All Exams >
JAMB >
Chemistry for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Electrolysis for JAMB Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Nernst equation for an electrode is based on the variation of electrode potential of an electrode with:
- A:
temperature only
- B:
Concentration of electrolyte only
- C:
Both a and b
- D:
Density of the electrodes
The answer is c.
Nernst equation for an electrode is based on the variation of electrode potential of an electrode with:
temperature only
Concentration of electrolyte only
Both a and b
Density of the electrodes
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Nernst equation for an electrode is based on the variation of electrode potential of an electrode with temperature and concentration of electrolyte.
Cell reaction is spontaneous when- a)EθRed is positive
- b)ΔGθ is positive
- c)ΔGθ is negative
- d)EθRed is negative.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell reaction is spontaneous when
a)
EθRed is positive
b)
ΔGθ is positive
c)
ΔGθ is negative
d)
EθRed is negative.
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
ΔGdegree must be negative for the reaction to be spontaneous.
Salt bridge is indicated in the cell representation by :- a)I
- b)!!
- c)((
- d)II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Salt bridge is indicated in the cell representation by :
a)
I
b)
!!
c)
((
d)
II
|
|
Khushi Pandey answered |
Indicàted by Twø parallel linés (||)
. In the construction of a salt bridge, saturated solution of KNO3 is used because:- a)Velocity of K+ and NO3– are same
- b)Velocity of NO3– is greater than that of K+
- c)Velocity of K+ is greater than that of NO3–
- d)KNO3 is highly soluble in water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
. In the construction of a salt bridge, saturated solution of KNO3 is used because:
a)
Velocity of K+ and NO3– are same
b)
Velocity of NO3– is greater than that of K+
c)
Velocity of K+ is greater than that of NO3–
d)
KNO3 is highly soluble in water
|
|
Riya Agarwal answered |
Velocities of both should be same to balance the amount of both ions in the soln. if the vel of any of them is more...then its ions will release more
The free energy change for the following cell reaction is given as :
2Au3+ (aq) + 3Cu (s) → 2Au (s) + 3Cu2+ (aq)
- a)6 FE°cell
- b)3 FE°cell
- c)-2 FE°cell
- d)-6 FE°cell
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The free energy change for the following cell reaction is given as :
2Au3+ (aq) + 3Cu (s) → 2Au (s) + 3Cu2+ (aq)
2Au3+ (aq) + 3Cu (s) → 2Au (s) + 3Cu2+ (aq)
a)
6 FE°cell
b)
3 FE°cell
c)
-2 FE°cell
d)
-6 FE°cell
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
EO = EOCa2+/ Ca - EOAu2+/ Au
= -2.87 - (1.50)
= -2.87 - 1.50
= -4.37 V
rGO = -nFEO
= -6 FEO
= -2.87 - (1.50)
= -2.87 - 1.50
= -4.37 V
rGO = -nFEO
= -6 FEO
The gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1 M Y- and 1 M Z- at 298 K.If the standard reduction potential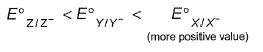 then,
then,- a)Y will oxidise X and not Z
- b)Y will oxidise Z and not X
- c)Y will oxidise both X and Z
- d)Z- will reduce both X and Y
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1 M Y- and 1 M Z- at 298 K.If the standard reduction potential
then,
a)
Y will oxidise X and not Z
b)
Y will oxidise Z and not X
c)
Y will oxidise both X and Z
d)
Z- will reduce both X and Y
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
In ECS, pair with more negative values of E°red reducing agent is above oxidising agent.
Thus, Z/Z- is the best reducing agent
Thus, Z- will reduce both X and Y and itself will be oxidised to Z .
For the cell, 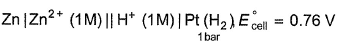 and for the cell Pt(H2) | H+ (1M)| Ag,
and for the cell Pt(H2) | H+ (1M)| Ag, 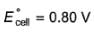 Thus Ecell for theAg|Ag+ (0.1M) || Zn2+ (0.1M) | Zn is ....................and cell reaction is...............
Thus Ecell for theAg|Ag+ (0.1M) || Zn2+ (0.1M) | Zn is ....................and cell reaction is...............- a)1.44 V ,spontaneous
- b)0.4 V ,spontaneous
- c)-1.44 V ,non-spontaneous
- d)-1.53 V ,non-spontaneous
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For the cell, 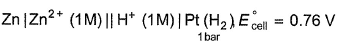 and for the cell Pt(H2) | H+ (1M)| Ag,
and for the cell Pt(H2) | H+ (1M)| Ag, 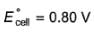
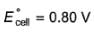
Thus Ecell for the
Ag|Ag+ (0.1M) || Zn2+ (0.1M) | Zn is ....................and cell reaction is...............
a)
1.44 V ,spontaneous
b)
0.4 V ,spontaneous
c)
-1.44 V ,non-spontaneous
d)
-1.53 V ,non-spontaneous
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Ecell < 0, hence reaction is non-spontaneous.
In the equation, ΔG° = – nF E° cell ; F is:- a)Boltzmann constant
- b)Faraday’s constant
- c)Gas constant
- d)Universal gas constant
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the equation, ΔG° = – nF E° cell ; F is:
a)
Boltzmann constant
b)
Faraday’s constant
c)
Gas constant
d)
Universal gas constant
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
The relationship between ΔGo and Eo is given by the following equation: ΔGo=−nFEo. Here, n is the number of moles of electrons and F is the Faraday constant.
The relationship between ΔGo and Eo is given by the following equation: ΔGo=−nFEo. Here, n is the number of moles of electrons and F is the Faraday constant.
Consider the cell reaction:
Cd(s) | Cd2+ (1.0 M) || Cu2+ (1.0 m) | Cu (s)
If we wish to make a cell with more positive voltage using the same substances, we should:
- a)Increase [Cd2+] as well as [Cu2+] to 2.0 M
- b)Increase only [Cu2+] to 2.0 M
- c)Reduce only [Cd2+] to 0.1 M
- d)Decreases [Cd2+] to 0.1M and increases [Cu2+] to 1.0M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the cell reaction:
Cd(s) | Cd2+ (1.0 M) || Cu2+ (1.0 m) | Cu (s)
If we wish to make a cell with more positive voltage using the same substances, we should:
Cd(s) | Cd2+ (1.0 M) || Cu2+ (1.0 m) | Cu (s)
If we wish to make a cell with more positive voltage using the same substances, we should:
a)
Increase [Cd2+] as well as [Cu2+] to 2.0 M
b)
Increase only [Cu2+] to 2.0 M
c)
Reduce only [Cd2+] to 0.1 M
d)
Decreases [Cd2+] to 0.1M and increases [Cu2+] to 1.0M
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Redox reaction:
Cd(s)→Cd2++2e
Cu2++2e→Cu(s)
Ecell = E°cell − (0.059/2) log ([Cd2+]/ [Cu2+])
Decreases [Cd2+] to 0.1M and increases [Cu2+] to 1.0M
Cd(s)→Cd2++2e
Cu2++2e→Cu(s)
Ecell = E°cell − (0.059/2) log ([Cd2+]/ [Cu2+])
Decreases [Cd2+] to 0.1M and increases [Cu2+] to 1.0M
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a lower reduction potential will act as:- a)Salt bridge
- b)Electrolyte
- c)Anode
- d)Cathode
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a lower reduction potential will act as:
a)
Salt bridge
b)
Electrolyte
c)
Anode
d)
Cathode
|
|
Sargam Singh answered |
A substance with lower reduction potential has more tendency to oxidize .in a electrochemical cell anode performs oxidation reaction hence the electrode will function as a anode
Gibbs free energy change for a cell reaction is positive what does it indicates?- a)cell will discharge easily
- b)Cell reaction is spontaneous
- c)Cell reaction is non spontaneous
- d)Cell will work under standard conditions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gibbs free energy change for a cell reaction is positive what does it indicates?
a)
cell will discharge easily
b)
Cell reaction is spontaneous
c)
Cell reaction is non spontaneous
d)
Cell will work under standard conditions
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
No, reaction cannot be spontaneous (continue to happen) when the change in gibbs free energy is positive. ... For a spontaneous process to happen , the change in Gibbs free energy must be negative. A roaring bonfire is an example of a spontaneous reaction.
Three cell A, B and C has equilibrium constant in the ratio 1:4 : 9 respectively. Arrange the following cells in the order of increasing Gibbs free energy.- a)A>B>C
- b)Cannot be answered
- c)B>C>A
- d)A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Three cell A, B and C has equilibrium constant in the ratio 1:4 : 9 respectively. Arrange the following cells in the order of increasing Gibbs free energy.
a)
A>B>C
b)
Cannot be answered
c)
B>C>A
d)
A
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
A>B>C
Smaller the value of equilibrium constant (k) larger will be value of Gibbs free energy.
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at cathode is:- a)Hydrolysis
- b)Reduction
- c)Oxidation
- d)Neutralization
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at cathode is:
a)
Hydrolysis
b)
Reduction
c)
Oxidation
d)
Neutralization
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
The electrode at which oxidation takes place is known as the anode, while the electrode at which reduction take place is called the cathode. If you see galvanic cell reduction take place at the left electrode, so the left one is the cathode. Oxidation takes place at the right electrode, so the right one is the anode.
For the following cell with hydrogen electrodes at two different pressure p1 and p2 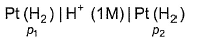 emf is given by
emf is given by- a)
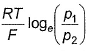
- b)
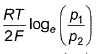
- c)
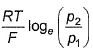
- d)
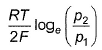
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the following cell with hydrogen electrodes at two different pressure p1 and p2 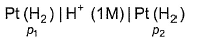
emf is given by
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
For SHE E°SHE = 0.00 V
Oxidation at anode (left)
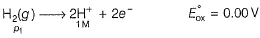
Reduction at cathode (right)
Net
Oxidation at anode (left)
Reduction at cathode (right)
Net
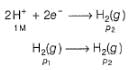
This is the type of the cell in which electrodes at different pressures are dipped in same electrolyte and connectivity is made by a salt-bridge.
Reaction Quotient (Q) 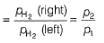
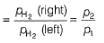
∵
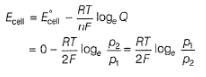
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at anode is:- a)Reduction
- b)Neutralization
- c)Hydrolysis
- d)Oxidation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at anode is:
a)
Reduction
b)
Neutralization
c)
Hydrolysis
d)
Oxidation
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Oxidation takes place at the right electrode, so the right one is the anode. While in electrolytic cell reduction takes place at the right electrode, so right one is the cathode. Oxidation takes place at the left electrode, so the left one is the anode.
At equilibrium:- a)Cell potential’ E cell‘ becomes zero
- b)Equilibrium constant becomes equal to electrode potential
- c)Equilibrium constant becomes zero
- d)Cell potential ‘E cell‘ becomes unity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At equilibrium:
a)
Cell potential’ E cell‘ becomes zero
b)
Equilibrium constant becomes equal to electrode potential
c)
Equilibrium constant becomes zero
d)
Cell potential ‘E cell‘ becomes unity

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
E cell is 0 in equilibrium that is E cathode becomes equal to E anode ………. ... So E cell is zero at equilibrium that is when the E(cathode) becomes equal to E(anode). E deg cell is zero in the concentration cell when both the electrodes are of the same metal.
A solution of Fe2+ is titrated potentiometrically using Ce4+ solution.Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e- , E0 = -0.77 Vemf of the Pt | Fe2+ , Fe3+ pair at 50% and 90% titration of Fe2+ are - a)0.77 V , 0.826 V
- b)-0.826 V , -0.77 V
- c)-0.77 V ,-0.826 V
- d)0.00 V , 0.00 V
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution of Fe2+ is titrated potentiometrically using Ce4+ solution.
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e- , E0 = -0.77 V
emf of the Pt | Fe2+ , Fe3+ pair at 50% and 90% titration of Fe2+ are
a)
0.77 V , 0.826 V
b)
-0.826 V , -0.77 V
c)
-0.77 V ,-0.826 V
d)
0.00 V , 0.00 V
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
When Fe2+ is 50% titrated
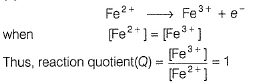
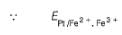 =
=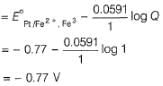
where Fe2+ is 90% titrated
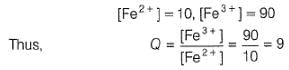
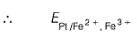
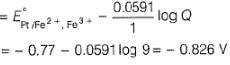
The cell representation of the given reaction is:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu(s)- a)Zn|zn2+||Cu2+|Cu
- b)Cu2+|Cu||Zn|zn2+
- c)Zn|zn2+||Cu|Cu2+
- d)Cu|Cu2+||zn2+|Zn
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell representation of the given reaction is:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu(s)
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu(s)
a)
Zn|zn2+||Cu2+|Cu
b)
Cu2+|Cu||Zn|zn2+
c)
Zn|zn2+||Cu|Cu2+
d)
Cu|Cu2+||zn2+|Zn
|
|
Atishay Jain answered |
Answer is A because Zn oxidized in Zn+2 and Cu+2 reduced in Cu.So Zn is anode and Cu is cathode.
A concentration cell reversible to anion (Cl-) is set up 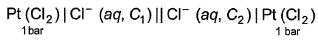 cell reaction is spontaneous ,if
cell reaction is spontaneous ,if - a)C1 > C2
- b)C1 < C2
- c)C1 = C2
- d)C1 = 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A concentration cell reversible to anion (Cl-) is set up
cell reaction is spontaneous ,if
a)
C1 > C2
b)
C1 < C2
c)
C1 = C2
d)
C1 = 0
|
|
Om Desai answered |
This is a type of concentration cell with gas electrodes at the same pressure (1 bar) but dipped in aqueous solution of different concentration. Hence, a potential difference is set up.
At anode
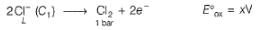
At cathode
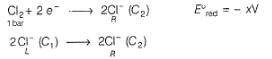
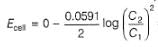
= 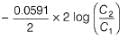
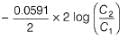
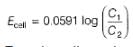
To make cell reaction spontaneous, Ecell > 0, hence C, > C2
If a salt bridge is removed between the half cells, the voltage- a)Decreases to zero
- b)Increases
- c)Increases rapidly
- d)Do not change
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a salt bridge is removed between the half cells, the voltage
a)
Decreases to zero
b)
Increases
c)
Increases rapidly
d)
Do not change
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
The purpose of a salt bridge is not to move electrons from the electrolyte, rather maintain charge balance because the electrons are moving from one-half cell to the other. The electrons flow from the anode to the cathode thus if a salt bridge is removed between the half cells, the voltage becomes zero.
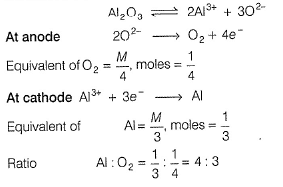
When Al2O3 is electrolysed ,cation and anions are discharged. For a given quantity of electricity,ratio of number of moles of Al and O2 gas is - a)1 : 1
- b)2 : 1
- c)2 : 3
- d)4 : 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When Al2O3 is electrolysed ,cation and anions are discharged. For a given quantity of electricity,ratio of number of moles of Al and O2 gas is
a)
1 : 1
b)
2 : 1
c)
2 : 3
d)
4 : 3
|
|
Niti Mishra answered |
When same quantity of electricity is passed, elements/gases are formed in the ratio of their equivalents
 .
.
"Maintenance-free" batteries now in use in place of commom batteries ,have- a)electrodes made of lead-lead oxide
- b)electrodes made of calcium-containing lead alloy
- c)non-aqueous solvents as medium
- d)platinum electrodes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
"Maintenance-free" batteries now in use in place of commom batteries ,have
a)
electrodes made of lead-lead oxide
b)
electrodes made of calcium-containing lead alloy
c)
non-aqueous solvents as medium
d)
platinum electrodes

|
Nishtha Bose answered |
In lead-acid storage battery, specific gravity of H2SO4 changes and water is to be added periodically. In maintenance free battery calcium-containing lead alloy that prevents the electrolytic decomposition of H2O. These batteries are sealed and no maintenance is required
In a Daniel cell, the oxidation and reduction halves occur at:- a)copper and zinc electrodes respectively
- b)zinc and copper electrodes respectively
- c)both occur at copper electrode respectively
- d)both occur at zinc electrode respectively
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a Daniel cell, the oxidation and reduction halves occur at:
a)
copper and zinc electrodes respectively
b)
zinc and copper electrodes respectively
c)
both occur at copper electrode respectively
d)
both occur at zinc electrode respectively
|
|
Ameya Pillai answered |
The correct answer is option 'B': zinc and copper electrodes respectively.
Explanation:
A Daniel cell is an electrochemical cell that consists of two half-cells connected by a salt bridge. The two half-cells are the oxidation half-cell and the reduction half-cell.
1. Oxidation Half-Cell:
In the oxidation half-cell, oxidation occurs. This means that electrons are lost by the electrode material and transferred to the external circuit. In the Daniel cell, the zinc electrode is the site of oxidation. Zinc atoms lose two electrons to form Zn2+ ions:
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e-
2. Reduction Half-Cell:
In the reduction half-cell, reduction occurs. This means that electrons are gained by the electrode material from the external circuit. In the Daniel cell, the copper electrode is the site of reduction. Copper(II) ions from the copper sulfate solution in the reduction half-cell gain two electrons to form copper atoms:
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)
3. Overall Cell Reaction:
The overall cell reaction can be obtained by combining the oxidation and reduction half-reactions. Since the number of electrons lost in the oxidation half-reaction is equal to the number of electrons gained in the reduction half-reaction, the two half-reactions can be added together to obtain the overall cell reaction:
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
4. Cell Diagram:
The cell diagram for a Daniel cell is represented as:
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
In conclusion, in a Daniel cell, the oxidation half occurs at the zinc electrode and the reduction half occurs at the copper electrode. This allows for the flow of electrons from the zinc electrode to the copper electrode through the external circuit, generating an electric current.
Explanation:
A Daniel cell is an electrochemical cell that consists of two half-cells connected by a salt bridge. The two half-cells are the oxidation half-cell and the reduction half-cell.
1. Oxidation Half-Cell:
In the oxidation half-cell, oxidation occurs. This means that electrons are lost by the electrode material and transferred to the external circuit. In the Daniel cell, the zinc electrode is the site of oxidation. Zinc atoms lose two electrons to form Zn2+ ions:
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e-
2. Reduction Half-Cell:
In the reduction half-cell, reduction occurs. This means that electrons are gained by the electrode material from the external circuit. In the Daniel cell, the copper electrode is the site of reduction. Copper(II) ions from the copper sulfate solution in the reduction half-cell gain two electrons to form copper atoms:
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)
3. Overall Cell Reaction:
The overall cell reaction can be obtained by combining the oxidation and reduction half-reactions. Since the number of electrons lost in the oxidation half-reaction is equal to the number of electrons gained in the reduction half-reaction, the two half-reactions can be added together to obtain the overall cell reaction:
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
4. Cell Diagram:
The cell diagram for a Daniel cell is represented as:
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
In conclusion, in a Daniel cell, the oxidation half occurs at the zinc electrode and the reduction half occurs at the copper electrode. This allows for the flow of electrons from the zinc electrode to the copper electrode through the external circuit, generating an electric current.
Two half-cells are given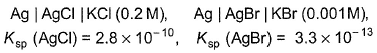 For a spontaneous cell reaction, cell set up is
For a spontaneous cell reaction, cell set up is - a)Ag| AgCI| KCI (0.2M) 11 KBr (0.001 M)| AgBr| Ag
- b)Ag| AgBr| KBr (0.001 M) 11 KCI (0.2 M) | AgCI | Ag
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two half-cells are given
For a spontaneous cell reaction, cell set up is
a)
Ag| AgCI| KCI (0.2M) 11 KBr (0.001 M)| AgBr| Ag
b)
Ag| AgBr| KBr (0.001 M) 11 KCI (0.2 M) | AgCI | Ag
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
None of the above
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Ksp (AgCI) = 2.8 x 10-10
[Ag+] [Cl-] = 2 .8 x 10-10
[Ag+] [Cl-] = 2 .8 x 10-10
∴ [Ag+]left = 
Ksp (AgBr) = 3.3 x 10-12
[Ag+][Br-] = 3.3 x 10-13

Ksp (AgBr) = 3.3 x 10-12
[Ag+][Br-] = 3.3 x 10-13
∴ [Ag+]left = 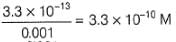
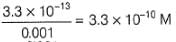
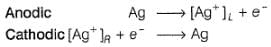
Net
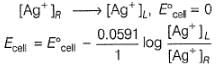
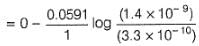
= -0.037 V
Thus, cell reaction is non-spontaneous
(b) Cell is reversed of (a), thus spontaneous.
Thus, cell reaction is non-spontaneous
(b) Cell is reversed of (a), thus spontaneous.
. For an equation: Ni(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Ni2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) the Nernst equation is written as:- a)
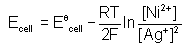
- b)
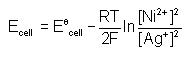
- c)
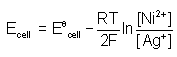
- d)
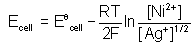
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
. For an equation: Ni(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Ni2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) the Nernst equation is written as:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Oxidation:
Ni(s) ---> Ni2+(aq) + 2e-
Reduction:
2Ni+(aq) + 2e- ----> 2Aq(s)
2e- are in the above reaction so;
n = 2
We know that
Ecell = Eocell – (RT/nF) lnKc
= Eocell – (RT/nF) ln ([Ni]2+ / [Ag+]2
Oxidation:
Ni(s) ---> Ni2+(aq) + 2e-
Reduction:
2Ni+(aq) + 2e- ----> 2Aq(s)
2e- are in the above reaction so;
n = 2
We know that
Ecell = Eocell – (RT/nF) lnKc
= Eocell – (RT/nF) ln ([Ni]2+ / [Ag+]2
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a higher reduction potential will act as:- a)salt bridge
- b)Electrolyte
- c)Anode
- d)Cathode
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a higher reduction potential will act as:
a)
salt bridge
b)
Electrolyte
c)
Anode
d)
Cathode
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is option D.
Reduction potential refers to the voltage required to reduce a material under standard conditions. If a material has a higher reduction potential it takes more energy to reduce it than a lower reduction potential material. Therefore the higher reduction potential material is actually oxidized to reduce the lower reduction potential material.
Cathode- The electrode where reduction occurs and
The one with the highest reduction potential selected as the reduction half-reaction and therefore is cathode.
Cathode- The electrode where reduction occurs and
The one with the highest reduction potential selected as the reduction half-reaction and therefore is cathode.
Select the correct statement(s).- a)In lead-storage battery,galvanic cell are linked in series
- b)Cathode and anode compartments are not seperated in a battery as oxidant and reductant both are solids
- c)Recharging of a storage battery is a non-spontaneous (ΔG° > 0)
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s).
a)
In lead-storage battery,galvanic cell are linked in series
b)
Cathode and anode compartments are not seperated in a battery as oxidant and reductant both are solids
c)
Recharging of a storage battery is a non-spontaneous (ΔG° > 0)
d)
All of the above
|
|
Kalyan Chavan answered |
(a) A typical 12V battery consists of six cells connected in series each cell providing a potential of about 2V -correct
(b) No separation of cathodic and anodic compartment, species being in solid state -correct
(c) During recharging, E° < 0, thus ΔG° > 0-correct.
(b) No separation of cathodic and anodic compartment, species being in solid state -correct
(c) During recharging, E° < 0, thus ΔG° > 0-correct.
Passage IIThe electrodes in a lead-storage battery are made of Pb and PbO2. During discharge following reactions occurs:Pb +PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O (Pb = 207); E0 = 2.00vQ. Under zero load ,average voltage is 2.00 V,then ΔG° is - a)386 kJ
- b)-386 kJ
- c)-193 kJ
- d)-572 kJ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
The electrodes in a lead-storage battery are made of Pb and PbO2. During discharge following reactions occurs:
Pb +PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O (Pb = 207); E0 = 2.00v
Q.
Under zero load ,average voltage is 2.00 V,then ΔG° is
a)
386 kJ
b)
-386 kJ
c)
-193 kJ
d)
-572 kJ

|
Aravind Mehra answered |
In battery H2SO4 ionises as
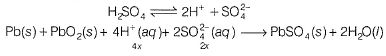
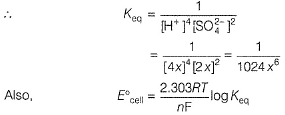
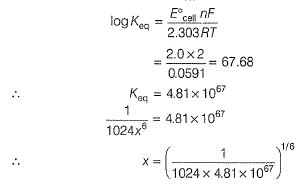
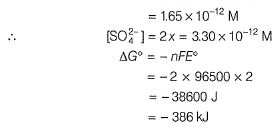
Following are certain facts about batteries.
I. They are classified as primary, secondary and flow batteries.
II. Leclanche cell is a primary battery.
III. Lead-acid (storage) battery is a secondary cell.Select the correct facts.- a)I , II
- b)I , III
- c)II , III
- d)I , II , III
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Following are certain facts about batteries.
I. They are classified as primary, secondary and flow batteries.
II. Leclanche cell is a primary battery.
III. Lead-acid (storage) battery is a secondary cell.
I. They are classified as primary, secondary and flow batteries.
II. Leclanche cell is a primary battery.
III. Lead-acid (storage) battery is a secondary cell.
Select the correct facts.
a)
I , II
b)
I , III
c)
II , III
d)
I , II , III

|
Shreya Gupta answered |
I. Primary Leclanche cell.
Secondary Lead-storage
Flow battery Fuel-cell
II. True
III. True
Secondary Lead-storage
Flow battery Fuel-cell
II. True
III. True
Passage IIThe electrodes in a lead-storage battery are made of Pb and PbO2. During discharge following reactions occurs:Pb +PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O (Pb = 207); E0 = 2.00vQ. [SO42-] due to 4.8 M H2SO4 in lead-storage battery is - a)1.0 X 10-12 M
- b)4.8 M
- c)3.3 X 10-12 M
- d)9.6 M
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
The electrodes in a lead-storage battery are made of Pb and PbO2. During discharge following reactions occurs:
Pb +PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O (Pb = 207); E0 = 2.00v
Q.
[SO42-] due to 4.8 M H2SO4 in lead-storage battery is
a)
1.0 X 10-12 M
b)
4.8 M
c)
3.3 X 10-12 M
d)
9.6 M

|
Ishani Yadav answered |
In battery H2SO4 ionises as
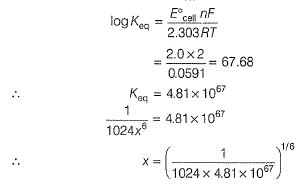
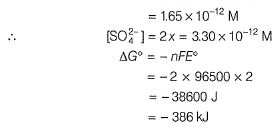
Only One Option Correct TypeThis section contains 16 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctQ. During the electrolysis of aqueous Zn(NO3)2 solution- a)Zn plates out at the cathode
- b)Zn plates out at the anode
- c)H2 gas is evolved at the anode
- d)O2 gas is evolved at the anode
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 16 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q.
During the electrolysis of aqueous Zn(NO3)2 solution
a)
Zn plates out at the cathode
b)
Zn plates out at the anode
c)
H2 gas is evolved at the anode
d)
O2 gas is evolved at the anode

|
Gauri Khanna answered |
In preference to reduction of Zn2+ at cathode, O2- (aq) is oxidised to O2 at anode.
In the electrorefining of metals, impure metal is- a)cathode and oxidation taken place
- b)anode and oxidation takes place
- c)anode and reduction takes place
- d)cathode and reduction takes place
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the electrorefining of metals, impure metal is
a)
cathode and oxidation taken place
b)
anode and oxidation takes place
c)
anode and reduction takes place
d)
cathode and reduction takes place

|
Ameya Basu answered |
Electrorefining of Metals:
In the electrorefining process, impure metal is purified through electrolysis.
Impure Metal as Anode:
- In electrorefining, the impure metal is attached to the anode.
- The anode undergoes oxidation, where the impurities present in the metal are oxidized and dissolve into the electrolyte.
- This leaves behind a more pure form of the metal at the cathode.
Therefore, the correct statement is:
Option B: Anode and oxidation takes place
In the electrorefining process, impure metal is purified through electrolysis.
Impure Metal as Anode:
- In electrorefining, the impure metal is attached to the anode.
- The anode undergoes oxidation, where the impurities present in the metal are oxidized and dissolve into the electrolyte.
- This leaves behind a more pure form of the metal at the cathode.
Therefore, the correct statement is:
Option B: Anode and oxidation takes place
A solution of copper(II) sulphate (VI) is electrolysed between copper electrodes by a currrent of 10.0 A for exactly 9650 s.Which remains unchanged?- a)Molar concentration of solution
- b)Cathodic plate
- c)Anodic plate
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution of copper(II) sulphate (VI) is electrolysed between copper electrodes by a currrent of 10.0 A for exactly 9650 s.Which remains unchanged?
a)
Molar concentration of solution
b)
Cathodic plate
c)
Anodic plate
d)
All of these

|
Ishani Patel answered |
0.5 mole of copper is dissolved from the anode. Thus, its mass decreases. 0.5 mole of copper from the anode is deposited at the cathode. Thus, its mass increases.
Thus, molar concentration of aqueous solution of CuSO4 remains unchanged.
One or More than One Options Correct TypeThis section contains 4 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Select the correct statement(s).- a)If salt-bridge is removed,potentials falls to zero
- b)Quinhydrone electrode is reversible to H+ ion
- c)Liquid-junction potential developed across the boundary of the two solutions of different concentration is minimised if concentrations cell are used
- d)Calomel electrode contains calcium chloride solution in contact with Pt electrode
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 4 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Select the correct statement(s).
a)
If salt-bridge is removed,potentials falls to zero
b)
Quinhydrone electrode is reversible to H+ ion
c)
Liquid-junction potential developed across the boundary of the two solutions of different concentration is minimised if concentrations cell are used
d)
Calomel electrode contains calcium chloride solution in contact with Pt electrode
|
|
Raghavendra Rane answered |
a) If salt-bridge is removed, anodic and cathodic solution intermix and potential difference falls to zero — correct.
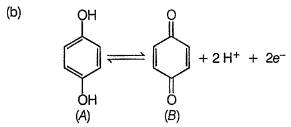
Quinhydrone is a mixture of A and S in (1:1) molar ratio joined by H-bonding. Above equilibrium is set up in aqueous solution.
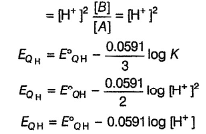
If [H+] changes, EQH also changes. Thus, quinhydrone electrode is reversible to H+ ion correct
(c) Liquid junction potential is minimised by use of concentration cell— correct.
(d) Calomel electrode is Hg(/), Hg2Cl2 (s)| Cl-.
Thus, (d) is incorrect.
Quinhydrone is a mixture of A and S in (1:1) molar ratio joined by H-bonding. Above equilibrium is set up in aqueous solution.
If [H+] changes, EQH also changes. Thus, quinhydrone electrode is reversible to H+ ion correct
(c) Liquid junction potential is minimised by use of concentration cell— correct.
(d) Calomel electrode is Hg(/), Hg2Cl2 (s)| Cl-.
Thus, (d) is incorrect.
Only One Option Correct TypeThis section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q.Cl2 gas is passed into a solution containing KF, Kl and KBr, and CHCI3 is added. There is a colour in CHCI3 (lower) layer. It is due to - a)formation of l2 (violet)
- b)formation of Br2 (orange)
- c)formation of l2 and Br2 both
- d)formation of F2 (colourless)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Cl2 gas is passed into a solution containing KF, Kl and KBr, and CHCI3 is added. There is a colour in CHCI3 (lower) layer. It is due to
a)
formation of l2 (violet)
b)
formation of Br2 (orange)
c)
formation of l2 and Br2 both
d)
formation of F2 (colourless)
|
|
Mihir Joshi answered |
Based on electro chemical series, oxidising power of
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2

On passing Cl2 in to a solution containing KF, Kl and KBr,
2KBr + Cl2 → 2KCI + Br2 (orange)
2KI + Cl2 → 2KCI + l2 (violet)
2KI + Br2 → 2KBr + l2 (violet)
Br2 formed also oxidises Kl to l2 (violet)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
On passing Cl2 in to a solution containing KF, Kl and KBr,
2KBr + Cl2 → 2KCI + Br2 (orange)
2KI + Cl2 → 2KCI + l2 (violet)
2KI + Br2 → 2KBr + l2 (violet)
Br2 formed also oxidises Kl to l2 (violet)
The standard reduction potential values of three metallic cations X, Y, Z are 0.52, -3.03 and -1.18 V respectively. The order of reducing power of the corresponding metals is- a)Y > Z > X
- b)X > Y > Z
- c)Z > Y > X
- d)Z > X > Y
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard reduction potential values of three metallic cations X, Y, Z are 0.52, -3.03 and -1.18 V respectively. The order of reducing power of the corresponding metals is
a)
Y > Z > X
b)
X > Y > Z
c)
Z > Y > X
d)
Z > X > Y

|
Keerthana Mehta answered |
E°x = - 0.52 V
E°y = -3.03 V
E°z = - 1.18 V
E°y = -3.03 V
E°z = - 1.18 V
Their placements in ECS is in order Y > Z > X.
Thus, reducing nature is also in same order y > Z > X
Thus, reducing nature is also in same order y > Z > X
100 mL of a buffer of 1 M NH3(aq) and 1 M NH4+(aq) are placed in two volatic cells separately.A current of 1.5 A is passed through both cells for 20 min. If electrolysis of water only takes place2H2O +O2 + 4e- → 4OH- (RHS2H2O → 4H+. + O2 + 4e- (LHS)then pH of the - a)LHS half-cell will increase
- b)RHS half-cell will increase
- c)both half-cell will increase
- d)both half-cell will decrease
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
100 mL of a buffer of 1 M NH3(aq) and 1 M NH4+(aq) are placed in two volatic cells separately.A current of 1.5 A is passed through both cells for 20 min. If electrolysis of water only takes place
2H2O +O2 + 4e- → 4OH- (RHS
2H2O → 4H+. + O2 + 4e- (LHS)
then pH of the
a)
LHS half-cell will increase
b)
RHS half-cell will increase
c)
both half-cell will increase
d)
both half-cell will decrease

|
Sinjini Tiwari answered |
In RHS, [NH3] increases hence, pOH decreases
pH = 14 - pOH
Hence, pH of RHS increases.
In LHS, [NH4+] increases, hence pOH increases and pH decreases.
In a fuel cell, following reactions takes place and electricity is produced. AnodicH2+2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-CathodicO2+2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-If 100.8 L of H2 at STP reacts in 96500 s,what is the average current produced (in ampere)? - a)1.0 mol
- b)2.0 mol
- c)3.0 mol
- d)4.0 mol
Correct answer is '9'. Can you explain this answer?
In a fuel cell, following reactions takes place and electricity is produced.
Anodic
H2+2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-
Cathodic
O2+2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-
If 100.8 L of H2 at STP reacts in 96500 s,what is the average current produced (in ampere)?
a)
1.0 mol
b)
2.0 mol
c)
3.0 mol
d)
4.0 mol

|
Dipanjan Majumdar answered |
-> 2H2O + 4e- + 4OH-
Cathodic
O2 + 4e- + 2H2O -> 4OH-
Overall reaction
2H2 + O2 -> 2H2O
Cathodic
O2 + 4e- + 2H2O -> 4OH-
Overall reaction
2H2 + O2 -> 2H2O
One Integer Value Correct TypeThis section contains a question, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q. An expensive but lighter alternate to the lead storage battery is the silver-zinc battery.Ag2O(s) + Zn(s) + H2O(l) → Zn (OH)2 (s) + 2Ag(s); E0 = 1.5544VNumerical value of ΔG° in scientific notation is X x 10Y J.What is the value of X + Y?
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
This section contains a question, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q.
An expensive but lighter alternate to the lead storage battery is the silver-zinc battery.
Ag2O(s) + Zn(s) + H2O(l) → Zn (OH)2 (s) + 2Ag(s); E0 = 1.5544V
Numerical value of ΔG° in scientific notation is X x 10Y J.What is the value of X + Y?

|
Shreya Gupta answered |
ΔG°= -nFE° = -2 x 96500 x 1.5544 J
= -3 x 105
= x x 10y
Thus, x + y = 8
= -3 x 105
= x x 10y
Thus, x + y = 8
Rusting of iron or corrosion of active metal is initiated by- a)cathodic reaction, when oxygen gas which is dissolved in H2O, is reduced to OH-
- b)acid rain which oxidises metal to metal ion
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rusting of iron or corrosion of active metal is initiated by
a)
cathodic reaction, when oxygen gas which is dissolved in H2O, is reduced to OH-
b)
acid rain which oxidises metal to metal ion
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
None of the above

|
Ishani Yadav answered |
Acid rain causes corrosion of metals. Even Cu, Ag and Pb are corroded.
Only One Option Correct TypeThis section contains 18 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Which cell will measure the standard electrode potential of zinc electrode?- a)P t(s)|H2(g, 0.1 bar) | H+ (aq, 0.1 M) || Zn2+ (aq, 0.1 M)|
- b)P t(s)|H2(g, 0.1 bar) | H+ (aq, 0.1 M) || Zn2+ (aq, 0.2 M)| Zn
- c)P t(s)|H2(g, 0.1 bar) | H+ (aq, 0.1 M) || Zn2+ (aq, 1.0 M)| Zn
- d)P t(s)|H2(g, 0.1 bar) | H+ (aq, 1.0 M) || Zn2+ (aq, 0.1 M)| Zn
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 18 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which cell will measure the standard electrode potential of zinc electrode?
a)
P t(s)|H2(g, 0.1 bar) | H+ (aq, 0.1 M) || Zn2+ (aq, 0.1 M)|
b)
P t(s)|H2(g, 0.1 bar) | H+ (aq, 0.1 M) || Zn2+ (aq, 0.2 M)| Zn
c)
P t(s)|H2(g, 0.1 bar) | H+ (aq, 0.1 M) || Zn2+ (aq, 1.0 M)| Zn
d)
P t(s)|H2(g, 0.1 bar) | H+ (aq, 1.0 M) || Zn2+ (aq, 0.1 M)| Zn

|
Mrinalini Chopra answered |
Standard electrode potential is the potential difference under standard state, i.e.
When [Mn+] = 1M
It can be measured by coupling it with SHE electrode
Pt (s) | H2(gr. 1 bar) | H+ (1.0 M)
When [Mn+] = 1M
It can be measured by coupling it with SHE electrode
Pt (s) | H2(gr. 1 bar) | H+ (1.0 M)
Select the correct observation about electrolysis.- a)Electric current is used to drive a non-spontaneous reaction
- b)Ecell is positive and ΔG is negative
- c)Cations and anions are discharged at the cathode and anode respectively
- d)Overvoltage is responsible that a particular reaction takes place
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct observation about electrolysis.
a)
Electric current is used to drive a non-spontaneous reaction
b)
Ecell is positive and ΔG is negative
c)
Cations and anions are discharged at the cathode and anode respectively
d)
Overvoltage is responsible that a particular reaction takes place
|
|
Shalini Choudhary answered |
Thus, electric current is used to carry out a non-spontaneous reaction.
Thus. (a) is correct.
(b) Since reactions are reverse of electrochemical cell, hence
Thus. (a) is correct.
(b) Since reactions are reverse of electrochemical cell, hence
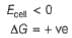
thus, (b) is incorrect
(c) cation goes to cathode and anion goes to anode and are discharged. Thus, correct
(d) some additional voltage called overvoltage is set up and thus other reactions also take place. thus correct
In the following batteries, alkaline electrolytes are usedI. Mercury
II. Nickel-cadmium
III. Modified Leclanche cell Cell potential is found to be independent of [OH-] in- a)I , II , III
- b)I ,II
- c)II , III
- d)Only III
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following batteries, alkaline electrolytes are used
I. Mercury
II. Nickel-cadmium
III. Modified Leclanche cell Cell potential is found to be independent of [OH-] in
II. Nickel-cadmium
III. Modified Leclanche cell Cell potential is found to be independent of [OH-] in
a)
I , II , III
b)
I ,II
c)
II , III
d)
Only III
|
|
Upasana Sen answered |
Mercury Battery:
- Mercury batteries, also known as mercuric oxide batteries, use a combination of mercuric oxide and zinc as the electrode materials.
- The electrolyte in mercury batteries is typically an alkaline electrolyte, which is a solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- The alkaline electrolyte facilitates the flow of ions between the electrodes, allowing the battery to generate an electric current.
- The cell potential of a mercury battery is not dependent on the concentration of hydroxide ions ([OH-]) in the electrolyte. Therefore, the cell potential remains constant regardless of the [OH-] concentration.
Nickel-Cadmium Battery:
- Nickel-cadmium batteries, also known as NiCd batteries, use nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as the electrode materials.
- The electrolyte in NiCd batteries is typically an alkaline electrolyte, which is usually a solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- Similar to mercury batteries, the alkaline electrolyte in NiCd batteries facilitates the flow of ions between the electrodes, allowing the battery to generate an electric current.
- The cell potential of a NiCd battery is also not dependent on the concentration of hydroxide ions ([OH-]) in the electrolyte. Therefore, the cell potential remains constant regardless of the [OH-] concentration.
Modified Leclanche Cell:
- The Leclanche cell is a type of primary battery that uses a zinc anode and a carbon cathode.
- In a modified Leclanche cell, the electrolyte is typically a paste made of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and zinc chloride (ZnCl2) dissolved in water.
- The cell potential of a modified Leclanche cell is not dependent on the concentration of hydroxide ions ([OH-]) in the electrolyte. Therefore, the cell potential remains constant regardless of the [OH-] concentration.
Overall Explanation:
- Alkaline electrolytes, such as solutions of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH), are commonly used in different types of batteries to facilitate ion flow and enable the generation of electric current.
- In the case of mercury batteries, nickel-cadmium batteries, and modified Leclanche cells, alkaline electrolytes are used.
- The cell potential of these batteries is not affected by the concentration of hydroxide ions ([OH-]) in the electrolyte.
- Therefore, the cell potential remains constant regardless of the [OH-] concentration.
- As a result, the correct answer to the given question is option 'A' - I, II, III, meaning that all three types of batteries mentioned (mercury battery, nickel-cadmium battery, and modified Leclanche cell) use alkaline electrolytes and have a cell potential that is independent of [OH-] concentration.
- Mercury batteries, also known as mercuric oxide batteries, use a combination of mercuric oxide and zinc as the electrode materials.
- The electrolyte in mercury batteries is typically an alkaline electrolyte, which is a solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- The alkaline electrolyte facilitates the flow of ions between the electrodes, allowing the battery to generate an electric current.
- The cell potential of a mercury battery is not dependent on the concentration of hydroxide ions ([OH-]) in the electrolyte. Therefore, the cell potential remains constant regardless of the [OH-] concentration.
Nickel-Cadmium Battery:
- Nickel-cadmium batteries, also known as NiCd batteries, use nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as the electrode materials.
- The electrolyte in NiCd batteries is typically an alkaline electrolyte, which is usually a solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- Similar to mercury batteries, the alkaline electrolyte in NiCd batteries facilitates the flow of ions between the electrodes, allowing the battery to generate an electric current.
- The cell potential of a NiCd battery is also not dependent on the concentration of hydroxide ions ([OH-]) in the electrolyte. Therefore, the cell potential remains constant regardless of the [OH-] concentration.
Modified Leclanche Cell:
- The Leclanche cell is a type of primary battery that uses a zinc anode and a carbon cathode.
- In a modified Leclanche cell, the electrolyte is typically a paste made of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and zinc chloride (ZnCl2) dissolved in water.
- The cell potential of a modified Leclanche cell is not dependent on the concentration of hydroxide ions ([OH-]) in the electrolyte. Therefore, the cell potential remains constant regardless of the [OH-] concentration.
Overall Explanation:
- Alkaline electrolytes, such as solutions of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH), are commonly used in different types of batteries to facilitate ion flow and enable the generation of electric current.
- In the case of mercury batteries, nickel-cadmium batteries, and modified Leclanche cells, alkaline electrolytes are used.
- The cell potential of these batteries is not affected by the concentration of hydroxide ions ([OH-]) in the electrolyte.
- Therefore, the cell potential remains constant regardless of the [OH-] concentration.
- As a result, the correct answer to the given question is option 'A' - I, II, III, meaning that all three types of batteries mentioned (mercury battery, nickel-cadmium battery, and modified Leclanche cell) use alkaline electrolytes and have a cell potential that is independent of [OH-] concentration.
Passage IIIn hydrogen economy fuel-cell,anodic and cathodic reactions are AnodicH2+2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-CathodicO2+2H2O + 2e- → 4OH-67.2 L H2 at STP react in 15 min.Entire current is used for electro deposition of copper from copper(II) sulphate solution. Average current produced in fuel cell is - a)610.00 A
- b)620.00 A
- c)617.8 A
- d)643.3 A
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
In hydrogen economy fuel-cell,anodic and cathodic reactions are
Anodic
H2+2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-
Cathodic
O2+2H2O + 2e- → 4OH-
67.2 L H2 at STP react in 15 min.Entire current is used for electro deposition of copper from copper(II) sulphate solution. Average current produced in fuel cell is
a)
610.00 A
b)
620.00 A
c)
617.8 A
d)
643.3 A

|
Shraddha Gupta answered |
Statement I : When AgNO3 solution is stirred with a spoon made of copper,solution turns blue.Statement II : In electrochemical series ,copper is above silver- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement I : When AgNO3 solution is stirred with a spoon made of copper,solution turns blue.
Statement II : In electrochemical series ,copper is above silver
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Ameya Tiwari answered |
In electrochemical series, copper is above silver thus is a better reducing agent. When AgNO3 solution is stirred with copper spoon, Ag is displaced and copper is oxidised to Cu2+ (blue).
Thus, statement I and II are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
Chapter doubts & questions for Electrolysis - Chemistry for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Electrolysis - Chemistry for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for JAMB
213 videos|209 docs|162 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










