All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Reproduction in Mammals for JAMB Exam
Interstitial cells or leydig cells are present between______.- a)Basal lamina
- b)Seminiferous tubules
- c)Tubuli recti
- d)Sertoli cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Interstitial cells or leydig cells are present between______.
a)
Basal lamina
b)
Seminiferous tubules
c)
Tubuli recti
d)
Sertoli cells
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Interstitial cells or leydig cells are present between seminiferous tubules..they secrete androgens..mainly testosterone
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?
- A:
Lactogen
- B:
Primary milk
- C:
Colostrum
- D:
None of these
The answer is c.
The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?
Lactogen
Primary milk
Colostrum
None of these
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Colostrum is a thick and sticky, yellow to orange colored milk that is created by your breasts to give your baby the nutrition he needs immediately after birth. It is low in fat, high in carbohydrates and has a laxative effect on the baby which helps him pass the first meconium stools that are sitting in his intestines. This also helps get rid of the bile and helps lessen the chance of jaundice in your newborn.
Ovulation occurs on the ------ day of menstrual cycle. - a)08-10
- b)12-14
- c)14-16
- d)16-18
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ovulation occurs on the ------ day of menstrual cycle.
a)
08-10
b)
12-14
c)
14-16
d)
16-18

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
The release of ovum from ovary during menstrual cycle is is called ovulation. Ovulation occurs in the middle of menstrual cycle that is on 14-16th day of start of menstrual cycle.
Shortest phase of the menstrual cycle is______.- a)Ovulatory phase
- b)Menses
- c)Follicular phase
- d)Luteal phase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Shortest phase of the menstrual cycle is______.
a)
Ovulatory phase
b)
Menses
c)
Follicular phase
d)
Luteal phase
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Menstrual cycle is divided into several phase starting from menses during which endometrium breaks and comes out through vagina for 4 to 5 days. Ovulatory phase occurs in the middle of menstrual cycle (14/15th day) during which egg is released.
Which one is the most likely reason of not occurring regular menstrual cycle?- a)Fertilization of ovum
- b)Retention of corpus luteum
- c)Maintenance of hypertropical endometrial lining
- d)Maintenance of high concentration of sex hormones
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is the most likely reason of not occurring regular menstrual cycle?
a)
Fertilization of ovum
b)
Retention of corpus luteum
c)
Maintenance of hypertropical endometrial lining
d)
Maintenance of high concentration of sex hormones

|
Sushant Goyal answered |
Menstrual cycles get stopped during pregnancy. Sometimes it becomes irregular due to stress and other hormonal activities of the body.
Preventive birth control measure is__________.- a)Preventing sperms from entering uterus
- b)Preventing union of ovum and sperm
- c)Test-tube babies
- d)MTP
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Preventive birth control measure is__________.
a)
Preventing sperms from entering uterus
b)
Preventing union of ovum and sperm
c)
Test-tube babies
d)
MTP
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Preventive birth control measures is preventing sperms from entering the uterus.
► Barrier methods of contraception: Diaphragms, Sponges, and Cervical caps that prevent the sperm from entering the uterine cavity.
Reproductive health includes:- a)Protection from STD’s, contraceptive and ARTs
- b)Financial independence
- c)Child education
- d)Child and mother care only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Reproductive health includes:
a)
Protection from STD’s, contraceptive and ARTs
b)
Financial independence
c)
Child education
d)
Child and mother care only
|
|
Pankaj Singh answered |
Answer :
- a)Protection from STD’s, contraceptive and ARTs
Successful implementation of various action plans to attainreproductive health requires strong infrastructural facilities, professionalexpertise and material support. These are essential to provide medicalassistance and care to people in reproduction-related problems likepregnancy, delivery, STDs, abortions, contraception, menstrual problems,infertility, etc. Implementation of better techniques and new strategiesfrom time to time are also required to provide more efficient care andassistance to people. Statutory ban on amniocentesis (a foetal sexdetermination test based on the chromosomal pattern in the amnioticfluid surrounding the developing embryo) for sex-determination to legallycheck increasing female foeticides, massive child immunisation, etc., aresome programmes that merit mention in this connection.
The cellular layer that disintegrates and regenerates again and again is _______.
- a)Dermis of skin
- b)Endometrium of uterus
- c)Cornea of eye
- d)Endometrium of blood vessels
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The cellular layer that disintegrates and regenerates again and again is _______.
a)
Dermis of skin
b)
Endometrium of uterus
c)
Cornea of eye
d)
Endometrium of blood vessels

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
- The functional layer of the human endometrium is a highly regenerative tissue undergoing monthly cycles of growth, differentiation, and shedding during a woman's reproductive years.
- Fluctuating levels of circulating estrogen and progesterone orchestrate this dramatic remodelling of human endometrium.
Hence, the correct option is B.
NCERT Reference: topic “MENSTRUAL CYCLE” of chapter: Human Reproduction.
NCERT Reference: topic “MENSTRUAL CYCLE” of chapter: Human Reproduction.
Which of the following birth control measures can be considered as the safest?- a)Termination of unwanted pregnancy
- b)The use of physical barriers
- c)Sterilisation techniques
- d)The rhythm method
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following birth control measures can be considered as the safest?
a)
Termination of unwanted pregnancy
b)
The use of physical barriers
c)
Sterilisation techniques
d)
The rhythm method

|
Sharvari Kuber answered |
In sterilisation method method, tubectomy or vasectomy is used in which the fallopian tube and vas deferens are cut respectively. This prevents the transfer of sperms in males and ova in females for fertilisation permanently. So this is the safest method.
Hormone responsible for milk ejection after the birth of baby is:
- a)Progesterone
- b)vasopressin
- c)Estrogens
- d)Oxytocin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormone responsible for milk ejection after the birth of baby is:
a)
Progesterone
b)
vasopressin
c)
Estrogens
d)
Oxytocin
|
|
Naina Choudhary answered |
Hormone responsible for milk ejection after the birth of baby is oxytocin.
Explanation:
After the birth of a baby, the mother's body undergoes various hormonal changes that promote milk production and ejection. The primary hormone responsible for milk ejection is oxytocin, which is produced in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary gland.
When a baby suckles at the breast, nerve endings in the nipple and areola are stimulated, which triggers the release of oxytocin. Oxytocin then causes the smooth muscle cells in the milk ducts to contract, which pushes the milk out of the breast and into the baby's mouth. This process is known as the milk ejection reflex or let-down reflex.
Other hormones that are involved in milk production and ejection include:
- Prolactin: This hormone is produced in the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates milk production in the mammary glands.
- Estrogens: These hormones are produced in the ovaries and play a role in breast development and milk production.
- Progesterone: This hormone is produced in the ovaries and plays a role in preparing the breast for milk production.
However, in terms of milk ejection specifically, oxytocin is the primary hormone involved.
Explanation:
After the birth of a baby, the mother's body undergoes various hormonal changes that promote milk production and ejection. The primary hormone responsible for milk ejection is oxytocin, which is produced in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary gland.
When a baby suckles at the breast, nerve endings in the nipple and areola are stimulated, which triggers the release of oxytocin. Oxytocin then causes the smooth muscle cells in the milk ducts to contract, which pushes the milk out of the breast and into the baby's mouth. This process is known as the milk ejection reflex or let-down reflex.
Other hormones that are involved in milk production and ejection include:
- Prolactin: This hormone is produced in the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates milk production in the mammary glands.
- Estrogens: These hormones are produced in the ovaries and play a role in breast development and milk production.
- Progesterone: This hormone is produced in the ovaries and plays a role in preparing the breast for milk production.
However, in terms of milk ejection specifically, oxytocin is the primary hormone involved.
A fluid-filled cavity present within blastula is called:- a)Blastoderm
- b)Blastopore
- c)Archenteron
- d)Blastocoel
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A fluid-filled cavity present within blastula is called:
a)
Blastoderm
b)
Blastopore
c)
Archenteron
d)
Blastocoel

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
A single-celled zygote will undergo multiple rounds of cleavage, or cell division, in order to produced a ball of cells, called a blastula, with a fluid-filled cavity in its center, called a blastocoel.
Which one is not a sexually transmitted disease?- a)Syphilis
- b)AIDS
- c)Encephalitis
- d)Genital herpes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not a sexually transmitted disease?
a)
Syphilis
b)
AIDS
c)
Encephalitis
d)
Genital herpes
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) comprise a diverse group that includes blood-borne diseases, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and ulcerative lesions. Examples : Syphilis, Genital herpes, HIV /Aids
Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain. The majority of cases are caused by either a viral infection or the immune system mistakenly attacking brain tissue.
Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain. The majority of cases are caused by either a viral infection or the immune system mistakenly attacking brain tissue.
Which of the following contraceptive method is useful to control STD’s as well as unwanted pregnancy?- a)Tubectomy
- b)Condom
- c)Copper-T
- d)Oral pills
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following contraceptive method is useful to control STD’s as well as unwanted pregnancy?
a)
Tubectomy
b)
Condom
c)
Copper-T
d)
Oral pills
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- Condoms are protective covering of penis that do not allow the passage of semen into vagina of female during sexual intercourse.
- This contracetive prevents the fusion of body fluid of male and female and protect from STDs.
The number of polar bodies formed during oogenesis in human being is:
- a)2
- b)3
- c)1
- d)Both 2 and 3.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of polar bodies formed during oogenesis in human being is:
a)
2
b)
3
c)
1
d)
Both 2 and 3.
|
|
Raj Yadav answered |
Polar bodies formed during oogenesis in humans
- During human oogenesis, three polar bodies are created.
- Polar bodies are tiny cytoplasmic exclusion structures that form to contain extra DNA produced during oocyte meiosis, which occurs after sperm fertilization.
- The zygote contains roughly 2-3 polar bodies, which are derived from the oocyte.
- This figure is determined by whether or not the first polar body (produced during meiosis I) splits during meiosis II.
- Excess DNA generated from reductive division makes up such an exclusion body (2nd and 3rd polar bodies are formed from meiosis II at the time of fertilization).
- Such polar bodies do not contribute to the zygote's, foetus', or embryo's future genetic complement.
Diaphragms are contraceptive devices used by females. Choose the correct option from the statements given below:
(i) They are introduced into the uterus.
(ii) They are placed to cover the cervical region.
(iii) They act as physical barriers for sperm entry.
(iv) They act as spermicidal agents.- a)(iii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Diaphragms are contraceptive devices used by females. Choose the correct option from the statements given below:
(i) They are introduced into the uterus.
(ii) They are placed to cover the cervical region.
(iii) They act as physical barriers for sperm entry.
(iv) They act as spermicidal agents.
(i) They are introduced into the uterus.
(ii) They are placed to cover the cervical region.
(iii) They act as physical barriers for sperm entry.
(iv) They act as spermicidal agents.
a)
(iii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(ii) and (iii)

|
Vanshika Rastogi answered |
Answer is Option D. Diaphragms ain't spermicidal Because it doesn't kill the sperms..instead prevents sperm entry as they are to be placed in the cervical region as a barrier / cover .
In ET technique the embryo is transferred into _________.
- a)Always fallopian tube
- b)Always uterus
- c)Fallopian tube or uterus
- d)Ovary
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In ET technique the embryo is transferred into _________.
a)
Always fallopian tube
b)
Always uterus
c)
Fallopian tube or uterus
d)
Ovary
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
In ET (embryo transfer) technique, in vitro fertilized embryo is transferred into the fallopian tube or uterus for further development.
- In this type of technique, male and female gametes are fused outside the mother's body. It is used either when the male cannot produce enough sperms to fertilize the ovum or the females can not release ova for the purpose.
- After the embryo reaches 8 celled stages, known as the morula, it is transferred to the female fallopian tubule. If it is in the 16 celled stages, known as blastomere, it is transferred directly to the female uterus.
Embryo Transfer technique:
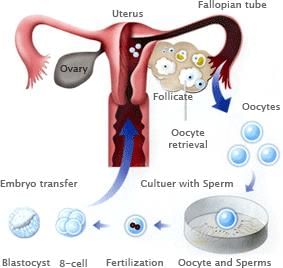

Hence, the correct option is C.
NCERT Reference: topic “INFERTILITY” of chapter: Reproductive Health of NCERT.
Now a day, there is less childless couple. This is due to_________.- a)Assisted reproductive technologies
- b)Awareness among the couples
- c)Educated population
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Now a day, there is less childless couple. This is due to_________.
a)
Assisted reproductive technologies
b)
Awareness among the couples
c)
Educated population
d)
None of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The couples can be assisted to have children through certain special techniques called the assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
The applications of reproductive technology are:
(i) Test tube baby
(ii) Artificial insemination technique (AIT)
(iii) Gamete intra Fallopian transfer (GIFT)
(iv) lntra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
(i) Test tube baby
(ii) Artificial insemination technique (AIT)
(iii) Gamete intra Fallopian transfer (GIFT)
(iv) lntra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
Disease or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are collectively called?- a)Venereal disease
- b)Fungal disease
- c)Bacterial disease
- d)Viral disease
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Disease or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are collectively called?
a)
Venereal disease
b)
Fungal disease
c)
Bacterial disease
d)
Viral disease
|
|
Shubham Kulkarni answered |
Answer :
- a)Venereal disease
Diseases or infection which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are collectively called
sexually transmitted disease or venereal disease or reproductive tract infections.
Which of the following hormone is produced in female only during pregnancy?
- a)Testosterone
- b)Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG).
- c)Progesterone
- d)Estrogen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following hormone is produced in female only during pregnancy?
a)
Testosterone
b)
Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG).
c)
Progesterone
d)
Estrogen
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
- It is made almost exclusively in the placenta.
- hCG hormone levels found in the mother's blood and urine, rise a lot during the first trimester.
- hCG Maintains the corpus luteum throughout the early stages of pregnancy. It is used to detect pregnancy.
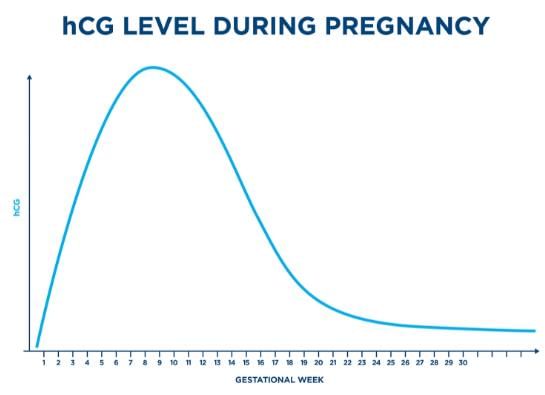
Hence, the correct option is B.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 53 of topic “3.6 PREGNANCY AND EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT” of chapter 3.
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland- a)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
a)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Kiran Singh answered |
Contributors to Seminal Plasma
Seminal plasma is the fluid part of semen that carries sperm. It is composed of a mixture of secretions from various male reproductive organs. The following are the contributors of seminal plasma:
(i) Seminal Vesicle - The seminal vesicle is a pair of glands that secrete a fluid that makes up 60-70% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains fructose, prostaglandins, and other substances that provide energy to the sperm and help them survive in the female reproductive tract.
(ii) Prostate - The prostate gland is a single gland located below the bladder that produces a milky fluid that makes up about 15-30% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains enzymes, citric acid, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which helps to liquefy semen after ejaculation.
(iii) Urethra - The urethra is a tube that runs through the penis and carries semen and urine out of the body. It contributes a small amount of fluid to the seminal plasma.
(iv) Bulbourethral Gland - The bulbourethral gland, also known as Cowper's gland, is a pair of small glands located at the base of the penis. They secrete a clear fluid that helps to lubricate the urethra and neutralize any acidic urine remaining in the urethra.
Conclusion
In conclusion, seminal plasma is a mixture of secretions from different male reproductive organs, including the seminal vesicle, prostate, urethra, and bulbourethral gland. The various secretions work together to provide energy to the sperm, help them survive in the female reproductive tract, and ensure that the semen can be ejaculated and transported effectively.
Seminal plasma is the fluid part of semen that carries sperm. It is composed of a mixture of secretions from various male reproductive organs. The following are the contributors of seminal plasma:
(i) Seminal Vesicle - The seminal vesicle is a pair of glands that secrete a fluid that makes up 60-70% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains fructose, prostaglandins, and other substances that provide energy to the sperm and help them survive in the female reproductive tract.
(ii) Prostate - The prostate gland is a single gland located below the bladder that produces a milky fluid that makes up about 15-30% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains enzymes, citric acid, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which helps to liquefy semen after ejaculation.
(iii) Urethra - The urethra is a tube that runs through the penis and carries semen and urine out of the body. It contributes a small amount of fluid to the seminal plasma.
(iv) Bulbourethral Gland - The bulbourethral gland, also known as Cowper's gland, is a pair of small glands located at the base of the penis. They secrete a clear fluid that helps to lubricate the urethra and neutralize any acidic urine remaining in the urethra.
Conclusion
In conclusion, seminal plasma is a mixture of secretions from different male reproductive organs, including the seminal vesicle, prostate, urethra, and bulbourethral gland. The various secretions work together to provide energy to the sperm, help them survive in the female reproductive tract, and ensure that the semen can be ejaculated and transported effectively.
1. Given below are four methods (A-D) and their modes of action (i) – (iv) in achieving contraception. Select their correct matching from the four options which follow.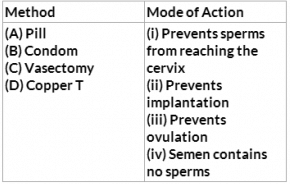
- a)A-(iii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(ii)
- b)A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
- c)A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(iv)
- d)A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(ii)
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
1. Given below are four methods (A-D) and their modes of action (i) – (iv) in achieving contraception. Select their correct matching from the four options which follow.
a)
A-(iii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(ii)
b)
A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
c)
A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(iv)
d)
A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(ii)

|
Kishan Kumar answered |
Copper T decrease sperms motility and fertilisation capacity
Choose the incorrect statement from the following:- a)Colostrum contains antibodies and nutrients.
- b)In birds and mammals internal fertilisation takes place.
- c)In the human female implantation occurs almost seven days after fertilisation.
- d)Polyspermy is prevented by the chemical changes in the egg surface.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the incorrect statement from the following:
a)
Colostrum contains antibodies and nutrients.
b)
In birds and mammals internal fertilisation takes place.
c)
In the human female implantation occurs almost seven days after fertilisation.
d)
Polyspermy is prevented by the chemical changes in the egg surface.
|
|
Rohan Kapoor answered |
The Option (C) is correct
During fertilisation, a sperm comes in contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum and induces changes in the membrane that block the entry of additional sperms. Thus, it ensures that only one sperm can fertilise an ovum.
During fertilisation, a sperm comes in contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum and induces changes in the membrane that block the entry of additional sperms. Thus, it ensures that only one sperm can fertilise an ovum.
A Human female reaches menopause around the age of_____.- a)25 years
- b)70 years
- c)50 years
- d)15 years
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A Human female reaches menopause around the age of_____.
a)
25 years
b)
70 years
c)
50 years
d)
15 years
|
|
Aravind Joshi answered |
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman's reproductive years. During menopause, the ovaries stop producing eggs and the levels of estrogen and progesterone hormones decline. Menopause is a gradual process that usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, with the average age being 51.
Explanation:
• Menopause is a natural biological process that occurs in women.
• It marks the end of a woman's reproductive years.
• During this process, the ovaries stop producing eggs and the levels of estrogen and progesterone hormones decline.
• Menopause is a gradual process that usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55.
• The average age of menopause is 51 years.
• Menopause can occur earlier or later than the average age depending on various factors, such as genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions.
• Menopause can occur as early as 40 years or as late as 60 years.
• Menopause is confirmed after a woman has gone 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period.
Explanation:
• Menopause is a natural biological process that occurs in women.
• It marks the end of a woman's reproductive years.
• During this process, the ovaries stop producing eggs and the levels of estrogen and progesterone hormones decline.
• Menopause is a gradual process that usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55.
• The average age of menopause is 51 years.
• Menopause can occur earlier or later than the average age depending on various factors, such as genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions.
• Menopause can occur as early as 40 years or as late as 60 years.
• Menopause is confirmed after a woman has gone 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period.
Amniocentesis is a method to_________.- a)Detect genetic disorder
- b)Medical termination of pregnancy
- c)Fertilize the egg
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Amniocentesis is a method to_________.
a)
Detect genetic disorder
b)
Medical termination of pregnancy
c)
Fertilize the egg
d)
None of these
|
|
Akash Menon answered |
Amniocentesis is a prenatal diagnostic procedure that involves the removal of a small amount of amniotic fluid from the sac surrounding the fetus. This procedure is performed during the second trimester of pregnancy, typically between the 15th and 20th week.
Detection of Genetic Disorders:
The main purpose of amniocentesis is to detect genetic disorders in the developing fetus. The amniotic fluid contains cells shed by the fetus, which can be analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations. This information can help parents and healthcare providers prepare for the birth of a child with a genetic disorder.
Procedure:
During the procedure, a thin needle is inserted through the belly into the amniotic sac, where a small amount of amniotic fluid is collected. The procedure is guided by ultrasound imaging to ensure that the needle is safely inserted and to monitor the fetus during the procedure. The collected fluid is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Risks:
Although amniocentesis is generally considered safe, there are some risks involved. These include a small risk of miscarriage or infection, as well as the possibility of injury to the fetus or mother during the procedure. However, the benefits of amniocentesis in detecting genetic disorders often outweigh these risks.
In conclusion, amniocentesis is a valuable tool for detecting genetic disorders during pregnancy, and it can help parents and healthcare providers make informed decisions about the care and treatment of the developing fetus.
Detection of Genetic Disorders:
The main purpose of amniocentesis is to detect genetic disorders in the developing fetus. The amniotic fluid contains cells shed by the fetus, which can be analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations. This information can help parents and healthcare providers prepare for the birth of a child with a genetic disorder.
Procedure:
During the procedure, a thin needle is inserted through the belly into the amniotic sac, where a small amount of amniotic fluid is collected. The procedure is guided by ultrasound imaging to ensure that the needle is safely inserted and to monitor the fetus during the procedure. The collected fluid is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Risks:
Although amniocentesis is generally considered safe, there are some risks involved. These include a small risk of miscarriage or infection, as well as the possibility of injury to the fetus or mother during the procedure. However, the benefits of amniocentesis in detecting genetic disorders often outweigh these risks.
In conclusion, amniocentesis is a valuable tool for detecting genetic disorders during pregnancy, and it can help parents and healthcare providers make informed decisions about the care and treatment of the developing fetus.
Indian population is_________________.- a)Mature population
- b)Young population
- c)Ageing population
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Indian population is_________________.
a)
Mature population
b)
Young population
c)
Ageing population
d)
None of these
|
|
Maya Gupta answered |
Lactational amenorrhea is a natural form of birth control that occurs when a woman is breastfeeding. It is caused by the hormones that are released during breastfeeding, which suppress ovulation. This means that women who are breastfeeding may not ovulate and therefore may not have a menstrual period for a period of time after giving birth.
Maximum Period after Parturition:
The maximum period after parturition during which lactational amenorrhea can prevent chances of fertilization is six months. After this time, the hormones that suppress ovulation begin to decrease, and the chances of ovulation and subsequent fertilization increase. Therefore, women who rely on lactational amenorrhea as a form of birth control should use another method of contraception after six months postpartum.
Effectiveness:
Lactational amenorrhea can be an effective form of birth control if certain conditions are met. These conditions include:
- The woman is exclusively breastfeeding, meaning that she is not giving the baby any other food or drink besides breast milk.
- The baby is less than six months old.
- The woman has not had a menstrual period since giving birth.
If these conditions are met, lactational amenorrhea can be up to 98% effective in preventing pregnancy. However, if any of these conditions change (for example, if the woman begins to supplement with formula or if the baby becomes older than six months), the effectiveness of lactational amenorrhea may decrease.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, lactational amenorrhea is a natural form of birth control that can be effective for up to six months postpartum. Women who rely on lactational amenorrhea as a form of birth control should be aware of its limitations and should use another form of contraception after the six-month period has ended.
Maximum Period after Parturition:
The maximum period after parturition during which lactational amenorrhea can prevent chances of fertilization is six months. After this time, the hormones that suppress ovulation begin to decrease, and the chances of ovulation and subsequent fertilization increase. Therefore, women who rely on lactational amenorrhea as a form of birth control should use another method of contraception after six months postpartum.
Effectiveness:
Lactational amenorrhea can be an effective form of birth control if certain conditions are met. These conditions include:
- The woman is exclusively breastfeeding, meaning that she is not giving the baby any other food or drink besides breast milk.
- The baby is less than six months old.
- The woman has not had a menstrual period since giving birth.
If these conditions are met, lactational amenorrhea can be up to 98% effective in preventing pregnancy. However, if any of these conditions change (for example, if the woman begins to supplement with formula or if the baby becomes older than six months), the effectiveness of lactational amenorrhea may decrease.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, lactational amenorrhea is a natural form of birth control that can be effective for up to six months postpartum. Women who rely on lactational amenorrhea as a form of birth control should be aware of its limitations and should use another form of contraception after the six-month period has ended.
Inability to conceive or produce children even after two years of unprotected sexual co-habitation is called?- a)Incapability
- b)Infertility
- c)Sterility
- d)Malfunction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Inability to conceive or produce children even after two years of unprotected sexual co-habitation is called?
a)
Incapability
b)
Infertility
c)
Sterility
d)
Malfunction
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Inability to conceive or produce children even after 2 years of unprotected sexual cohabitation is called infertility
During which month of pregnancy first movement of fetus is observed?- a)Sixth month
- b)Fourth month
- c)Fifth month
- d)Third month
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During which month of pregnancy first movement of fetus is observed?
a)
Sixth month
b)
Fourth month
c)
Fifth month
d)
Third month
|
|
Saranya Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option C, i.e., fifth month.
Explanation:
The first movement of the fetus is called quickening. It is the first noticeable movement of the fetus by the mother. Quickening is the first sign that the pregnancy is progressing as expected. It usually occurs between the 16th and 25th weeks of pregnancy. However, it is most commonly felt around the 20th week of pregnancy, which is the fifth month.
During the first trimester, the fetus is too small and underdeveloped to produce movements that can be felt by the mother. The fetal movements at this stage are mostly uncoordinated and involuntary.
During the second trimester, the fetus grows and becomes more active. The movements become more coordinated and frequent. By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs around 1 pound. The movements of the fetus become more pronounced and can be felt by the mother.
In summary, the first movement of the fetus can be observed in the fifth month of pregnancy, which is around the 20th week.
Explanation:
The first movement of the fetus is called quickening. It is the first noticeable movement of the fetus by the mother. Quickening is the first sign that the pregnancy is progressing as expected. It usually occurs between the 16th and 25th weeks of pregnancy. However, it is most commonly felt around the 20th week of pregnancy, which is the fifth month.
During the first trimester, the fetus is too small and underdeveloped to produce movements that can be felt by the mother. The fetal movements at this stage are mostly uncoordinated and involuntary.
During the second trimester, the fetus grows and becomes more active. The movements become more coordinated and frequent. By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs around 1 pound. The movements of the fetus become more pronounced and can be felt by the mother.
In summary, the first movement of the fetus can be observed in the fifth month of pregnancy, which is around the 20th week.
Which of the following control the function of Sertoli cell?- a)FSH
- b)Estrogens
- c)Testosterone
- d)ACTH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following control the function of Sertoli cell?
a)
FSH
b)
Estrogens
c)
Testosterone
d)
ACTH
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) stimulates Sertoli cells to secrete spermatogenic substance. Sertoli cells function as nurse cells for differentiating spermatozoa.
Beginning of menstrual cycle is called as ___.- a)Ovulation
- b)Oogenesis
- c)Menarche
- d)Menopause
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Beginning of menstrual cycle is called as ___.
a)
Ovulation
b)
Oogenesis
c)
Menarche
d)
Menopause
|
|
Gaurav Basu answered |
Menarche
Menarche is the beginning of the menstrual cycle, which is the process of shedding the uterine lining that occurs in women of reproductive age. It is a significant event in a girl's life as it indicates the onset of puberty and the ability to conceive a child.
Puberty
Puberty is the stage of development when a child's body becomes capable of reproduction. It is a gradual process that occurs over several years and involves physical changes such as the growth of breasts and pubic hair, as well as psychological changes such as the onset of sexual attraction and the development of a sense of identity.
Age of Menarche
The age of menarche varies widely among girls, but it typically occurs between the ages of 11 and 14. Factors that can influence the age of menarche include genetics, nutrition, and overall health.
Signs of Menarche
The signs of menarche include the onset of vaginal bleeding, which may be light or heavy, and may last for several days. Other signs may include abdominal cramping, mood swings, and breast tenderness.
Importance of Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is an important process that allows women to conceive and bear children. It also plays a role in maintaining overall health by regulating hormone levels and removing waste products from the body.
Conclusion
In conclusion, menarche is the beginning of the menstrual cycle and marks the onset of puberty in girls. It is a significant event that has both physical and psychological implications and is an important part of a woman's reproductive health.
Menarche is the beginning of the menstrual cycle, which is the process of shedding the uterine lining that occurs in women of reproductive age. It is a significant event in a girl's life as it indicates the onset of puberty and the ability to conceive a child.
Puberty
Puberty is the stage of development when a child's body becomes capable of reproduction. It is a gradual process that occurs over several years and involves physical changes such as the growth of breasts and pubic hair, as well as psychological changes such as the onset of sexual attraction and the development of a sense of identity.
Age of Menarche
The age of menarche varies widely among girls, but it typically occurs between the ages of 11 and 14. Factors that can influence the age of menarche include genetics, nutrition, and overall health.
Signs of Menarche
The signs of menarche include the onset of vaginal bleeding, which may be light or heavy, and may last for several days. Other signs may include abdominal cramping, mood swings, and breast tenderness.
Importance of Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is an important process that allows women to conceive and bear children. It also plays a role in maintaining overall health by regulating hormone levels and removing waste products from the body.
Conclusion
In conclusion, menarche is the beginning of the menstrual cycle and marks the onset of puberty in girls. It is a significant event that has both physical and psychological implications and is an important part of a woman's reproductive health.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Each testis has about 250 compartment called as____.
- A:
Oogonia
- B:
Seminiferous tubules
- C:
Lactiferous lobules
- D:
Testicular lobules
The answer is d.
Each testis has about 250 compartment called as____.
Oogonia
Seminiferous tubules
Lactiferous lobules
Testicular lobules

|
Pooja Pillai answered |
Each testis contains about 250 compartments called testicular lobules. Each testicular lobule contains one to three highly coiled seminiferous tubules that produce sperms.
Identify the intra-uterine contraceptive device from the figure given below
- a)Copper-T
- b)Loop
- c)LNG-20
- d)Progestasert
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the intra-uterine contraceptive device from the figure given below
a)
Copper-T
b)
Loop
c)
LNG-20
d)
Progestasert
|
|
Anchal Maurya answered |
This intra uterine device is Cu- T .read ncert
Which of the following is formed first out of the following in growing foetus: hairs, limbs and digits, heart, eye lids?- a)Eye lids
- b)Limbs and digits
- c)Heart
- d)Hairs on head
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is formed first out of the following in growing foetus: hairs, limbs and digits, heart, eye lids?
a)
Eye lids
b)
Limbs and digits
c)
Heart
d)
Hairs on head
|
|
Deepanshi Mishra answered |
In growing foetus first of all heart is formed. Doctor diagnose the foetus by hearing the heart sound firstly, after that other organs develope. Cardiovascular developments starts at 3rd to 6th week of pregnancy. Heart beat can be heard at starting of 4th week.
_________involve the transfer of embryo at 8-celled stage in the fallopian tube of female.- a)POST
- b)ZIFT
- c)IVF
- d)GIFT
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_________involve the transfer of embryo at 8-celled stage in the fallopian tube of female.
a)
POST
b)
ZIFT
c)
IVF
d)
GIFT
|
|
Akanksha Das answered |
ZIFT (Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer) involves the transfer of an embryo at the 8-celled stage into the fallopian tube of a female. This is a type of assisted reproductive technology used to treat infertility.
Process of ZIFT:
The process of ZIFT involves the following steps:
1. Ovarian Stimulation: The female patient is given medication to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
2. Egg Retrieval: The eggs are retrieved from the ovaries using a needle guided by ultrasound.
3. Fertilization: The eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish to create embryos.
4. Embryo Transfer: The embryos are transferred into the fallopian tube through a laparoscopic procedure.
5. Pregnancy Test: The patient is monitored for pregnancy through a blood test or ultrasound.
Advantages of ZIFT:
1. Higher Success Rates: ZIFT has higher success rates compared to traditional IVF methods.
2. Natural Implantation: The embryo is transferred into the fallopian tube, which is a natural environment for implantation, increasing the chances of pregnancy.
3. Fewer Multiple Pregnancies: ZIFT reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies compared to other assisted reproductive technologies.
Disadvantages of ZIFT:
1. Invasive Procedure: ZIFT requires a laparoscopic procedure, which is an invasive procedure that carries risks.
2. Limited Availability: ZIFT is not widely available in all fertility clinics.
3. Higher Cost: ZIFT is more expensive than traditional IVF methods.
Conclusion:
ZIFT is a type of assisted reproductive technology that involves transferring an embryo at the 8-celled stage into the fallopian tube of a female. It has higher success rates compared to traditional IVF methods and reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies. However, it is an invasive procedure that is not widely available and is more expensive than traditional IVF methods.
Process of ZIFT:
The process of ZIFT involves the following steps:
1. Ovarian Stimulation: The female patient is given medication to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
2. Egg Retrieval: The eggs are retrieved from the ovaries using a needle guided by ultrasound.
3. Fertilization: The eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish to create embryos.
4. Embryo Transfer: The embryos are transferred into the fallopian tube through a laparoscopic procedure.
5. Pregnancy Test: The patient is monitored for pregnancy through a blood test or ultrasound.
Advantages of ZIFT:
1. Higher Success Rates: ZIFT has higher success rates compared to traditional IVF methods.
2. Natural Implantation: The embryo is transferred into the fallopian tube, which is a natural environment for implantation, increasing the chances of pregnancy.
3. Fewer Multiple Pregnancies: ZIFT reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies compared to other assisted reproductive technologies.
Disadvantages of ZIFT:
1. Invasive Procedure: ZIFT requires a laparoscopic procedure, which is an invasive procedure that carries risks.
2. Limited Availability: ZIFT is not widely available in all fertility clinics.
3. Higher Cost: ZIFT is more expensive than traditional IVF methods.
Conclusion:
ZIFT is a type of assisted reproductive technology that involves transferring an embryo at the 8-celled stage into the fallopian tube of a female. It has higher success rates compared to traditional IVF methods and reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies. However, it is an invasive procedure that is not widely available and is more expensive than traditional IVF methods.
Morula is a developmental stage:- a)Between the zygote and blastocyst
- b)Between the blastocyst and gastrula
- c)Between implantation and parturition
- d)After the implantation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Morula is a developmental stage:
a)
Between the zygote and blastocyst
b)
Between the blastocyst and gastrula
c)
Between implantation and parturition
d)
After the implantation
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The embryo with 8 to 16 blastomeres is called a morula. Morula is the solid mass of cells and is mulberry like. Morula is a developmental stage between the zygote and blastocyst.
Study of human population is called as?- a)Anthropology
- b)Sociology
- c)Ethnology
- d)Demography
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study of human population is called as?
a)
Anthropology
b)
Sociology
c)
Ethnology
d)
Demography
|
|
Shounak Chakraborty answered |
Preventing Transmission of STDs
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are spread through sexual contact. The following measures can help in preventing the transmission of STDs:
Using Condoms during Intercourse
Using condoms is one of the most effective ways to prevent the transmission of STDs during sexual activity. Condoms act as a barrier and reduce the risk of infection. They should be used consistently and correctly to maximize their effectiveness.
Avoiding Sex with Multiple Partners
Having sex with multiple partners increases the risk of contracting STDs. Limiting sexual partners or being in a mutually monogamous relationship can decrease the risk of transmission.
Visiting a Qualified Doctor if Symptoms are Observed
If an individual experiences symptoms such as genital sores, abnormal discharge, or pain during urination, they should visit a qualified doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the spread of STDs.
Not Sharing Shaving Blades with Friends
Sharing personal items such as shaving blades, towels, or underwear can increase the risk of transmission of STDs. It is important to use personal items and avoid sharing them with others to prevent the spread of infection.
Conclusion
Preventing the transmission of STDs is crucial for maintaining sexual health. Using condoms, limiting sexual partners, seeking medical attention if symptoms are observed, and avoiding sharing personal items can all help decrease the risk of infection.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are spread through sexual contact. The following measures can help in preventing the transmission of STDs:
Using Condoms during Intercourse
Using condoms is one of the most effective ways to prevent the transmission of STDs during sexual activity. Condoms act as a barrier and reduce the risk of infection. They should be used consistently and correctly to maximize their effectiveness.
Avoiding Sex with Multiple Partners
Having sex with multiple partners increases the risk of contracting STDs. Limiting sexual partners or being in a mutually monogamous relationship can decrease the risk of transmission.
Visiting a Qualified Doctor if Symptoms are Observed
If an individual experiences symptoms such as genital sores, abnormal discharge, or pain during urination, they should visit a qualified doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the spread of STDs.
Not Sharing Shaving Blades with Friends
Sharing personal items such as shaving blades, towels, or underwear can increase the risk of transmission of STDs. It is important to use personal items and avoid sharing them with others to prevent the spread of infection.
Conclusion
Preventing the transmission of STDs is crucial for maintaining sexual health. Using condoms, limiting sexual partners, seeking medical attention if symptoms are observed, and avoiding sharing personal items can all help decrease the risk of infection.
Which one of the following is the most widely accepted method of contraception in India at present?- a)Tubectomy
- b)Cervical caps
- c)Diaphragms
- d)IUDs (Intrauterine devices)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the most widely accepted method of contraception in India at present?
a)
Tubectomy
b)
Cervical caps
c)
Diaphragms
d)
IUDs (Intrauterine devices)
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Intra uterine device (IUD) is a method of contraception in India. The IUD is inserted in the woman’s uterus through the cervix.
How many sperms are formed by 4 primary spermatocytes? - a)1
- b)4
- c)32
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many sperms are formed by 4 primary spermatocytes?
a)
1
b)
4
c)
32
d)
16
|
|
Juhi Reddy answered |
Each primary spermatocyte undergoes first meiotic division to produce 2 secondary spermatocytes, which further proceeds to second meiotic division to form 2 spermatids. So, each primary spermatocyte produces 4 sperms.
In sectional view of female reproductive system, which one is correctly labeled?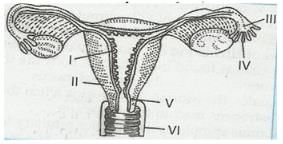
- a)Infundibulum(IV), Perimetrium(V)
- b)Fimbriae(V), Endometrium(I)
- c)Infundibulum(III), Fimbriae(IV)
- d)Uterus(II), Ovary(III)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In sectional view of female reproductive system, which one is correctly labeled?

a)
Infundibulum(IV), Perimetrium(V)
b)
Fimbriae(V), Endometrium(I)
c)
Infundibulum(III), Fimbriae(IV)
d)
Uterus(II), Ovary(III)
|
|
Sakshi Kasture answered |
This is the same diagram in ncert and there u will get all the names. finger like projections called as fimbre & part next of fimbre called as infundibulum
Which of the following arise from endoderm?- a)Eye
- b)Heart
- c)Pigment cells
- d)Lungs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following arise from endoderm?
a)
Eye
b)
Heart
c)
Pigment cells
d)
Lungs
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Ectoderm is the germ layer that develops primarily into skin and neural tissue. Mesoderm primarily develops into muscle tissues and red blood cells. Endoderm develops into many of the internal organs including the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, and endocrine system.
Antrum is the cavity of:- a)Ovary
- b)Graafian follicle
- c)Blastula
- d)Gastrula
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Antrum is the cavity of:
a)
Ovary
b)
Graafian follicle
c)
Blastula
d)
Gastrula
|
|
Krish Kapoor answered |
A graafian follicle can be defined structurally as a heterogeneous family of relatively large follicles (0.4 to 23 mm) characterized by a cavity or antrum containing a fluid called follicular fluid or liquor folliculi. The characteristic structural unit of all graafian follicle is the antrum. For this reason, the term antral follicle is used correctly as a synonym for graafian follicle.
Seminal plasma in human males is rich in_____.- a)Fructose and Calcium
- b)Ribose and Potassium
- c)DNA and testosterone
- d)Glucose and Calcium
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma in human males is rich in_____.
a)
Fructose and Calcium
b)
Ribose and Potassium
c)
DNA and testosterone
d)
Glucose and Calcium
|
|
Rahul answered |
The male accessory glands include paired seminal vesicles, a prostate and paired bulbourethral gland. Secretions of these glands constitute the seminal plasma which is rich in Fructose calcium and certain enzymes
Enzyme for fertilization present in -- a)Acrosome of Sperm
- b)Nucleus of Sperm
- c)Tail of Sperm
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzyme for fertilization present in -
a)
Acrosome of Sperm
b)
Nucleus of Sperm
c)
Tail of Sperm
d)
None
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
In Eutherian mammals the acrosome contains degradative enzymes (including hyaluronidase and acrosin). These enzymes break down the outer membrane of the ovum, called the zona pellucida, allowing the haploid nucleus in the sperm cell to join with the haploid nucleus in the ovum.
So, correct answer is "Acrosome of sperm".
A human female is born with a million of primary oocytes at the time of birth. How many eggs get a chance to mature?
- a)About 1000
- b)More than 500
- c)About 1500
- d)Some 500
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A human female is born with a million of primary oocytes at the time of birth. How many eggs get a chance to mature?
a)
About 1000
b)
More than 500
c)
About 1500
d)
Some 500
|
|
Jithin Unni answered |
Answer:
A human female is born with a million of primary oocytes, which are immature eggs. However, only a small fraction of these oocytes will actually mature into eggs that can be fertilized. The process of egg maturation is called oogenesis and it takes place in the ovaries.
Factors Affecting Egg Maturation:
Several factors influence how many eggs get a chance to mature, including:
- Hormonal signals from the pituitary gland
- The age of the female
- Environmental factors such as stress, diet, and exposure to toxins
Process of Egg Maturation:
The process of egg maturation begins at puberty when the pituitary gland starts producing hormones that stimulate the ovaries. Each month, several immature oocytes begin to mature in response to these hormonal signals. However, only one of these oocytes will actually reach full maturity and be released during ovulation.
Number of Eggs Matured:
On average, a human female will release about 400-500 mature eggs during her reproductive lifetime. This means that out of the million primary oocytes that are present at birth, only a small fraction will actually mature into eggs that can be fertilized.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'D', which states that about 500 eggs get a chance to mature.
A human female is born with a million of primary oocytes, which are immature eggs. However, only a small fraction of these oocytes will actually mature into eggs that can be fertilized. The process of egg maturation is called oogenesis and it takes place in the ovaries.
Factors Affecting Egg Maturation:
Several factors influence how many eggs get a chance to mature, including:
- Hormonal signals from the pituitary gland
- The age of the female
- Environmental factors such as stress, diet, and exposure to toxins
Process of Egg Maturation:
The process of egg maturation begins at puberty when the pituitary gland starts producing hormones that stimulate the ovaries. Each month, several immature oocytes begin to mature in response to these hormonal signals. However, only one of these oocytes will actually reach full maturity and be released during ovulation.
Number of Eggs Matured:
On average, a human female will release about 400-500 mature eggs during her reproductive lifetime. This means that out of the million primary oocytes that are present at birth, only a small fraction will actually mature into eggs that can be fertilized.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'D', which states that about 500 eggs get a chance to mature.
In which part of sperm, mitochondria are present?- a)Head
- b)Middle piece
- c)Tail
- d)Neck
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which part of sperm, mitochondria are present?
a)
Head
b)
Middle piece
c)
Tail
d)
Neck
|
|
Jaya Chavan answered |
Mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
Explanation:
The sperm is composed of three parts: head, middle piece, and tail.
1. Head:
The head of the sperm contains the nucleus which carries genetic material in the form of DNA.
2. Middle piece:
The middle piece of the sperm contains a large number of mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the movement of the sperm.
3. Tail:
The tail of the sperm is also known as the flagellum. It provides motility to the sperm and helps in the movement towards the egg.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' that mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
Explanation:
The sperm is composed of three parts: head, middle piece, and tail.
1. Head:
The head of the sperm contains the nucleus which carries genetic material in the form of DNA.
2. Middle piece:
The middle piece of the sperm contains a large number of mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the movement of the sperm.
3. Tail:
The tail of the sperm is also known as the flagellum. It provides motility to the sperm and helps in the movement towards the egg.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' that mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
Which period of menstrual cycle is called risky period of conception?- a)7th to 13th day
- b)17th to 25th day
- c)3rd to 7th day
- d)10th to 17th day
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which period of menstrual cycle is called risky period of conception?
a)
7th to 13th day
b)
17th to 25th day
c)
3rd to 7th day
d)
10th to 17th day
|
|
Akshara Choudhary answered |
The risky period of conception in the menstrual cycle is the ovulation period, which occurs around the 14th day of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
Explanation:
- Menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible.
- The menstrual cycle is typically 28 days long, but can vary from 21 to 35 days.
- The cycle is divided into three phases: the follicular phase (days 1-14), ovulation (day 14), and the luteal phase (days 15-28).
- Ovulation is the process where an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm.
- Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
- The period around ovulation is considered the risky period of conception, as it is the time when the egg is available to be fertilized by sperm.
- Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, so the fertile window for conception is actually the five days leading up to ovulation, as well as ovulation day itself.
- Therefore, the risky period of conception is considered to be from the 10th to the 17th day of the menstrual cycle (assuming a 28-day cycle).
Explanation:
- Menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible.
- The menstrual cycle is typically 28 days long, but can vary from 21 to 35 days.
- The cycle is divided into three phases: the follicular phase (days 1-14), ovulation (day 14), and the luteal phase (days 15-28).
- Ovulation is the process where an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm.
- Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
- The period around ovulation is considered the risky period of conception, as it is the time when the egg is available to be fertilized by sperm.
- Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, so the fertile window for conception is actually the five days leading up to ovulation, as well as ovulation day itself.
- Therefore, the risky period of conception is considered to be from the 10th to the 17th day of the menstrual cycle (assuming a 28-day cycle).
Human placenta is derived from:- a)Allantois and chorion
- b)Chorion
- c)Amnion
- d)Allantois
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Human placenta is derived from:
a)
Allantois and chorion
b)
Chorion
c)
Amnion
d)
Allantois
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
In humans, ovum is released from the ovary in the secondary oocyte stage. The wall of the ovary gets ruptured to release the oocyte. In humans ovulation occurs about 14 days before the onset of the next menstruation. Ovulation is induced by LH.
Acrosome is filled with _________.- a)Lipids
- b)Hormones
- c)Enzymes
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Acrosome is filled with _________.
a)
Lipids
b)
Hormones
c)
Enzymes
d)
None of the above
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- The head of mature mammalian sperm is made of elongated nucleus covered by acrosome.
- The acrosome is filled with hydrolytic enzymes that help in fertilization of ovum.
- These enzymes called sperm lysins that dissolve the membranes enveloping the ovum and help the sperm cell to enter the ovum by penetrating egg membrane.
Testosterone is secreted by____.- a)Sertoli cells
- b)Leydig cells
- c)Kupffer cells
- d)Mast cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Testosterone is secreted by____.
a)
Sertoli cells
b)
Leydig cells
c)
Kupffer cells
d)
Mast cells
|
|
Soumya Dyavanagoudar answered |
Leydig cells are interstial cells present in the testis which produce testosterone .FSH stimulates the production of testosterone
Induced abortion is also called- a)MTP
- b)PID
- c)SID
- d)IUD
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Induced abortion is also called
a)
MTP
b)
PID
c)
SID
d)
IUD
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
MTP is Medical Termination of Pregnancy. It also called induced abortion. It is the medical way of getting rid of unwanted pregnancy. Any qualified gynecologist (MD/DGO) can perform MTP. Any MBBS Doctor, who has obtained training in MTP, is allowed to perform this procedure. However, MTP should always be performed at a place recognized by government authorities.
Chapter doubts & questions for Reproduction in Mammals - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Reproduction in Mammals - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









