All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Reproduction in Flowering Plants for JAMB Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below: Which tissue is required to be present in between stock and scion during grafting?
- A:
Xylem
- B:
Phloem
- C:
Meristem
- D:
Parenchyma.
The answer is b.
Which tissue is required to be present in between stock and scion during grafting?
Xylem
Phloem
Meristem
Parenchyma.
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Phloem, also called bast, tissues in plants that conduct foods made in the leaves to all other parts of the plant. Phloem is composed of various specialized cells called sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma cells. Primary phloem is formed by the apical meristems (zones of new cell production) of root and shoot tips; it may be either protophloem, the cells of which are matured before elongation (during growth) of the area in which it lies, or metaphloem, the cells of which mature after elongation. Sieve tubes of protophloem are unable to stretch with the elongating tissues and are torn and destroyed as the plant ages. The other cell types in the phloem may be converted to fibres. The later maturing metaphloem is not destroyed and may function during the rest of the plant’s life in plants such as palms but is replaced by secondary phloem in plants that have a cambium.
Wind pollination is common in- a)Lilies
- b)Legumes
- c)Grasses
- d)Orchids
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Wind pollination is common in
a)
Lilies
b)
Legumes
c)
Grasses
d)
Orchids
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Grasses are wind-pollinated, and a single flower head of an average grass can produce ten million pollen grains! Any one of those only has a miniscule chance of landing on the stigma of one of is own kind, so while the pollen may be carried incredible distances, the majority of the grains tend to land within just a few metres of the plant. Therefore wind-pollinated plants usually grow closely together, to increase the likelihood of pollination.
Sporopollenin an organic material is present in- a)Exine
- b)Intine
- c)Style
- d)Stigma
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sporopollenin an organic material is present in
a)
Exine
b)
Intine
c)
Style
d)
Stigma

|
Shraddha Gupta answered |
The exine of the pollen grain is made of sporopollenin. Sporopollenin is one of the most resistant organic compounds. It can withstand high temperature, strong acids and alkalis and cannot be degraded by any of the known enzymes. Hence, it acts as a shield and protects the pollen grain from getting damaged.
When pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same plant, pollination is referred to:
- a)Geitonogamy
- b)Allogamy
- c)Xenogamy
- d)Siphonogamy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same plant, pollination is referred to:
a)
Geitonogamy
b)
Allogamy
c)
Xenogamy
d)
Siphonogamy
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- In self-pollinating plants, there is less dependence on external factors to cause pollination.
- These plants depend on wind or other smaller insects that visit the flower regularly.
- In self- pollinating flowers, the anthers, and stigma are of similar lengths to facilitate the transfer of pollen.
Self -pollination can be further divided into two types:
- Autogamy– In this type of self-pollination, the pollen is transferred from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of the same flower.
- Geitonogamy– In this type of self- pollination, the anthers are transferred from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower but on the same plant.
Self Pollination:
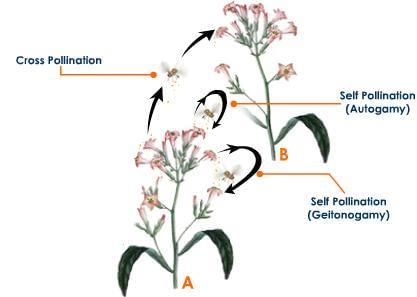

Hence, the correct option is A
NCERT Reference: Topic “Pollination” of chapter "Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants" of NCERT
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The female gametophyte in angiosperm is
- A:
Ovule
- B:
Carpel
- C:
Embryo sac
- D:
Egg
The answer is c.
The female gametophyte in angiosperm is
Ovule
Carpel
Embryo sac
Egg

|
Aiims New Delhi answered |
Embryosacline of ncert in sexual reproduction in flowering plants chapter😀😀😀💯💯💯👍👍👍
In which one of the following is pollination autogamous?- a)Cleistogamy
- b)Geitonogamy
- c)Xenogamy
- d)Chasmogamy
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following is pollination autogamous?
a)
Cleistogamy
b)
Geitonogamy
c)
Xenogamy
d)
Chasmogamy
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Cleistogamy is autogamous pollinatin. When pollination and fertilization occur in unopened flower bud, it is known as cleistogamy. It ensures self-pollination and prevents cross-pollination.
Eight nucleate embryo sacs are- a)Always tetrasporic
- b)Sometimes monosporic, bisporic and tetrasporic
- c)Always monosporic
- d)Always bisporic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Eight nucleate embryo sacs are
a)
Always tetrasporic
b)
Sometimes monosporic, bisporic and tetrasporic
c)
Always monosporic
d)
Always bisporic
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Embryo sacs can be divided into three types: monosporic, bisporic, and tetrasporic. In the monosporic, or Polygonum-type embryo sac, meiosis of the diploid megaspore mother cell in the nucellus produces four haploid megaspores.
The type of pollination that brings genetically different types of pollen grains to the stigma of a plant is- a)Geitonogamy
- b)Xenogamy
- c)Chasmogamy
- d)Autogamy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The type of pollination that brings genetically different types of pollen grains to the stigma of a plant is
a)
Geitonogamy
b)
Xenogamy
c)
Chasmogamy
d)
Autogamy
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Xenogamy : Only types of pollination which brings genetically different types of pollen grains to the stigma.
In some plants, the anthers and stigma grow and mature at the same time. This phenomenon is called- a)Syngamy
- b)Fusion
- c)Allogamy
- d)Homogamy
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In some plants, the anthers and stigma grow and mature at the same time. This phenomenon is called
a)
Syngamy
b)
Fusion
c)
Allogamy
d)
Homogamy
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Homogamy is the condition in which male and female parts of a flower mature simultaneously.
Fusion of a male gamete with an egg in the embryo sac is called- a)Autogamy
- b)Syngamy
- c)Double fertilisation
- d)Triple fusion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Fusion of a male gamete with an egg in the embryo sac is called
a)
Autogamy
b)
Syngamy
c)
Double fertilisation
d)
Triple fusion
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The two male gametes are discharged within the embryo sac. One of the male gamete fuses with the egg cell to form a diploid zygote. This fusion is known as fertilization or syngamy. The second male gamete fuses with the diploid secondary nucleus and forms the triploid Primary Endosperm Nucleus (PEN).
Assertion: In monosporic development, all four megaspores produced from the megaspore mother cell (MMC) do not contribute to the formation of the female gametophyte.
Reason: Monosporic development results in the formation of four functional megaspores.
- a)Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion.
- b)Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not a correct explanation of the assertion.
- c)The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
- d)The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: In monosporic development, all four megaspores produced from the megaspore mother cell (MMC) do not contribute to the formation of the female gametophyte.
Reason: Monosporic development results in the formation of four functional megaspores.
a)
Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion.
b)
Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not a correct explanation of the assertion.
c)
The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
d)
The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Explanation: In monosporic development, only one megaspore out of the four produced from the megaspore mother cell (MMC) develops into the female gametophyte. The other three megaspores typically degenerate. Therefore, the assertion is correct. However, the reason is incorrect as it states that all four megaspores become functional, which is not the case in monosporic development.
Cucurbits and coconuts are examples of _______.- a)Polycious
- b)Dioecious
- c)Trioecious
- d)Monoecious
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cucurbits and coconuts are examples of _______.
a)
Polycious
b)
Dioecious
c)
Trioecious
d)
Monoecious
|
|
Jhanvi Tiwari answered |
Cucurbits and coconuts are examples of Monoecious plants.
Explanation:
Monoecious plants are those which have separate male and female flowers on the same plant. The term "monoecious" is derived from two Greek words, "monos" meaning "single" and "oikos" meaning "house". In monoecious plants, both male and female flowers are present in the same "house" or plant.
Cucurbits, which include plants like cucumber, pumpkin, and watermelon, are monoecious. They produce separate male and female flowers on the same plant. The male flowers have long, thin stalks with a single anther, while the female flowers have a swollen base which will eventually develop into the fruit.
Coconuts are also monoecious. The male and female flowers are borne on the same inflorescence, which is a type of flower cluster. The male flowers are small and yellow while the female flowers are larger and green. Once pollinated, the female flowers develop into the coconut fruit.
Explanation:
Monoecious plants are those which have separate male and female flowers on the same plant. The term "monoecious" is derived from two Greek words, "monos" meaning "single" and "oikos" meaning "house". In monoecious plants, both male and female flowers are present in the same "house" or plant.
Cucurbits, which include plants like cucumber, pumpkin, and watermelon, are monoecious. They produce separate male and female flowers on the same plant. The male flowers have long, thin stalks with a single anther, while the female flowers have a swollen base which will eventually develop into the fruit.
Coconuts are also monoecious. The male and female flowers are borne on the same inflorescence, which is a type of flower cluster. The male flowers are small and yellow while the female flowers are larger and green. Once pollinated, the female flowers develop into the coconut fruit.
A typical angiospemic embryo sac is though 8 nucleate is 7-celled. 8 nuclei includes______.
- a)2 egg apparatus, 3 polar nuclei and 3 antipodal
- b)Either (a) or (b)
- c)3 egg apparatus, 3 polar nuclei and 2 antipodal
- d)3 egg apparatus, 2 polar nuclei and 3 antipodal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A typical angiospemic embryo sac is though 8 nucleate is 7-celled. 8 nuclei includes______.
a)
2 egg apparatus, 3 polar nuclei and 3 antipodal
b)
Either (a) or (b)
c)
3 egg apparatus, 3 polar nuclei and 2 antipodal
d)
3 egg apparatus, 2 polar nuclei and 3 antipodal
|
|
Swati Malkani answered |
Option B is correct.
Filiform apparatus is a characteristic feature of- a)Synergid
- b)Egg
- c)Suspensor
- d)Zygote
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Filiform apparatus is a characteristic feature of
a)
Synergid
b)
Egg
c)
Suspensor
d)
Zygote
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Filiform apparatus are finger-like projections present at the micropylar end of synergids of embryo sac.
Which of the following is an example of false fruit?- a)Apple
- b)Coconut
- c)Mango
- d)Papaya
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of false fruit?
a)
Apple
b)
Coconut
c)
Mango
d)
Papaya
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Apple - An accessory fruit (also called false fruit or spurious fruit) is a fruit in which some of the flesh is derived not from the ovary but from some adjacent tissue exterior to the carpel. Examples of accessory tissue are the receptacle of strawberries, figs, or mulberries, Pomes, such as apples and pears.
Which of the following plant is not pollinated by water?- a)Hydrilla
- b)Zostera
- c)Lotus
- d)Vallisneria
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following plant is not pollinated by water?
a)
Hydrilla
b)
Zostera
c)
Lotus
d)
Vallisneria
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Lotus is an aquatic plant but the flower of lotus is outside and above the water surface. So, it cannot be pollinated by water. It is generally pollinated by insects.
Embryo sac represents:
- a)Megagametophyte
- b)Megasporangium
- c)Microgametophyte
- d)Microsporangium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Embryo sac represents:
a)
Megagametophyte
b)
Megasporangium
c)
Microgametophyte
d)
Microsporangium
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The female gametophyte specifically termed a megagametophyte is also called the embryo sac in angiosperms. The megagametophyte produces an egg cell (or several in some groups) for the purpose of fertilization.
Which of the following statements regarding the structure of microsporangium are correct?
(i) Microsporangium is generally surrounded by four wall layers-epidermis, endothecium, middle layers, and tapetum.
(ii) Outer three layers perform functions of protection and dehiscence of anthers.
(iii) Cells of tapetum undergo meiosis and produce microspore tetrads.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding the structure of microsporangium are correct?
(i) Microsporangium is generally surrounded by four wall layers-epidermis, endothecium, middle layers, and tapetum.
(ii) Outer three layers perform functions of protection and dehiscence of anthers.
(iii) Cells of tapetum undergo meiosis and produce microspore tetrads.
(i) Microsporangium is generally surrounded by four wall layers-epidermis, endothecium, middle layers, and tapetum.
(ii) Outer three layers perform functions of protection and dehiscence of anthers.
(iii) Cells of tapetum undergo meiosis and produce microspore tetrads.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
A microsporangium or future pollen sac is a cylindrical sac that appears circular in the transverse section. It consists of two parts, the outer wall, and central homogeneous sporogenous tissue.
Microsporangial wall has four types of layers - epidermis, endothecium, 1−3 middle layers, and tapetum.
The outer three layers perform the function of protection in the young anther and mechanism of dehiscence in the ripe anther.
Microsporangial wall has four types of layers - epidermis, endothecium, 1−3 middle layers, and tapetum.
The outer three layers perform the function of protection in the young anther and mechanism of dehiscence in the ripe anther.
A bilobed dithecous anther had 100 microspore mother cells per microsporangium. How many male gametes this anther can produce?
- a)400
- b)1600
- c)100
- d)200
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A bilobed dithecous anther had 100 microspore mother cells per microsporangium. How many male gametes this anther can produce?
a)
400
b)
1600
c)
100
d)
200

|
Swara Desai answered |
Each microsporangium has 100 microspore mother cells which by meiosis form 400 microspores ( 100 × 4). In an anther there are four microsporangia , so, total number of microspores will be 4 × 400 = 1600 4 × 400 = 1600 . As each microspore forms one male gametophyte, hence , 1600 male gametophytes can be produced.
The cotyledon of maize grain is technically called as? - a)Funicle
- b)Dicots
- c)Scutellum
- d)Testa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cotyledon of maize grain is technically called as?
a)
Funicle
b)
Dicots
c)
Scutellum
d)
Testa

|
Anand Jain answered |
The cotyledons are known as seed leaves, they are attached to the embryonic axis. Dicotyledons typically have two cotyledons and monocotyledons have oly one cotyledon. The single shield-shaped cotyledon in grains known as scutellum. Cotyledon of maize grain is called scutellum.
The meiocyte of an onion plant contains 32 chromosomes. Calculate the number of chromosomes found in its endosperm?- a)96 chromosomes
- b)32 chromosomes
- c)16 chromosomes
- d)48 chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The meiocyte of an onion plant contains 32 chromosomes. Calculate the number of chromosomes found in its endosperm?
a)
96 chromosomes
b)
32 chromosomes
c)
16 chromosomes
d)
48 chromosomes

|
Pankaj Kulkarni answered |
If the number of chromosomes in meiocytes of onion is 32, then the number of chromosomes in gamete cells will be 16. Furthermore, as endosperm is formed after fusion of one sperm nucleus with two egg nucleus called triple fusion, then its chromosome number will be 48.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Starting from the innermost part, the correct sequence of parts in an ovule are
- A:
Egg, integument, embryo sac and nucellus.
- B:
Egg, embryo sac, nucellus and integument.
- C:
Embryo sac, nucellus, integument and egg.
- D:
Egg, nucellus, embryo sac and integument.
The answer is b.
Starting from the innermost part, the correct sequence of parts in an ovule are
Egg, integument, embryo sac and nucellus.
Egg, embryo sac, nucellus and integument.
Embryo sac, nucellus, integument and egg.
Egg, nucellus, embryo sac and integument.
|
|
Preethi Saha answered |
The correct sequence of parts in an ovule starting from the innermost part is:
Egg, embryo sac, nucellus and integument.
Explanation:
• An ovule is a structure present in the ovary of a flower that contains the female reproductive cells.
• The ovule is composed of different parts, each playing a specific role in pollination and fertilization.
• The innermost part of the ovule is the egg cell, which is the female gamete.
• The egg cell is surrounded by the embryo sac, which is a structure that contains the synergids, antipodal cells, and the central cell.
• The central cell contains two nuclei, which will fuse with the sperm nuclei during fertilization to form the endosperm.
• The embryo sac is surrounded by the nucellus, which is the tissue that supplies nutrients to the developing embryo.
• The nucellus is surrounded by the integuments, which are two layers of tissue that form the outer covering of the ovule.
• The integuments develop into the seed coat after fertilization.
Therefore, the correct sequence of parts in an ovule starting from the innermost part is egg, embryo sac, nucellus and integument.
Egg, embryo sac, nucellus and integument.
Explanation:
• An ovule is a structure present in the ovary of a flower that contains the female reproductive cells.
• The ovule is composed of different parts, each playing a specific role in pollination and fertilization.
• The innermost part of the ovule is the egg cell, which is the female gamete.
• The egg cell is surrounded by the embryo sac, which is a structure that contains the synergids, antipodal cells, and the central cell.
• The central cell contains two nuclei, which will fuse with the sperm nuclei during fertilization to form the endosperm.
• The embryo sac is surrounded by the nucellus, which is the tissue that supplies nutrients to the developing embryo.
• The nucellus is surrounded by the integuments, which are two layers of tissue that form the outer covering of the ovule.
• The integuments develop into the seed coat after fertilization.
Therefore, the correct sequence of parts in an ovule starting from the innermost part is egg, embryo sac, nucellus and integument.
Pollen grain of large number of species can be stored in: - a)Liquid oxygen
- b)Liquid carbon dioxide
- c)Liquid sulphur dioxide
- d)Liquid nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pollen grain of large number of species can be stored in:
a)
Liquid oxygen
b)
Liquid carbon dioxide
c)
Liquid sulphur dioxide
d)
Liquid nitrogen
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Pollen grain consists of hard covering of exine but their viability may lost with time. For Hybridisation pollen grains are collected and stored in liquid nitrogen below -196 degree Celsius temperature.
Endosperm type in which first division of primary endosperm nucleus and few subsequent division are not accompanied by wall formation is called?- a)Cellular type
- b)Micropylar type
- c)Free nuclear type
- d)Helobial type
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Endosperm type in which first division of primary endosperm nucleus and few subsequent division are not accompanied by wall formation is called?
a)
Cellular type
b)
Micropylar type
c)
Free nuclear type
d)
Helobial type
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Nuclear type:
In nuclear type of endosperm the first division of primary endosperm nucleus and few subsequent nuclear divisions are not accompanied by wall formation. The nuclei produced are free in the cytoplasm of the embryo sac and they may remain free indefinitely or wall formation takes place later. In the coconut, cell wall formation of endosperm is never found complete. In Areca and Phoenix the endosperm becomes very hard .
Triploid tissue in angiosperms is- a)Endothecium
- b)Tapetum
- c)Endosperm
- d)Nucellus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Triploid tissue in angiosperms is
a)
Endothecium
b)
Tapetum
c)
Endosperm
d)
Nucellus

|
Abhilasa Mohapatra answered |
In angiosperms sperm cell fuses with egg to form zygote and another sperm cell fuses with 2 polar nuclei to form endosperm nucleus...so sperm(n)+1 polar nuclei (n)+ 1 polar nuclei (n)=3n
Inside the ovary the ovule is attached to placenta by means of- - a)Chalaza
- b)Micropyle
- c)Hilum
- d)Funicle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Inside the ovary the ovule is attached to placenta by means of-
a)
Chalaza
b)
Micropyle
c)
Hilum
d)
Funicle
|
|
Anjali Patel answered |
The ovule is the female reproductive structure of the flower and it is located inside the ovary. The ovule contains the female gametophyte and is attached to the placenta by means of the funicle.
Explanation:
- The ovary is the part of the flower that contains the ovules. It is the female reproductive organ of the flower.
- The ovule is a structure that contains the female gametophyte, the egg cell, and the surrounding protective layers.
- The placenta is the tissue inside the ovary that provides nutrients and support to the developing ovules.
- The funicle is the stalk-like structure that attaches the ovule to the placenta. It is also known as the stalk or the seed stalk.
- The funicle is responsible for transporting nutrients and water from the placenta to the developing ovule.
- The funicle also provides the pathway for the sperm cells to reach the egg cell during fertilization.
- The funicle is usually located at the base of the ovule and is often visible as a small, thin stalk.
In summary, the funicle is the structure that attaches the ovule to the placenta inside the ovary. It plays a vital role in the development and fertilization of the female reproductive structure in the flower.
Explanation:
- The ovary is the part of the flower that contains the ovules. It is the female reproductive organ of the flower.
- The ovule is a structure that contains the female gametophyte, the egg cell, and the surrounding protective layers.
- The placenta is the tissue inside the ovary that provides nutrients and support to the developing ovules.
- The funicle is the stalk-like structure that attaches the ovule to the placenta. It is also known as the stalk or the seed stalk.
- The funicle is responsible for transporting nutrients and water from the placenta to the developing ovule.
- The funicle also provides the pathway for the sperm cells to reach the egg cell during fertilization.
- The funicle is usually located at the base of the ovule and is often visible as a small, thin stalk.
In summary, the funicle is the structure that attaches the ovule to the placenta inside the ovary. It plays a vital role in the development and fertilization of the female reproductive structure in the flower.
Chiropterophily means- a)Pollination by bats
- b)Pollination by snails
- c)Pollination by insects
- d)Pollination by wind
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Chiropterophily means
a)
Pollination by bats
b)
Pollination by snails
c)
Pollination by insects
d)
Pollination by wind
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Bat pollination (chiropterophily) Bat-pollinated flowers tend to be large and showy, white or light coloured, open at night and have strong musty odours. They are often large and bell-shaped or a ball of stamens. Flowers are typically borne away from the trunk or other obstructions.
Dormancy is the____.- a)State of hyperactivity
- b)Condition of senescence
- c)State of maturity
- d)State of inactivity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Dormancy is the____.
a)
State of hyperactivity
b)
Condition of senescence
c)
State of maturity
d)
State of inactivity
|
|
Sandy Naaz answered |
Dormancy is a period in an organism's life cycle when growth, development, and (in animals) physical activity are temporarily stopped. This minimizes metabolic activity and therefore helps an organism to conserve energy. Dormancy tends to be closely associated with environmental conditions
In double fertilisation- a)One male gamete fuses with the egg and the other fuses with the secondary nucleus
- b)One male gamete fuses with the antipodal, while the other fuses with the diploid nucleus
- c)Two male gametes fuse with two eggs
- d)One male gamete fuses with the egg, while the other fuses with the antipodal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In double fertilisation
a)
One male gamete fuses with the egg and the other fuses with the secondary nucleus
b)
One male gamete fuses with the antipodal, while the other fuses with the diploid nucleus
c)
Two male gametes fuse with two eggs
d)
One male gamete fuses with the egg, while the other fuses with the antipodal
|
|
Subhankar Banerjee answered |
Double fertilisation is a unique process that occurs only in flowering plants. It involves the fusion of two male gametes with two female gametes to produce a zygote and an endosperm. The correct option is (A), one male gamete fuses with the egg and the other fuses with the secondary nucleus.
Process of Double Fertilisation
Double fertilisation occurs in the embryo sac of a flower, which contains the female gametes. The process can be divided into two steps:
First Step: Pollination
During pollination, the male gametes are transferred from the pollen grains to the stigma of the flower. The pollen tube grows down the style and enters the ovary where the embryo sac is located. The pollen tube releases two male gametes into the embryo sac.
Second Step: Fertilisation
In the embryo sac, there are two types of female gametes - the egg and the two polar nuclei. One male gamete fuses with the egg to form a zygote, which will develop into an embryo. The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei to form a triploid nucleus, which will develop into the endosperm.
The Correct Option (A)
In double fertilisation, one male gamete fuses with the egg and the other fuses with the secondary nucleus. The secondary nucleus is also known as the central cell, which contains the two polar nuclei. The fusion of the male gamete with the secondary nucleus forms the triploid nucleus, which develops into the endosperm. The endosperm provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
Conclusion
Double fertilisation is a unique process that occurs only in flowering plants. It involves the fusion of two male gametes with two female gametes to produce a zygote and an endosperm. In double fertilisation, one male gamete fuses with the egg and the other fuses with the secondary nucleus to form the endosperm.
Process of Double Fertilisation
Double fertilisation occurs in the embryo sac of a flower, which contains the female gametes. The process can be divided into two steps:
First Step: Pollination
During pollination, the male gametes are transferred from the pollen grains to the stigma of the flower. The pollen tube grows down the style and enters the ovary where the embryo sac is located. The pollen tube releases two male gametes into the embryo sac.
Second Step: Fertilisation
In the embryo sac, there are two types of female gametes - the egg and the two polar nuclei. One male gamete fuses with the egg to form a zygote, which will develop into an embryo. The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei to form a triploid nucleus, which will develop into the endosperm.
The Correct Option (A)
In double fertilisation, one male gamete fuses with the egg and the other fuses with the secondary nucleus. The secondary nucleus is also known as the central cell, which contains the two polar nuclei. The fusion of the male gamete with the secondary nucleus forms the triploid nucleus, which develops into the endosperm. The endosperm provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
Conclusion
Double fertilisation is a unique process that occurs only in flowering plants. It involves the fusion of two male gametes with two female gametes to produce a zygote and an endosperm. In double fertilisation, one male gamete fuses with the egg and the other fuses with the secondary nucleus to form the endosperm.
In which of the following plants fruit contain larger number of seed?- a)Neem fruits
- b)Orchid fruits
- c)Lemon fruits
- d)Mango fruits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following plants fruit contain larger number of seed?
a)
Neem fruits
b)
Orchid fruits
c)
Lemon fruits
d)
Mango fruits

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
The number of ovule present in ovary determine the number of seeds produced inside the fruit. Mango and neem produce single seed in each fruit. Lemon contain a number of seeds but orchid contain many small size seeds.
Which of the following options is correct?- a)Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower - Autogamy.
- b)Transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of same plant - Geitonogamy.
- c)Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a genetically different plant - Xenogamy.
- d)All of these.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options is correct?
a)
Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower - Autogamy.
b)
Transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of same plant - Geitonogamy.
c)
Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a genetically different plant - Xenogamy.
d)
All of these.
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Autogamy (Gk. autos-self, gamos-marriage) is a type of self-pollination in which an intersexual or perfect flower is pollinated by its own pollen.
Geitonogamy is a type of pollination in which pollen grains of one flower are transferred to the stigma of another flower belonging to either the same plant or a genetically similar plant. In geitonogamy, the flowers often show modifications similar to ones found in xenogamy or cross-pollination.
Xenogamy or cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of a genetically different flower.
Placenta is located inside the-------.- a)Micropyle
- b)Funicle
- c)Ovule cavity
- d)Ovarian cavity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Placenta is located inside the-------.
a)
Micropyle
b)
Funicle
c)
Ovule cavity
d)
Ovarian cavity
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Inside the ovary is the ovarian cavity (locule). The placenta is located inside the ovarian cavity. Arising from the placenta are the megasporangia, commonly called ovules.
Number of nuclei participating in double fertilisation is?- a)2
- b)5
- c)4
- d)3
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of nuclei participating in double fertilisation is?
a)
2
b)
5
c)
4
d)
3

|
Sadiya Siddique answered |
The two polar nuclei, 2 male gamates nuclei and an egg cell nucleus participates in double fertilization.thus, op B.
Refer to the given characteristics of some flowers.
(i) LIght and non-sticky pollen grains
(ii) Exserted stigmas and anthers
(iii) Large, often feathert stigmas
(iv) Flowers colourless, odourless and nectarless
(v) Common in grassesAbove features are the characteristics of - a)anemophily
- b)hydrophily
- c)entomophily
- d)zoophily.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer to the given characteristics of some flowers.
(i) LIght and non-sticky pollen grains
(ii) Exserted stigmas and anthers
(iii) Large, often feathert stigmas
(iv) Flowers colourless, odourless and nectarless
(v) Common in grasses
(i) LIght and non-sticky pollen grains
(ii) Exserted stigmas and anthers
(iii) Large, often feathert stigmas
(iv) Flowers colourless, odourless and nectarless
(v) Common in grasses
Above features are the characteristics of
a)
anemophily
b)
hydrophily
c)
entomophily
d)
zoophily.
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Anemophily is a mode of cross pollination or transfer of pollen grains from a mature anther to the stigma of a pistil which is accomplished through the agency of wind, e.g., coconut palm, data palm, maize, many grasses, Cannabis, etc.
In most of angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at_______.- a)4-celled stage
- b)3-celled stage
- c)2-celled stage
- d)8-celled stage
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In most of angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at_______.
a)
4-celled stage
b)
3-celled stage
c)
2-celled stage
d)
8-celled stage
|
|
Satakshi Kumari answered |
Generally pollengrain has two cells one vegetative and the other generative
so in many of the angiosperms about 60% of them shed off from anther at this two celled stage
and in remaining 40% of angiosperms the generative cell divides into two cells called as male gamets when present in the anther and at this three celled stage of the pollen grain they shed out..... three cells means one vegetative ,two male gametes
so in many of the angiosperms about 60% of them shed off from anther at this two celled stage
and in remaining 40% of angiosperms the generative cell divides into two cells called as male gamets when present in the anther and at this three celled stage of the pollen grain they shed out..... three cells means one vegetative ,two male gametes
Seed of castor is- a)non-endospermic, exalbuminous
- b)endospermic, albuminous
- c)endospermic, exalbuminous
- d)non-endospermic, albuminous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Seed of castor is
a)
non-endospermic, exalbuminous
b)
endospermic, albuminous
c)
endospermic, exalbuminous
d)
non-endospermic, albuminous

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- Endospermic: Castor seeds contain endosperm, which is the tissue that provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
- Albuminous: The endosperm in castor seeds remains in the mature seed and is not consumed during seed development, so it is termed albuminous.
Topic in NCERT: Seed
Line in NCERT: "Albuminous seeds retain a part of endosperm as it is not completely used up during embryo development (e.g., wheat, maize, barley, castor)."
If an endosperm cell of angiosperm contain 24 chromosome, the number of chromosome in each cell of root is? - a)24
- b)16
- c)8
- d)48
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If an endosperm cell of angiosperm contain 24 chromosome, the number of chromosome in each cell of root is?
a)
24
b)
16
c)
8
d)
48

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Endosperm of angiosperms is triploid (3n) While as root cell is diploid(2n). Hence, number of chromosomes in each root cell = 2n = 2 x 8 = 16.
The anther is a four sided structure consisting of four------------ located at the corner. - a)Microsporangia
- b)Megasporangia
- c)Macrosoporangia
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The anther is a four sided structure consisting of four------------ located at the corner.
a)
Microsporangia
b)
Megasporangia
c)
Macrosoporangia
d)
None of these

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
Anther is bilobed structure at the tips of stamen. Each lobe consists of two theca. Each theca change into microsporangium. Anther forms four sided structure having four microsporangia in which pollen grains are formed.
Identify “A” and “B” in the T.S of mature anther: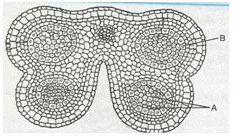
- a)Middle layer and Tapetum
- b)Microspore mother cell and Tapetum
- c)Epidermis and tapetum
- d)Stomium and microspore mother cell
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify “A” and “B” in the T.S of mature anther:
a)
Middle layer and Tapetum
b)
Microspore mother cell and Tapetum
c)
Epidermis and tapetum
d)
Stomium and microspore mother cell
|
|
Anirban Nambiar answered |
The mature anther consists of four microsporangia which contain four layers. The inner most layer is called tapetum that provide nutrient to growing microspores and tissues inside it are called microspore mother cell that produce pollen grain.
A typical angiosperm embryo sac at maturity is_______.- a)2 nucleate
- b)7 nucleate
- c)4 nucleate
- d)8 nucleate
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A typical angiosperm embryo sac at maturity is_______.
a)
2 nucleate
b)
7 nucleate
c)
4 nucleate
d)
8 nucleate

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Angiospermic embryo sac is 8-nucleate but 7-celled at maturity. This includes 3- celled egg Synergids, 3 antipodal cells and 2 polar nuclei.
Sporopollenin an organic material is present in- a)Exine
- b)Intine
- c)Style
- d)Stigma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sporopollenin an organic material is present in
a)
Exine
b)
Intine
c)
Style
d)
Stigma
|
|
Ritu Joshi answered |
The exine is made up of sporopollenin, which is one of the most resistant organic material. The in tine layer is made up of cellulose and pectin materials.The exine is hard and hence protects the pollen grains during adverse conditions.
One of the major contributors to pollen allergy is ____- a)carrot grass
- b)lawn grass
- c)wheat grass
- d)paddy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the major contributors to pollen allergy is ____
a)
carrot grass
b)
lawn grass
c)
wheat grass
d)
paddy
|
|
Gayatri Chauhan answered |
Carrot grass as a major contributor to pollen allergy:
Pollen Allergy:
Pollen allergy, also known as hay fever or allergic rhinitis, is a common allergic reaction to pollen particles released by plants during their reproductive process.
Carrot grass:
Carrot grass, also known as timothy grass, is a common grass species that is a major contributor to pollen allergy in many individuals.
Pollen Production:
Carrot grass produces large amounts of pollen during its flowering season, which typically occurs in the spring and summer months.
Allergic Reactions:
When individuals with pollen allergies come into contact with carrot grass pollen, their immune system may overreact, leading to symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and respiratory issues.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis of a pollen allergy usually involves skin prick tests or blood tests. Treatment options may include antihistamines, decongestants, nasal corticosteroids, and allergen immunotherapy.
The inner most wall layer of anther is tapetum, the main function of tapetum is- a)Dehiscence
- b)Mechanical
- c)Nutrition
- d)Protection
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The inner most wall layer of anther is tapetum, the main function of tapetum is
a)
Dehiscence
b)
Mechanical
c)
Nutrition
d)
Protection
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The tapetal layer is of great physiological significance as all the food material entering into the sporogenous tissue diffuses through this layer. Ultimately the cells of tapetal layer disorganise. Thus, tapetum makes a nutritive layer for the developing microspores.
What is the function of filiform apparatus in an angiosperm embryo sac?- a)Guides pollen tube from synergid to egg
- b)Helps in the entry of more than one pollen tube into a synergid
- c)Prevents entry of more than one pollen tube into a synergid
- d)Brings about opening of the pollen tube
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the function of filiform apparatus in an angiosperm embryo sac?
a)
Guides pollen tube from synergid to egg
b)
Helps in the entry of more than one pollen tube into a synergid
c)
Prevents entry of more than one pollen tube into a synergid
d)
Brings about opening of the pollen tube
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
In the ovule, the pollen tube is attracted by secretions of synergids. Jensen (1965) suggested that the filiform apparatus may be aiding the synergid in the absorption and transportation of materials into the embryo sac from the nucellus. He held the opinion that the filiform apparatus
What is the correct sequence of the formation of female gametophyte in angiosperms?- a)Nucellus, megaspore tetrad, megaspore mother cell, megaspore, female gametophyte
- b)Megaspore tetrad, nucellus, megaspore mother cell, megaspore, female gametophyte
- c)Nucellus, megaspore mother cell, megaspore tetrad, megaspore, female gametophyte
- d)Megaspore mother cell, megaspore tetrad, megaspore, nucellus, female gametophyte
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct sequence of the formation of female gametophyte in angiosperms?
a)
Nucellus, megaspore tetrad, megaspore mother cell, megaspore, female gametophyte
b)
Megaspore tetrad, nucellus, megaspore mother cell, megaspore, female gametophyte
c)
Nucellus, megaspore mother cell, megaspore tetrad, megaspore, female gametophyte
d)
Megaspore mother cell, megaspore tetrad, megaspore, nucellus, female gametophyte
|
|
Lakshmi Bose answered |
Formation of Female Gametophyte in Angiosperms
The development of the female gametophyte in angiosperms follows a specific sequence, which can be outlined as follows:
1. Nucellus
- The nucellus is the tissue within the ovule that contains the megasporangium.
- It provides nourishment and support for the developing gametophyte.
2. Megaspore Mother Cell
- The megaspore mother cell (megasporocyte) is located within the nucellus.
- This diploid cell undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores.
3. Megaspore Tetrad
- After meiosis, the four megaspores form a tetrad.
- Typically, three of the megaspores degenerate, leaving one functional megaspore.
4. Megaspore
- The surviving megaspore undergoes mitotic divisions.
- It divides to form the female gametophyte, also known as the embryo sac.
5. Female Gametophyte
- The final structure is the mature female gametophyte, which usually contains seven cells and eight nuclei.
- This structure is crucial for fertilization, as it will eventually form the egg cell, synergids, and polar nuclei.
Conclusion
The correct sequence of formation of the female gametophyte is:
Nucellus → Megaspore Mother Cell → Megaspore Tetrad → Megaspore → Female Gametophyte
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C'. Understanding this sequence is vital for comprehending the reproductive processes in flowering plants, which is essential for NEET aspirants.
The development of the female gametophyte in angiosperms follows a specific sequence, which can be outlined as follows:
1. Nucellus
- The nucellus is the tissue within the ovule that contains the megasporangium.
- It provides nourishment and support for the developing gametophyte.
2. Megaspore Mother Cell
- The megaspore mother cell (megasporocyte) is located within the nucellus.
- This diploid cell undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores.
3. Megaspore Tetrad
- After meiosis, the four megaspores form a tetrad.
- Typically, three of the megaspores degenerate, leaving one functional megaspore.
4. Megaspore
- The surviving megaspore undergoes mitotic divisions.
- It divides to form the female gametophyte, also known as the embryo sac.
5. Female Gametophyte
- The final structure is the mature female gametophyte, which usually contains seven cells and eight nuclei.
- This structure is crucial for fertilization, as it will eventually form the egg cell, synergids, and polar nuclei.
Conclusion
The correct sequence of formation of the female gametophyte is:
Nucellus → Megaspore Mother Cell → Megaspore Tetrad → Megaspore → Female Gametophyte
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C'. Understanding this sequence is vital for comprehending the reproductive processes in flowering plants, which is essential for NEET aspirants.
Which one of the following statements is false in respect of flowering plants?
1. Parthenocarpy can be induced through the application of growth hormones
2. Integuments encircle the ovule except at the tip where a small opening called the germ pore is organized
3. Endosperm development precedes embryo development
4. Apomicts have several advantages in horticulture and agriculture
- a)Statement 1
- b)Statement 2
- c)Statement 3
- d)Statement 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is false in respect of flowering plants?
1. Parthenocarpy can be induced through the application of growth hormones
2. Integuments encircle the ovule except at the tip where a small opening called the germ pore is organized
3. Endosperm development precedes embryo development
4. Apomicts have several advantages in horticulture and agriculture
a)
Statement 1
b)
Statement 2
c)
Statement 3
d)
Statement 4

|
Bs Academy answered |
Statement 1: Parthenocarpy, the development of fruit without fertilization, can indeed be induced through the application of growth hormones.
Statement 2: Integuments encircle the ovule except at the tip where there is an opening called the micropyle, not the germ pore. The germ pore is found in pollen grains, not ovules.
Statement 3: Endosperm development typically precedes embryo development in most flowering plants.
Statement 4: Apomicts, plants that can reproduce without fertilization, have several advantages in horticulture and agriculture, such as maintaining desirable traits without genetic variation.
Therefore, Statement 2 is false because the correct term for the opening at the tip of the ovule is the micropyle, not the germ pore.
Statement 2: Integuments encircle the ovule except at the tip where there is an opening called the micropyle, not the germ pore. The germ pore is found in pollen grains, not ovules.
Statement 3: Endosperm development typically precedes embryo development in most flowering plants.
Statement 4: Apomicts, plants that can reproduce without fertilization, have several advantages in horticulture and agriculture, such as maintaining desirable traits without genetic variation.
Therefore, Statement 2 is false because the correct term for the opening at the tip of the ovule is the micropyle, not the germ pore.
Choose the correct statement from the following:- a)Chasmogamous flowers never exhibit autogamy
- b)Chasmogamous flowers always exhibit geitonogamy
- c)Cleistogamous flowers exhibit both autogamy and geitonogamy
- d)Cleistogamous flowers always exhibit autogamy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement from the following:
a)
Chasmogamous flowers never exhibit autogamy
b)
Chasmogamous flowers always exhibit geitonogamy
c)
Cleistogamous flowers exhibit both autogamy and geitonogamy
d)
Cleistogamous flowers always exhibit autogamy

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Correct Answer: D
- Autogamy refers to the process where a flower is self-pollinated, ensuring fertilization without needing another flower.
- Cleistogamous flowers are self-pollinating flowers that never open, ensuring autogamy.
- Therefore, it is accurate to say that cleistogamous flowers always exhibit autogamy as they are designed to self-pollinate without the need for external agents like insects or wind.
- Autogamy refers to the process where a flower is self-pollinated, ensuring fertilization without needing another flower.
- Cleistogamous flowers are self-pollinating flowers that never open, ensuring autogamy.
- Therefore, it is accurate to say that cleistogamous flowers always exhibit autogamy as they are designed to self-pollinate without the need for external agents like insects or wind.
Topic in NCERT: Cleistogamous flowers
Line in NCERT: "Cleistogamous flowers are invariably autogamous as there is no chance of cross-pollen landing on the stigma."
The part of gynoecium that determines the compatible nature of pollen is?- a)stigma
- b)style
- c)ovary
- d)synergids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The part of gynoecium that determines the compatible nature of pollen is?
a)
stigma
b)
style
c)
ovary
d)
synergids
|
|
Niti Das answered |
Answer:
Stigma determines the compatible nature of pollen.
Explanation:
The gynoecium is the female reproductive part of the flower consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the uppermost part of the gynoecium, which is sticky and receptive to pollen. The style is a long slender tube-like structure that connects the stigma to the ovary. The ovary is the swollen part of the gynoecium that contains the ovules, which develop into seeds after fertilization. The synergids are the two small cells present in the embryo sac, which help in the entry of pollen tube into the ovule.
The stigma plays a crucial role in determining the compatible nature of pollen. When pollen lands on the stigma, it germinates and grows a long tube-like structure called the pollen tube, which travels down the style and enters the ovary to fertilize the ovule. However, not all pollen can germinate on every stigma. The stigma has specific molecular characteristics that determine which pollen can successfully germinate on it. This is known as stigma specificity.
The molecular basis of stigma specificity is still being studied, but it is known that there is a mutual recognition process between the stigma and the pollen. The stigma produces chemicals that attract compatible pollen, which in turn releases chemicals that help it recognize the stigma. This recognition process is necessary to ensure successful fertilization and seed production.
Therefore, the stigma plays a crucial role in determining the compatible nature of pollen, and it is the part of the gynoecium that is responsible for ensuring successful fertilization and seed production.
Stigma determines the compatible nature of pollen.
Explanation:
The gynoecium is the female reproductive part of the flower consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the uppermost part of the gynoecium, which is sticky and receptive to pollen. The style is a long slender tube-like structure that connects the stigma to the ovary. The ovary is the swollen part of the gynoecium that contains the ovules, which develop into seeds after fertilization. The synergids are the two small cells present in the embryo sac, which help in the entry of pollen tube into the ovule.
The stigma plays a crucial role in determining the compatible nature of pollen. When pollen lands on the stigma, it germinates and grows a long tube-like structure called the pollen tube, which travels down the style and enters the ovary to fertilize the ovule. However, not all pollen can germinate on every stigma. The stigma has specific molecular characteristics that determine which pollen can successfully germinate on it. This is known as stigma specificity.
The molecular basis of stigma specificity is still being studied, but it is known that there is a mutual recognition process between the stigma and the pollen. The stigma produces chemicals that attract compatible pollen, which in turn releases chemicals that help it recognize the stigma. This recognition process is necessary to ensure successful fertilization and seed production.
Therefore, the stigma plays a crucial role in determining the compatible nature of pollen, and it is the part of the gynoecium that is responsible for ensuring successful fertilization and seed production.
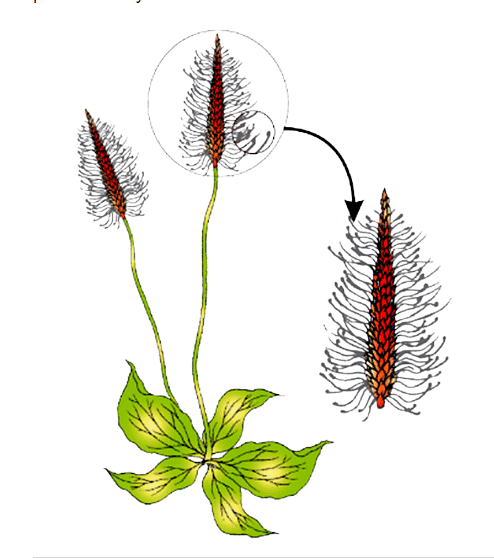
The plant shown in the given diagram is most likely to be pollinated by:
- a)Wind
- b)Water
- c)Bees
- d) Bats
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The plant shown in the given diagram is most likely to be pollinated by:

a)
Wind
b)
Water
c)
Bees
d)
Bats
|
|
Mitrabinda Dhanalakota answered |
The correct answer for this question is A ( wind ) because the hairy like substance look very light so it is likely to be pollinated by wind
While planning for an artificial hybridization programme involving dioecious plants, which of the following steps would not be relevant?- a) Bagging of the female flower
- b)Dusting of pollen on the stigma
- c) Emasculation
- d)Collection of pollen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
While planning for an artificial hybridization programme involving dioecious plants, which of the following steps would not be relevant?
a)
Bagging of the female flower
b)
Dusting of pollen on the stigma
c)
Emasculation
d)
Collection of pollen

|
Ambition Institute answered |
In an artificial hybridization program with dioecious plants:
- Bagging of the female flower: Relevant to prevent unwanted pollen contamination.
- Dusting of pollen on the stigma: Essential for pollination to occur.
- Emasculation: Not relevant because dioecious plants have separate sexes; emasculation is for monoecious plants.
- Collection of pollen: Necessary for controlled pollination process.
Therefore, in this context, the step that would not be relevant is C: Emasculation.
Topic in NCERT: Artificial Hybridization Techniques
Line in NCERT: "Emasculated flowers have to be covered with a bag of suitable size, generally made up of butter paper, to prevent contamination of its stigma with unwanted pollen."
- Bagging of the female flower: Relevant to prevent unwanted pollen contamination.
- Dusting of pollen on the stigma: Essential for pollination to occur.
- Emasculation: Not relevant because dioecious plants have separate sexes; emasculation is for monoecious plants.
- Collection of pollen: Necessary for controlled pollination process.
Therefore, in this context, the step that would not be relevant is C: Emasculation.
Topic in NCERT: Artificial Hybridization Techniques
Line in NCERT: "Emasculated flowers have to be covered with a bag of suitable size, generally made up of butter paper, to prevent contamination of its stigma with unwanted pollen."
Chapter doubts & questions for Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









