant k = 4mg/R where 2R is the natural length of the spring. The other end of the spring is fixed to the ground at a horizontal distance 2R from the base of the rod. The mass is released at a height of 1.5R from the ground.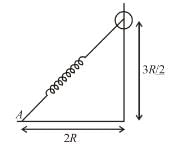
- a)the velocity of the ring when it reaches the ground will be
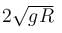
- b)the velocity of the ring when it reaches the ground will be
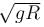
- c)work done by the spring will be 9mgR
- d)work done by the spring will be 3mgR/2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ring of mass m can slide over a smooth vertical rod. The ring is connected to a spring of force constant k = 4mg/R where 2R is the natural length of the spring. The other end of the spring is fixed to the ground at a horizontal distance 2R from the base of the rod. The mass is released at a height of 1.5R from the ground.

a)
the velocity of the ring when it reaches the ground will be 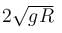
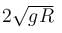
b)
the velocity of the ring when it reaches the ground will be 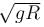
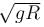
c)
work done by the spring will be 9mgR
d)
work done by the spring will be 3mgR/2

|
Vandana Chopra answered |
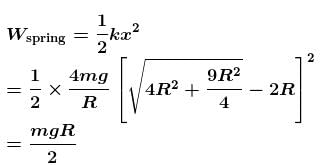
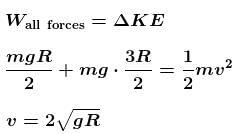
The correct answer is: the velocity of the ring when it reaches the ground will be
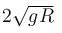
Chapter doubts & questions for Fundamental Concepts - Physics for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Fundamental Concepts - Physics for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for ACT
169 videos|131 docs|69 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup

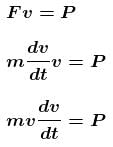
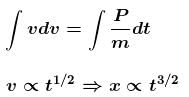
 with the vertical. Neglecting friction, its potential energy at the highest point will be :
with the vertical. Neglecting friction, its potential energy at the highest point will be :