All Exams >
JAMB >
Mathematics for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Probability for JAMB Exam
One card is randomly drawn from a pack of 52 cards. What is the probability that the card drawn is a face card(Jack, Queen or King)- a)
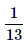
- b)
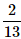
- c)
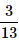
- d)
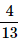
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One card is randomly drawn from a pack of 52 cards. What is the probability that the card drawn is a face card(Jack, Queen or King)
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Jay Sharma answered |
Total Face Cards = 12(Probable or Favourable Outcome)
Total Cards = 52(Possible Outcomes)
Probability = Favorable Outcomes÷Total Outcomes
= 12÷52
= 3/13
Total Cards = 52(Possible Outcomes)
Probability = Favorable Outcomes÷Total Outcomes
= 12÷52
= 3/13
A die is rolled twice. What is the probability of getting a sum equal to 9?- a)
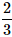
- b)
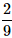
- c)
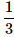
- d)
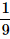
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A die is rolled twice. What is the probability of getting a sum equal to 9?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Target Study Academy answered |
Total number of outcomes possible when a die is rolled = 6 (∵ any one face out of the 6 faces)
- Hence, total number of outcomes possible when a die is rolled twice, n(S) = 6 x 6 = 36
E = Getting a sum of 9 when the two dice fall = {(3,6), (4,5), (5,4), (6,3)}
- Hence, n(E) = 4
A bag contains 2 yellow, 3 green and 2 blue balls. Two balls are drawn at random. What is the probability that none of the balls drawn is blue?- a)
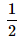
- b)
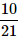
- c)
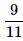
- d)
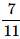
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A bag contains 2 yellow, 3 green and 2 blue balls. Two balls are drawn at random. What is the probability that none of the balls drawn is blue?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Future Foundation Institute answered |
Total number of balls = 2 + 3 + 2 = 7
► Let S be the sample space.
- n(S) = Total number of ways of drawing 2 balls out of 7 = 7C2
► Let E = Event of drawing 2 balls, none of them is blue.
- n(E) = Number of ways of drawing 2 balls from the total 5 (= 7-2) balls = 5C2
(∵ There are two blue balls in the total 7 balls. Total number of non-blue balls = 7 - 2 = 5)
Amamath appears in an exam that has 4 subjects. The chance he passes an individual subject’s test is 0.8. What is the probability that he will (i) pass in all the subjects?- a)0.84
- b)0.34
- c)0.73
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Amamath appears in an exam that has 4 subjects. The chance he passes an individual subject’s test is 0.8. What is the probability that he will (i) pass in all the subjects?
a)
0.84
b)
0.34
c)
0.73
d)
None of these

|
Divey Sethi answered |
The event definitions are:
(a) Passes the first AND Passes the second AND Passes the third AND Passes the fourth
(b) Fails the first AND Fails the second AND Fails the third AND Fails the fourth
(c) Fails all is the non-event
Find the chance of throwing at least one ace in a simple throw with two dice- a)1/12
- b)1/3
- c)1/4
- d)11/36
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the chance of throwing at least one ace in a simple throw with two dice
a)
1/12
b)
1/3
c)
1/4
d)
11/36
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
The possible number of cases is 6×6, or 36.
An ace on one die may be associated with any of the 6 numbers on the other die, and the remaining 5 numbers on the first die may each be associated with the ace on the second die; thus the number of favourable cases is 11.
Therefore the required chance is 11/36
An ace on one die may be associated with any of the 6 numbers on the other die, and the remaining 5 numbers on the first die may each be associated with the ace on the second die; thus the number of favourable cases is 11.
Therefore the required chance is 11/36
Three numbers are chosen at random without replacement from (1, 2, 3 ..., 10). The probability that the minimum number is 3 or the maximum number is 7 is- a)12/37
- b)11/40
- c)13/35
- d)14/35
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Three numbers are chosen at random without replacement from (1, 2, 3 ..., 10). The probability that the minimum number is 3 or the maximum number is 7 is
a)
12/37
b)
11/40
c)
13/35
d)
14/35
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
Given information:
Three numbers are chosen at random without replacement from (1, 2, 3 ..., 10).
To find:
The probability that the minimum number is 3 or the maximum number is 7.
Solution:
Step 1:
Total number of outcomes:
When three numbers are chosen from (1, 2, 3 ..., 10) without replacement, the total number of outcomes is given by the combination formula:
nCr = n! / (r!(n-r)!)
Here, n = 10 (total numbers to choose from)
r = 3 (number of numbers chosen)
Total number of outcomes = 10C3 = 10! / (3!(10-3)!) = 10! / (3!7!) = (10*9*8*7!)/(3*2*1*7!) = (10*9*8)/(3*2*1) = 120
Hence, there are 120 possible outcomes.
Step 2:
Favorable outcomes:
To find the favorable outcomes, we need to consider two cases separately:
Case 1: The minimum number is 3
Case 2: The maximum number is 7
Case 1: The minimum number is 3
If the minimum number is 3, then we can choose the other two numbers from the remaining 9 numbers (4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10). The number of ways to choose 2 numbers from 9 is given by the combination formula:
9C2 = 9! / (2!(9-2)!) = 9! / (2!7!) = (9*8)/(2*1) = 36
Case 2: The maximum number is 7
If the maximum number is 7, then we can choose the other two numbers from the remaining 9 numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6). The number of ways to choose 2 numbers from 6 is given by the combination formula:
6C2 = 6! / (2!(6-2)!) = 6! / (2!4!) = (6*5)/(2*1) = 15
Total favorable outcomes:
Total favorable outcomes = favorable outcomes in Case 1 + favorable outcomes in Case 2 = 36 + 15 = 51
Step 3:
Probability:
Probability = (Total favorable outcomes) / (Total number of outcomes) = 51 / 120 = 17 / 40
Therefore, the probability that the minimum number is 3 or the maximum number is 7 is 17/40, which is equivalent to option B.
Three numbers are chosen at random without replacement from (1, 2, 3 ..., 10).
To find:
The probability that the minimum number is 3 or the maximum number is 7.
Solution:
Step 1:
Total number of outcomes:
When three numbers are chosen from (1, 2, 3 ..., 10) without replacement, the total number of outcomes is given by the combination formula:
nCr = n! / (r!(n-r)!)
Here, n = 10 (total numbers to choose from)
r = 3 (number of numbers chosen)
Total number of outcomes = 10C3 = 10! / (3!(10-3)!) = 10! / (3!7!) = (10*9*8*7!)/(3*2*1*7!) = (10*9*8)/(3*2*1) = 120
Hence, there are 120 possible outcomes.
Step 2:
Favorable outcomes:
To find the favorable outcomes, we need to consider two cases separately:
Case 1: The minimum number is 3
Case 2: The maximum number is 7
Case 1: The minimum number is 3
If the minimum number is 3, then we can choose the other two numbers from the remaining 9 numbers (4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10). The number of ways to choose 2 numbers from 9 is given by the combination formula:
9C2 = 9! / (2!(9-2)!) = 9! / (2!7!) = (9*8)/(2*1) = 36
Case 2: The maximum number is 7
If the maximum number is 7, then we can choose the other two numbers from the remaining 9 numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6). The number of ways to choose 2 numbers from 6 is given by the combination formula:
6C2 = 6! / (2!(6-2)!) = 6! / (2!4!) = (6*5)/(2*1) = 15
Total favorable outcomes:
Total favorable outcomes = favorable outcomes in Case 1 + favorable outcomes in Case 2 = 36 + 15 = 51
Step 3:
Probability:
Probability = (Total favorable outcomes) / (Total number of outcomes) = 51 / 120 = 17 / 40
Therefore, the probability that the minimum number is 3 or the maximum number is 7 is 17/40, which is equivalent to option B.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A bag contains 4 black, 5 yellow and 6 green balls. Three balls are drawn at random from the bag. What is the probability that all of them are yellow?
- A:
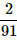
- B:
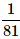
- C:
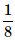
- D:
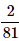
The answer is A.
A bag contains 4 black, 5 yellow and 6 green balls. Three balls are drawn at random from the bag. What is the probability that all of them are yellow?

|
Divey Sethi answered |
Total number of balls = 4 + 5 + 6 = 15
Let S be the sample space.
- n(S) = Total number of ways of drawing 3 balls out of 15 = 15C3
Let E = Event of drawing 3 balls, all of them are yellow.
- n(E) = Number of ways of drawing 3 balls from the total 5 = 5C3
(∵ there are 5 yellow balls in the total balls)
[∵ nCr = nC(n-r). So 5C3 = 5C2. Applying this for the ease of calculation]
What is the probability of selecting a prime number from 1,2,3,... 10 ?- a)
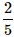
- b)
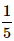
- c)
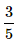
- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the probability of selecting a prime number from 1,2,3,... 10 ?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Total count of numbers, n(S) = 10
Prime numbers in the given range are 2,3,5 and 7
Hence, total count of prime numbers in the given range, n(E) = 4
Prime numbers in the given range are 2,3,5 and 7
Hence, total count of prime numbers in the given range, n(E) = 4
John and Dani go for an interview for two vacancies. The probability for the selection of John is 1/3 and whereas the probability for the selection of Dani is 1/5. What is the probability that none of them are selected?- a)
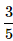
- b)
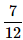
- c)
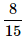
- d)
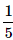
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
John and Dani go for an interview for two vacancies. The probability for the selection of John is 1/3 and whereas the probability for the selection of Dani is 1/5. What is the probability that none of them are selected?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
If 8 coins are tossed, what is the chance that one and only one will turn up Head?- a)1/16
- b)3/35
- c)3/32
- d)1/32
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If 8 coins are tossed, what is the chance that one and only one will turn up Head?
a)
1/16
b)
3/35
c)
3/32
d)
1/32

|
Jaya Gupta answered |
One head and seven tails would have eight positions where the head can come.
Thus, 8 x (1/2)8 = (1/32)
Thus, 8 x (1/2)8 = (1/32)
A life insurance company insured 25,000 young boys, 14,000 young girls and 16,000 young adults. The probability of death within 10 years of a young boy, young girl and a young adult are 0.02, 0.03 and 0.15 respectively. One of the insured persons dice. What is the probability that the dead person is a young boy?
- a)36/165
- b)25/166
- c)26/165
- d)32/165
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A life insurance company insured 25,000 young boys, 14,000 young girls and 16,000 young adults. The probability of death within 10 years of a young boy, young girl and a young adult are 0.02, 0.03 and 0.15 respectively. One of the insured persons dice. What is the probability that the dead person is a young boy?
a)
36/165
b)
25/166
c)
26/165
d)
32/165

|
Prasad Nair answered |

There are 15 boys and 10 girls in a class. If three students are selected at random, what is the probability that 1 girl and 2 boys are selected?
- a)

- b)

- c)
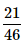
- d)
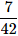
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are 15 boys and 10 girls in a class. If three students are selected at random, what is the probability that 1 girl and 2 boys are selected?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Let S be the sample space.
- n(S) = Total number of ways of selecting 3 students from 25 students = 25C3
Let E = Event of selecting 1 girl and 2 boys
- n(E) = Number of ways of selecting 1 girl and 2 boys
15 boys and 10 girls are there in a class. We need to select 2 boys from 15 boys and 1 girl from 10 girls
Number of ways in which this can be done:
15C2 × 10C1
Hence n(E) = 15C2 × 10C1
15C2 × 10C1
Hence n(E) = 15C2 × 10C1
Out of a pack of 52 cards one is lost; from the remainder of the pack, two cards are drawn and are found to be spades. Find the chance that the missing card is a spade.- a)11/50
- b)11/49
- c)10/49
- d)10/50
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of a pack of 52 cards one is lost; from the remainder of the pack, two cards are drawn and are found to be spades. Find the chance that the missing card is a spade.
a)
11/50
b)
11/49
c)
10/49
d)
10/50

|
Dhruv Mehra answered |
Intuitively, the answer should be slightly less than 1/4.
As if you consider two cases:
1) The lost card is spades. (12 spades cards remained out of 51 cards)
2) The lost card is other suits (13 spades cards remained out of 51 cards)
The probability of having two cards drew to be spades is less for 1) than 2), as there are less spades cards for 1).
For more formal calculation:
Let H be the event that the last card is spades.
Let S be the event that the 2 cards drew are spades.
The answer to this question is: P(H|S) = P(S|H)*P(H)/P(S)
We know
P(S|H) = 12/51 * 11/50
P(H) = 1/4
P(S) = 13/52 * 12/51
Hence, the answer is ((12/51 * 11/50) * (1/4)) / (13/52 * 12/51) = 11/50
There are these two sets of letters, and you are going to pick exactly one letter from each set. What is the probability of picking at least one vowel?
- a)1/6
- b)1/3
- c)1/2
- d)2/3
- e)5/6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are these two sets of letters, and you are going to pick exactly one letter from each set. What is the probability of picking at least one vowel?
a)
1/6
b)
1/3
c)
1/2
d)
2/3
e)
5/6
|
|
Krish Joshi answered |
Explanation:
Understanding the Sets:
- Set 1: {a, e, i, o, u}
- Set 2: {b, c, d, f, g, h, j, k, l, m, n, p, q, r, s, t, v, w, x, y, z}
Finding the Probability:
- To find the probability of picking at least one vowel, we need to consider all possible outcomes when picking one letter from each set.
- Total number of outcomes = 5 (from Set 1) * 20 (from Set 2) = 100
Finding the Number of Outcomes with at least one Vowel:
- Number of outcomes with at least one vowel = Total number of outcomes - Number of outcomes with no vowels
- Number of outcomes with no vowels = 15 (from Set 1) * 20 (from Set 2) = 300
- Number of outcomes with at least one vowel = 100 - 300 = 70
Calculating the Probability:
- Probability of picking at least one vowel = Number of outcomes with at least one vowel / Total number of outcomes
- Probability = 70 / 100 = 7 / 10 = 0.7 = 1/2
Therefore, the probability of picking at least one vowel when choosing one letter from each set is 1/2 or 50%. So, the correct answer is option 'c) 1/2'.
Understanding the Sets:
- Set 1: {a, e, i, o, u}
- Set 2: {b, c, d, f, g, h, j, k, l, m, n, p, q, r, s, t, v, w, x, y, z}
Finding the Probability:
- To find the probability of picking at least one vowel, we need to consider all possible outcomes when picking one letter from each set.
- Total number of outcomes = 5 (from Set 1) * 20 (from Set 2) = 100
Finding the Number of Outcomes with at least one Vowel:
- Number of outcomes with at least one vowel = Total number of outcomes - Number of outcomes with no vowels
- Number of outcomes with no vowels = 15 (from Set 1) * 20 (from Set 2) = 300
- Number of outcomes with at least one vowel = 100 - 300 = 70
Calculating the Probability:
- Probability of picking at least one vowel = Number of outcomes with at least one vowel / Total number of outcomes
- Probability = 70 / 100 = 7 / 10 = 0.7 = 1/2
Therefore, the probability of picking at least one vowel when choosing one letter from each set is 1/2 or 50%. So, the correct answer is option 'c) 1/2'.
Three coins are tossed. What is the probability of getting (i) 2 Tails and 1 Head- a)1/4
- b)3/8
- c)2/3
- d)1/8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Three coins are tossed. What is the probability of getting (i) 2 Tails and 1 Head
a)
1/4
b)
3/8
c)
2/3
d)
1/8
|
|
Sagar Sharma answered |
Understanding the Problem
When tossing three coins, each coin has two possible outcomes: Heads (H) or Tails (T). We want to find the probability of getting exactly 2 Tails and 1 Head.
Total Outcomes
- Each coin toss has 2 outcomes.
- For three coins, the total number of outcomes is:
2 * 2 * 2 = 8.
Possible Outcomes
The possible combinations when tossing three coins are:
- HHH
- HHT
- HTH
- HTT
- THH
- THT
- TTH
- TTT
Out of these, we identify the outcomes with exactly 2 Tails and 1 Head:
- HTT
- THT
- TTH
Thus, there are 3 favorable outcomes.
Calculating Probability
- The probability formula is:
Probability = (Number of Favorable Outcomes) / (Total Outcomes).
- Here, the number of favorable outcomes is 3 (HTT, THT, TTH) and the total outcomes are 8.
- Therefore, the probability is:
Probability = 3 / 8.
Conclusion
The probability of getting exactly 2 Tails and 1 Head when tossing three coins is indeed 3/8, which corresponds to option 'B'.
When tossing three coins, each coin has two possible outcomes: Heads (H) or Tails (T). We want to find the probability of getting exactly 2 Tails and 1 Head.
Total Outcomes
- Each coin toss has 2 outcomes.
- For three coins, the total number of outcomes is:
2 * 2 * 2 = 8.
Possible Outcomes
The possible combinations when tossing three coins are:
- HHH
- HHT
- HTH
- HTT
- THH
- THT
- TTH
- TTT
Out of these, we identify the outcomes with exactly 2 Tails and 1 Head:
- HTT
- THT
- TTH
Thus, there are 3 favorable outcomes.
Calculating Probability
- The probability formula is:
Probability = (Number of Favorable Outcomes) / (Total Outcomes).
- Here, the number of favorable outcomes is 3 (HTT, THT, TTH) and the total outcomes are 8.
- Therefore, the probability is:
Probability = 3 / 8.
Conclusion
The probability of getting exactly 2 Tails and 1 Head when tossing three coins is indeed 3/8, which corresponds to option 'B'.
The odds in favour of standing first of three students Amit, Vikas and Vivek appearing at an examination are 1 : 2. 2 : 5 and 1 : 7 respectively. What is the probability that either of them will stand first (assume that a tie for the first place is not possible).- a)168/178
- b)124/168
- c)5/168
- d)125/168
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The odds in favour of standing first of three students Amit, Vikas and Vivek appearing at an examination are 1 : 2. 2 : 5 and 1 : 7 respectively. What is the probability that either of them will stand first (assume that a tie for the first place is not possible).
a)
168/178
b)
124/168
c)
5/168
d)
125/168
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
To find the probability that either Amit, Vikas, or Vivek will stand first, we need to consider the individual probabilities of each student standing first and then add them together.
Given that the odds in favor of Amit standing first are 1:2, we can determine the probability as follows:
Probability of Amit standing first = 1 / (1 + 2) = 1/3
Similarly, the probability of Vikas standing first is:
Probability of Vikas standing first = 2 / (2 + 5) = 2/7
And the probability of Vivek standing first is:
Probability of Vivek standing first = 1 / (1 + 7) = 1/8
Now, since the events of Amit, Vikas, and Vivek standing first are mutually exclusive (meaning only one of them can stand first), we can add the probabilities together to find the probability that either of them will stand first:
Probability = Probability of Amit standing first + Probability of Vikas standing first + Probability of Vivek standing first
= 1/3 + 2/7 + 1/8
= (56 + 24 + 21) / (3 * 7 * 8)
= 101 / 168
So, the correct answer is option D, 125/168.
Given that the odds in favor of Amit standing first are 1:2, we can determine the probability as follows:
Probability of Amit standing first = 1 / (1 + 2) = 1/3
Similarly, the probability of Vikas standing first is:
Probability of Vikas standing first = 2 / (2 + 5) = 2/7
And the probability of Vivek standing first is:
Probability of Vivek standing first = 1 / (1 + 7) = 1/8
Now, since the events of Amit, Vikas, and Vivek standing first are mutually exclusive (meaning only one of them can stand first), we can add the probabilities together to find the probability that either of them will stand first:
Probability = Probability of Amit standing first + Probability of Vikas standing first + Probability of Vivek standing first
= 1/3 + 2/7 + 1/8
= (56 + 24 + 21) / (3 * 7 * 8)
= 101 / 168
So, the correct answer is option D, 125/168.
A randomly selected year is containing 53 Mondays then probability that it is a leap year- a)2 / 5
- b)3 / 4
- c)1 / 4
- d)2 / 7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A randomly selected year is containing 53 Mondays then probability that it is a leap year
a)
2 / 5
b)
3 / 4
c)
1 / 4
d)
2 / 7

|
KS Coaching Center answered |
The correct option is A
- Selected year will be a non leap year with a probability 3/4
- Selected year will be a leap year with a probability 1/4
- A selected leap year will have 53 Mondays with probability 2/7
- A selected non leap year will have 53 Mondays with probability 1/7
- E→ Event that randomly selected year contains 53 Mondays
P(E) = (3/4 × 1/7) + (1/4 × 2/7)
P(Leap Year/ E) = (2/28) / (5/28) = 2/5
P(Leap Year/ E) = (2/28) / (5/28) = 2/5
The ratio of number of officers and ladies in the Scorpion Squadron and in the Gunners Squadron are 3 : 1 and 2 : 5 respectively. An individual is selected to be the chairperson of their association. The chance that this individual is selected from the Scorpions is 2/3. Find the probability that the chairperson will be an officer- a)25/42
- b)13/43
- c)11/43
- d)7/42
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of number of officers and ladies in the Scorpion Squadron and in the Gunners Squadron are 3 : 1 and 2 : 5 respectively. An individual is selected to be the chairperson of their association. The chance that this individual is selected from the Scorpions is 2/3. Find the probability that the chairperson will be an officer
a)
25/42
b)
13/43
c)
11/43
d)
7/42

|
Uday Nambiar answered |
(2/3) x (3/4) + (1/3) x (2/7) = (1/2) + (2/21) = (25/42)
Two fairdices are thrown. Giventh at the sum of the dice is less than or equal to 4, find the probability that only one dice shows two.- a)1/4
- b)1/2
- c)2/3
- d)1/3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two fairdices are thrown. Giventh at the sum of the dice is less than or equal to 4, find the probability that only one dice shows two.
a)
1/4
b)
1/2
c)
2/3
d)
1/3

|
Manasa Chavan answered |
The possible outcomes are: (1, 1); (1, 2); (2, 1), (2, 2); (3, 1); (1, 3).
Out of six cases, in two cases there is exactly one ‘2’ Thus, the correct answer is 2/6 =1/3.
Out of six cases, in two cases there is exactly one ‘2’ Thus, the correct answer is 2/6 =1/3.
A card is randomly drawn from a deck of 52 cards. What is the probability getting either a King or a Diamond?- a)
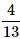
- b)
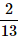
- c)
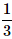
- d)
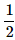
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A card is randomly drawn from a deck of 52 cards. What is the probability getting either a King or a Diamond?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
Total number of cards = 52
Total Number of King Cards = 4
Total Number of King Cards = 4
Total Number of Diamond Cards = 13
Total Number of Cards which are both King and Diamond = 1
Here a card can be both a Diamond card and a King. Hence these are not mutually exclusive events. (Reference : mutually exclusive events) . By Addition Theorem of Probability, we have P(King or a Diamond) = P(King) + P(Diamond) – P(King and Diamond)
A group of investigators took a fair sample of 1972 children from the general population and found that there are 1000 boys and 972 girls. If the investigators claim that their research is so accurate that the sex of a new bom child can be predicted based on the ratio of the sample of the population, then what is the expectation in terms of the probability that a new child bom will be a girl?- a)243/250
- b)250/257
- c)9/10
- d)243/493
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A group of investigators took a fair sample of 1972 children from the general population and found that there are 1000 boys and 972 girls. If the investigators claim that their research is so accurate that the sex of a new bom child can be predicted based on the ratio of the sample of the population, then what is the expectation in terms of the probability that a new child bom will be a girl?
a)
243/250
b)
250/257
c)
9/10
d)
243/493

|
Manasa Chavan answered |
972/1972 = 243/ 493.
A husband and a wife appear in an interview for two vacancies for the same post. The probability of husband’s selection is (1/7) and that of the wife’s selection is 1/5. What is the probability that (i) both of them will be selected?- a)1/35
- b)2/35
- c)3/35
- d)1/7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A husband and a wife appear in an interview for two vacancies for the same post. The probability of husband’s selection is (1/7) and that of the wife’s selection is 1/5. What is the probability that (i) both of them will be selected?
a)
1/35
b)
2/35
c)
3/35
d)
1/7

|
Jaya Gupta answered |
(i) 1/5 x 1/7 = 1/35
A and B are two mutually exclusive events of an experiment. If P(A') = 0.65, P(A u B) = 0.65 and P(B) = p , find the value o f p.- a)0.25
- b)0.3
- c)0.1
- d)0.2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A and B are two mutually exclusive events of an experiment. If P(A') = 0.65, P(A u B) = 0.65 and P(B) = p , find the value o f p.
a)
0.25
b)
0.3
c)
0.1
d)
0.2
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
Given: P(A) = 0.65, P(A u B) = 0.65, P(B) = p
Explanation:
We know that A and B are mutually exclusive events which means that they cannot occur together. So, P(A u B) = P(A) + P(B).
Therefore, substituting the given values, we get:
0.65 = P(A) + P(B)
0.65 = 0.65 + P(B)
P(B) = 0
But this contradicts the fact that A and B are mutually exclusive events. So, P(B) cannot be zero.
Hence, we need to recheck our calculations. We know that P(A u B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A n B).
As A and B are mutually exclusive, P(A n B) = 0. So, we get:
0.65 = 0.65 + P(B) - 0
P(B) = 0
Again, we get P(B) = 0 which contradicts the fact that A and B are mutually exclusive.
Therefore, there is no solution to this problem as the given information is not consistent.
Answer: None of the options (a), (b), (c), (d) are correct.
Explanation:
We know that A and B are mutually exclusive events which means that they cannot occur together. So, P(A u B) = P(A) + P(B).
Therefore, substituting the given values, we get:
0.65 = P(A) + P(B)
0.65 = 0.65 + P(B)
P(B) = 0
But this contradicts the fact that A and B are mutually exclusive events. So, P(B) cannot be zero.
Hence, we need to recheck our calculations. We know that P(A u B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A n B).
As A and B are mutually exclusive, P(A n B) = 0. So, we get:
0.65 = 0.65 + P(B) - 0
P(B) = 0
Again, we get P(B) = 0 which contradicts the fact that A and B are mutually exclusive.
Therefore, there is no solution to this problem as the given information is not consistent.
Answer: None of the options (a), (b), (c), (d) are correct.
A dice is thrown. What is the probability that the number shown in the dice is divisible by 3?- a)
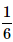
- b)
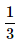
- c)
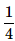
- d)
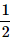
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A dice is thrown. What is the probability that the number shown in the dice is divisible by 3?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Gowri Chakraborty answered |
Total number of outcomes possible when a die is rolled, n(S) = 6 (∵ 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6)
E = Event that the number shown in the dice is divisible by 3 = {3, 6}
Hence, n(E) = 2
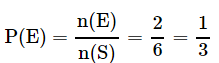
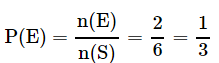
John draws a card from a pack of cards. What is the probability that the card drawn is a card of black suit?- a)
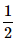
- b)
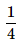
- c)
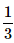
- d)
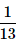
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
John draws a card from a pack of cards. What is the probability that the card drawn is a card of black suit?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Naroj Boda answered |
Total number of cards, n(S) = 52
Total number of black cards, n(E) = 26
Total number of black cards, n(E) = 26
A bag contains 6 red, 4 white and 8 blue balls. If three balls are drawn at random, find the probability that (i) all the three balls are of the same colour.- a)17/240
- b)5/51
- c)31/204
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A bag contains 6 red, 4 white and 8 blue balls. If three balls are drawn at random, find the probability that (i) all the three balls are of the same colour.
a)
17/240
b)
5/51
c)
31/204
d)
None of these

|
Kajal Kulkarni answered |
The required probability would be given by: All are Red OR All are white OR All are Blue = (6/18) x (5/17) x (4/16) + (4/18) x (3/17) x (2/16) + (8/18) x (7/17)x (6/16) = 480/(18 x 17 x 16) 5/51
If from each of three boxes containing 3 white and 1 black, 2 white and 2 black, 1 white and 3 black balls, one ball is drawn at random, then the probability that 2 white and 1 black ball will be drawn is- a)13/32
- b)12/14
- c)12/25
- d)3/13
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If from each of three boxes containing 3 white and 1 black, 2 white and 2 black, 1 white and 3 black balls, one ball is drawn at random, then the probability that 2 white and 1 black ball will be drawn is
a)
13/32
b)
12/14
c)
12/25
d)
3/13

|
Sameer Rane answered |
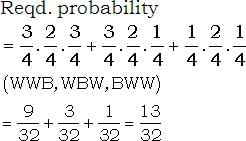
A speaks the truth 3 out o f 4 times, and B 5 out o f 6 times. What is the probability that they will contradict each other in stating the same fact?- a)2/3
- b)1/3
- c)5/6
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A speaks the truth 3 out o f 4 times, and B 5 out o f 6 times. What is the probability that they will contradict each other in stating the same fact?
a)
2/3
b)
1/3
c)
5/6
d)
None of these
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
To solve this problem, we need to find the probability that A and B will contradict each other in stating the same fact.
Given information:
- A speaks the truth 3 out of 4 times, which means A has a probability of 3/4 = 0.75 of speaking the truth.
- B speaks the truth 5 out of 6 times, which means B has a probability of 5/6 ≈ 0.83 of speaking the truth.
We can approach this problem by considering two scenarios:
1. A tells the truth and B lies.
2. A lies and B tells the truth.
Probability of A telling the truth and B lying:
- Probability of A telling the truth = 0.75
- Probability of B lying = 1 - (Probability of B telling the truth) = 1 - 0.83 = 0.17
Probability of A lying and B telling the truth:
- Probability of A lying = 1 - (Probability of A telling the truth) = 1 - 0.75 = 0.25
- Probability of B telling the truth = 0.83
Now, we can calculate the probability of the two scenarios occurring:
- Probability of scenario 1 = Probability of A telling the truth * Probability of B lying = 0.75 * 0.17 = 0.1275
- Probability of scenario 2 = Probability of A lying * Probability of B telling the truth = 0.25 * 0.83 = 0.2075
Finally, we add the probabilities of the two scenarios to get the total probability of A and B contradicting each other:
- Probability of A and B contradicting each other = Probability of scenario 1 + Probability of scenario 2 = 0.1275 + 0.2075 = 0.335
Therefore, the probability that A and B will contradict each other in stating the same fact is approximately 0.335, which can be simplified to 1/3. Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Given information:
- A speaks the truth 3 out of 4 times, which means A has a probability of 3/4 = 0.75 of speaking the truth.
- B speaks the truth 5 out of 6 times, which means B has a probability of 5/6 ≈ 0.83 of speaking the truth.
We can approach this problem by considering two scenarios:
1. A tells the truth and B lies.
2. A lies and B tells the truth.
Probability of A telling the truth and B lying:
- Probability of A telling the truth = 0.75
- Probability of B lying = 1 - (Probability of B telling the truth) = 1 - 0.83 = 0.17
Probability of A lying and B telling the truth:
- Probability of A lying = 1 - (Probability of A telling the truth) = 1 - 0.75 = 0.25
- Probability of B telling the truth = 0.83
Now, we can calculate the probability of the two scenarios occurring:
- Probability of scenario 1 = Probability of A telling the truth * Probability of B lying = 0.75 * 0.17 = 0.1275
- Probability of scenario 2 = Probability of A lying * Probability of B telling the truth = 0.25 * 0.83 = 0.2075
Finally, we add the probabilities of the two scenarios to get the total probability of A and B contradicting each other:
- Probability of A and B contradicting each other = Probability of scenario 1 + Probability of scenario 2 = 0.1275 + 0.2075 = 0.335
Therefore, the probability that A and B will contradict each other in stating the same fact is approximately 0.335, which can be simplified to 1/3. Hence, the correct answer is option B.
A bag contains four black and five red balls. If three balls from the bag are chosen at random, what is the chance that they are all black?- a)1/21
- b)1/20
- c)2/23
- d)1/9
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A bag contains four black and five red balls. If three balls from the bag are chosen at random, what is the chance that they are all black?
a)
1/21
b)
1/20
c)
2/23
d)
1/9
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
**Problem Analysis**
We are given a bag containing four black and five red balls. We need to find the probability that when three balls are chosen randomly from the bag, they are all black.
**Total Number of Outcomes**
The total number of ways to choose three balls from nine balls is given by the combination formula C(n, r), where n is the total number of balls and r is the number of balls to be chosen. In this case, n = 9 and r = 3, so the total number of outcomes is C(9, 3) = 9! / (3! * (9-3)!) = 84.
**Favorable Outcomes**
To find the number of favorable outcomes, we need to consider the situation where all three balls chosen are black. Since there are four black balls in the bag, the number of ways to choose three black balls is C(4, 3) = 4! / (3! * (4-3)!) = 4.
**Probability Calculation**
The probability of an event occurring is given by the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the number of total outcomes. In this case, the probability of choosing three black balls is 4/84 = 1/21.
**Answer**
Therefore, the chance that all three balls chosen at random from the bag are black is 1/21. Hence, the correct answer is option A.
We are given a bag containing four black and five red balls. We need to find the probability that when three balls are chosen randomly from the bag, they are all black.
**Total Number of Outcomes**
The total number of ways to choose three balls from nine balls is given by the combination formula C(n, r), where n is the total number of balls and r is the number of balls to be chosen. In this case, n = 9 and r = 3, so the total number of outcomes is C(9, 3) = 9! / (3! * (9-3)!) = 84.
**Favorable Outcomes**
To find the number of favorable outcomes, we need to consider the situation where all three balls chosen are black. Since there are four black balls in the bag, the number of ways to choose three black balls is C(4, 3) = 4! / (3! * (4-3)!) = 4.
**Probability Calculation**
The probability of an event occurring is given by the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the number of total outcomes. In this case, the probability of choosing three black balls is 4/84 = 1/21.
**Answer**
Therefore, the chance that all three balls chosen at random from the bag are black is 1/21. Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Five children, Anaxagoras, Beatrice, Childeric, Desdemona, and Ethelred, sit randomly in five chairs in a row. What is the probability that Childeric and Ethelred sit next to each other?- a)1/30
- b)1/15
- c)1/5
- d)2/5
- e)7/20
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Five children, Anaxagoras, Beatrice, Childeric, Desdemona, and Ethelred, sit randomly in five chairs in a row. What is the probability that Childeric and Ethelred sit next to each other?
a)
1/30
b)
1/15
c)
1/5
d)
2/5
e)
7/20
|
|
Ashish Chatterjee answered |
Understanding the Problem
To find the probability that Childeric and Ethelred sit next to each other among five children, we can use combinatorial methods.
Total Arrangements
- There are 5 children, which can be arranged in 5! (factorial) ways.
- 5! = 120 total arrangements.
Grouping Childeric and Ethelred
- To simplify the problem, we can treat Childeric and Ethelred as a single unit or block.
- This block can be arranged in two ways: Childeric next to Ethelred or Ethelred next to Childeric.
Calculating the Block Arrangements
- By treating Childeric and Ethelred as one block, we effectively have 4 units to arrange: (CE), Anaxagoras, Beatrice, and Desdemona.
- The arrangements can be calculated as 4! = 24 ways.
Arranging the Block
- Since the block (CE) can be arranged in 2 ways (CE or EC), the total arrangements for this case are:
- Total = 4! * 2 = 24 * 2 = 48 arrangements.
Calculating the Probability
- The probability that Childeric and Ethelred sit next to each other is the number of favorable arrangements divided by the total arrangements.
- Probability = 48 (favorable) / 120 (total) = 48/120 = 2/5.
Final Result
- Therefore, the probability that Childeric and Ethelred sit next to each other is 2/5.
This aligns with option 'D'.
To find the probability that Childeric and Ethelred sit next to each other among five children, we can use combinatorial methods.
Total Arrangements
- There are 5 children, which can be arranged in 5! (factorial) ways.
- 5! = 120 total arrangements.
Grouping Childeric and Ethelred
- To simplify the problem, we can treat Childeric and Ethelred as a single unit or block.
- This block can be arranged in two ways: Childeric next to Ethelred or Ethelred next to Childeric.
Calculating the Block Arrangements
- By treating Childeric and Ethelred as one block, we effectively have 4 units to arrange: (CE), Anaxagoras, Beatrice, and Desdemona.
- The arrangements can be calculated as 4! = 24 ways.
Arranging the Block
- Since the block (CE) can be arranged in 2 ways (CE or EC), the total arrangements for this case are:
- Total = 4! * 2 = 24 * 2 = 48 arrangements.
Calculating the Probability
- The probability that Childeric and Ethelred sit next to each other is the number of favorable arrangements divided by the total arrangements.
- Probability = 48 (favorable) / 120 (total) = 48/120 = 2/5.
Final Result
- Therefore, the probability that Childeric and Ethelred sit next to each other is 2/5.
This aligns with option 'D'.
When two dice are rolled, what is the probability that the sum is either 7 or 11?- a)
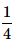
- b)
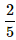
- c)
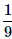
- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When two dice are rolled, what is the probability that the sum is either 7 or 11?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Target Study Academy answered |
Total number of outcomes possible when a die is rolled = 6 (? any one face out of the 6 faces)
Hence, total number of outcomes possible when two dice are rolled = 6 × 6 = 36
To get a sum of 7, the following are the favourable cases.
(1, 6), (2, 5), {3, 4}, (4, 3), (5, 2), (6,1)
=> Number of ways in which we get a sum of 7 = 6
Hence, total number of outcomes possible when two dice are rolled = 6 × 6 = 36
To get a sum of 7, the following are the favourable cases.
(1, 6), (2, 5), {3, 4}, (4, 3), (5, 2), (6,1)
=> Number of ways in which we get a sum of 7 = 6
To get a sum of 11, the following are the favourable cases. (5, 6), (6, 5) => Number of ways in which we get a sum of 11 = 2
Here, clearly the events are mutually exclusive events. By Addition Theorem of Probability, we have P(a sum of 7 or a sum of 11) = P(a sum of 7) + P( a sum of 11)
5 coins are tossed together. What is the probability of getting exactly 2 heads?- a)
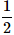
- b)
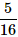
- c)
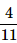
- d)
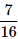
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
5 coins are tossed together. What is the probability of getting exactly 2 heads?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
Total number of outcomes possible when a coin is tossed = 2 (? Head or Tail)
Hence, total number of outcomes possible when 5 coins are tossed, n(S) = 25
E = Event of getting exactly 2 heads when 5 coins are tossed
n(E) = Number of ways of getting exactly 2 heads when 5 coins are tossed = 5C2
Hence, total number of outcomes possible when 5 coins are tossed, n(S) = 25
E = Event of getting exactly 2 heads when 5 coins are tossed
n(E) = Number of ways of getting exactly 2 heads when 5 coins are tossed = 5C2
A pair of fair dice are rolled together till a sum of either 5 or 7 is obtained. The probability that 5 comes before 7 is- a)0.45
- b)0.4
- c)0.5
- d)0.7
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A pair of fair dice are rolled together till a sum of either 5 or 7 is obtained. The probability that 5 comes before 7 is
a)
0.45
b)
0.4
c)
0.5
d)
0.7

|
Uday Nambiar answered |
We do not have to consider any sum other than 5 or 7 occurring.
A sum of 5 can be obtained by any of [4 + 1, 3 + 2, 2 + 3, 1 + 4]
Similarly a sum of 7 can be obtained by any of [6 + 1, 5 + 2, 4 + 3, 3 + 4, 2 + 5, 1 + 6]
For 6: n(E) = 4, n(S) = 6 + 4 P = 0.4
For 7: n(E) = 6 n(S) = 6 + 4 P = 0.6
A sum of 5 can be obtained by any of [4 + 1, 3 + 2, 2 + 3, 1 + 4]
Similarly a sum of 7 can be obtained by any of [6 + 1, 5 + 2, 4 + 3, 3 + 4, 2 + 5, 1 + 6]
For 6: n(E) = 4, n(S) = 6 + 4 P = 0.4
For 7: n(E) = 6 n(S) = 6 + 4 P = 0.6
A and B are two candidates seeking admission to the IIMs. The probability that A is selected is 0.5 and the probability that both A and B are selected is at most 0.3. Is it possible that the probability of B getting selected is 0.9.- a)No
- b)Yes
- c)Either (a) or (b)
- d)Can’t say
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A and B are two candidates seeking admission to the IIMs. The probability that A is selected is 0.5 and the probability that both A and B are selected is at most 0.3. Is it possible that the probability of B getting selected is 0.9.
a)
No
b)
Yes
c)
Either (a) or (b)
d)
Can’t say

|
Jaya Gupta answered |
P (Both are selected) = P(A) x P(B) Since P(A) = 0.5, we get 0.3 = 0.5 x 0.6.
The maximum value of P(B) = 0.6.
Thus P{B) = 0.9 is not possible.
The maximum value of P(B) = 0.6.
Thus P{B) = 0.9 is not possible.
In the above question, find the probability that the remaining two balls are red.- a)10/231
- b)12/231
- c)12/363
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the above question, find the probability that the remaining two balls are red.
a)
10/231
b)
12/231
c)
12/363
d)
None of these

|
Prasad Nair answered |
The required probability would be given by the event definition: First is red and second is red = 5/22 x 4/21 = 10/231
In throwing a fair dice, what is the probability of getting the number ‘3’?- a)1/3
- b)1/6
- c)1/9
- d)1/12
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In throwing a fair dice, what is the probability of getting the number ‘3’?
a)
1/3
b)
1/6
c)
1/9
d)
1/12
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
Out of a total of 6 occurrences, 3 is one possibility = 1/ 6 .
A card is randomly drawn from a deck of 52 cards. What is the probability getting an Ace or King or Queen?- a)
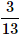
- b)
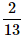
- c)
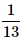
- d)
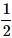
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A card is randomly drawn from a deck of 52 cards. What is the probability getting an Ace or King or Queen?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Total number of cards = 52
Total number of Ace cards = 4
Total number of Ace cards = 4
AMS employs 8 professors on their staff. Their respective probability of remaining in employment for 10 years are 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9. The probability that after 10 years at least 6 of them still work in AMS is- a)0.19
- b)1.22
- c)0.1
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
AMS employs 8 professors on their staff. Their respective probability of remaining in employment for 10 years are 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9. The probability that after 10 years at least 6 of them still work in AMS is
a)
0.19
b)
1.22
c)
0.1
d)
None of these

|
Ishani Rane answered |
here 8 professors are there.
Asking atleast 6 of them continue ,
it has 3 cases.
1 all 8 professors continue.
2 7 professors continue and 1 professors discontinue.
3 6 professors continue and 2 professors discontinue.
1st case all 8 continue is = 2/10*3/10*4/10*5/10*6/10*7/10*/8/10*9/10=9factorial/10power8
=362880/100000000
=>0.00363.
2nd case any 7 professors continue, and 1out of 8 discontinue ,8C1 means 8 ways.
= 2/10*3/10.8/10*1/10, (9/10 prodbability professor discontinue then 1/10)
in this way if we calculate for 8 possibilities then value is =>0.03733.
3rd case any 6 professors continue and 2out of 8 discontinue , 8C2 means 28 ways.
= 2/10*3/10.2/10*1/10( 2 professors discontinue.
if we calculate for 28 possibilites P value is=>0.1436
=0.00363+0.03733+0.1436=0.18456=
0.19
The probability of a bomb hitting a bridge is 1/2 and two direct hits are needed to destroy it. The least number of bombs required so that the probability of the bridge being destroyed is greater than 0.9 is:- a)7 bombs
- b)3 bombs
- c)8 bombs
- d)9 bombs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The probability of a bomb hitting a bridge is 1/2 and two direct hits are needed to destroy it. The least number of bombs required so that the probability of the bridge being destroyed is greater than 0.9 is:
a)
7 bombs
b)
3 bombs
c)
8 bombs
d)
9 bombs

|
Nandita Tiwari answered |
Try to find the number of ways in which 0 or 1 bomb hits the bridge if n bombs are thrown.
The required value of the number of bombs will be such that the probability of 0 or 1 bomb hitting the bridge should be less than 0.1.
The required value of the number of bombs will be such that the probability of 0 or 1 bomb hitting the bridge should be less than 0.1.
In a bag there are 12 black and 6 white balls. Two balls are chosen at random and the first one is found to be black. The probability that the second one is also black is:- a)11/17
- b)12/17
- c)13/18
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a bag there are 12 black and 6 white balls. Two balls are chosen at random and the first one is found to be black. The probability that the second one is also black is:
a)
11/17
b)
12/17
c)
13/18
d)
None of these
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
Probability of choosing a black ball as the first ball:
There are 12 black balls out of a total of 18 balls in the bag. Therefore, the probability of choosing a black ball as the first ball is given by:
P(Black) = 12/18 = 2/3
Probability of choosing a black ball as the second ball:
After the first ball is chosen and found to be black, there are now 11 black balls left out of a total of 17 balls in the bag. Therefore, the probability of choosing a black ball as the second ball, given that the first ball is black, is given by:
P(Black|Black) = 11/17
Explanation:
When the first ball is chosen and found to be black, it reduces the total number of balls in the bag to 17. Out of these 17 balls, there are still 11 black balls remaining. Therefore, the probability of choosing a black ball as the second ball, given that the first ball is black, is 11/17.
The reason why the answer is not 12/17 is because the first black ball that was chosen is not put back into the bag. Therefore, the total number of balls in the bag is reduced by 1, and the total number of black balls is also reduced by 1.
Since the two events (choosing the first ball and choosing the second ball) are dependent, we need to use conditional probability to calculate the probability of the second ball being black given that the first ball is black.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) 11/17, which represents the probability of the second ball being black given that the first ball is black.
There are 12 black balls out of a total of 18 balls in the bag. Therefore, the probability of choosing a black ball as the first ball is given by:
P(Black) = 12/18 = 2/3
Probability of choosing a black ball as the second ball:
After the first ball is chosen and found to be black, there are now 11 black balls left out of a total of 17 balls in the bag. Therefore, the probability of choosing a black ball as the second ball, given that the first ball is black, is given by:
P(Black|Black) = 11/17
Explanation:
When the first ball is chosen and found to be black, it reduces the total number of balls in the bag to 17. Out of these 17 balls, there are still 11 black balls remaining. Therefore, the probability of choosing a black ball as the second ball, given that the first ball is black, is 11/17.
The reason why the answer is not 12/17 is because the first black ball that was chosen is not put back into the bag. Therefore, the total number of balls in the bag is reduced by 1, and the total number of black balls is also reduced by 1.
Since the two events (choosing the first ball and choosing the second ball) are dependent, we need to use conditional probability to calculate the probability of the second ball being black given that the first ball is black.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) 11/17, which represents the probability of the second ball being black given that the first ball is black.
A letter is chosen at random from the letters of the word PROBABILITY. Find the probability that letter chosen is a vowel
- a)1/30
- b)4/11
- c)1/6
- d)1/5
- e)1/3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A letter is chosen at random from the letters of the word PROBABILITY. Find the probability that letter chosen is a vowel
a)
1/30
b)
4/11
c)
1/6
d)
1/5
e)
1/3

|
Riverdale Learning Institute answered |
On the first pick, two of the five letters are vowels — A & E — so the probability of picking a vowel on the first pick is 2/5. On the second pick, only one letter out of the six is a vowel — O — so the probability of picking a vowel on the second pick is 1/6. The two picks are independent: what one selects from one set has absolutely no bearing on what one picks from the other set. Therefore, we can use the generalized AND rule.
P(two vowels) = P(vowel on first pick)*P(vowel on second pick) = (2/5)*(1/6) = 2/30 = 1/15
Out of all the 2 - digit integers between 1 to 200, a 2-digit number has to be selected at random. What is the probability that the selected number is not divisible by 7?- a)11/90
- b)33/90
- c)55/90
- d)77/90
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of all the 2 - digit integers between 1 to 200, a 2-digit number has to be selected at random. What is the probability that the selected number is not divisible by 7?
a)
11/90
b)
33/90
c)
55/90
d)
77/90

|
Gowri Chakraborty answered |
There are total 90 two digit numbers, out of them 13 are divisible by 7, these are 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70, 77, 84, 91, 98.
Therefore, probability that selected number is not divisible by 7 = 1 – 13/90 = 77/90.
So, option (D) is true.
The odds against an event is 5 : 3 and the odds in favour of another independent event is 7 : 5. Find the probability that at least one of the two events will occur.- a)52/96
- b)69/96
- c)71/96
- d)13/96
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The odds against an event is 5 : 3 and the odds in favour of another independent event is 7 : 5. Find the probability that at least one of the two events will occur.
a)
52/96
b)
69/96
c)
71/96
d)
13/96

|
Jaya Gupta answered |
P (E1) 3/8
P (E2) = 7/12.
Event definition is: E1 occurs and E2 does not occur or E1 occurs and E2 occurs or E2 occurs and E1 does not occur.
Event definition is: E1 occurs and E2 does not occur or E1 occurs and E2 occurs or E2 occurs and E1 does not occur.
(3/8) x (5/12) + (3/8) x (7/12) + (5/8) x (7/12) = 71/96.
There are two sets of letters, and you are going to pick exactly one letter from each set.
Event A = {A, B, C, D, E}
Event B= {K, L, M, N, O, P}
What is the probability of picking a C or an M?
- a)1/30
- b)1/15
- c)1/6
- d)1/5
- e)1/3
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
There are two sets of letters, and you are going to pick exactly one letter from each set.
Event A = {A, B, C, D, E}
Event B= {K, L, M, N, O, P}
Event A = {A, B, C, D, E}
Event B= {K, L, M, N, O, P}
What is the probability of picking a C or an M?
a)
1/30
b)
1/15
c)
1/6
d)
1/5
e)
1/3

|
EduRev CLAT answered |
Picking an M is not disjoint with picking a C — they both could happen on the same round of the game. We have to use the generalized OR rule for this:
P(C or M) = P(C) + P(M) – P(C and M)
Fortunately, we know the first two, and we calculated the value of the third term already in #1.
P(C or M) = P(C) + P(M) – P(C and M)
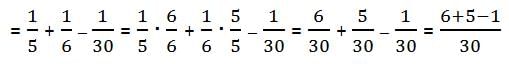
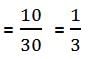
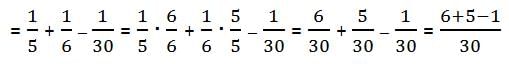
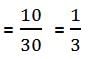
Chapter doubts & questions for Probability - Mathematics for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Probability - Mathematics for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Mathematics for JAMB
134 videos|94 docs|102 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily