All Exams >
Primary 5 >
Basic Science for Primary 5 >
All Questions
All questions of Reproduction in Plants for Primary 5 Exam
The small bulb-like projection coming out from yeast cell is called a ______.- a)Pseudopodia
- b)Bud
- c)Fragment
- d)False - feet
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The small bulb-like projection coming out from yeast cell is called a ______.
a)
Pseudopodia
b)
Bud
c)
Fragment
d)
False - feet
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
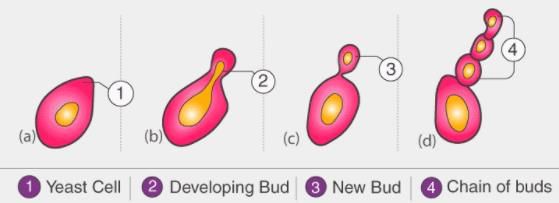
- Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. The small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is called a bud.
- Organisms such as hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction in the process of budding.
Which part of the flower develops into a fruit?- a)Ovule
- b)Ovary
- c)Stamen
- d)Pollen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Ovule
b)
Ovary
c)
Stamen
d)
Pollen

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
After fertilization, the ovary of the flower develops into a fruit. The ovary contains the ovules, which become seeds upon fertilization.
Potato used as vegetable is ____________ part of potato plant.- a)Modified root
- b)Tap root
- c)Modified stem
- d)Fibrous root
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Potato used as vegetable is ____________ part of potato plant.
a)
Modified root
b)
Tap root
c)
Modified stem
d)
Fibrous root

|
Keerthana Mukherjee answered |
Potato used as vegetable is modified stem of potato plant. Food is stored inside the potato tuber.
Banana is a _______________ plant.- a)Endospermic
- b)Dicots
- c)Hybrid
- d)Monocots
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Banana is a _______________ plant.
a)
Endospermic
b)
Dicots
c)
Hybrid
d)
Monocots

|
Anshu Basu answered |
Banana is a monocot plant as contain leaf having parallel venation.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Male gametes in pollen grain reach to female gamete by
- A:
Ovary tube
- B:
Ovule tube
- C:
Funicular
- D:
Pollen tube
The answer is D.
Male gametes in pollen grain reach to female gamete by
Ovary tube
Ovule tube
Funicular
Pollen tube

|
Lekshmi Gupta answered |
Male gametes in pollen grain reach to female gamete by pollen tube to form zygote.
The process of fusion of the female and male gamete is called
- a)Reproduction
- b)Seed formation
- c)Fertilization
- d)Layering
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of fusion of the female and male gamete is called
a)
Reproduction
b)
Seed formation
c)
Fertilization
d)
Layering

|
Nidhi Nair answered |
The process of fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilization. The fusion of male and female gametes, also known as sperm and ovary, usually occurs in the fallopian tube of the female reproductive system. The cell that results from the fusion of the gametes is called a zygote. The zygote divides multiple times to form the embryo inside the seed.
Which type of reproduction involves the breaking up of an organism into fragments?
- a)Budding
- b)Fission
- c)Fragmentation
- d)Regeneration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of reproduction involves the breaking up of an organism into fragments?
a)
Budding
b)
Fission
c)
Fragmentation
d)
Regeneration
|
|
Aurora Institute answered |
Fission is a form of asexual reproduction where an organism splits into two or more separate individuals. This method is common in single-celled organisms like bacteria.
In lower organisms asexual reproduction takes place by
- a)Fission and budding
- b)Pollination
- c)Fertilization
- d)Gametes formation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In lower organisms asexual reproduction takes place by
a)
Fission and budding
b)
Pollination
c)
Fertilization
d)
Gametes formation

|
Shraddha Nambiar answered |
In lower organisms asexual reproduction takes place by fission and budding.
Onion is propagated through its- a)Seeds
- b)Bulbs
- c)Tubers
- d)Rhizomes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Onion is propagated through its
a)
Seeds
b)
Bulbs
c)
Tubers
d)
Rhizomes
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
Onion is propagated through its bulbs, vegetative mode of propagation.
What is the primary reproductive part of a plant?- a)Leaf
- b)Stem
- c)Root
- d)Flower
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Leaf
b)
Stem
c)
Root
d)
Flower
|
|
Aurora Institute answered |
The flower is the primary reproductive part of a plant. It contains the organs necessary for sexual reproduction, including the stamens (male organs) and pistils (female organs).
What is the process called when pollen lands on the stigma of a flower of a different plant of the same kind?- a)Self-pollination
- b)Cross-pollination
- c)Fertilisation
- d)Germination
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Self-pollination
b)
Cross-pollination
c)
Fertilisation
d)
Germination

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Cross-pollination occurs when pollen from a flower lands on the stigma of a different plant of the same kind. This helps in genetic diversity and the creation of healthy plants.
State whether the following statement is True or FalsePlants can grow into healthy plants if all seeds of a plant were to fall at the same place and grow there.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State whether the following statement is True or False
Plants can grow into healthy plants if all seeds of a plant were to fall at the same place and grow there.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Maanvi Prabhu answered |
False. Reason:
There would be severe competition for sunlight, water, minerals and space. It also enables the plants to invade new habitats for wider distribution. The seeds would not grow into healthy plants.
There will be shortage of space for the germination of the seeds. Even if they germinate, they cannot grow properly due to scarcity of food resources and also space. Thus some of them will fail to grow.
There would be severe competition for sunlight, water, minerals and space. It also enables the plants to invade new habitats for wider distribution. The seeds would not grow into healthy plants.
There will be shortage of space for the germination of the seeds. Even if they germinate, they cannot grow properly due to scarcity of food resources and also space. Thus some of them will fail to grow.
How do yeast cells reproduce to make more yeast cells?- a)By forming chains of buds
- b)By breaking up into fragments
- c)By developing spores covered with a protective coat
- d)By growing roots into the soil
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How do yeast cells reproduce to make more yeast cells?
a)
By forming chains of buds
b)
By breaking up into fragments
c)
By developing spores covered with a protective coat
d)
By growing roots into the soil

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
When yeast cells want to make more yeast cells, they create chains of small buds. These buds grow on the parent cell and then separate to become new yeast cells. This way, yeast cells keep multiplying and making more of themselves. It's like a little yeast family growing together!
State whether the following statement is True or FalsePlants can reproduce only through sexual means.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State whether the following statement is True or False
Plants can reproduce only through sexual means.
a)
True
b)
False

|
Aishani Choudhury answered |
The answer is false
BECAUSE
Plants can reproduce through sexual means as well as through asexual means.
Sexual means: POLLINATION AND FERTILIZATION
Asexual means: VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION
BECAUSE
Plants can reproduce through sexual means as well as through asexual means.
Sexual means: POLLINATION AND FERTILIZATION
Asexual means: VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION
Flowers with both androecium and gynoecium are called- a)Bisexual flowers
- b)Anther
- c)Stamens
- d)Unisexual flowers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Flowers with both androecium and gynoecium are called
a)
Bisexual flowers
b)
Anther
c)
Stamens
d)
Unisexual flowers

|
Dipanjan Goyal answered |
Flowers are called bisexual if they bear both androecium and gynoecium.
Bread mold reproduce by- a)Budding
- b)Fragmentation
- c)Regeneration
- d)Spore formation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bread mold reproduce by
a)
Budding
b)
Fragmentation
c)
Regeneration
d)
Spore formation

|
Abhiram Roy answered |
Bread mold reproduces by spore formation. Large number of spore is formed inside the sporangium.
Flowers with both Androecium and the Gynoecium are called - a)Anthers
- b)Stamens
- c)Bisexual flowers
- d)Unisexual flowers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Flowers with both Androecium and the Gynoecium are called
a)
Anthers
b)
Stamens
c)
Bisexual flowers
d)
Unisexual flowers
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
Bisexual flowers have both male (androecium) and female (gynoecium) reproductive structures, including stamens and an ovary.
How do algae reproduce rapidly when water and nutrients are available?- a)By budding
- b)By fragmentation
- c)By spore formation
- d)By binary fission
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How do algae reproduce rapidly when water and nutrients are available?
a)
By budding
b)
By fragmentation
c)
By spore formation
d)
By binary fission
|
|
Aurora Institute answered |
- Fragmentation is a common method of reproduction in algae.
- Algae can break into two or more fragments, each capable of growing into a new organism.
- This method is efficient in favorable conditions with abundant water and nutrients.
- It allows rapid population increase as each fragment develops independently.
- Algae can break into two or more fragments, each capable of growing into a new organism.
- This method is efficient in favorable conditions with abundant water and nutrients.
- It allows rapid population increase as each fragment develops independently.
Which plant reproduces through spore formation?- a)Potato
- b)Bread mould
- c)Ginger
- d)Rose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Potato
b)
Bread mould
c)
Ginger
d)
Rose
|
|
Shreya bhatia answered |
Understanding Spore Formation
Spore formation is a type of asexual reproduction commonly found in certain organisms, particularly fungi and some plants. Among the options provided, bread mould stands out as the correct answer.
What is Bread Mould?
- Bread mould, scientifically known as Rhizopus, is a type of fungus that thrives in damp and warm environments.
- It reproduces primarily through spores, which are microscopic cells capable of developing into a new organism.
How Does Spore Formation Work?
- Spore Production: Bread mould produces spores in specialized structures called sporangia.
- Dispersal: These spores are released into the environment, where they can be carried by air, water, or other organisms.
- Germination: When conditions are favorable (e.g., moisture and warmth), the spores germinate, growing into new mould colonies.
Comparison with Other Options
- Potato: Reproduces through tubers, which are underground stems that store nutrients.
- Ginger: Reproduces through rhizomes, which are horizontal underground stems.
- Rose: Reproduces primarily through seeds and vegetative methods like cuttings.
Conclusion
In summary, bread mould is the only organism among the options that reproduces through spore formation, highlighting its unique reproductive strategy in the fungal kingdom. Understanding this process is essential for recognizing the diverse methods of reproduction in different organisms.
Spore formation is a type of asexual reproduction commonly found in certain organisms, particularly fungi and some plants. Among the options provided, bread mould stands out as the correct answer.
What is Bread Mould?
- Bread mould, scientifically known as Rhizopus, is a type of fungus that thrives in damp and warm environments.
- It reproduces primarily through spores, which are microscopic cells capable of developing into a new organism.
How Does Spore Formation Work?
- Spore Production: Bread mould produces spores in specialized structures called sporangia.
- Dispersal: These spores are released into the environment, where they can be carried by air, water, or other organisms.
- Germination: When conditions are favorable (e.g., moisture and warmth), the spores germinate, growing into new mould colonies.
Comparison with Other Options
- Potato: Reproduces through tubers, which are underground stems that store nutrients.
- Ginger: Reproduces through rhizomes, which are horizontal underground stems.
- Rose: Reproduces primarily through seeds and vegetative methods like cuttings.
Conclusion
In summary, bread mould is the only organism among the options that reproduces through spore formation, highlighting its unique reproductive strategy in the fungal kingdom. Understanding this process is essential for recognizing the diverse methods of reproduction in different organisms.
In asexual reproduction- a)Gametes formation do not occurs
- b)Fertilization occurs
- c)Gametes formation occurs
- d)Variation is created
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In asexual reproduction
a)
Gametes formation do not occurs
b)
Fertilization occurs
c)
Gametes formation occurs
d)
Variation is created
|
|
Sonia rao answered |
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves only one parent and does not require the formation of gametes (sex cells). In this process, offspring are produced that are genetically identical to the parent. Let's explore why option 'A' is the correct answer in more detail.
Gametes formation does not occur:
Asexual reproduction does not involve the formation of gametes, which are specialized sex cells. Gametes are typically formed through a process called meiosis, where the parent cell undergoes two rounds of cell division to produce cells with half the number of chromosomes. These cells then combine during fertilization to form a new individual with a unique combination of genes.
Fertilization does not occur:
Since asexual reproduction does not involve the formation of gametes, there is no need for fertilization. Fertilization is the process by which male and female gametes combine to create a zygote, which develops into a new individual. In asexual reproduction, the offspring are produced directly from the parent without the involvement of another individual or the fusion of gametes.
Gametes formation does not occur:
As mentioned earlier, asexual reproduction does not involve the formation of gametes. Instead, the parent organism directly produces offspring that are genetically identical to itself. This is typically accomplished through various methods such as budding, fission, fragmentation, or spore formation. These processes allow the parent organism to produce clones or exact copies of itself.
Variation is not created:
One of the key characteristics of asexual reproduction is that it does not create genetic variation. Since the offspring are genetically identical to the parent, there is no opportunity for new combinations of genes to occur. This means that any genetic traits or mutations present in the parent organism will be passed on unchanged to the offspring. As a result, asexual reproduction tends to produce populations of organisms that are very similar to each other.
In conclusion, asexual reproduction does not involve the formation of gametes, fertilization, or the creation of genetic variation. The parent organism directly produces offspring that are genetically identical to itself, resulting in populations of organisms that are highly similar.
Gametes formation does not occur:
Asexual reproduction does not involve the formation of gametes, which are specialized sex cells. Gametes are typically formed through a process called meiosis, where the parent cell undergoes two rounds of cell division to produce cells with half the number of chromosomes. These cells then combine during fertilization to form a new individual with a unique combination of genes.
Fertilization does not occur:
Since asexual reproduction does not involve the formation of gametes, there is no need for fertilization. Fertilization is the process by which male and female gametes combine to create a zygote, which develops into a new individual. In asexual reproduction, the offspring are produced directly from the parent without the involvement of another individual or the fusion of gametes.
Gametes formation does not occur:
As mentioned earlier, asexual reproduction does not involve the formation of gametes. Instead, the parent organism directly produces offspring that are genetically identical to itself. This is typically accomplished through various methods such as budding, fission, fragmentation, or spore formation. These processes allow the parent organism to produce clones or exact copies of itself.
Variation is not created:
One of the key characteristics of asexual reproduction is that it does not create genetic variation. Since the offspring are genetically identical to the parent, there is no opportunity for new combinations of genes to occur. This means that any genetic traits or mutations present in the parent organism will be passed on unchanged to the offspring. As a result, asexual reproduction tends to produce populations of organisms that are very similar to each other.
In conclusion, asexual reproduction does not involve the formation of gametes, fertilization, or the creation of genetic variation. The parent organism directly produces offspring that are genetically identical to itself, resulting in populations of organisms that are highly similar.
Flowers perform the function of _____ in plants.- a)Reproduction
- b)Photosynthesis
- c)Respiration
- d)Transpiration
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Flowers perform the function of _____ in plants.
a)
Reproduction
b)
Photosynthesis
c)
Respiration
d)
Transpiration

|
Kajal Desai answered |
Function of Flowers in Plants
Flowers are essential reproductive structures in flowering plants, known scientifically as angiosperms. Their primary function is reproduction, which is critical for the continuation of plant species. Here's a closer look at why flowers are crucial for this purpose.
Reproductive Structures
- Flowers contain the male and female reproductive organs:
- The stamens (male parts) produce pollen.
- The pistils (female parts) contain ovules.
Pollination Process
- Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the stamens to the pistils. This can occur through:
- Wind: Some plants rely on wind to carry pollen.
- Animals: Many flowers attract insects (like bees) and birds, which help in this process by moving pollen from one flower to another.
Fertilization and Seed Formation
- Once the pollen reaches the ovule inside the pistil, fertilization occurs:
- A sperm cell from the pollen unites with an egg cell in the ovule.
- This process leads to the formation of seeds, which will eventually grow into new plants.
Conclusion
While flowers may play roles in other functions like attracting pollinators (which can indirectly support photosynthesis) and contributing to plant health, their primary role remains reproduction. Without flowers, many plants would be unable to reproduce, leading to a decline in plant diversity and ecosystems. Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': Reproduction.
Flowers are essential reproductive structures in flowering plants, known scientifically as angiosperms. Their primary function is reproduction, which is critical for the continuation of plant species. Here's a closer look at why flowers are crucial for this purpose.
Reproductive Structures
- Flowers contain the male and female reproductive organs:
- The stamens (male parts) produce pollen.
- The pistils (female parts) contain ovules.
Pollination Process
- Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the stamens to the pistils. This can occur through:
- Wind: Some plants rely on wind to carry pollen.
- Animals: Many flowers attract insects (like bees) and birds, which help in this process by moving pollen from one flower to another.
Fertilization and Seed Formation
- Once the pollen reaches the ovule inside the pistil, fertilization occurs:
- A sperm cell from the pollen unites with an egg cell in the ovule.
- This process leads to the formation of seeds, which will eventually grow into new plants.
Conclusion
While flowers may play roles in other functions like attracting pollinators (which can indirectly support photosynthesis) and contributing to plant health, their primary role remains reproduction. Without flowers, many plants would be unable to reproduce, leading to a decline in plant diversity and ecosystems. Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': Reproduction.
Light pollen grain is carried by- a)Water
- b)Bats
- c)Insects
- d)Wind
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Light pollen grain is carried by
a)
Water
b)
Bats
c)
Insects
d)
Wind

|
Niharika Mukherjee answered |
Pollen grains are transfer from anther to stigma of another flower during pollination. Light pollen grain is carried by winds.
Fragmentation is mode of asexual reproduction in- a)Fungi
- b)Algae
- c)Angiosperms
- d)Gymnosperms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Fragmentation is mode of asexual reproduction in
a)
Fungi
b)
Algae
c)
Angiosperms
d)
Gymnosperms

|
Abhiram Roy answered |
Fragmentation is mode of asexual reproduction in which body parts splits into two or more parts to develop as new plant.
It is more economical to propagate potato through- a)Whole tuber
- b)Seeds
- c)Tissue culture
- d)Piece of tubers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
It is more economical to propagate potato through
a)
Whole tuber
b)
Seeds
c)
Tissue culture
d)
Piece of tubers

|
Anushka Kaur answered |
It is more economical to propagate potato through piece of tuber containing eyes as each eye produce bud.
Why are flowers colorful and fragrant?- a)To scare away insects
- b)To hide from insects
- c)To attract insects
- d)To confuse insects
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Why are flowers colorful and fragrant?
a)
To scare away insects
b)
To hide from insects
c)
To attract insects
d)
To confuse insects
|
|
Aurora Institute answered |
Flowers are colorful and fragrant to attract insects. Insects help in the process of pollination by carrying pollen from one flower to another. This helps plants reproduce and make seeds and fruits.
How do new plants produced by vegetative propagation differ from those produced from seeds?- a)They take less time to grow and bear flowers and fruits earlier.
- b)They are not exact copies of the parent plant.
- c)They are produced from multiple parents.
- d)They are always smaller in size.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How do new plants produced by vegetative propagation differ from those produced from seeds?
a)
They take less time to grow and bear flowers and fruits earlier.
b)
They are not exact copies of the parent plant.
c)
They are produced from multiple parents.
d)
They are always smaller in size.
|
|
Ayush Kulkarni answered |
Differences Between Vegetative Propagation and Seed Production
When comparing new plants produced by vegetative propagation to those produced from seeds, several key differences emerge, particularly regarding growth time and flowering.
Faster Growth and Early Fruiting
- Rapid Development: Plants grown through vegetative propagation typically take less time to develop. This is because they are clones of the parent plant, inheriting the same genetic material. As a result, they already possess the traits necessary for growth.
- Early Flowering and Fruiting: These plants often bear flowers and fruits sooner than seed-grown plants. Since they do not need to go through the process of germination and early development from a seed, they can allocate energy to reproduction much faster.
Other Options Explained
- Exact Copies: Option B states that plants from vegetative propagation are not exact copies of the parent plant. This is incorrect; they are indeed genetic clones.
- Multiple Parents: Option C suggests they are produced from multiple parents. In vegetative propagation, new plants come from a single parent, making this option false.
- Size: Option D claims they are always smaller in size. This is not accurate; the size of the plant can vary based on environmental factors and care rather than the method of propagation used.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option A. Plants produced by vegetative propagation grow faster and can flower and fruit earlier than those grown from seeds, making this method highly effective for certain horticultural practices.
When comparing new plants produced by vegetative propagation to those produced from seeds, several key differences emerge, particularly regarding growth time and flowering.
Faster Growth and Early Fruiting
- Rapid Development: Plants grown through vegetative propagation typically take less time to develop. This is because they are clones of the parent plant, inheriting the same genetic material. As a result, they already possess the traits necessary for growth.
- Early Flowering and Fruiting: These plants often bear flowers and fruits sooner than seed-grown plants. Since they do not need to go through the process of germination and early development from a seed, they can allocate energy to reproduction much faster.
Other Options Explained
- Exact Copies: Option B states that plants from vegetative propagation are not exact copies of the parent plant. This is incorrect; they are indeed genetic clones.
- Multiple Parents: Option C suggests they are produced from multiple parents. In vegetative propagation, new plants come from a single parent, making this option false.
- Size: Option D claims they are always smaller in size. This is not accurate; the size of the plant can vary based on environmental factors and care rather than the method of propagation used.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option A. Plants produced by vegetative propagation grow faster and can flower and fruit earlier than those grown from seeds, making this method highly effective for certain horticultural practices.
Within the reproductive structures of flowering plants, where is the site of male gamete formation?- a)Ovary
- b)Anther
- c)Pistil
- d)Ovule
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Within the reproductive structures of flowering plants, where is the site of male gamete formation?
a)
Ovary
b)
Anther
c)
Pistil
d)
Ovule

|
Coachify answered |
In flowering plants, male gamete is formed inside Anther present at the top of Stamen.
Transfer of pollen grain from anther to stigma is called- a)Hybridization
- b)Syngamy
- c)Pollination
- d)Fertilization
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Transfer of pollen grain from anther to stigma is called
a)
Hybridization
b)
Syngamy
c)
Pollination
d)
Fertilization

|
Snehal Basak answered |
Transfer of pollen grain from anther to stigma is called pollination.
The mode of reproduction in which plants parts are used to develop new plant is called- a)Spore formation
- b)Vegetative propagation
- c)Gametogenesis
- d)Sexual reproduction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mode of reproduction in which plants parts are used to develop new plant is called
a)
Spore formation
b)
Vegetative propagation
c)
Gametogenesis
d)
Sexual reproduction

|
Snehal Basak answered |
The mode of reproduction in which plants parts are used to develop new plant is called vegetative propagation. Cutting, layering and grafting is common means of vegetative propagation.
Pollen grains can be carried by wind or water for pollination. Is this statement TRUE or FALSE?- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pollen grains can be carried by wind or water for pollination. Is this statement TRUE or FALSE?
a)
True
b)
False

|
Learning Enablers answered |
- Yes, it is true! Pollen grains are very light, so they can be carried by the wind or water to other flowers for pollination.
- Pollen grains can indeed be carried by both wind and water for pollination. Wind pollination is common and occurs because pollen grains are very light. Water pollination, or hydrophily, occurs in specific aquatic plant species where pollen is transferred through water. This is less common than wind or insect pollination and is specific to certain environmental conditions and plant species.
What term is used to describe a flower that has either male or female reproductive parts, but not both?- a)Bisexual
- b)Unisexual
- c)Asexual
- d)Hermaphrodite
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Bisexual
b)
Unisexual
c)
Asexual
d)
Hermaphrodite

|
Learning Education answered |
Unisexual flowers contain either male (stamens) or female (pistils) reproductive organs, but not both. This promotes cross-pollination, which can lead to greater genetic diversity in the offspring.
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as:- a)Fertilization
- b)Pollination
- c)Germination
- d)Propagation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Fertilization
b)
Pollination
c)
Germination
d)
Propagation
|
|
Eduskill Classes answered |
Pollination is the process by which pollen is transferred from the male part of a flower (anther) to the female part (stigma). This is a crucial step in the sexual reproduction of flowering plants.
In flowering plants, which structure serves as the enlarged basal portion of the pistil and contains ovules that develop into seeds upon fertilization?- a)Pistil
- b)Stamen
- c)Seed
- d)Ovary
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In flowering plants, which structure serves as the enlarged basal portion of the pistil and contains ovules that develop into seeds upon fertilization?
a)
Pistil
b)
Stamen
c)
Seed
d)
Ovary

|
Rohini Seth answered |
In flowering plants, the ovary is the enlarged basal portion of the pistil, which is the female reproductive organ of a flower. The ovary contains ovules, which are structures that contain the female gametes or egg cells. After fertilization occurs, these ovules develop into seeds. The ovary itself undergoes further development and matures into a fruit, which protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal. So, the ovary plays a crucial role in the reproduction and propagation of flowering plants.
Which part of a seed grows into the root system of a new plant?- a)Plumule
- b)Cotyledon
- c)Seed coat
- d)Radicle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of a seed grows into the root system of a new plant?
a)
Plumule
b)
Cotyledon
c)
Seed coat
d)
Radicle
|
|
Pranav Majumdar answered |
Understanding Seed Structure
Seeds are vital for plant reproduction and growth. They contain various parts that play specific roles during the germination process. Among these parts, the radicle is crucial.
What is the Radicle?
- The radicle is the embryonic root of the seed.
- It is the first part of the seedling to emerge during germination.
- The radicle grows downward into the soil, establishing the root system of the new plant.
Functions of the Radicle
- Root Development: The radicle develops into the primary root, anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
- Nutrient Uptake: A strong root system allows the plant to access essential minerals and water, which are vital for growth and development.
How Germination Works
1. Water Absorption: When a seed absorbs water, it swells and activates the enzymes necessary for growth.
2. Radicle Emergence: The radicle breaks through the seed coat and begins to grow downwards.
3. Plant Growth: As the radicle establishes itself, it supports the growth of the plant's stem and leaves.
Conclusion
In summary, the radicle is the part of the seed that grows into the root system of a new plant. Its role is fundamental for the plant's survival, as it provides stability and facilitates nutrient absorption. Understanding the functions of the radicle enhances our appreciation of plant biology and the germination process.
Seeds are vital for plant reproduction and growth. They contain various parts that play specific roles during the germination process. Among these parts, the radicle is crucial.
What is the Radicle?
- The radicle is the embryonic root of the seed.
- It is the first part of the seedling to emerge during germination.
- The radicle grows downward into the soil, establishing the root system of the new plant.
Functions of the Radicle
- Root Development: The radicle develops into the primary root, anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
- Nutrient Uptake: A strong root system allows the plant to access essential minerals and water, which are vital for growth and development.
How Germination Works
1. Water Absorption: When a seed absorbs water, it swells and activates the enzymes necessary for growth.
2. Radicle Emergence: The radicle breaks through the seed coat and begins to grow downwards.
3. Plant Growth: As the radicle establishes itself, it supports the growth of the plant's stem and leaves.
Conclusion
In summary, the radicle is the part of the seed that grows into the root system of a new plant. Its role is fundamental for the plant's survival, as it provides stability and facilitates nutrient absorption. Understanding the functions of the radicle enhances our appreciation of plant biology and the germination process.
Reproduction in Bryophyllum takes place by its- a)Root
- b)Flower
- c)Leaf
- d)Stem
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Reproduction in Bryophyllum takes place by its
a)
Root
b)
Flower
c)
Leaf
d)
Stem

|
Pragati Choudhary answered |
Reproduction in Bryophyllum takes place by its leaf. Leaf margin contains a number of plantlets.
Most common means of pollination is- a)Honey bee
- b)Air
- c)Human
- d)Water
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most common means of pollination is
a)
Honey bee
b)
Air
c)
Human
d)
Water

|
Naina Basu answered |
Air is the most common means of pollination. The pollen grain must be light, dry and winged.
What do plants such as cacti produce when their parts get detached?- a)Leaves
- b)Flowers
- c)New plants
- d)Fruits
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What do plants such as cacti produce when their parts get detached?
a)
Leaves
b)
Flowers
c)
New plants
d)
Fruits
|
|
Aurora Institute answered |
When parts of plants like cacti get detached, they can grow into new plants. So, plants like cacti produce new plants when their parts get detached.
Which of the following organism reproduce by budding- a)Yeast
- b)Bacteria
- c)Bread mold
- d)Opuntia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organism reproduce by budding
a)
Yeast
b)
Bacteria
c)
Bread mold
d)
Opuntia

|
Shraddha Nambiar answered |
Yeast reproduce asexually by budding in which small outgrowth is formed on the body that separate from parent body.
Mature ovule forms- a)Buds
- b)Endosperm
- c)Fruit
- d)Seed
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mature ovule forms
a)
Buds
b)
Endosperm
c)
Fruit
d)
Seed

|
Pragati Choudhary answered |
Mature ovule forms seeds inside the ovary and ovary mature to form fruits.
Fertilization is- a)Fusion of female gametes
- b)All of above.
- c)Fusion of male and female gametes
- d)Fusion of male gametes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fertilization is
a)
Fusion of female gametes
b)
All of above.
c)
Fusion of male and female gametes
d)
Fusion of male gametes

|
Prashanth Singh answered |
The fusion of male and female gamete to produce zygote is called fertilization.
Rose plant is grown by- a)Leaf cutting
- b)Stem cutting
- c)Seed
- d)Root cutting
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rose plant is grown by
a)
Leaf cutting
b)
Stem cutting
c)
Seed
d)
Root cutting

|
Krish Chawla answered |
Rose plant is grown by stem cutting in which small part of stem is placed in moist soil to form root.
Small bulb like projection coming out of the yeast cell is called- a)Bud
- b)Spore
- c)Node
- d)Bulb
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Small bulb like projection coming out of the yeast cell is called
a)
Bud
b)
Spore
c)
Node
d)
Bulb

|
Naina Basu answered |
Small bulb like projection coming out of the yeast cell is called bud. Bud detach from the parent body to form new organism.
Which of the following plants uses underground stems to store food and reproduce asexually?- a)Bryophyllum
- b)Onion
- c)Rose
- d)Mango
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following plants uses underground stems to store food and reproduce asexually?
a)
Bryophyllum
b)
Onion
c)
Rose
d)
Mango

|
Rainbow Rise Classes answered |
Onion uses underground stems (bulbs) to store food and reproduce asexually. New plants grow from the bulb’s buds, a form of vegetative propagation.
What is the process called when new individuals are produced from the vegetative parts of the parent plant?- a)Budding
- b)Spore formation
- c)Vegetative propagation
- d)Fragmentation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Budding
b)
Spore formation
c)
Vegetative propagation
d)
Fragmentation

|
Rainbow Rise Classes answered |
Vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction in plants where new plants are produced from the vegetative parts such as roots, stems, and leaves. This method allows plants to reproduce without seeds, ensuring the survival and spread of the species.
Which method of asexual reproduction involves the formation of a new individual from a bulb-like projection?- a)Fission
- b)Budding
- c)Fragmentation
- d)Spore formation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Fission
b)
Budding
c)
Fragmentation
d)
Spore formation

|
Malavika Kulkarni answered |
Understanding Asexual Reproduction: Budding
Asexual reproduction is a process where a new individual is formed from a single parent organism. One of the common methods of asexual reproduction is budding, which involves a specific mechanism of growth.
What is Budding?
- Budding is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism develops from an outgrowth or "bud" on the parent.
- This bud is a bulb-like projection that forms on the body of the parent organism.
How Does Budding Work?
- As the bud develops, it grows and eventually detaches from the parent, becoming an independent individual.
- The new organism is genetically identical to the parent, making it a clone.
Examples of Budding in Nature
- Yeast: A well-known example of budding occurs in yeast, where small buds grow on the parent cell and eventually separate.
- Hydras: These small aquatic animals also reproduce through budding, forming new hydras from their bodies.
Why is Budding Important?
- Budding allows for rapid population growth in stable environments.
- It also enables organisms to exploit available resources efficiently since they can reproduce without the need for a mate.
In summary, budding is a fascinating method of asexual reproduction that highlights the diversity of life forms and their reproductive strategies.
Asexual reproduction is a process where a new individual is formed from a single parent organism. One of the common methods of asexual reproduction is budding, which involves a specific mechanism of growth.
What is Budding?
- Budding is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism develops from an outgrowth or "bud" on the parent.
- This bud is a bulb-like projection that forms on the body of the parent organism.
How Does Budding Work?
- As the bud develops, it grows and eventually detaches from the parent, becoming an independent individual.
- The new organism is genetically identical to the parent, making it a clone.
Examples of Budding in Nature
- Yeast: A well-known example of budding occurs in yeast, where small buds grow on the parent cell and eventually separate.
- Hydras: These small aquatic animals also reproduce through budding, forming new hydras from their bodies.
Why is Budding Important?
- Budding allows for rapid population growth in stable environments.
- It also enables organisms to exploit available resources efficiently since they can reproduce without the need for a mate.
In summary, budding is a fascinating method of asexual reproduction that highlights the diversity of life forms and their reproductive strategies.
Chapter doubts & questions for Reproduction in Plants - Basic Science for Primary 5 2025 is part of Primary 5 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Primary 5 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Primary 5 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Reproduction in Plants - Basic Science for Primary 5 in English & Hindi are available as part of Primary 5 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Primary 5 Exam by signing up for free.
Basic Science for Primary 5
33 videos|96 docs|19 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










