All Exams >
JAMB >
Physics for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Pressure & Fluid Dynamics for JAMB Exam
The formula used to find the pressure on a swimmer h metres below the surface of a lake is: (where Pa is the atmospheric pressure.)- a)Pa +hρ
- b)hρg
- c)Pa - hρg
- d)Pa + hρg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula used to find the pressure on a swimmer h metres below the surface of a lake is: (where Pa is the atmospheric pressure.)
a)
Pa +hρ
b)
hρg
c)
Pa - hρg
d)
Pa + hρg
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
We know that the pressure at some point inside the water can be represented by: Pa + ρhg
where,
ρ = Density of the liquid
Pa = Atmospheric pressure
H = Depth at which the body is present
g = Gravitational acceleration
where,
ρ = Density of the liquid
Pa = Atmospheric pressure
H = Depth at which the body is present
g = Gravitational acceleration
Two vessels with equal base and unequal height have water filled to same height. The force at the base of the vessels is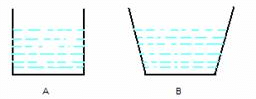
- a)Force doesn’t depend on such factors
- b)Equal
- c)varies with time
- d)Unequal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two vessels with equal base and unequal height have water filled to same height. The force at the base of the vessels is
a)
Force doesn’t depend on such factors
b)
Equal
c)
varies with time
d)
Unequal
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Two vessels having the same base area have identical force and equal pressure acting on their common base area. Since the shapes of the two vessels are different, the force exerted on the sides of the vessels has non-zero vertical components. When these vertical components are added, the total force on one vessel comes out to be greater than that on the other vessel. Hence, when these vessels are filled with water to the same height, they give different readings on a weighing scale.
Find the density when a liquid 5 m high in a column exerts a pressure of 80 Pa- a)625 kg/m3
- b)1.6 kg/m3
- c)0.625 kg/m3
- d)2.625 kg/m3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the density when a liquid 5 m high in a column exerts a pressure of 80 Pa
a)
625 kg/m3
b)
1.6 kg/m3
c)
0.625 kg/m3
d)
2.625 kg/m3
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
► Pressure = Density x Gravity x Height = ρgh
⇒ ρ = P/(g*h) = 80 Pa / (9.8 m/s2 x 5 m)
⇒ Density = 1.632 kg/m3
⇒ ρ = P/(g*h) = 80 Pa / (9.8 m/s2 x 5 m)
⇒ Density = 1.632 kg/m3
A slender homogeneous rod of length 2L floats partly immersed in water, being supported by a string fastened to one of its ends, as shown. The specific gravity of the rod is 0.75. The length of rod that extends out of water is 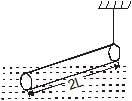
- a)L
- b)
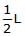
- c)
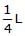
- d)3L
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A slender homogeneous rod of length 2L floats partly immersed in water, being supported by a string fastened to one of its ends, as shown. The specific gravity of the rod is 0.75. The length of rod that extends out of water is
a)
L
b)
c)
d)
3L
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
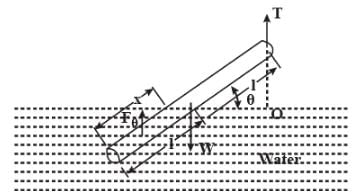
Let's say x length of the rod is dipped into the water.
Since the buoyant force acts through the centre of gravity the displaced water , the condition for rotational equilibrium is, taking moments about a point O along the line of action of T,
0=Στo
⇒0=wl cosθ−FB(2l−x/2)cosθ
⇒0=ρrodgA(2l)(lcosθ)−ρwatergAx(2l−x/2)cosθ
⇒0=(1/2ρwatergAcosθ) (x2−4lx+4 (ρrod/ρwater)l2) where A=cross section area
⇒x2−4lx+3l2=0
⇒x=l,3l.
x=3l is not a possible solution, hence 2l−x=2l−l=l length of the rod extends out of the water.
An open-ended U-tube of uniform cross-sectional area contains water (density 1.0 gram/centimeter3) standing initially 20 centimeters from the bottom in each arm. An immiscible liquid of density 4.0 grams/centimeter3 is added to one arm until a layer 5 centimeters high forms, as shown in the figure above. What is the ratio h2/h1 of the heights of the liquid in the two arms ? 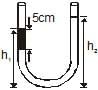
- a) 3/1
- b)5/2
- c)2/1
- d)3/2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An open-ended U-tube of uniform cross-sectional area contains water (density 1.0 gram/centimeter3) standing initially 20 centimeters from the bottom in each arm. An immiscible liquid of density 4.0 grams/centimeter3 is added to one arm until a layer 5 centimeters high forms, as shown in the figure above. What is the ratio h2/h1 of the heights of the liquid in the two arms ?
a)
3/1
b)
5/2
c)
2/1
d)
3/2

|
Ambition Institute answered |
5 × 4 × 10 + (h1 - 5) × 10 = h2 × 1 × 10
200 + 10h1 – 50 = 10h2
10h2 - 10h1 = 150
h2 - h1 = 15
h2 + h1 = 20 + 20 + 5 = 45
2h2 = 60
h2 = 30
h1 = 15
h2/h1 = 30/15
h2/h1 = 2/1
200 + 10h1 – 50 = 10h2
10h2 - 10h1 = 150
h2 - h1 = 15
h2 + h1 = 20 + 20 + 5 = 45
2h2 = 60
h2 = 30
h1 = 15
h2/h1 = 30/15
h2/h1 = 2/1
Hydraulic brakes use- a)Gas law
- b)Stoke’s Law
- c)Pascal’s Law
- d)Archimide’s Principle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydraulic brakes use
a)
Gas law
b)
Stoke’s Law
c)
Pascal’s Law
d)
Archimide’s Principle
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Hydraulic Brakes
Hydraulic brakes work on the principle of Pascal’s law. According to this law whenever pressure is applied on a fluid it travels uniformly in all the directions.
Therefore when we apply force on a small piston, pressure gets created which is transmitted through the uid to a larger piston. As a result of this larger force,uniformbrakingis applied on all four wheels.
As braking force is generateddue to hydraulic pressure,theyare known as hydraulic brakes.
Liquids are used instead of gas as liquids are incompressible.
Water is flowing in a tube of non-uniform radius. The ratio of the radii at entrance and exit ends of tube is 3 : 2. The ratio of the velocities of water entering in and exiting from the tube will be –- a)8 : 27
- b)4 : 9
- c) 1 : 1
- d) 9 : 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing in a tube of non-uniform radius. The ratio of the radii at entrance and exit ends of tube is 3 : 2. The ratio of the velocities of water entering in and exiting from the tube will be –
a)
8 : 27
b)
4 : 9
c)
1 : 1
d)
9 : 4
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
We know, for the fluid flowing through the non-uniform pipe the velocity of fluid is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section.
Hence, if v1, v2 are the velocities of entry and exit end of the pipe and a1, a2 are the area of cross-sections of entry and exit end of the pipe, then
v1/v2=a2/a1
⇒v1/v2=(r2)2/(r1)2
∴v1/v2=(2)2/(3)2=4/9
Hence, if v1, v2 are the velocities of entry and exit end of the pipe and a1, a2 are the area of cross-sections of entry and exit end of the pipe, then
v1/v2=a2/a1
⇒v1/v2=(r2)2/(r1)2
∴v1/v2=(2)2/(3)2=4/9
The area of cross-section of the wider tube shown in figure is 800 cm2. If a mass of 12 kg is placed on the massless piston, the difference in heights h in the level of water in the two tubes is : 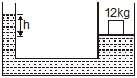
- a)10 cm
- b)6 cm
- c)15 cm
- d)2 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The area of cross-section of the wider tube shown in figure is 800 cm2. If a mass of 12 kg is placed on the massless piston, the difference in heights h in the level of water in the two tubes is :
a)
10 cm
b)
6 cm
c)
15 cm
d)
2 cm

|
EduRev JEE answered |
h × ρ × 10 = 120/800 × 10-4
h × ρ = 12/8 × 102
h × ρ = 150m
h × 1000 = 150m
h = 15cm
h × ρ = 12/8 × 102
h × ρ = 150m
h × 1000 = 150m
h = 15cm
Water is flowing in a horizontal pipe ofnon-uniform cross - section. At the most contracted place of the pipe –- a)Velocity of water will be maximum and pressure minimum
- b)Pressure of water will be maximum and velocity minimum
- c)Both pressure and velocity of water will be maximum
- d)Both pressure and velocity of water will be
minimum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing in a horizontal pipe of
non-uniform cross - section. At the most contracted place of the pipe –
a)
Velocity of water will be maximum and pressure minimum
b)
Pressure of water will be maximum and velocity minimum
c)
Both pressure and velocity of water will be maximum
d)
Both pressure and velocity of water will be
minimum
minimum
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Continuity equation states that, "For a non-viscous liquid and streamlined flow the volume flow rate (Area of cross section x velocity) is constant throughout the flow at any point".
According to this, Av = constant. So if at any point the cross-section area decreases then velocity of liquid at that point increases and vice-versa.
Bernoulli's equation states that, "For a streamlined and non-viscous flow the total energy (kinetic energy and pressure gradient) remains constant throughout the liquid.
According to this, kinetic energy + Pressure gradient = constant. So, if at any point the velocity increases the pressure at that point decreases and vice-versa.
At the most contracted place of the pipe area of cross section is minimum
⇒ velocity is maximum
⇒ pressure is minimum
According to this, Av = constant. So if at any point the cross-section area decreases then velocity of liquid at that point increases and vice-versa.
Bernoulli's equation states that, "For a streamlined and non-viscous flow the total energy (kinetic energy and pressure gradient) remains constant throughout the liquid.
According to this, kinetic energy + Pressure gradient = constant. So, if at any point the velocity increases the pressure at that point decreases and vice-versa.
At the most contracted place of the pipe area of cross section is minimum
⇒ velocity is maximum
⇒ pressure is minimum
What is torr?- a)Unit to measure elasticity
- b)Unit to measure adherence.
- c)Unit to measure surface tension
- d)Unit to measure pressure.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is torr?
a)
Unit to measure elasticity
b)
Unit to measure adherence.
c)
Unit to measure surface tension
d)
Unit to measure pressure.
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The torr (symbol: Torr) is a non-SI unit of pressure with the ratio of 760 to 1 standard atmosphere, chosen to be roughly equal to the fluid pressure exerted by a millimeter of mercury, i.e., a pressure of 1 Torr is approximately equal to one millimeter of mercury. Note that the symbol is spelled exactly the same as the unit, but the symbol is capitalized, as is customary in metric units derived from names. It was named after Evangelista Torricelli, an Italian physicist and mathematician who discovered the principle of the barometer in 1644.
Which of the following is not an application of Pascal’s Law?- a)Brahma Press
- b)Submarine
- c)Hydraulic Lift
- d)both a and c
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an application of Pascal’s Law?
a)
Brahma Press
b)
Submarine
c)
Hydraulic Lift
d)
both a and c
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Applications of Pascal's law. The underlying principle of the hydraulic jack and hydraulic press. Force amplification in the braking system of most motor vehicles. Used in artesian wells, water towers, and dams.
large tank is filled with water to a height H. A small hole is made at the base of the tank. It takes T1 time to decrease the height of water to H/h, (h > 1) and it takes T2 time to take out the rest of water. If T1 = T2, then the value of h is :- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
large tank is filled with water to a height H. A small hole is made at the base of the tank. It takes T1 time to decrease the height of water to H/h, (h > 1) and it takes T2 time to take out the rest of water. If T1 = T2, then the value of h is :
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
t=A/a √2/g[√H1−√H2]
T1= A/a√2/g[√H1√H/η]
T2=A/a√2/g[√H/η−0]
Given, T1=T2
√H−√H/η=√H/η−0
⇒√H=2√H/η
⇒η=4
T1= A/a√2/g[√H1√H/η]
T2=A/a√2/g[√H/η−0]
Given, T1=T2
√H−√H/η=√H/η−0
⇒√H=2√H/η
⇒η=4
A piece of steel has a weight W in air, W1 when completely immersed in water and W2 when completely immersed in an unknown liquid. The relative density (specific gravity) of liquid is :- a)
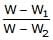
- b)
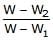
- c)
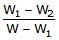
- d)
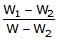
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A piece of steel has a weight W in air, W1 when completely immersed in water and W2 when completely immersed in an unknown liquid. The relative density (specific gravity) of liquid is :
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
If the loss of weight of a body in water is 'a' while in liquid is 'b' then
Sigma in liquid / sigma in water = upthrust on body in liquid / upthrust on body in water
Then a / b = (W air - W liquid) / (W air - W water).
Sigma in liquid / sigma in water = upthrust on body in liquid / upthrust on body in water
Then a / b = (W air - W liquid) / (W air - W water).
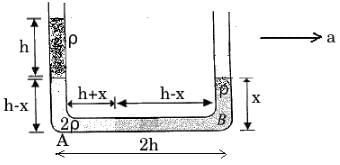
The vertical limbs of a U shaped tube are filled with a liquid of density r upto a height h on each side. The horizontal portion of the U tube having length 2h contains a liquid of density 2r. The U tube is moved horizontally with an accelerator g/2 parallel to the horizontal arm. The difference in heights in liquid levels in the two vertical limbs, at steady state will be- a)2h/7
- b)8h/7
- c)4h/7
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The vertical limbs of a U shaped tube are filled with a liquid of density r upto a height h on each side. The horizontal portion of the U tube having length 2h contains a liquid of density 2r. The U tube is moved horizontally with an accelerator g/2 parallel to the horizontal arm. The difference in heights in liquid levels in the two vertical limbs, at steady state will be
a)
2h/7
b)
8h/7
c)
4h/7
d)
None
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Given:
a=g/2
Pressure at A
PA=Po+ρgh+(2ρ)g(h−x)=Po+3ρgh−2ρgx
Pressure at B
PB=Po+ρgx
Using
PA−PB=[2ρ(h+x)+ρ(h−x)]a
∴ (Po+3ρgh−2ρgx)−(Po+ρgx)=[3ρh+ρx]×g/2
OR 3ρgh−3ρgx=3ρgh/2+1ρgx/2
OR 3ρgh/2=7ρgx/2 ⟹x=3h/7
∴ Difference in the heights between two columns ΔH=(2h−x)−x=2h−2x
⟹ ΔH=2h−6h/7=8h/7
a=g/2
Pressure at A
PA=Po+ρgh+(2ρ)g(h−x)=Po+3ρgh−2ρgx
Pressure at B
PB=Po+ρgx
Using
PA−PB=[2ρ(h+x)+ρ(h−x)]a
∴ (Po+3ρgh−2ρgx)−(Po+ρgx)=[3ρh+ρx]×g/2
OR 3ρgh−3ρgx=3ρgh/2+1ρgx/2
OR 3ρgh/2=7ρgx/2 ⟹x=3h/7
∴ Difference in the heights between two columns ΔH=(2h−x)−x=2h−2x
⟹ ΔH=2h−6h/7=8h/7

A beaker containing water is placed on the platform of a spring balance. The balance reads 1.5 kg. A stone of mass 0.5 kg and density 500 kg/m3 is immersed in water without touching the walls of beaker. What will be the balance reading now ?- a)2 Kg
- b)2.5 Kg
- c)1 KG
- d)3 Kg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A beaker containing water is placed on the platform of a spring balance. The balance reads 1.5 kg. A stone of mass 0.5 kg and density 500 kg/m3 is immersed in water without touching the walls of beaker. What will be the balance reading now ?
a)
2 Kg
b)
2.5 Kg
c)
1 KG
d)
3 Kg
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Since the weight of the block must be equal to the buoyant force acting on the block for it to remain in equilibrium,
B=0.5kg
The reading of the spring balance = Weight of water + Buoyant force' reaction pair force downwards
=1.5kg+0.5kg=2kg
A boy carries a fish in one hand and a bucket (not full) of water in the other hand. If the places the fish in the bucket, the weight now carried by him (assume that water does not spill) :- a)Is less than before
- b)Is more than before
- c)Is the same as before
- d)Depends upon his speed
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A boy carries a fish in one hand and a bucket (not full) of water in the other hand. If the places the fish in the bucket, the weight now carried by him (assume that water does not spill) :
a)
Is less than before
b)
Is more than before
c)
Is the same as before
d)
Depends upon his speed
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Buoyant force on fish due to water will be equal and opposite to the force on water by fish.
These two forces are internal forces for the fish bucket system.
Hence, they will not affect the weight the boy carries.
These two forces are internal forces for the fish bucket system.
Hence, they will not affect the weight the boy carries.
A light semi cylindrical gate of radius R is piovted at its mid point O, of the diameter as shown in the figure holding liquid of density r. The force F required to prevent the rotation of the gate is equal to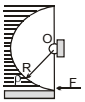
- a) 2pR3rg
- b)2rgR3l
- c)
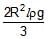
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A light semi cylindrical gate of radius R is piovted at its mid point O, of the diameter as shown in the figure holding liquid of density r. The force F required to prevent the rotation of the gate is equal to
a)
2pR3rg
b)
2rgR3l
c)
d)
None of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The force is normal to the surface of the cylinder and hence will pass through the centre. And since the forces pass through the centre it means that the net torque will be zero.
In the figure shown, the heavy cylinder (radius R) resting on a smooth surface separates two liquids of densities 2r and 3r. The height `h' for the equilibrium of cylinder must be 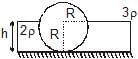
- a)3R/2
- b)
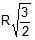
- c) R√2
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the figure shown, the heavy cylinder (radius R) resting on a smooth surface separates two liquids of densities 2r and 3r. The height `h' for the equilibrium of cylinder must be
a)
3R/2
b)
c)
R√2
d)
None
|
|
Om Desai answered |
First, let’s concentrate on the force exerted by the liquid of density 3ρ on the cylinder in the horizontal direction.
Let the length of the cylinder be L.
Consider a small segment of length rdθ at an angle θ from the horizontal line.
Height of this segment from the topmost point of fluid 3ρ is R sinθ
Hence, the pressure exerted by the fluid will be 3ρgRsinθ
The force exerted in the horizontal direction, dF=3ρgRsinθRLcosθdθ
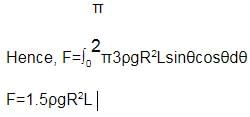
Similarly, proceeding for the fluid with density 2ρ
Height of any segment, above horizontal =h−R−Rsinθ
below horizontal, h−R+Rsinθ
Thus, horizontal force on the cylinder because of fluid,
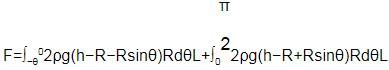
For equilibrium, both the forces should be equal, hence solving the above equation,
h = R √3/2
Let the length of the cylinder be L.
Consider a small segment of length rdθ at an angle θ from the horizontal line.
Height of this segment from the topmost point of fluid 3ρ is R sinθ
Hence, the pressure exerted by the fluid will be 3ρgRsinθ
The force exerted in the horizontal direction, dF=3ρgRsinθRLcosθdθ
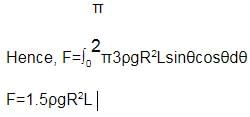
Similarly, proceeding for the fluid with density 2ρ
Height of any segment, above horizontal =h−R−Rsinθ
below horizontal, h−R+Rsinθ
Thus, horizontal force on the cylinder because of fluid,
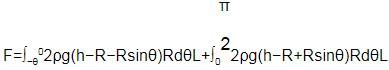
For equilibrium, both the forces should be equal, hence solving the above equation,
h = R √3/2
A cylindrical drum, open at the top, contains 30 litres of water. It drains out through a small opening at the bottom.10 litre of water comes out in time t, the next 10 litres in a further time t2 and the last 10 litres in a further time t3.Then- a)t1 = t2 = t3
- b)t1> t2 > t3
- c)t1 < t2 < t3
- d)t2> t1 = t3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylindrical drum, open at the top, contains 30 litres of water. It drains out through a small opening at the bottom.10 litre of water comes out in time t, the next 10 litres in a further time t2 and the last 10 litres in a further time t3.Then
a)
t1 = t2 = t3
b)
t1> t2 > t3
c)
t1 < t2 < t3
d)
t2> t1 = t3
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
We know that,
Velocity of efflux is given as v = √2gh
As the water level in the tank decreases, the velocity with which water comes out from the opening decreases due to decrease in pressure with height. Hence, the time taken to empty the tank increases with decrease in velocity and height of water level.
Hence C is the correct answer.
Velocity of efflux is given as v = √2gh
As the water level in the tank decreases, the velocity with which water comes out from the opening decreases due to decrease in pressure with height. Hence, the time taken to empty the tank increases with decrease in velocity and height of water level.
Hence C is the correct answer.
Which of the following devices in not based on Pascal’s law.- a)syringe
- b)hydraulic brakes
- c)hydraulic lift
- d)Atomiser
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following devices in not based on Pascal’s law.
a)
syringe
b)
hydraulic brakes
c)
hydraulic lift
d)
Atomiser

|
Riya Singh answered |
In Atomiser Pascal's law is interpreted .... Because ... In Atomiser ... Change in pressure at any point in an enclosed fluid at rest is transmitted undiminished to all point in the fluid ...
A fluid container is containing a liquid of density r is is accelerating upward with acceleration a along the inclined place of inclination a as shwon. Then the angle of inclination q of free surface is : 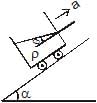
- a)tan_1
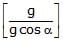
- b)
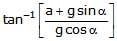
- c)
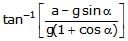
- d)
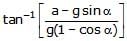
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A fluid container is containing a liquid of density r is is accelerating upward with acceleration a along the inclined place of inclination a as shwon. Then the angle of inclination q of free surface is :
a)
tan_1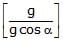
b)
c)
d)

|
Lohit Matani answered |
First resolve all components in the along and perpendicular to incline. Pressure difference is created in a vertical column full of liquid. This is because of gravity acting in downward direction. Similarly, pressure difference will be created too along the incline. So, p = h * d * g * cosa (in perpendicular direction) and
p = hd (a + g sina) (along incline).
So, tan(theta) = (a + gsina)/(gcosa)
p = hd (a + g sina) (along incline).
So, tan(theta) = (a + gsina)/(gcosa)
Some liquid is filled in a cylindrical vessel of radius R. Let F1 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of the cylinder. Now the same liquid is poured into a vessel of uniform square cross-section of side R. Let F2 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of this new vessel. Then :- a) F1 = pF2
- b)F1 =
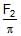
- c)F1 =
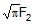
- d) F1 = F2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Some liquid is filled in a cylindrical vessel of radius R. Let F1 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of the cylinder. Now the same liquid is poured into a vessel of uniform square cross-section of side R. Let F2 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of this new vessel. Then :
a)
F1 = pF2
b)
F1 = 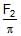
c)
F1 = 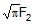
d)
F1 = F2

|
Lohit Matani answered |
Force applied on the base is equal to the weight of the liquid, since in both cases the same liquid has been poured in the container, it will exert the same force on the base of the container.
F1=F2
F1=F2
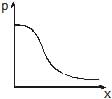
Water flows through a frictionless duct with a cross-section varying as shown in figure. Pressure p at points along the axis is represented by 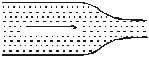
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Water flows through a frictionless duct with a cross-section varying as shown in figure. Pressure p at points along the axis is represented by
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
When the cross section of duct decreases the velocity of water increases and in accordance with Bernoulli's theorem the pressure decreases at that place.
Therefore, in this case, the pressure remains constant initially and then decreases as the area of cross section decreases along the neck of the tube and then remains constant along the mouth of the tube.
Hence, the graph in option A is correct.
Therefore, in this case, the pressure remains constant initially and then decreases as the area of cross section decreases along the neck of the tube and then remains constant along the mouth of the tube.
Hence, the graph in option A is correct.
A large tank is filled with water (density = 103 kg/m3). A small hole is made at a depth 10m below water surface. The range of water issuing out of the hole is Ron ground. What extra pressure must be applied on the water surface so that the range becomes 2R (take 1 atm = 105 Pa and g = 10 m/s2) : 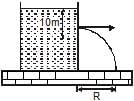
- a)9 Atm
- b)4 Atm
- c)5 Atm
- d)3 Atm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A large tank is filled with water (density = 103 kg/m3). A small hole is made at a depth 10m below water surface. The range of water issuing out of the hole is Ron ground. What extra pressure must be applied on the water surface so that the range becomes 2R (take 1 atm = 105 Pa and g = 10 m/s2) :
a)
9 Atm
b)
4 Atm
c)
5 Atm
d)
3 Atm
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Range will become twice, if the velocity of efflux becomes twice. Since velocity of efflux is √2gh, it will become twice, if h becomes 4 times, or 40m.
Thus, an extra pressure equivalent to 30m of water should be applied.
1atm=0.76×13.6 m of water =10.336m of water
30m of water ≈3atm
Thus, an extra pressure equivalent to 30m of water should be applied.
1atm=0.76×13.6 m of water =10.336m of water
30m of water ≈3atm
A rectangular tank is placed on a horizontal ground and is filled with water to a height H above the base. A small hole is made on one vertical side at a depth D below the level of the water in the tank. The distance x from the bottom of the tank at which the water jet from the tank will hit the ground is- a)
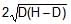
- b)
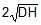
- c)
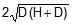
- d)
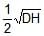
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A rectangular tank is placed on a horizontal ground and is filled with water to a height H above the base. A small hole is made on one vertical side at a depth D below the level of the water in the tank. The distance x from the bottom of the tank at which the water jet from the tank will hit the ground is
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Time taken by liquid drop to fall
S=ut+(1/2)at2
t=√2(H−D)/g
Horizontal velocity of liquid =√2gD
Range =√2(H−D)/g× √2gD
Range =2√D(H−D)
S=ut+(1/2)at2
t=√2(H−D)/g
Horizontal velocity of liquid =√2gD
Range =√2(H−D)/g× √2gD
Range =2√D(H−D)
A cuboidal piece of wood has dimensions a, b and c. Its relative density is d. It is floating in a larger body of water such that side a is vertical. It is pushed down a bit and released. The time period of SHM executed by it is :- a)
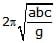
- b)
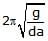
- c)
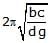
- d)
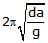
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cuboidal piece of wood has dimensions a, b and c. Its relative density is d. It is floating in a larger body of water such that side a is vertical. It is pushed down a bit and released. The time period of SHM executed by it is :
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Time period of SHM of small vertical oscillations in a liquid is given by T=2π√l/g, where l is the length of cube/cylinder dipped in the water.
So according to law of floatation,
weight of the cube = weight of the water displaced
abc × d × g=bcl × 1×g
⇒l=da
⇒T=2π√da/g
So according to law of floatation,
weight of the cube = weight of the water displaced
abc × d × g=bcl × 1×g
⇒l=da
⇒T=2π√da/g
A body is just floating in a liquid (their densities are equal) If the body is slightly pressed down and released it will -
- a) Start oscillating
- b)Sink to the bottom
- c)Come back to the same position immediately
- d)Come back to the same position slowly
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body is just floating in a liquid (their densities are equal) If the body is slightly pressed down and released it will -
a)
Start oscillating
b)
Sink to the bottom
c)
Come back to the same position immediately
d)
Come back to the same position slowly
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The body will sink to the bottom as it gains a downward velocity and has no force to bring it back up. The weight becomes greater than upwards thrust.
As body is just floating, its density is same as that of the liquid.
If pressed below, it will gain momentum downwards, and continue to sink till bottom.
When the body is slightly pressed, the contraction in volume decreases upthrust, so weight becomes greater than upthrust, body moves down. The upthrust further decreases, since more and more contraction occurs as the body moves down. The body thus, sinks to the bottom.
If pressed below, it will gain momentum downwards, and continue to sink till bottom.
When the body is slightly pressed, the contraction in volume decreases upthrust, so weight becomes greater than upthrust, body moves down. The upthrust further decreases, since more and more contraction occurs as the body moves down. The body thus, sinks to the bottom.
Figure shows a three arm tube in which a liquid is filled upto levels of height l. It is now rotated at an angular frequency w about an axis passing through arm B. The angular frequency w at which level of liquid of arm B becomes zero. 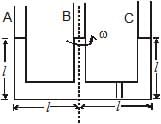
- a)
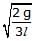
- b)
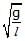
- c)
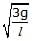
- d)
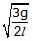
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure shows a three arm tube in which a liquid is filled upto levels of height l. It is now rotated at an angular frequency w about an axis passing through arm B. The angular frequency w at which level of liquid of arm B becomes zero.
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The pressure at the bottom of a tank of water is 3P where P is the atmospheric pressure. If the water is drawn out till the level of water is lowered by one fifth., the pressure at the bottom of the tank will now be
- a)2 P
- b)(13/5) P
- c)(8/5) P
- d)(4/5) P
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure at the bottom of a tank of water is 3P where P is the atmospheric pressure. If the water is drawn out till the level of water is lowered by one fifth., the pressure at the bottom of the tank will now be
a)
2 P
b)
(13/5) P
c)
(8/5) P
d)
(4/5) P

|
Stepway Academy answered |

The cross sectional area of a horizontal tube increases along its length linearly, as we move in the direction of flow. The variation of pressure, as we move along its length in the direction of flow (x-direction), is best depicted by which of the following graphs- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cross sectional area of a horizontal tube increases along its length linearly, as we move in the direction of flow. The variation of pressure, as we move along its length in the direction of flow (x-direction), is best depicted by which of the following graphs
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
So, it will be a downward facing parabola.
A jet of water with cross section of 6 cm2 strikes a wall at an angle of 60º to the normal and rebounds elastically from the wall without losing energy. If the velocity of the water in the jet is 12 m/s, the force acting on the wall is- a)0.864 Nt
- b)86.4 Nt
- c)72 Nt
- d)7.2 Nt
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A jet of water with cross section of 6 cm2 strikes a wall at an angle of 60º to the normal and rebounds elastically from the wall without losing energy. If the velocity of the water in the jet is 12 m/s, the force acting on the wall is
a)
0.864 Nt
b)
86.4 Nt
c)
72 Nt
d)
7.2 Nt
|
|
Bhargavi Yadav answered |
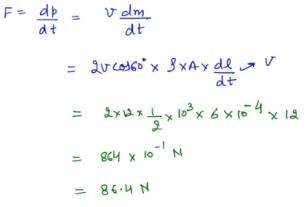
An open cubical tank was initially fully filled with water. When the tank was accelerated on a horizontal plane along one of its side it was found that one third of volume of water spilled out. The acceleration was- a) g/4
- b) g/3
- c)3g/2
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An open cubical tank was initially fully filled with water. When the tank was accelerated on a horizontal plane along one of its side it was found that one third of volume of water spilled out. The acceleration was
a)
g/4
b)
g/3
c)
3g/2
d)
None
|
|
Pooja Kulkarni answered |
Let say the tank is accelerating by some acceleration a, such that the rest water in the tanks forms shape like this -
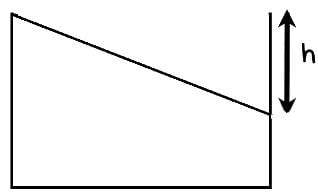
Acceleration, a is right wards.
Where let say h is the height from top till which there is no water
Now if we say V is total volume and B is area of its base and S be its height
We have ½ h X B = V / 3
Thus we get h = S/3
Thus the angle in this cross section of vacant triangle is tan-1 ⅓
Also the same triangle relates a and g, which can be seen when we make the block a inertial frame by adding pseudo force of magnitude ma and directing leftwards, thus we get a/g = ⅓
Thus we get a = g/3

Acceleration, a is right wards.
Where let say h is the height from top till which there is no water
Now if we say V is total volume and B is area of its base and S be its height
We have ½ h X B = V / 3
Thus we get h = S/3
Thus the angle in this cross section of vacant triangle is tan-1 ⅓
Also the same triangle relates a and g, which can be seen when we make the block a inertial frame by adding pseudo force of magnitude ma and directing leftwards, thus we get a/g = ⅓
Thus we get a = g/3
n drops of liquid, each with surface energy E, join to form a single drop. In this process - a)some energy will be absorbed
- b)energy absorbed is E(n – n2/3)
- c)energy released will be E (n – n2/3)
- d)energy released will be E(22/3 – 1)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
n drops of liquid, each with surface energy E, join to form a single drop. In this process
a)
some energy will be absorbed
b)
energy absorbed is E(n – n2/3)
c)
energy released will be E (n – n2/3)
d)
energy released will be E(22/3 – 1)

|
Manisha Patel answered |
A U-tube having horizontal arm of length 20 cm, has uniform cross-sectional area = 1 cm2. It is filled with water of volume 60 cc. What volume of a liquid of density 4 g/cc should be poured from one side into the U-tube so that no water is left in the horizontal arm of the tube?- a)60 cc
- b)45 cc
- c)50 cc
- d)35 cc
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A U-tube having horizontal arm of length 20 cm, has uniform cross-sectional area = 1 cm2. It is filled with water of volume 60 cc. What volume of a liquid of density 4 g/cc should be poured from one side into the U-tube so that no water is left in the horizontal arm of the tube?
a)
60 cc
b)
45 cc
c)
50 cc
d)
35 cc
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
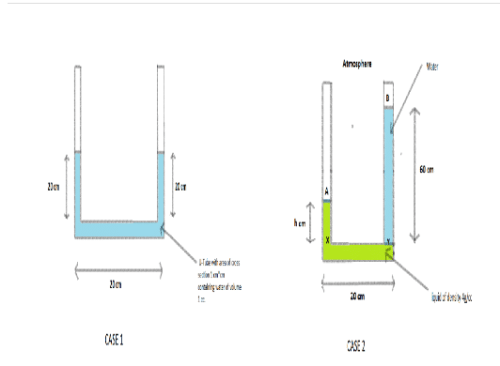

In a car lift, compressed air exerts a force F1 on a small piston having a radius of 5cm. This pressure is transmitted to the second piston of a radius of 15cm. If the mass of the car to be lifted is 1350 kg. What is F1?- a)14.7 * 103 N
- b)2.47 * 103 N
- c)1.47 * 103 N
- d)24.7 * 103 N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a car lift, compressed air exerts a force F1 on a small piston having a radius of 5cm. This pressure is transmitted to the second piston of a radius of 15cm. If the mass of the car to be lifted is 1350 kg. What is F1?
a)
14.7 * 103 N
b)
2.47 * 103 N
c)
1.47 * 103 N
d)
24.7 * 103 N
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
From Pascal’s law:
P1 = P2
F1/A1 = F2/A2
F1/A1 = F2/A2
► F1/πr12 = F
► F1 = (F2 * r12 ) / r22
► F1 = 1350 * 9.8 * (5 * 10-2)2 / (15 * 10-2)2
► F1 = 1470N = 1.47 * 103N
2
/πr22 ► F1 = (F2 * r12 ) / r22
► F1 = 1350 * 9.8 * (5 * 10-2)2 / (15 * 10-2)2
► F1 = 1470N = 1.47 * 103N
There is a metal cube inside a block of ice which is floating on the surface of water. The ice melts completely and metal falls in the water. Water level in thecontainer- a) Rises
- b)Falls
- c)Remains same
- d)Nothing can be concluded
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There is a metal cube inside a block of ice which is floating on the surface of water. The ice melts completely and metal falls in the water. Water level in the
container
a)
Rises
b)
Falls
c)
Remains same
d)
Nothing can be concluded
|
|
Sinjini Pillai answered |
Vt = total volume, Vi = volume of ice, Vm = volume of metal, Vw = volume of water
Vt = Vw + Vi + Vm
Since Mi = Mw and ρi x Vi = (ρw)i x (Vw)i and ρi < (ρw)i
So, Vi > (Vw)i
Finally, Vt = (Vw)i + Vi + Vm
Vt = Vw + Vi + Vm
Since Mi = Mw and ρi x Vi = (ρw)i x (Vw)i and ρi < (ρw)i
So, Vi > (Vw)i
Finally, Vt = (Vw)i + Vi + Vm
The terminal speed of a sphere of gold (density = 19.5 g/cm3) is 0.2 m/s in a viscous liquid (density = 1.5 g/cm3). Find the terminal speed of a sphere of silver (density =10.5 g/cm3) of the same size in the same liquid (in m/s)
- a)0.2 m/s
- b)0.4 m/s
- c)0.133 m/s
- d)0.1m/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The terminal speed of a sphere of gold (density = 19.5 g/cm3) is 0.2 m/s in a viscous liquid (density = 1.5 g/cm3). Find the terminal speed of a sphere of silver (density =10.5 g/cm3) of the same size in the same liquid (in m/s)
a)
0.2 m/s
b)
0.4 m/s
c)
0.133 m/s
d)
0.1m/s
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |

Two stretched membranes of areas 2 and 3 m2 are placed in a liquid at the same depth. The ratio of the pressure on them is -- a) 1 : 1
- b) 2 : 3
- c)
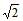 :
: 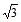
- d)22 : 32
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two stretched membranes of areas 2 and 3 m2 are placed in a liquid at the same depth. The ratio of the pressure on them is -
a)
1 : 1
b)
2 : 3
c)
d)
22 : 32
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Pressure depends on depth of container irrespective of its shape and in the above case depth for both the vessels are given same. Therefore the hydraulic pressure for the containers will be in the ratio 1: 1
A heavy hollow cone of radius R and height h is placed on a horizontal table surface, with its flat base on the table. The whole volume inside the cone is filled with water of density r. The circular rim of the cone's base has a watertight seal with the table's surface and the top apex of the cone has a small hole. Neglecting atmospheric pressure find the total upward force exerted by water on the cone is- a)(2/3)pR2hrg
- b)(1/3)pR2hrg
- c)pR2hrg
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A heavy hollow cone of radius R and height h is placed on a horizontal table surface, with its flat base on the table. The whole volume inside the cone is filled with water of density r. The circular rim of the cone's base has a watertight seal with the table's surface and the top apex of the cone has a small hole. Neglecting atmospheric pressure find the total upward force exerted by water on the cone is
a)
(2/3)pR2hrg
b)
(1/3)pR2hrg
c)
pR2hrg
d)
None
|
|
Sandeep Chawla answered |
Total force exerted on the base by water and cone’s slant surface = mg = 1/3 πR2 Hρg downwards
Force exerted by the water = (ρgH) (πR2) (downwards)
So force exerted by the slant surface = 2/3 ρgH πR2 (upwards)
So force exerted by water on slant surface = 2/3 ρgHπR2
Force exerted by the water = (ρgH) (πR2) (downwards)
So force exerted by the slant surface = 2/3 ρgH πR2 (upwards)
So force exerted by water on slant surface = 2/3 ρgHπR2
A metal ball of density 7800 kg/m3 is suspected to have a large number of cavities. It weighs 9.8 kg when weighed directly on a balance and 1.5 kg less when immersed in water. The fraction by volume of the cavities in the metal ball is approximately :- a)20%
- b)30%
- c)16%
- d)11%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal ball of density 7800 kg/m3 is suspected to have a large number of cavities. It weighs 9.8 kg when weighed directly on a balance and 1.5 kg less when immersed in water. The fraction by volume of the cavities in the metal ball is approximately :
a)
20%
b)
30%
c)
16%
d)
11%
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Answer- volume of cavity/ball=0.16
Explaination-
Here when put in water the water displaces/fills the empty cavity.
Volume of only metal=mass/density =9.8/7800=1.25X10^-3cu.m
Volume of whole ball including cavity= weight of water dispaced/density of water
Density of water is 1000kg/cu.m.
Volume of whole ball=1.5X10^-3cu.m
Volume of cavity=Volume of ball-volume of metal
=1.5X10^-3 - 1.25X10^-3
=0.25X10^-3cu.m
Ratio of volume of cavity/ball = 0.25X10^-3 / 1.5X10^-3 = 0.16 = 16%
0.16 fraction of whole ball is a cavity. i.e.16%.
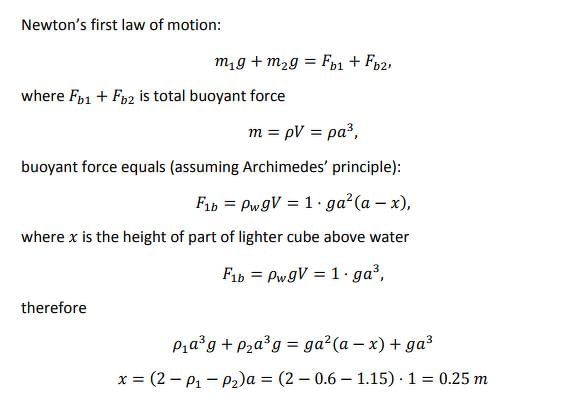
Two cubes of size 1.0 m sides, one of relative density 0.60 and another of relative density = 1.15 are connected by weightless wire and placed in a large tank of water. Under equilibrium the lighter cube will project above the water surface to a height of- a)50 cm
- b)25 cm
- c)10 cm
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two cubes of size 1.0 m sides, one of relative density 0.60 and another of relative density = 1.15 are connected by weightless wire and placed in a large tank of water. Under equilibrium the lighter cube will project above the water surface to a height of
a)
50 cm
b)
25 cm
c)
10 cm
d)
Zero
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Chapter doubts & questions for Pressure & Fluid Dynamics - Physics for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Pressure & Fluid Dynamics - Physics for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for JAMB
259 videos|253 docs|230 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup


















