All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Internal Structure of Mammal for JAMB Exam
Interstitial cells or leydig cells are present between______.- a)Basal lamina
- b)Seminiferous tubules
- c)Tubuli recti
- d)Sertoli cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Interstitial cells or leydig cells are present between______.
a)
Basal lamina
b)
Seminiferous tubules
c)
Tubuli recti
d)
Sertoli cells
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Interstitial cells or leydig cells are present between seminiferous tubules..they secrete androgens..mainly testosterone
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?
- A:
Lactogen
- B:
Primary milk
- C:
Colostrum
- D:
None of these
The answer is c.
The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?
Lactogen
Primary milk
Colostrum
None of these
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Colostrum is a thick and sticky, yellow to orange colored milk that is created by your breasts to give your baby the nutrition he needs immediately after birth. It is low in fat, high in carbohydrates and has a laxative effect on the baby which helps him pass the first meconium stools that are sitting in his intestines. This also helps get rid of the bile and helps lessen the chance of jaundice in your newborn.
Ovulation occurs on the ------ day of menstrual cycle. - a)08-10
- b)12-14
- c)14-16
- d)16-18
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ovulation occurs on the ------ day of menstrual cycle.
a)
08-10
b)
12-14
c)
14-16
d)
16-18

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
The release of ovum from ovary during menstrual cycle is is called ovulation. Ovulation occurs in the middle of menstrual cycle that is on 14-16th day of start of menstrual cycle.
The cellular layer that disintegrates and regenerates again and again is _______.
- a)Dermis of skin
- b)Endometrium of uterus
- c)Cornea of eye
- d)Endometrium of blood vessels
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The cellular layer that disintegrates and regenerates again and again is _______.
a)
Dermis of skin
b)
Endometrium of uterus
c)
Cornea of eye
d)
Endometrium of blood vessels

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
- The functional layer of the human endometrium is a highly regenerative tissue undergoing monthly cycles of growth, differentiation, and shedding during a woman's reproductive years.
- Fluctuating levels of circulating estrogen and progesterone orchestrate this dramatic remodelling of human endometrium.
Hence, the correct option is B.
NCERT Reference: topic “MENSTRUAL CYCLE” of chapter: Human Reproduction.
NCERT Reference: topic “MENSTRUAL CYCLE” of chapter: Human Reproduction.
Hormone responsible for milk ejection after the birth of baby is:
- a)Progesterone
- b)vasopressin
- c)Estrogens
- d)Oxytocin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormone responsible for milk ejection after the birth of baby is:
a)
Progesterone
b)
vasopressin
c)
Estrogens
d)
Oxytocin
|
|
Naina Choudhary answered |
Hormone responsible for milk ejection after the birth of baby is oxytocin.
Explanation:
After the birth of a baby, the mother's body undergoes various hormonal changes that promote milk production and ejection. The primary hormone responsible for milk ejection is oxytocin, which is produced in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary gland.
When a baby suckles at the breast, nerve endings in the nipple and areola are stimulated, which triggers the release of oxytocin. Oxytocin then causes the smooth muscle cells in the milk ducts to contract, which pushes the milk out of the breast and into the baby's mouth. This process is known as the milk ejection reflex or let-down reflex.
Other hormones that are involved in milk production and ejection include:
- Prolactin: This hormone is produced in the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates milk production in the mammary glands.
- Estrogens: These hormones are produced in the ovaries and play a role in breast development and milk production.
- Progesterone: This hormone is produced in the ovaries and plays a role in preparing the breast for milk production.
However, in terms of milk ejection specifically, oxytocin is the primary hormone involved.
Explanation:
After the birth of a baby, the mother's body undergoes various hormonal changes that promote milk production and ejection. The primary hormone responsible for milk ejection is oxytocin, which is produced in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary gland.
When a baby suckles at the breast, nerve endings in the nipple and areola are stimulated, which triggers the release of oxytocin. Oxytocin then causes the smooth muscle cells in the milk ducts to contract, which pushes the milk out of the breast and into the baby's mouth. This process is known as the milk ejection reflex or let-down reflex.
Other hormones that are involved in milk production and ejection include:
- Prolactin: This hormone is produced in the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates milk production in the mammary glands.
- Estrogens: These hormones are produced in the ovaries and play a role in breast development and milk production.
- Progesterone: This hormone is produced in the ovaries and plays a role in preparing the breast for milk production.
However, in terms of milk ejection specifically, oxytocin is the primary hormone involved.
Conditional reabsorption of sodium ions and water takes place in- a)DCT
- b)Collecting duct
- c)Henle’s loop
- d)PCT
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Conditional reabsorption of sodium ions and water takes place in
a)
DCT
b)
Collecting duct
c)
Henle’s loop
d)
PCT

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
Conditional reabsorption of sodium ions and water takes place in distal convoluted tubule.
The number of polar bodies formed during oogenesis in human being is:
- a)2
- b)3
- c)1
- d)Both 2 and 3.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of polar bodies formed during oogenesis in human being is:
a)
2
b)
3
c)
1
d)
Both 2 and 3.
|
|
Raj Yadav answered |
Polar bodies formed during oogenesis in humans
- During human oogenesis, three polar bodies are created.
- Polar bodies are tiny cytoplasmic exclusion structures that form to contain extra DNA produced during oocyte meiosis, which occurs after sperm fertilization.
- The zygote contains roughly 2-3 polar bodies, which are derived from the oocyte.
- This figure is determined by whether or not the first polar body (produced during meiosis I) splits during meiosis II.
- Excess DNA generated from reductive division makes up such an exclusion body (2nd and 3rd polar bodies are formed from meiosis II at the time of fertilization).
- Such polar bodies do not contribute to the zygote's, foetus', or embryo's future genetic complement.
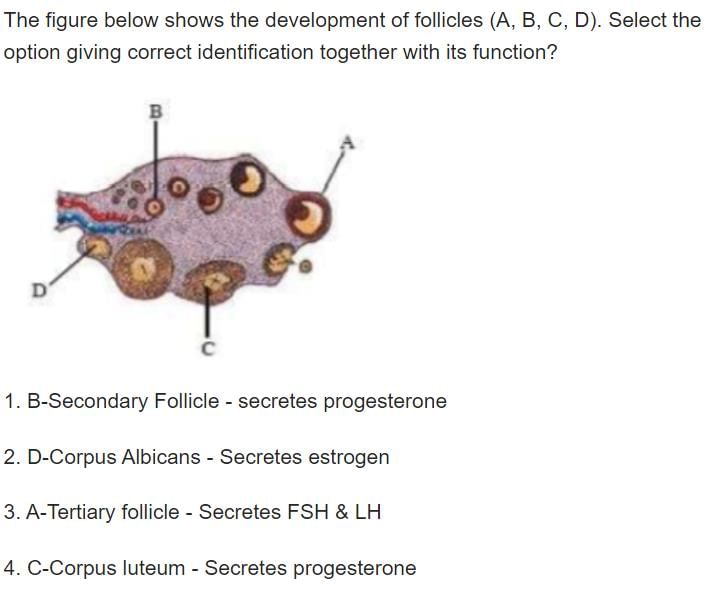
Which of the following hormone is produced in female only during pregnancy?
- a)Testosterone
- b)Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG).
- c)Progesterone
- d)Estrogen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following hormone is produced in female only during pregnancy?
a)
Testosterone
b)
Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG).
c)
Progesterone
d)
Estrogen
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
- It is made almost exclusively in the placenta.
- hCG hormone levels found in the mother's blood and urine, rise a lot during the first trimester.
- hCG Maintains the corpus luteum throughout the early stages of pregnancy. It is used to detect pregnancy.
Hence, the correct option is B.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 53 of topic “3.6 PREGNANCY AND EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT” of chapter 3.
The filtration fraction is the ratio of GFR to RPF where both the values are in ml/min and FF is expressed in percentage. Calculate FF for a normal adult human being, if RPF= 600ml/min :- a)2.08%
- b)20.73%
- c)10.38%
- d)20.83%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The filtration fraction is the ratio of GFR to RPF where both the values are in ml/min and FF is expressed in percentage. Calculate FF for a normal adult human being, if RPF= 600ml/min :
a)
2.08%
b)
20.73%
c)
10.38%
d)
20.83%
|
|
Janhavi Rane answered |
FF = (125/600)*100 = 20.83%
The following substances are the excretory products in animals. Choose the least toxic form among them?- a)Urea
- b)Uric acid
- c) Ammonia
- d)Carbon dioxide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following substances are the excretory products in animals. Choose the least toxic form among them?
a)
Urea
b)
Uric acid
c)
Ammonia
d)
Carbon dioxide
|
|
Anshu Saha answered |
The least toxic form among the excretory products in animals is uric acid.
Explanation:
• Animals excrete waste products that are formed during metabolic processes.
• The excretory products are mainly classified into three types: ammonia, urea, and uric acid.
• Ammonia is highly toxic and water-soluble. It is excreted by aquatic animals, but not by terrestrial animals because of its toxicity.
• Urea is less toxic than ammonia and water-soluble. It is excreted by most terrestrial animals, including humans.
• Uric acid is the least toxic form among the three. It is insoluble in water and is excreted in the form of a paste or a solid.
• Uric acid is the excretory product of birds, reptiles, and insects. It is also excreted by some other animals, such as snails and spiders.
• Uric acid is less toxic than ammonia and urea because it requires less water for its excretion.
• The excretion of uric acid conserves water, which is essential for survival in arid environments.
• In humans, excess uric acid can lead to gout, a painful condition caused by the deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints.
Therefore, uric acid is the least toxic form among the excretory products in animals.
Explanation:
• Animals excrete waste products that are formed during metabolic processes.
• The excretory products are mainly classified into three types: ammonia, urea, and uric acid.
• Ammonia is highly toxic and water-soluble. It is excreted by aquatic animals, but not by terrestrial animals because of its toxicity.
• Urea is less toxic than ammonia and water-soluble. It is excreted by most terrestrial animals, including humans.
• Uric acid is the least toxic form among the three. It is insoluble in water and is excreted in the form of a paste or a solid.
• Uric acid is the excretory product of birds, reptiles, and insects. It is also excreted by some other animals, such as snails and spiders.
• Uric acid is less toxic than ammonia and urea because it requires less water for its excretion.
• The excretion of uric acid conserves water, which is essential for survival in arid environments.
• In humans, excess uric acid can lead to gout, a painful condition caused by the deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints.
Therefore, uric acid is the least toxic form among the excretory products in animals.
During which month of pregnancy first movement of fetus is observed?- a)Sixth month
- b)Fourth month
- c)Fifth month
- d)Third month
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During which month of pregnancy first movement of fetus is observed?
a)
Sixth month
b)
Fourth month
c)
Fifth month
d)
Third month
|
|
Saranya Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option C, i.e., fifth month.
Explanation:
The first movement of the fetus is called quickening. It is the first noticeable movement of the fetus by the mother. Quickening is the first sign that the pregnancy is progressing as expected. It usually occurs between the 16th and 25th weeks of pregnancy. However, it is most commonly felt around the 20th week of pregnancy, which is the fifth month.
During the first trimester, the fetus is too small and underdeveloped to produce movements that can be felt by the mother. The fetal movements at this stage are mostly uncoordinated and involuntary.
During the second trimester, the fetus grows and becomes more active. The movements become more coordinated and frequent. By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs around 1 pound. The movements of the fetus become more pronounced and can be felt by the mother.
In summary, the first movement of the fetus can be observed in the fifth month of pregnancy, which is around the 20th week.
Explanation:
The first movement of the fetus is called quickening. It is the first noticeable movement of the fetus by the mother. Quickening is the first sign that the pregnancy is progressing as expected. It usually occurs between the 16th and 25th weeks of pregnancy. However, it is most commonly felt around the 20th week of pregnancy, which is the fifth month.
During the first trimester, the fetus is too small and underdeveloped to produce movements that can be felt by the mother. The fetal movements at this stage are mostly uncoordinated and involuntary.
During the second trimester, the fetus grows and becomes more active. The movements become more coordinated and frequent. By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs around 1 pound. The movements of the fetus become more pronounced and can be felt by the mother.
In summary, the first movement of the fetus can be observed in the fifth month of pregnancy, which is around the 20th week.
A renal corpuscle is :- a)malpighian body
- b)malpighian tubule
- c)nephron
- d)Bowman’s capsule
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A renal corpuscle is :
a)
malpighian body
b)
malpighian tubule
c)
nephron
d)
Bowman’s capsule

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
Renal corpuscle, also called malpighian body, filtration unit of vertebrate nephrons, functional units of the kidney. It consists of a knot of capillaries (glomerulus) surrounded by a double-walled capsule (Bowman's capsule) that opens into a tubule.
Beginning of menstrual cycle is called as ___.- a)Ovulation
- b)Oogenesis
- c)Menarche
- d)Menopause
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Beginning of menstrual cycle is called as ___.
a)
Ovulation
b)
Oogenesis
c)
Menarche
d)
Menopause
|
|
NEET Aspirant 2021 answered |
The first menstrual period occurs after the onset of pubertal growth, and is called menarche.
so the correct answer is option c) Menarche
so the correct answer is option c) Menarche
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Each testis has about 250 compartment called as____.
- A:
Oogonia
- B:
Seminiferous tubules
- C:
Lactiferous lobules
- D:
Testicular lobules
The answer is d.
Each testis has about 250 compartment called as____.
Oogonia
Seminiferous tubules
Lactiferous lobules
Testicular lobules

|
Pooja Pillai answered |
Each testis contains about 250 compartments called testicular lobules. Each testicular lobule contains one to three highly coiled seminiferous tubules that produce sperms.
During urine formation, the tubular cells secrete ------------------ into the filtrate.- a)Potassium ions and ammonia
- b)Hydrogen ions and potassium ions
- c)Hydrogen ions, potassium ions and ammonia
- d)Only ammonia
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During urine formation, the tubular cells secrete ------------------ into the filtrate.
a)
Potassium ions and ammonia
b)
Hydrogen ions and potassium ions
c)
Hydrogen ions, potassium ions and ammonia
d)
Only ammonia

|
Kunal Rane answered |
During urine formation, the tubular cells secrete substances like hydrogen ions, potassium ions and ammonia into the filtrate.
Which of the following arise from endoderm?- a)Eye
- b)Heart
- c)Pigment cells
- d)Lungs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following arise from endoderm?
a)
Eye
b)
Heart
c)
Pigment cells
d)
Lungs
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Ectoderm is the germ layer that develops primarily into skin and neural tissue. Mesoderm primarily develops into muscle tissues and red blood cells. Endoderm develops into many of the internal organs including the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, and endocrine system.
pH of urine under healthy conditions is :- a)slightly alkaline
- b)neutral
- c)highly alkaline
- d)slightly acidic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
pH of urine under healthy conditions is :
a)
slightly alkaline
b)
neutral
c)
highly alkaline
d)
slightly acidic

|
Soumya Ahuja answered |
The pH of urine under healthy conditions is slightly less than 7 so, slightly acidic in nature.
Seminal plasma in human males is rich in_____.- a)Fructose and Calcium
- b)Ribose and Potassium
- c)DNA and testosterone
- d)Glucose and Calcium
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma in human males is rich in_____.
a)
Fructose and Calcium
b)
Ribose and Potassium
c)
DNA and testosterone
d)
Glucose and Calcium
|
|
Rahul answered |
The male accessory glands include paired seminal vesicles, a prostate and paired bulbourethral gland. Secretions of these glands constitute the seminal plasma which is rich in Fructose calcium and certain enzymes
In which part of sperm, mitochondria are present?- a)Head
- b)Middle piece
- c)Tail
- d)Neck
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which part of sperm, mitochondria are present?
a)
Head
b)
Middle piece
c)
Tail
d)
Neck
|
|
Jaya Chavan answered |
Mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
Explanation:
The sperm is composed of three parts: head, middle piece, and tail.
1. Head:
The head of the sperm contains the nucleus which carries genetic material in the form of DNA.
2. Middle piece:
The middle piece of the sperm contains a large number of mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the movement of the sperm.
3. Tail:
The tail of the sperm is also known as the flagellum. It provides motility to the sperm and helps in the movement towards the egg.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' that mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
Explanation:
The sperm is composed of three parts: head, middle piece, and tail.
1. Head:
The head of the sperm contains the nucleus which carries genetic material in the form of DNA.
2. Middle piece:
The middle piece of the sperm contains a large number of mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the movement of the sperm.
3. Tail:
The tail of the sperm is also known as the flagellum. It provides motility to the sperm and helps in the movement towards the egg.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' that mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
Blood enters glomerular capillaries through _____ arteriole and leaves through _____ arteriole:- a)efferent, afferent
- b)radial, collecting
- c)distributing, collecting
- d)afferent, efferent
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood enters glomerular capillaries through _____ arteriole and leaves through _____ arteriole:
a)
efferent, afferent
b)
radial, collecting
c)
distributing, collecting
d)
afferent, efferent
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Our nervous system has different types of neurons that are constantly at work. Neurons that receive information from our sensory organs (e.g. eye, skin) and transmit this input to the central nervous system are called afferent neurons. Neurons that send impulses from the central nervous system to your limbs and organs are called efferent neurons.
Therefore, as the afferent neurons convey the sensory stimulus to the brain (like burning sensation of a candle), the efferent neurons convey the motor stimulus to the muscles (moving the hand away from the candle). To sum it up: Afferent = Receive and Efferent = Act.
The tracts that are conveying sensations up to the brain are also referred to as the ascending tracts. Going in the opposite direction than the ascending tracts, the tracts linking the brain to all the muscles and organs of the body are called descending tracts.
Which types of fibers are damaged after a spinal cord injury determine the individual failures. If motor (= efferent) fibers are destroyed, you are not able to lift your leg, because the command can’t be transmitted from the brain to the muscles in the leg. If sensory (= afferent) fibers are affected, you and your brain won’t be notified by the sensory organs, e.g. if somebody strikes your leg. In fact, mostly a combination of efferent and afferent fibers is damaged after a spinal cord injury.
Acrosome is filled with _________.- a)Lipids
- b)Hormones
- c)Enzymes
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Acrosome is filled with _________.
a)
Lipids
b)
Hormones
c)
Enzymes
d)
None of the above
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- The head of mature mammalian sperm is made of elongated nucleus covered by acrosome.
- The acrosome is filled with hydrolytic enzymes that help in fertilization of ovum.
- These enzymes called sperm lysins that dissolve the membranes enveloping the ovum and help the sperm cell to enter the ovum by penetrating egg membrane.
Which of the following is not a part of glomerular filtrate?- a)globulins
- b)inorganic salts
- c)glucose
- d)creatinine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a part of glomerular filtrate?
a)
globulins
b)
inorganic salts
c)
glucose
d)
creatinine

|
Maheshwar Saini answered |
Glomerular filtrate contains glucose, inorganic salts and creatinine but it do not contain globulins protein.
Read the following :
i. Infants and toddlers are often under habit of bed wetting since micturition is a reflex process.
ii. Adults and grown up children can control this reflex process, voluntarily to some extent.- a)both are correct
- b)Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong
- c)both are wrong
- d)Statement i) is wrong and ii) is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following :
i. Infants and toddlers are often under habit of bed wetting since micturition is a reflex process.
ii. Adults and grown up children can control this reflex process, voluntarily to some extent.
i. Infants and toddlers are often under habit of bed wetting since micturition is a reflex process.
ii. Adults and grown up children can control this reflex process, voluntarily to some extent.
a)
both are correct
b)
Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong
c)
both are wrong
d)
Statement i) is wrong and ii) is correct

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
The process of release of urine is called micturition and the neural mechanism causing it is called the micturition reflex. Adults and grown up children can control the reflex process of micturition voluntarily to some extent.
Sertoli cells present in the testis act as _____.- a)Germ cell
- b)Nurse cell
- c)Protective cell
- d)Receptor cell
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sertoli cells present in the testis act as _____.
a)
Germ cell
b)
Nurse cell
c)
Protective cell
d)
Receptor cell
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Nurse cells are specialized macrophages residing in the bone marrow that assist in the development of red blood cells. They absorb the nuclei of immature red blood cells and may provide growth factors to help the red blood cells mature.
All of the following organs help in excretion except :- a)Liver
- b)Lungs
- c)Heart
- d)Skin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
All of the following organs help in excretion except :
a)
Liver
b)
Lungs
c)
Heart
d)
Skin
|
|
Sapna Patel answered |
The function of heart is different from the rest options in a way that heart is an organ that pumps blood throughout
the body tissues and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes. And hence does not helps in excretion.
During micturition, the muscles of urinary bladder and urethral sphincters will- a)contract and relax respectively.
- b)none of these
- c)show fatigue
- d)relaxand contract respectively.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During micturition, the muscles of urinary bladder and urethral sphincters will
a)
contract and relax respectively.
b)
none of these
c)
show fatigue
d)
relaxand contract respectively.
|
|
Jyoti Desai answered |
Micturition is the process of voiding urine from the body. During this process, the muscles of the urinary bladder and urethral sphincters play a crucial role in controlling the flow of urine. The correct answer to the given question is option 'A', i.e., the muscles of the urinary bladder will contract, and the urethral sphincters will relax.
Explanation:
The process of micturition involves the following steps:
1. Filling of the urinary bladder: The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine until it is eliminated from the body. As the bladder fills with urine, its walls stretch, and the pressure inside the bladder increases.
2. Sensory input to the spinal cord: The stretch receptors in the bladder walls send signals to the spinal cord, indicating that the bladder is full.
3. Activation of the micturition reflex: The spinal cord processes the sensory input and generates a reflex response that activates the muscles of the bladder and urethral sphincters.
4. Contraction of the bladder muscles: The muscles of the bladder wall contract, forcing urine out of the bladder and into the urethra.
5. Relaxation of the urethral sphincters: The urethral sphincters, which are circular muscles that control the flow of urine through the urethra, relax, allowing urine to pass out of the body.
Therefore, during micturition, the muscles of the urinary bladder will contract, and the urethral sphincters will relax to allow the flow of urine out of the body.
Explanation:
The process of micturition involves the following steps:
1. Filling of the urinary bladder: The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine until it is eliminated from the body. As the bladder fills with urine, its walls stretch, and the pressure inside the bladder increases.
2. Sensory input to the spinal cord: The stretch receptors in the bladder walls send signals to the spinal cord, indicating that the bladder is full.
3. Activation of the micturition reflex: The spinal cord processes the sensory input and generates a reflex response that activates the muscles of the bladder and urethral sphincters.
4. Contraction of the bladder muscles: The muscles of the bladder wall contract, forcing urine out of the bladder and into the urethra.
5. Relaxation of the urethral sphincters: The urethral sphincters, which are circular muscles that control the flow of urine through the urethra, relax, allowing urine to pass out of the body.
Therefore, during micturition, the muscles of the urinary bladder will contract, and the urethral sphincters will relax to allow the flow of urine out of the body.
Which of the following hormones are secreted by the placenta?
A. Human chorionic gonadotropin
B. Chorionic thyrotropin
C. Estrogen
D. Progesterone- a)A only
- b)A & B
- c)A, B & C
- d)A, B, C & D
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A. Human chorionic gonadotropin
B. Chorionic thyrotropin
C. Estrogen
D. Progesterone
a)
A only
b)
A & B
c)
A, B & C
d)
A, B, C & D
|
|
Krithika Sharma answered |
Introduction
The placenta plays a crucial role in pregnancy by producing various hormones that support fetal development and maintain the pregnancy. The hormones secreted by the placenta include:
1. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
- hCG is one of the first hormones produced by the placenta.
- It helps maintain the corpus luteum, which in turn produces progesterone during early pregnancy.
- hCG is also the hormone detected in pregnancy tests.
2. Chorionic Thyrotropin
- Chorionic thyrotropin, also known as human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT), is involved in stimulating the thyroid gland.
- It helps increase the production of thyroid hormones, which are essential for the metabolism and development of both the mother and the fetus.
3. Estrogen
- The placenta produces significant amounts of estrogen, particularly estriol.
- Estrogen plays a vital role in the growth and development of the uterus and breast tissues.
- It also helps regulate other hormones and supports fetal development.
4. Progesterone
- Progesterone is another critical hormone secreted by the placenta.
- It maintains the uterine lining, allowing for implantation and growth of the embryo.
- Progesterone also helps suppress maternal immune responses to prevent rejection of the fetus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the placenta secretes all four hormones: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, Chorionic Thyrotropin, Estrogen, and Progesterone. Each of these hormones plays a significant role in ensuring a healthy pregnancy and supporting fetal growth, making option 'D' the correct answer.
The placenta plays a crucial role in pregnancy by producing various hormones that support fetal development and maintain the pregnancy. The hormones secreted by the placenta include:
1. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
- hCG is one of the first hormones produced by the placenta.
- It helps maintain the corpus luteum, which in turn produces progesterone during early pregnancy.
- hCG is also the hormone detected in pregnancy tests.
2. Chorionic Thyrotropin
- Chorionic thyrotropin, also known as human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT), is involved in stimulating the thyroid gland.
- It helps increase the production of thyroid hormones, which are essential for the metabolism and development of both the mother and the fetus.
3. Estrogen
- The placenta produces significant amounts of estrogen, particularly estriol.
- Estrogen plays a vital role in the growth and development of the uterus and breast tissues.
- It also helps regulate other hormones and supports fetal development.
4. Progesterone
- Progesterone is another critical hormone secreted by the placenta.
- It maintains the uterine lining, allowing for implantation and growth of the embryo.
- Progesterone also helps suppress maternal immune responses to prevent rejection of the fetus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the placenta secretes all four hormones: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, Chorionic Thyrotropin, Estrogen, and Progesterone. Each of these hormones plays a significant role in ensuring a healthy pregnancy and supporting fetal growth, making option 'D' the correct answer.
Ascending limb of Henle’s loop is not permeable for :- a)Cl−
- b)K+
- c)Na+
- d)H2O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ascending limb of Henle’s loop is not permeable for :
a)
Cl−
b)
K+
c)
Na+
d)
H2O
|
|
Anu Mukherjee answered |
The ascending limb of Henle is a segment of the nephron in the kidney that is responsible for reabsorbing certain ions from the filtrate. It is located in the loop of Henle, which is a U-shaped structure that dips into the medulla of the kidney.
The ascending limb is divided into two parts: the thin ascending limb and the thick ascending limb.
The thin ascending limb is permeable to water but not to ions. As the filtrate moves up this segment, water is reabsorbed into the surrounding interstitial fluid through osmosis, leading to an increase in the concentration of the filtrate.
The thick ascending limb, on the other hand, is impermeable to water but actively reabsorbs ions, such as sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), and chloride (Cl-), through a process called active transport. This results in the further dilution of the filtrate and the establishment of a concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney.
Overall, the ascending limb of Henle plays a crucial role in the formation of concentrated urine by reabsorbing ions and establishing a concentration gradient in the medulla.
The ascending limb is divided into two parts: the thin ascending limb and the thick ascending limb.
The thin ascending limb is permeable to water but not to ions. As the filtrate moves up this segment, water is reabsorbed into the surrounding interstitial fluid through osmosis, leading to an increase in the concentration of the filtrate.
The thick ascending limb, on the other hand, is impermeable to water but actively reabsorbs ions, such as sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), and chloride (Cl-), through a process called active transport. This results in the further dilution of the filtrate and the establishment of a concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney.
Overall, the ascending limb of Henle plays a crucial role in the formation of concentrated urine by reabsorbing ions and establishing a concentration gradient in the medulla.
The ________ are kidney tissues that are shaped like cones.- a)Renal calculi
- b)Renal pelvis
- c)Renal pyramids
- d)Renal vasculitis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ________ are kidney tissues that are shaped like cones.
a)
Renal calculi
b)
Renal pelvis
c)
Renal pyramids
d)
Renal vasculitis
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Renal pyramids, also known as malpighian pyramids, are kidney tissues that are shaped like cones.
Around 7 to 18 pyramids exist in the innermost part of the kidney, which is called the renal medulla.
In humans, there are usually only seven of the pyramids.
In humans, there are usually only seven of the pyramids.
What activates osmoreceptors in the body?- a)Changes in body temperature
- b)Changes in blood volume
- c)Changes in heart rate
- d)Changes in respiratory rate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What activates osmoreceptors in the body?
a)
Changes in body temperature
b)
Changes in blood volume
c)
Changes in heart rate
d)
Changes in respiratory rate

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Osmoreceptors in the body are activated by changes in blood volume, body fluid volume, and ionic concentration.
- Osmoreceptors are specialized cells that detect changes in the osmotic pressure or concentration of solutes in the blood. They are primarily sensitive to changes in blood volume, body fluid volume, and ionic concentration.
- When there is a decrease in blood volume or an excessive loss of fluid from the body, the osmoreceptors are activated.
- These changes in blood volume trigger a response in the hypothalamus, which then releases antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or vasopressin. This hormone helps in water reabsorption from the latter parts of the tubules, preventing excessive urine formation and maintaining fluid balance in the body.
Therefore, changes in blood volume play a crucial role in activating osmoreceptors and regulating fluid levels in the body.
The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?- a)Lactogen
- b)Primary milk
- c)Colostrum
- d)None of these
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?
a)
Lactogen
b)
Primary milk
c)
Colostrum
d)
None of these

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
After parturition, mammary glands start producing milk. The yellowish coloured milk is called colostrums. This milk contains antibodies that provide immunity newly born baby.
The epithelial cells of Bowman’s capsule are called:- a)Podocytes
- b)Calyces
- c)Filtration slits
- d)Slit pores
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The epithelial cells of Bowman’s capsule are called:
a)
Podocytes
b)
Calyces
c)
Filtration slits
d)
Slit pores

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
The parietal layer of Bowman's capsule consists of squamous epithelial cells resting on a basement membrane. The cells are of polygonal shape and contain prominent bundles of actin filaments running in all directions.
At the birth of a female child, the follicles in her ovaries contain:- a)Primary oocytes that have been arrested at the S phase of the cell cycle
- b)Primary oocytes that have been arrested at the Prophase I of Meiosis I
- c)Secondary oocytes that have been arrested at the Prophase I of Meiosis I
- d)Secondary oocytes that have been arrested at the Metaphase II of Meiosis II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Primary oocytes that have been arrested at the S phase of the cell cycle
b)
Primary oocytes that have been arrested at the Prophase I of Meiosis I
c)
Secondary oocytes that have been arrested at the Prophase I of Meiosis I
d)
Secondary oocytes that have been arrested at the Metaphase II of Meiosis II

|
Stepway Academy answered |
At birth, the follicles in a female's ovaries contain primary oocytes that are arrested at Prophase I of Meiosis I. These oocytes remain in this arrested state until puberty and further stages of maturation.
The correct sequence of spermatogenetic stages leading to the formation of sperms in a mature human testis is:- a)spermatocyte - spermatogonia - spermatid - sperms
- b)spermatogonia - spermatocyte - spermatid - sperms
- c)spermatid - spermatocyte - spermatogonia - sperms
- d)spermatogonia - spermatid - spermatocyte - sperms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence of spermatogenetic stages leading to the formation of sperms in a mature human testis is:
a)
spermatocyte - spermatogonia - spermatid - sperms
b)
spermatogonia - spermatocyte - spermatid - sperms
c)
spermatid - spermatocyte - spermatogonia - sperms
d)
spermatogonia - spermatid - spermatocyte - sperms

|
Lead Academy answered |
The correct sequence of spermatogenesis in the human testis is:
Spermatogonia: The precursor germ cells that divide mitotically.
Spermatocyte: These cells undergo meiosis; primary spermatocytes give rise to secondary spermatocytes.
Spermatid: Haploid cells that result from the second meiotic division.
Sperms: Mature sperm cells formed from the differentiation of spermatids.
Thus, the sequence is spermatogonia → spermatocyte → spermatid → sperms.
Spermatogonia: The precursor germ cells that divide mitotically.
Spermatocyte: These cells undergo meiosis; primary spermatocytes give rise to secondary spermatocytes.
Spermatid: Haploid cells that result from the second meiotic division.
Sperms: Mature sperm cells formed from the differentiation of spermatids.
Thus, the sequence is spermatogonia → spermatocyte → spermatid → sperms.
What is the main function of the hormonal feedback mechanisms involving the hypothalamus, JGA, and heart?- a)Regulate body temperature
- b)Regulate blood glucose levels
- c)Regulate blood pressure
- d)Regulate hormone production
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the main function of the hormonal feedback mechanisms involving the hypothalamus, JGA, and heart?
a)
Regulate body temperature
b)
Regulate blood glucose levels
c)
Regulate blood pressure
d)
Regulate hormone production
|
|
Maya Gupta answered |
Regulation of Blood Pressure by Hormonal Feedback Mechanisms involving the Hypothalamus, JGA, and Heart
The main function of the hormonal feedback mechanisms involving the hypothalamus, JGA (juxtaglomerular apparatus), and heart is to regulate blood pressure. This involves a complex interplay between various hormones, organs, and feedback loops that work together to maintain blood pressure within a normal range.
1. Role of the Hypothalamus:
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure through the release of hormones. It senses changes in blood pressure and activates the sympathetic nervous system to initiate appropriate responses.
2. Role of the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA):
The JGA is a specialized structure located in the kidneys that plays a key role in blood pressure regulation. It consists of juxtaglomerular cells and macula densa cells. The juxtaglomerular cells secrete the enzyme renin in response to decreased blood pressure or decreased sodium levels. Renin initiates a cascade of events leading to the production of angiotensin II.
3. Role of the Heart:
The heart also contributes to blood pressure regulation through the release of hormones. When blood pressure decreases, specialized cells in the atria of the heart called atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) are released. ANP acts to relax blood vessels, reduce sodium reabsorption in the kidneys, and increase urine output, all of which help to lower blood pressure.
4. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS):
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is a hormonal pathway that plays a critical role in blood pressure regulation. When renin is released from the JGA, it converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) then converts angiotensin I into angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. Angiotensin II increases blood pressure by constricting blood vessels and stimulating the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands. Aldosterone acts on the kidneys to increase sodium reabsorption and water retention, thereby increasing blood volume and blood pressure.
5. Negative Feedback Loop:
The hormonal feedback mechanisms involving the hypothalamus, JGA, and heart operate through a negative feedback loop. When blood pressure is too low, the hypothalamus stimulates the release of hormones to increase blood pressure. Once blood pressure returns to a normal range, the release of these hormones is inhibited, and blood pressure is maintained within a homeostatic range.
In conclusion, the main function of the hormonal feedback mechanisms involving the hypothalamus, JGA, and heart is to regulate blood pressure. This is achieved through the release of hormones such as renin, angiotensin, aldosterone, and atrial natriuretic peptide, which act on various organs and systems to increase or decrease blood pressure as needed.
The main function of the hormonal feedback mechanisms involving the hypothalamus, JGA (juxtaglomerular apparatus), and heart is to regulate blood pressure. This involves a complex interplay between various hormones, organs, and feedback loops that work together to maintain blood pressure within a normal range.
1. Role of the Hypothalamus:
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure through the release of hormones. It senses changes in blood pressure and activates the sympathetic nervous system to initiate appropriate responses.
2. Role of the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA):
The JGA is a specialized structure located in the kidneys that plays a key role in blood pressure regulation. It consists of juxtaglomerular cells and macula densa cells. The juxtaglomerular cells secrete the enzyme renin in response to decreased blood pressure or decreased sodium levels. Renin initiates a cascade of events leading to the production of angiotensin II.
3. Role of the Heart:
The heart also contributes to blood pressure regulation through the release of hormones. When blood pressure decreases, specialized cells in the atria of the heart called atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) are released. ANP acts to relax blood vessels, reduce sodium reabsorption in the kidneys, and increase urine output, all of which help to lower blood pressure.
4. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS):
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is a hormonal pathway that plays a critical role in blood pressure regulation. When renin is released from the JGA, it converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) then converts angiotensin I into angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. Angiotensin II increases blood pressure by constricting blood vessels and stimulating the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands. Aldosterone acts on the kidneys to increase sodium reabsorption and water retention, thereby increasing blood volume and blood pressure.
5. Negative Feedback Loop:
The hormonal feedback mechanisms involving the hypothalamus, JGA, and heart operate through a negative feedback loop. When blood pressure is too low, the hypothalamus stimulates the release of hormones to increase blood pressure. Once blood pressure returns to a normal range, the release of these hormones is inhibited, and blood pressure is maintained within a homeostatic range.
In conclusion, the main function of the hormonal feedback mechanisms involving the hypothalamus, JGA, and heart is to regulate blood pressure. This is achieved through the release of hormones such as renin, angiotensin, aldosterone, and atrial natriuretic peptide, which act on various organs and systems to increase or decrease blood pressure as needed.
Assertion (A): The male reproductive system includes the testes, which produce sperm and hormones.Reason (R): The Leydig cells in the testes are responsible for the production of androgens, which are essential for sperm formation.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The male reproductive system includes the testes, which produce sperm and hormones.
Reason (R): The Leydig cells in the testes are responsible for the production of androgens, which are essential for sperm formation.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Lead Academy answered |
- The Assertion is true because the male reproductive system does indeed include the testes, which are responsible for sperm production and hormone secretion.
- The Reason is also true, as Leydig cells do produce androgens, which play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of male reproductive tissues, including spermatogenesis.
- The Reason correctly explains the Assertion because the hormones produced by Leydig cells are vital for the processes mentioned in the Assertion.
The presence of ketone bodies is an indication of which of the following diseases?- a)Diabetes insipidus
- b)Diabetes mellitus
- c)High blood cholesterol
- d)Liver Cirrhosis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The presence of ketone bodies is an indication of which of the following diseases?
a)
Diabetes insipidus
b)
Diabetes mellitus
c)
High blood cholesterol
d)
Liver Cirrhosis

|
Lead Academy answered |
- Analysis of urine helps in the clinical diagnosis of many metabolic disorders.
- The presence of glucose or Glycosuria and ketone bodies or Ketonuria in urine is indicative of diabetes mellitus.
Line in NCERT: Not Found
Which of the following is not accumulated by the body of living organisms?- a)Oxygen
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Urea
- d)Ammonia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not accumulated by the body of living organisms?
a)
Oxygen
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Urea
d)
Ammonia

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Oxygen is not accumulated by the body of living organisms as this is required by the cells to perform respiration. Also, it is not a waste product of the cells. Animals accumulate ammonia, urea, uric acid, carbon dioxide, water, and ions like Na+, K+, Cl–, phosphate, sulphate, etc., by certain metabolic activities.
The conversion of spermatid into spermatozoa is called?
- a)Spermatogenesis
- b)Cytokinesis
- c)Spermiogenesis
- d)Vitellogenesis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The conversion of spermatid into spermatozoa is called?
a)
Spermatogenesis
b)
Cytokinesis
c)
Spermiogenesis
d)
Vitellogenesis
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Spermiogenesis is the final stage of spermatogenesis, which sees the maturation of spermatids into mature, motile spermatozoa. The spermatid is a more or less circular cell containing a nucleus, Golgi apparatus, centriole and mitochondria. All these components take part in forming the spermatozoan.
Homeostasis in the body is largely maintained by : excretion and osmoregulation egestion and osmoregulation excretion and egestion osmoregulation, excretion and egestion Homeostasis is the maintenance of constant body temperature. It is mainly maintained by excretion and osmoregulation, which is the function of kidney.- a)osmoregulation, excretion and egestion
- b)egestion and osmoregulation
- c)excretion and osmoregulation
- d)excretion and egestion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Homeostasis in the body is largely maintained by : excretion and osmoregulation egestion and osmoregulation excretion and egestion osmoregulation, excretion and egestion Homeostasis is the maintenance of constant body temperature. It is mainly maintained by excretion and osmoregulation, which is the function of kidney.
a)
osmoregulation, excretion and egestion
b)
egestion and osmoregulation
c)
excretion and osmoregulation
d)
excretion and egestion

|
Nikita Pati answered |
Homeostasis means maintain the excretion and osmoregulation
Which hormone is released by the JG cells in response to a fall in glomerular blood flow?- a)Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF)
- b)Aldosterone
- c)Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- d) Renin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which hormone is released by the JG cells in response to a fall in glomerular blood flow?
a)
Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF)
b)
Aldosterone
c)
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
d)
Renin
|
|
Nayanika Chavan answered |
Renin is the hormone released by the Juxtaglomerular (JG) cells in response to a fall in glomerular blood flow.
The Juxtaglomerular cells are specialized cells located in the afferent arterioles of the kidney. These cells function as mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors, sensing changes in blood pressure and sodium levels.
The release of renin is part of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure, fluid balance, and electrolyte homeostasis.
Function of Renin:
Renin plays a pivotal role in this system by initiating a cascade of events that ultimately leads to the increase in blood pressure and restoration of glomerular filtration rate. The main functions of renin include:
1. Conversion of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensin I: Renin acts on angiotensinogen, a protein produced by the liver, and converts it into angiotensin I, an inactive precursor.
2. Conversion of Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II: Angiotensin I is then converted into angiotensin II by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) present in the lungs. Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor that causes the constriction of blood vessels, leading to an increase in systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure.
3. Stimulation of Aldosterone Release: Angiotensin II also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands. Aldosterone acts on the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the kidney, promoting the reabsorption of sodium and water and the excretion of potassium. This results in an increase in blood volume and blood pressure.
4. Stimulation of ADH Release: Additionally, angiotensin II stimulates the release of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland. ADH acts on the collecting ducts of the kidney, increasing water reabsorption and concentrating the urine.
Overall, the release of renin by the Juxtaglomerular cells in response to a fall in glomerular blood flow is a crucial step in maintaining blood pressure and fluid balance in the body.
The Juxtaglomerular cells are specialized cells located in the afferent arterioles of the kidney. These cells function as mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors, sensing changes in blood pressure and sodium levels.
The release of renin is part of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure, fluid balance, and electrolyte homeostasis.
Function of Renin:
Renin plays a pivotal role in this system by initiating a cascade of events that ultimately leads to the increase in blood pressure and restoration of glomerular filtration rate. The main functions of renin include:
1. Conversion of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensin I: Renin acts on angiotensinogen, a protein produced by the liver, and converts it into angiotensin I, an inactive precursor.
2. Conversion of Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II: Angiotensin I is then converted into angiotensin II by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) present in the lungs. Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor that causes the constriction of blood vessels, leading to an increase in systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure.
3. Stimulation of Aldosterone Release: Angiotensin II also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands. Aldosterone acts on the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the kidney, promoting the reabsorption of sodium and water and the excretion of potassium. This results in an increase in blood volume and blood pressure.
4. Stimulation of ADH Release: Additionally, angiotensin II stimulates the release of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland. ADH acts on the collecting ducts of the kidney, increasing water reabsorption and concentrating the urine.
Overall, the release of renin by the Juxtaglomerular cells in response to a fall in glomerular blood flow is a crucial step in maintaining blood pressure and fluid balance in the body.
Assertion (A): Oogenesis results in the formation of a single ovum during each menstrual cycle.Reason (R): The cyclical changes in the ovaries are influenced solely by the levels of ovarian hormones, without any involvement from pituitary hormones.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Oogenesis results in the formation of a single ovum during each menstrual cycle.
Reason (R): The cyclical changes in the ovaries are influenced solely by the levels of ovarian hormones, without any involvement from pituitary hormones.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false
|
|
Aashna Rane answered |
Assertion Explanation
Oogenesis is the process of egg (ovum) formation in females, and it typically results in the development of a single mature ovum during each menstrual cycle. This is due to the fact that among the several primary oocytes that develop, usually only one reaches maturity and is released during ovulation.
Reason Explanation
While it is true that ovarian hormones such as estrogen and progesterone play a significant role in the menstrual cycle, pituitary hormones, specifically follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), are also crucial. FSH stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles, and LH triggers ovulation. Therefore, the assertion that cyclical changes in the ovaries are solely influenced by ovarian hormones is incorrect.
Conclusion
Given that:
- The assertion (A) is true: Oogenesis results in the formation of a single ovum during each menstrual cycle.
- The reason (R) is false: The cyclical changes in the ovaries are influenced by both ovarian and pituitary hormones.
The correct answer is option 'C': If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
This clearly indicates that the statement regarding the sole influence of ovarian hormones on ovarian changes is not accurate, making the assertion valid while the reason is not.
Oogenesis is the process of egg (ovum) formation in females, and it typically results in the development of a single mature ovum during each menstrual cycle. This is due to the fact that among the several primary oocytes that develop, usually only one reaches maturity and is released during ovulation.
Reason Explanation
While it is true that ovarian hormones such as estrogen and progesterone play a significant role in the menstrual cycle, pituitary hormones, specifically follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), are also crucial. FSH stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles, and LH triggers ovulation. Therefore, the assertion that cyclical changes in the ovaries are solely influenced by ovarian hormones is incorrect.
Conclusion
Given that:
- The assertion (A) is true: Oogenesis results in the formation of a single ovum during each menstrual cycle.
- The reason (R) is false: The cyclical changes in the ovaries are influenced by both ovarian and pituitary hormones.
The correct answer is option 'C': If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
This clearly indicates that the statement regarding the sole influence of ovarian hormones on ovarian changes is not accurate, making the assertion valid while the reason is not.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?i. LH and FSH both reach peak levels around the 14th day of the menstrual cycle.ii. The LH surge causes the degeneration of the corpus luteum.iii. Progesterone secreted by the corpus luteum is essential for maintaining the endometrium.iv. Menstruation occurs if fertilization does not take place, leading to the start of a new cycle.- a) ii and iv
- b) i and iii
- c) i, iii, and iv
- d) i, ii, iii, and iv
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. LH and FSH both reach peak levels around the 14th day of the menstrual cycle.
ii. The LH surge causes the degeneration of the corpus luteum.
iii. Progesterone secreted by the corpus luteum is essential for maintaining the endometrium.
iv. Menstruation occurs if fertilization does not take place, leading to the start of a new cycle.
a)
ii and iv
b)
i and iii
c)
i, iii, and iv
d)
i, ii, iii, and iv

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- Statement i is correct because LH (Luteinizing Hormone) and FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) both peak around the 14th day of the menstrual cycle, which is known as ovulation.
- Statement ii is incorrect; the LH surge is responsible for the rupture of the Graafian follicle, leading to ovulation, not for the degeneration of the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum degenerates only in the absence of fertilization.
- Statement iii is correct; the corpus luteum secretes progesterone, which is crucial for maintaining the endometrium, making it suitable for implantation.
- Statement iv is also correct; if fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates, leading to the disintegration of the endometrium and the onset of menstruation.
Therefore, the correct answer is C: i, iii, and iv.
Topic in NCERT: Menstrual cycle
Line in NCERT: "both lh and fsh attain a peak level in the middle of cycle (about 14th day). rapid secretion of lh leading to its maximum level during the mid-cycle called lh surge induces rupture of graafian follicle and thereby the release of ovum (ovulation)."
"the corpus luteum secretes large amounts of progesterone which is essential for maintenance of the endometrium."
"in the absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum degenerates. this causes disintegration of the endometrium leading to menstruation, marking a new cycle."
"the corpus luteum secretes large amounts of progesterone which is essential for maintenance of the endometrium."
"in the absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum degenerates. this causes disintegration of the endometrium leading to menstruation, marking a new cycle."
The process of formation of primary organ rudiment is called?- a)Mesogenesis
- b)Neurogenesis
- c)Tubulation
- d)Notogenesis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of formation of primary organ rudiment is called?
a)
Mesogenesis
b)
Neurogenesis
c)
Tubulation
d)
Notogenesis

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
During gestation period organs formation started after three weeks these organs are not completely developed and called primary organ rudiment. The process of formation of primary organ rudiment is called tabulation.
Which of the following depicts the correct pathway of transport of sperms?- a)Rete testis → Efferent ductules → Epididymis → Vas deferens
- b)Rete testis → Epididymis → Efferent ductules → Vas deferens
- c)Rete testis → Vas deferens → Efferent ductules → Epididymis
- d)Efferent ductules → Rete testis → Vas deferens → Epididymis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Rete testis → Efferent ductules → Epididymis → Vas deferens
b)
Rete testis → Epididymis → Efferent ductules → Vas deferens
c)
Rete testis → Vas deferens → Efferent ductules → Epididymis
d)
Efferent ductules → Rete testis → Vas deferens → Epididymis
|
|
Gopal Mehra answered |
Understanding the Pathway of Sperm Transport
The transport of sperm through the male reproductive system follows a specific pathway essential for sperm maturation and storage. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each component involved in this process:
1. Rete Testis
- The rete testis is a network of tubules located in the testis.
- It collects sperm from the seminiferous tubules where spermatogenesis occurs.
2. Efferent Ductules
- After collection, sperm move from the rete testis into the efferent ductules.
- These ductules transport sperm to the epididymis.
3. Epididymis
- The epididymis is a coiled tube where sperm undergo maturation and storage.
- Here, sperm gain motility and the ability to fertilize an egg.
4. Vas Deferens
- Upon ejaculation, mature sperm travel from the epididymis into the vas deferens.
- The vas deferens transports sperm to the ejaculatory duct, leading to the urethra.
Conclusion
The correct pathway of sperm transport is Rete testis → Efferent ductules → Epididymis → Vas deferens (Option A). This sequence ensures that sperm are collected, matured, and ultimately delivered during ejaculation. Understanding this pathway is crucial for comprehending male reproductive physiology, especially in contexts like fertility and reproductive health.
The transport of sperm through the male reproductive system follows a specific pathway essential for sperm maturation and storage. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each component involved in this process:
1. Rete Testis
- The rete testis is a network of tubules located in the testis.
- It collects sperm from the seminiferous tubules where spermatogenesis occurs.
2. Efferent Ductules
- After collection, sperm move from the rete testis into the efferent ductules.
- These ductules transport sperm to the epididymis.
3. Epididymis
- The epididymis is a coiled tube where sperm undergo maturation and storage.
- Here, sperm gain motility and the ability to fertilize an egg.
4. Vas Deferens
- Upon ejaculation, mature sperm travel from the epididymis into the vas deferens.
- The vas deferens transports sperm to the ejaculatory duct, leading to the urethra.
Conclusion
The correct pathway of sperm transport is Rete testis → Efferent ductules → Epididymis → Vas deferens (Option A). This sequence ensures that sperm are collected, matured, and ultimately delivered during ejaculation. Understanding this pathway is crucial for comprehending male reproductive physiology, especially in contexts like fertility and reproductive health.
What effect does ADH have on the kidney function?
- a)Increases glomerular blood flow
- b)to release less water, decreasing the amount of urine produced.
- c)Decreases glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- d)Decreases blood pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What effect does ADH have on the kidney function?
a)
Increases glomerular blood flow
b)
to release less water, decreasing the amount of urine produced.
c)
Decreases glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
d)
Decreases blood pressure
|
|
Mansi Chakraborty answered |
ADH, or antidiuretic hormone, also known as vasopressin, is a hormone produced by the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland. Its main function is to regulate the water balance in the body by controlling the reabsorption of water in the kidneys. ADH acts on the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephrons in the kidneys, altering their permeability to water.
The correct answer is option 'B': ADH increases the reabsorption of sodium in the kidneys. This has several effects on kidney function:
1. **Increased water reabsorption**: ADH binds to receptors in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephrons, which results in an increase in the permeability of these tubules to water. This allows more water to be reabsorbed from the filtrate back into the bloodstream, reducing urine volume and preventing excessive water loss.
2. **Increased sodium reabsorption**: By increasing the reabsorption of sodium in the kidneys, ADH indirectly increases water reabsorption. Sodium ions are actively transported out of the tubules and into the interstitial fluid, creating an osmotic gradient that drives the reabsorption of water. This helps to concentrate the urine and retain water in the body.
3. **Increased urine osmolality**: ADH increases the concentration of solutes in the urine by increasing water reabsorption. This leads to a higher osmolality of the urine, which helps to conserve water and maintain the body's water balance.
4. **Decreased urine volume**: As a result of increased water reabsorption, the volume of urine produced is reduced. This helps to conserve water and prevent dehydration.
It is important to note that ADH does not directly affect glomerular filtration rate (GFR) or glomerular blood flow. GFR is primarily regulated by the constriction or dilation of the afferent and efferent arterioles in the glomerulus, which are controlled by other mechanisms such as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. ADH's main role is to regulate water reabsorption in the renal tubules.
The correct answer is option 'B': ADH increases the reabsorption of sodium in the kidneys. This has several effects on kidney function:
1. **Increased water reabsorption**: ADH binds to receptors in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephrons, which results in an increase in the permeability of these tubules to water. This allows more water to be reabsorbed from the filtrate back into the bloodstream, reducing urine volume and preventing excessive water loss.
2. **Increased sodium reabsorption**: By increasing the reabsorption of sodium in the kidneys, ADH indirectly increases water reabsorption. Sodium ions are actively transported out of the tubules and into the interstitial fluid, creating an osmotic gradient that drives the reabsorption of water. This helps to concentrate the urine and retain water in the body.
3. **Increased urine osmolality**: ADH increases the concentration of solutes in the urine by increasing water reabsorption. This leads to a higher osmolality of the urine, which helps to conserve water and maintain the body's water balance.
4. **Decreased urine volume**: As a result of increased water reabsorption, the volume of urine produced is reduced. This helps to conserve water and prevent dehydration.
It is important to note that ADH does not directly affect glomerular filtration rate (GFR) or glomerular blood flow. GFR is primarily regulated by the constriction or dilation of the afferent and efferent arterioles in the glomerulus, which are controlled by other mechanisms such as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. ADH's main role is to regulate water reabsorption in the renal tubules.
What structure gets implanted on the wall of the uterus during embryonic development?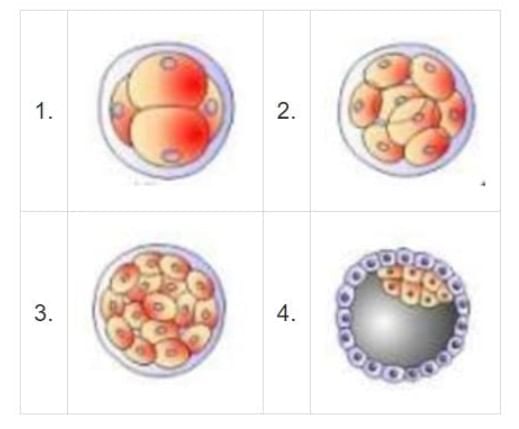
- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What structure gets implanted on the wall of the uterus during embryonic development?

a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Ambition Institute answered |
4 structure is implanted named Blastocyst.
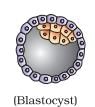
The mitotic division starts as the zygote moves through the isthmus of the oviduct called cleavage towards the uterus and forms 2, 4, 8, 16 daughter cells called blastomeres. The embryo with 8 to 16 blastomeres is called a morula.(Figure 3) The morula continues to divide and transforms into blastocyst as it moves further into the uterus. The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into an outer layer called trophoblast and an inner group of cells attached to trophoblast called the inner cell mass. The trophoblast layer then gets attached to the endometrium and the inner cell mass gets differentiated as the embryo. After attachment, the uterine cells divide rapidly and covers the blastocyst. As a result, the blastocyst becomes embedded in the endometrium of the uterus
Topic in NCERT: Pregnancy and embryonic development
Line in NCERT: "the trophoblast layer then gets attached to the endometrium and the inner cell mass gets differentiated as the embryo."
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?i. Oogenesis is initiated during the embryonic development stage when oogonia are formed in the ovaries.ii. A primary oocyte completes its first meiotic division before birth.iii. The secondary follicle develops a fluid-filled cavity known as the antrum.iv. At puberty, approximately 100,000 primary follicles remain in each ovary.- a) ii and iv
- b) i and iii
- c) i, iii, and iv
- d) i and ii
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Oogenesis is initiated during the embryonic development stage when oogonia are formed in the ovaries.
ii. A primary oocyte completes its first meiotic division before birth.
iii. The secondary follicle develops a fluid-filled cavity known as the antrum.
iv. At puberty, approximately 100,000 primary follicles remain in each ovary.
a)
ii and iv
b)
i and iii
c)
i, iii, and iv
d)
i and ii
|
|
Aravind Chavan answered |
Understanding Oogenesis Statements
In this discussion, we evaluate the provided statements regarding oogenesis and identify the correct ones.
Statement Analysis
- i. Oogenesis is initiated during the embryonic development stage when oogonia are formed in the ovaries.
This statement is correct. Oogenesis begins during embryonic development, where primordial germ cells differentiate into oogonia in the ovaries.
- ii. A primary oocyte completes its first meiotic division before birth.
This statement is incorrect. A primary oocyte does not complete its first meiotic division until ovulation, which occurs after birth, typically during the menstrual cycle.
- iii. The secondary follicle develops a fluid-filled cavity known as the antrum.
This statement is correct. The secondary follicle is characterized by the formation of the antrum, which is a fluid-filled space that develops as the follicle matures.
- iv. At puberty, approximately 100,000 primary follicles remain in each ovary.
This statement is correct. At the onset of puberty, it is estimated that around 100,000 primary follicles are present in each ovary, although this number can vary.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis:
- Correct statements: i, iii, iv
- Incorrect statement: ii
Therefore, the correct answer is option b) i and iii. This highlights the importance of understanding the stages of oogenesis and the development of ovarian follicles.
In this discussion, we evaluate the provided statements regarding oogenesis and identify the correct ones.
Statement Analysis
- i. Oogenesis is initiated during the embryonic development stage when oogonia are formed in the ovaries.
This statement is correct. Oogenesis begins during embryonic development, where primordial germ cells differentiate into oogonia in the ovaries.
- ii. A primary oocyte completes its first meiotic division before birth.
This statement is incorrect. A primary oocyte does not complete its first meiotic division until ovulation, which occurs after birth, typically during the menstrual cycle.
- iii. The secondary follicle develops a fluid-filled cavity known as the antrum.
This statement is correct. The secondary follicle is characterized by the formation of the antrum, which is a fluid-filled space that develops as the follicle matures.
- iv. At puberty, approximately 100,000 primary follicles remain in each ovary.
This statement is correct. At the onset of puberty, it is estimated that around 100,000 primary follicles are present in each ovary, although this number can vary.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis:
- Correct statements: i, iii, iv
- Incorrect statement: ii
Therefore, the correct answer is option b) i and iii. This highlights the importance of understanding the stages of oogenesis and the development of ovarian follicles.
Chapter doubts & questions for Internal Structure of Mammal - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Internal Structure of Mammal - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup